-
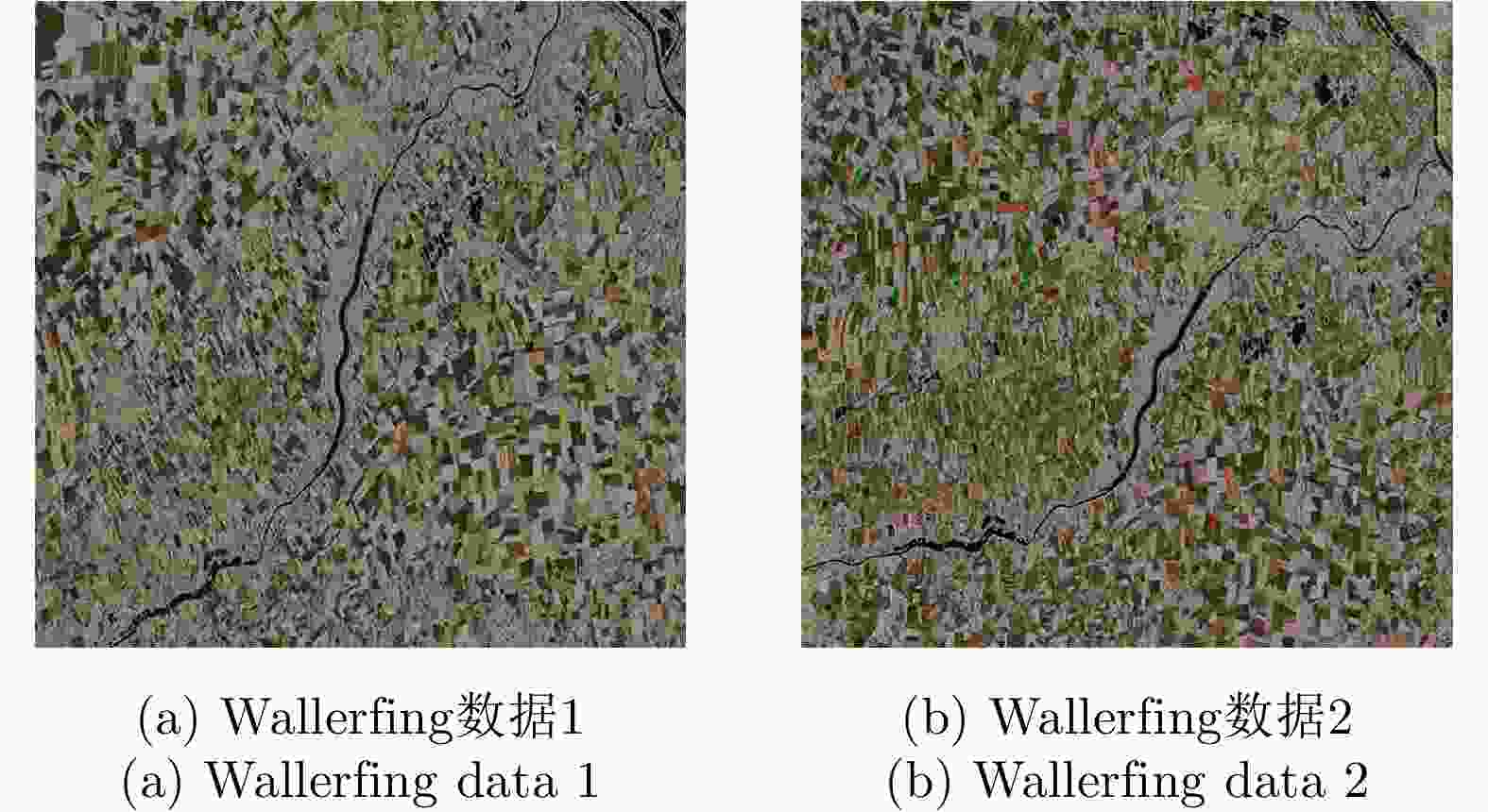
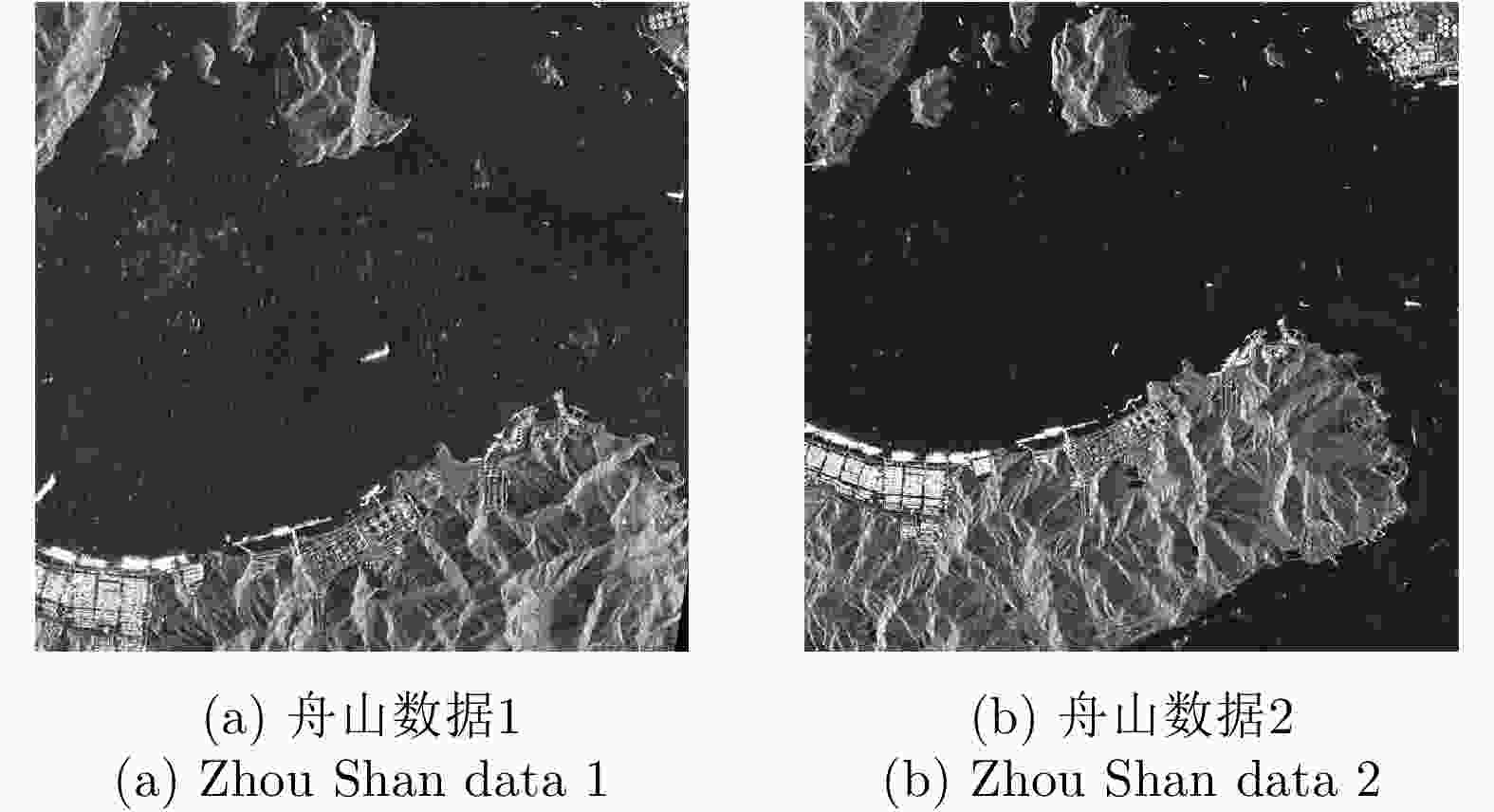
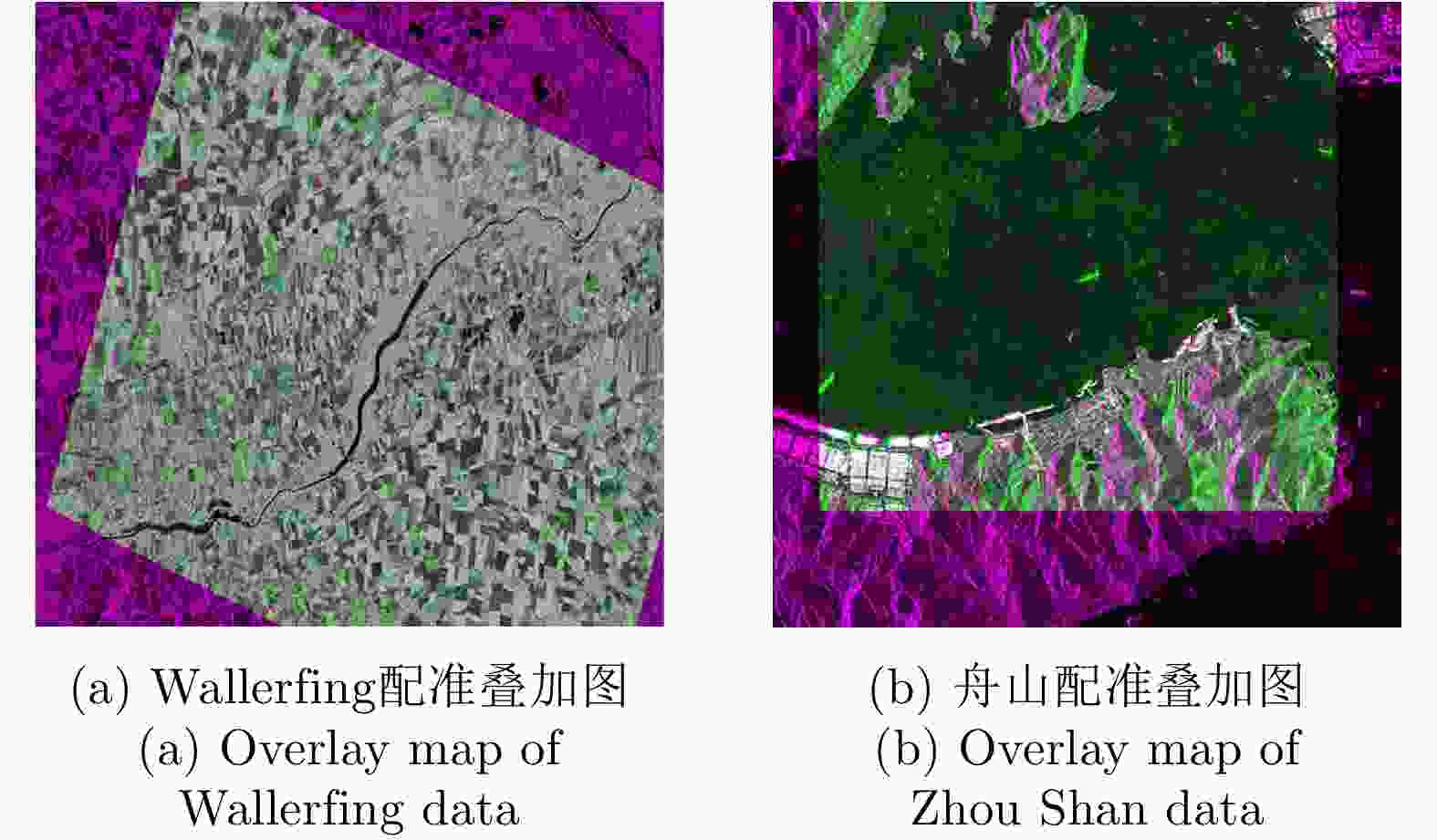
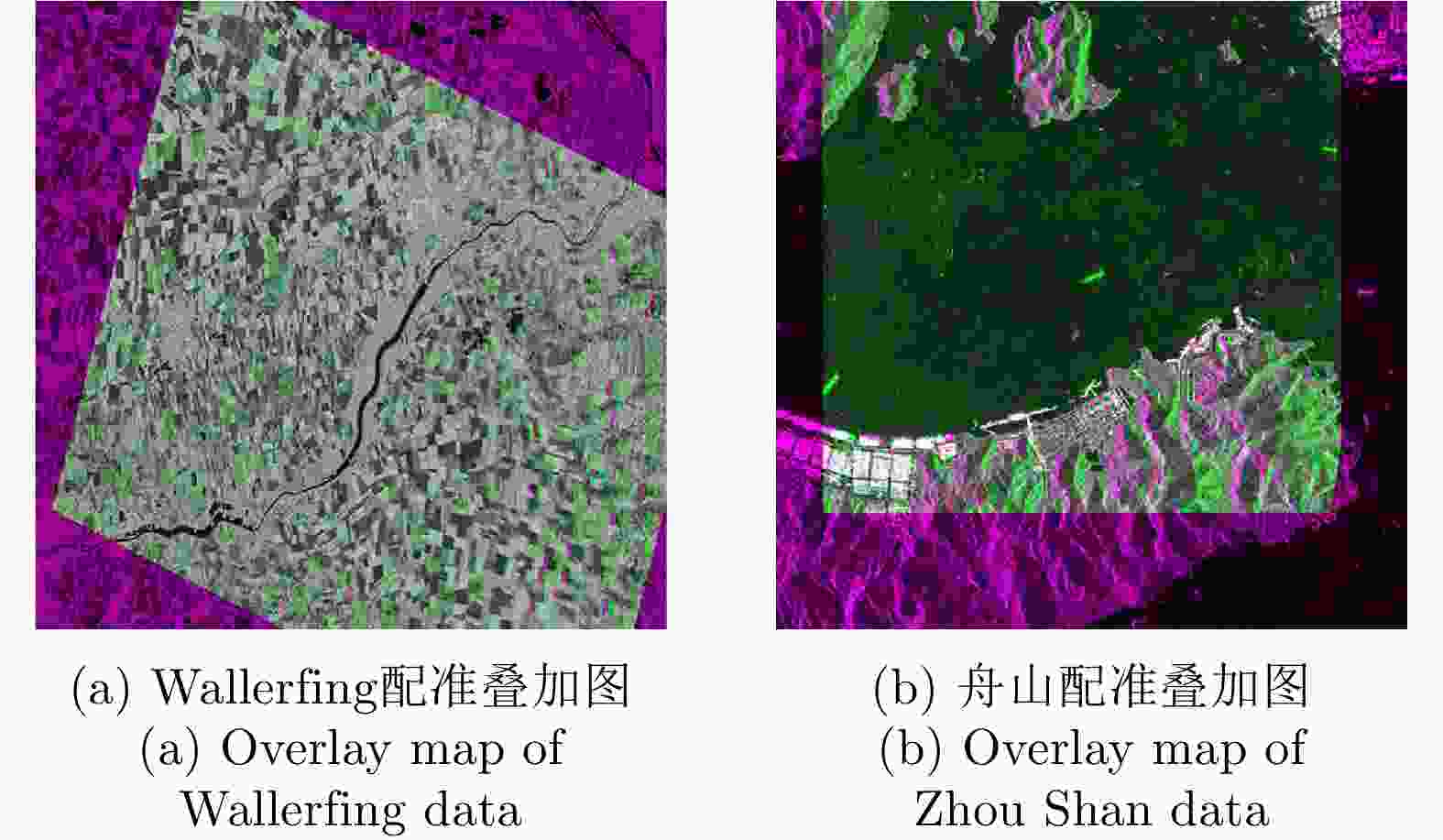
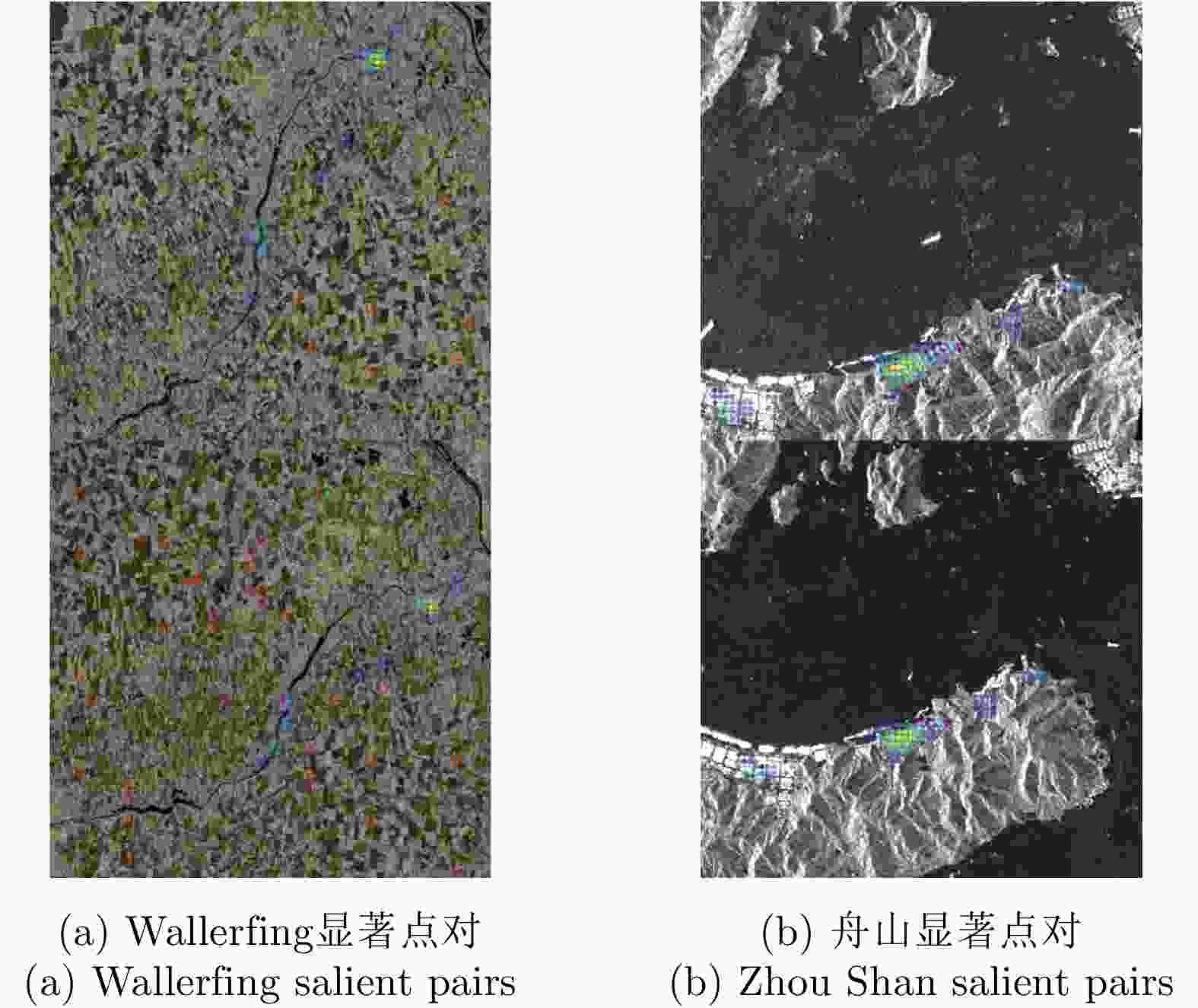
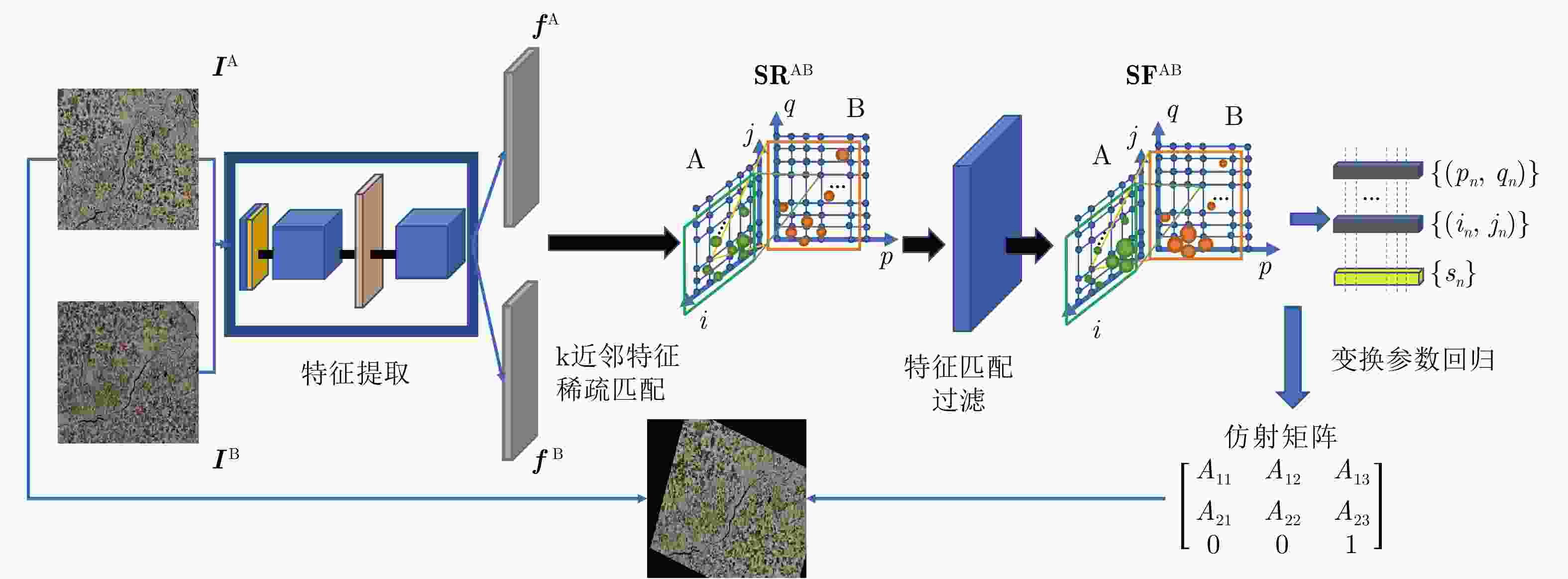
摘要: 极化SAR图像的配准是极化SAR图像处理的基础,需要具备较高的精度与速度。基于深度学习的极化SAR图像配准大多数是结合图像块特征的匹配与基于随机抽样一致性的参数迭代估计来实现的。目前尚未实现端到端的基于深度卷积神经网络的一步仿射配准。该文提出了一种基于弱监督学习的端到端极化SAR图像配准框架,无需图像切块处理或迭代参数估计。首先,对输入图像对进行特征提取,得到密集的特征图。在此基础上,针对每个特征点保留k对相关度最高的特征点对。之后,将该4D稀疏特征匹配图输入4D稀疏卷积网络,基于邻域一致性进行特征匹配的过滤。最后,结合输出的匹配点对置信度,利用带权最小二乘法进行仿射参数回归,实现图像对的配准。该文采用RADARSAT-2卫星获取的德国Wallerfing地区农田数据以及PAZ卫星获取的中国舟山港口地区数据作为测试图像对。通过对升降轨、不同成像模式、不同极化方式、不同分辨率的极化SAR图像对的配准测试,并与4种现有方法进行对比,验证了该方法具有较高的配准精度与较快的速度。Abstract: As the base of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) image processing, the registration of polarimetric SAR images requires high accuracy and a fast speed. Most methods used to register polarimetric SAR images based on deep learning are combined with patch matching and iterative estimation, e.g. the random sample consensus algorithm. However, end-to-end deep convolutional neural networks have not been used in the non-iterative affine registration of polarimetric SAR images. This paper proposes a framework for end-to-end polarimetric SAR image registration that is based on weakly-supervised learning and uses no image patch processing or iterative parameter estimation. First, feature extraction is performed on input image pairs to obtain dense feature maps with the most relevant k matches kept for each feature point. To filter the matched feature pairs, the 4D sparse feature matching maps are then fed into a 4D sparse convolutional network based on neighborhood consensus. Lastly, the affine parameters are solved by the weighted least square method according to the degree of confidence of the matches, which enables the affine registration of the input image pair. As test image pairs, we use farmland data from Wallerfing, Germany obtained by the RADARSAT-2 satellite and Zhoushan port data from China obtained by the PAZ satellite. Comprehensive experiments were conducted on polarimetric SAR image pairs using different orbit directions, imaging modes, polarization types and resolutions. Compared with four existing methods, the proposed method was found to have high accuracy and a fast speed.
-
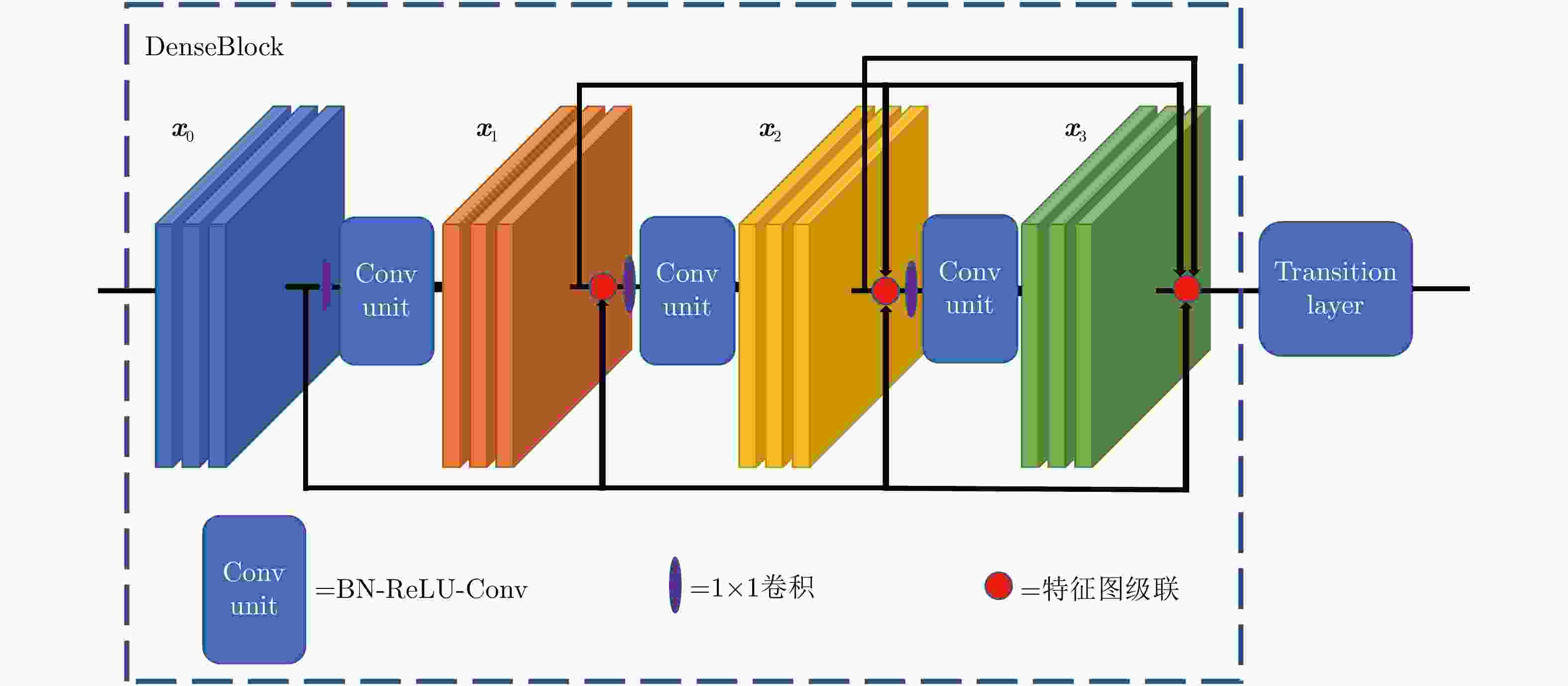
表 1 特征提取模块的结构
Table 1. Structure of the feature extraction module
网络的层 该层输出的尺寸 特征提取模块 Convolution
Pooling600×600×64
300×300×647×7 conv, stride 2
3×3 Max Pooling, stride 2DenseBlock(1) 300×300×256 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1 \times 1\;\;\,{\rm{conv}}} \\ {3 \times 3\;\;\,{\rm{conv}}} \end{array}} \right] \times 6$ Transition layer(1) 300×300×128
150×150×1281×1 conv
2×2 Average Pooling, stride 2DenseBlock(2) 150×150×512 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1 \times 1\;\;\,{\rm{conv}}} \\ {3 \times 3\;\;\,{\rm{conv}}} \end{array}} \right] \times 12$ Transition layer(2) 150×150×256
75×75×1281×1 conv
2×2 Average Pooling, stride 2DenseBlock(3) 75×75×1792 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1 \times 1\;\;\,{\rm{conv}}} \\ {3 \times 3\;\;\,{\rm{conv}}} \end{array}} \right] \times 48$ 表 2 各种配准算法的APE值
Table 2. APE of different registration algorithms
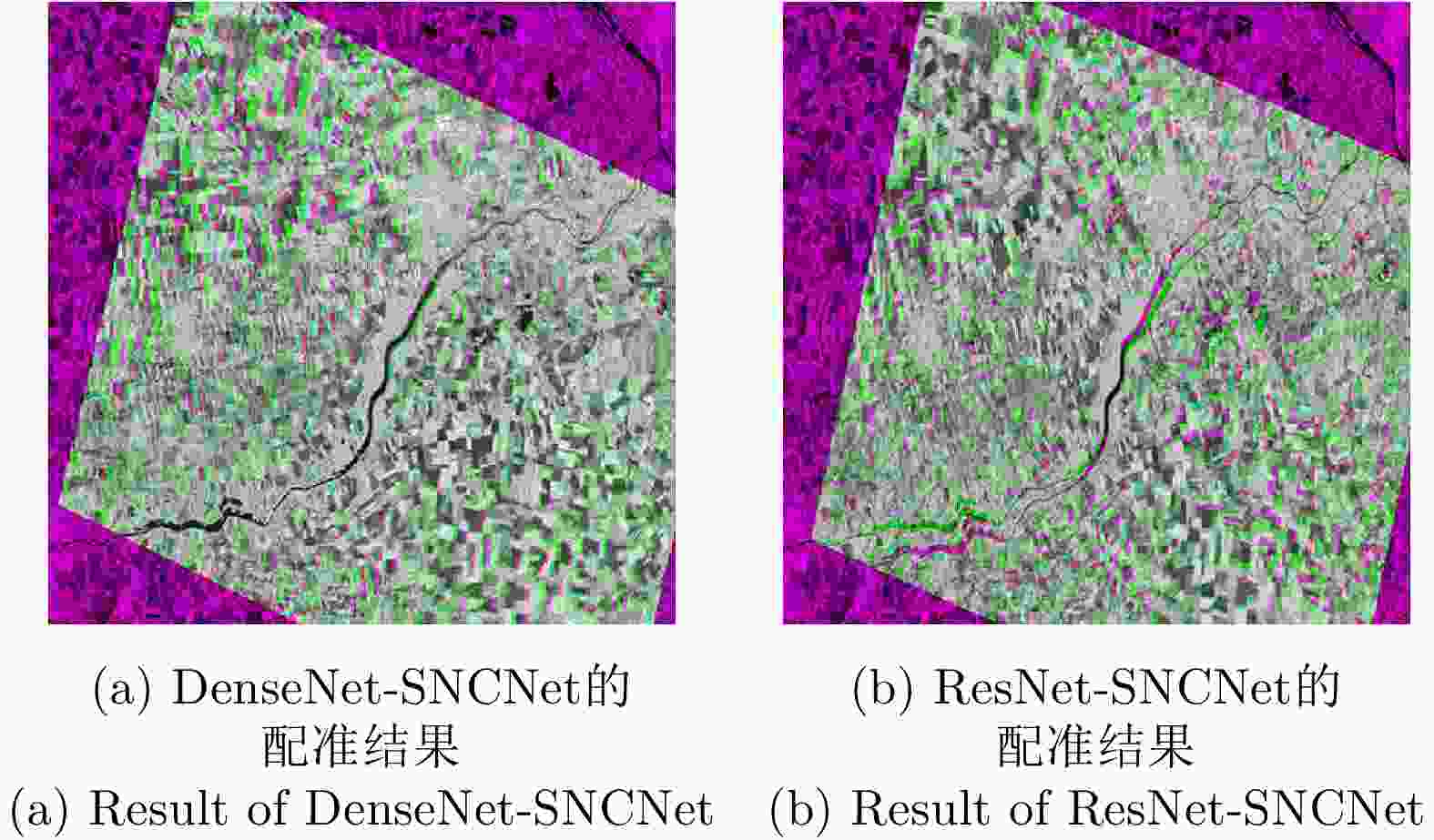
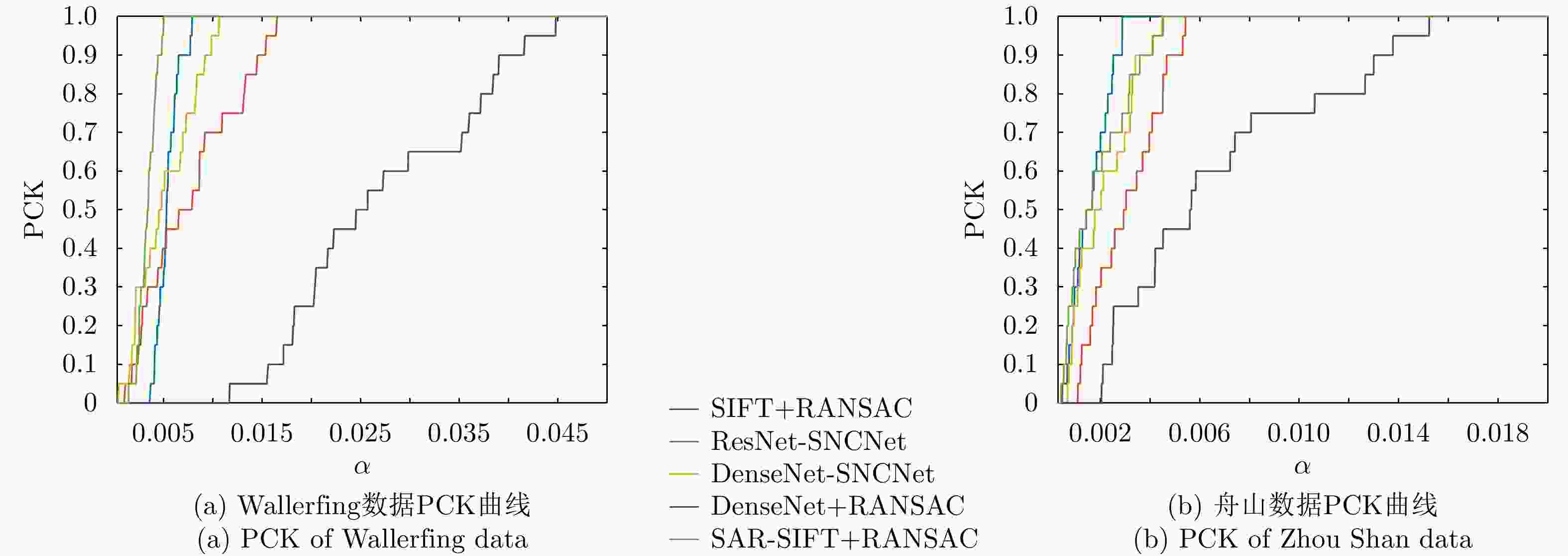
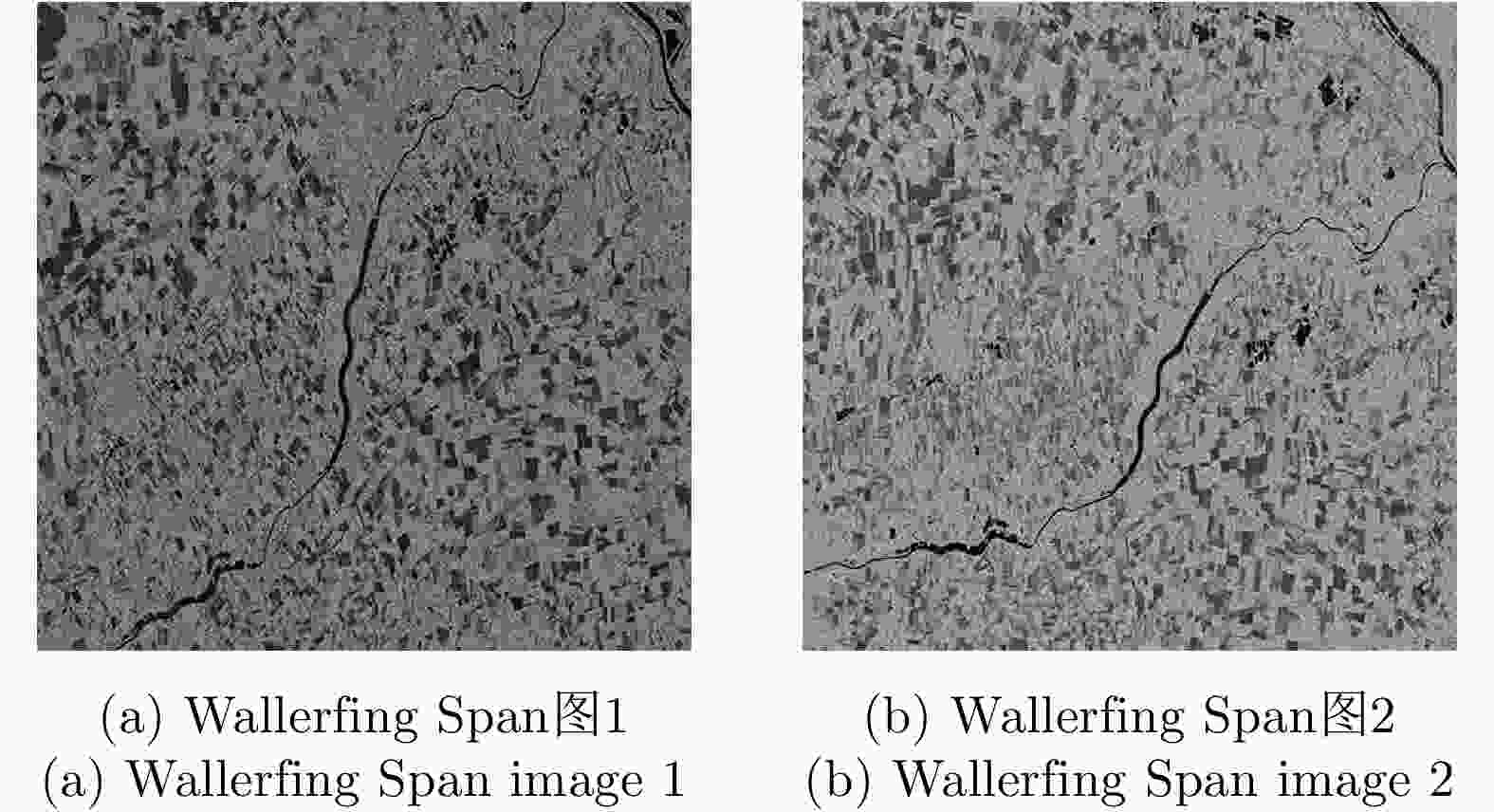
Method Wallerfing Pauli images Wallerfing Span images Zhou Shan images SIFT+RANSAC 6.521 9.058 1.924 SAR-SIFT+RANSAC 4.053 6.927 2.252 ResNet-SNCNet 9.222 9.641 3.677 DenseNet-SNCNet 6.175 7.545 2.553 DenseNet+RANSAC 32.715 40.042 7.988 表 3 k取不同值时,DenseNet+SNCNet配准结果的APE值
Table 3. APE of registration result by DenseNet+SNCNet with different k
k Wallerfing Pauli images Zhou Shan images 2 7.497 2.443 5 8.929 2.080 8 8.157 3.154 10 6.175 2.553 16 13.416 2.383 表 4 k取不同值时,基于GPU的DenseNet+SNCNet运算时间
Table 4. Time consuming of registration based on GPU by DenseNet+SNCNet with different k
k Wallerfing Pauli images Zhou Shan images 2 0.6267 0.6364 5 0.7335 0.7379 8 0.8525 0.9292 10 0.9943 0.9542 16 1.1793 1.2199 -
[1] WANG Shuang, QUAN Dou, LIANG Xuefeng, et al. A deep learning framework for remote sensing image registration[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2018, 145: 148–164. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.12.012 [2] YANG Zhuoqian, DAN Tingting, and YANG Yang. Multi-temporal remote sensing image registration using deep convolutional features[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 38544–38555. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2853100 [3] SARVAIYA J N, PATNAIK S, and BOMBAYWALA S. Image registration by template matching using normalized cross-correlation[C]. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Advances in Computing, Control, and Telecommunication Technologies, Trivandrum, India, 2009: 819–822. doi: 10.1109/ACT.2009.207. [4] GAN Rui, WU Jue, CHUNG A C S, et al. Multiresolution image registration based on Kullback-Leibler distance[C]. The 7th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Saint-Malo, France, 2004: 599–606. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-30135-6_73. [5] 张涛, 王正勇, 张影, 等. 基于和声算法的图像配准技术[J]. 电视技术, 2014, 38(7): 9–12. doi: 10.16280/j.videoe.2014.07.032ZHANG Tao, WANG Zhengyong, ZHANG Ying, et al. Image registration techniques based on harmony search algorithm[J]. Video Engineering, 2014, 38(7): 9–12. doi: 10.16280/j.videoe.2014.07.032 [6] AVERBUCH A and KELLER Y. FFT based image registration[C]. 2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Orlando, USA, 2002: IV-3608–IV-3611. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2002.5745436. [7] HARRIS C and STEPHENS M. A combined corner and edge detector[C]. The 4th Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 1988. doi: 10.5244/C.2.23. [8] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [9] WANG Yufan, YU Qiuze, and YU Wenxian. An improved normalized cross correlation algorithm for SAR image registration[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 2086–2089. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6350961. [10] DELLINGER F, DELON J, GOUSSEAU Y, et al. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-like algorithm for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 453–466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2323552 [11] MA Wenping, WEN Zelian, WU Yue, et al. Remote sensing image registration with modified SIFT and enhanced feature matching[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1): 3–7. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2600858 [12] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [13] 徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130 [14] JIN Kan, CHEN Yilun, XU Bin, et al. A patch-to-pixel convolutional neural network for small ship detection with PolSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6623–6638. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2978268 [15] DETONE D, MALISIEWICZ T, and RABINOVICH A. Deep image homography estimation[J]. arXiv: 1606.03798, 2016. [16] ROCCO I, ARANDJELOVIC R, and SIVIC J. Convolutional neural network architecture for geometric matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(11): 2553–2567. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2865351 [17] BALAKRISHNAN G, ZHAO A, SABUNCU M R, et al. VoxelMorph: A learning framework for deformable medical image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(8): 1788–1800. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2897538 [18] ROCCO I, CIMPOI M, ARANDJELOVIĆ R, et al. Neighbourhood consensus networks[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 1651–1662. [19] ROCCO I, ARANDJELOVIĆ R, and SIVIC J. Efficient neighbourhood consensus networks via submanifold sparse convolutions[J]. arXiv: 2004.10566, 2020. [20] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4700–4708. [21] CHOY C, GWAK J Y, and SAVARESE S. 4D Spatio-temporal Convnets: Minkowski convolutional neural networks[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3075–3084. [22] YANG Yi and RAMANAN D. Articulated human detection with flexible mixtures of parts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 35(12): 2878–2890. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.261 [23] 魏天华. 基于多核DSP的加速SAR-SIFT算法并行计算设计[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020.WEI Tianhua. Parallel calculation of speed-up SAR-SIFT algorithm based on multi-score DSP[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: