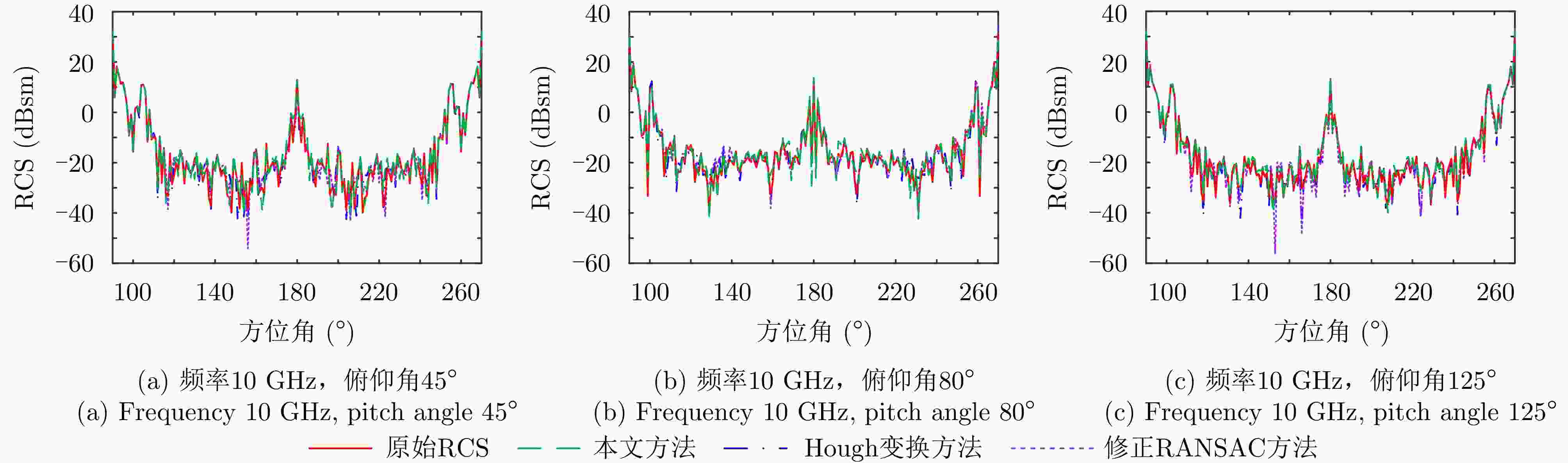
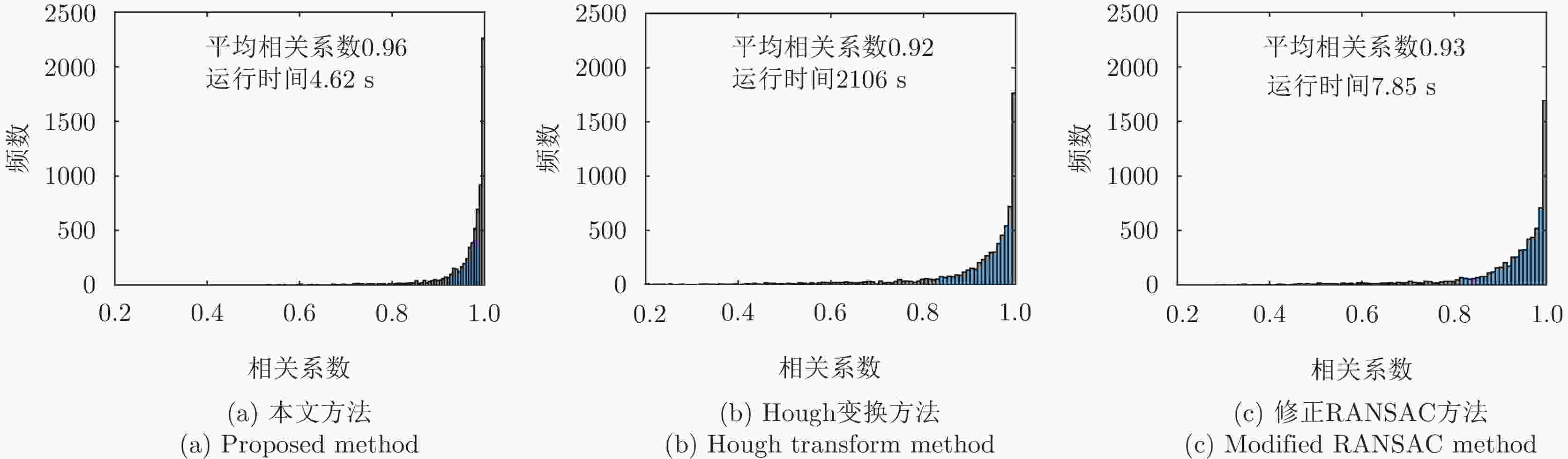
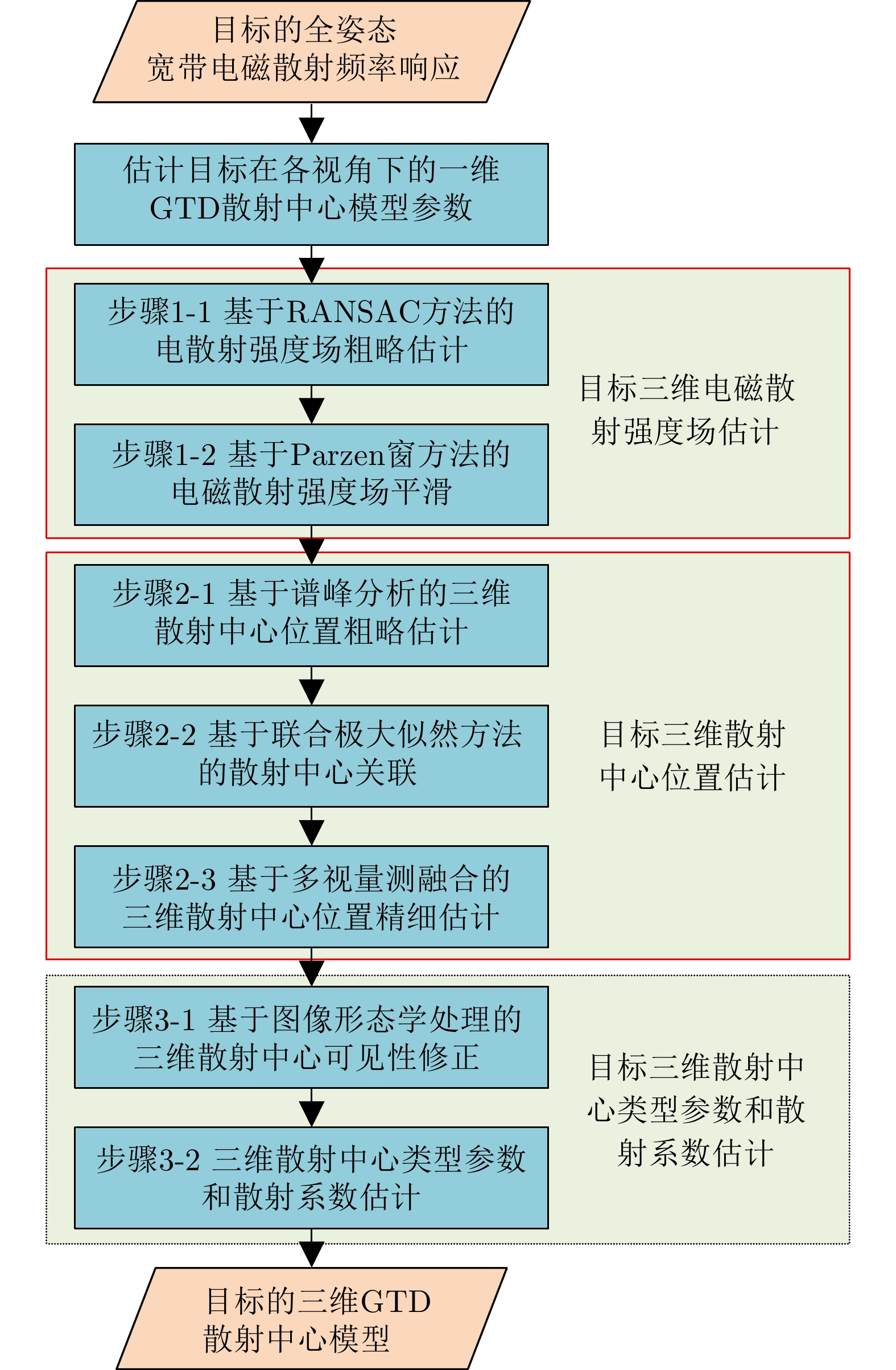
-
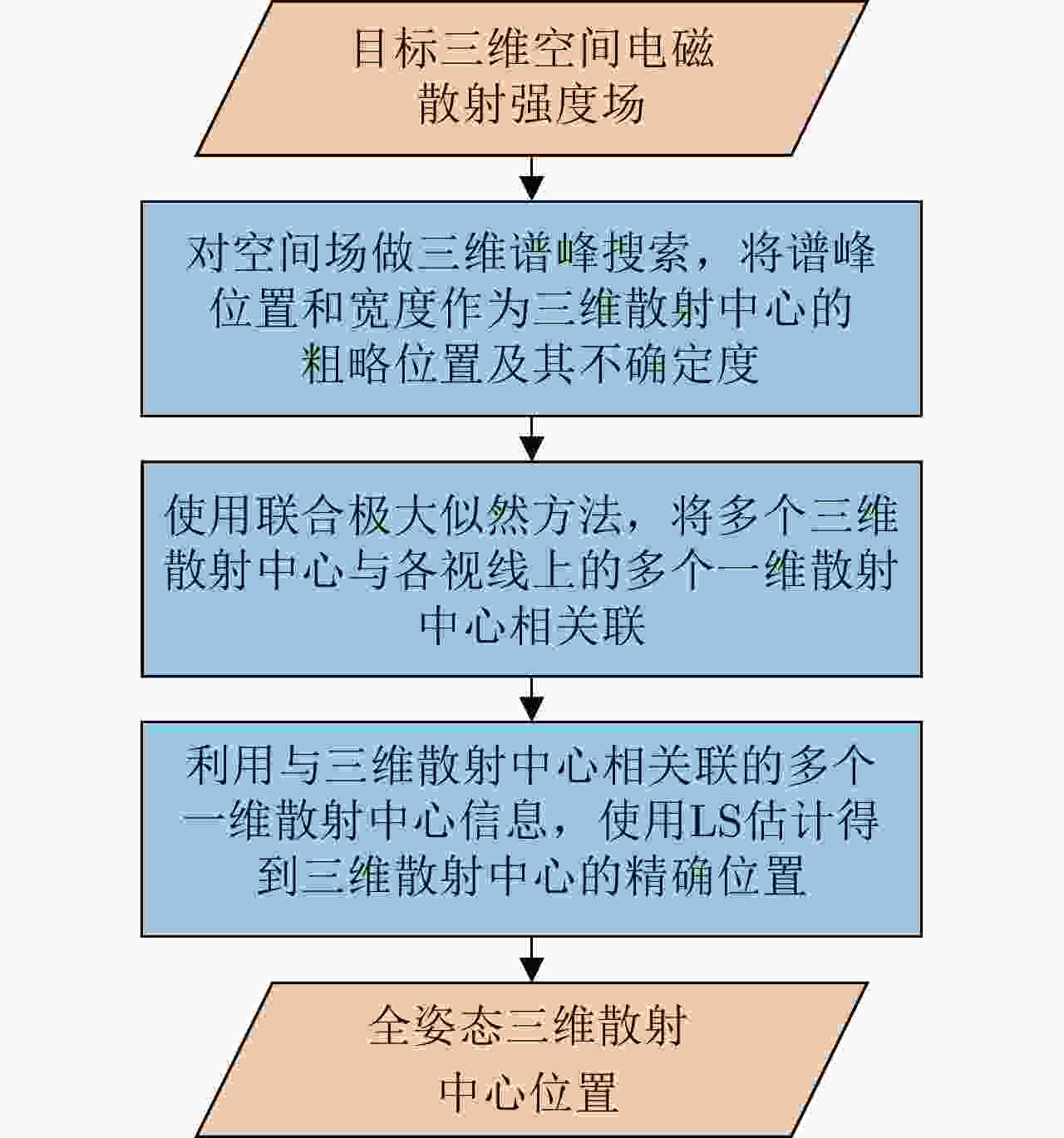
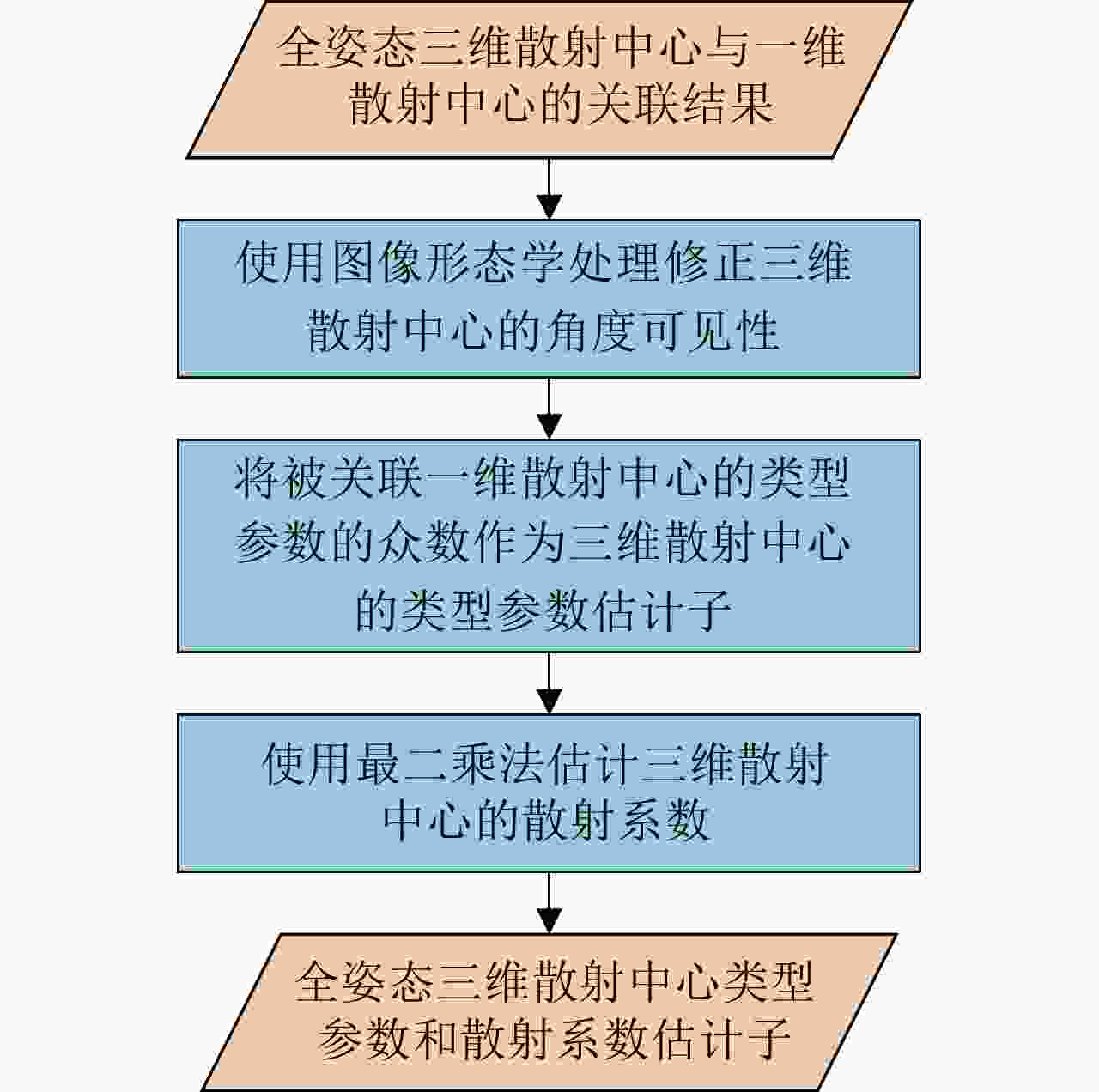
摘要: 全姿态散射中心模型是一种性能优良的光学区复杂目标电磁散射参数化模型。针对传统的基于候选点筛选和聚类的全姿态散射中心建模方法易出现虚假散射中心和遗漏真实散射中心的问题,该文提出了一种基于目标三维空间电磁散射强度场谱峰分析的建模方法。首先,基于目标多视一维散射中心参数,利用随机采样一致性(RANSAC)方法和Parzen窗函数方法估计目标在三维空间中的电磁散射强度场。然后,通过谱峰分析、散射中心关联和多视量测融合,得到全姿态三维散射中心的位置。最后,利用二值形态学处理修正全姿态散射中心的角度可见性,估计全姿态散射中心的散射系数和类型参数。仿真结果表明,该文方法所提取的全姿态散射中心与目标几何结构具有极强的关联性,相较传统方法,在缩减三维散射中心数量的同时提升了模型的表示精度。Abstract: The global scattering-center model is a high-performance electromagnetic scattering parametric model for complex targets in an optical region. The traditional methods for constructing global scattering models are usually based on candidate-point screening and clustering and are prone to producing false scattering centers and ignoring actual scattering centers. To address this issue, this study proposes a novel modeling method based on the spectral peak analysis of the target electromagnetic scattering intensity field. First, the three-dimensional (3D) electromagnetic scattering intensity field of the target is estimated based on the multiperspective, one-dimensional scattering-center parameters of the target using the RANdom SAmple Consensus (RANSAC) and Parzen window methods. Next, the positions of the global 3D scattering centers are determined through spectral peak analysis, scattering-center association, and multivision measurement fusion. Finally, the scattering coefficients and type parameters of the global scattering centers are estimated after the visibility of the global scattering center is corrected through binary image morphological processing. Simulation results demonstrate that the global scattering center model extracted using this method, which is highly consistent with the geometrical structure of the target, achieves higher expression accuracy while using fewer scattering centers than those used in traditional methods.
-
表 1 不同机理的散射中心的类型参数取值
Table 1. Values of type parameters for scattering centers of different mechanisms
$ {\text{ }}{\alpha _m} $取值 散射机理 –1 角绕射,尖顶绕射 –1/2 边缘绕射 0 点散射,双曲面反射,直边镜面反射 1/2 单曲面反射 1 平板法向发射,二面角反射,三面角反射 表 2 简单目标的全姿态散射中心参数表
Table 2. Parameter table of the global scattering centers of the simple target
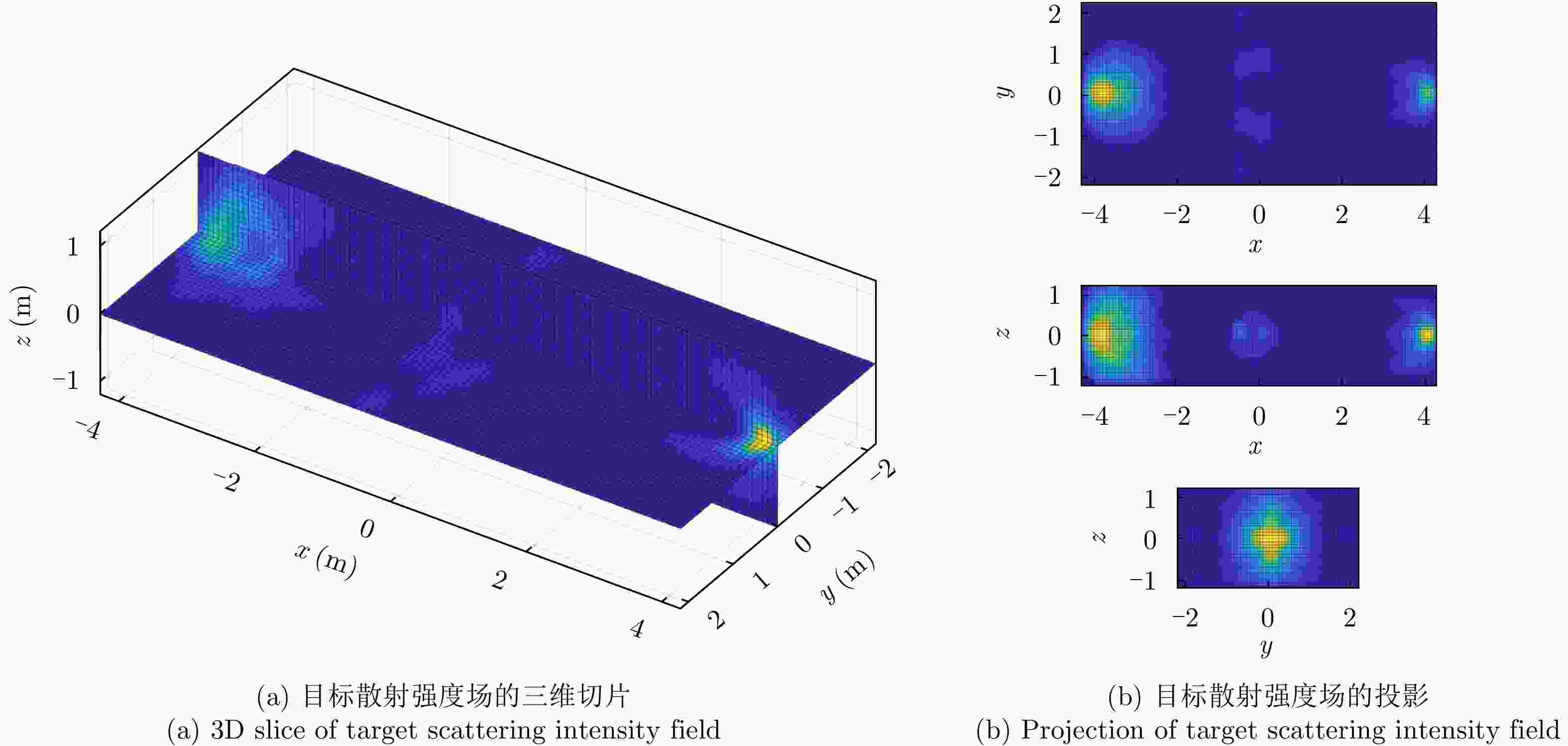
编号 空间位置(x,y,z) 散射强度 散射类型 1 (3,2,1) 74.56–66.64j 0 2 (–2,1,0.5) 46.10–38.40j –1/2 3 (4,–0.2,0.2) –84.22+31.74j 1/2 4 (–3,–2.2,1.2) –36.64+16.04j 1 表 3 100次蒙特卡罗仿真实验结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of 100 Monte Carlo simulation experimental results
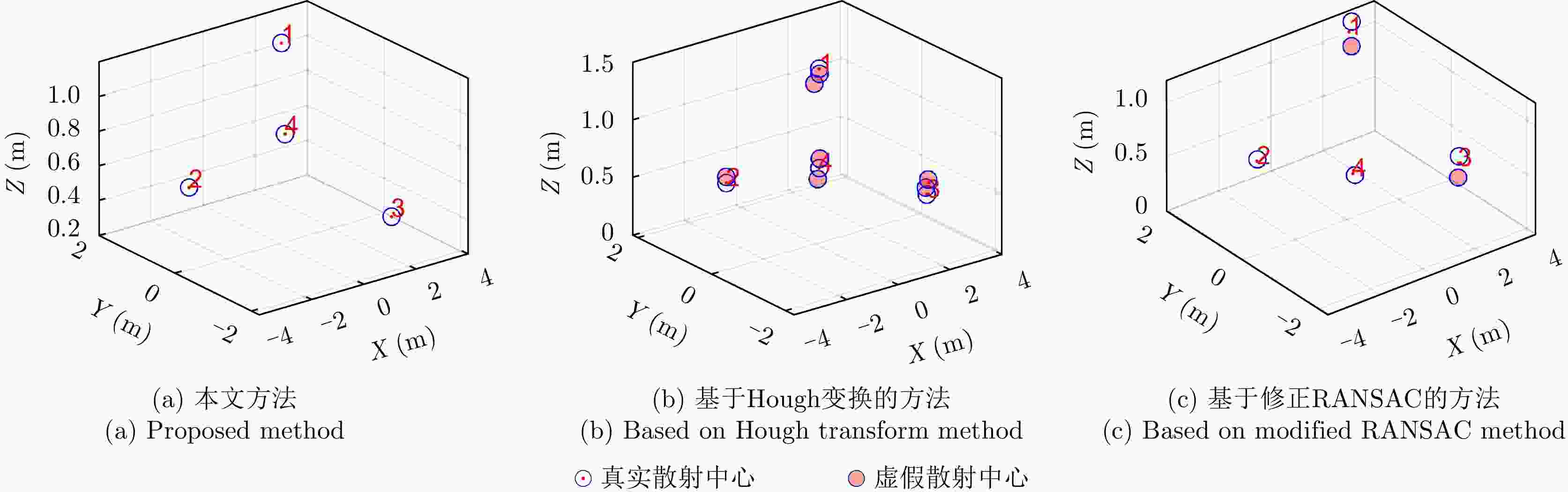
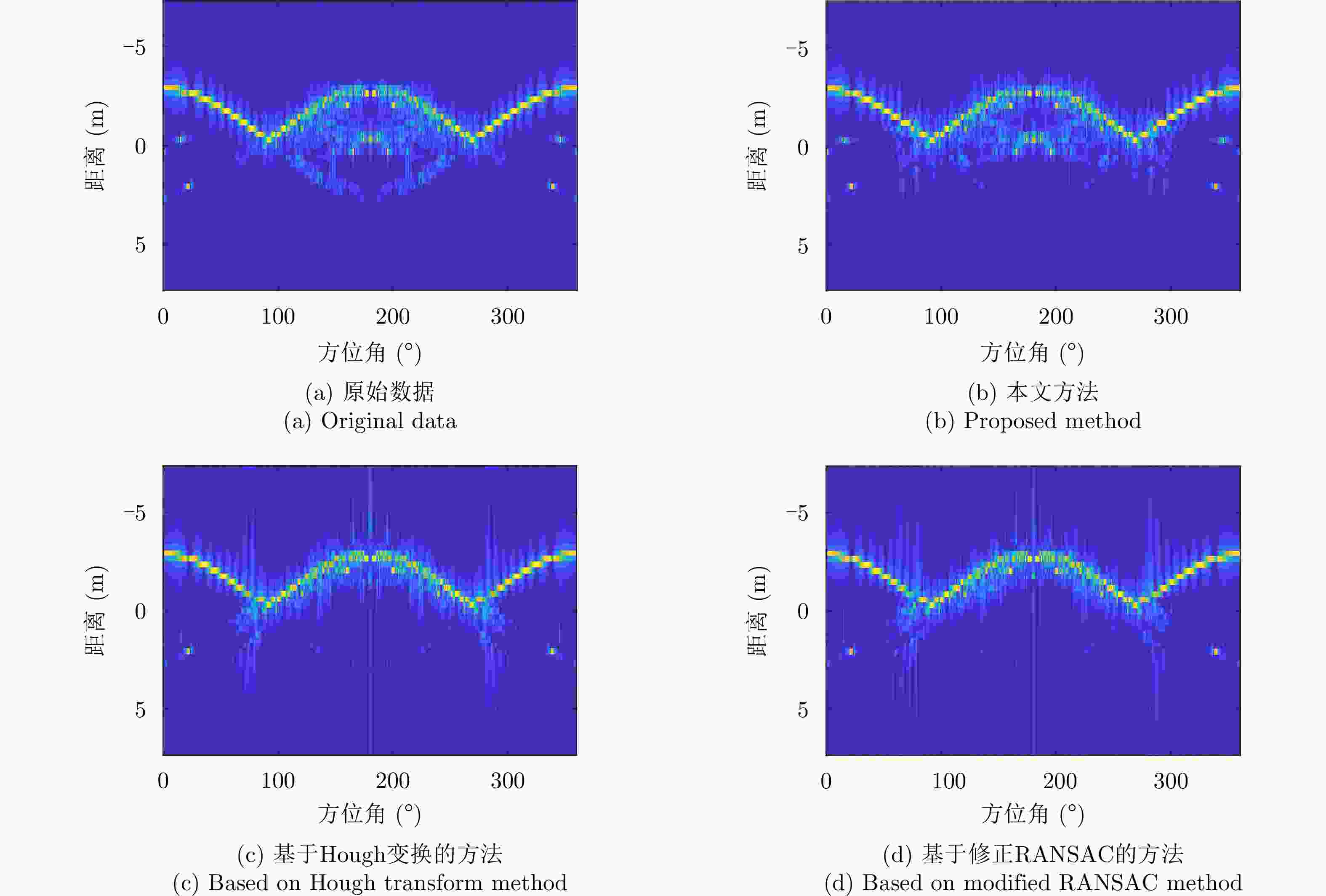
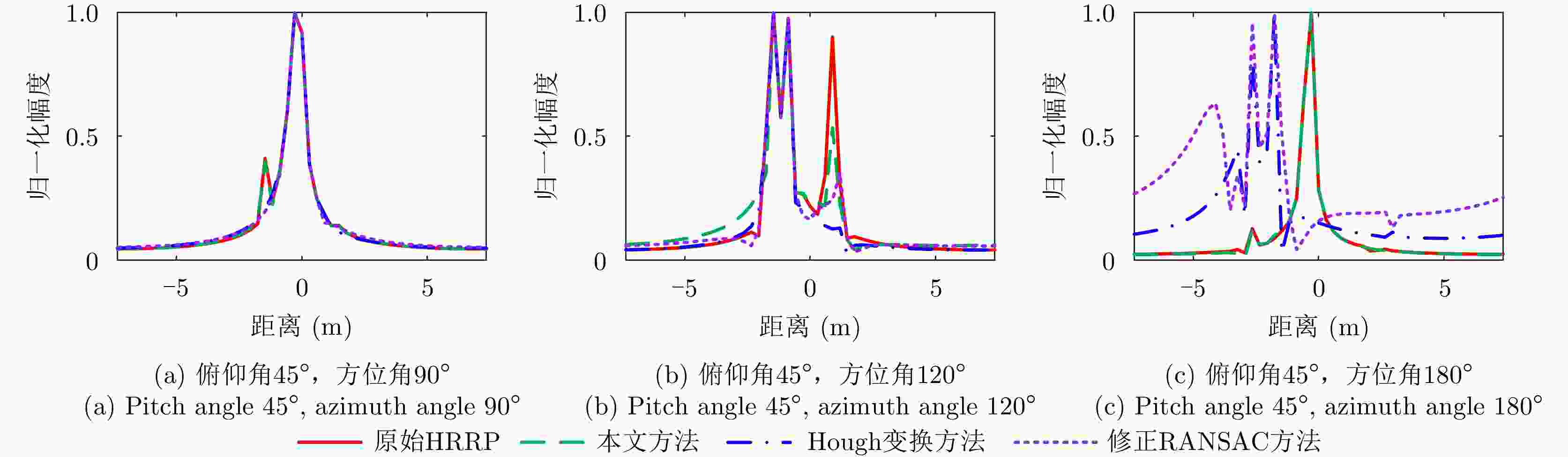
方法 虚假散射中心个数 平均运行时长(s) 位置估计误差(m) 5 dB 10 dB 15 dB 5 dB 10 dB 15 dB 5 dB 10 dB 15 dB 修正RANSAC法 5.58 5.49 3.47 59.42 51.22 24.43 0.0732 0.0734 0.0635 霍夫变换法 3.34 3.23 2.19 3639 3545 3378 0.0163 0.0155 0.0131 本文方法 0 0 0 17.26 16.45 9.690 0.0012 0.0012 0.0010 表 4 目标全姿态散射中心与目标部件的对应关系
Table 4. Correspondence between the global scattering centers and the target components
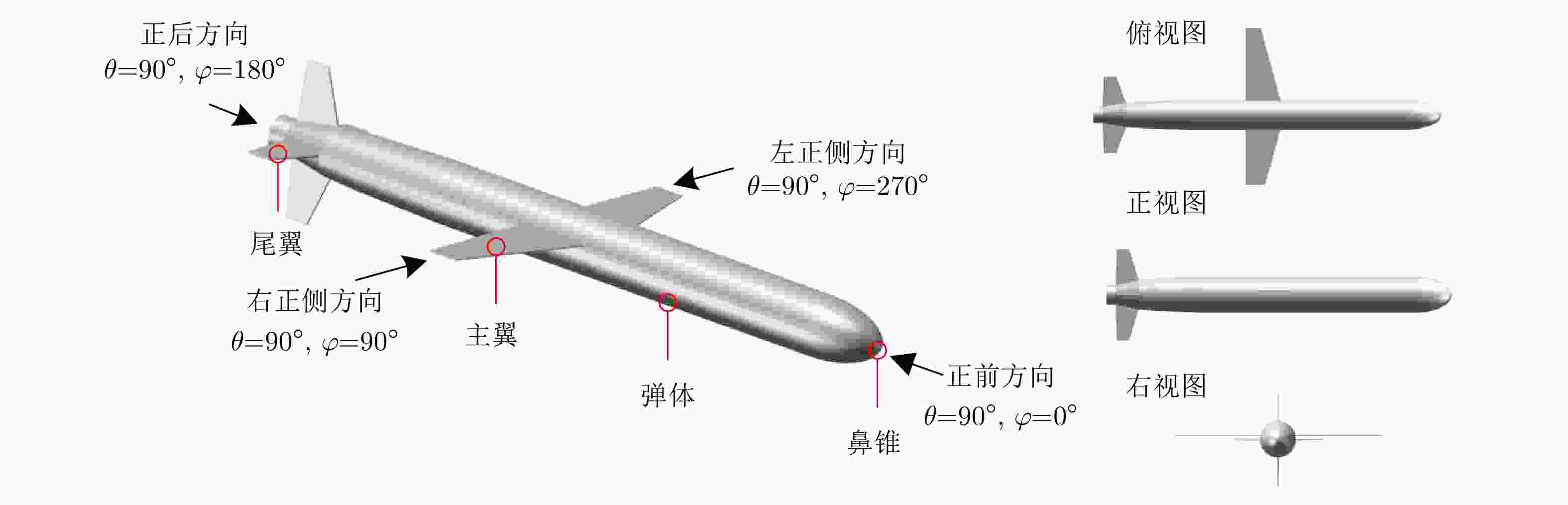
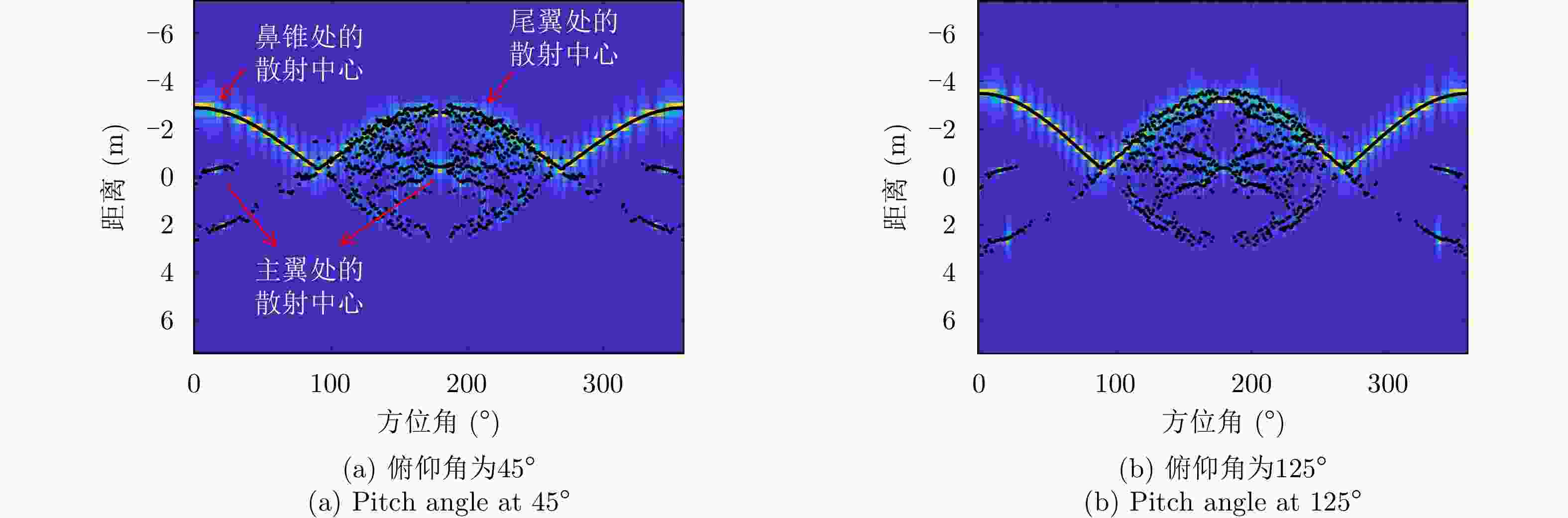
散射中心编号 与散射中心相关的目标部件 1 鼻锥 7, 10, 11 右主翼 8, 9, 12 左主翼 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 尾翼 表 5 不同信号带宽和俯仰角范围组合条件下全姿态散射中心模型的性能
Table 5. Performance of the global scattering center model under various combinations of signal bandwidth and pitch angle domain
带壳 重构模型指标 散射中心
数量平均相关
系数相关系数大于
0.8的比例250 MHz 70°~110° 9 0.98 1.00 45°~135° 10 0.96 0.96 500 MHz 70°~110° 11 0.96 0.95 45°~135° 12 0.96 0.97 -
[1] 黄培康. 雷达目标特征信号[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 230–237.HUANG Peikang. Radar Target Characteristic Signal[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 230–237. [2] 文贡坚, 朱国强, 殷红成, 等. 基于三维电磁散射参数化模型的SAR目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 115–135. doi: 10.12000/JR17034.WEN Gongjian, ZHU Guoqiang, YIN Hongcheng, et al. SAR ATR based on 3D parametric electromagnetic scattering model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 115–135. doi: 10.12000/JR17034. [3] 邢孟道, 谢意远, 高悦欣, 等. 电磁散射特征提取与成像识别算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232.XING Mengdao, XIE Yiyuan, GAO Yuexin, et al. Electromagnetic scattering characteristic extraction and imaging recognition algorithm: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232. [4] 张武才, 潘明海, 陈诗弘. 基于LFM子脉冲的宽带雷达目标回波模拟方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(4): 768–774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.04.11.ZHANG Wucai, PAN Minghai, and CHEN Shihong. Method of wide-band radar target echo signal simulation based on LFM subpulse[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(4): 768–774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.04.11. [5] 胡利平, 闫华, 钟卫军, 等. 舰船目标三维散射中心建模及SAR快速仿真方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2021, 48(2): 72–83. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2021.02.010.HU Liping, YAN Hua, ZHONG Weijun, et al. Three-dimensional scattering center modeling and a fast SAR simulation method for ship targets[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2021, 48(2): 72–83. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2021.02.010. [6] GUO Kunyi, XIAO Guangliang, ZHAI Yun, et al. Angular glint error simulation using attributed scattering center models[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 35194–35205. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2846538. [7] HURST M and MITTRA R. Scattering center analysis via Prony’s method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1987, 35(8): 986–988. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1987.1144210. [8] POTTER L C and MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098. [9] GERRY M J, POTTER L C, GUPTA I J, et al. A parametric model for synthetic aperture radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(7): 1179–1188. doi: 10.1109/8.785750. [10] BHALLA R and LING Hao. Three-dimensional scattering center extraction using the shooting and bouncing ray technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1996, 44(11): 1445–1453. doi: 10.1109/8.542068. [11] KENNAUGH E M and MOFFATT D L. Transient and impulse response approximations[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1965, 53(8): 893–901. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1965.4068. [12] BHALLA R, LING Hao, MOORE J, et al. 3D scattering center representation of complex targets using the shooting and bouncing ray technique: A review[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 1998, 40(5): 30–39. doi: 10.1109/74.735963. [13] 闫华, 陈勇, 李胜, 等. 基于弹跳射线法的海面舰船目标三维散射中心快速建模方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 107–116. doi: 10.12000/JR18078.YAN Hua, CHEN Yong, LI Sheng, et al. A fast algorithm for establishing 3-D scattering center model for ship targets over sea surface using the shooting and bouncing ray technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 107–116. doi: 10.12000/JR18078. [14] HE Yang, HE Siyuan, ZHANG Yunhua, et al. A forward approach to establish parametric scattering center models for known complex radar targets applied to SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(12): 6192–6205. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2360700. [15] LIU Jin, HE Siyuan, ZHANG Lei, et al. An automatic and forward method to establish 3-D parametric scattering center models of complex targets for target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(12): 8701–8716. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2989856. [16] 刘久祥, 肖光亮, 郭琨毅, 等. 薄涂覆目标散射中心的精确建模[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(6): 1589–1596. doi: 210.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.06.01.LIU Jiuxiang, XIAO Guangliang, GUO Kunyi, et al. Accurate scattering center modeling of thin-coated target[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(6): 1589–1596. doi: 210.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.06.01. [17] 蒋文, 李王哲. 基于幅相分离的属性散射中心参数估计新方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 606–615. doi: 10.12000/JR18097.JIANG Wen and LI Wangzhe. A new method for parameter estimation of attributed scattering centers based on amplitude-phase separation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 606–615. doi: 10.12000/JR18097. [18] 谢意远, 高悦欣, 邢孟道, 等. 跨谱段SAR散射中心多维参数解耦和估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 632–639. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200319.XIE Yiyuan, GAO Yuexin, XING Mengdao, et al. A decoupling and dimension dividing multi-parameter estimation method for cross-band SAR scattering centers[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 632–639. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200319. [19] YANG Dongwen, NI Wei, DU Lan, et al. Efficient attributed scatter center extraction based on image-domain sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 4368–4381. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3011332. [20] 徐嘉华, 张小宽, 郑舒予, 等. 基于改进正交匹配追踪算法的属性散射中心提取[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(8): 2076–2082. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.08.07.XU Jiahua, ZHANG Xiaokuan, ZHENG Shuyu, et al. Attribute scattering center extraction based on improved orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(8): 2076–2082. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.08.07. [21] 郑舒予, 张小宽, 郭艺夺, 等. 一维GTD散射中心模型参数估计的改进MUSIC算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(11): 2149–2155. doi: 10.13700/j.h.1001-5965.2019.0576.ZHENG Shuyu, ZHANG Xiaokuan, GUO Yidao, et al. Parameter estimation of 1D GTD scattering center model based on an improved MUSIC algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(11): 2149–2155. doi: 10.13700/j.h.1001-5965.2019.0576. [22] 李尚生, 王旭坤, 付哲泉, 等. 基于Hankel矩阵改进TLS-ESPRIT算法的散射中心参数提取及RCS重构[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(1): 62–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.01.09.LI Shangsheng, WANG Xukun, FU Zhequan, et al. Extraction of scattering center parameter and RCS reconstruction based on the improved TLS-ESPRIT algorithm of Hankel matrix[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(1): 62–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.01.09. [23] 徐嘉华, 张小宽, 郑舒予, 等. 基于改进3D-ESPRIT算法的GTD模型参数估计与目标识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(2): 336–342. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.02.07.XU Jiahua, ZHANG Xiaokuan, ZHENG Shuyu, et al. GTD model Parameter estimation and target recognition based on improved 3D-ESPRIT algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(2): 336–342. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.02.07. [24] NAISHADHAM K and PIOU J E. A robust state space model for the characterization of extended returns in radar target signatures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2008, 56(6): 1742–1751. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2008.916932. [25] 魏少明, 洪文衍, 王俊, 等. 基于改进矩阵束的超宽带一维散射中心提取方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1231–1240. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210602.WEI Shaoming, HONG Wenyan, WANG Jun, et al. Extracting UWB one-dimensional scattering center based on improved matrix pencil[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1231–1240. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210602. [26] GHASEMI M and SHEIKHI A. Joint scattering center enumeration and parameter estimation in GTD model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(6): 4786–4798. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2975197. [27] ZHOU Jianxiong, ZHAO Hongzhong, SHI Zhiguang, et al. Global scattering center model extraction of radar targets based on wideband measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2008, 56(7): 2051–2060. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2008.924698. [28] HU Jiemin, WANG Wei, ZHAI Qinglin, et al. Global scattering center extraction for radar targets using a modified RANSAC method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 64(8): 3573–3586. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2016.2574880. [29] 闫华, 张磊, 陆金文, 等. 任意多次散射机理的GTD散射中心模型频率依赖因子表达[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 370–381. doi: 10.12000/JR21005.YAN Hua, ZHANG Lei, LU Jinwen, et al. Frequency-dependent factor expression of the GTD scattering center model for the arbitrary multiple scattering mechanism[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 370–381. doi: 10.12000/JR21005. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: