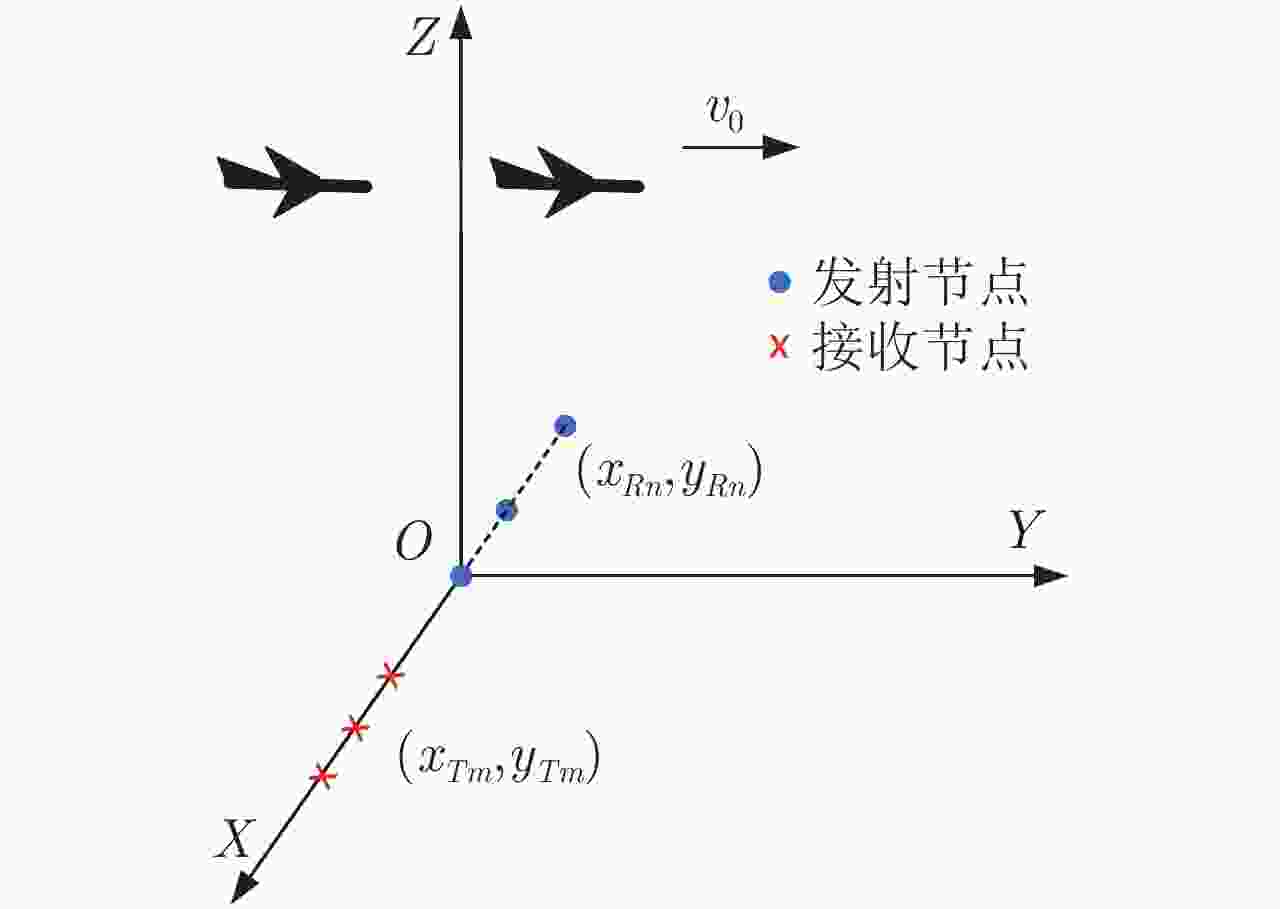
A Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging Method Based on Multidimensional Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers
-
摘要: 基于傅里叶变换的传统逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)成像方法存在数据存储量大、数据采集时间长的问题。压缩感知(CS)理论利用图像的稀疏性,可以利用有限的数据恢复图像,这极大降低了数据采集成本。但对于多维数据,传统压缩感知方法要将多维数据转化成一维向量,这造成了很大存储和计算负担。因此,该文提出一种基于多维度-交替方向乘子法(MD-ADMM)的多输入多输出-逆合成孔径雷达(MIMO-ISAR)成像快速稀疏重建方法。首先建立基于张量信号的压缩感知模型,然后用ADMM算法对模型进行优化,将测量矩阵分解为张量模态积,用张量元素除法替代矩阵求逆,显著减少所需的内存和计算负担。该方法只需少量的数据采样,就能实现快速成像。与其他基于张量的压缩感知方法相比,该方法具有鲁棒性强、图像质量好、计算效率高的优点。仿真和实测数据验证了该方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 多维度-交替方向乘子法 /
- 压缩感知 /
- 多输入多输出-逆合成孔径雷达
Abstract: The disadvantages of the traditional Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) imaging method based on Fourier transform include large data storage and long collection time. The Compressive Sensing (CS) theory can use limited data to restore an image with the sparsity of the image, reducing the cost of data collection. However for multidimensional data, the traditional compressive sensing methods need to convert three-dimensional data into a one-dimensional vector, causing the storage and calculation burden. Therefore, this study proposes a fast MultiDimensional Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers ((MD-ADMM)) sparse reconstruction method for Multiple-Input Multiple-Output ISAR (MIMO-ISAR) imaging. The CS model based on the tensor signal was established, and the model with the ADMM algorithm was optimized. The measured matrix is decomposed into a tensor modal product, and matrix inversion is replaced by tensor element division, significantly reducing memory consumption and computational burden. Fast ISAR imaging can be achieved by a small amount of data sampling by the proposed method. Compared with other tensor compressed sensing methods, this method has the advantages of stronger robustness, higher image quality, and computational efficiency. The effectiveness of the proposed method can be invalidated by simulated and measured data. -
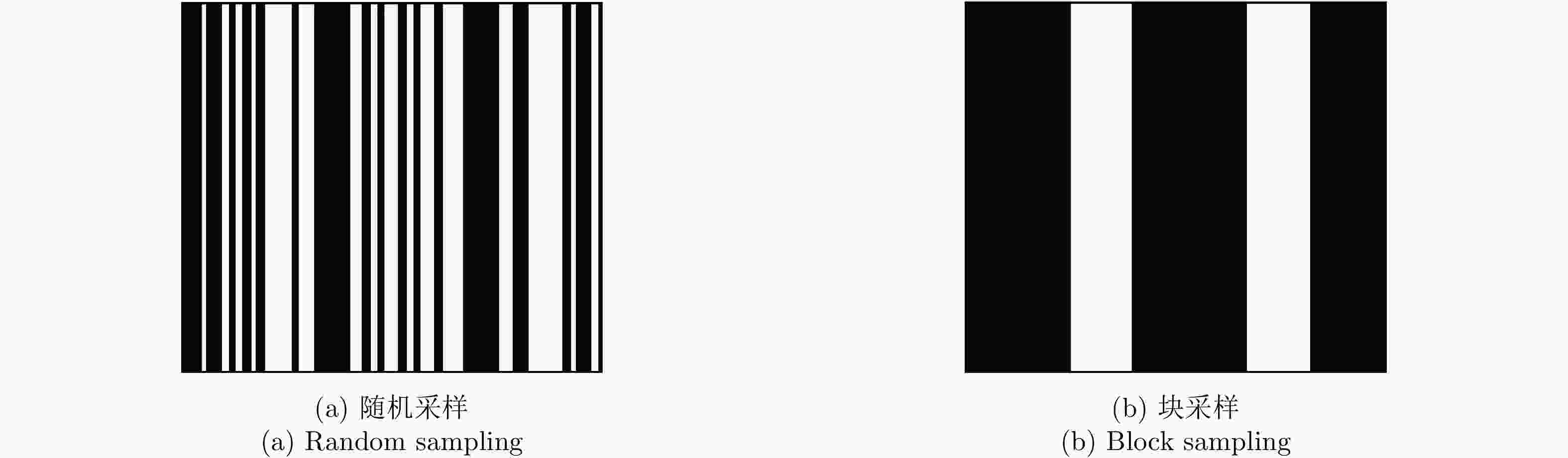
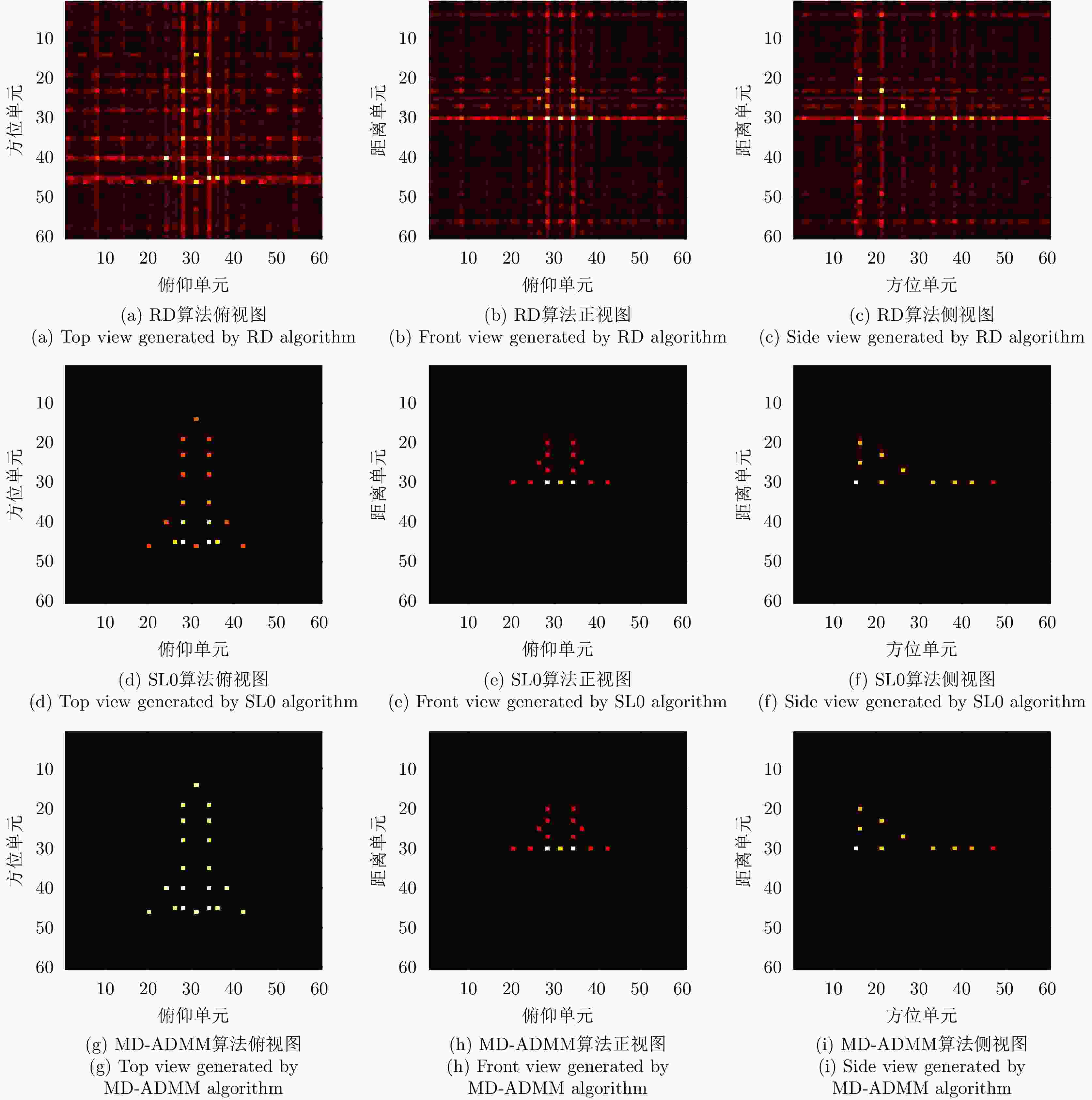
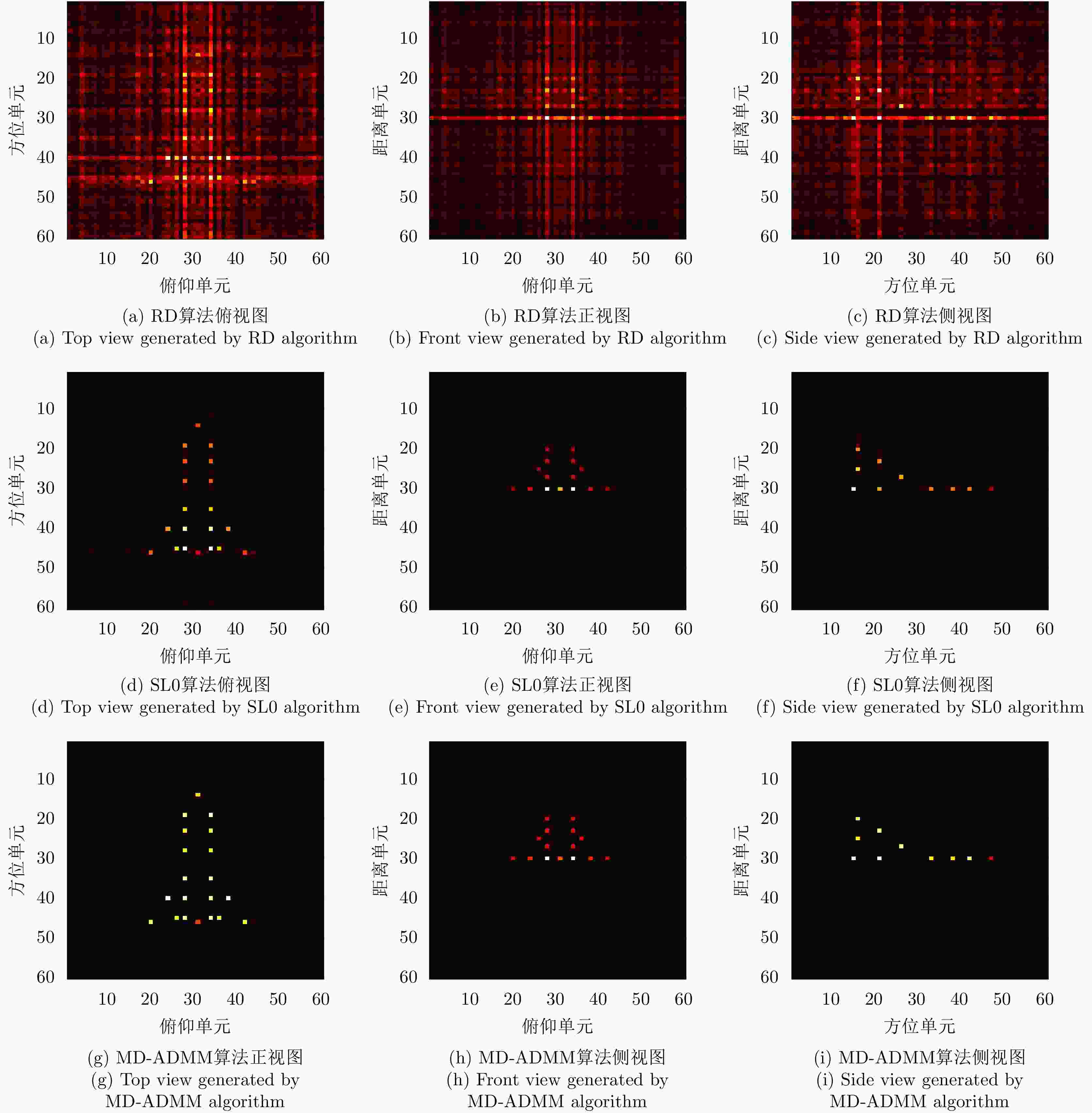
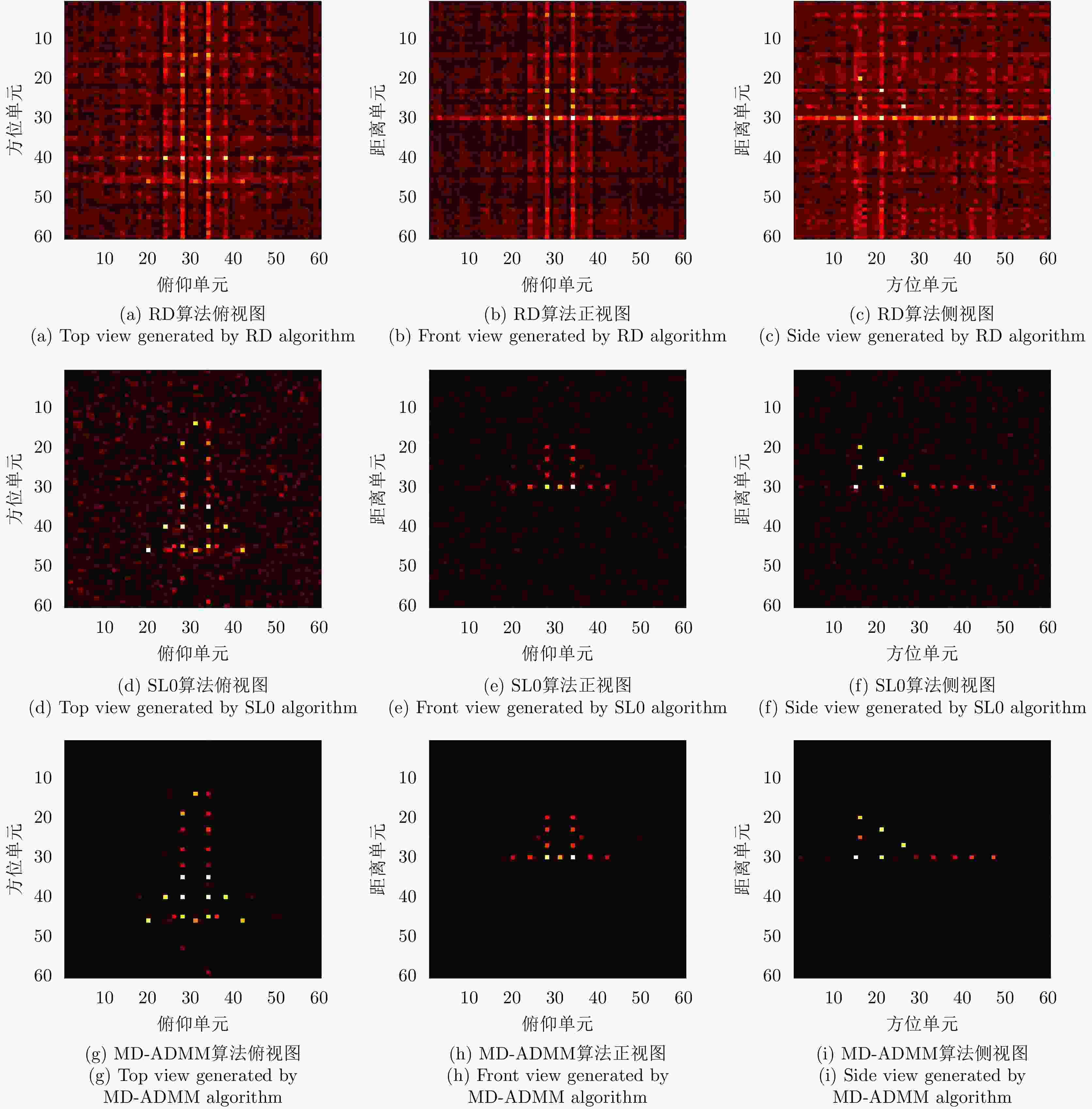
表 1 随机稀疏采样条件下数值结果
Table 1. Numerical results under random sparse sampling condition
稀疏度 算法 图像熵 PSNR 计算时间 50.0% RD 9.490 34.075 0.012 DR-2D-SL0 3.138 57.714 35.053 MD-SL0 3.138 57.714 6.954 MD-ADMM 3.006 61.678 3.518 33.3% RD 10.505 28.430 0.010 DR-2D-SL0 3.200 52.702 29.091 MD-SL0 3.200 52.702 12.546 MD-ADMM 2.959 53.888 6.088 25.0% RD 10.965 26.003 0.0131 DR-2D-SL0 3.373 48.755 54.008 MD-SL0 3.373 48.755 28.509 MD-ADMM 3.023 49.386 11.996 表 2 块稀疏采样条件下数值结果
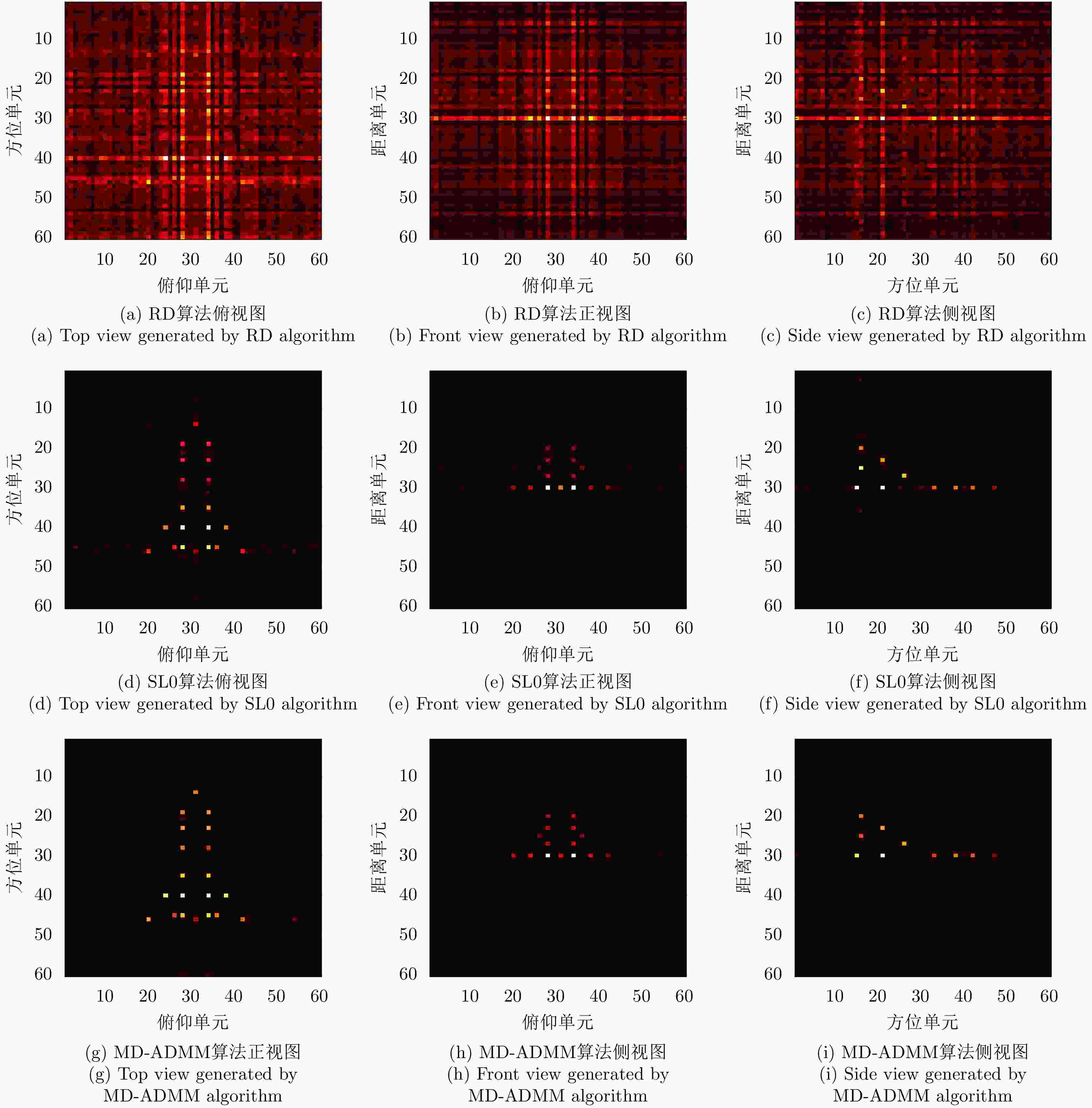
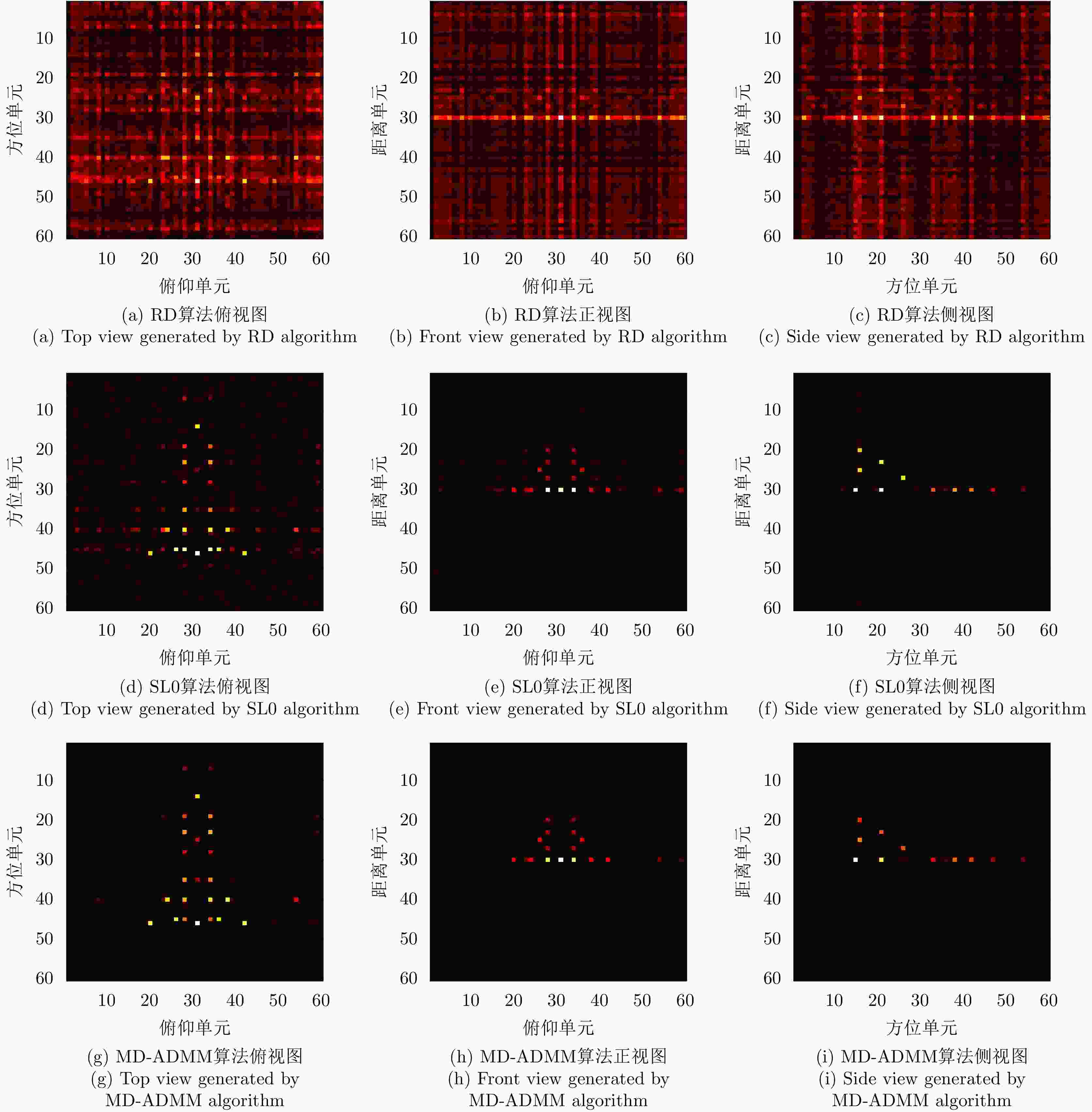
Table 2. Numerical results under block sparse sampling condition
稀疏度 算法 图像熵 PSNR 计算时间 50.0% RD 8.336 32.885 0.012 DR-2D-SL0 3.246 51.232 41.907 MD-SL0 3.246 51.232 8.029 MD-ADMM 3.037 53.274 3.660 33.3% RD 8.553 27.495 0.0098 DR-2D-SL0 3.700 42.188 42.518 MD-SL0 3.700 42.188 17.954 MD-ADMM 3.233 42.336 5.758 25.0% RD 9.500 26.906 0.0092 DR-2D-SL0 3.894 45.196 51.463 MD-SL0 3.894 45.196 25.702 MD-ADMM 3.337 47.201 11.536 表 3 不同信噪比条件下数值结果
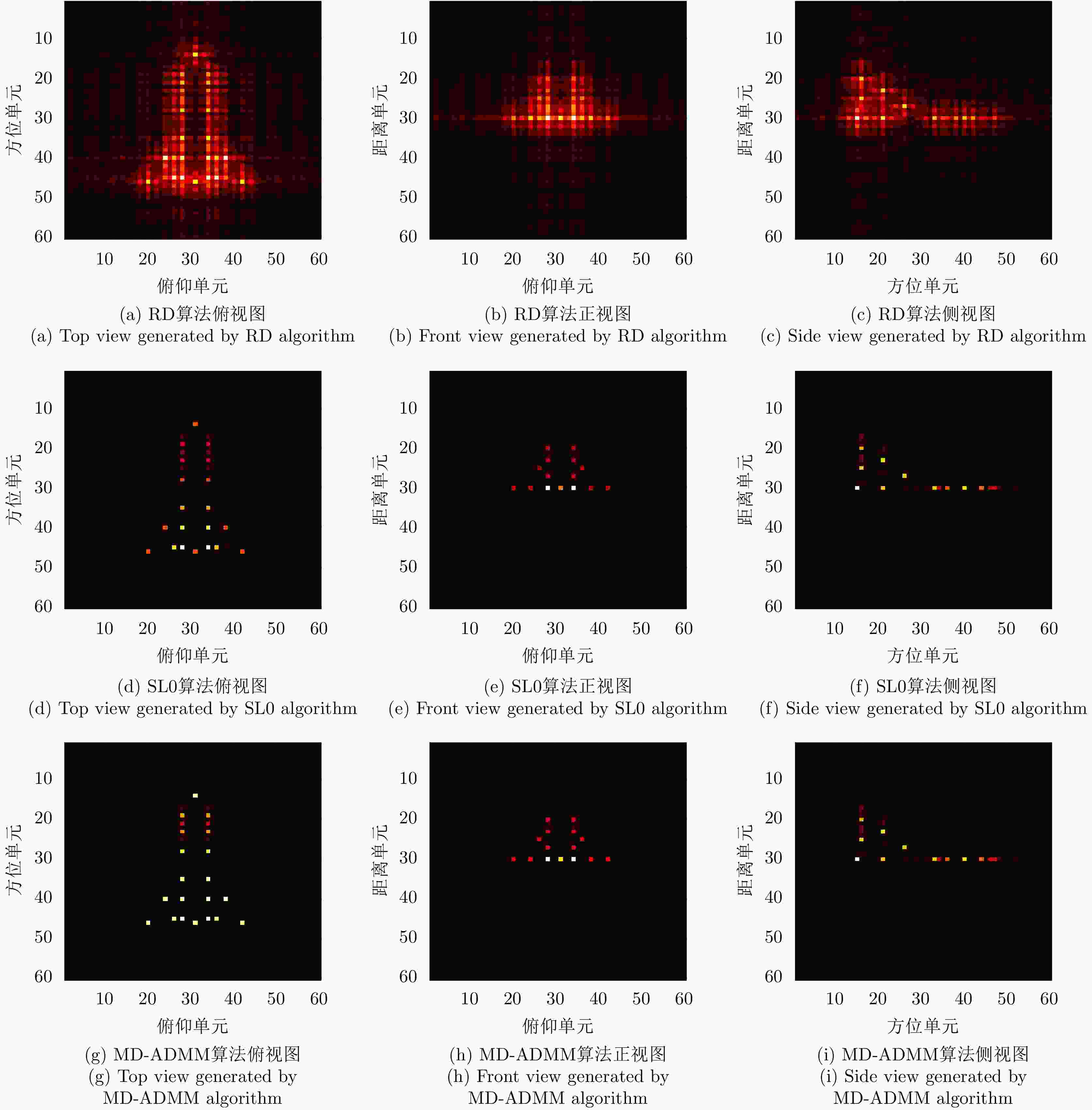
Table 3. Numerical results under different SNR conditions
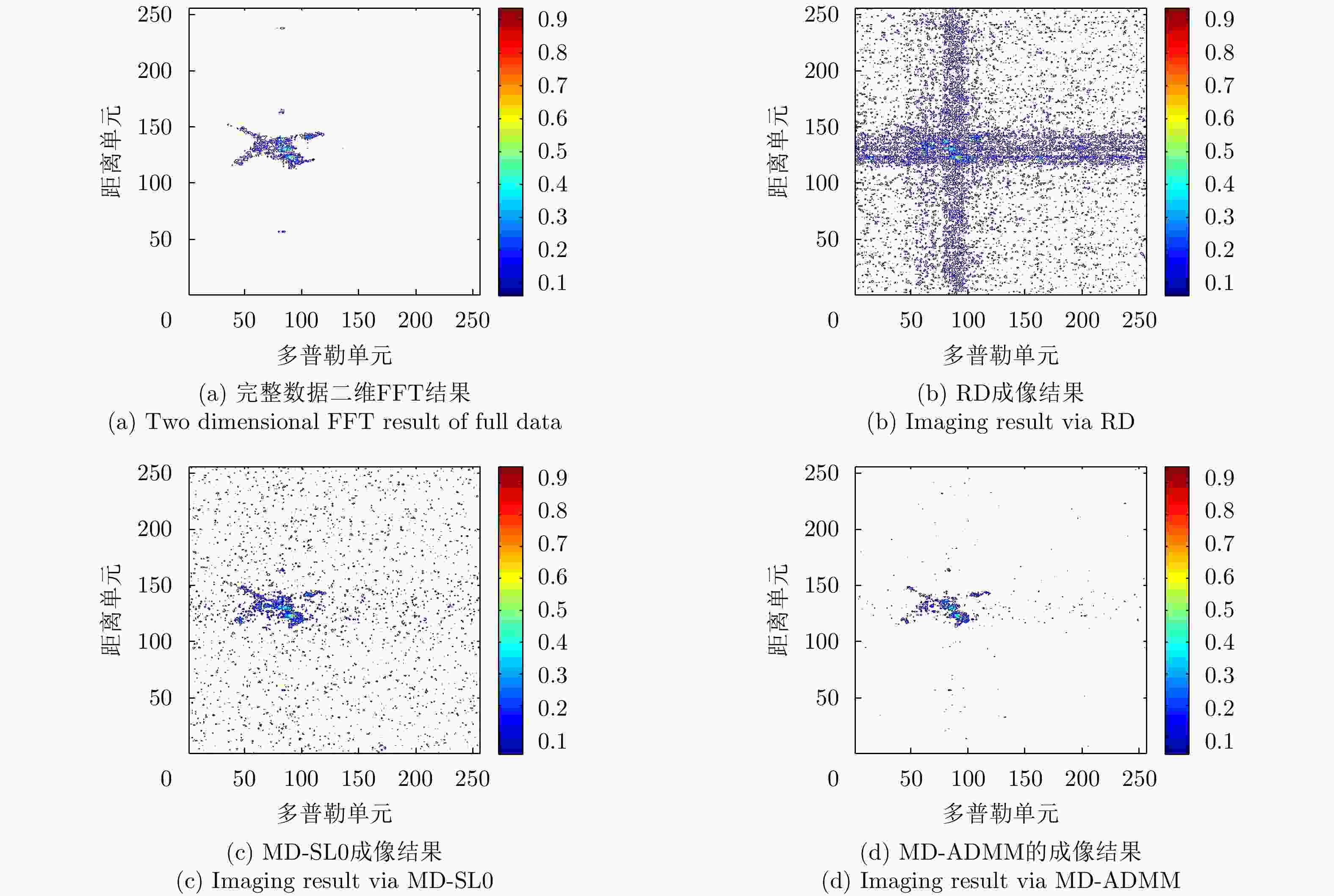
信噪比 算法 图像熵 PSNR 计算时间 –5 dB RD 11.8042 18.320 0.0177 DR-2D-SL0 7.3218 37.639 49.998 MD-SL0 7.3218 37.639 23.540 MD-ADMM 4.779 43.352 10.775 0 dB RD 11.535 23.452 0.013 DR-2D-SL0 5.4086 43.285 48.776 MD-SL0 5.4086 43.285 23.303 MD-ADMM 2.977 47.449 10.715 10 dB RD 11.116 27.145 0.0124 DR-2D-SL0 3.948 45.619 48.754 MD-SL0 3.948 45.619 23.484 MD-ADMM 3.066 47.561 10.521 表 4 实测数据不同信噪比条件下的数值结果
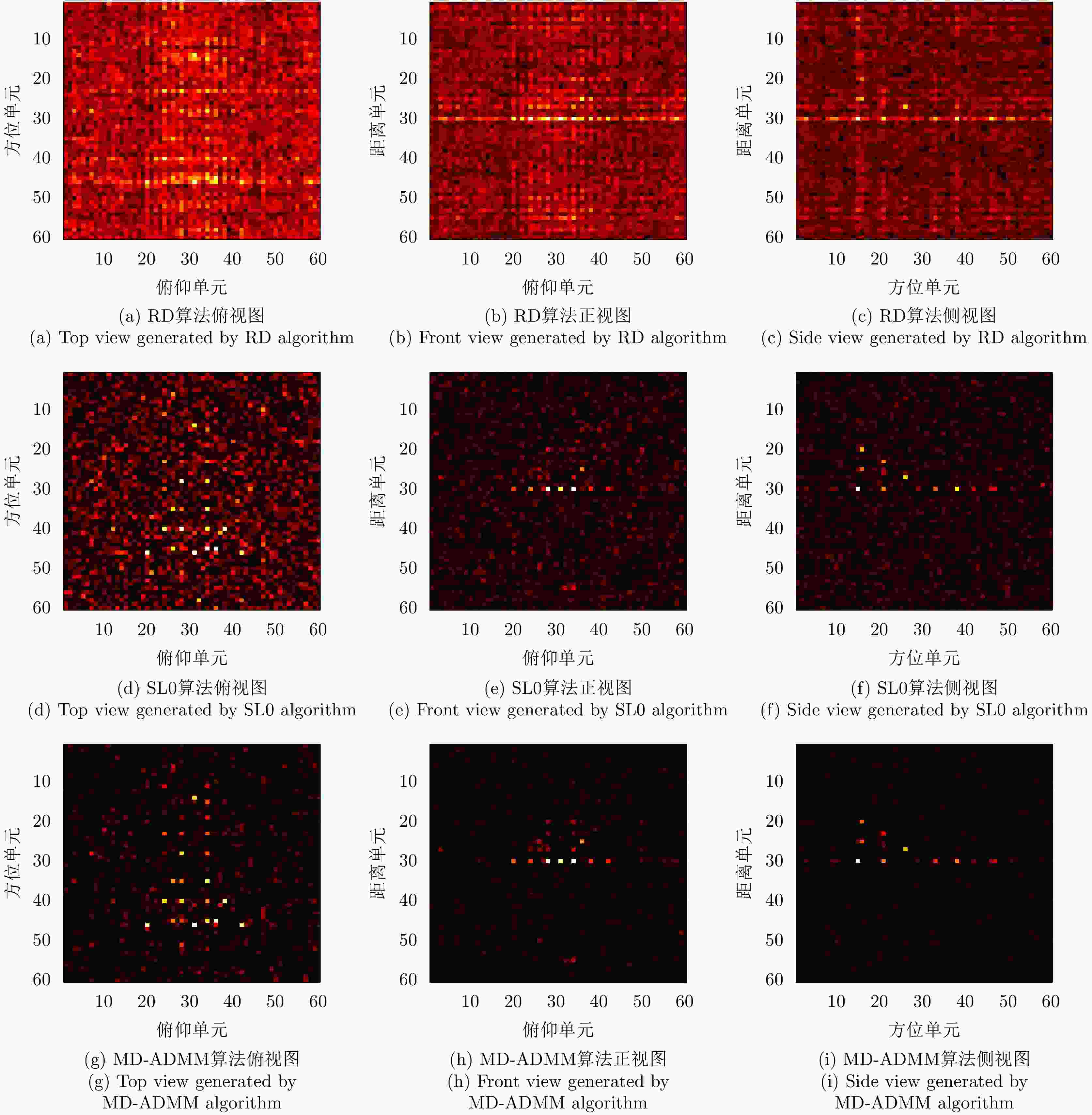
Table 4. Numerical results of measured data for different signal-to-noise ratio conditions
信噪比 算法 图像熵 PSNR 计算时间 原始数据 RD 9.639 29.816 0.010 MD-SL0 6.459 40.378 10.553 MD-ADMM 5.296 41.364 3.743 0 dB RD 10.242 26.909 0.0131 MD-SL0 7.571 35.241 12.064 MD-ADMM 6.183 39.090 4.274 -
[1] MUSMAN S, KERR D, and BACHMANN C. Automatic recognition of ISAR ship images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1996, 32(4): 1392–1404. doi: 10.1109/7.543860 [2] MARTORELLA M, GIUSTI E, DEMI L, et al. Target recognition by means of polarimetric ISAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(1): 225–239. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5705672 [3] BARANIUK R and STEEGHS P. Compressive radar imaging[C]. 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Waltham, USA, 2007: 128–133. [4] DUAN Guangqing, WANG Dangwei, MA Xiaoyan, et al. Three-dimensional imaging via wideband MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2010, 7(3): 445–449. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2038728 [5] HU Xiaowei, TONG Ningning, WANG Heming, et al. Multiple-input-multiple-output radar superresolution three-dimensional imaging based on multidimensional smoothed L0[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2016, 10(3): 035017. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.10.035017 [6] WANG Yong and LI Xuelu. 3-D imaging based on combination of the ISAR technique and a MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 6033–6054. doi: 0.1109/TGRS.2018.2829912 [7] CANDES E J and WAKIN M B. An introduction to compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21–30. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914731 [8] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [9] DUARTE M F and BARANIUK R G. Kronecker compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(2): 494–504. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2165289 [10] QIU Wei, MARTORELLA M, ZHOU Jianxiong, et al. Three-dimensional inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging based on compressive sensing[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(4): 411–420. [11] HU Xiaowei, TONG Ningning, GUO Yiduo, et al. MIMO radar 3-D imaging based on multi-dimensional sparse recovery and signal support prior information[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(8): 3152–3162. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2810705 [12] QIU Wei, ZHOU Jianxiong, ZHAO Hongzhong, et al. Three-dimensional sparse turntable microwave imaging based on compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 826–830. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2363238 [13] ZHANG Shuanghui, LIU Yongxiang, and LI Xiang. Computationally efficient sparse aperture ISAR autofocusing and imaging based on fast ADMM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(12): 8751–8765. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2990445 [14] ZHU Yutao, SU Yi, and YU Wenxian. An ISAR imaging method based on MIMO technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(8): 3290–3299. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2045230 [15] BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: