Radar Waveform Design Method Based on Cascade Optimization Processing under Missing Clutter Prior Data
-
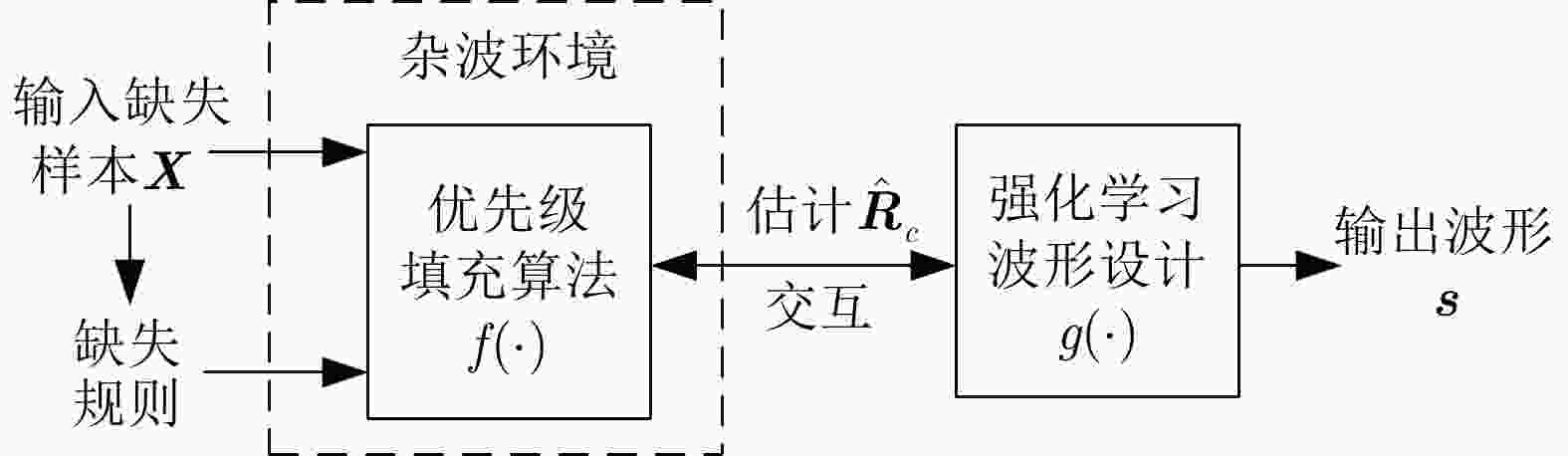
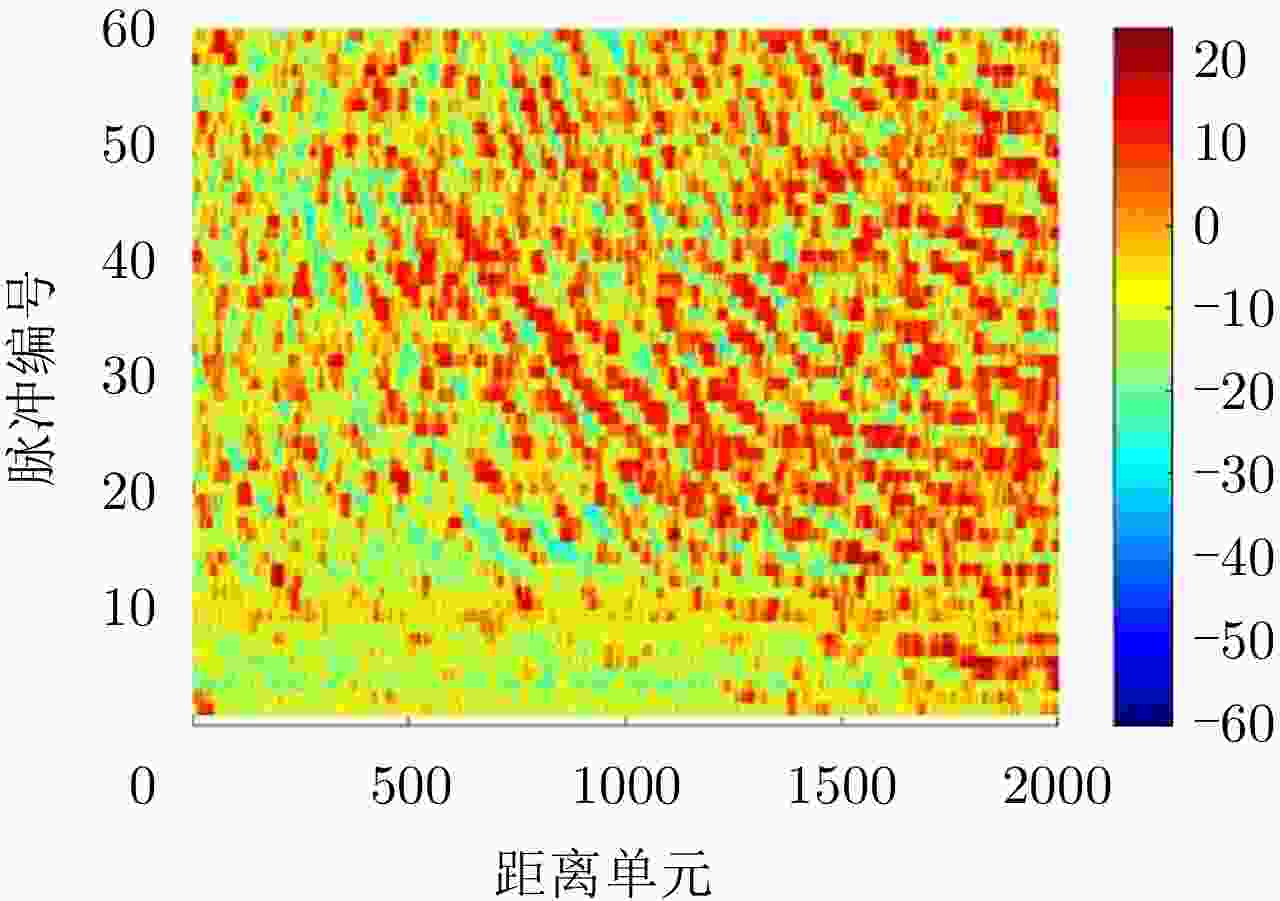
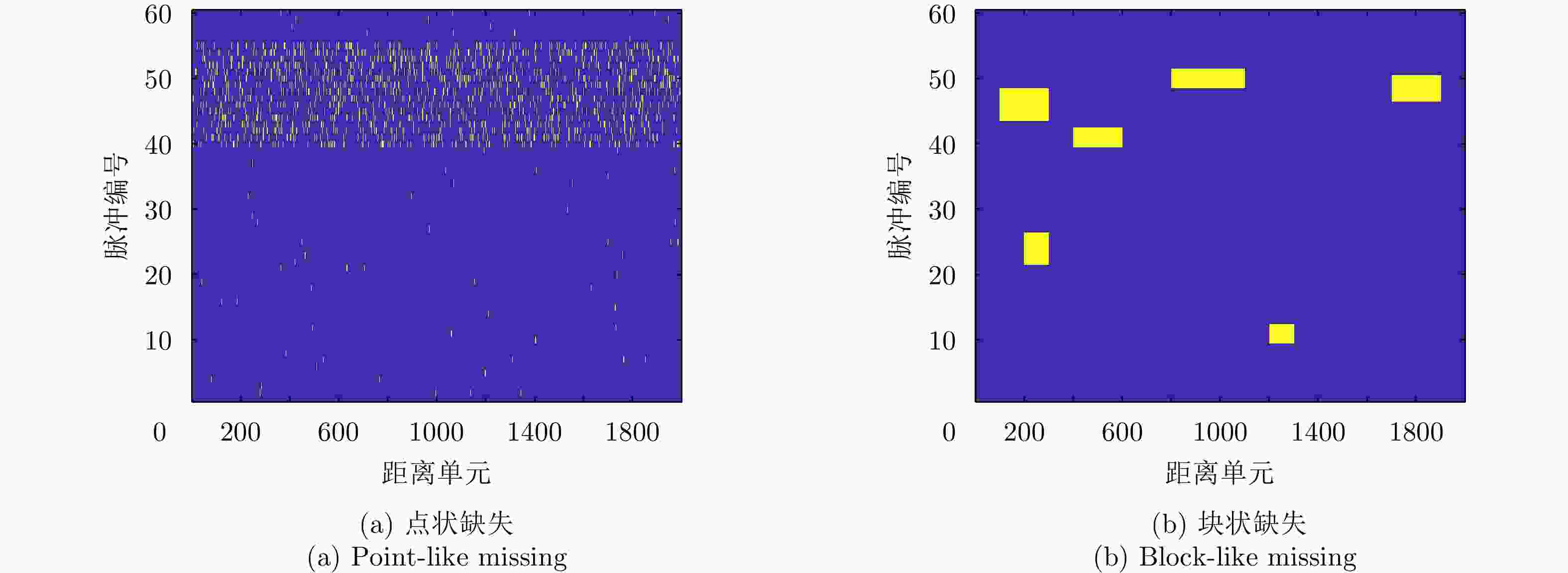
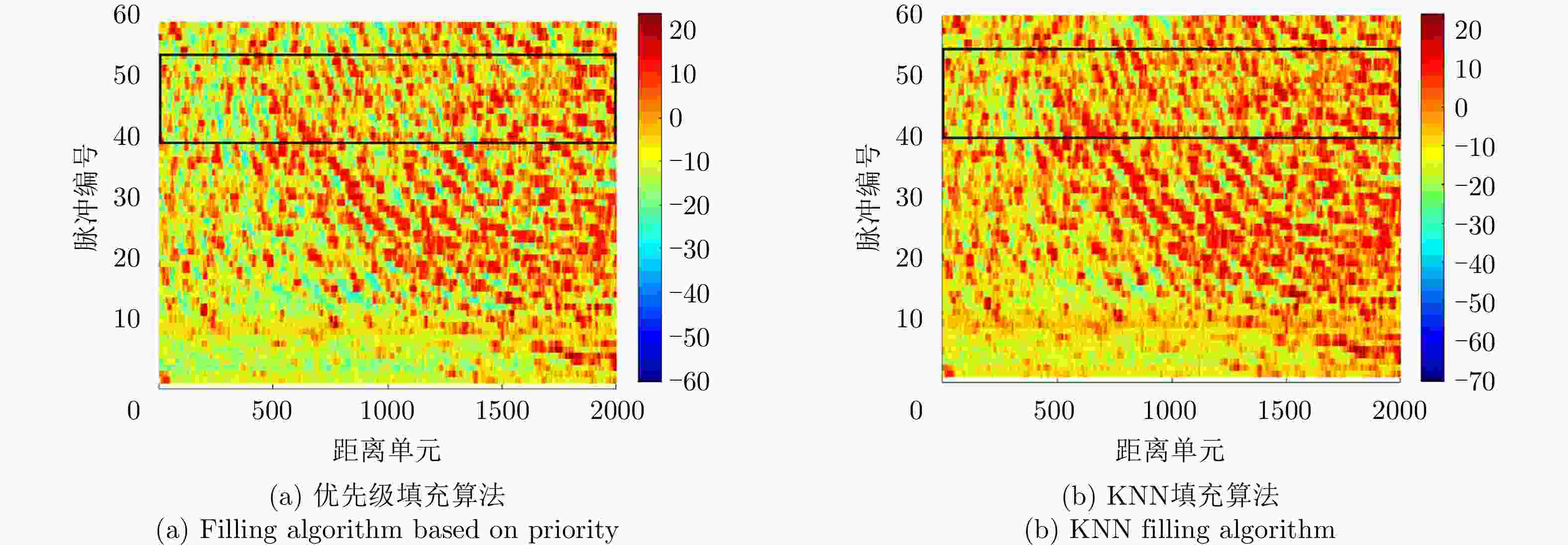
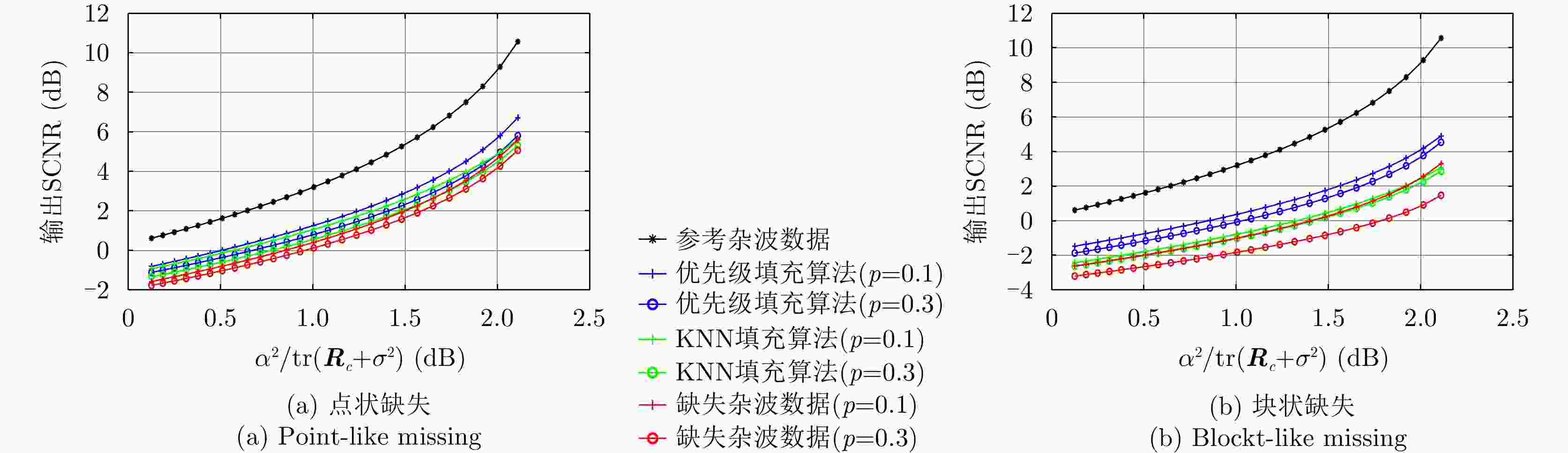
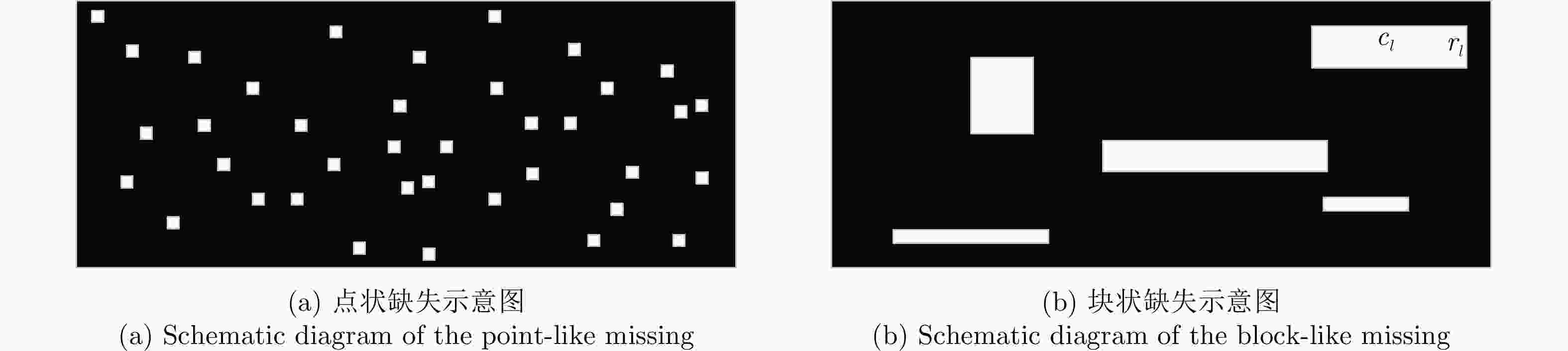
摘要: 认知雷达波形设计往往依赖于精准的杂波先验信息,当先验信息数据存在缺失时,所构建的杂波模型会严重失配,进而影响雷达对杂波的抑制能力。该文针对杂波先验数据缺失条件下的雷达波形优化问题,建立完全随机缺失机制下的点状与块状缺失场景,设计恒模与相似性约束的波形优化模型,提出基于优先级填充-强化学习级联优化的雷达波形训练算法:即采用强化学习智能体与填充算法修复后的杂波环境相交互的级联方法,以最大化信杂噪比为优化目标,通过迭代训练得到雷达最佳波形参数配置策略。最后,仿真验证不同缺失概率条件下所提算法的优越性。结果表明:相比于传统非级联优化算法,该文所提算法均可获得更优的杂波抑制性能,有效提升雷达的探测能力。Abstract: Cognitive radar waveform design often relies on accurate clutter prior information. When prior information data is missing, the constructed clutter model will be severely mismatched, affecting the radar’s ability to suppress clutter. Aiming at the radar waveform optimization problem under missing clutter prior data, this paper establishes point and block-like missing scenarios under the completely random missing mechanism, designs a waveform optimization model with constant modulus and similarity constraints, and proposes a radar waveform training algorithm based on priority filling−reinforcement learning cascade optimization: that is, a cascade method in which the reinforcement learning agent interacts with the clutter environment repaired by a filling algorithm, with the optimization goal of maximizing the signal-to-noise ratio, and the optimal configuration strategy with waveform parameters is obtained through iterative training. Finally, simulations verify the superiority of the proposed algorithm under different missing probability conditions. The results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the traditional non-cascading optimization algorithm, regarding clutter suppression and effectively improves the detection ability of radar.
-
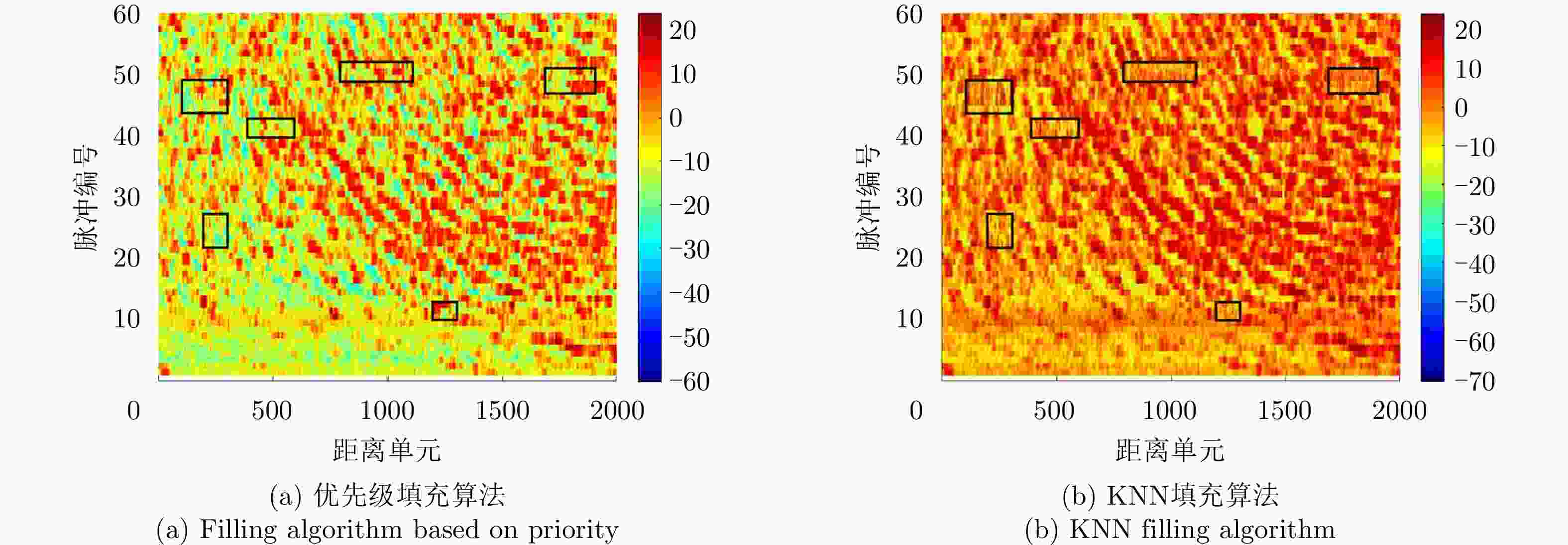
表 1 优先级填充算法
Table 1. Priority filling algorithm
输入:杂波缺失矩阵$ \tilde {\boldsymbol C} $,滑窗维度M 输出:杂波修复矩阵$\hat {\boldsymbol{C}}$ 1:将杂波缺失矩阵$ \tilde {\boldsymbol C} $分为目标区域${\boldsymbol{\varOmega}}$和源区域${\boldsymbol{\varPhi}}$ 2:根据式(13)初始化置信度$C(p)$ 3:识别目标区域轮廓${\boldsymbol{\delta \varOmega}}$ 4:根据式(10)计算优先级$P(p)$, $\forall p \in {\boldsymbol{\delta \varOmega}}$ 5:找到优先级最高的待填充样本$ {{\boldsymbol{\varPsi}} _{\hat p}} \in {\mathbb{C}^{M \times M}} $,即
$\hat p = \arg \mathop {\max }\limits_{p \in {\boldsymbol{\delta \varOmega } } }P(p)$6:根据式(14)得到最相似样本$ {{\boldsymbol{\varPsi}} _{\hat q}} $ 7:将最相似样本$ {{\boldsymbol{\varPsi}} _{\hat q}} $内的数据信息复制到$ {{\boldsymbol{\varPsi}} _{\hat p}} $内 8:根据式(15)更新置信度$C(p)$ 9:判断${\boldsymbol{\varOmega}}$是否为空集,如果是,算法结束;否则跳转3 表 2 基于DDPG的波形优化算法
Table 2. Algorithm for waveform optimization based on DDPG
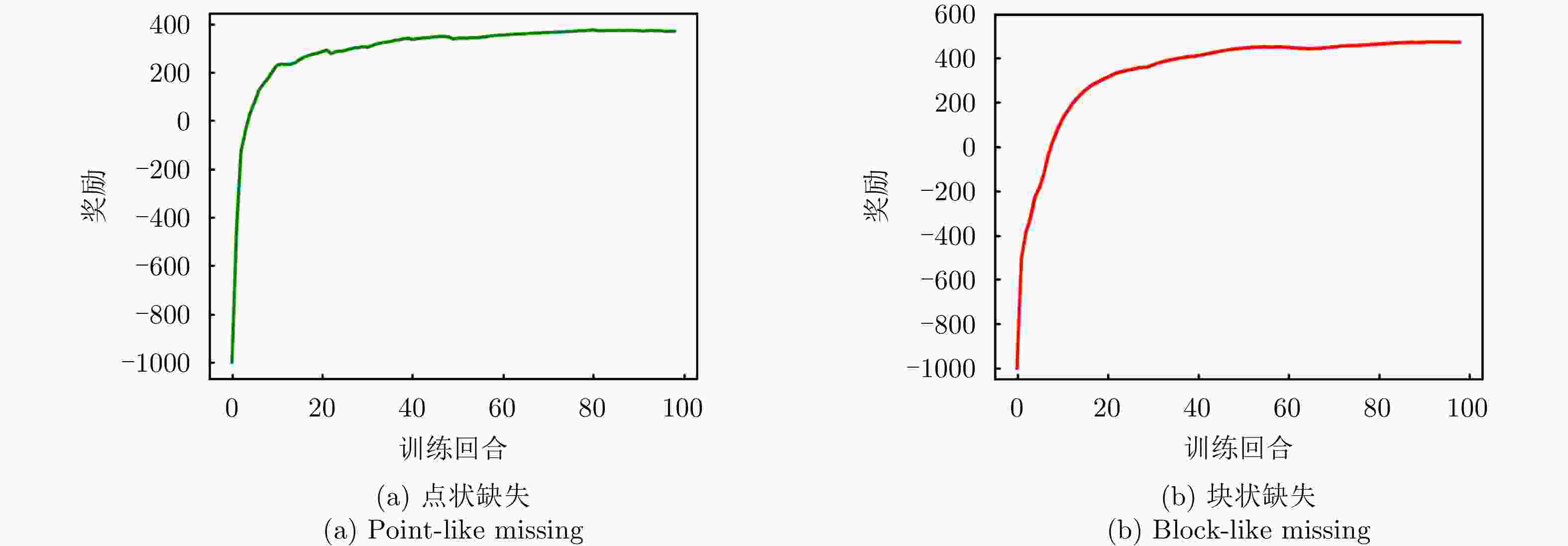
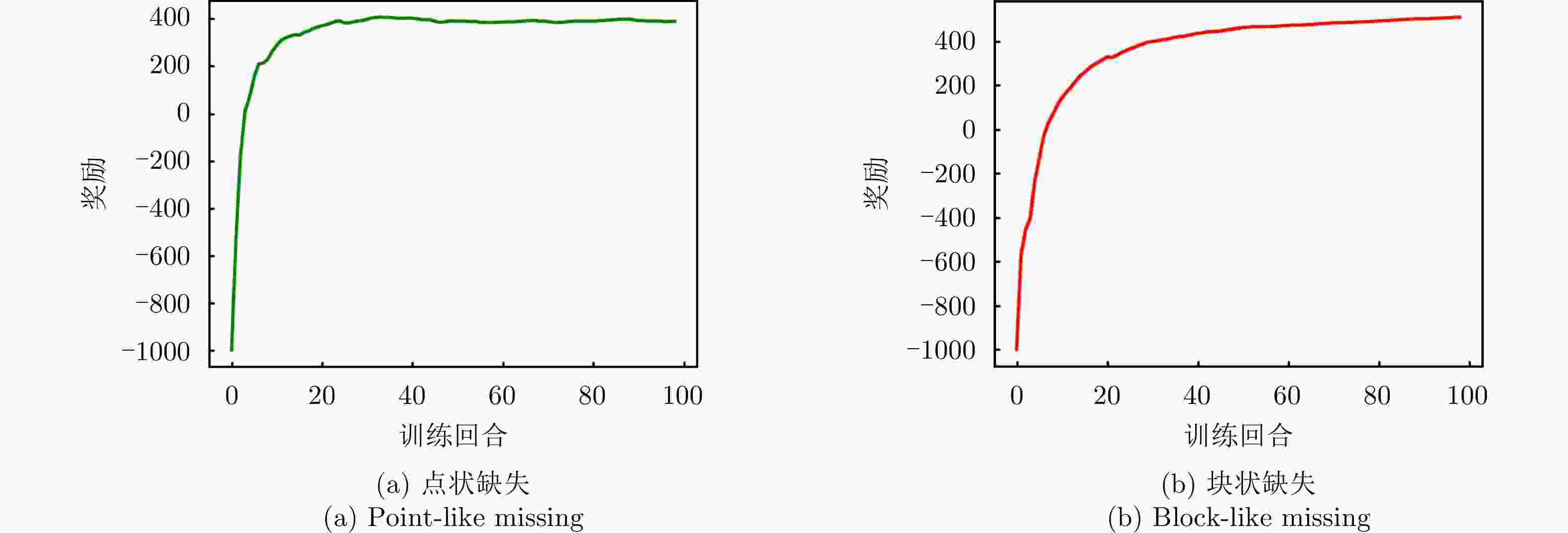
输入:Actor策略网络及其目标网络,Critic评估网络及其目标网络,网络参数分别为$\theta ,{\theta '},\omega ,{\omega'}$,奖励衰减因子$\gamma $,软更新系数$\tau $,最大迭
代次数T,经验回放池${ \rm{R} }$,采样样本数K输出:最佳Actor策略网络${\pi _*}(a|s)$ 1:随机初始化Actor策略网络参数$\theta $和Critic评估网络参数$\omega $ 2:初始化目标网络参数${\theta'} = \theta$, ${\omega'} = \omega$ 3:初始化经验回放池${ \rm{R} }$ 4:for 回合$e \in \{ 1,2, \cdots ,T\} $ do 5: 初始化随机噪声$ \mathcal{N} $,初始化状态s 6: 根据式(16)得到Actor网络的输出动作${a_t}$ 7: 执行动作${a_t}$,获得下一时刻状态${s_{t + 1}}$,反馈奖励${r_t}$ 8: 将$\left\{ {{s_t},{a_t},{r_t},{s_{t + 1}}} \right\}$存入经验回放池${ \rm{R} }$ 9: 从经验回放池中随机采样K个经验样本$\left\{ {{s_i},{a_i},{r_i},{s_{i + 1}}} \right\}$, $i = 1,2, \cdots ,K$ 10: 根据式(17)和式(18)更新Actor策略网络和Critic评估网络 11: 根据式(19)更新目标网络参数${\theta '}$和${\omega '}$ 12: 判断${s_{t + 1}}$是否为终止状态,如果是,迭代完毕,否则跳转步骤5 表 3 强化学习参数表
Table 3. Reinforcement learning parameters table
参数 数值 经验池大小 200000 训练批次大小 64 训练总次数 100000 回合训练次数 1000 学习率 0.001 惩罚因子 0.98 Actor, Critic网络层节点数 [400, 300] -
[1] TANG Bo and TANG Jun. Joint design of transmit waveforms and receive filters for MIMO radar space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(18): 4707–4722. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2569431 [2] TANG Bo, TUCK J, and STOICA P. Polyphase waveform design for MIMO radar space time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 2143–2154. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2983833 [3] YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, YANG Jing, et al. Wideband MIMO radar waveform design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(13): 3487–3501. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2916732 [4] WU Linlong and PALOMAR D P. Radar Waveform Design Via the Majorization-Minimization Framework[M]. CUI Guolong, DE MAIO A, FARINA A, et al. Radar Waveform Design Based on Optimization Theory. London: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2020: 185–220. [5] O’ROURKE S M, SETLUR P, RANGASWAMY M, et al. Quadratic semidefinite programming for waveform-constrained joint filter-signal design in STAP[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1744–1759. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2977271 [6] TANG Bo, NAGHSH M M, and TANG Jun. Relative entropy-based waveform design for MIMO radar detection in the presence of clutter and interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(14): 3783–3796. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2423257 [7] WANG Yikai, XIA Wei, HE Zishu, et al. Polarimetric detection in compound Gaussian clutter with Kronecker structured covariance matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(17): 4562–4576. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2716912 [8] SUN Guohao, HE Zishu, TONG Jun, et al. Mutual information-based waveform design for MIMO radar space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(4): 2909–2921. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3008320 [9] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 杨婧, 等. 认知雷达波形优化设计方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, YANG Jing, et al. An overview of waveform optimization methods for cognitive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072 [10] 王珽, 赵拥军, 胡涛. 机载MIMO雷达空时自适应处理技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR14091WANG Ting, ZHAO Yongjun, and HU Tao. Overview of space-time adaptive processing for airborne MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR14091 [11] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, MARANO S, et al. Structured covariance matrix estimation with missing-(complex) data for radar applications via expectation-maximization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 5920–5934. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3111587 [12] HIPPERT-FERRER A, EL KORSO M N, BRELOY A, et al. Robust low-rank covariance matrix estimation with a general pattern of missing values[J]. Signal Processing, 2022, 195: 108460. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2022.108460 [13] PAVEZ E and ORTEGA A. Covariance matrix estimation with non uniform and data dependent missing observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2021, 67(2): 1201–1215. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2020.3039118 [14] ZHANG Ying, LIE J P, NG B P, et al. Robust minimum ℓ1-norm adaptive beamformer against intermittent sensor failure and steering vector error[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(5): 1796–1801. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2044353 [15] XIONG Can, XIAO Gaobiao, HOU Yibei, et al. A compressed sensing-based element failure diagnosis method for phased array antenna during beam steering[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2019, 18(9): 1756–1760. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2019.2929353 [16] GAO Yongchan, LIAO Guisheng, and LIU Weijian. High-resolution radar detection in interference and nonhomogeneous noise[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(10): 1359–1363. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2597738 [17] LIM D, GIANELLI C D, and LI Jian. Automatic target recognition in missing data cases[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2017, 32(7): 40–49. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2017.150273 [18] SHEN Lei, LIU Zhiwen, XU Yougen, et al. Robust polarimetric adaptive detector against target steering matrix mismatch[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(1): 442–455. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2916708 [19] LOUNICI K. High-dimensional covariance matrix estimation with missing observations[J]. Bernoulli, 2014, 20(3): 1029–1058. doi: 10.3150/12-BEJ487 [20] LIU Junyan and PALOMAR D P. Regularized robust estimation of mean and covariance matrix for incomplete data[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 165: 278–291. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.07.009 [21] XU Danlei, DU Lan, LIU Hongwei, et al. Compressive sensing of stepped-frequency radar based on transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3076–3087. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2421473 [22] LV Qinzhe, QUAN Yinghui, WEI Feng, et al. Radar deception jamming recognition based on weighted ensemble CNN with transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5107511. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3129645 [23] JIANG Wei, HAIMOVICH A M, and SIMEONE O. Joint design of radar waveform and detector via end-to-end learning with waveform constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(1): 552–567. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3103560 [24] LI Jian, GUERCI J R, and XU Luzhou. Signal waveform’s optimal-under-restriction design for active sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2006, 13(9): 565–568. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2006.874465 [25] BELLMAN R. A Markovian decision process[J]. Journal of Mathematics and Mechanics, 1957, 6(5): 679–684. [26] CRIMINISI A, PEREZ P, and TOYAMA K. Region filling and object removal by exemplar-based image inpainting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(9): 1200–1212. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2004.833105 [27] LILLICRAP T P, HUNT J J, PRITZEL A, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1509.02971, 2015. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: