Pseudo-random Agility Technology for Interpulse Waveform Parameters in Airborne Radar
-
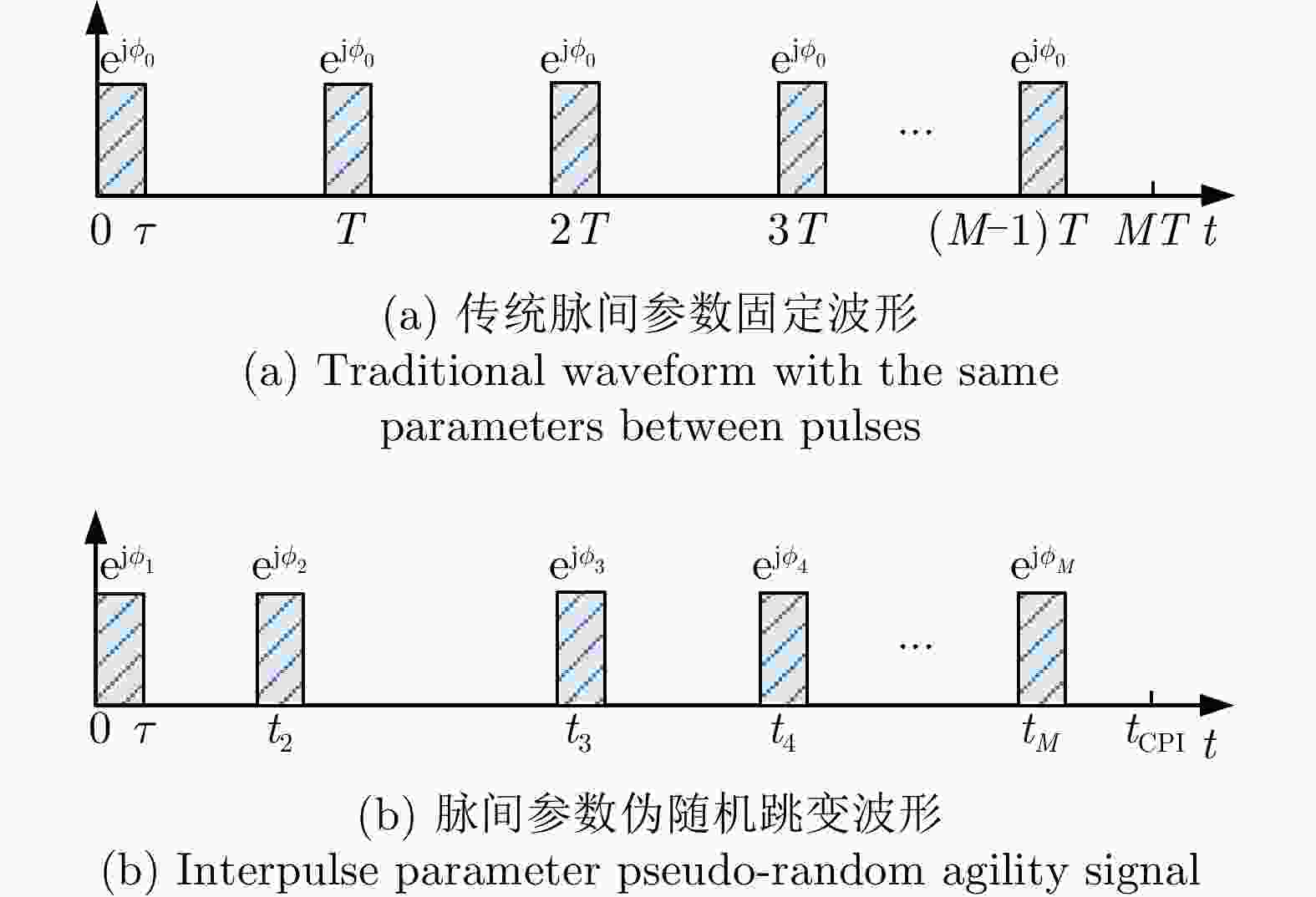
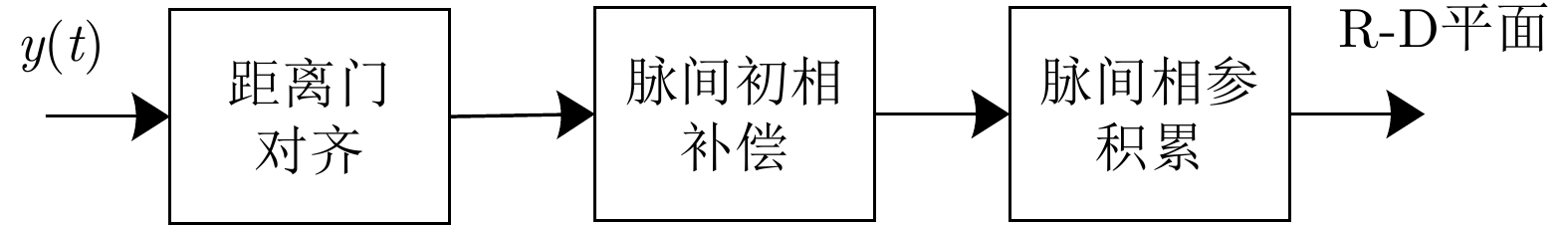
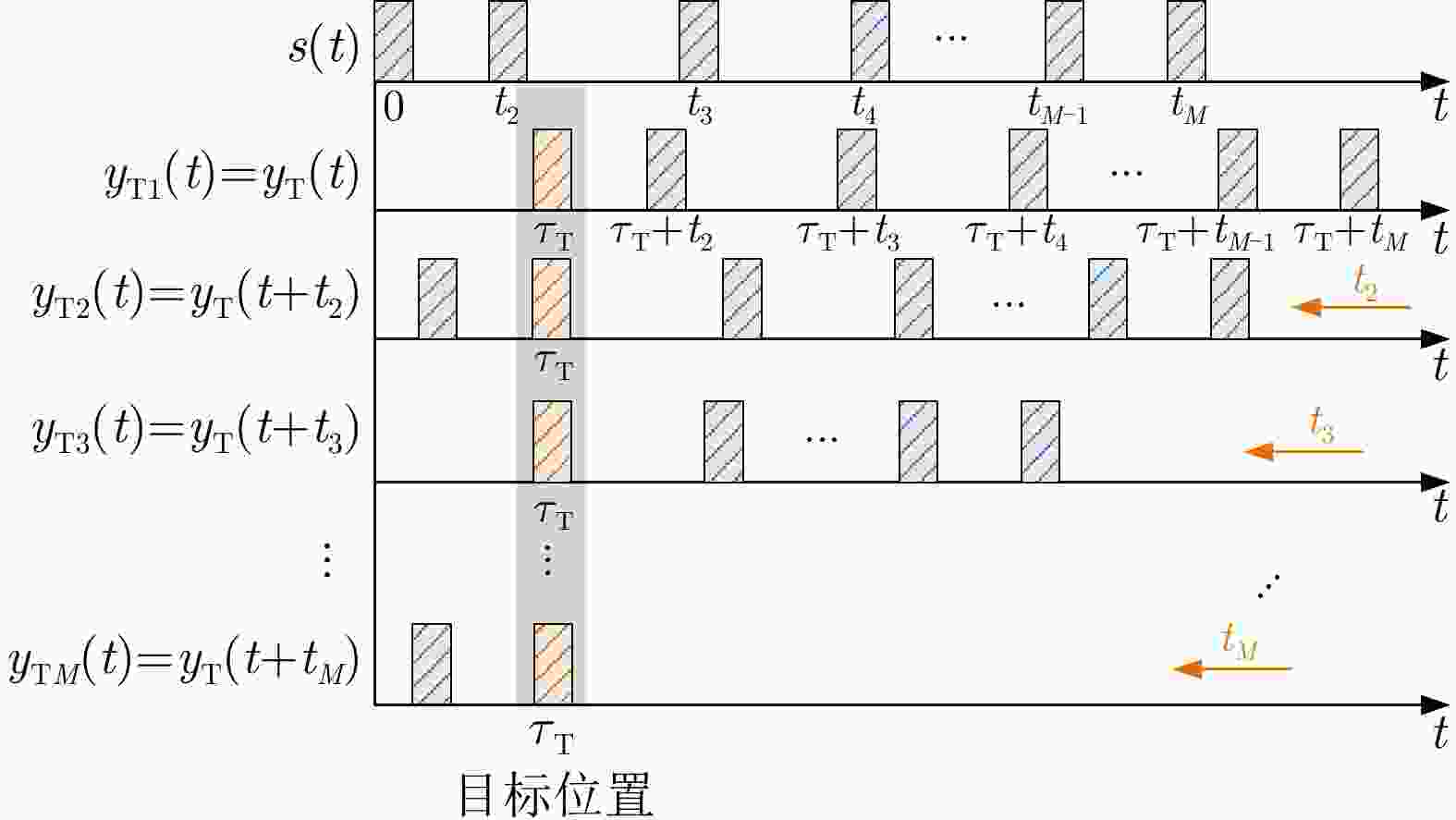
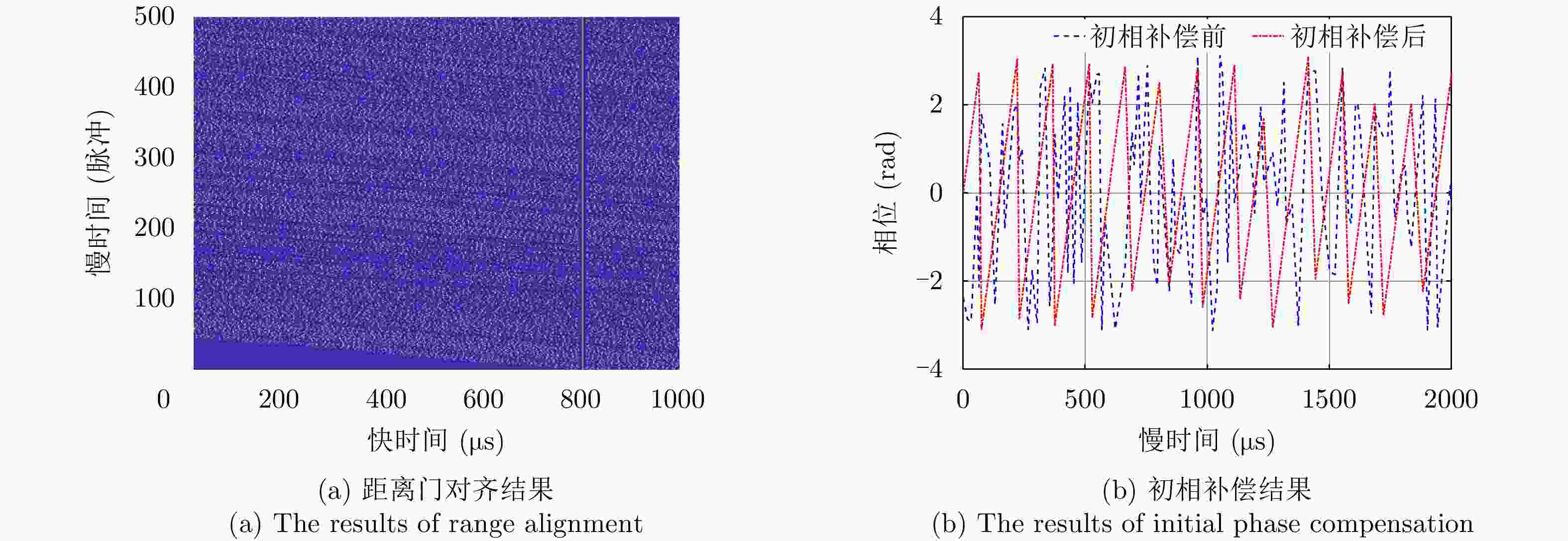
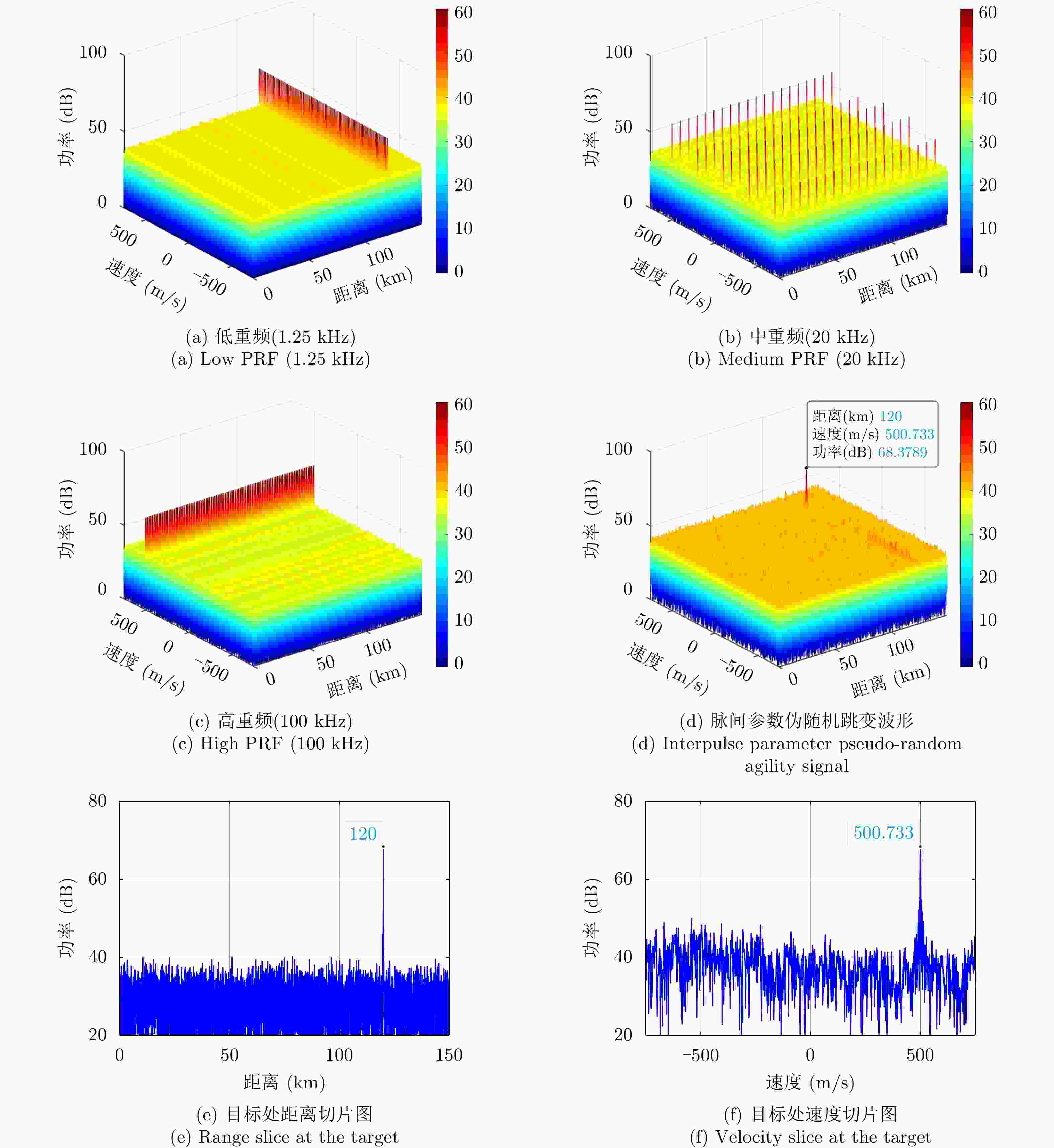
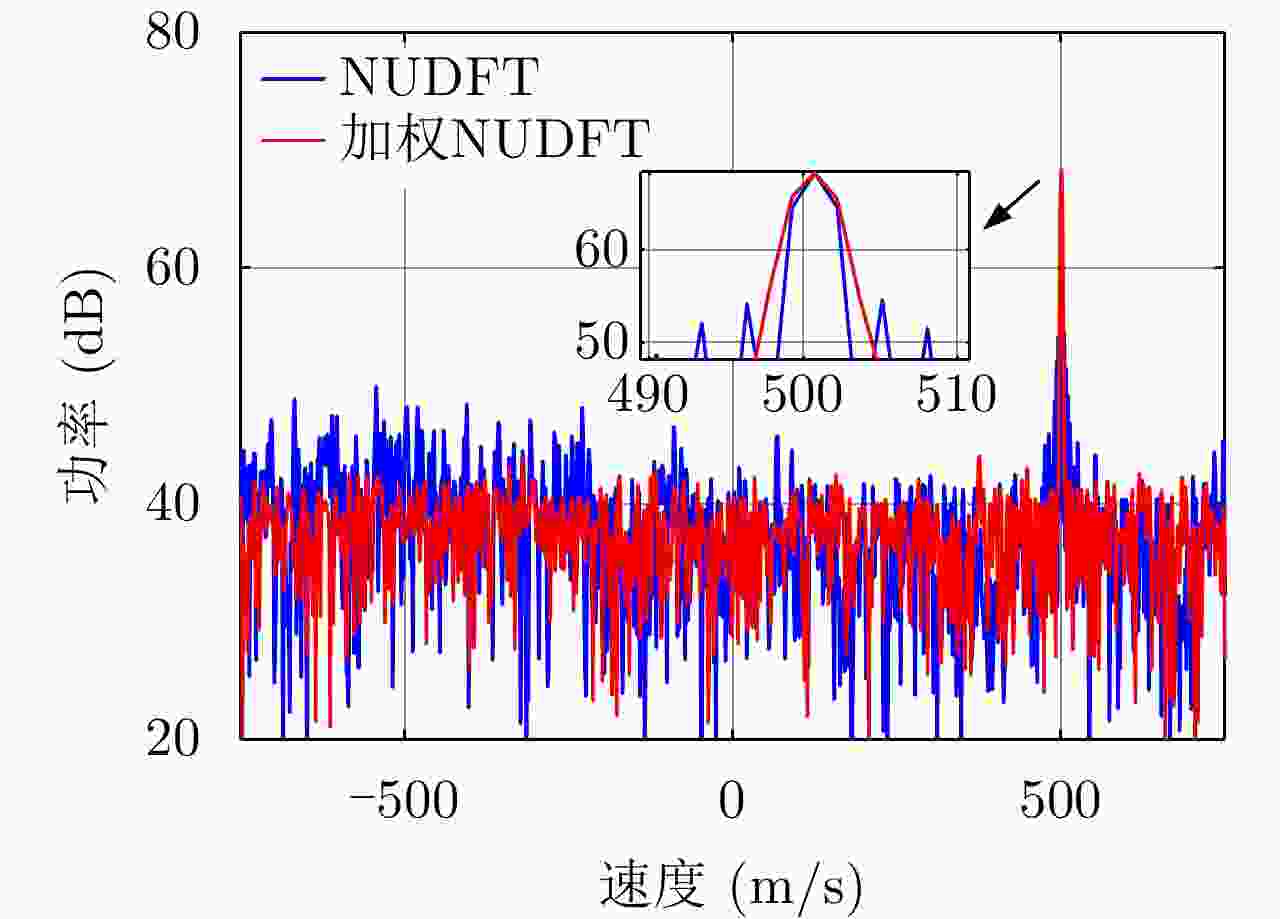
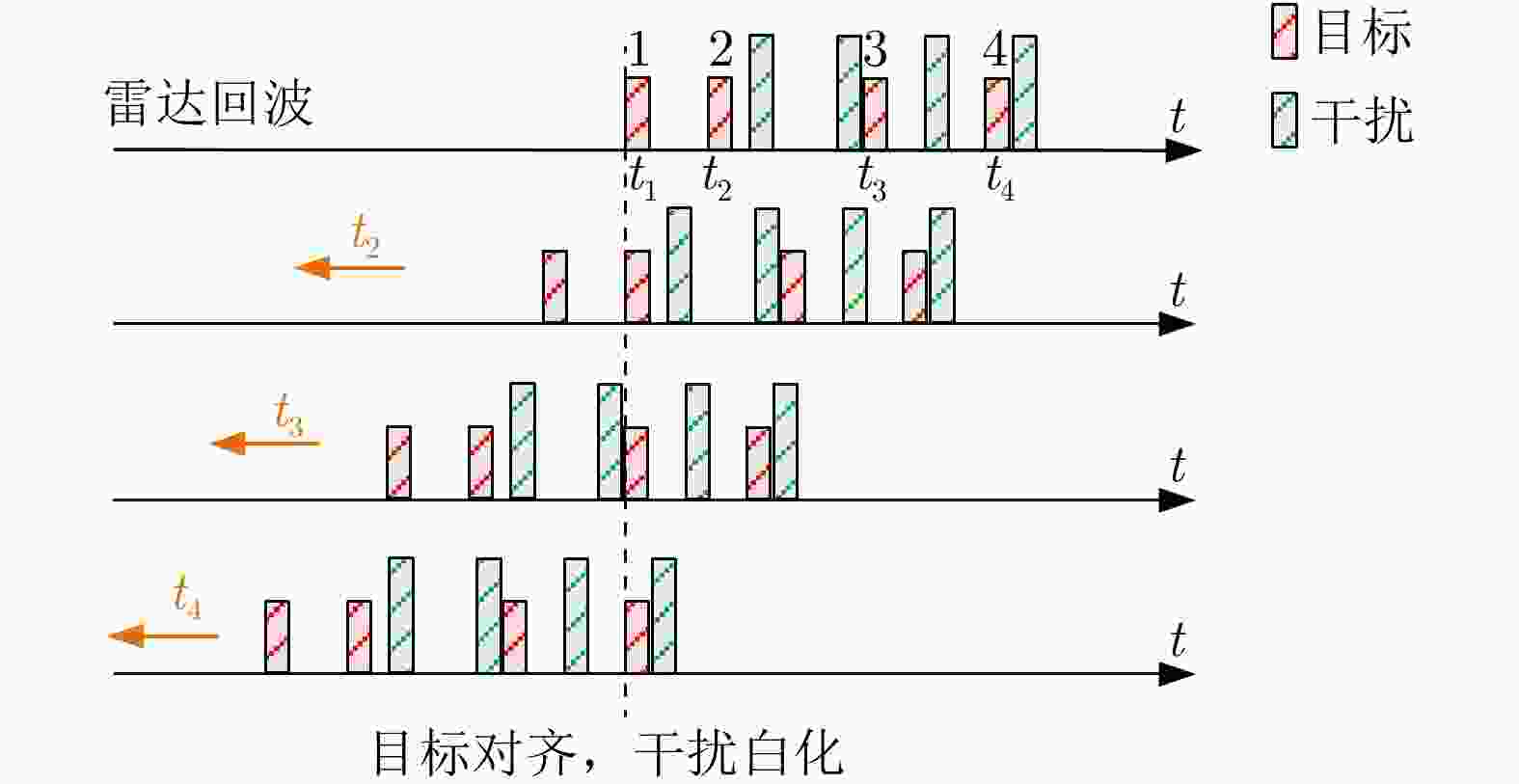
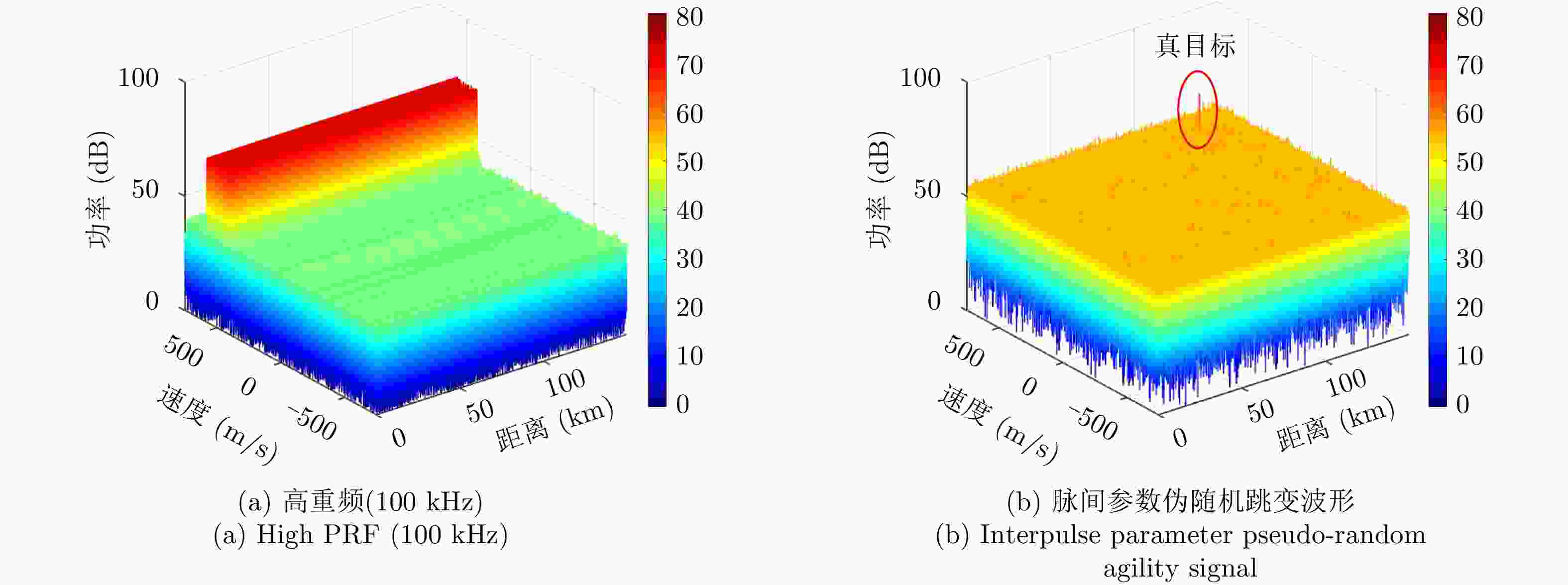
摘要: 机载雷达脉间波形参数伪随机跳变主要是通过优化设计脉冲重复间隔、初相、频率和幅度等参数,增加雷达波形的复杂度与不确定性,提升机载雷达反杂波和抗干扰能力,是机载雷达技术的主要发展方向之一。脉间参数的伪随机跳变给多脉冲相参积累、杂波谱特性建模等带来困难。该文建立了脉间参数伪随机跳变信号模型,提出了非均匀参数捷变脉间相参处理方法,并分析了抗干扰性能。在此基础上,研究了脉冲重复间隔捷变下的机载雷达杂波回波模型,提出了发射-接收滤波器联合优化设计的强杂波处理方法,并进行了仿真验证。Abstract: The pseudo-random agility technology for interpulse waveform parameters in airborne radar increases the complexity and uncertainty of radar waveform and improves its anti-clutter and anti-interference ability by optimizing the pulse repetition interval, initial phase, frequency, and amplitude, which is one of the main developmental directions of airborne radar technology. The pseudo-random agility of interpulse parameters makes multi-pulse coherent accumulation and modeling of clutter spectrum characteristics difficult. In this paper, a pseudo-random agility signal model of interpulse parameters is established. Furthermore, a non-uniform parameter coherent processing method is proposed, and the anti-interference performance is analyzed. Based on the analysis, the clutter echo model of airborne radar with random pulse repetition interval is studied, and a joint transmitter-receiver filter design is proposed for strong clutter processing. Finally, numerical simulation is conducted to verify the results.
-
Key words:
- Airborne radar /
- Interpulse waveform /
- Pseudo-random agility /
- Coherent processing /
- Clutter suppression
-
表 1 杂波仿真参数
Table 1. Clutter simulation parameters
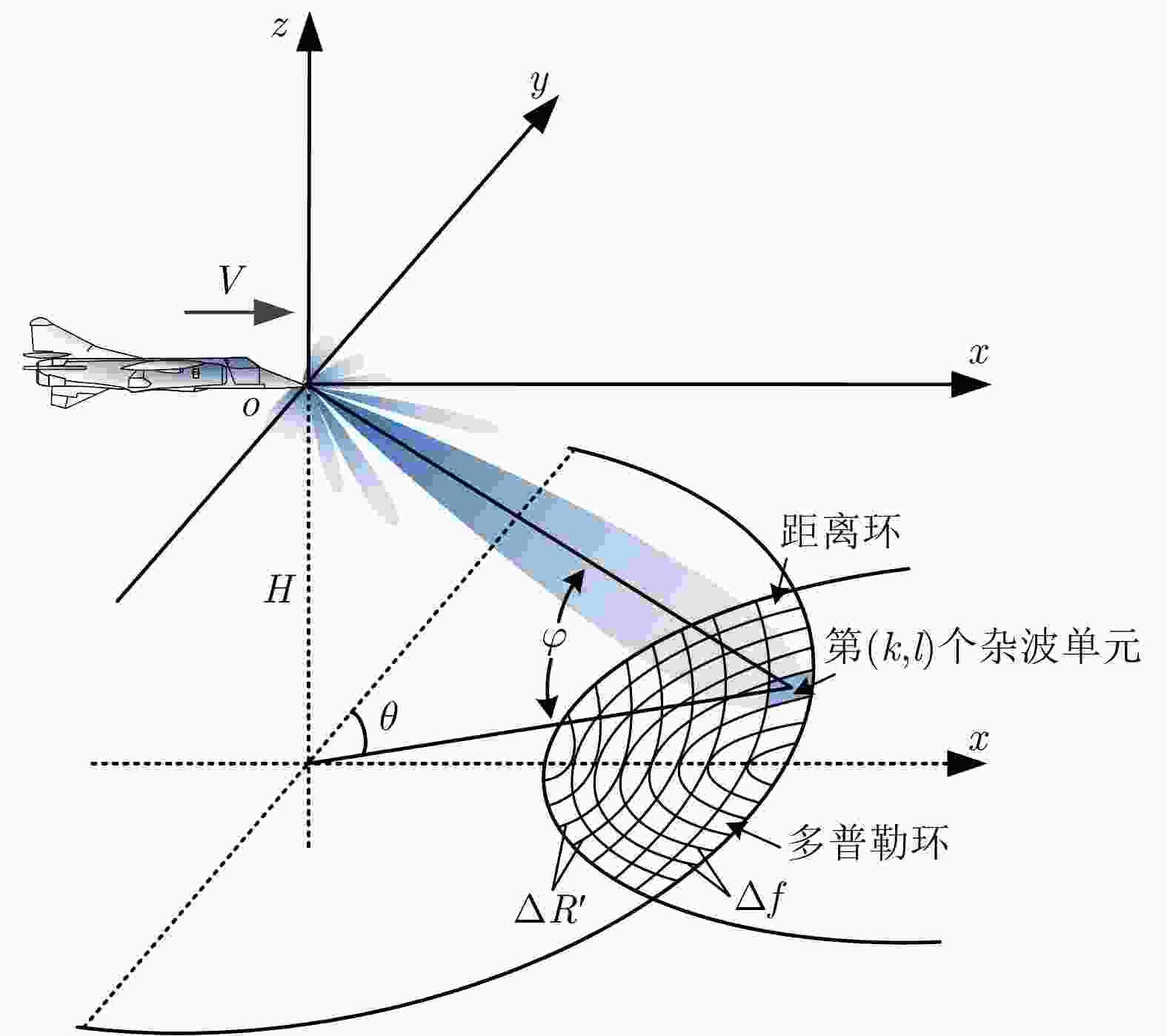
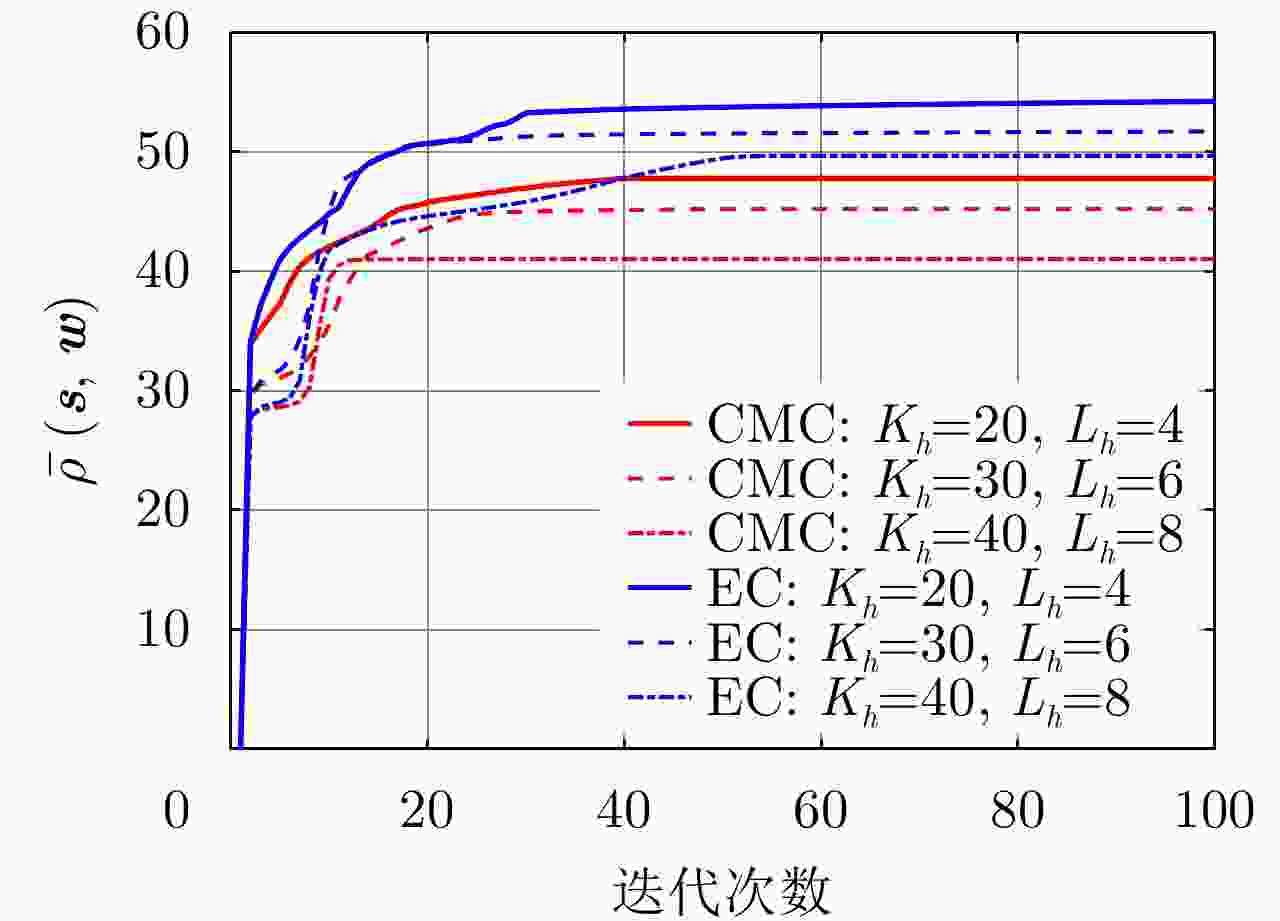
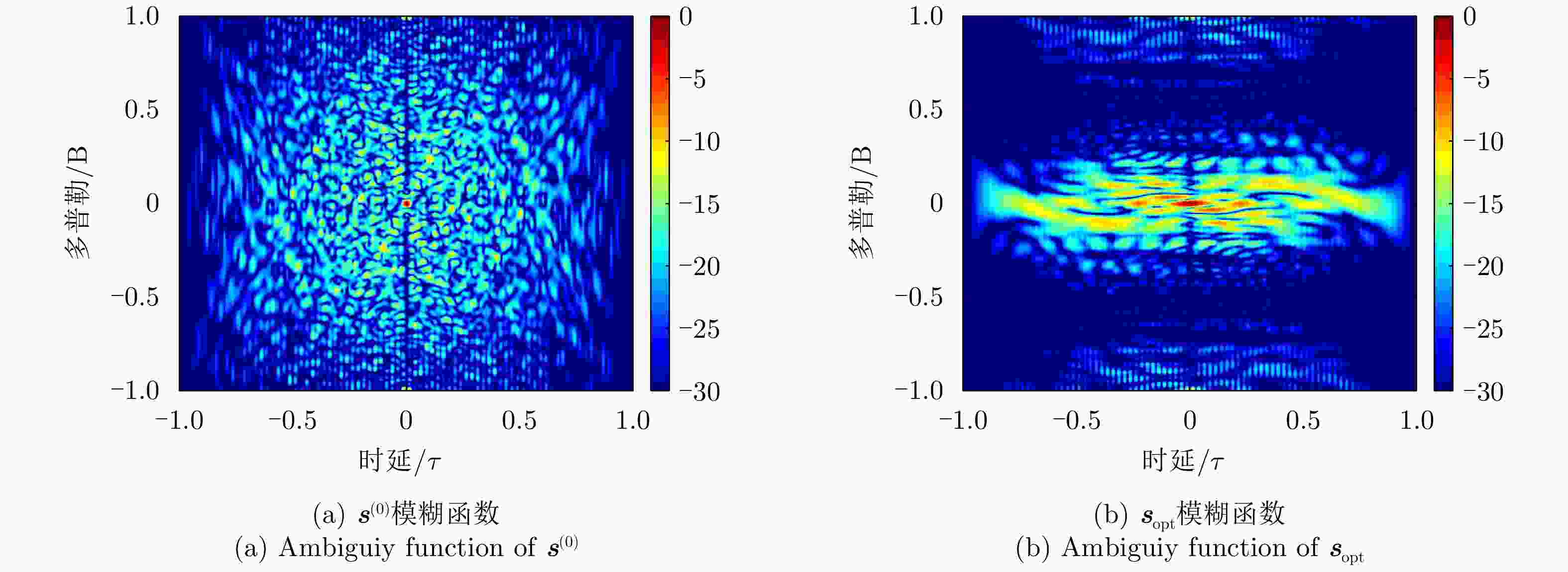
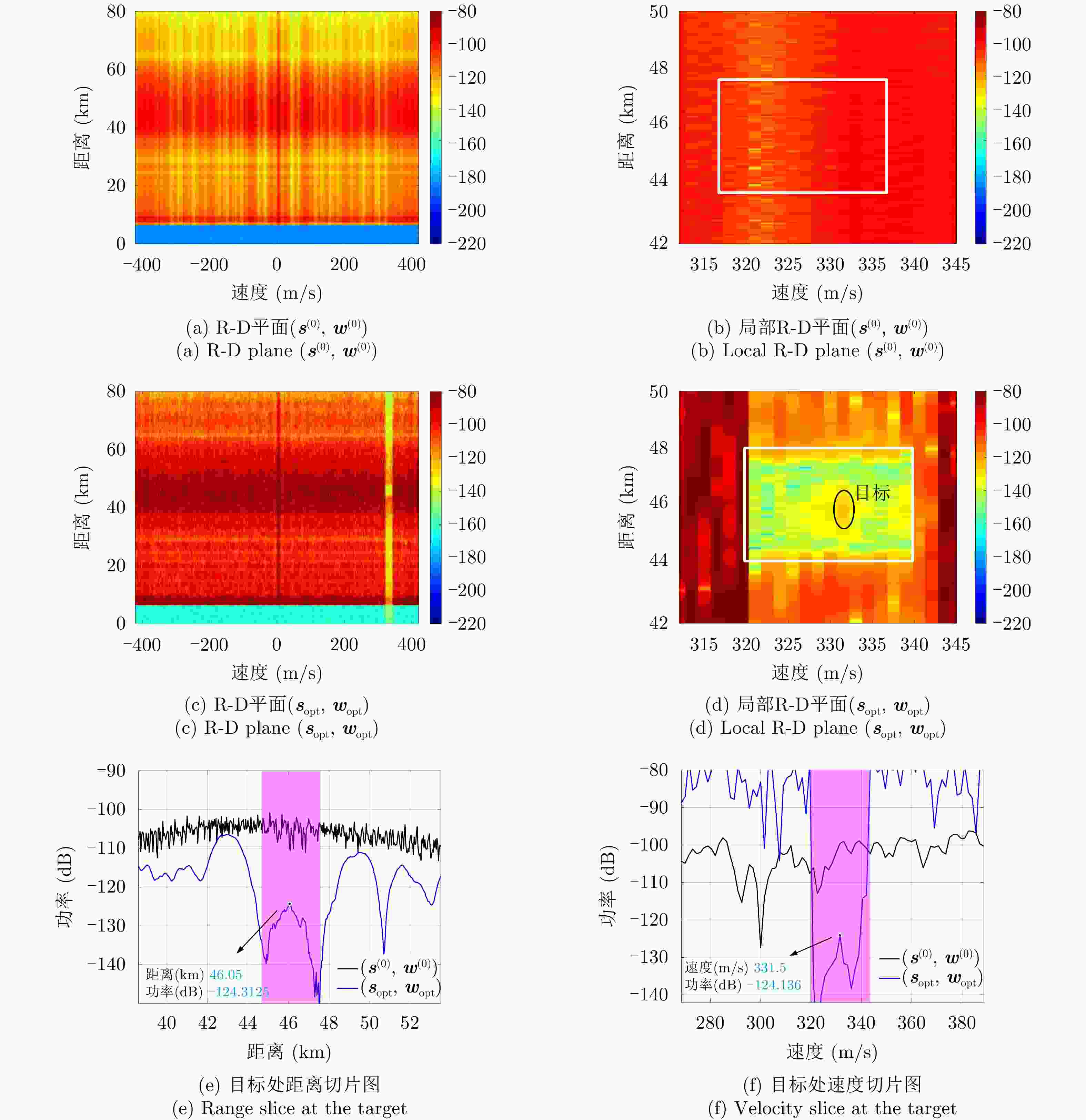
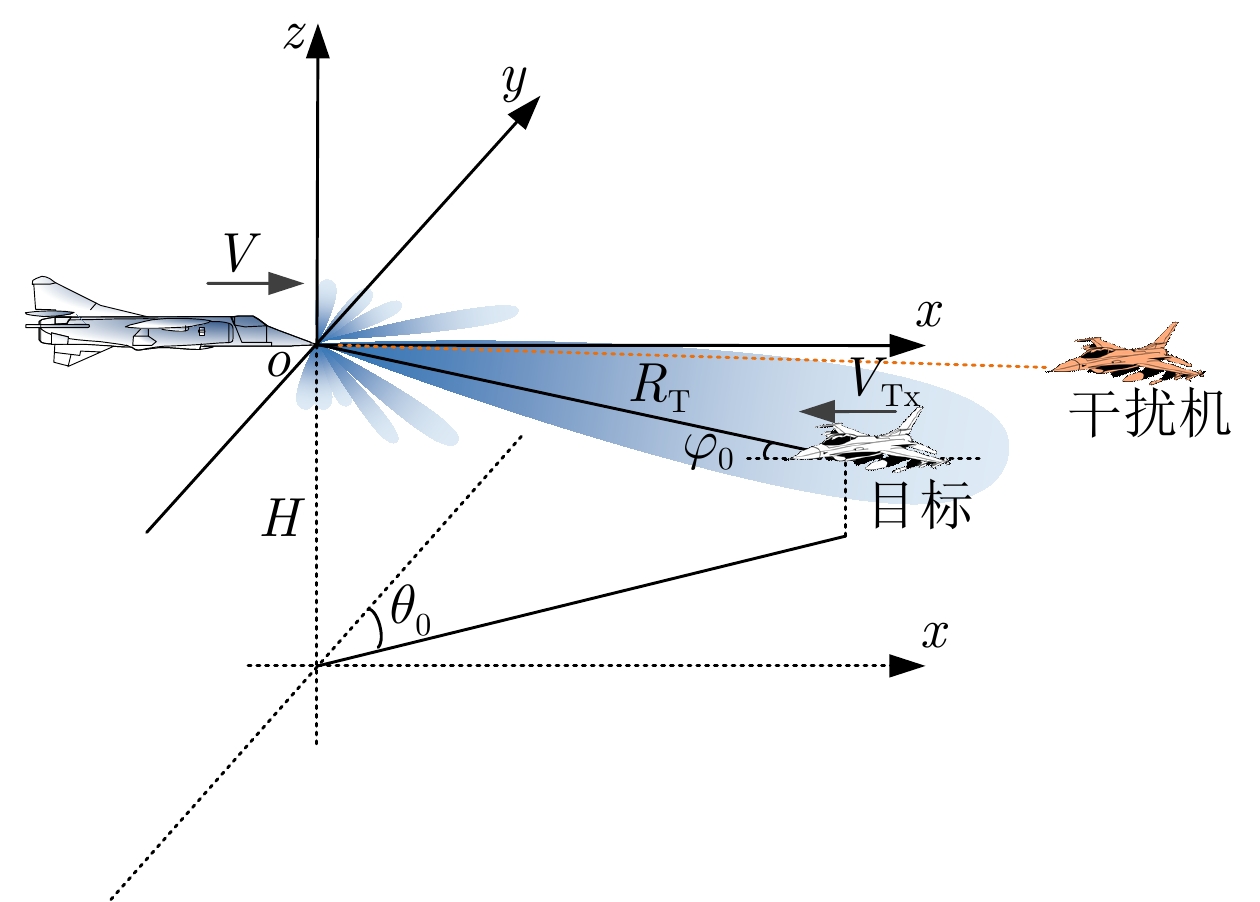
参数 数值 参数 数值 波长$\lambda $ 0.03 m 载机高度$H$ 8 km 相控阵规模$N \times N$ 40×40 载机速度$V$ 140 m/s 阵元间隔$d$ ${\lambda \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\lambda 2}} \right. } 2}$ 距离环间隔$\Delta R$ 15 m 波束指向$\left({\theta }_{0},\,{\varphi }_{0}\right)$ (2°, –10°) 多普勒环间隔$\Delta f$ 100 Hz 阵元加权类型 泰勒加权 最大多普勒频率${f_m}$ ${{4V} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{4V} \lambda }} \right. } \lambda }$ 波束最大增益$G$ 30 dB 杂波后向散射率模型 Morchin模型[38] 雷达发射功率${P_{\text{T}}}$ 10 kW 噪声功率$\sigma _{\text{w}}^2$ –130 dBW -
[1] SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008. [2] STIMSON G W. Introduction to Airborne Radar[M]. 2nd ed. Mendham: SciTech Publishing, Inc. , 1998. [3] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, JIANG Bo, et al. Ambiguity function shaping for cognitive radar via complex quartic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(22): 5603–5619. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2273885 [4] ALHUJAILI K, MONGA V, and RANGASWAMY M. Quartic gradient descent for tractable radar slow-time ambiguity function shaping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1474–1489. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2934336 [5] NAGHSH M M, SOLTANALIAN M, STOICA P, et al. A doppler robust design of transmit sequence and receive filter in the presence of signal-dependent interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(4): 772–785. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288082 [6] 全英汇, 方文, 沙明辉, 等. 频率捷变雷达波形对抗技术现状与展望[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(11): 3126–3136. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.11QUAN Yinghui, FANG Wen, SHA Minghui, et al. Present situation and prospects of frequency agility radar waveform countermeasures[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3126–3136. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.11 [7] LONG Xingwang, LI Kun, TIAN Jing, et al. Ambiguity function analysis of random frequency and PRI agile signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 382–396. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3016851 [8] 吴耀君. 脉间频率捷变雷达抗干扰研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.WU Yaojun. Research on anti-jamming performance of frequency agility radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2018. [9] HUANG Tianyao, LIU Yimin, MENG Huadong, et al. Cognitive random stepped frequency radar with sparse recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 858–870. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.120443 [10] DE MAIO A, DE NICOLA S, HUANG Yongwei, et al. Design of phase codes for radar performance optimization with a similarity constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 610–621. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2008247 [11] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 杨婧, 等. 认知雷达波形优化设计方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, YANG Jing, et al. An overview of waveform optimization methods for cognitive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072 [12] LIN K. Anti-jamming MTI radar using variable pulse-codes[D]. [Master dissertation], Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2002. [13] 苏峰, 高梅国, 田黎育, 等. 基于脉间码型捷变的相位编码旁瓣抑制方法[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2009, 29(5): 441–445.SU Feng, GAO Meiguo, TIAN Liyu, et al. Sidelobe suppression of phase-coded radar signal based on interpulse code agility[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2009, 29(5): 441–445. [14] ZHANG Jindong, ZHU Daiyin, and ZHANG Gong. New antivelocity deception jamming technique using pulses with adaptive initial phases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(2): 1290–1330. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6494414 [15] XIONG Wei, WANG Xinhai, and ZHANG Gong. Cognitive waveform design for anti-velocity deception jamming with adaptive initial phases[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–5. [16] 吴健. 基于波形分集的雷达抗有源欺骗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士学位], 电子科技大学, 2015: 48–64.WU Jian. Research of technology against radar active deception jamming based on waveform diversity[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015: 48–64. [17] YANG Ya, WU Jian, CUI Guolong, et al. Optimized phase-coded waveform design against velocity deception[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 400–404. [18] 葛鹏. 基于知识辅助的雷达波形设计算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017: 60–97.GE Peng. Research on methods of knowledge-aided radar waveform design[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017: 60–97. [19] 张洋, 位寅生. 基于认知的抗折叠扩展杂波波形设计方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(10): 2216–2222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.09ZHANG Yang and WEI Yinsheng. Waveform design of range-folded spread clutter mitigation based on cognition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(10): 2216–2222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.09 [20] 葛萌萌, 余显祥, 严正欣, 等. 脉间波形幅相联合设计抗欺骗干扰方法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2021, 50(4): 481–487. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021075GE Mengmeng, YU Xianxiang, YAN Zhengxin, et al. Optimized amplitude-phase waveform against deceptive jamming[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021, 50(4): 481–487. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021075 [21] AUBRY A, DEMAIO A, FARINA A, et al. Knowledge-aided (potentially cognitive) transmit signal and receive filter design in signal-dependent clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(1): 93–117. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6404093 [22] 黄琼丹, 李勇, 卢光跃. 脉间Costas跳频脉内多载波混沌相位编码雷达信号设计与分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(6): 1483–1489. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140653HUANG Qiongdan, LI Yong, and LU Guangyue. Design and analysis of inter-pulse costas frequency hopping and intra-pulse multi-carrier chaotic phase coded radar signal[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(6): 1483–1489. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140653 [23] TANG Bo and TANG Jun. Joint design of transmit waveforms and receive filters for MIMO radar space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(18): 4707–4722. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2569431 [24] GE Mengmeng, YU Xianxiang, YAN Zhengxin, et al. Joint cognitive optimization of transmit waveform and receive filter against deceptive interference[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 185: 108084. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108084 [25] TANG Bo, LI Jun, ZHANG Yu, et al. Design of MIMO radar waveform covariance matrix for clutter and jamming suppression based on space time adaptive processing[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 121: 60–69. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.10.033 [26] TANG Bo, TUCK J, and STOICA P. Polyphase waveform design for MIMO radar space time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 2143–2154. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2983833 [27] CUI Guolong, FU Yue, YU Xianxiang, et al. Robust transmitter-receiver design in the presence of signal-dependent clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(4): 1871–1882. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2805147 [28] YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, YANG Jing, et al. MIMO radar transmit-receive design for moving target detection in signal-dependent clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(1): 522–536. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2951399 [29] FAN Tao, GE Mengmeng, GAN Na, et al. Transmit-receive design for non-uniform pulse repetition interval airborne radar in the presence of signal-dependent clutter[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference, Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6. [30] MAIER M W. Non-uniform PRI pulse-Doppler radar[C]. The 1993 (25th) Southeastern Symposium on System Theory, Tuscaloosa, USA, 1993: 164–168. [31] FAN Tao, KONG Yukai, WANG Mingxing, et al. Doppler filter bank design for non-uniform PRI radar in signal-dependent clutter[C]. 2021 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, USA, 2021: 1–5. [32] KAVEH M and COOPER G R. Average ambiguity function for a randomly staggered pulse sequence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1976, AES-12(3): 410–413. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1976.308245 [33] LIU Zhen, WEI Xizhang, and LI Xiang. Aliasing-free moving target detection in random pulse repetition interval radar based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2013, 13(7): 2523–2534. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2013.2249762 [34] 刘振, 魏玺章, 黎湘. 一种新的随机PRI脉冲多普勒雷达无模糊MTD算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 28–35. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.10063LIU Zhen, WEI Xizhang, and LI Xiang. Novel method of unambiguous moving target detection in pulse-Doppler radar with random pulse repetition interval[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 28–35. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.10063 [35] KONG Yukai, CUI Guolong, GUO Shisheng, et al. Coherent radar detection framework with non-uniform pulse repetition intervals[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 18645–18657. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963374 [36] LU Yuxiang, TANG Ziyue, ZHANG Yuanpeng, et al. Maximum unambiguous frequency of random PRI radar[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5. [37] JAO J K and GOGGINS W B. Efficient, closed-form computation of airborne pulse-Doppler radar clutter[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 1985: 17–22. [38] MORCHIN W C. Airborne Early Warning Radar[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1990. [39] FAN Tao, YU Xianxiang, GAN Na, et al. Transmit-receive design for airborne radar with nonuniform pulse repetition intervals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 4067–4084. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3090915 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: