Research Progress of Electrically Controlled Reconfigurable Polarization Manipulation Using Metasurface
-
摘要: 作为一种由众多亚波长单元周期性或非周期性排列构成的二维人工结构,超表面展示了其在电磁波极化调控领域的卓越能力,开辟了电磁波调控的新途径。电控可重构极化调控超表面,可通过电信号实时调整其结构或材料特性进而动态地调控电磁波的极化状态,因而受到广泛研究关注。该文全面综述了电控可重构极化调控超表面的发展历程,详细探讨了微波段具备不同传输特性的电控可重构极化调控超表面的技术进展,并对电控可重构极化调控超表面技术的未来发展进行了深入的探讨和展望。Abstract: Metasurfaces are two-dimensional artificial structures with numerous subwavelength elements arranged periodically or aperiodically. They have demonstrated their exceptional capabilities in electromagnetic wave polarization manipulation, opening new avenues for manipulating electromagnetic waves. Metasurfaces exhibiting electrically controlled reconfigurable polarization manipulation have garnered widespread research interest. These unique metasurfaces can dynamically adjust the polarization state of electromagnetic waves through real-time modification of their structure or material properties via electrical signals. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the development of metasurfaces exhibiting electrically controlled reconfigurable polarization manipulation and explores the technological advancements of metasurfaces with different transmission characteristics in the microwave region in detail. Furthermore, it delves into and anticipates the future development of this technology.
-
表 1 y极化入射时极化方位角随偏置电压变化情况(°)[45]
Table 1. Variation of polarization angle with bias voltage under y-polarized wave incidence (°)[45]
Cy (pF) Cx (pF) 0.18 0.20 0.22 0.24 0.26 0.30 0.18 –0.007 11.82 24.69 35.77 45.23 59.23 0.20 –12.58 0.008 14.09 26.24 35.33 50.67 0.22 –28.89 –15.33 0 13.12 22.69 38.08 0.24 –43.90 –29.94 –13.82 0.004 9.937 25.38 0.26 –54.39 –40.57 –24.23 –10.13 –0.001 15.64 0.30 –69.27 –56.03 –40.10 –26.13 –15.97 –0.006 表 2 透射型电控可重构极化调控超表面总结
Table 2. Summary of transmission-type electronically controlled reconfigurable polarization modulation metasurface
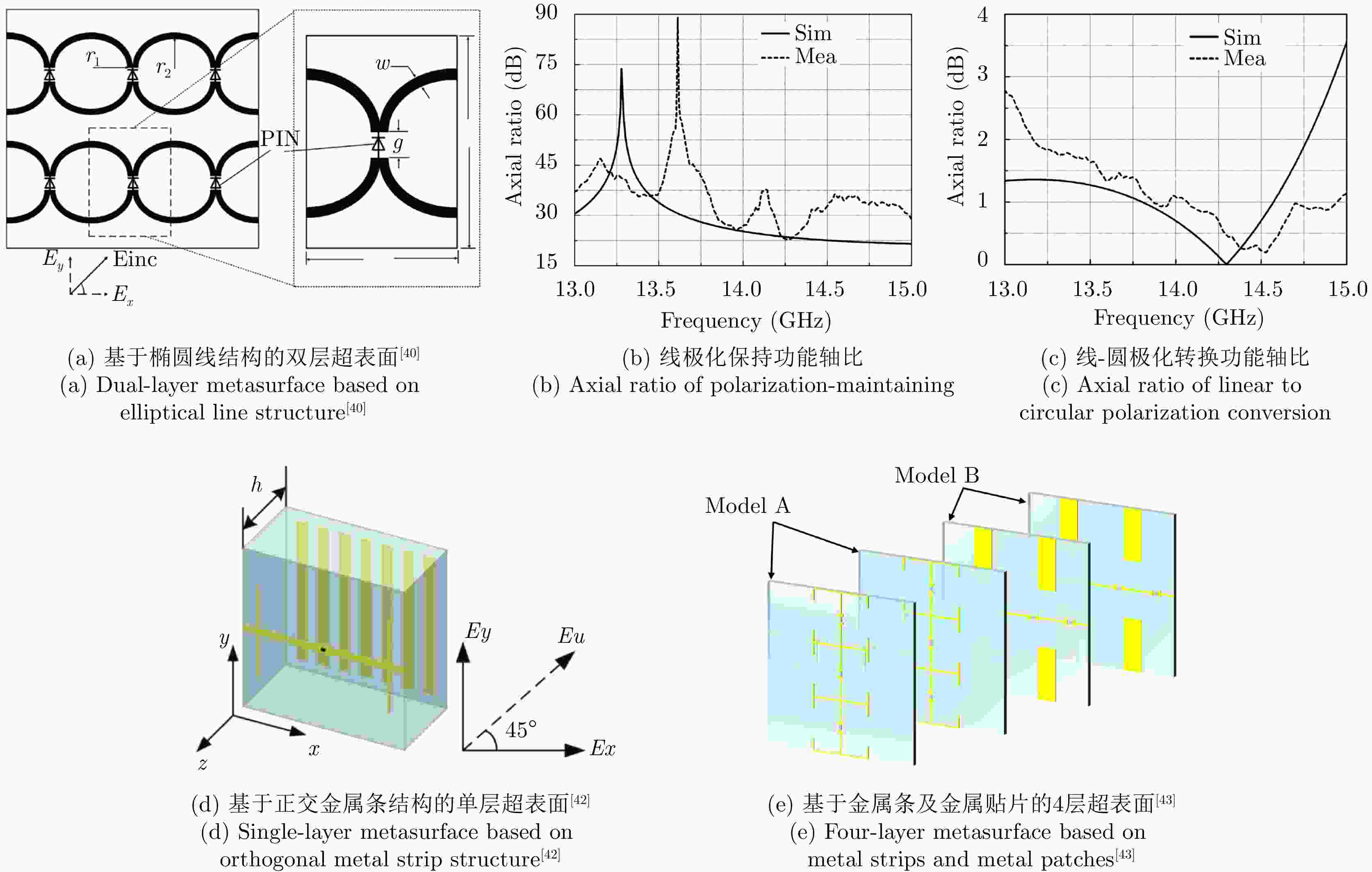
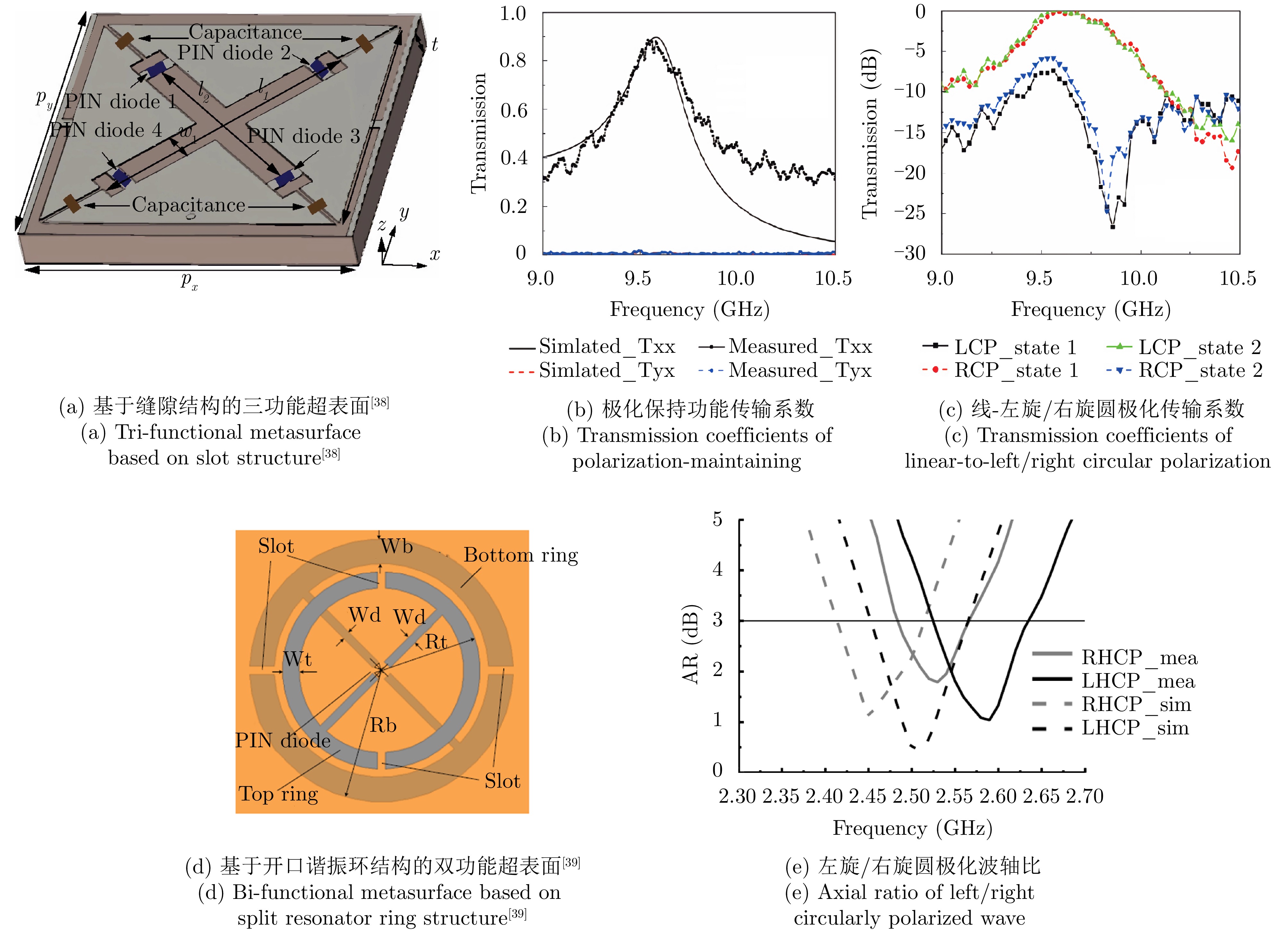
文献 结构类型 电控器件 工作频段(GHz) 极化调控能力 极化隔离度 插入损耗 剖面 入射角稳定性 [38] 手性 PIN二极管 9.70 线-左旋圆极化转换
线-右旋圆极化转换
线极化保持≥20 dB
≥20 dB
—1.32 dB
1.32 dB
1 dB0.05λ0 — [39] 手性 PIN二极管 2.50 线-左旋圆极化转换
线-右旋圆极化转换— — 0.07λ0 — [40] 各向异性 PIN二极管 14.10~15.00 线极化保持
线-左旋圆极化转换≥10 dB ≤2 dB 0.15λ0 — [41] 各向异性 PIN二极管 14.00~16.00 线极化保持
线-左旋圆极化转换— — 0.15λ0 — [42] 各向异性 PIN二极管 2.50~3.64 线极化保持
线-右旋圆极化转换≥15 dB ≤3 dB 0.07λ0 — [43] 各向异性 PIN二极管 1.00~3.74
2.41~3.76
2.48~3.79
2.58~3.89线极化保持
线-左旋圆极化转换
线-右旋圆极化转换
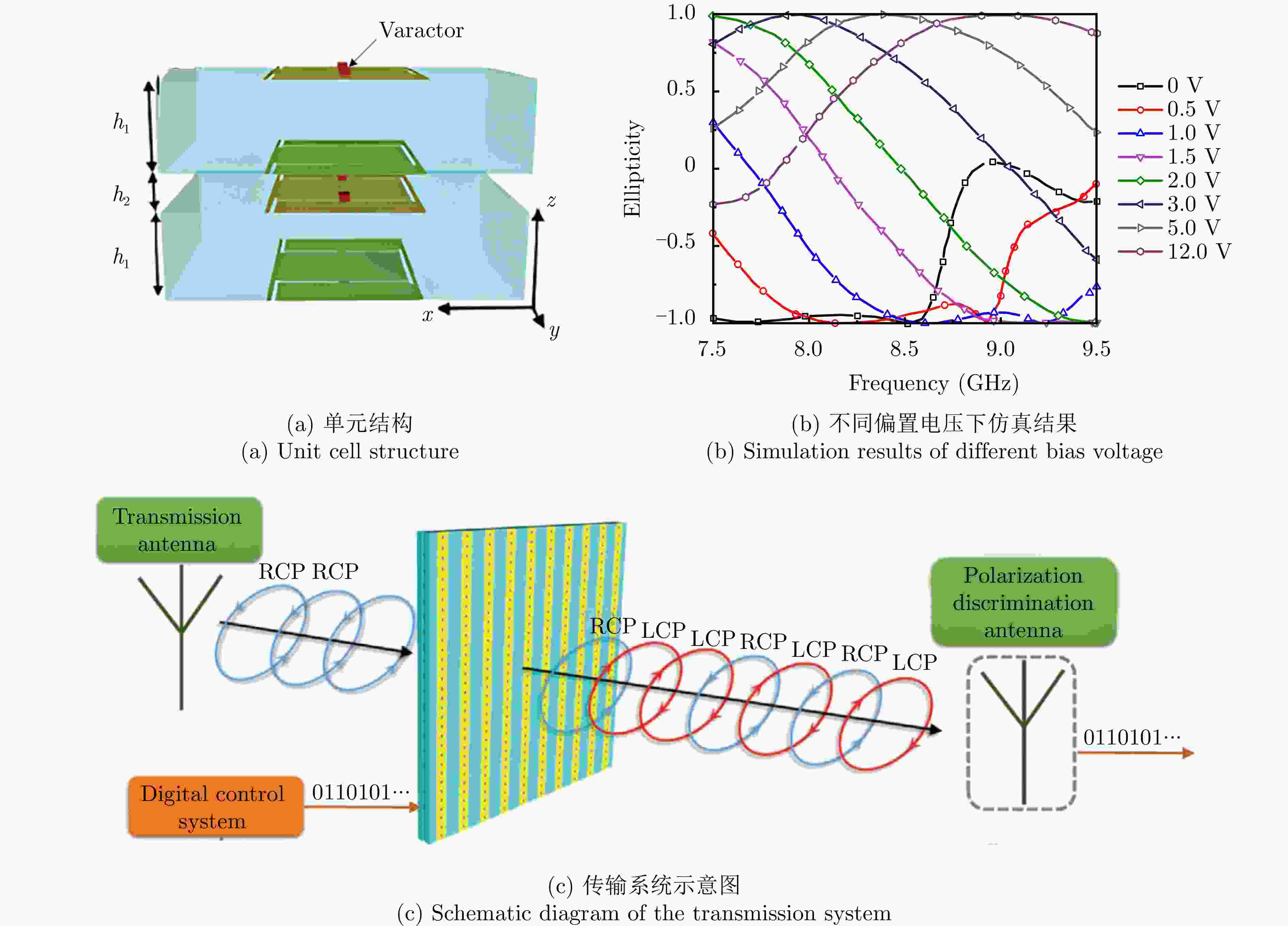
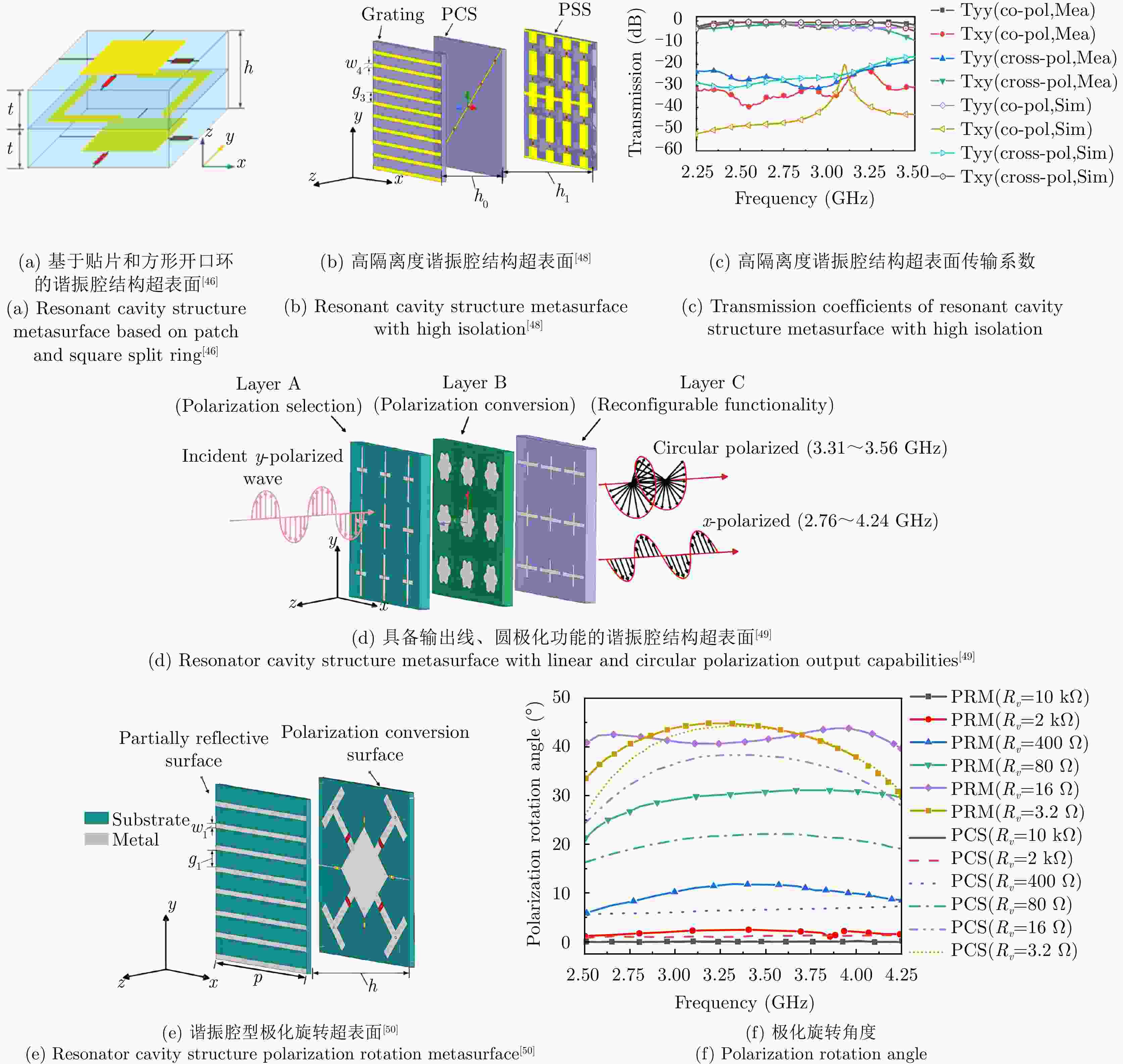
线-交叉线极化转换≥10 dB ≤3 dB 0.37λ0 — [44] 各向异性 变容二极管 7.50~9.50 极化椭圆度–1至1 — — 0.25λ0 — [45] 各向异性 变容二极管 10.00 极化方位角旋转 — — 0.52λ0 — [46] 谐振腔型 PIN二极管 5.20~16.70
8.00~14.30线极化保持
线-交叉线极化转换≥15 dB ≤3 dB 0.05λ0 60° [47] 谐振腔型 PIN二极管 7.80~10.80
8.30~11.20线极化保持
线-交叉线极化转换≥10 dB ≤2 dB 0.08λ0 — [48] 谐振腔型 PIN二极管 2.39~3.21 线极化保持
线-交叉线极化转换≥20 dB ≤3 dB 0.44λ0 — [49] 谐振腔型 PIN二极管 2.76~4.24
3.31~3.56线-左旋圆极化转换
线-交叉线极化转换≥20 dB — 0.16λ0 — [50] 谐振腔型 PIN二极管 3.03~3.60 线极化方位角旋转 — ≤2 dB 0.21λ0 — 表 3 反射型电控可重构极化调控超表面总结
Table 3. Summary of reflection-type electronically controlled reconfigurable polarization modulation metasurface
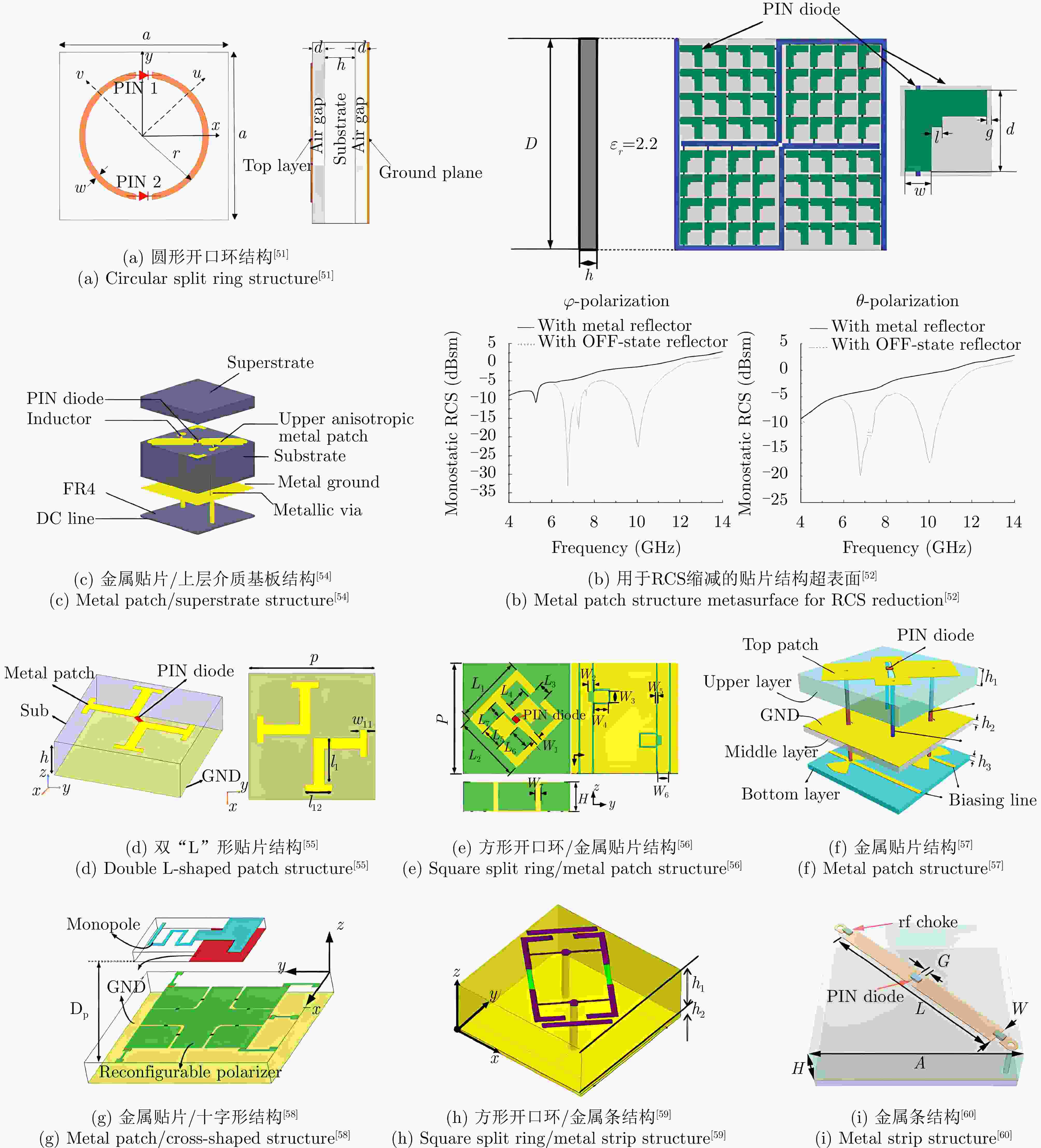
文献 电控器件 工作频段(GHz) 极化调控能力 极化隔离度 插入损耗 剖面 入射角稳定性 [51] PIN二极管 2.45~3.52 线极化保持
线-交叉线极化转换— ≤2 dB 0.07λ0 — [52] PIN二极管 4.00~14.00
6.40~10.30线极化保持
线-交叉线极化转换— ≤0.1 dB
—0.03λ0 —
15°[53] PIN二极管 3.83~4.74
3.39~5.01线极化保持
线-交叉线极化转换≥10 dB ≤1 dB
—0.06λ0 85°
30°[54] PIN二极管 7.60~23.60
6.50~19.90线-左旋圆极化转换
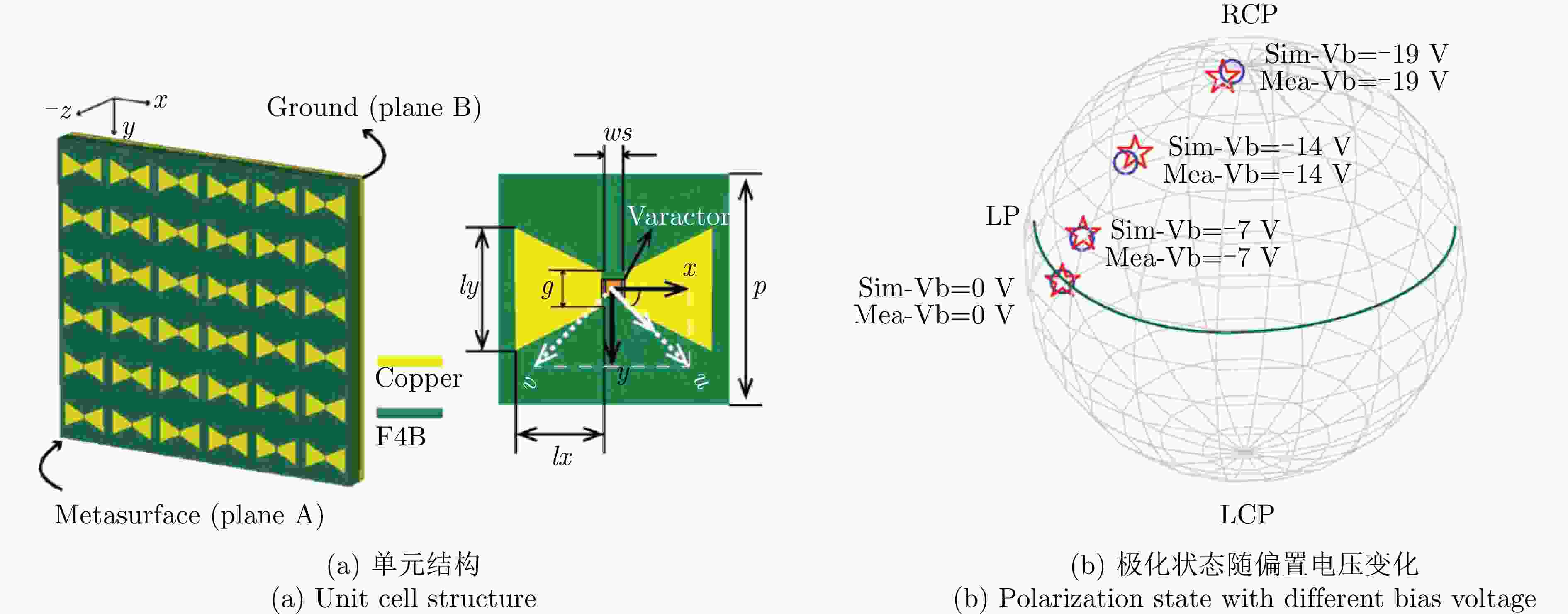
线-交叉线极化转换≥10 dB —
≤1 dB0.12λ0 — [55] PIN二极管 5.96~15.34
6.05~14.76线-左旋圆极化转换
线-交叉线极化转换≥10 dB —
≤1 dB0.09λ0 20°
20°[56] PIN二极管 11.80~24.10
10.50~13.90/17.70~27.20线-左旋圆极化转换
线-交叉线极化转换≥10 dB —
≤3 dB0.07λ0 10°
30°[57] PIN二极管 7.40~12.00 线/圆极化保持
线/圆-交叉线/圆极化转换≥10 dB ≤1 dB 0.07λ0 30° [58] PIN二极管 3.05~3.70 线极化保持
线-左旋圆极化转换
线-右旋圆极化转换— —
≤1.5 dB
≤1.5 dB0.03λ0 — [59] PIN二极管 2.00~3.66/8.46~9.52
3.77~6.20
7.75~8.60
5.20~6.10极化保持
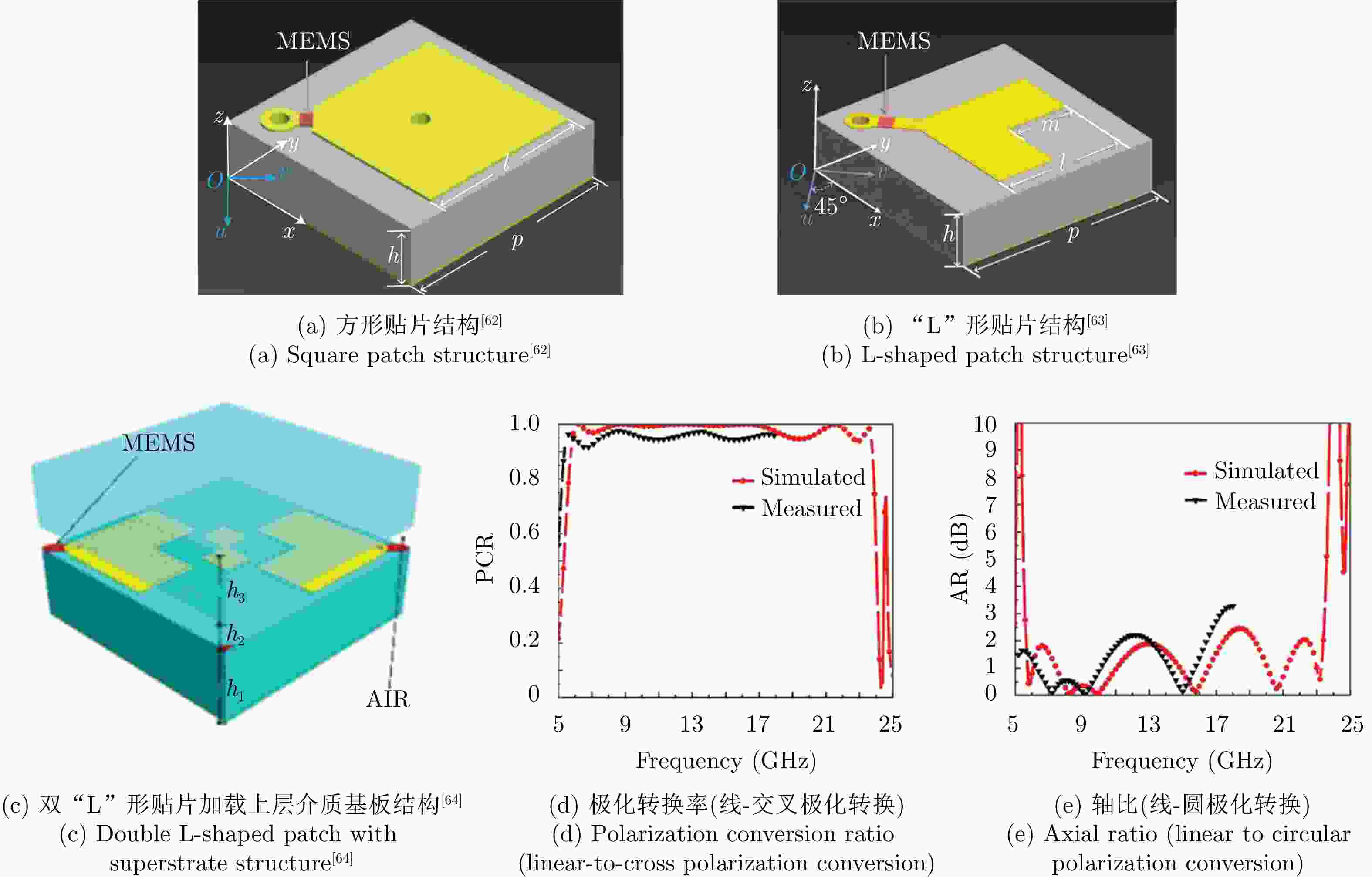
线-交叉线极化转换
线-左旋圆极化转换
线-右旋圆极化转换≥10 dB ≤1 dB
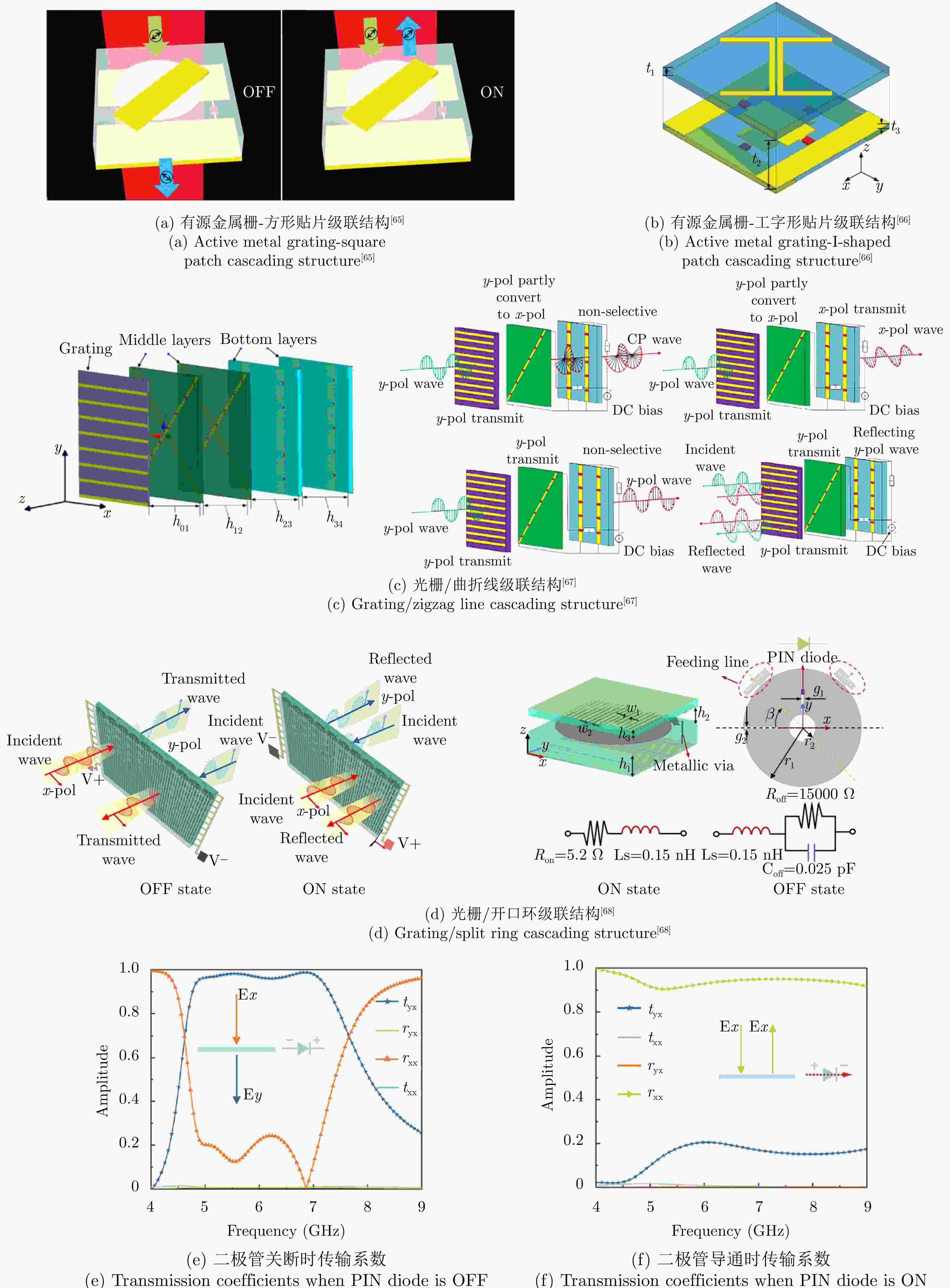
≤1 dB
—
—0.04λ0 15° [60] PIN二极管 9.80 线极化旋转 — — 0.07λ0 — [61] 变容二极管 4.90~8.20
3.90~7.90线-左旋圆极化转换
线-交叉线极化转换≥10 dB
≤2 dB0.08λ0 20°
30°[62] MEMS 7.00~14.00 线极化保持
线-交叉线极化转换— ≤1 dB 0.05λ0 30° [63] MEMS 8.07~10.77
7.93~12.42线-左旋圆极化转换
线-交叉线极化转换— —
≤1 dB0.08λ0 — [64] MEMS 5.7~23.8 GHz
5.6~23.5 GHz线-左旋圆极化转换
线-交叉线极化转换— —
≤1 dB0.12λ0 — 表 4 透/反射一体型电控可重构极化调控超表面总结
Table 4. Summary of integrated transmission/reflection electrically controlled reconfigurable polarization modulation metasurfaces
文献 电控器件 工作频段(GHz) 极化调控能力 插入损耗 剖面 入射角稳定性 [65] PIN二极管 2.10 透射:线-交叉线极化转换
反射:线极化保持≤1 dB 0.02λ0 — [66] PIN二极管 9.70
9.70
4.62~13.56透射:线极化保持
透射:线-交叉线极化转换
反射:线极化保持≤0.5 dB
≤0.5 dB
≤1 dB0.13λ0 — [67] PIN二极管 2.09~5.00
2.29~3.16
1.85~2.69
1.72~2.53透射:线极化保持
透射:线-左旋圆极化转换
透射:线-交叉线极化转换
反射:线极化保持≤2 dB 0.46λ0 — [68] PIN二极管 4.90~7.00 透射:线-交叉线极化转换
反射:线极化保持≤2 dB 0.10λ0 40° -
[1] BORN M and WOLF E. Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light[M]. 6th ed. New York: Pergamon Press, 1980: 36–67. [2] WAKAKI M, KOMACHI Y, MACHIDA H, et al. Fiber-optic polarizer using birefringent crystal as a cladding[J]. Applied Optics, 1996, 35(15): 2591–2594. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.002591. [3] 魏克珠, 潘健, 刘博, 等. 微波铁氧体器件与变极化应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 113–120.WEI Kezhu, PAN Jian, LIU Bo, et al. Microwave Ferrite Device and Variable Polarization Application[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 113–120. [4] SMITH D R, PENDRY J B, and WILTSHIRE M C K. Metamaterials and negative refractive index[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5685): 788–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1096796. [5] SMITH D R and KROLL N. Negative refractive index in left-handed materials[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 85(14): 2933–2936. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.2933. [6] PENDRY J B. A chiral route to negative refraction[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5700): 1353–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.1104467. [7] LAROUCHE S, TSAI Y J, TYLER T, et al. Infrared metamaterial phase holograms[J]. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(5): 450–454. doi: 10.1038/nmat3278. [8] ZHENG Guoxing, MÜHLENBERND H, KENNEY M, et al. Metasurface holograms reaching 80% efficiency[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(4): 308–312. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.2. [9] JOHN-HERPIN A, TITTL A, KÜHNER L, et al. Metasurface-enhanced infrared spectroscopy: An abundance of materials and functionalities[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(34): 2110163. doi: 10.1002/adma.202110163. [10] LI Lianlin, CUI Tiejun, JI Wei, et al. Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 197. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00164-9. [11] ALAEE R, ALBOOYEH M, and ROCKSTUHL C. Theory of metasurface based perfect absorbers[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2017, 50(50): 503002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/aa94a8. [12] WEN Dandan, YUE Fuyong, KUMAR S, et al. Metasurface for characterization of the polarization state of light[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(8): 10272–10281. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.010272. [13] LIN Dianmin, FAN Pengyu, HASMAN E, et al. Dielectric gradient metasurface optical elements[J]. Science, 2014, 345(6194): 298–302. doi: 10.1126/science.1253213. [14] LIU Xiaoming, ZHOU Yixin, WANG Chen, et al. Dual-band dual-rotational-direction angular stable linear-to-circular polarization converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(7): 6054–6059. doi: 10.1109/tap.2021.3138533. [15] MAJEED A, ZHANG Jinling, ASHRAF M A, et al. An ultra-wideband linear-to-circular polarization converter based on a circular, pie-shaped reflective metasurface[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(11): 1681. doi: 10.3390/electronics11111681. [16] VU T L and SEO C. A high angular stability, single-layer transmission linear-to-circular polarization converter for dual ISM-band operation[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 30188–30196. doi: 10.1109/access.2023.3261563. [17] DICANDIA F A and GENOVESI S. Linear-to-circular polarization transmission converter exploiting meandered metallic slots[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2022, 21(11): 2191–2195. doi: 10.1109/lawp.2022.3188063. [18] YANG Pei, DANG Ruirong, and LI Lipin. Dual-linear-to-circular polarization converter based polarization-twisting metasurface antenna for generating dual band dual circularly polarized radiation in Ku-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(10): 9877–9881. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3178803. [19] WANG Hongbin and CHENG Yujian. Single-layer dual-band linear-to-circular polarization converter with wide axial ratio bandwidth and different polarization modes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(6): 4296–4301. doi: 10.1109/tap.2019.2905962. [20] SOFI M A, SAURAV K, and KOUL S K. Linear-to-circular polarization converter with wide angular stability and near unity ellipticity—application to linearly polarized antenna array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(12): 4779–4783. doi: 10.1109/tcsii.2022.3196385. [21] XU Peng, JIANG Weixiang, WANG Shenyun, et al. An ultrathin cross-polarization converter with near unity efficiency for transmitted waves[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(8): 4370–4373. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2839972. [22] LIU Chuan, GAO Renjing, WANG Qi, et al. A design of ultra-wideband linear cross-polarization conversion metasurface with high efficiency and ultra-thin thickness[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 127(15): 153103. doi: 10.1063/1.5143831. [23] DEY S, DEY S, and KOUL S K. Miniaturized dual stop band frequency selective surface with broadband linear co to cross polarization conversion ability[J]. International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer‐Aided Engineering, 2021, 31(9): e22779. doi: 10.1002/mmce.22779. [24] SONG Kun, LIU Yahong, LUO Chunrong, et al. High-efficiency broadband and multiband cross-polarization conversion using chiral metamaterial[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2014, 47(50): 505104. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/47/50/505104. [25] LIU Chuan, GAO Renjing, LIU Shutian, et al. Meander-line based high-efficiency ultrawideband linear cross-polarization conversion metasurface[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2021, 14(7): 074001. doi: 10.35848/1882-0786/ac0b06. [26] BAGHEL A K, KULKARNI S S, and NAYAK S K. Linear-to-cross-polarization transmission converter using ultrathin and smaller periodicity metasurface[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2019, 18(7): 1433–1437. doi: 10.1109/lawp.2019.2919423. [27] FEI Peng, VANDENBOSCH G A E, GUO Weihua, et al. Versatile cross-polarization conversion chiral metasurface for linear and circular polarizations[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2020, 8(13): 2000194. doi: 10.1002/adom.202000194. [28] LIN Baoqin, GUO Jianxin, LV Lintao, et al. Ultra-wideband and high-efficiency reflective polarization converter for both linear and circular polarized waves[J]. Applied Physics A, 2019, 125(2): 76. doi: 10.1007/S00339-018-2368-9. [29] PENG Lin, LI Xiaofeng, JIANG Xing, et al. A novel THz half-wave polarization converter for cross-polarization conversions of both linear and circular polarizations and polarization conversion ratio regulating by Graphene[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2018, 36(19): 4250–4258. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2018.2836904. [30] LIN Baoqin, HUANG Wenzhun, GUO Jianxin, et al. A high efficiency ultra-wideband circular-to-linear polarization conversion metasurface[J]. Optics Communications, 2023, 529: 129102. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2022.129102. [31] SUN Xiaoning, QU Zhaoming, YUAN Jianghang, et al. Reconfigurable broadband polarisation conversion metasurface based on VO2[J]. Photonics and Nanostructures-Fundamentals and Applications, 2022, 50: 101012. doi: 10.1016/j.photonics.2022.101012. [32] ZHU H L, CHEUNG S W, LIU X H, et al. Design of polarization reconfigurable antenna using metasurface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(6): 2891–2898. doi: 10.1109/tap.2014.2310209. [33] LI Long, LI Yongjiu, WU Zhao, et al. Novel polarization-reconfigurable converter based on multilayer frequency-selective surfaces[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2015, 103(7): 1057–1070. doi: 10.1109/jproc.2015.2437611. [34] CERVENY M, FORD K L, and TENNANT A. Reflective switchable polarization rotator based on metasurface with PIN diodes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(3): 1483–1492. doi: 10.1109/tap.2020.3026883. [35] DE LUSTRAC A, RATNI B, PIAU G P, et al. Tri-state metasurface-based electromagnetic screen with switchable reflection, transmission, and absorption functionalities[J]. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2021, 3(3): 1184–1190. doi: 10.1021/acsaelm.0c01038. [36] XU Shitong, FAN Fei, CAO Hongzhong, et al. Liquid crystal integrated metamaterial for multi-band terahertz linear polarization conversion[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19(9): 093701. doi: 10.3788/COL202119.093701. [37] VASIĆ B, ZOGRAFOPOULOS D C, ISIĆ G, et al. Electrically tunable terahertz polarization converter based on overcoupled metal-isolator-metal metamaterials infiltrated with liquid crystals[J]. Nanotechnology, 2017, 28(12): 124002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa5bbd. [38] MA Xiaoliang, PAN Wenbo, HUANG Cheng, et al. An active metamaterial for polarization manipulating[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2014, 2(10): 945–949. doi: 10.1002/adom.201400212. [39] LI Wenting, GAO S, CAI Yuanming, et al. Polarization-reconfigurable circularly polarized planar antenna using switchable polarizer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(9): 4470–4477. doi: 10.1109/tap.2017.2730240. [40] LI Wei, XIA Song, HE Bin, et al. A reconfigurable polarization converter using active metasurface and its application in horn antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 64(12): 5281–5290. doi: 10.1109/tap.2016.2620484. [41] SOFI M A, SAURAV K, and KOUL S K. A linear to circular polarization reconfigurable converter based on frequency selective surface[J]. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2021, 63(5): 1425–1433. doi: 10.1002/mop.32779. [42] ZHU Shuangshuang, WANG Ping, ZHANG Yong, et al. A reconfigurable polarization converter and related application as horn antenna cladding[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2023, 133(2): 023102. doi: 10.1063/5.0130212. [43] ZHOU Hongcheng, YU Xiaoran, WANG Ping, et al. Wideband linear-to-multi-polarization converter based on active metasurface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2023, 71(6): 5246–5255. doi: 10.1109/tap.2023.3256581. [44] HUANG Chenxi, ZHANG Jingjing, CHENG Qiang, et al. Polarization modulation for wireless communications based on metasurfaces[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(36): 2103379. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202103379. [45] WU Zhanni, RA’DI Y, and GRBIC A. Tunable metasurfaces: A polarization rotator design[J]. Physical Review X, 2019, 9(1): 011036. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.9.011036. [46] LI You, CAO Qunsheng, and WANG Yi. A wideband multifunctional multilayer switchable linear polarization metasurface[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2018, 17(7): 1314–1318. doi: 10.1109/lawp.2018.2843816. [47] WEI Zeyong, ZHAO Yunlong, ZHANG Yujing, et al. High-efficiency modulation of broadband polarization conversion with a reconfigurable chiral metasurface[J]. Nanoscale Advances, 2022, 4(20): 4344–4350. doi: 10.1039/d2na00382a. [48] WANG Ping, LIN Feihong, WANG Yu, et al. Tunable polarization converter with high polarization isolation based on metasurface and its application on horn antenna[J]. Applied Physics A, 2022, 128(10): 863. doi: 10.1007/s00339-022-05930-1. [49] WANG Ping, WANG Yu, YAN Zhongming, et al. Transmission-type reconfigurable metasurface for linear-to-circular and linear-to-linear polarization conversions[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2022, 31(12): 124201. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/ac8ce0. [50] WANG Ping, QIN Yifei, WANG Yu, et al. Wideband switchable linear polarization rotator based on metasurface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2023, 123(1): 011701. doi: 10.1063/5.0155015. [51] SAIKIA M, GHOSH S, and SRIVASTAVA K V. Switchable reflective metamaterial polarisation rotator[J]. Electronics Letters, 2016, 52(12): 1030–1032. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.0742. [52] WANG Fuwei, LI Ke, and REN Yuhui. Reconfigurable polarization rotation surfaces applied to the wideband antenna radar cross section reduction[J]. International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer‐Aided Engineering, 2018, 28(5): e21262. doi: 10.1002/mmce.21262. [53] SUN Shangyi, JIANG Wen, GONG Shuxi, et al. Reconfigurable linear-to-linear polarization conversion metasurface based on PIN diodes[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2018, 17(9): 1722–1726. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2018.2864797. [54] TIAN Jianghao, CAO Xiangyu, GAO Jun, et al. A reconfigurable ultra-wideband polarization converter based on metasurface incorporated with PIN diodes[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 125(13): 135105. doi: 10.1063/1.5067383. [55] YANG Heng, WANG Shicong, LI Peng, et al. A broadband multifunctional reconfigurable polarization conversion metasurface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2023, 71(7): 5759–5767. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2023.3266498. [56] YANG Zhengyi, KOU Na, YU Shixing, et al. Reconfigurable multifunction polarization converter integrated with PIN diode[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2021, 31(6): 557–560. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2021.3064039. [57] LIU Wei, KE Junchen, XIAO Cong, et al. Broadband polarization-reconfigurable converter using active metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2023, 71(4): 3725–3730. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2023.3240861. [58] BHATTACHARJEE A and DWARI S. Design of an anisotropic reconfigurable reflective polarization converter for realizing circular polarization-reconfigurable antenna[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2022, 21(12): 2392–2396. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2022.3194347. [59] PRAMANIK S, BAKSHI S C, KOLEY C, et al. Active metasurface-based reconfigurable polarization converter with multiple and simultaneous functionalities[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2022, 22(3): 522–526. doi: 10.1109/lawp.2022.3217130. [60] MA Qian, HONG Qiaoru, BAI Guodong, et al. Editing arbitrarily linear polarizations using programmable metasurface[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2020, 13(2): 021003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.13.021003. [61] GAO Xi, YANG Wanli, MA Huifeng, et al. A reconfigurable broadband polarization converter based on an active metasurface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(11): 6086–6095. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2866636. [62] 于惠存, 曹祥玉, 高军, 等. 一种宽带可重构反射型极化旋转表面[J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67(22): 224101. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20181041.YU Huicun, CAO Xiangyu, GAO Jun, et al. Broadband reconfigurable reflective polarization convertor[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(22): 224101. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20181041. [63] YU Huicun, CAO Xiangyu, GAO Jun, et al. Design of a wideband and reconfigurable polarization converter using a manipulable metasurface[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2018, 8(11): 3373–3381. doi: 10.1364/OME.8.003373. [64] GUO Zexu, CAO Xiangyu, GAO Jun, et al. A novel reconfigurable metasurface with coincident and ultra-wideband LTL and LTC polarization conversion functions[J]. Radioengineering, 2019, 28(4): 696–702. doi: 10.13164/re.2019.0696. [65] TAO Zui, WAN Xiang, PAN Baicao, et al. Reconfigurable conversions of reflection, transmission, and polarization states using active metasurface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(12): 121901. doi: 10.1063/1.4979033. [66] LI You, WANG Yi, and CAO Qunsheng. Design of a multifunctional reconfigurable metasurface for polarization and propagation manipulation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 129183–129191. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2939200. [67] WANG Ping, ZHANG Yong, WANG Yu, et al. Multifunctional polarization converter based on multilayer reconfigurable metasurface[J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 28: 136–145. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.12.008. [68] YANG Jianing, ZHANG Yanting, TANG Mingchun, et al. A reconfigurable asymmetric-transmission metasurface for dynamic manipulation of transmission, reflection, and polarization[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2023, 133(8): 083101. doi: 10.1063/5.0134540. [69] SHI Xin, QIU Tianshuo, WANG Jiafu, et al. Metasurface inverse design using machine learning approaches[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2020, 53(27): 275105. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ab8036. [70] HU Yanwen, MA Yaodong, ZHANG Tingrong, et al. Inverse design of transmission-type linear-to-circular polarization control metasurface based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2023, 56(47): 475001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/acefdf. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: