-
摘要:
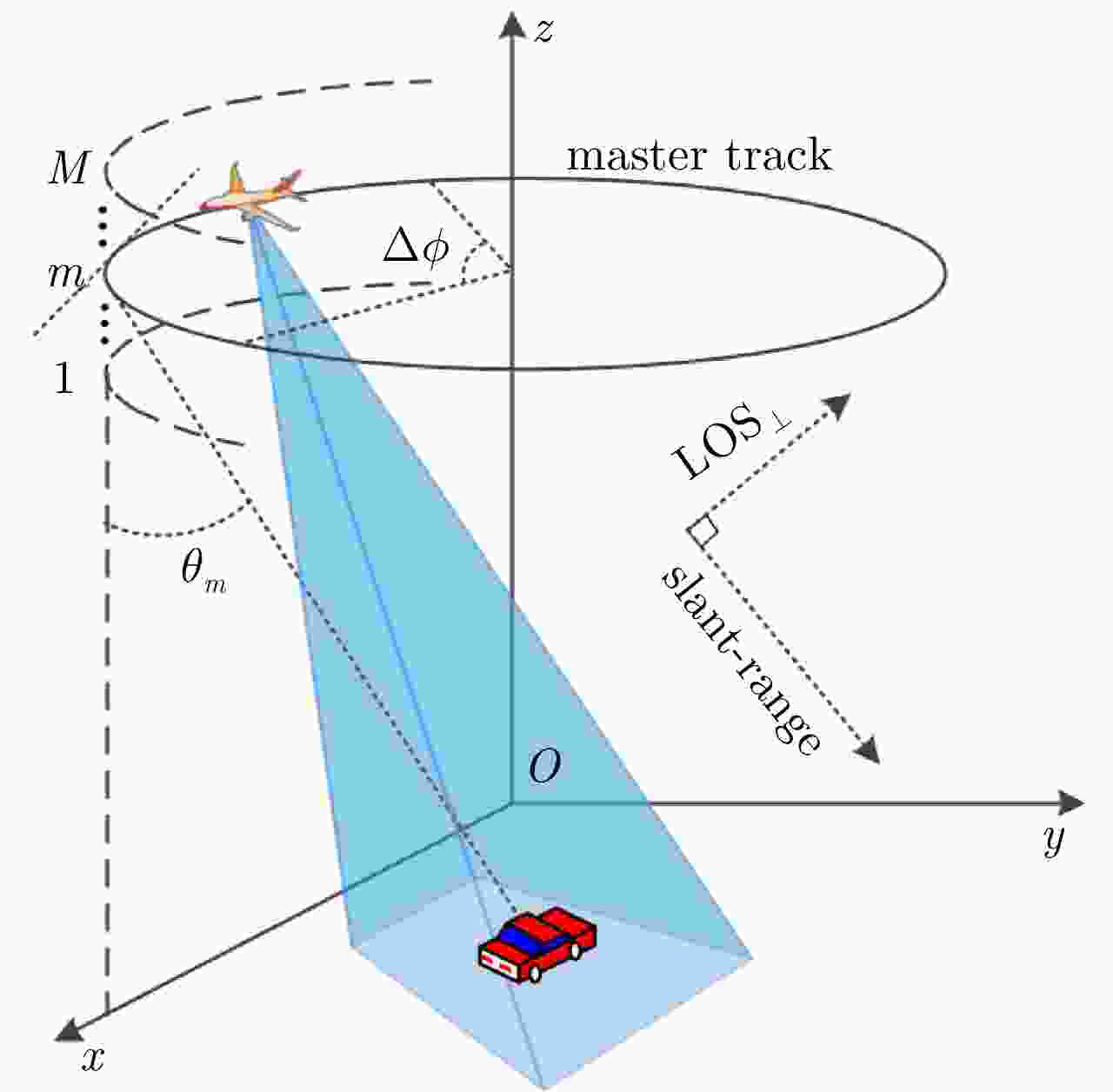
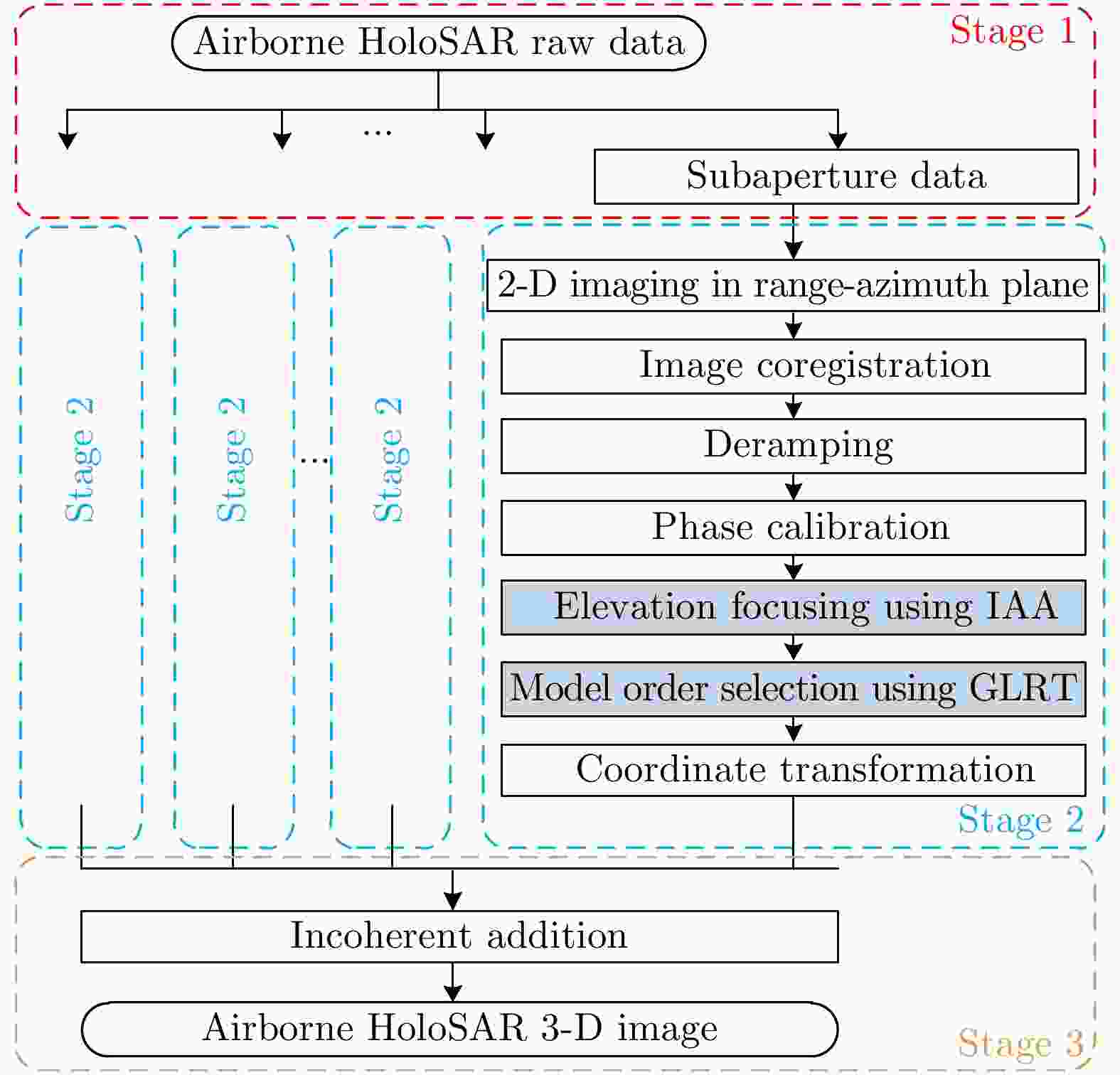
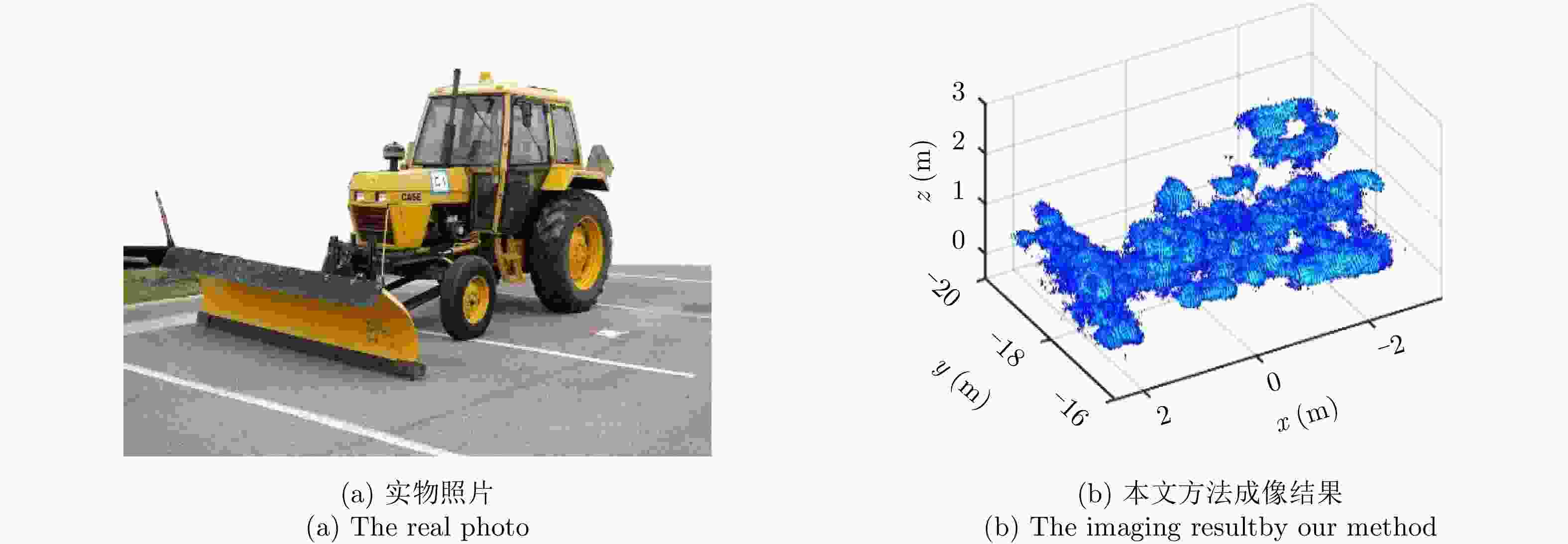
机载圆周合成孔径雷达(CSAR)作为一种新兴的成像模式,具有全方位观测、高空间分辨率和可三维成像等优点。随着CSAR成像技术的不断发展,现已逐渐成为对重点区域实施精确观测的有效手段之一。该文重点阐述了作者所在研究团队近年来在机载CSAR成像技术方面完成的研究工作,包括机载CSAR成像模型,空间分辨率评估,CSAR二维成像,基于单圆周CSAR的目标三维图像重构和多基线CSAR(HoloSAR)三维成像等技术,并给出了P, X两个频段机载CSAR的实测数据处理结果。已取得的研究成果证明了机载CSAR成像的有效性和实用性。该文主要内容基于作者2019年8月16日在“雷达学报第五届青年科学家论坛”上的学术报告。
Abstract:Circular Synthetic Aperture Radar (CSAR) is a novel imaging mode, which has the advantages of all-directional observation, high spatial resolution, and three-dimensional imaging. With the development of airborne CSAR imaging techniques, it has become one of the effective methods for key point area observation. This paper introduces works on airborne CSAR imaging techniques performed by our research team in recent years, including airborne CSAR imaging mode, spatial resolution evaluation, two-dimensional CSAR imaging, three-dimensional target image reconstruction based on a single CSAR, and three-dimensional holographic SAR imaging. In this paper, experimental results based on raw data acquired using airborne CSAR systems with P and X bands are presented. The obtained research results prove the effectivity and practicability of the airborne CSAR imaging mode. The content of this paper is based on a keynote speech presented by the author at the Fifth Young Scientists Forum of Journal of Radars on August 15, 2019.
-
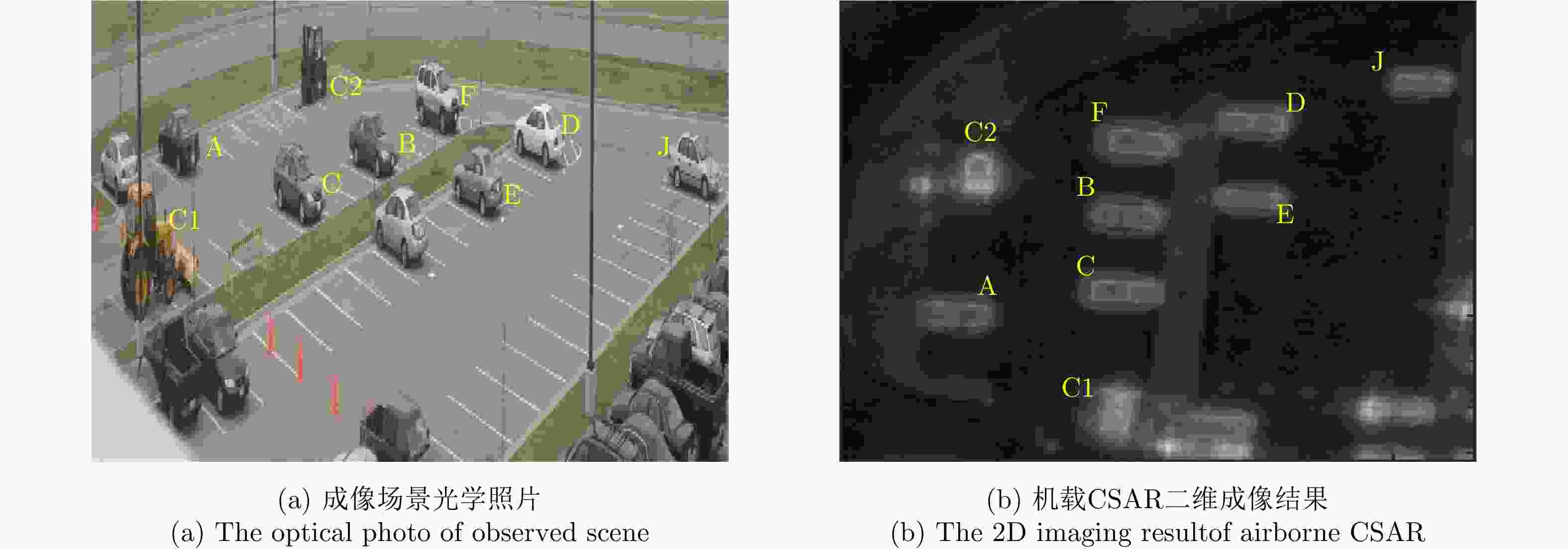
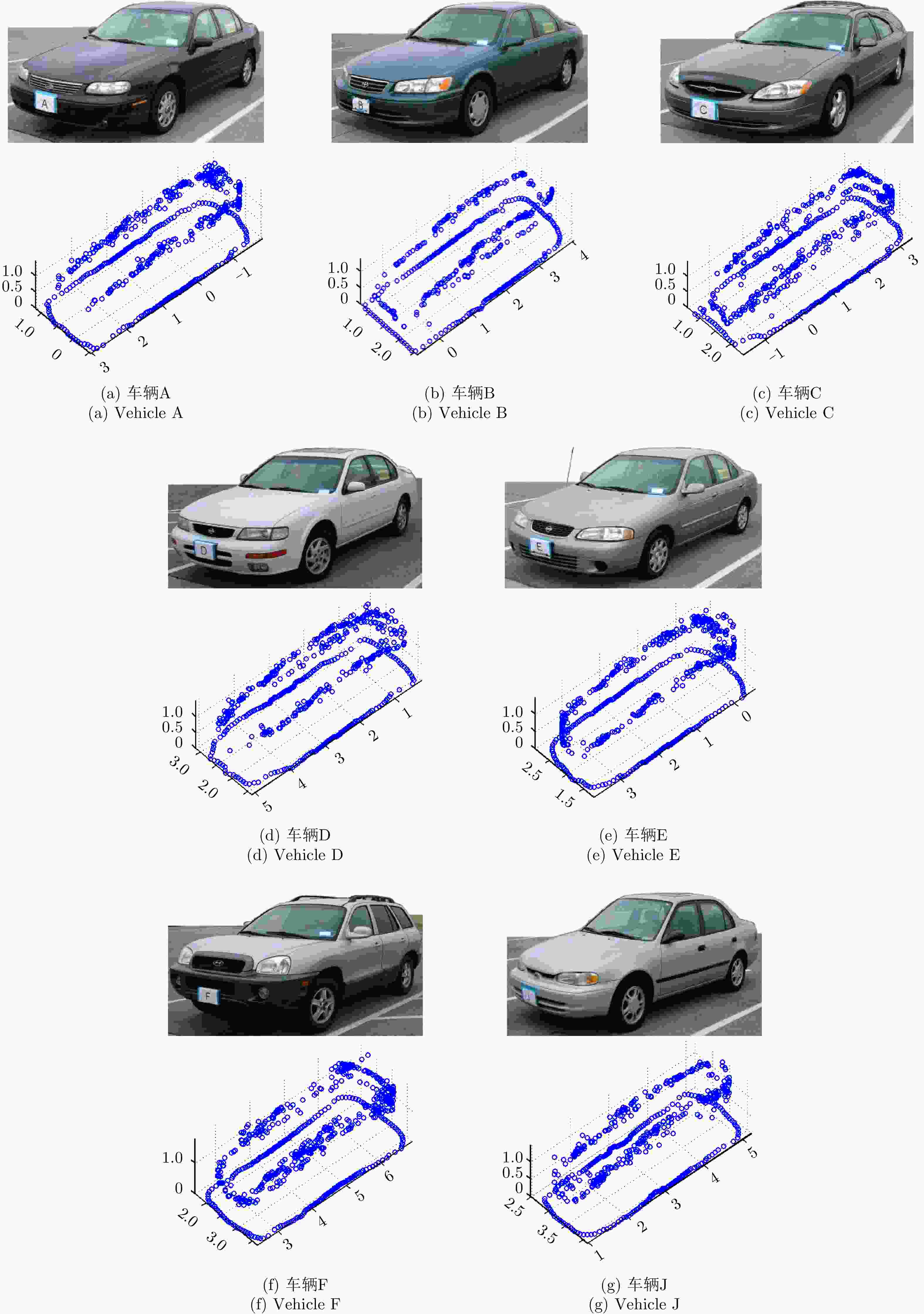
表 1 车辆的真实尺寸与估计值对比(mm)
Table 1. The comparisons between the actual size of the vehicles and their estimated values
车辆编号(品牌) 长 宽 高 $l$ $\hat l$ $\Delta l$ $w$ $\hat w$ $\Delta w$ $h$ $\hat h$ $\Delta h$ 车辆A(Chevy Malibu) 4840 4814 26 1760 1616 144 1430 1433 –3 车辆B(Toyota Camry) 4790 4710 80 1780 1711 69 1410 1332 78 车辆C(Ford Taurus) 5020 4873 147 1850 1737 113 1470 1482 –12 车辆D(Nissan Maxima) 4770 4834 –64 1770 1687 83 1410 1371 39 车辆E(Nissan Sentra) 4510 4208 302 1710 1610 100 1440 1459 –19 车辆F(Hyundai Santa Fe) 4500 4517 –17 1840 1771 69 1670 1684 –14 车辆J(Chevy Prizm) 4420 4226 194 1690 1447 243 1360 1339 21 误差均值和标准差 ${\mu _{\Delta l} } = 95,\; {\sigma _{\Delta l} } = 128$ ${\mu _{\Delta w} } = {\rm{117} }, \;{\sigma _{\Delta w} } = {\rm{61} }$ ${\mu _{\Delta h} } = {\rm{13} },\; {\sigma _{\Delta h} } = {\rm{36} }$ 表 2 车辆的真实尺寸与估计值(mm)
Table 2. Comparison of the actual size of the vehicle with the estimated value
车辆编号(品牌) 长 宽 高 $l$ $\hat l$ $\Delta l$ $w$ $\hat w$ $\Delta w$ $h$ $\hat h$ $\Delta h$ 车辆A(Chevy Malibu) 4840 4800 40 1760 1750 10 1430 1450 –20 车辆B(Toyota Camry) 4790 4800 –10 1780 1800 –20 1410 1400 10 车辆C(Ford Taurus) 5020 5050 –30 1850 1850 0 1470 1480 –10 车辆D(Nissan Maxima) 4770 4750 20 1770 1800 –30 1410 1390 20 车辆E(Nissan Sentra) 4510 4350 160 1710 1450 260 1440 1430 10 车辆F(Hyundai Santa Fe) 4500 4500 0 1840 1850 –10 1670 1680 –10 车辆J(Chevy Prizm) 4420 4300 120 1690 1600 90 1360 1320 40 误差均值和标准差 ${\mu _{\Delta l} } = 40,\; {\sigma _{\Delta l} } = 70$ ${\mu _{\Delta w} } = {\rm{40} },\; {\sigma _{\Delta w} } = 100$ ${\mu _{\Delta h} } = {\rm{10} },\; {\sigma _{\Delta h} } = 20$ -
[1] ISHIMARU A, CHAN T K, and KUGA Y. An imaging technique using confocal circular synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(5): 1524–1530. doi: 10.1109/36.718856 [2] SOUMEKH M, NOBLES D A, WICKS M C, et al. Signal processing of wide bandwidth and wide beamwidth P-3 SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(4): 1122–1141. doi: 10.1109/7.976954 [3] BRYANT M L, GOSTIN L L, and SOUMEKH M. 3-D E-CSAR imaging of a T-72 tank and synthesis of its SAR reconstructions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(1): 211–227. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1188905 [4] BOSS N, ERTIN E, and MOSES R. Autofocus for 3D imaging with multipass SAR[C]. Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVII, Orlando, USA, 2010: 769909. doi: 10.1117/12.855948. [5] ASH J, ERTIN E, POTTER L C, et al. Wide-angle synthetic aperture radar imaging: Models and algorithms for anisotropic scattering[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 16–26. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2311828 [6] DUNGAN K E and POTTER L C. Classifying vehicles in wide-angle radar using pyramid match hashing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2011, 5(3): 577–591. doi: 10.1109/jstsp.2010.2085420 [7] DUNGAN K E and POTTER L C. 3-D imaging of vehicles using wide aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(1): 187–200. doi: 10.1109/taes.2011.5705669 [8] SAVILLE M A, JACKSON J A, and FULLER D F. Rethinking vehicle classification with wide-angle polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2014, 29(1): 41–49. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2014.130057 [9] MOORE L, POTTER L, and ASH J. Three-dimensional position accuracy in circular synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2014, 29(1): 29–40. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2014.130076 [10] PONCE O, PRATS-IRAOLA P, PINHEIRO M, et al. Fully polarimetric high-resolution 3-D imaging with circular SAR at L-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3074–3090. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2013.2269194 [11] PONCE O, PRATS P, RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, et al. Processing of circular SAR trajectories with fast factorized back-projection[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 3692–3695. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2011.6050026. [12] FRÖLIND P O, GUSTAVSSON A, LUNDBERG M, et al. Circular-aperture VHF-band synthetic aperture radar for detection of vehicles in forest concealment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(4): 1329–1339. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2011.2166081 [13] PONCE O, PRATS-IRAOLA P, SCHEIBER R, et al. Polarimetric 3-D reconstruction from multicircular SAR at P-band[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(4): 803–807. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2279236 [14] PONCE O, PRATS-IRAOLA P, SCHEIBER R, et al. First airborne demonstration of holographic SAR tomography with fully polarimetric multicircular acquisitions at L-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6170–6196. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2016.2582959 [15] PONCE O, PRATS P, SCHEIBER R, et al. Study of the 3-D impulse response function of holographic SAR tomography with multicircular acquisitions[C]. The 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 2014: 1–4. [16] NEHRU D N, VU V T, SJÖGREN T K, et al. SAR resolution enhancement with circular aperture in theory and empirical scenario[C]. 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, USA, 2014: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.6875544. [17] ORIOT H and CANTALLOUBE H. Circular SAR imagery for urban remote sensing[C]. The 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1–4. [18] PALM S, ORIOT H M, and CANTALLOUBE H M. Radargrammetric DEM extraction over urban area using circular SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(11): 4720–4725. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2191414 [19] ERTIN E, MOSES R L, and POTTER L C. Interferometric methods for three-dimensional target reconstruction with multipass circular SAR[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(3): 464–473. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0048 [20] CHEN Leping, AN Daoxiang, and HUANG Xiaotao. A backprojection-based imaging for circular synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(8): 3547–3555. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2683497 [21] CHEN Leping, AN Daoxiang, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. P-band ultra wideband circular synthetic aperture radar experiment and imaging[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059352. [22] JIA Gaowei, BUCHROITHNER M F, CHANG Wenge, et al. Fourier-based 2-D imaging algorithm for circular synthetic aperture radar: Analysis and application[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(1): 475–489. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2502430 [23] JIA Gaowei, CHANG Weige, ZHANG Qilei, et al. The analysis and realization of motion compensation for circular synthetic aperture radar data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(7): 3060–3071. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2553051 [24] LI Yanghuang, JIN Tian, and SONG Qian. 3-D back-projection imaging in circular SAR with impulse signal[C]. The 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xi’an, China, 2009: 775–778. doi: 10.1109/APSAR.2009.5374171. [25] 张祥坤. 高分辨率圆迹合成孔径雷达成像机理及方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院研究生院, 2007.ZHANG Xiangkun. Study on imaging mechanism and algorithm of high-resolution circular synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Space Science and Applied Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2007. [26] 林赟. 圆迹合成孔径雷达成像算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2011.LIN Yun. Research on circular SAR imaging algorithm[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011. [27] LI Yun, HONG Wen, TAN Weixian, et al. Interferometric circular SAR method for three-dimensional imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(6): 1026–1030. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2011.2150732 [28] 洪文. 圆迹SAR成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046HONG Wen. Progress in circular SAR imaging technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046 [29] 张佳佳, 姚佰栋, 孙龙, 等. 低频圆周SAR系统设计与试验验证[J]. 电子技术与软件工程, 2017(15): 111–113.ZHANG Jiajia, YAO Baidong, SUN Long, et al. Design and test verification of low-frequency circumferential SAR system[J]. Electronic Technology, 2017(15): 111–113. [30] 刘燕, 吴元, 孙光才, 等. 圆轨迹SAR快速成像处理[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(4): 852–858. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01008LIU Yan, WU Yuan, SUN Guang-Cai, et al. Fast imaging processing of circular SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(4): 852–858. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01008 [31] KOU Leilei, WANG Xiaoqing, XIANG Maosheng, et al. Interferometric estimation of three-dimensional surface deformation using geosynchronous circular SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(2): 1619–1635. doi: 10.1109/taes.2012.6178082 [32] 王本君. 圆周SAR三维成像技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2012.WANG Benjun. Research on circular SAR 3-D imaging[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2012. [33] 田甲申. 圆周SAR成像算法及相关技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2013.TIAN Jiasheng. Study on image formation for circular SAR and related technologies[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2013. [34] 吴堃. 线阵及圆周SAR三维成像算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2012.WU Kun. Research on three-dimensional imaging algorithm of linear array and circle SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2012. [35] 查鹏. 圆迹SAR快速高精度极坐标格式成像算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 上海交通大学, 2015.ZHA Peng. Research on fast and high precision circular SAR polar format imaging algorithm[D]. [Master dissertation], Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2015. [36] 吴琦. 圆迹SAR系统DEM提取及运动补偿技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2017.WU Qi. Research on the DEM extraction and motion compensation technology of circular SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017. [37] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005. [38] VU V T, SJÖGREN T K, PETTERSSON M I, et al. Studying CSAR systems using IRF-CSAR[C]. IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Glasgow, UK, 2012: 1–6. doi: 10.1049/cp.2012.1605. [39] CHEN Leping, AN Daoxiang, and HUANG Xiaotao. Resolution analysis of circular synthetic aperture radar noncoherent imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(1): 231–240. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2890932 [40] AN Daoxiang, LI Yanghuan, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. Performance evaluation of frequency-domain algorithms for chirped low frequency UWB SAR data processing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(2): 678–690. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2013.2265272 [41] SOUMEKH M. Reconnaissance with slant plane circular SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1996, 5(8): 1252–1265. doi: 10.1109/83.506760 [42] FREY O, MAGNARD C, RUEGG M, et al. Focusing of airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar data from highly nonlinear flight tracks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(6): 1844–1858. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2008.2007591 [43] FREY O. Synthetic aperture radar imaging in the time domain for nonlinear sensor trajectories and SAR tomography[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Zurich, 2010. [44] ULANDER L M H, HELLSTEN H, and STENSTROM G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. doi: 10.1109/taes.2003.1238734 [45] DUNGAN K E and NEHRBASS J W. Wide-area wide-angle SAR focusing[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2014, 29(1): 21–28. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2014.130055 [46] DUNGAN K E and NEHRBASS J W. SAR Focusing using Multiple Trihedrals[C]. SPIE-Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XX, Baltimore, USA, 2013: 874606. doi: 10.1117/12.2015088. [47] DUPUIS X and MARTINEAU P. Very high resolution circular SAR imaging at X band[C]. 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014: 930–933. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946578. [48] ASH J N. An autofocus method for backprojection imagery in synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(1): 104–108. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2161456 [49] HU Kebin, ZHANG Xiaoling, HE Shufeng, et al. A less-memory and high-efficiency autofocus back projection algorithm for SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 890–894. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2365612 [50] CHEN Leping, AN Daoxiang, and HUANG Xiaotao. Extended autofocus backprojection algorithm for low-frequency SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(8): 1323–1327. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2711005 [51] CHEN Leping, AN Daoxiang, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. A 3D reconstruction strategy of vehicle outline based on single-pass single-polarization CSAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(11): 5545–5554. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2738566 [52] POTTER L C and MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098 [53] SPETNER L and KATZ I. Two statistical models for radar terrain return[J]. IRE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1960, 8(3): 242–246. doi: 10.1109/tap.1960.1144838 [54] GIANELLI C D and XU Luzhou. Focusing, imaging, and ATR for the Gotcha 2008 wide angle SAR collection[J]. Proceedings of SPIE Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XX, Baltimore, United States, 2013: 87460N. [55] DUNGAN K E, AUSTIN C, NEHRBASS J, et al. Civilian vehicle radar data domes[J]. Proceedings of SPIE Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVII, Orlando, United States, 2010: 76990P. doi: 10.1117/12.850151 [56] FENG Dong, AN Daoxiang, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. Holographic SAR tomographic processing of the multicircular data[C]. 2018 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Kyoto, Japan, 2018: 830–832. doi: 10.23919/APMC.2018.8617268. [57] FENG Dong, AN Daoxiang, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. A phase calibration method based on phase gradient autofocus for airborne holographic SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(12): 1864–1868. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2911932 [58] TRINTINALIA L C, BHALLA R, and LING Hao. Scattering center parameterization of wide-angle backscattered data using adaptive Gaussian representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1997, 45(11): 1664–1668. doi: 10.1109/8.650078 [59] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873 [60] FREY O and MEIER E. 3-D time-domain SAR imaging of a forest using airborne multibaseline data at L- and P-bands[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3660–3664. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2128875 [61] NANNINI M, SCHEIBER R, and MOREIRA A. Estimation of the minimum number of tracks for SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(2): 531–543. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2007846 [62] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183 [63] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1-norm regularization-The compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117 [64] AGUILERA E, NANNINI M, and REIGBER A. Wavelet-based compressed sensing for SAR tomography of forested areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(12): 5283–5295. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2231081 [65] YARDIBI T, LI Jian, STOICA P, et al. Source localization and sensing: A nonparametric iterative adaptive approach based on weighted least squares[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(1): 425–443. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5417172 [66] ROBERTS W, STOICA P, LI Jian, et al. Iterative adaptive approaches to MIMO radar imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(1): 5–20. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2009.2038964 [67] PAUCIULLO A, REALE D, DE MAIO A, et al. Detection of double scatterers in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(9): 3567–3586. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2183002 [68] BUDILLON A and SCHIRINZI G. GLRT based on support estimation for multiple scatterers detection in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1086–1094. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2494376 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: