Imaging Simulation and Damage Assessment Feature Analysis of Ku Band Polarized SAR of Buildings
-
摘要: 建筑物损毁评估在灾害应急监测中十分重要。近年来,随着SAR硬件多极化能力的增加,极化SAR为建筑物损毁评估提供了更多的可能性,基于极化特征的建筑物损毁评估方法逐渐成为了研究的重点。然而,由于极化SAR数据获取的限制,当前的研究主要集中在L, C, X等有限波段内。为了进一步加深对SAR图像损毁建筑物极化特征的理解并丰富其它波段下SAR图像损毁建筑物的极化特征应用,该文进行了建筑物Ku波段极化SAR仿真实验,并通过SAR图像极化分解的方法进行了损毁评估特征分析。该文首先制作了真实材料的建筑物缩比模型,利用微波特性测量与仿真成像科学实验平台对损毁前后的建筑物目标进行SAR仿真成像,获取了建筑物损毁前后的Ku波段极化SAR图像。然后,借助
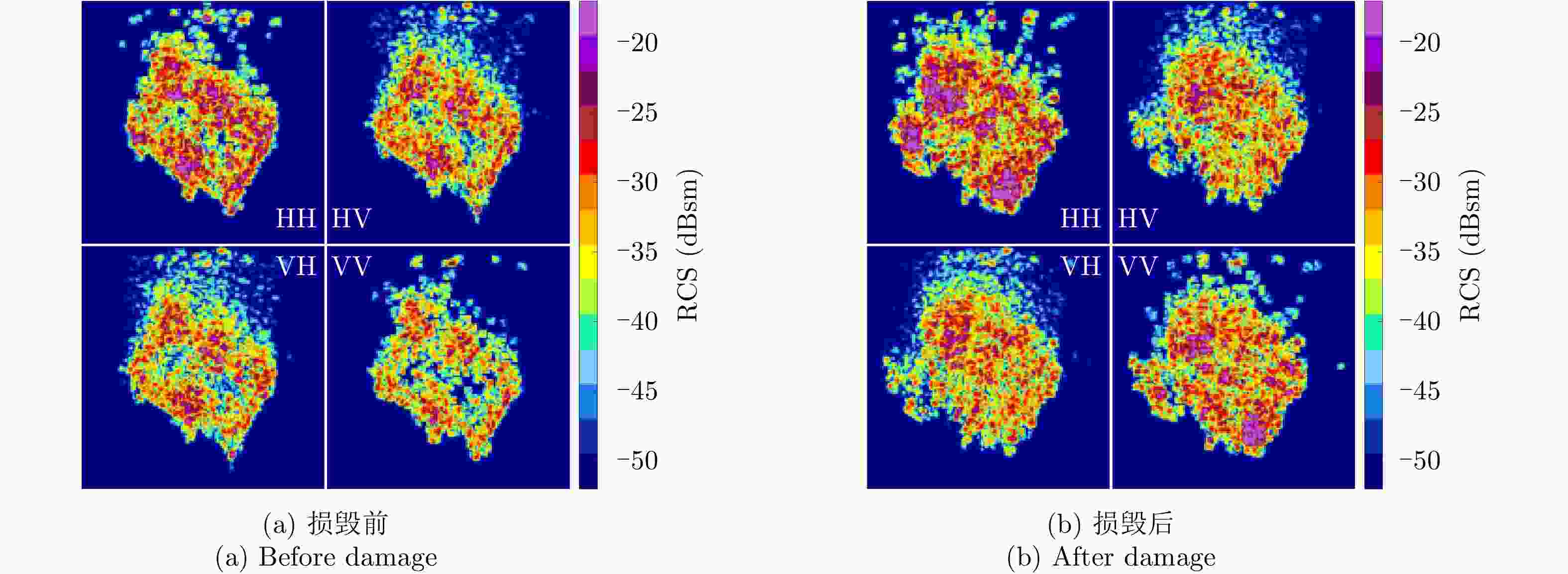
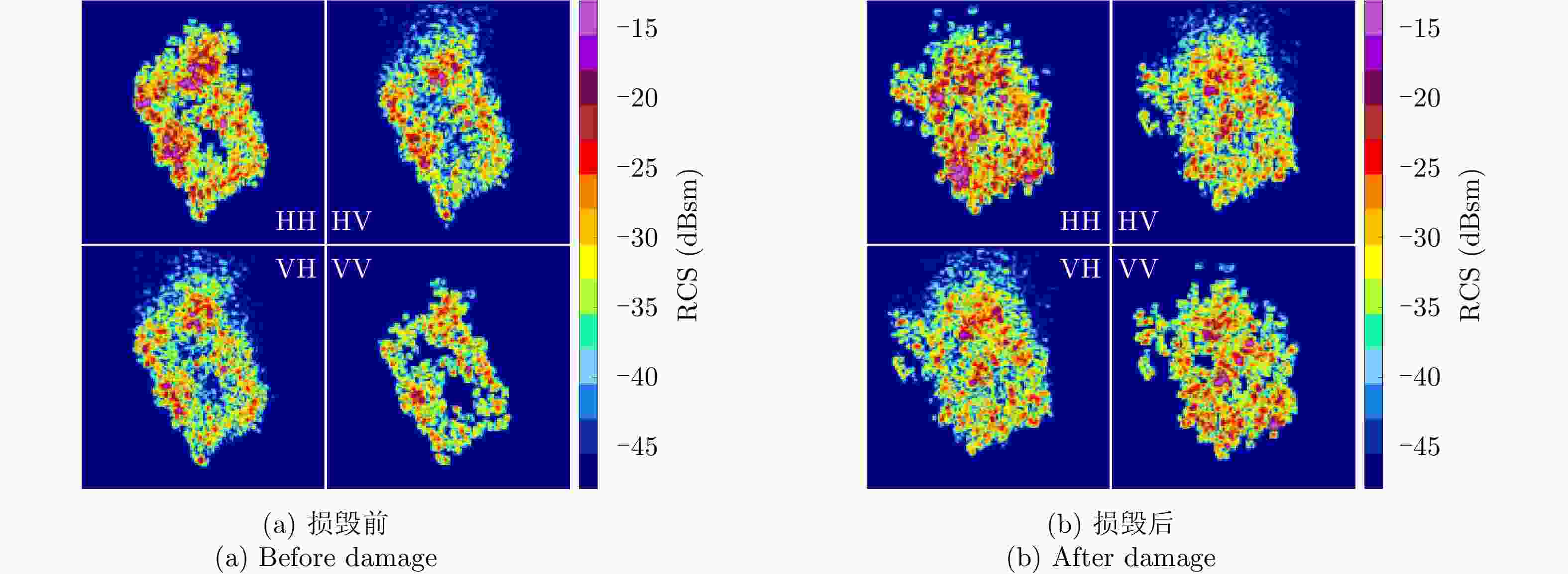
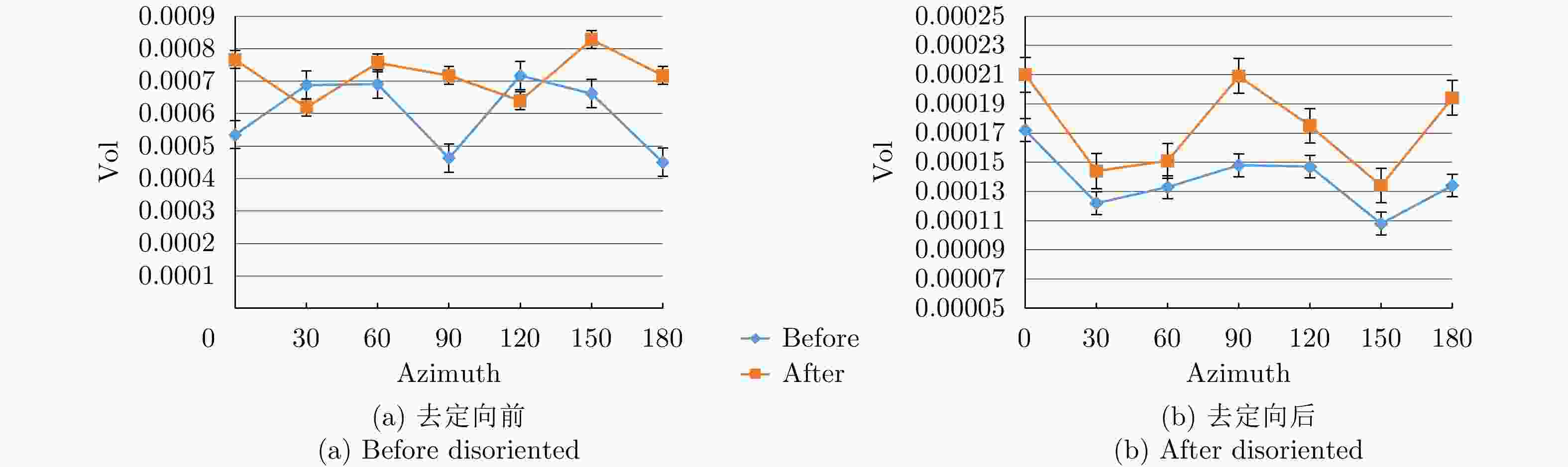
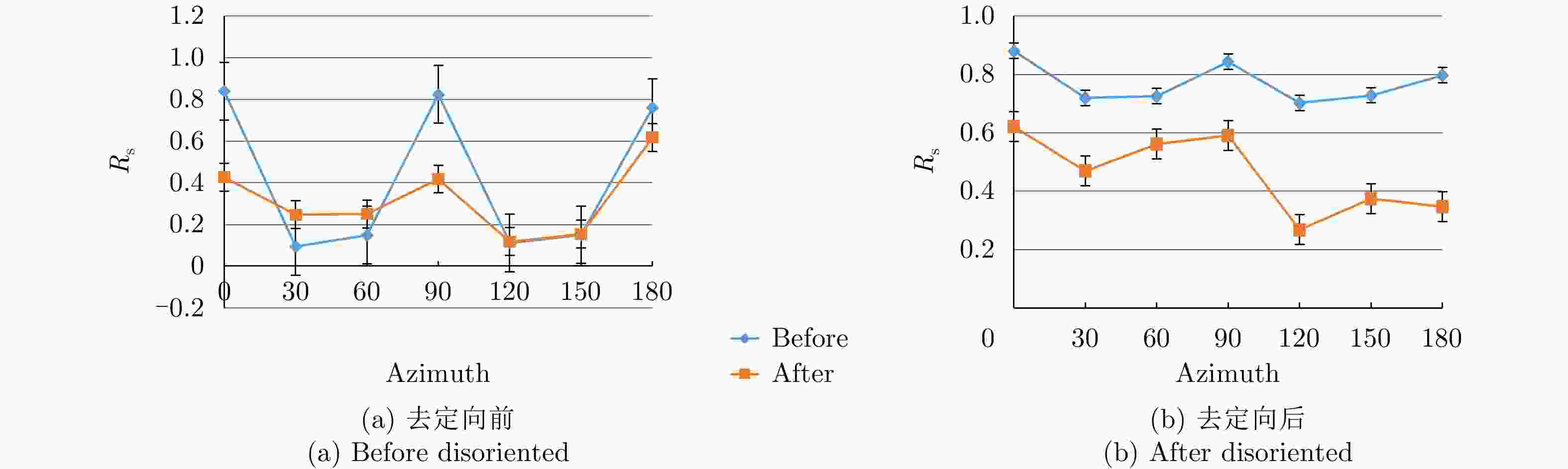
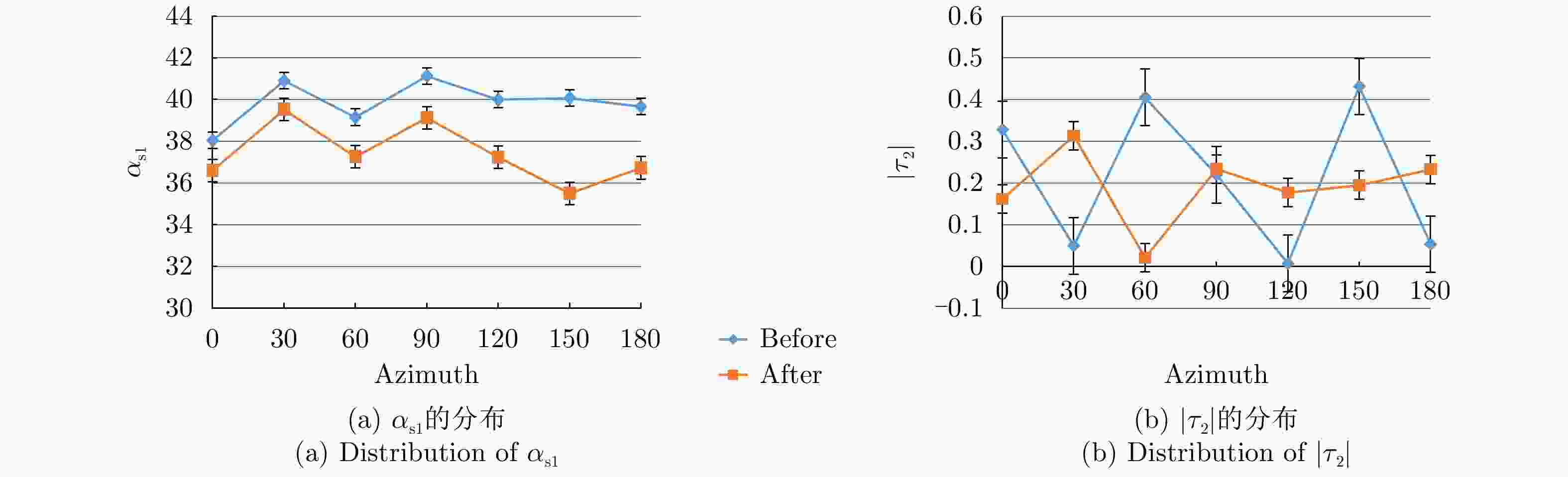
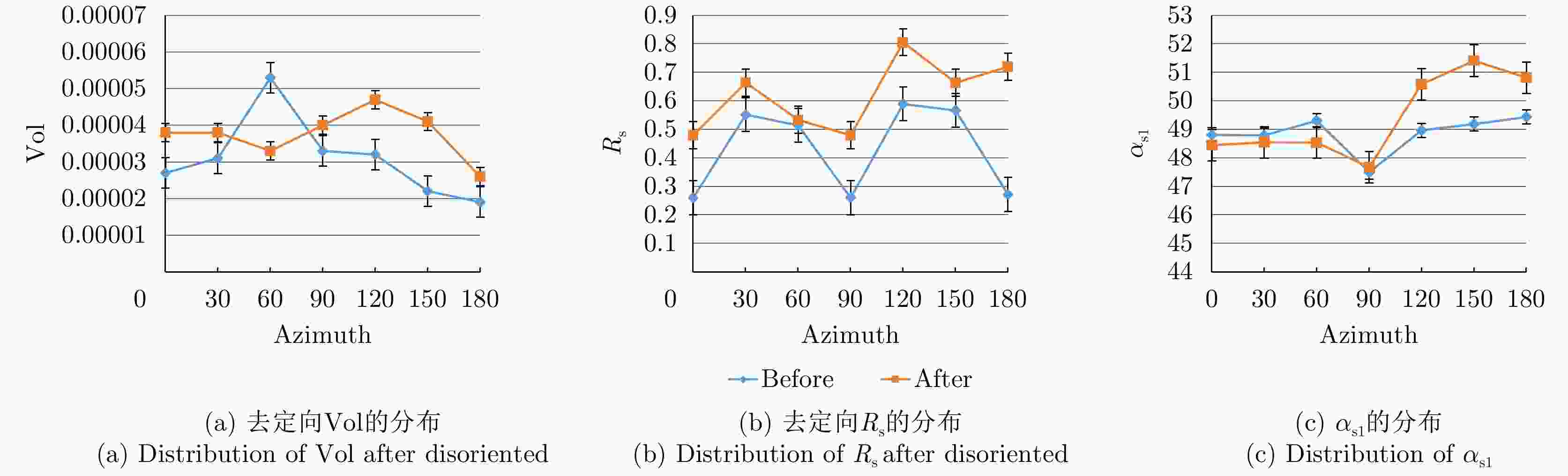
$ H/A/\alpha $ 分解、Yamaguchi分解、Touzi分解等极化分解方法分析了Ku波段建筑物目标损毁前后的极化散射特征,分析表明,Yamaguchi分解得到的去定向后的体散射分量、二次散射分量占比以及Touzi分解得到的$ {\alpha }_{\rm s1} $ 分量对于Ku波段建筑物损毁评估具有较好的指示意义;通过与X波段实验测量结果的对比,发现Ku波段对建筑物损毁评估更敏感,这对于未来雷达遥感应用具有重要的启发意义。Abstract: Building damage assessment is important in disaster emergency monitoring. In recent years, with the increase of multi-polarization capability of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) provides more possibilities for building damage assessment, and the polarization-characteristic-based building damage assessment method has gradually become the focus of research. However, because of the limitations of data acquisition in PolSAR, current research mainly focuses on the L, C, X, and other limited bands. To obtain an in depth understanding of the polarization characteristics of damaged buildings in SAR images and develop the application of the polarization characteristics of damaged buildings to other bands, this study conducted a simulation experiment of Ku band polarized SAR of buildings, and performed damage assessment feature analysis using the SAR image polarization decomposition method. In this study, a scale model of real materials was built and the “microwave characteristic measurement and simulation imaging scientific experiment platform” was used to conduct SAR simulation imaging of the target buildings. The Ku band polarized SAR images before and after building damage were obtained. Then, the polarization scattering characteristics of buildings before and after damage were analyzed using various common polarization decomposition methods such as$ {H/A/\alpha} $ decomposition, Yamaguchi decomposition and Touzi decomposition. Results show that the disoriented volume scattering component and the proportion of the disoriented secondary scattering component obtained by the Yamaguchi decomposition and the${ {\alpha }_{\rm s1}} $ component obtained by the Touzi decomposition have good indicative significance for building damage assessment in the Ku band. Compared with the X band measurement results, the Ku band is more sensitive to building damage assessment, which has important implications for future radar remote sensing applications.-
Key words:
- Polarimetric SAR(PolSAR) /
- Image simulation /
- Polarimetric decomposition /
- Building /
- Damage assessment
-
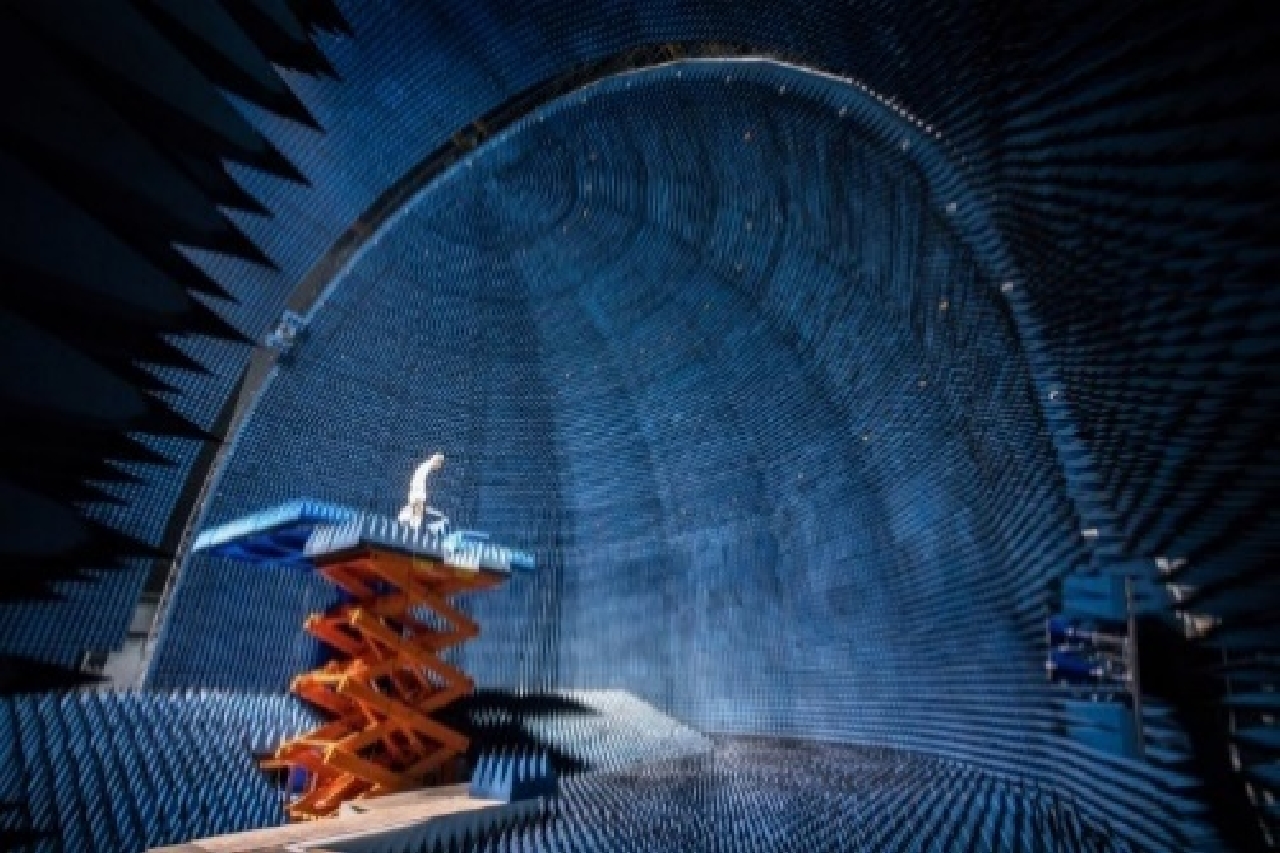
表 1 实验平台功能及性能参数
Table 1. The function and performance parameters of experiment platform
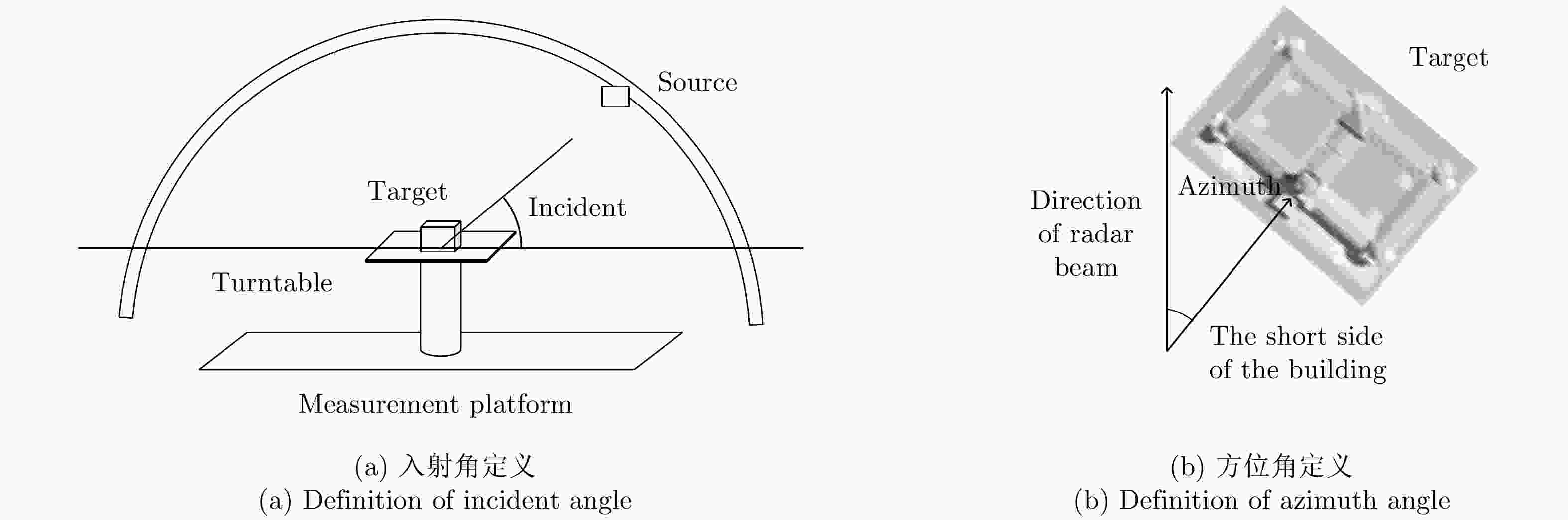
功能 参数 波段范围 0.8~20 GHz 极化方式 单极化/双极化/全极化 入射角 0°~90° 方位向 0°~360° 轨道精度 mm级精确控制 成像模式 SpotLight/StripMap/ISAR等模式
双天线InSAR成像技术
3D层析SAR成像技术
双站测量被测目标尺寸 1 cm×1 cm×1 cm~4 m×3 m×3 m 表 2 仿真图像指标参数
Table 2. Simulation image index parameters
序号 波段 极化方式 入射角(°) 方位角(°) 像元大小(cm) 实际分辨率(m) 1 Ku HH, HV, VH, VV 50 0 2.5 1.25 2 Ku HH, HV, VH, VV 50 30 2.5 1.25 3 Ku HH, HV, VH, VV 50 60 2.5 1.25 4 Ku HH, HV, VH, VV 50 90 2.5 1.25 5 Ku HH, HV, VH, VV 50 120 2.5 1.25 6 Ku HH, HV, VH, VV 50 150 2.5 1.25 7 Ku HH, HV, VH, VV 50 180 2.5 1.25 -
[1] Tadono T, Ohki M, and Abe T. Summary of natural disaster responses by the Advanced Land Observing Satellite-2(ALOS-2)[C]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing & Spatial Information Sciences, Kyoto, Japan, 2019: 69–72. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-3-W7-69-2019. [2] 张风丽, 邵芸. 城市目标高分辨率SAR遥感监测技术研究进展[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2010, 25(3): 415–422. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2010.3.415ZHANG Fengli and SHAO Yun. Urban target monitoring using high resolution SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2010, 25(3): 415–422. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2010.3.415 [3] CHEN Qihao, LI Linlin, JIANG Ping, et al. Building collapse extraction using modified freeman decomposition from post-disaster polarimetric SAR image[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience And Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 2016: 5769–5772. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730507. [4] WANG Xiaoqing, DOU Aixia, JIN Dingjian, et al. Study on the comparation of building damage extracted from different RS images acquired after 2010 M = 7.1 Yushu, Qinghai, China earthquake[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 935–938. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6351401. [5] ZHANG Haizhen, WANG Qing, ZENG Qiming, et al. A novel approach to building collapse detection from post-seismic polarimetric SAR imagery by using optimization of polarimetric contrast enhancement[C]. 2015 IEEE International Geoscience And Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 2015: 3270–3273. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2015.7326516. [6] PARK S E, YAMAGUCHI Y, and KIM D J. Polarimetric SAR remote sensing of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake using ALOS/PALSAR[J]. Remote sensing of Environment, 2013, 132: 212–220. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.01.018 [7] ZHAI Wei, SHEN Huanfeng, HUANG Chunlin, et al. Building earthquake damage information extraction from a single post-earthquake PolSAR image[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(3): 171. doi: 10.3390/rs8030171 [8] SATO M, CHEN Siwei, and SATAKE M. Polarimetric SAR analysis of tsunami damage following the March 11, 2011 East Japan earthquake[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(10): 2861–2875. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2200649 [9] WATANABE M, MOTOHKA T, MIYAGI Y, et al. 2012. Analysis of urban areas affected by the 2011 off the pacific coast of Tohoku earthquake and tsunami with L-Band SAR full-polarimetric mode[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(3): 472–476. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2182030 [10] ZHAI Wei and HUANG Chunlin. Fast building damage mapping using a single post-earthquake PolSAR image: A case study of the 2010 Yushu earthquake[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2016, 68(1): 86. doi: 10.1186/s40623-016-0469-2 [11] ZHAI Wei, HUANG Chunlin, and PEI Wansheng. Two new polarimetric feature parameters for the recognition of the different kinds of buildings in earthquake-stricken areas based on entropy and eigenvalues of PolSAR decomposition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(10): 1613. doi: 10.3390/rs10101613 [12] LI Xinwu, GUO Huadong, ZHANG Lu, et al. A new approach to collapsed building extraction using RADARSAT-2 polarimetric SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4): 677–681. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2178392 [13] SUN Weidong, SHI Lei, YANG Jie, et al. Building collapse assessment in urban areas using texture information from postevent SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(8): 3792–3808. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2580610 [14] ZHAO Lingli, YANG Jie, LI Pingxiang, et al. Damage assessment in urban areas using post-earthquake airborne PolSAR imagery[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 34(24): 8952–8966. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2013.860566 [15] GE Pinglan, GOKON H, and MEGURO K. A review on synthetic aperture radar-based building damage assessment in disasters[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 240: 111693. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111693 [16] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, and SATO M. Urban damage level mapping based on scattering mechanism investigation using fully polarimetric SAR data for the 3.11 East Japan earthquake[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(12): 6919–6929. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2588325 [17] 王雪松, 陈思伟. 合成孔径雷达极化成像解译识别技术的进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109WANG Xuesong and CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interpretation and recognition: Advances and perspectives[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109 [18] FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687 [19] YAMAGUCHI Y, SATO A, BOERNER W M, et al. Four-component scattering power decomposition with rotation of coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(6): 2251–2258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2099124 [20] JI Kefeng and WU Yonghui. Scattering mechanism extraction by a modified cloude-pottier decomposition for dual polarization SAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(6): 7447–7470. doi: 10.3390/rs70607447 [21] CHIEN L L C, EWE H T, and SAW S H. Understanding the correlation in scattering mechanisms between H-Alpha decomposition and theoretical modelling[C]. 2018 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS-Toyama), Toyama, Japan, 2018: 1198–1203. doi: 10.23919/PIERS.2018.8597662. [22] TOUZI R. Target scattering decomposition in terms of roll-invariant target parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(1): 73–84. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.886176 [23] AN Wentao, XIE Chunhua, YUAN Xinzhe, et al. Four-component decomposition of polarimetric SAR images with deorientation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(6): 1090–1094. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2157078 [24] 孙翔, 宋红军, 王宇, 等. 基于高分辨率全极化SAR图像的取向角校正方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 465–474. doi: 10.12000/JR18026SUN Xiang, SONG Hongjun, WANG R, et al. POA correction method using high-resolution full-polarization SAR image[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 465–474. doi: 10.12000/JR18026 [25] LIU Shan, ZHANG Fengli, WEI Shiying, et al. Building damage mapping based on Touzi decomposition using quad-polarimetric ALOS PALSAR data[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2020: 1–12. doi: 10.1007/s11707-019-0779-3 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公





 下载:
下载: