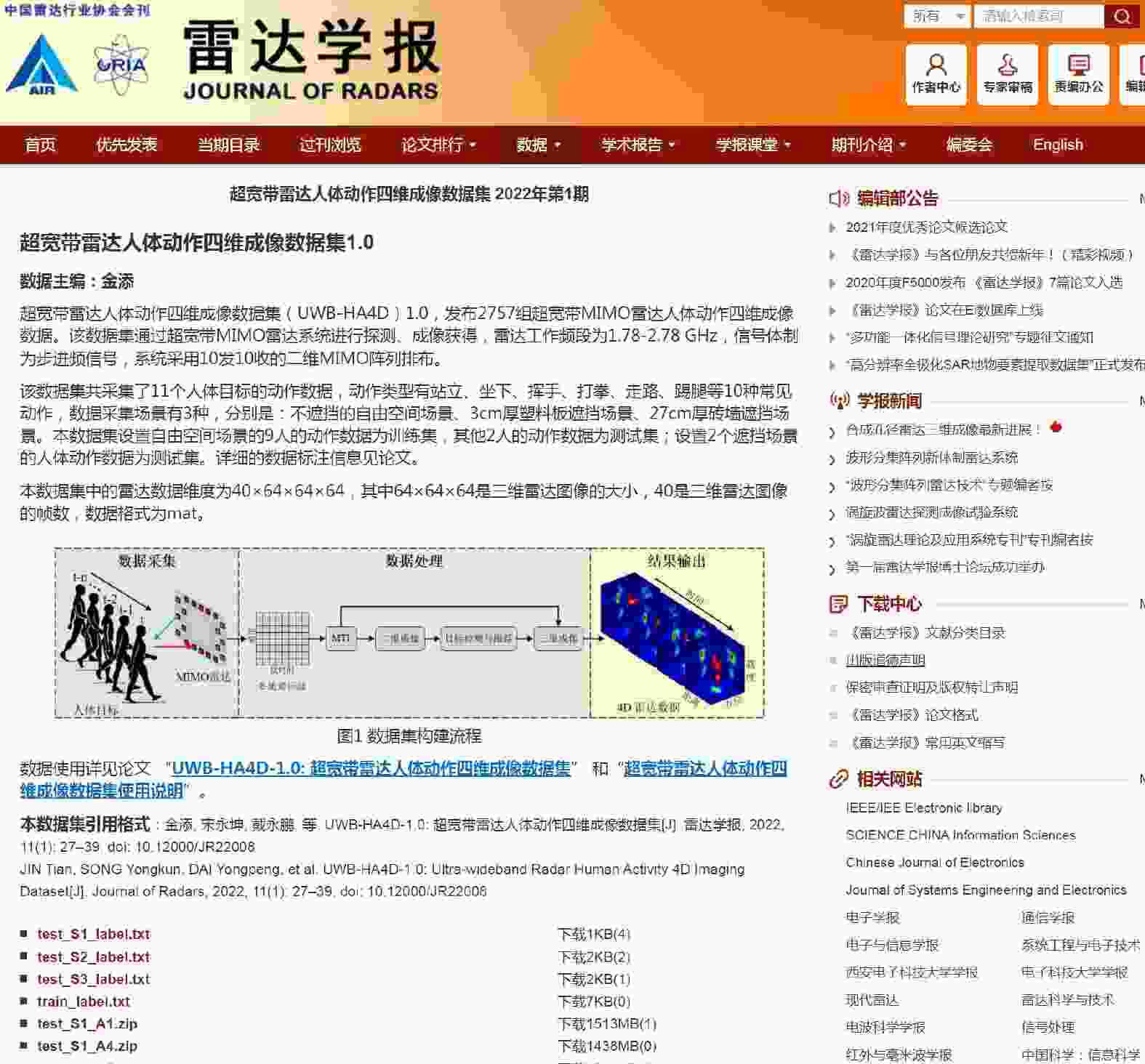
-
摘要: 雷达人体行为感知系统具有穿透探测能力,在安防、救援、医疗等领域具有广泛的应用前景。近年来,深度学习技术的出现促进了雷达传感器在人体行为感知领域的发展,同时对相关数据集的样本规模和丰富性提出了更高的要求。该文公开了一个超宽带雷达人体动作四维成像数据集,该数据集以超宽带多输入多输出雷达为探测传感器来获取了人体目标的距离-方位-高度-时间四维动作数据,共采集了11个人体目标的2757组动作数据,动作类型包含走路、挥手、打拳等10种常见动作,有穿透探测和不穿透探测的实验场景。该文详细介绍了数据集的系统参数、制作流程、数据分布等信息。同时,基于飞桨平台使用计算机视觉领域应用较多的深度学习算法对该数据集进行人体动作识别实验,实验对比结果可以作为参考,为学者使用该数据集提供技术支撑,方便在此基础上进一步探索研究。Abstract: A radar human behavior perception system has penetration detection ability, which gives it a wide application prospect in the fields of security, rescue, medical treatment, and so on. Although the development of deep learning technology has promoted radar sensor research in human behavior perception, it requires more prompted dataset availability. This paper provides a four-dimensional imaging dataset of human activity using ultra-wideband radar, UWB-HA4D, which uses three-dimensional ultra-wideband multiple-input multiple-output radar as the detection sensor to capture the range-azimuth-height-time four-dimensional activity data of a human target. The dataset contains the activity data of 2757 groups for 11 human targets, including 10 common activities, such as walking, waving, and boxing. It also contains penetration and nonpenetration detection experimental scenarios. The radar system parameters, data generation process, data distribution, and other information of the dataset are introduced in detail herein. Meanwhile, several deep learning algorithms that are based on the PaddlePaddle framework and are widely used in the computer version field are applied to this dataset for human activity recognition. The experimental comparison results can be used to provide references for scholars and facilitate further investigation and research on this basis.
-
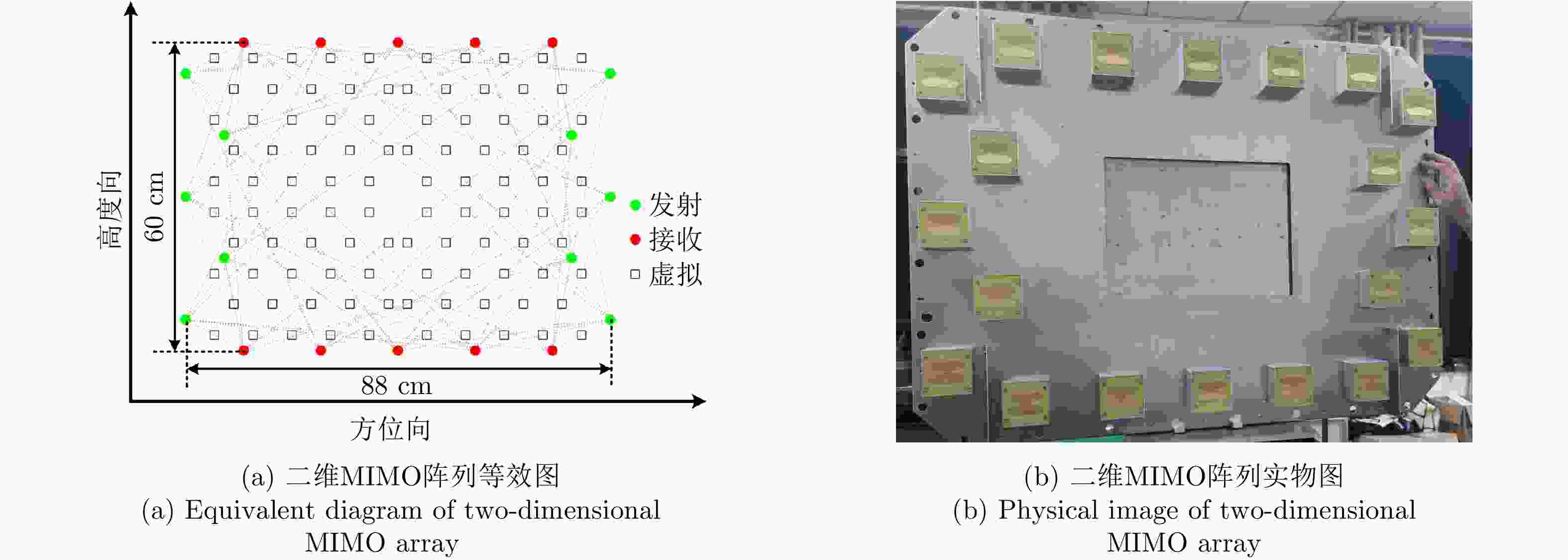
表 1 雷达系统参数
Table 1. Radar system parameters
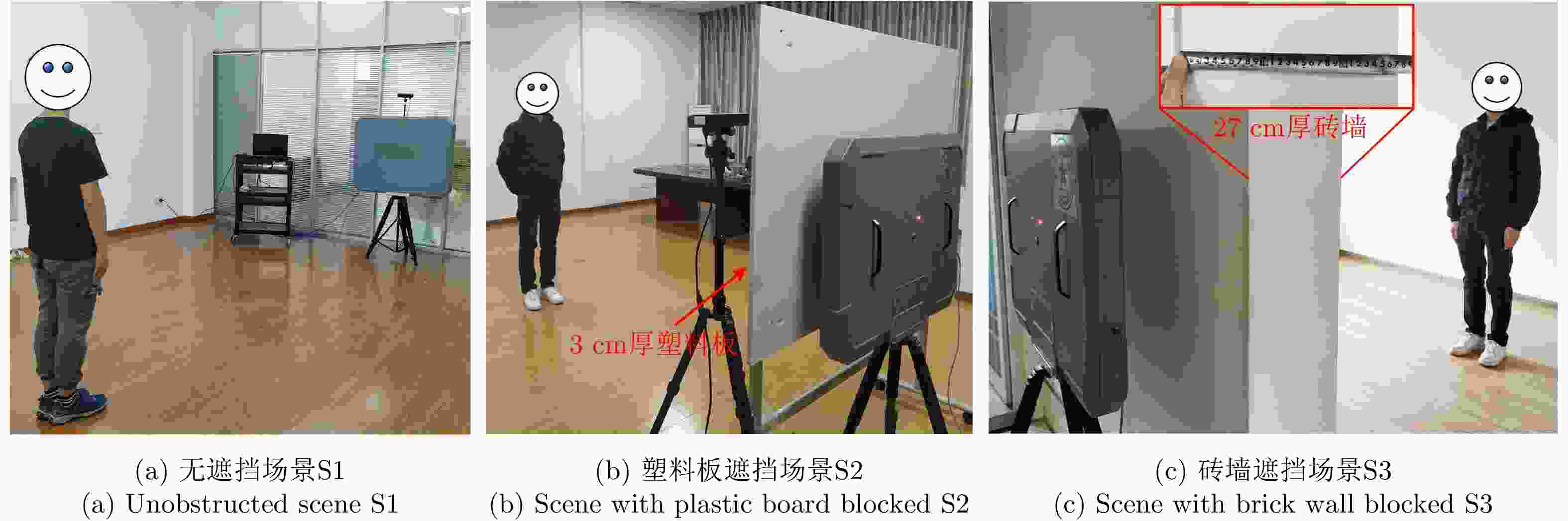
参数 指标 工作频段 1.78~2.78 GHz 信号带宽 1 GHz 信号体制 步进频信号 信号步进带宽 4 MHz 脉冲重复频率 10 Hz 天线阵元数 10发10收(MIMO) 信号发射功率 20 dBm (100 mW) 系统尺寸 60 cm×88 cm 可穿透介质 幕布、木板、塑料、泡沫、砖墙等 表 2 数据集采集场景信息
Table 2. Dataset collection scene information
场景编号 遮挡情况 训练集 测试集 S1 无遮挡 √ √ S2 3 cm塑料板遮挡 × √ S3 27 cm砖墙遮挡 × √ 注:√表示有,×表示无。 表 3 不同动作的数据量(组)
Table 3. The amount of data for different actions (groups)
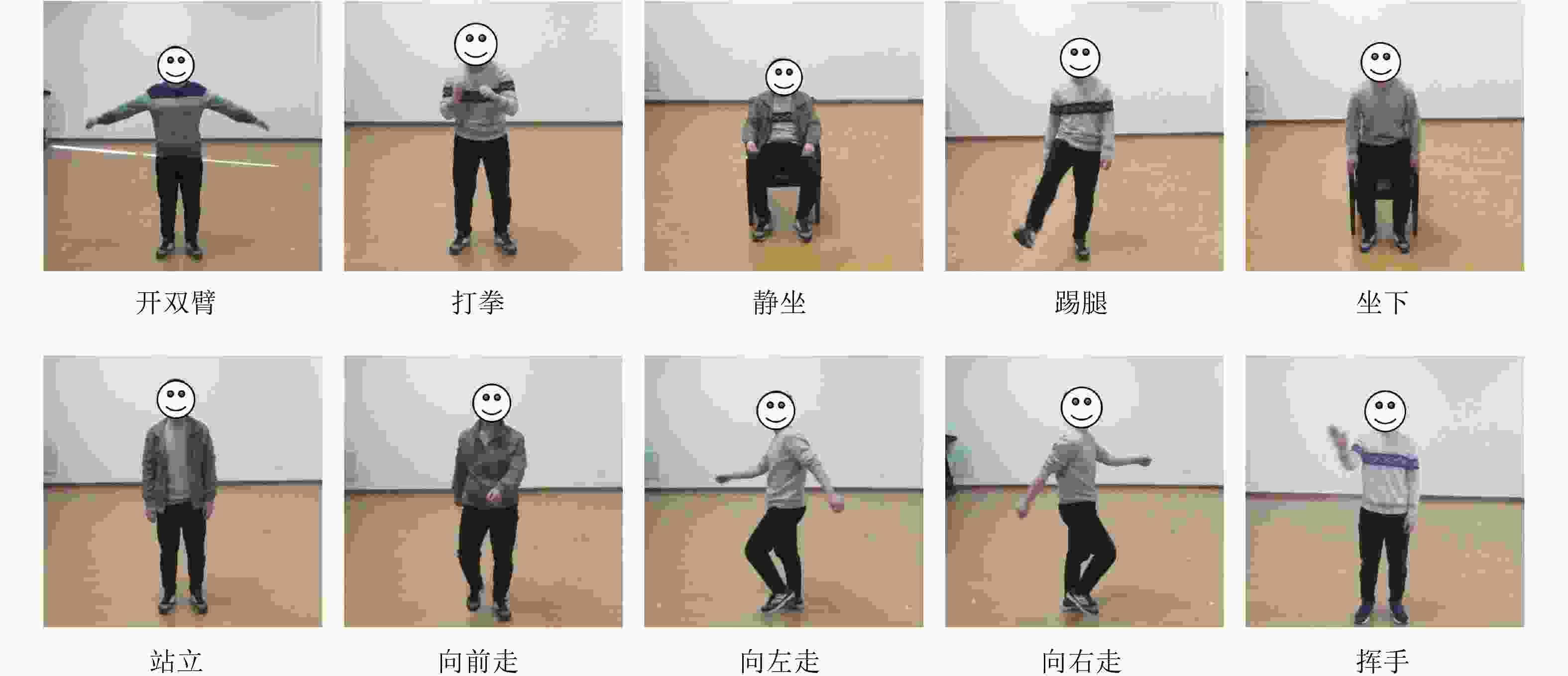
标号 动作 S1场景训练 S1场景测试 S2场景测试 S3场景测试 总数 1 开双臂 149 40 40 40 269 2 打拳 155 40 40 40 275 3 静坐 156 40 40 40 276 4 踢腿 158 40 40 40 278 5 坐下 155 40 40 40 275 6 站立 156 40 40 40 276 7 向前走 157 40 40 40 277 8 向左走 156 40 40 40 276 9 向右走 158 40 40 40 278 10 挥手 157 40 40 40 277 表 4 人体目标信息
Table 4. Human target information
目标编号 身高(cm) 体重(kg) S1场景 S2场景 S3场景 H1 175 70 √ × × H2 172 72 √ × × H3 178 68 √ × × H4 182 85 √ × × H5 170 75 √ × × H6 179 74 √ √ √ H7 165 60 √ × × H8 169 65 √ √ √ H9 162 53 √ × × H10 186 80 √ × × H11 171 67 √ × × 表 5 人体动作标号
Table 5. Human activity labels
动作编号 动作类型 真值标号 动作编号 动作类型 真值标号 A1 开双臂 0 A6 站立 5 A2 打拳 1 A7 向前走 6 A3 静坐 2 A8 向左走 7 A4 踢腿 3 A9 向右走 8 A5 坐下 4 A10 挥手 9 表 6 实验结果对比表
Table 6. Experimental results comparison table
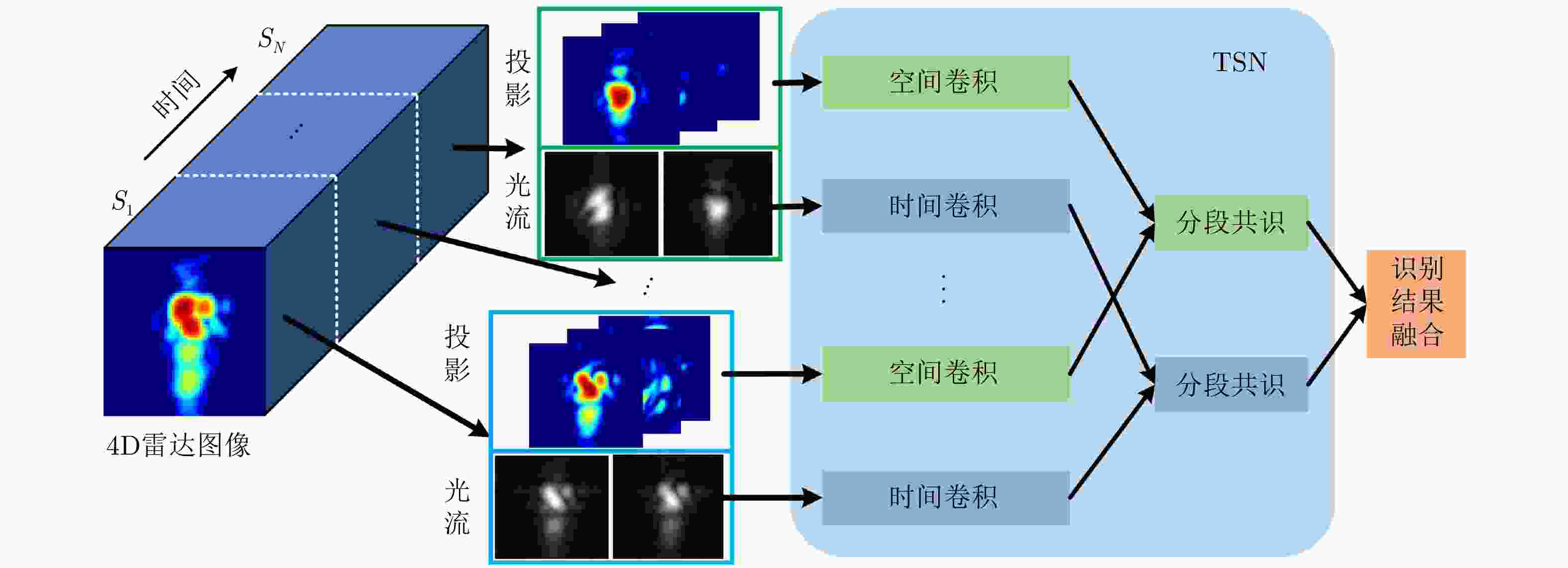
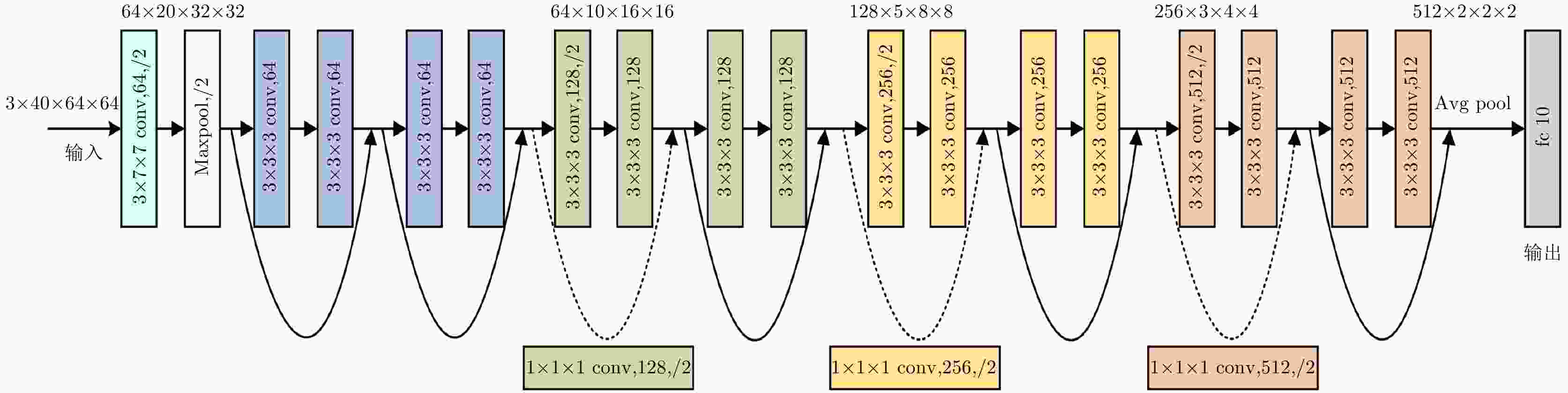
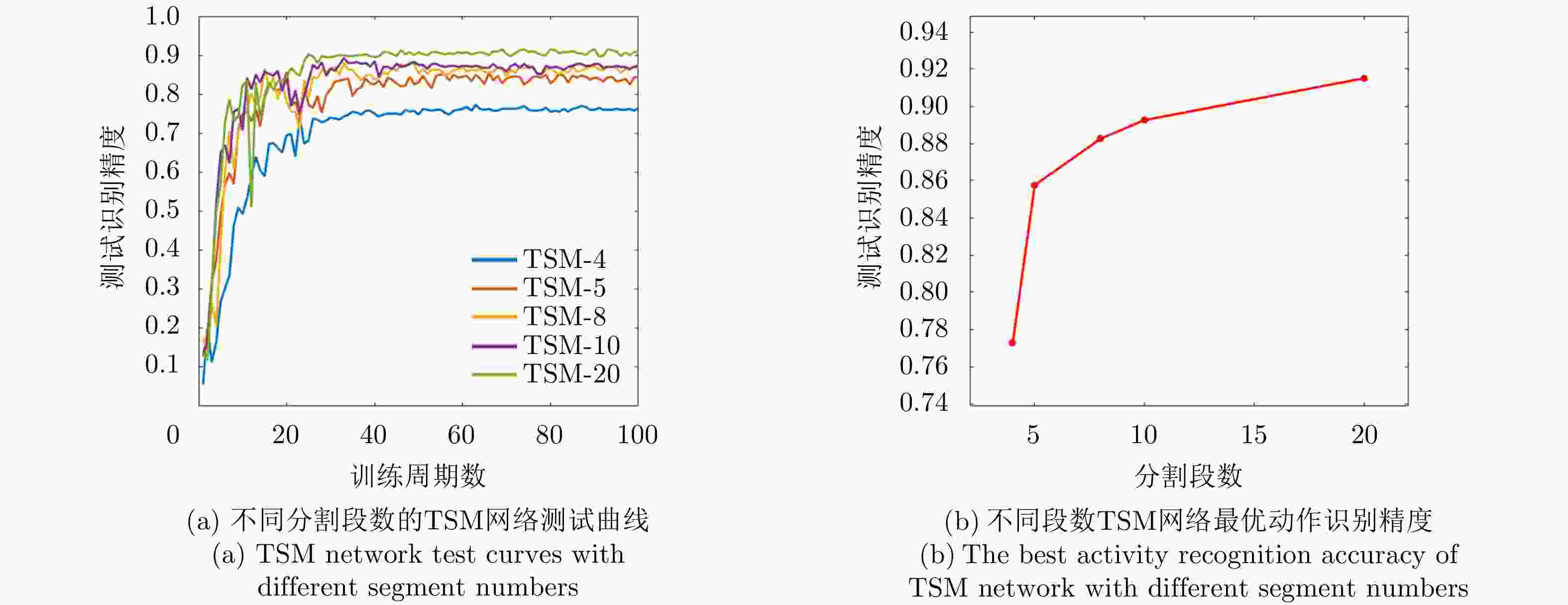
识别方法 网络框架 S1识别精度 S2识别精度 S3识别精度 2D CNN TSN 85.75% 83.5% 60.75% TSM 91.50% 88.0% 73.75% 3D CNN SFN 88.00% 80.5% 70.25% Res3D 92.25% 90.0% 77.00% 表 7 Res3D网络在不同场景下的动作识别精度(%)
Table 7. Human activity recognition accuracy of Res3D networks in different scenes (%)
探测场景 张开双臂 打拳 静坐 踢腿 坐下 站立 向前走 向左走 向右走 挥手 平均 S1场景 90 90.0 97.5 82.5 100 85.0 97.5 100 100 80 92.25 S2场景 85 92.5 100.0 85.0 100 82.5 85.0 100 100 70 90.00 S3场景 90 82.5 100.0 42.5 100 65.0 50.0 70 100 70 77.00 -
[1] KUMAR P. Human activity recognition with deep learning: Overview, challenges & possibilities[J]. CCF Transactions on Pervasive Computing and Interaction, 2021, 339(3): 1–29. doi: 10.20944/preprints202102.0349.v1. [2] 黄晴晴, 周风余, 刘美珍. 基于视频的人体动作识别算法综述[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2020, 37(11): 3213–3219. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2019.08.0253HUANG Qingqing, ZHOU Fengyu, and LIU Meizhen. Survey of human action recognition algorithms based on video[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2020, 37(11): 3213–3219. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2019.08.0253 [3] 钱慧芳, 易剑平, 付云虎. 基于深度学习的人体动作识别综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2021, 15(3): 438–455. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2009095QIAN Huifang, YI Jianping, and FU Yunhu. Review of human action recognition based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science &Technology, 2021, 15(3): 438–455. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2009095 [4] SCHULDT C, LAPTEV I, and CAPUTO B. Recognizing human actions: A local SVM approach[C]. 2004 IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, 2004: 32–36. [5] SOOMRO K, ZAMIR A R, and SHAH M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1212.0402, 2012. [6] KUEHNE H, JHUANG H, GARROTE E, et al. HMDB: A large video database for human motion recognition[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 2556–2563. [7] KAY W, CARREIRA J, SIMONYAN K, et al. The kinetics human action video dataset[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.06950, 2017. [8] SHAHROUDY A, LIU Jun, NG T T, et al. NTU RGB+D: A large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1010–1019. [9] 杜浩. 基于深度学习的超宽带雷达人体行为辨识研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2020: 1–5.DU Hao. Research on deep learning-based human behavior recognition in ultra-wideband radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2020: 1–5. [10] PAULI M, GOTTEL B, SCHERR S, et al. Miniaturized millimeter-wave radar sensor for high-accuracy applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(5): 1707–1715. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2017.2677910 [11] 刘熠辰, 徐丰. 基于雷达技术的手势识别[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2016, 11(6): 609–613. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2016.06.009LIU Yichen and XU Feng. Gesture recognition based on radar technology[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2016, 11(6): 609–613. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2016.06.009 [12] DING Chuanwei, ZHANG Li, GU Chen, et al. Non-contact human motion recognition based on UWB radar[J]. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2018, 8(2): 306–315. doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2018.2797313 [13] KIM Y and MOON T. Human detection and activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(1): 8–12. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2491329 [14] CRALEY J, MURRAY T S, MENDAT D R, et al. Action recognition using micro-Doppler signatures and a recurrent neural network[C]. 2017 51st Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, Baltimore, USA, 2017: 1–5. [15] WANG Mingyang, ZHANG Y D, and CUI Guolong. Human motion recognition exploiting radar with stacked recurrent neural network[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 87: 125–131. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2019.01.013 [16] LI Xinyu, HE Yuan, FIORANELLI F, et al. Semisupervised human activity recognition with radar micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5103112. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3090106 [17] DU Hao, JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, et al. A three-dimensional deep learning framework for human behavior analysis using range-Doppler time points[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(4): 611–615. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2930636 [18] 李廉林, 崔铁军. 智能电磁感知的若干进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(2): 183–190. doi: 10.12000/JR21049LI Lianlin and CUI Tiejun. Recent progress in intelligent electromagnetic sensing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(2): 183–190. doi: 10.12000/JR21049 [19] LI Lianlin, SHUANG Ya, MA Qian, et al. Intelligent metasurface imager and recognizer[J]. Light:Science & Applications, 2019, 8(1): 97. doi: 10.1038/s41377-019-0209-z [20] FIORANELLI F, SHAH S A, LI Haobo, et al. Radar sensing for healthcare[J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(19): 1022–1024. doi: 10.1049/el.2019.2378 [21] MENG Zhen, FU Song, YAN Jie, et al. Gait recognition for co-existing multiple people using millimeter wave sensing[C]. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 849–856. [22] ZHU Zhengliang, YANG Degui, ZHANG Junchao, et al. Dataset of human motion status using IR-UWB through-wall radar[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32(5): 1083–1096. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000093 [23] SONG Yongkun, JIN Tian, DAI Yongpeng, et al. Through-wall human pose reconstruction via UWB MIMO radar and 3D CNN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(2): 241. doi: 10.3390/rs13020241 [24] AMIN M G, 朱国富, 陆必应, 金添, 等译. 穿墙雷达成像[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2014: 22–25.AMIN M G, ZHU Guofu, LU Biying, JIN Tian, et al. translation. Through-The-Wall Radar Imaging[M]. Beijing, China: Publishing House of Electronic Industry, 2014: 22–25. [25] 詹姆斯 D. 泰勒, 胡春明, 王建明, 孙俊, 等译. 超宽带雷达应用与设计[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2017: 54–55.TAYLOR J D, HU Chunming, WANG Jianming, SUN Jun, et al. translation. Ultrawideband Radar: Applications and Design[M]. Beijing, China: Publishing House of Electronic Industry, 2017: 54–55. [26] 孙鑫. 超宽带穿墙雷达成像方法与技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2015: 16–17.SUN Xin. Research on method and technique of ultra-wideband through-the-wall radar imaging[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2015: 16–17. [27] 金添, 宋勇平. 穿墙雷达人体目标探测技术综述[J]. 电波科学学报, 2020, 35(4): 486–495. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040804JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Review on human target detection using through-wall radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2020, 35(4): 486–495. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040804 [28] ASH M, RITCHIE M, and CHETTY K. On the application of digital moving target indication techniques to short-range FMCW radar data[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(10): 4167–4175. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2823588 [29] SONG Yongping, LOU Jun, and TIAN Jin. A novel II-CFAR detector for ROI extraction in SAR image[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication and Computing, Kunming, China, 2013: 1–4. [30] NORTON-WAYNE L. Image reconstruction from projections[J]. Optica Acta:International Journal of Optics, 1980, 27(3): 281–282. doi: 10.1080/713820221 [31] MCCORKLE J W. Focusing of synthetic aperture ultra wideband data[C]. 1991 IEEE International Conference on Systems Engineering, Dayton, USA, 1991: 1–5. [32] BOBICK A F and DAVIS J W. The recognition of human movement using temporal templates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2001, 23(3): 257–267. doi: 10.1109/34.910878 [33] DAS DAWN D and SHAIKH S H. A comprehensive survey of human action recognition with spatio-temporal interest point (STIP) detector[J]. The Visual Computer, 2016, 32(3): 289–306. doi: 10.1007/s00371-015-1066-2 [34] WANG Heng, KLÄSER A, SCHMID C, et al. Dense trajectories and motion boundary descriptors for action recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 103(1): 60–79. doi: 10.1007/s11263-012-0594-8 [35] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 568–576. [36] WANG Limin, XIONG Yuanjun, WANG Zhe, et al. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition[C]. 2016 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 20–36. [37] LIN Ji, GAN Chuang, and HAN Song. TSM: Temporal shift module for efficient video understanding[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 7083–7093. [38] JI Shuiwang, XU Wei, YANG Ming, et al. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 221–231. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59 [39] TRAN D, BOURDEV L, FERGUS R, et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4489–4497. [40] TRAN D, RAY J, SHOU Zheng, et al. ConvNet architecture search for spatiotemporal feature learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.05038, 2017. [41] FEICHTENHOFER C, FAN Haoqi, MALIK J, et al. SlowFast networks for video recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 6202–6210. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: