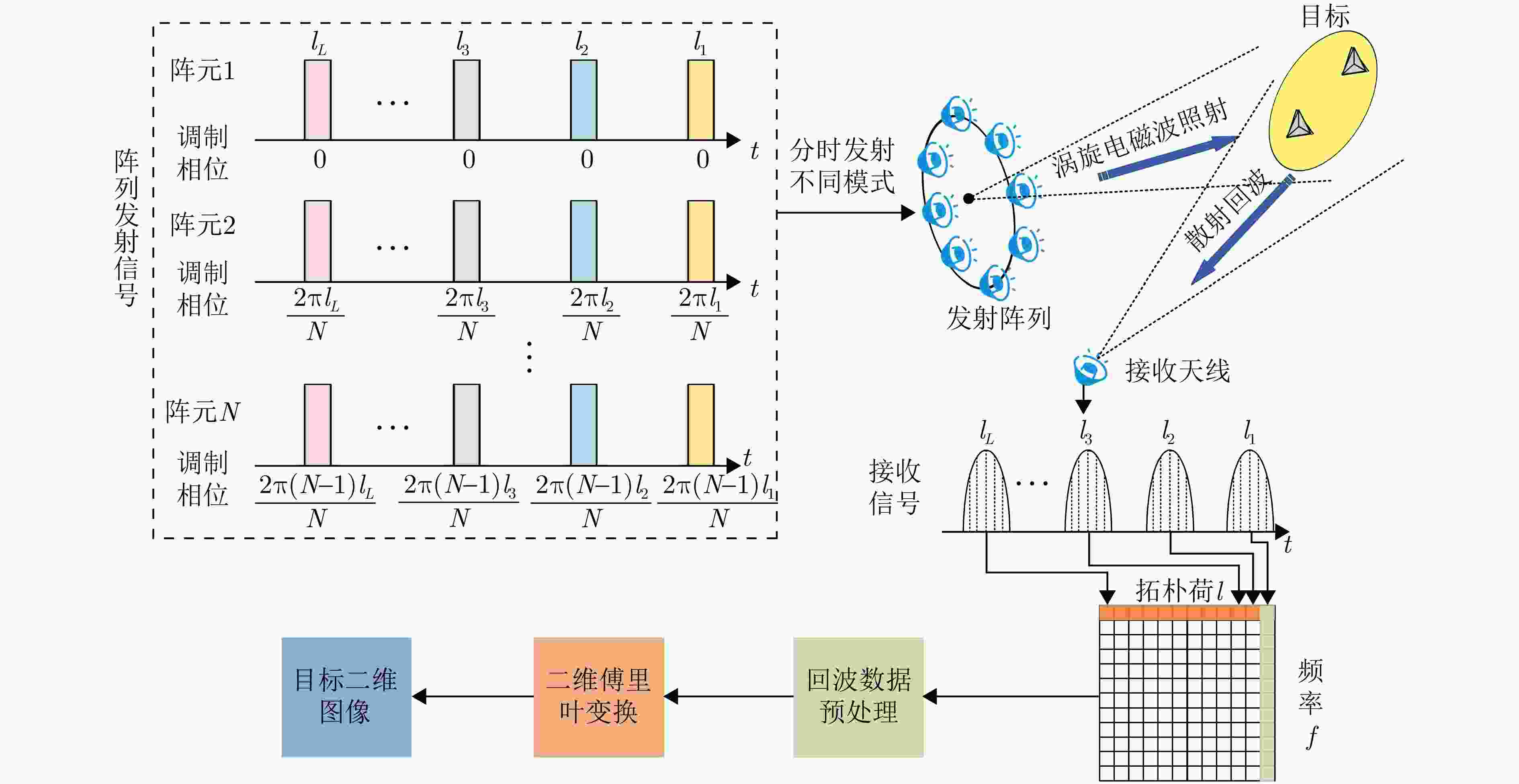
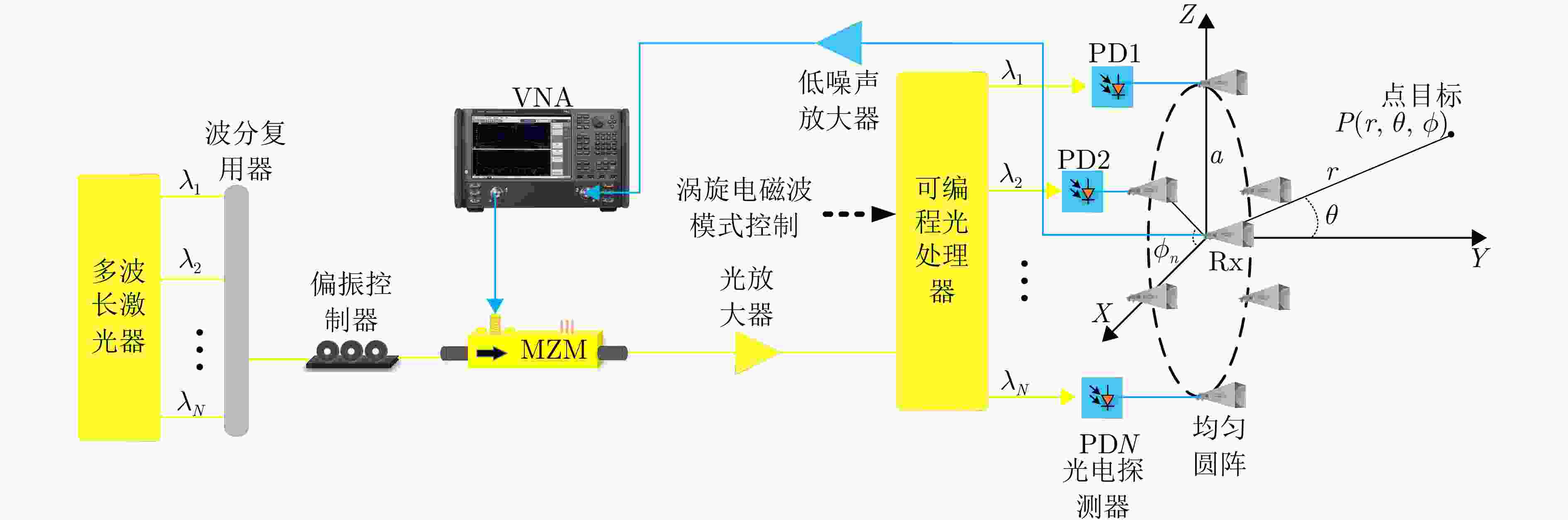
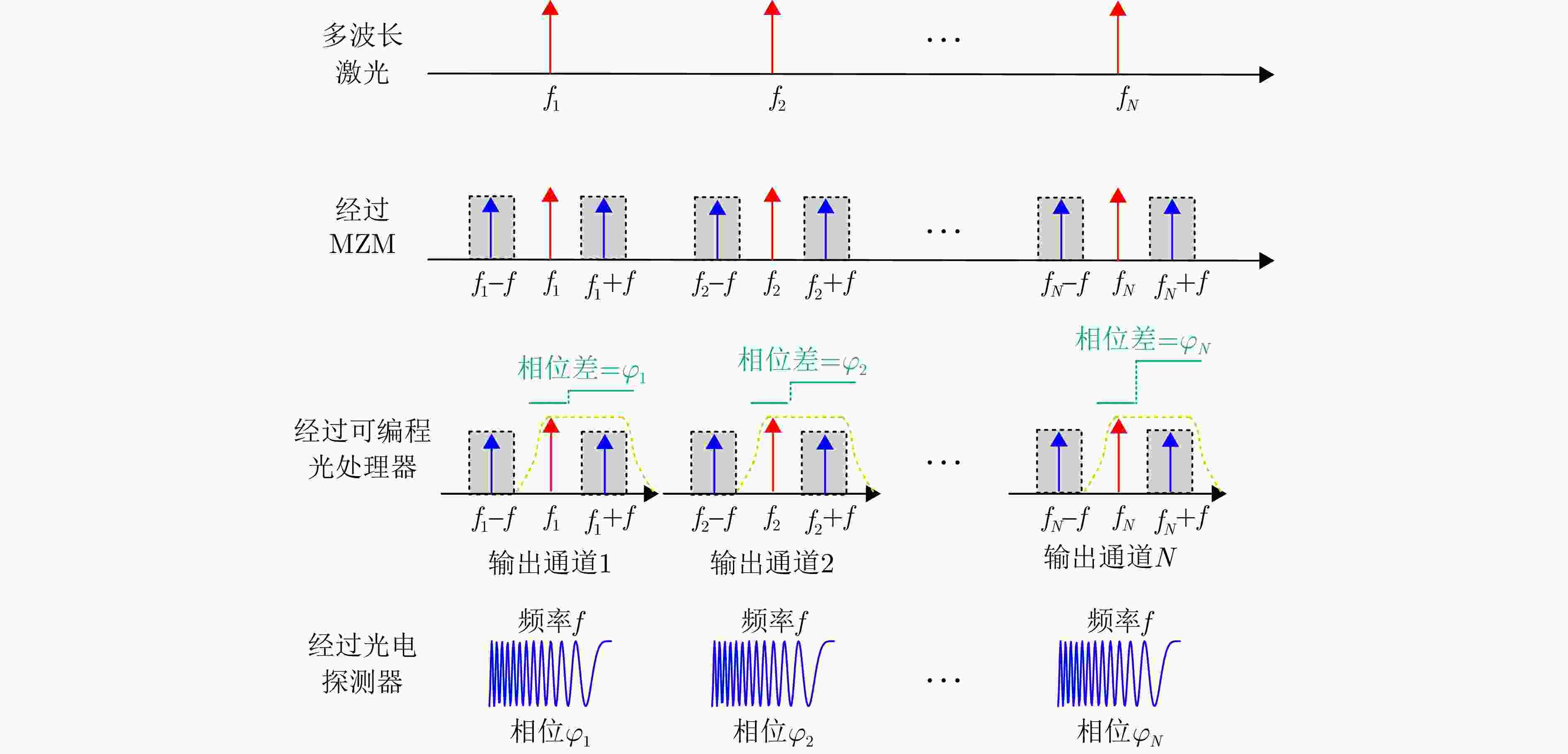
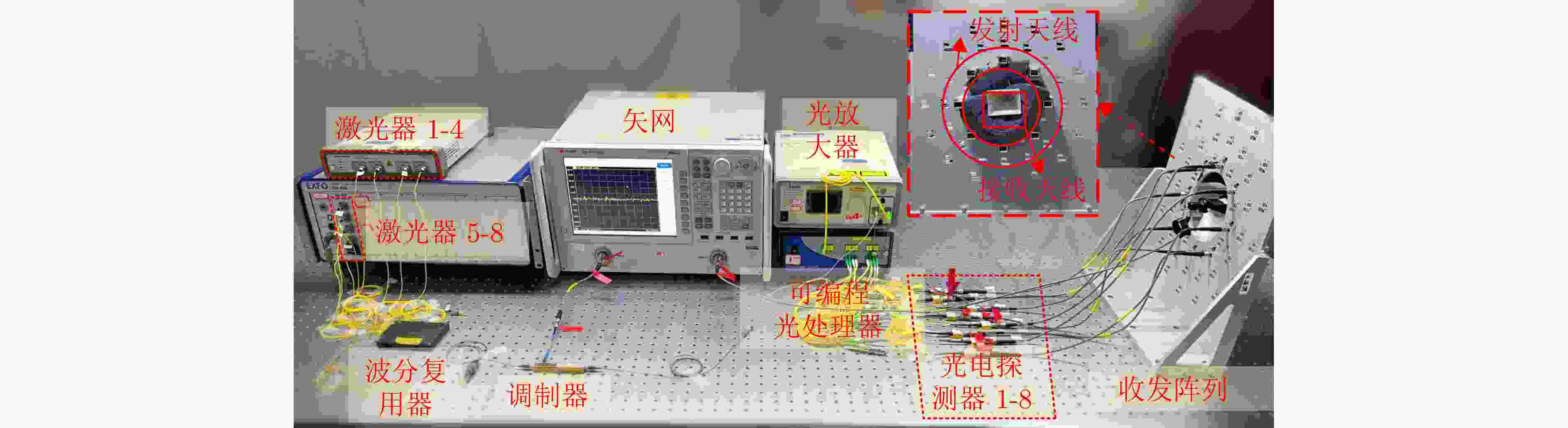
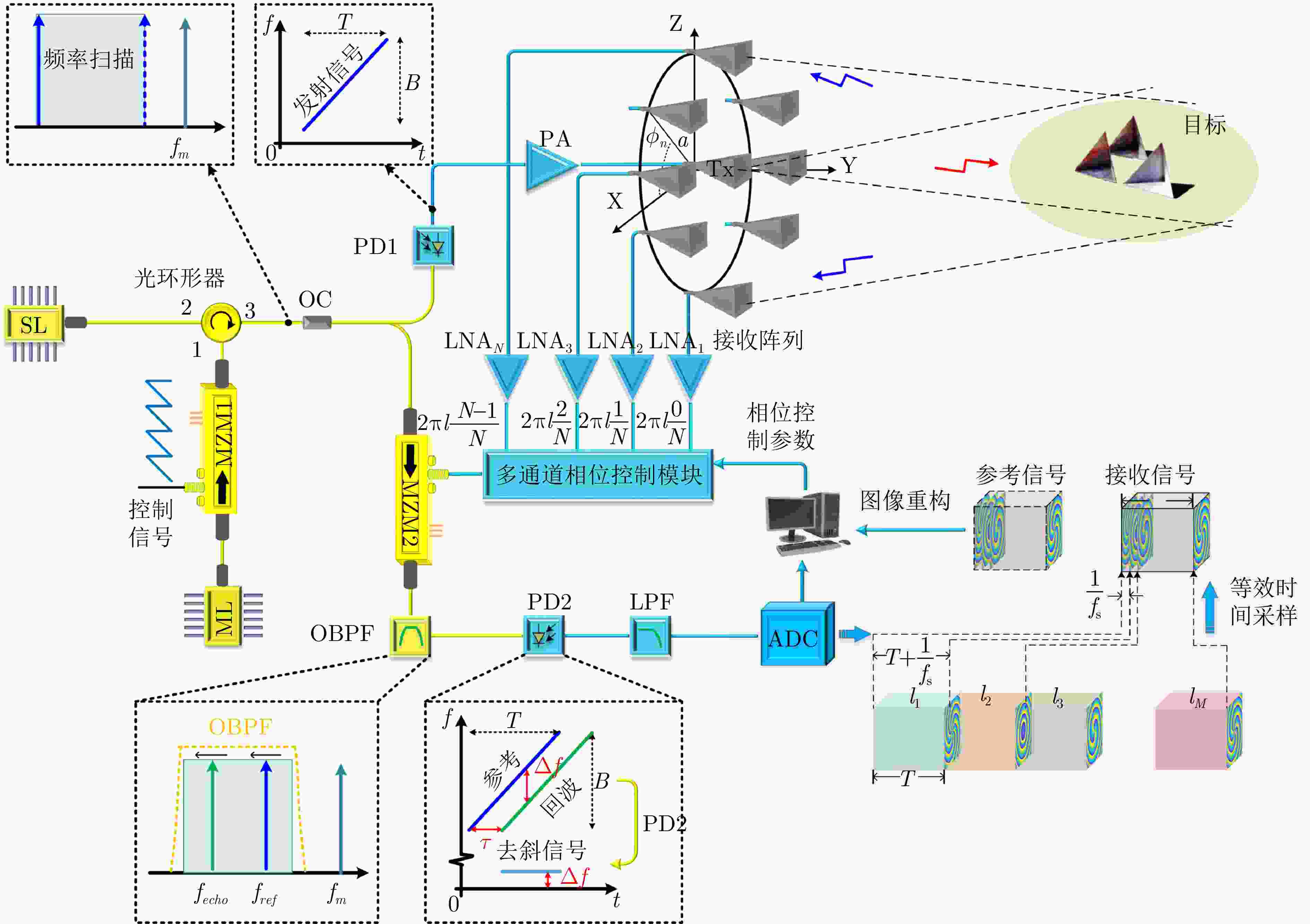
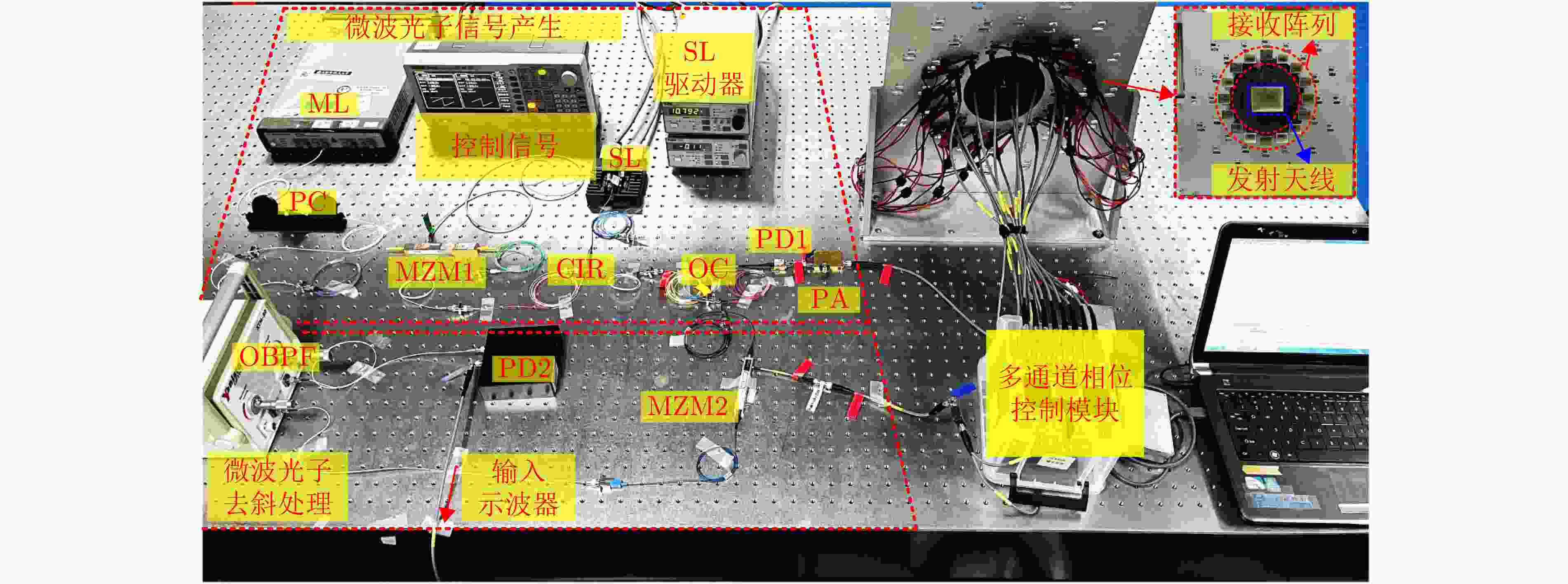
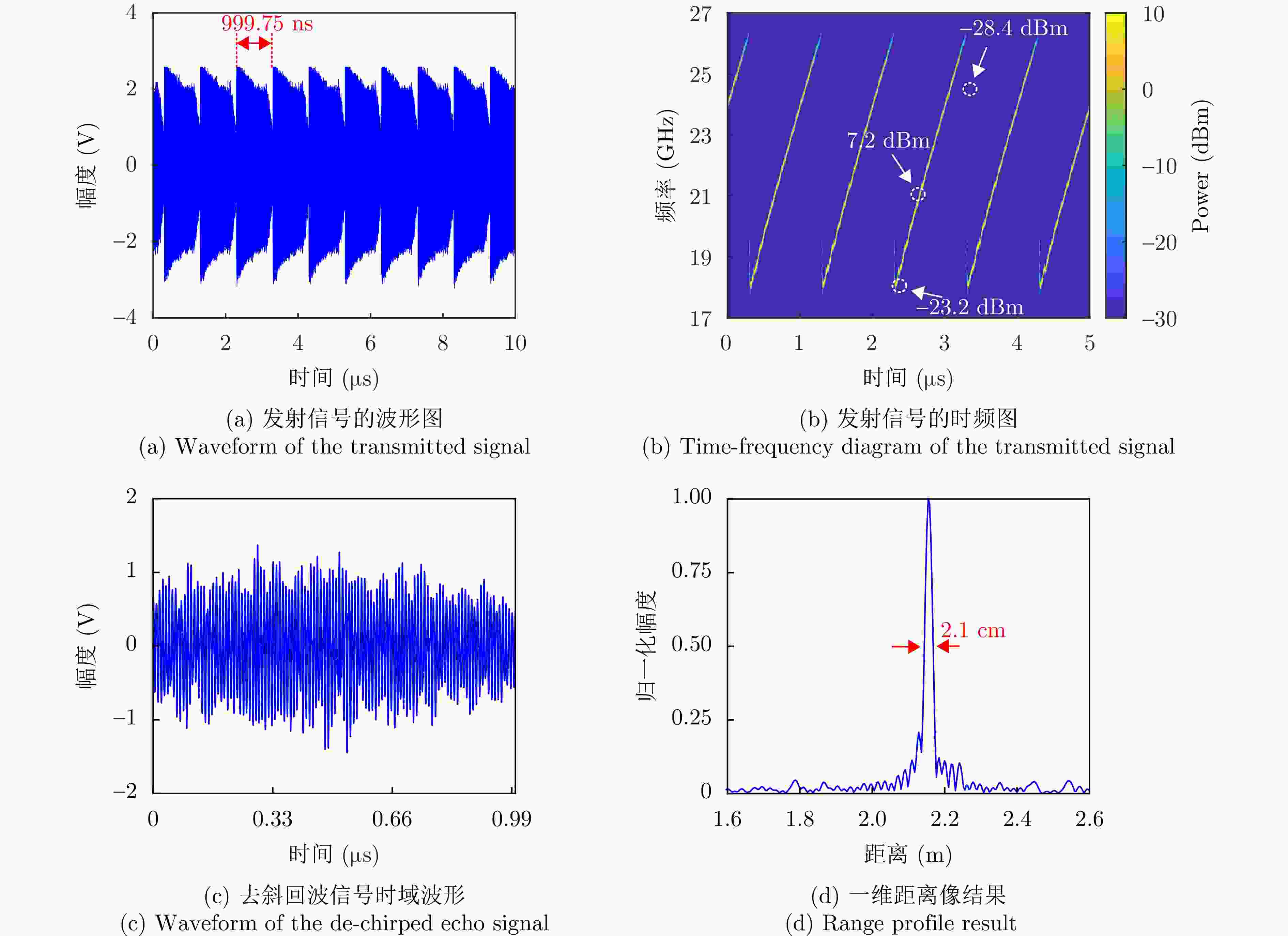
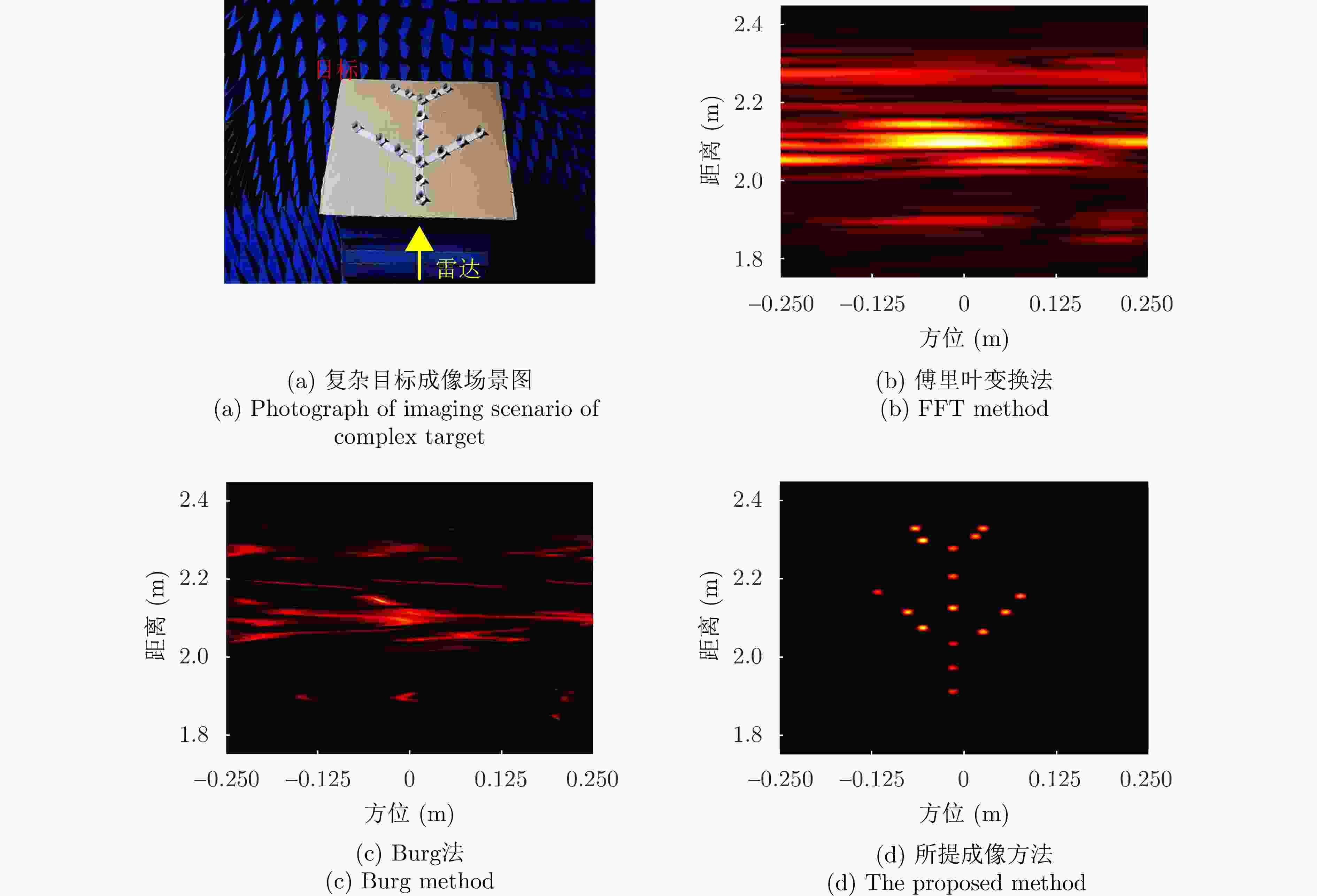
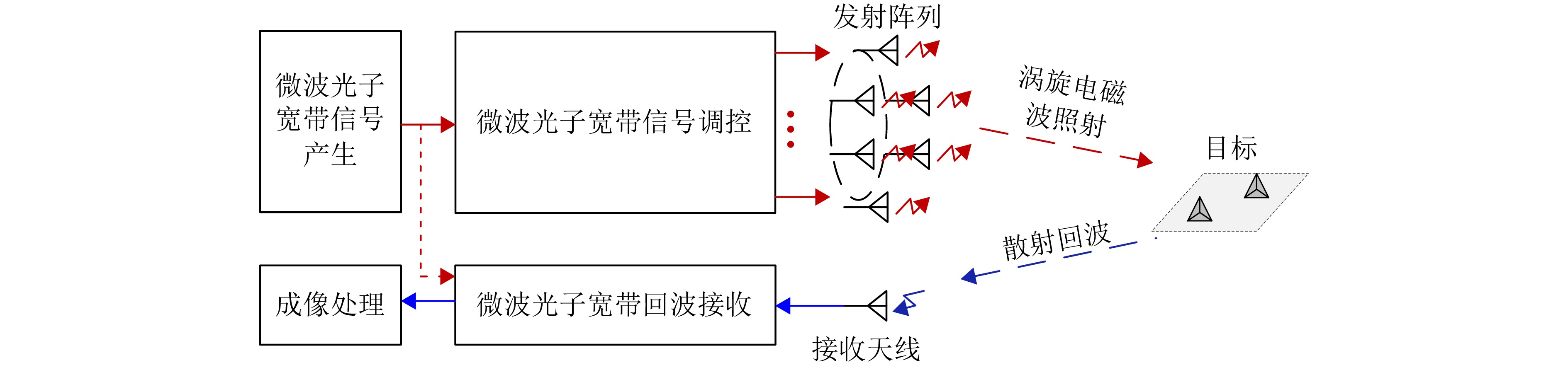
| [1] |
AUSHERMAN D A, KOZMA A, WALKER J L, et al. Developments in radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1984, AES-20(4): 363–400. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1984.4502060.
|
| [2] |
杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099.YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099.
|
| [3] |
刘永坦. 雷达成像技术[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2014: 169–170.LIU Yongtan. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2014: 169–170.
|
| [4] |
许会, 陈艳玲. 微波成像技术及其算法综述[J]. 无损检测, 2012, 34(10): 67–71,82.XU Hui and CHEN Yanling. Overview of the technology and algorithm of microwave imaging[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2012, 34(10): 67–71,82.
|
| [5] |
程永强, 王宏强, 曹凯程, 等. 微波关联成像研究进展及展望(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(12): 20210790. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210790.CHENG Yongqiang, WANG Hongqiang, CAO Kaicheng, et al. Progress and prospect of microwave coincidence imaging (Invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(12): 20210790. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210790.
|
| [6] |
CHEN C C and ANDREWS H C. Target-motion-induced radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1980, AES-16(1): 2–14. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1980.308873.
|
| [7] |
WAHL D E, EICHEL P H, GHIGLIA D C, et al. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 827–835. doi: 10.1109/7.303752.
|
| [8] |
STEINBERG B D. Microwave imaging of aircraft[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1988, 76(12): 1578–1592. doi: 10.1109/5.16351.
|
| [9] |
STEINBERG B D. Radar imaging from a distorted array: The radio camera algorithm and experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1981, 29(5): 740–748. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1981.1142652.
|
| [10] |
刘克成, 宋学诚. 天线原理[M]. 长沙: 国防科技大学出版社, 1989:178.LIU Kecheng and SONG Xuecheng. Principles of Antennas[M]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology Press, 1989:178.
|
| [11] |
MOHAMMADI S M, DALDORFF L K S, BERGMAN J E S, et al. Orbital angular momentum in radio—A system study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(2): 565–572. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2009.2037701.
|
| [12] |
WILLNER A E, HUANG Hao, YAN Yan, et al. Optical communications using orbital angular momentum beams[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2015, 7(1): 66–106. doi: 10.1364/AOP.7.000066.
|
| [13] |
TRINDER J R. Parabolic reflector[P]. WO, 2005069443A1, 2005.
|
| [14] |
THIDÉ B, THEN H, SJÖHOLM J, et al. Utilization of photon orbital angular momentum in the low-frequency radio domain[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(8): 087701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.087701.
|
| [15] |
郭桂蓉, 胡卫东, 杜小勇. 基于电磁涡旋的雷达目标成像[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2013, 35(6): 71–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.06.013.GUO Guirong, HU Weidong, and DU Xiaoyong. Electromagnetic vortex based radar target imaging[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2013, 35(6): 71–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.06.013.
|
| [16] |
LIU Kang, CHENG Yongqiang, YANG Zhaocheng, et al. Orbital-angular-momentum-based electromagnetic vortex imaging[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2015, 14: 711–714. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2376970.
|
| [17] |
QU Haiyou, LI Shiyuan, CHEN Chang, et al. High-resolution orbital angular momentum imaging with the removal of Bessel function modulation effect[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2024, 72(4): 2577–2590. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2023.3314107.
|
| [18] |
GHELFI P, LAGHEZZA F, SCOTTI F, et al. A fully photonics-based coherent radar system[J]. Nature, 2014, 507(7492): 341–345. doi: 10.1038/nature13078.
|
| [19] |
XU Shaofu, ZOU Weiwen, YANG Guang, et al. Ultra-high range resolution demonstration of a photonics-based microwave radar using a high-repetition-rate mode-locked fiber laser[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(6): 062801. doi: 10.3788/COL201816.062801.
|
| [20] |
ZHANG Siteng, ZOU Weiwen, QIAN Na, et al. Enlarged range and filter-tuned reception in photonic time-stretched microwave radar[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2018, 30(11): 1028–1031. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2018.2828459.
|
| [21] |
MA Cong, YANG Yue, CAO Fengting, et al. High-resolution microwave photonic radar with sparse stepped frequency chirp signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 2007010. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3208112.
|
| [22] |
SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, and PAN Shilong. Millimeter-level resolution through-the-wall radar imaging enabled by an optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(22): 5659–5662. doi: 10.1364/OL.441803.
|
| [23] |
BERLAND F, FROMENTEZE T, BOUDESCOQUE D, et al. Microwave photonic MIMO radar for short-range 3D imaging[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 107326–107334. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3000801.
|
| [24] |
DONG Jingwen, ZHANG Fubo, JIAO Zekun, et al. Microwave photonic radar with a fiber-distributed antenna array for three-dimensional imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(13): 19113–19125. doi: 10.1364/OE.393502.
|
| [25] |
SERAFINO G, MARESCA S, DI MAURO L, et al. A photonics-assisted multi-band MIMO radar network for the port of the future[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2021, 27(6): 6000413. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2021.3092880.
|
| [26] |
MARESCA S, SERAFINO G, NOVIELLO C, et al. Field trial of a coherent, widely distributed, dual-band photonics-based MIMO radar with ISAR imaging capabilities[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2022, 40(20): 6626–6635. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3182421.
|
| [27] |
SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, ZHAO Keyi, et al. Photonics-based broadband vortex electromagnetic wave generation for high-resolution imaging[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2024, 42(6): 1894–1900. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2023.3329424.
|
| [28] |
SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, and PAN Shilong. Frequency-dependent vortex electromagnetic wave imaging[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2025, 24(1): 23–27. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2024.3481634.
|
| [29] |
SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, YU Xiaoyue, et al. Photonics-based broadband single-input-multiple- output-OAM coincidence imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radar Systems, 2024, 2: 690–698. doi: 10.1109/TRS.2024.3418461.
|
| [30] |
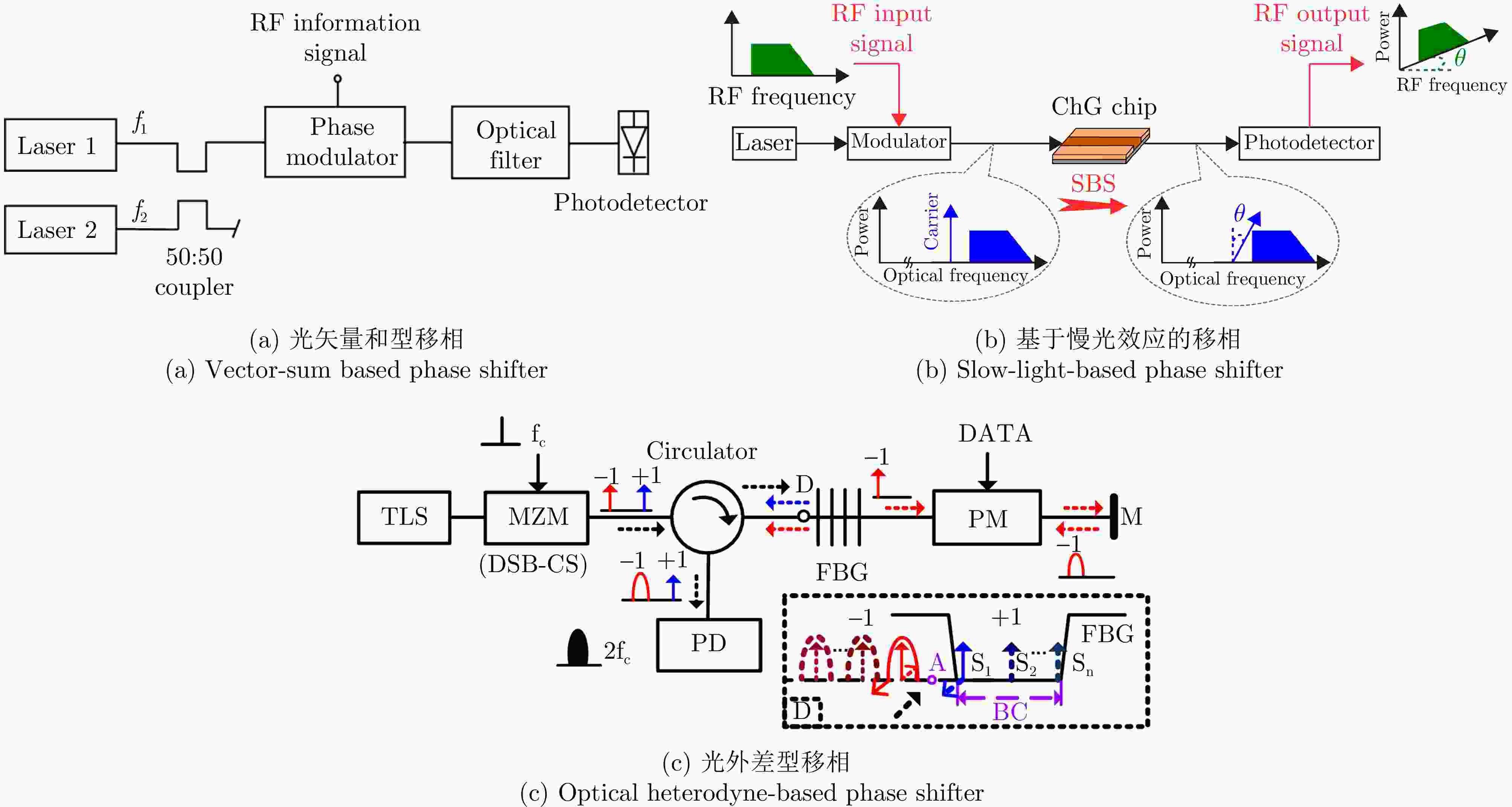
WANG Xudong, CHAN E H W, and MINASIAN R A. All-optical photonic microwave phase shifter based on an optical filter with a nonlinear phase response[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2013, 31(20): 3323–3330. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2013.2281833.
|
| [31] |
BUI L A, MITCHELL A, GHORBANI K, et al. Wideband RF photonic vector sum phase-shifter[J]. Electronics Letters, 2003, 39(6): 536–537. doi: 10.1049/el:20030332.
|
| [32] |
SUN Xiaoqiang, FU Songnian, XU Kun, et al. Photonic RF phase shifter based on a vector-sum technique using stimulated Brillouin scattering in dispersion shifted fiber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2010, 58(11): 3206–3212. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2010.2074811.
|
| [33] |
PAGANI M, MARPAUNG D, CHOI D Y, et al. Tunable wideband microwave photonic phase shifter using on-chip stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(23): 28810–28818. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.028810.
|
| [34] |
THÉVENAZ L. Slow and fast light in optical fibres[J]. Nature Photonics, 2008, 2(8): 474–481. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2008.147.
|
| [35] |
HERRÁEZ M G, SONG K Y, and THÉVENAZ L. Arbitrary-bandwidth Brillouin slow light in optical fibers[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(4): 1395–1400. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.001395.
|
| [36] |
LOAYSSA A, GALECH S, and LAHOZ F. Broadband microwave photonic phase-shifter based on stimulated Brillouin scattering[C]. The IEEE LEOS Annual Meeting, Sydney, Australia, 2005: 839–840. doi: 10.1109/LEOS.2005.1548269.
|
| [37] |
XUE Weiqi, SALES S, CAPMANY J, et al. Wideband 360° microwave photonic phase shifter based on slow light in semiconductor optical amplifiers[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(6): 6156–6163. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.006156.
|
| [38] |
DONG Yi, HE Hao, HU Weisheng, et al. Photonic microwave phase shifter/modulator based on a nonlinear optical loop mirror incorporating a Mach–Zehnder interferometer[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(7): 745–747. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.000745.
|
| [39] |
PU Minhao, LIU Liu, XUE Weiqi, et al. Tunable microwave phase shifter based on silicon-on-insulator microring resonator[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2010, 22(12): 869–871. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2010.2046725.
|
| [40] |
JIANG Hengyun, YAN Lianshan, YE Jia, et al. Photonic generation of phase-coded microwave signals with tunable carrier frequency[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(8): 1361–1363. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.001361.
|
| [41] |
LI Ze, LI Wangzhe, CHI Hao, et al. Photonic generation of phase-coded microwave signal with large frequency tunability[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2011, 23(11): 712–714. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2011.2132121.
|
| [42] |
WEI Kai and DARYOUSH A S. Self-forced opto-electronic oscillators using Sagnac-loop PM-IM convertor[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2020, 38(19): 5278–5285. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.2997652.
|
| [43] |
LI Wei, SUN Wenhui, WANG Wenting, et al. Photonic-assisted microwave phase shifter using a DMZM and an optical bandpass filter[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(5): 5522–5527. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.005522.
|
| [44] |
ZHANG Yamei and PAN Shilong. Broadband microwave signal processing enabled by polarization-based photonic microwave phase shifters[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2018, 54(4): 0700112. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2018.2847398.
|
| [45] |
SHIN J D, LEE B S, and KIM B G. Optical true time-delay feeder for X-band phased array antennas composed of 2×2 optical MEMS switches and fiber delay lines[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2004, 16(5): 1364–1366. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2004.826083.
|
| [46] |
MOREIRA R L, GARCIA J, LI Wenzao, et al. Integrated ultra-low-loss 4-bit tunable delay for broadband phased array antenna applications[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2013, 25(12): 1165–1168. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2013.2261807.
|
| [47] |
LIU Yang, CHOUDHARY A, MARPAUNG D, et al. Gigahertz optical tuning of an on-chip radio frequency photonic delay line[J]. Optica, 2017, 4(4): 418–423. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.000418.
|
| [48] |
YI Xiaoke, LI Liwei, HUANG T X H, et al. Programmable multiple true-time-delay elements based on a Fourier-domain optical processor[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(4): 608–610. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.000608.
|
| [49] |
LIU Yunqi, YANG Jianliang, and YAO Jianping. Continuous true-time-delay beamforming for phased array antenna using a tunable chirped fiber grating delay line[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2002, 14(8): 1172–1174. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2002.1022008.
|
| [50] |
CARDENAS J, FOSTER M A, SHERWOOD-DROZ N, et al. Wide-bandwidth continuously tunable optical delay line using silicon microring resonators[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(25): 26525–26534. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.026525.
|
| [51] |
CRUZ J L, ORTEGA B, ANDRES M V, et al. Chirped fibre Bragg gratings for phased-array antennas[J]. Electronics Letters, 1997, 33(7): 545–546. doi: 10.1049/el:19970407.
|
| [52] |
MATTHEWS P J, LIU P L, MEDBERRY J B, et al. Demonstration of a wide-band fiber-optic nulling system for array antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1999, 47(7): 1327–1331. doi: 10.1109/22.775474.
|
| [53] |
SHI Nuannuan, LI Wei, ZHU Ninghua, et al. Optically controlled phase array antenna [Invited][J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2019, 17(5): 052301. doi: 10.3788/COL201917.052301.
|
| [54] |
WANG Chao and YAO Jianping. Photonic generation of chirped microwave pulses using superimposed chirped fiber Bragg gratings[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2008, 20(11): 882–884. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2008.922333.
|
| [55] |
WANG Chao and YAO Jianping. Chirped microwave pulse generation based on optical spectral shaping and wavelength-to-time mapping using a Sagnac loop mirror incorporating a chirped fiber Bragg grating[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2009, 27(16): 3336–3341. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2008.2010561.
|
| [56] |
LI Ming, SHAO Liyang, ALBERT J, et al. Tilted fiber Bragg grating for chirped microwave waveform generation[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2011, 23(5): 314–316. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2010.2102013.
|
| [57] |
RASHIDINEJAD A and WEINER A M. Photonic radio-frequency arbitrary waveform generation with maximal time-bandwidth product capability[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2014, 32(20): 3383–3393. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2014.2331491.
|
| [58] |
GUO Qingshui, ZHANG Fangzheng, ZHOU Pei, et al. Dual-band LFM signal generation by optical frequency quadrupling and polarization multiplexing[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(16): 1320–1323. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2722004.
|
| [59] |
YAO Yao, ZHANG Fangzheng, ZHANG Ying, et al. Demonstration of ultra-high-resolution photonics-based Ka-band inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging[C]. Optical Fiber Communication Conference, San Diego, USA, 2018: Th3G.5. doi: 10.1364/OFC.2018.Th3G.5.
|
| [60] |
YACOUBIAN A and DAS P K. Digital-to-analog conversion using electrooptic modulators[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2003, 15(1): 117–119. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2002.805844.
|
| [61] |
NISHITANI T, KONISHI T, FURUKAWA H, et al. All-optical digital-to-analog conversion using pulse pattern recognition based on optical correlation processing[J]. Optics Express, 2005, 13(25): 10310–10315. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.010310.
|
| [62] |
GAO Bindong, ZHANG Fangzheng, and PAN Shilong. Experimental demonstration of arbitrary waveform generation by a 4-bit photonic digital-to-analog converter[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 383: 191–196. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.08.083.
|
| [63] |
LI Jiading, XUE Xiaoxiao, ZHA Yu, et al. A segmented photonic digital-to-analog converter with a high effective number of bits[C]. 2019 International Topical Meeting on Microwave Photonics, Ottawa, Canada, 2019: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/MWP.2019.8892090.
|
| [64] |
ZHANG Bowen, ZHU Dan, ZHOU Pei, et al. Tunable triangular frequency modulated microwave waveform generation with improved linearity using an optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(20): 5479–5485. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.005479.
|
| [65] |
ZHOU Pei, ZHANG Fangzheng, GUO Qingshui, et al. Linearly chirped microwave waveform generation with large time-bandwidth product by optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(16): 18460–18467. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.018460.
|
| [66] |
ZHOU Pei, ZHANG Fangzheng, GUO Qingshui, et al. Reconfigurable radar waveform generation based on an optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2017, 23(6): 1801109. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2017.2699659.
|
| [67] |
ZHOU Pei, ZHANG Fangzheng, YE Xingwei, et al. Flexible frequency-hopping microwave generation by dynamic control of optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2016, 8(6): 5501909. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2016.2629082.
|
| [68] |
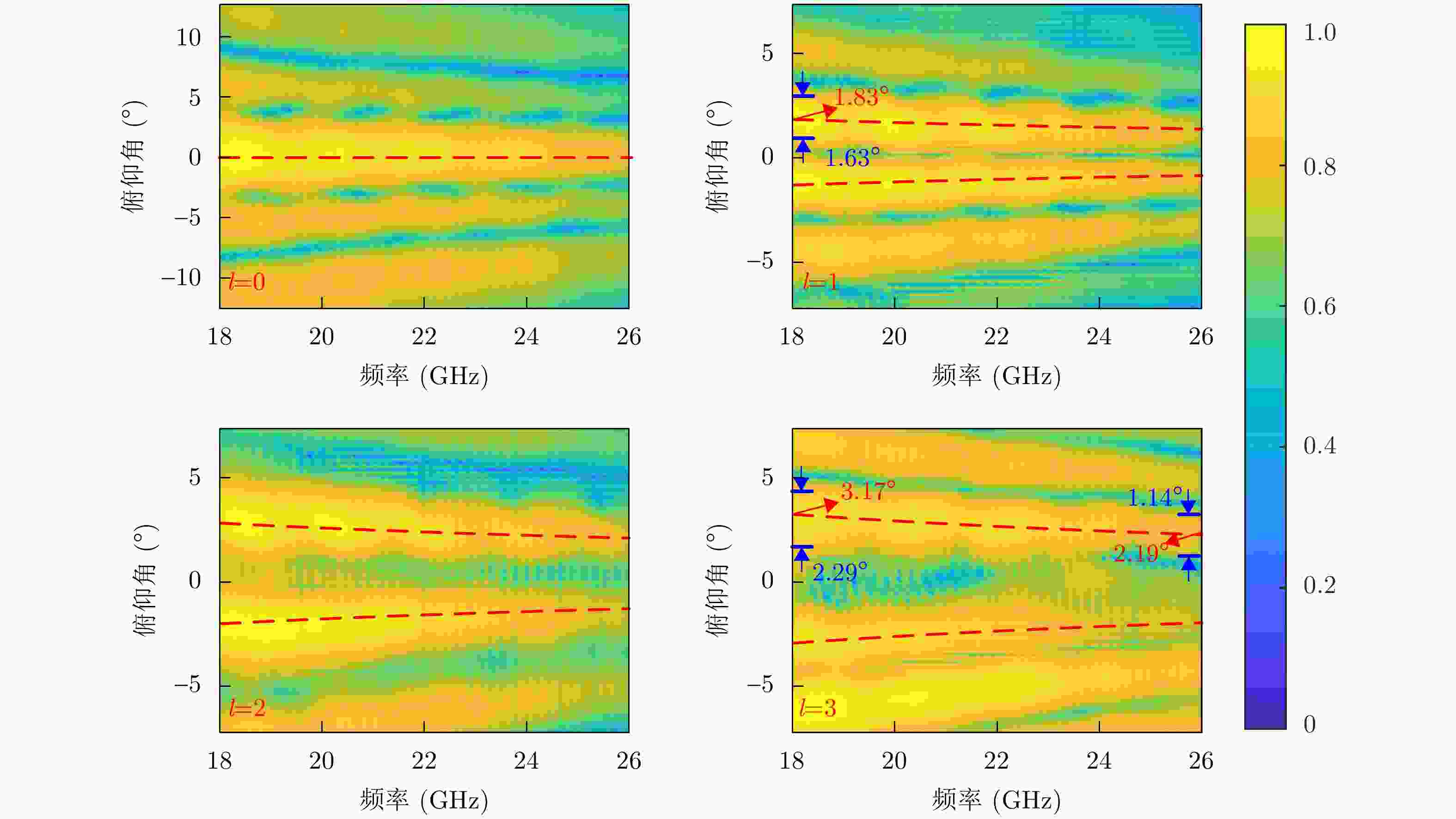
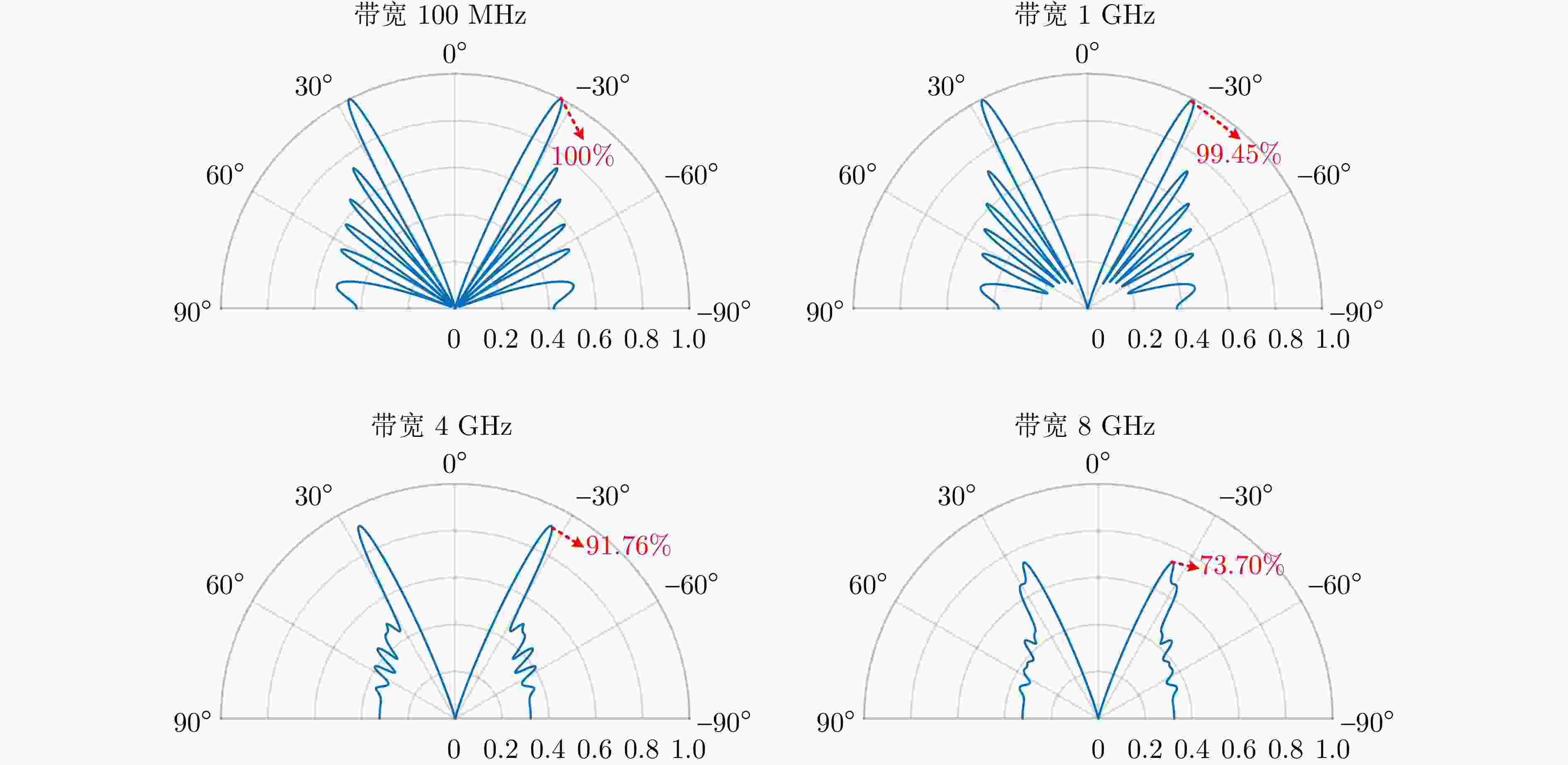
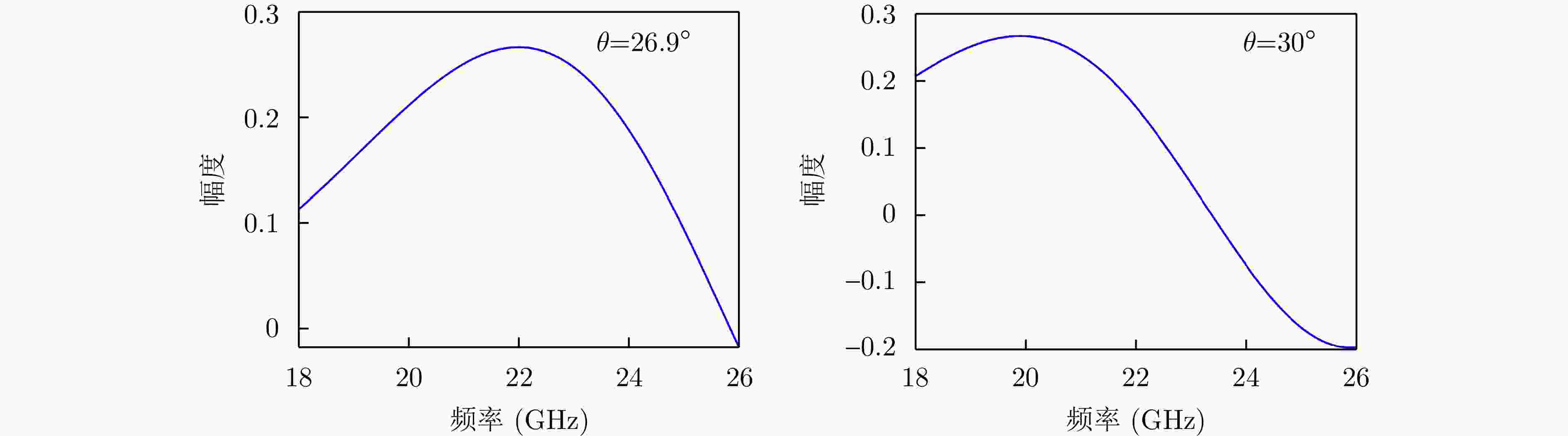
YUAN Tiezhu, WANG Hongqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, et al. Electromagnetic vortex-based radar imaging using a single receiving antenna: Theory and experimental results[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 630. doi: 10.3390/s17030630.
|
| [69] |
LIU Kang, LI Xiang, GAO Yue, et al. High-resolution electromagnetic vortex imaging based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(21): 6918–6927. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2754554.
|
| [70] |
LIU Da, SHI Hongyin, YANG Ting, et al. Autofocusing and imaging algorithm for moving target by vortex electromagnetic wave radar[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2023, 134: 103903. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103903.
|



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
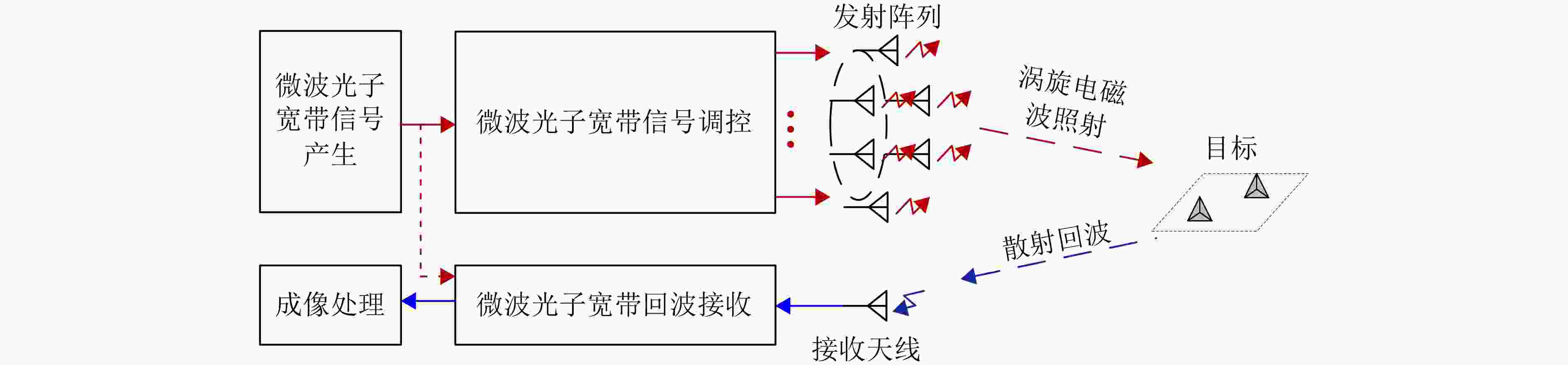
 下载:
下载: