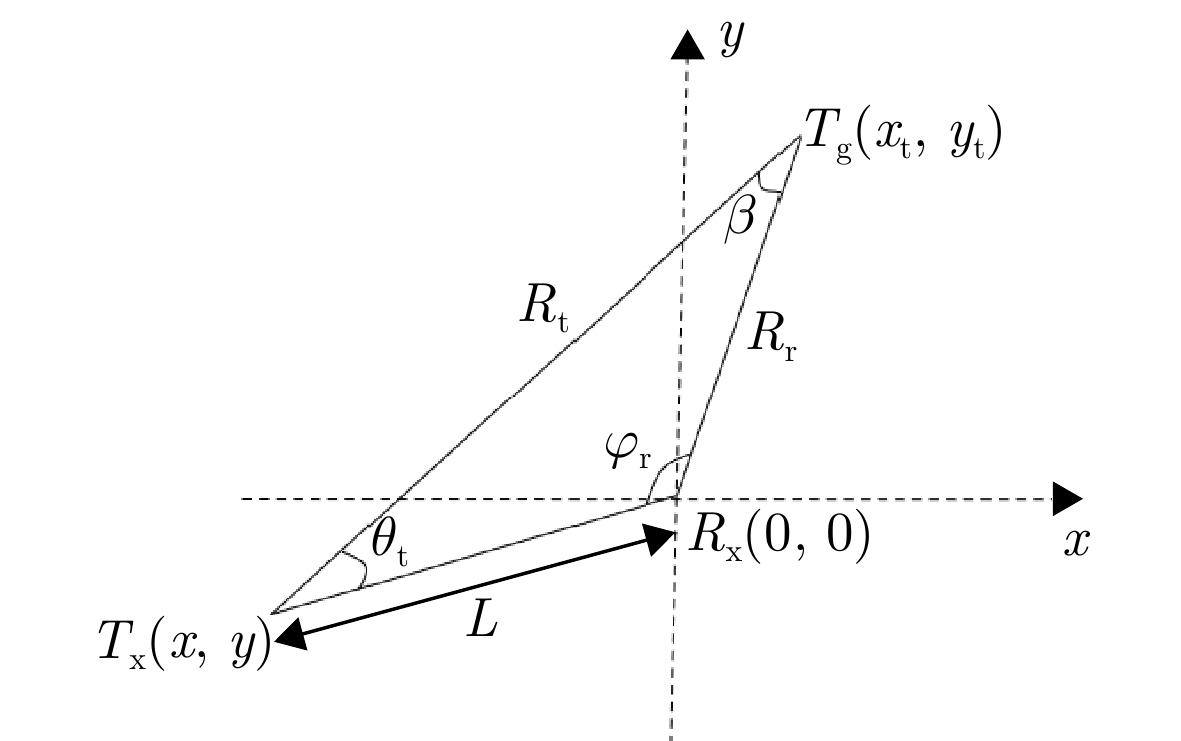
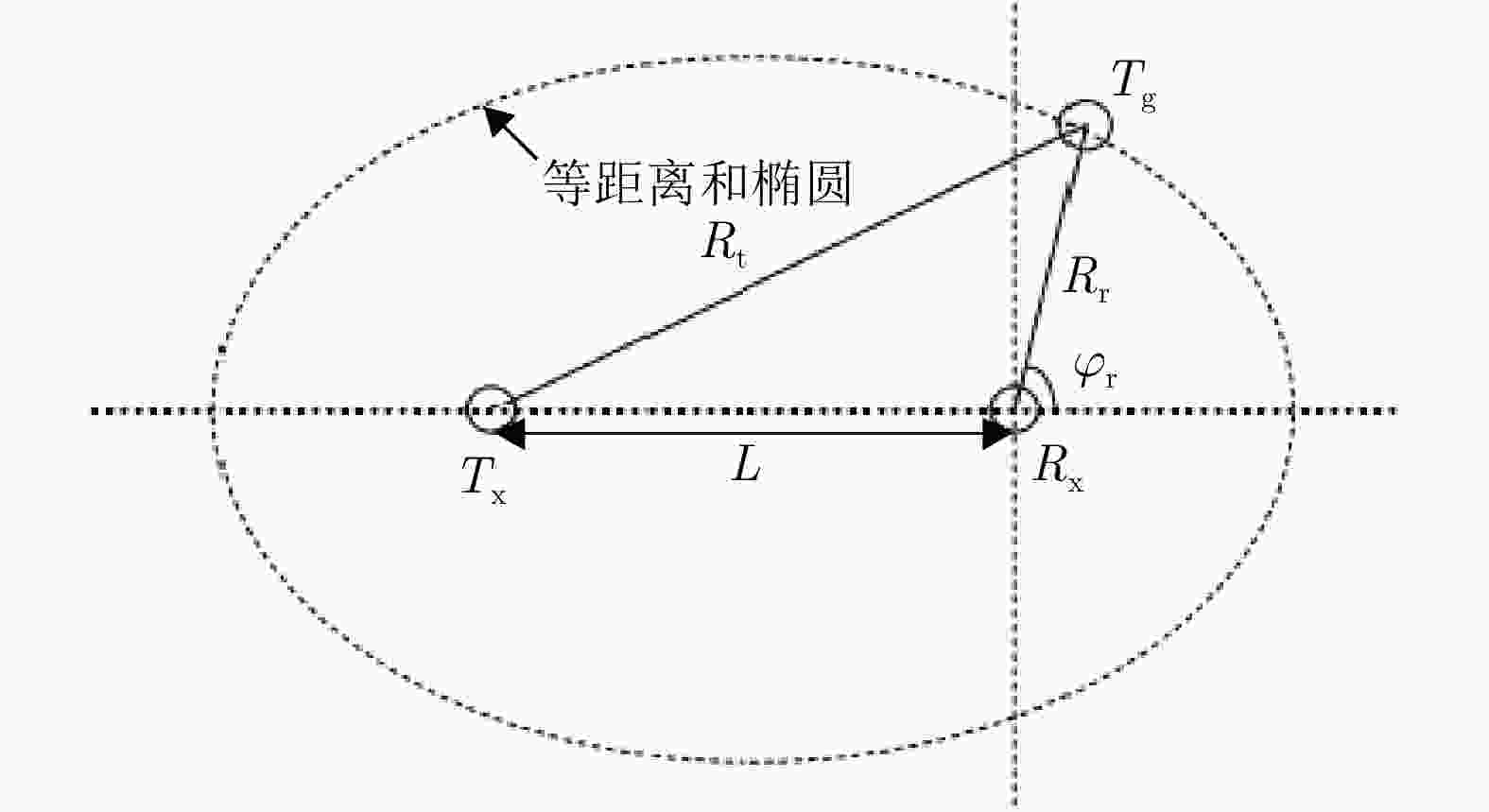
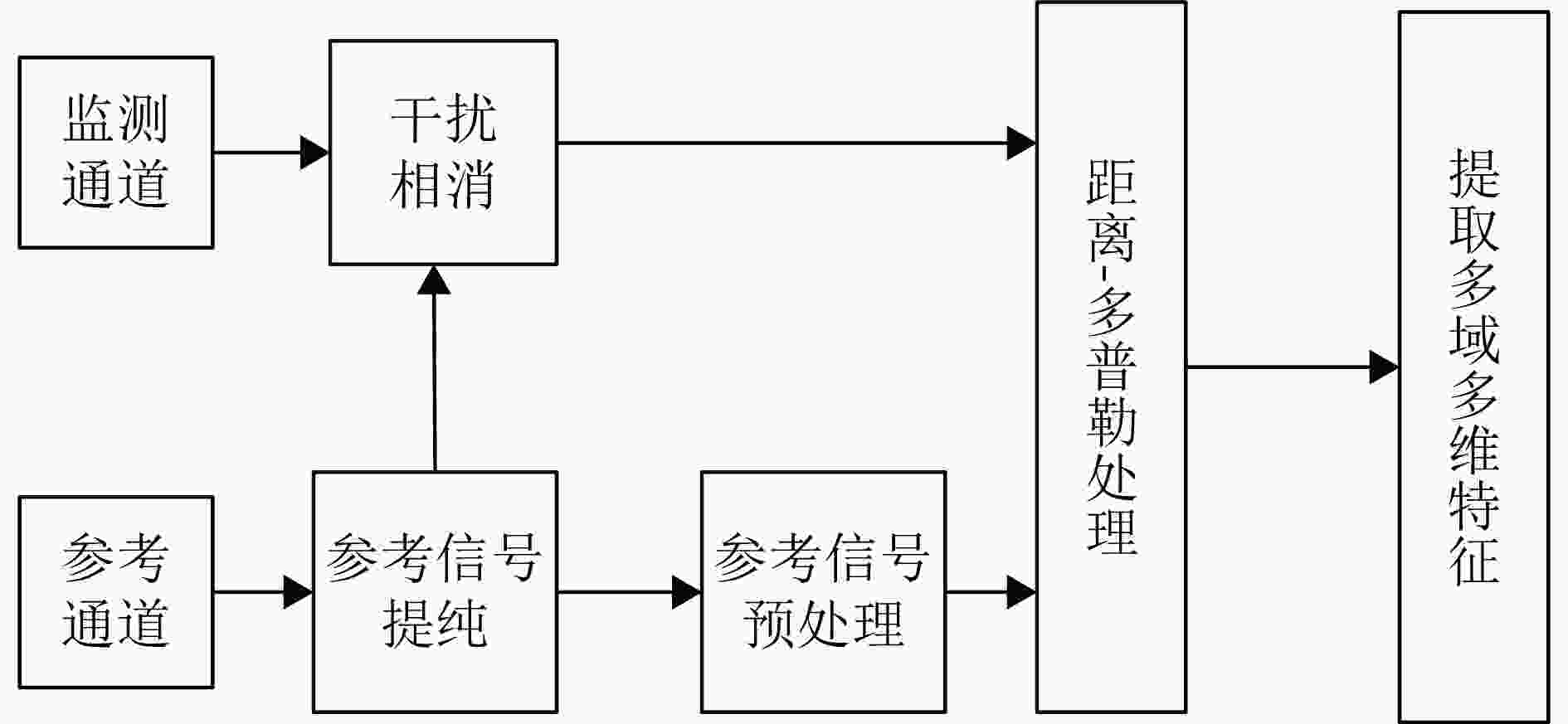
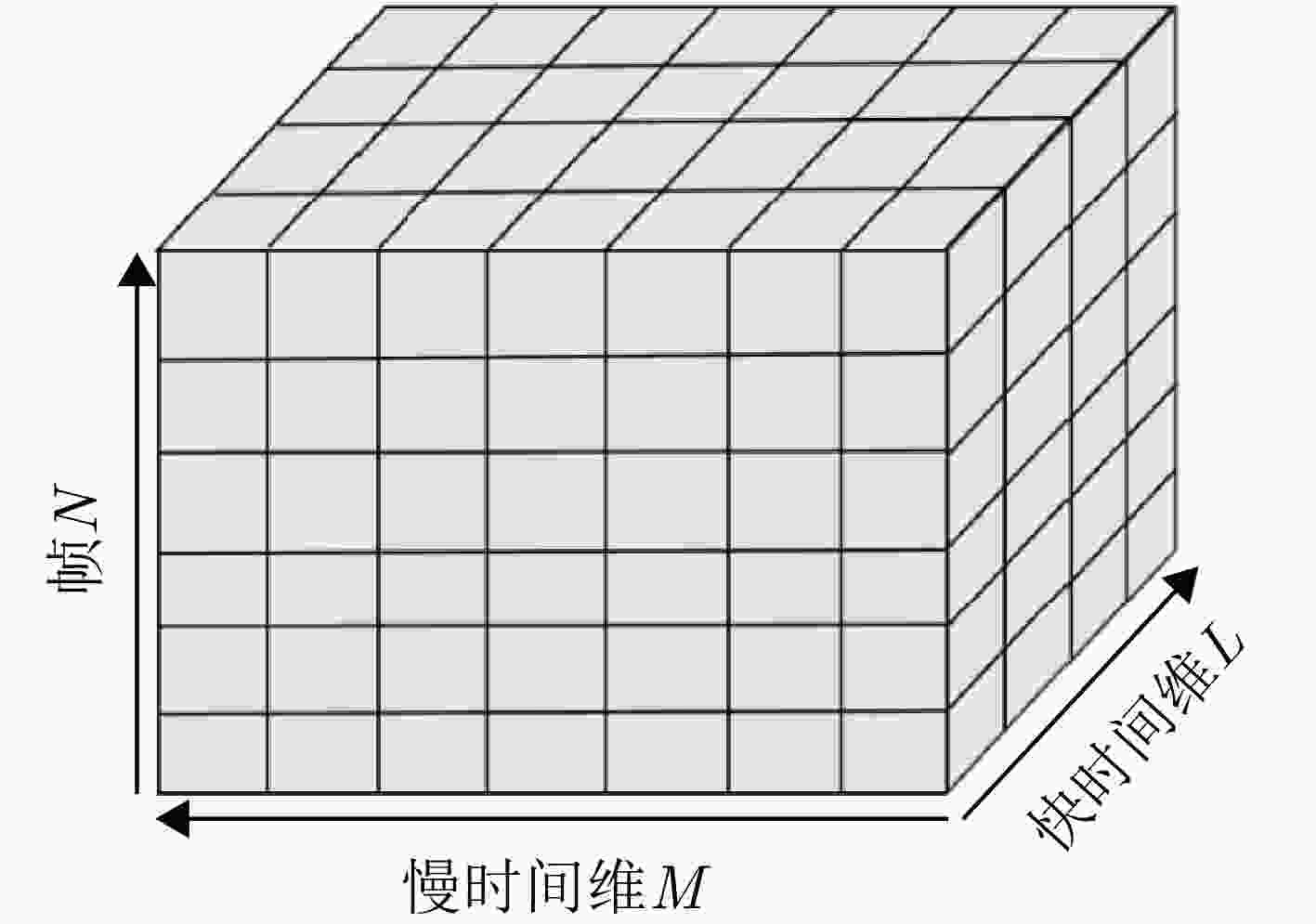
Passive Radar Low Slow Small Detection Dataset (LSS-PR-1.0) and Multi-domain Feature Extraction and Analysis Methods
-
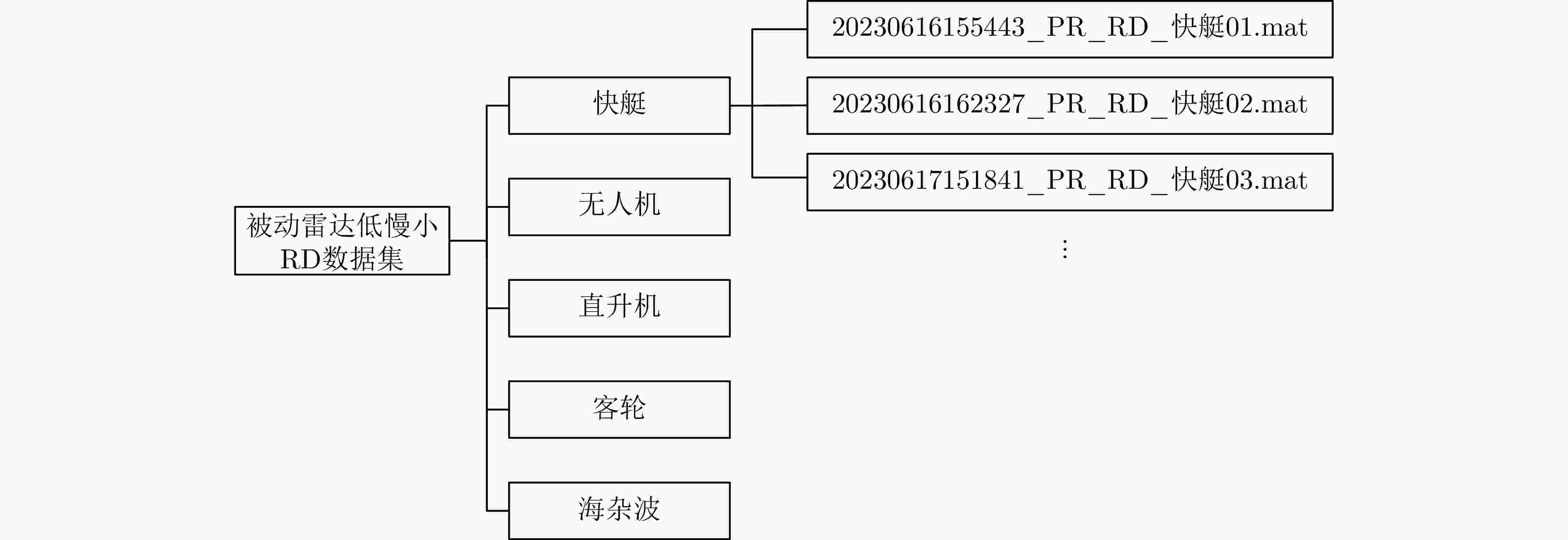
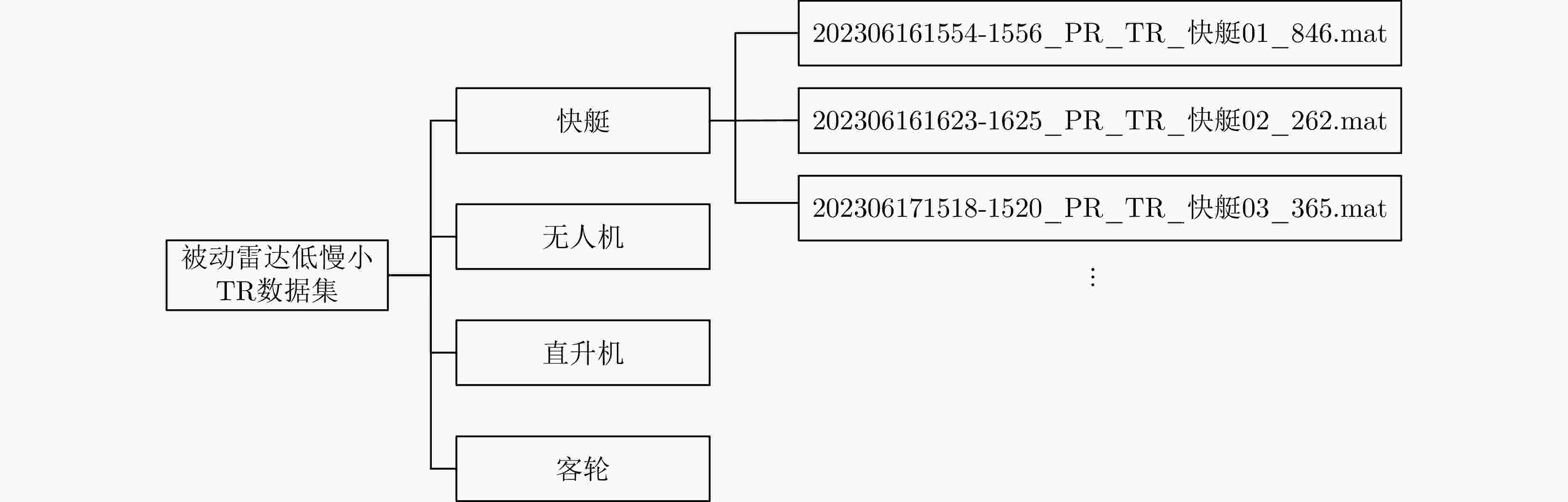
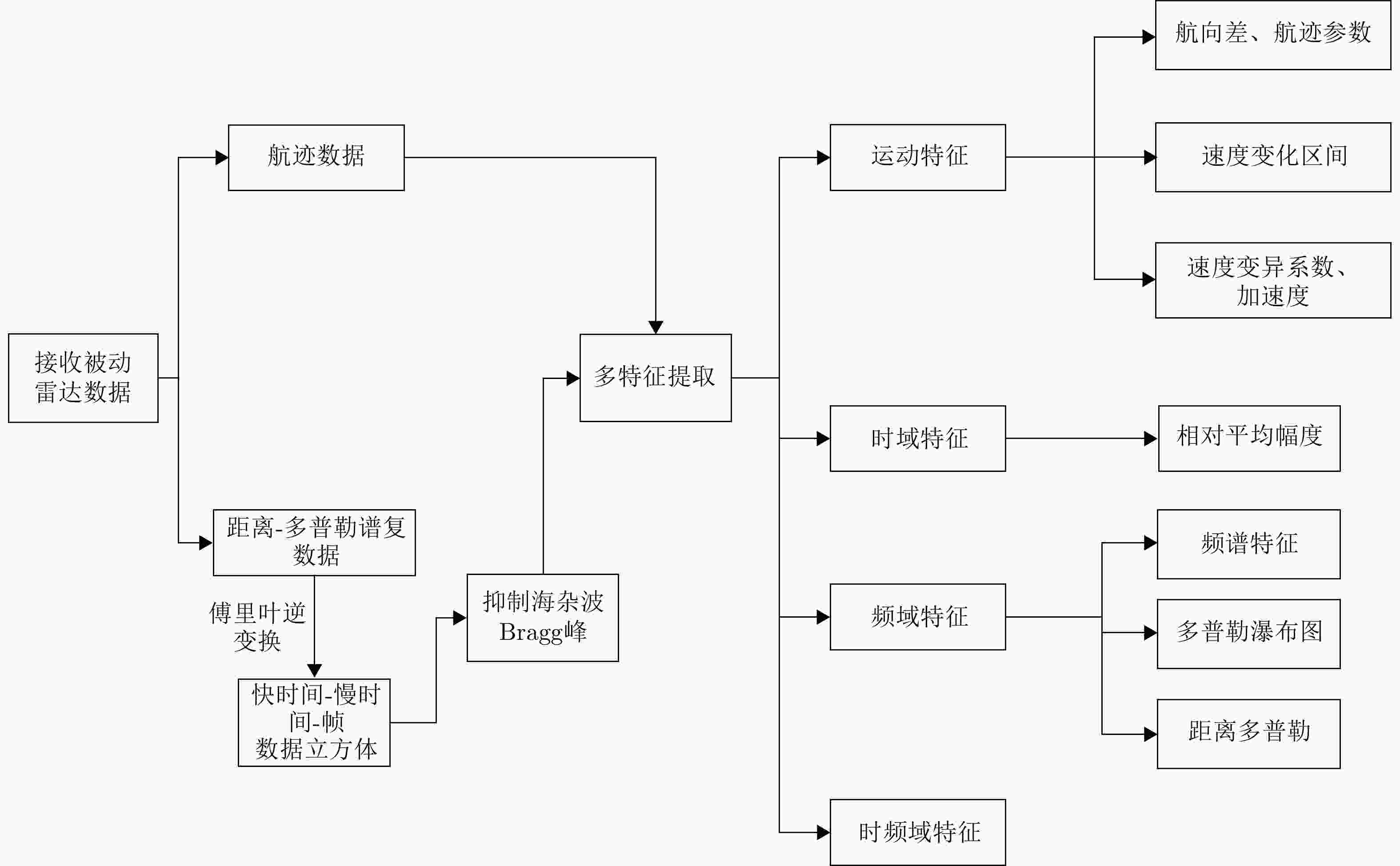
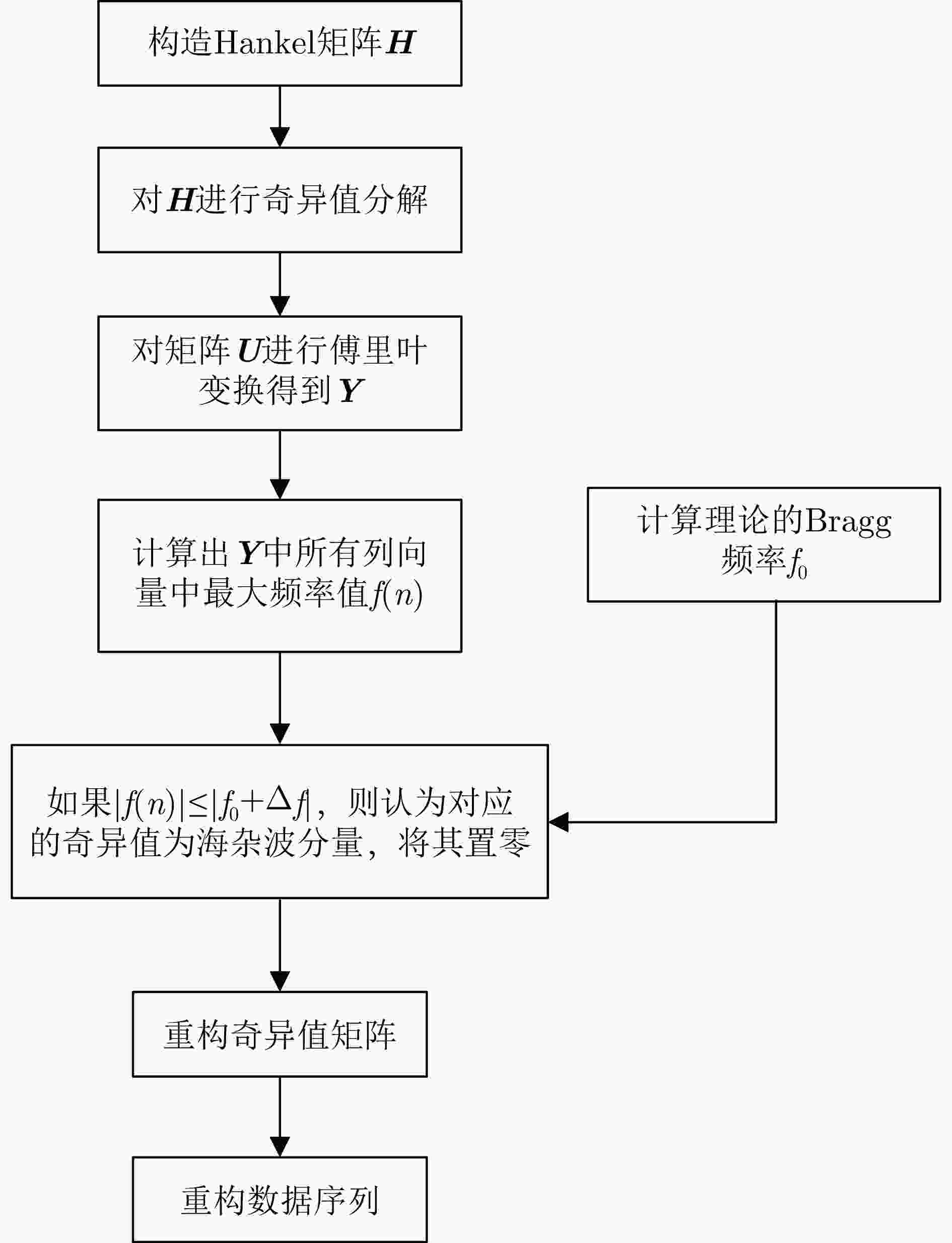
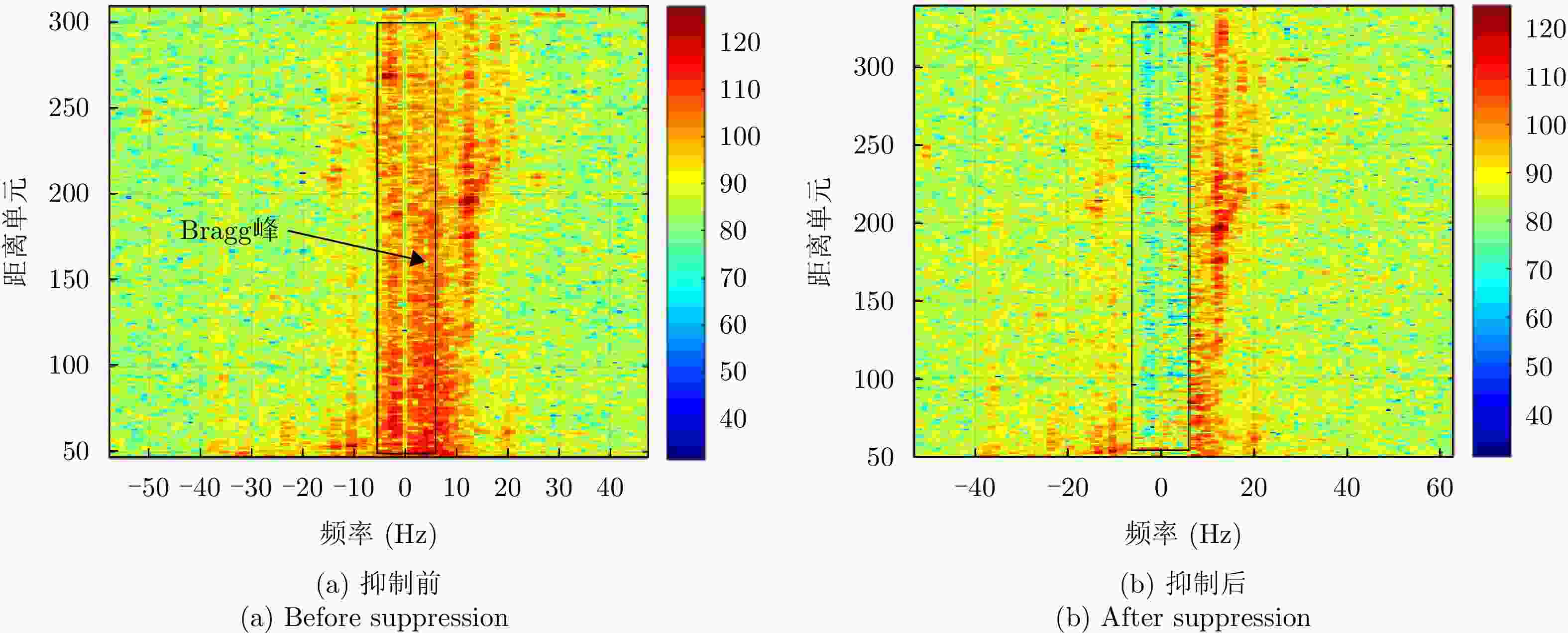
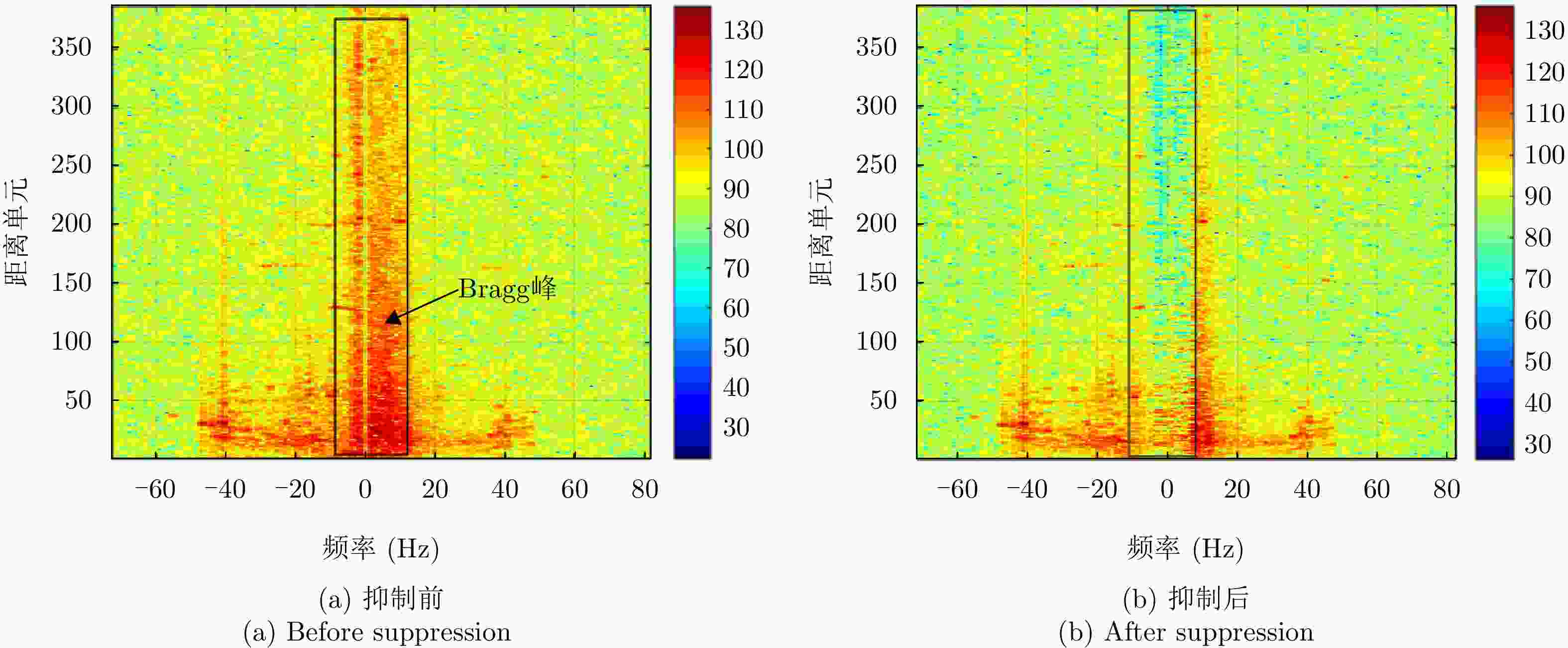
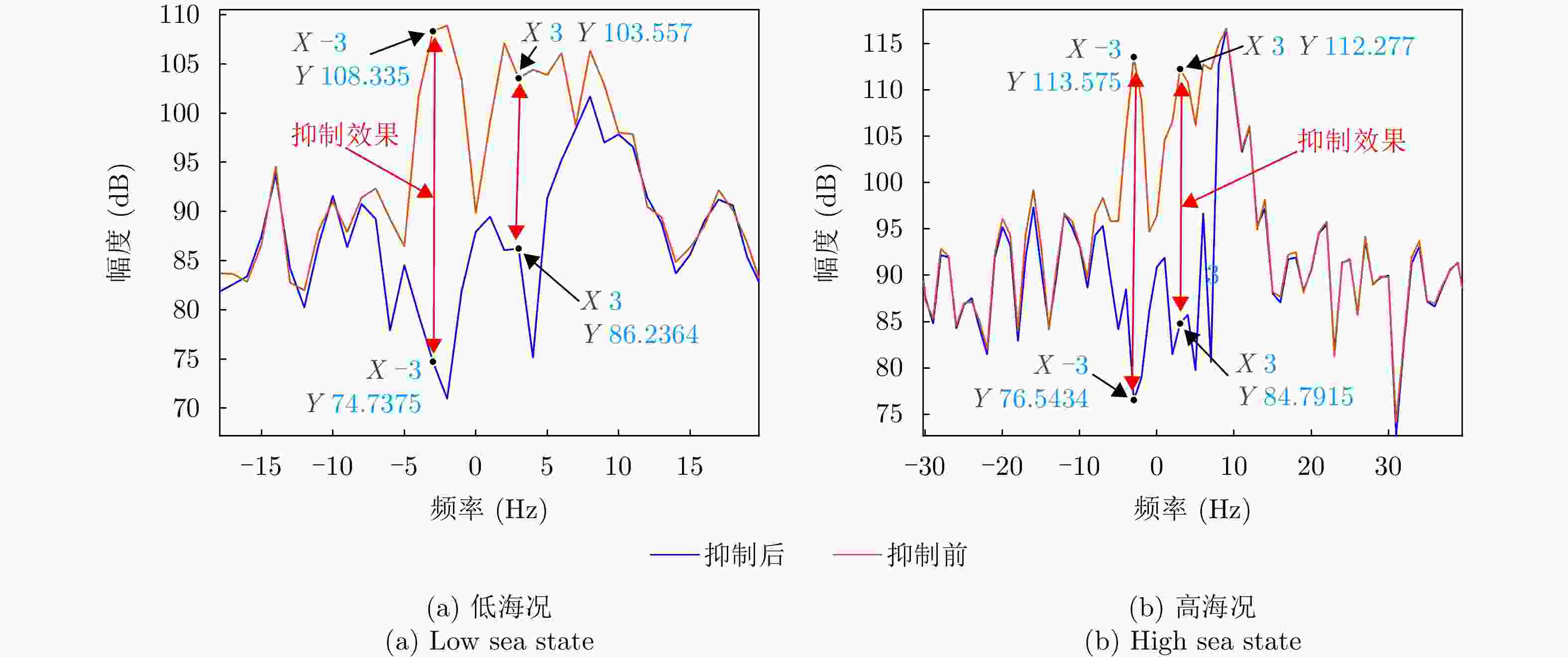
摘要: 被动雷达在预警探测和低慢小目标(LSS)检测中具有重要作用。由于被动雷达信号辐射源不可控,目标特性更为复杂,导致检测和识别极其困难。该文构建了被动雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-PR-1.0),该数据集包含了直升机、无人机、快艇、客轮4种典型海空目标的雷达回波信号,以及低高海况的海杂波数据,为该领域研究提供了数据支撑。在目标特征提取和分析方面,首先采用奇异值分解海杂波抑制方法,去除海杂波强Bragg峰对目标回波的影响。在此基础上,提出4类10种多域特征提取和分析方法,包括时域特征(相对平均幅度)、频域特征(频谱特征、多普勒瀑布图、距离多普勒特征)、时频域特征、运动特征(航向差、航迹参数、速度变化区间、速度变异系数、加速度)等。基于实测数据对4种海空目标特性进行了对比分析,总结各类目标特性规律,为后续目标识别奠定了基础。Abstract: Passive radar plays an important role in early warning detection and Low Slow Small (LSS) target detection. Due to the uncontrollable source of passive radar signal radiations, target characteristics are more complex, which makes target detection and identification extremely difficult. In this paper, a passive radar LSS detection dataset (LSS-PR-1.0) is constructed, which contains the radar echo signals of four typical sea and air targets, namely helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles, speedboats, and passenger ships, as well as sea clutter data at low and high sea states. It provides data support for radar research. In terms of target feature extraction and analysis, the singular-value-decomposition sea-clutter-suppression method is first adopted to remove the influence of the strong Bragg peak of sea clutter on target echo. On this basis, four categories of ten multi-domain feature extraction and analysis methods are proposed, including time-domain features (relative average amplitude), frequency-domain features (spectral features, Doppler waterfall plot, and range Doppler features), time-frequency-domain features, and motion features (heading difference, trajectory parameters, speed variation interval, speed variation coefficient, and acceleration). Based on the actual measurement data, a comparative analysis is conducted on the characteristics of four types of sea and air targets, summarizing the patterns of various target characteristics and laying the foundation for subsequent target recognition.
-
表 1 被动雷达基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of passive radar
参数 数值 可接收频率范围 470~806 MHz DTMB信号带宽 7.56 MHz 距离分辨单元 39.68 m 方位精度 1° 数据更新周期 1 s 表 2 文中使用的外辐射源雷达数据
Table 2. Passive radar data used in the paper
目标类型 RD数据文件名 编号 快艇 20230616162327 _PR_RD_快艇02#S2 20240525180546 _PR_RD_快艇12#S12 客轮 20230617153740 _PR_RD_客轮01#L1 20231125153335 _PR_RD_客轮07#L7 20240522153628 _PR_RD_客轮11#L11 直升机 20230705162446 _PR_RD_直升机01#H1 20231114193839 _PR_RD_直升机05#H5 20240515174613 _PR_RD_直升机09#H9 无人机 20240113131753 _PR_RD_无人机02#D2 20240407094458 _PR_RD_无人机09#D9 表 3 海空典型目标时域特征比较
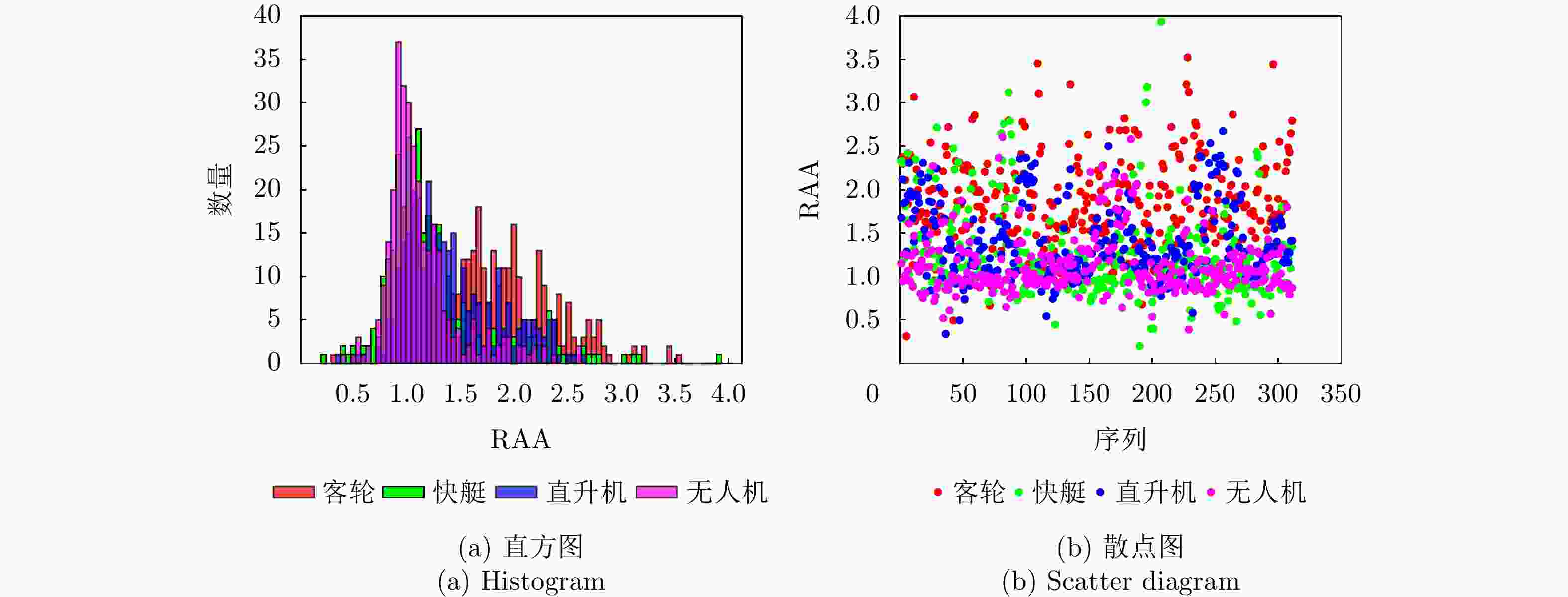
Table 3. Comparison of time-domain characteristics of typical targets in sea and air
目标类型 相对平均幅度(RAA) 直升机 0.34~2.67 无人机 0.39~2.61 快艇 0.20~3.93 客轮 0.31~3.52 表 4 目标双基距离和双基速度
Table 4. Bistatic range and velocity of targets
目标类型 双基距离(m) 双基速度(m/s) 直升机 8730 78 无人机 1231 22 快艇 5955 31 客轮 9647 –9 表 5 海空典型目标频域特征值比较
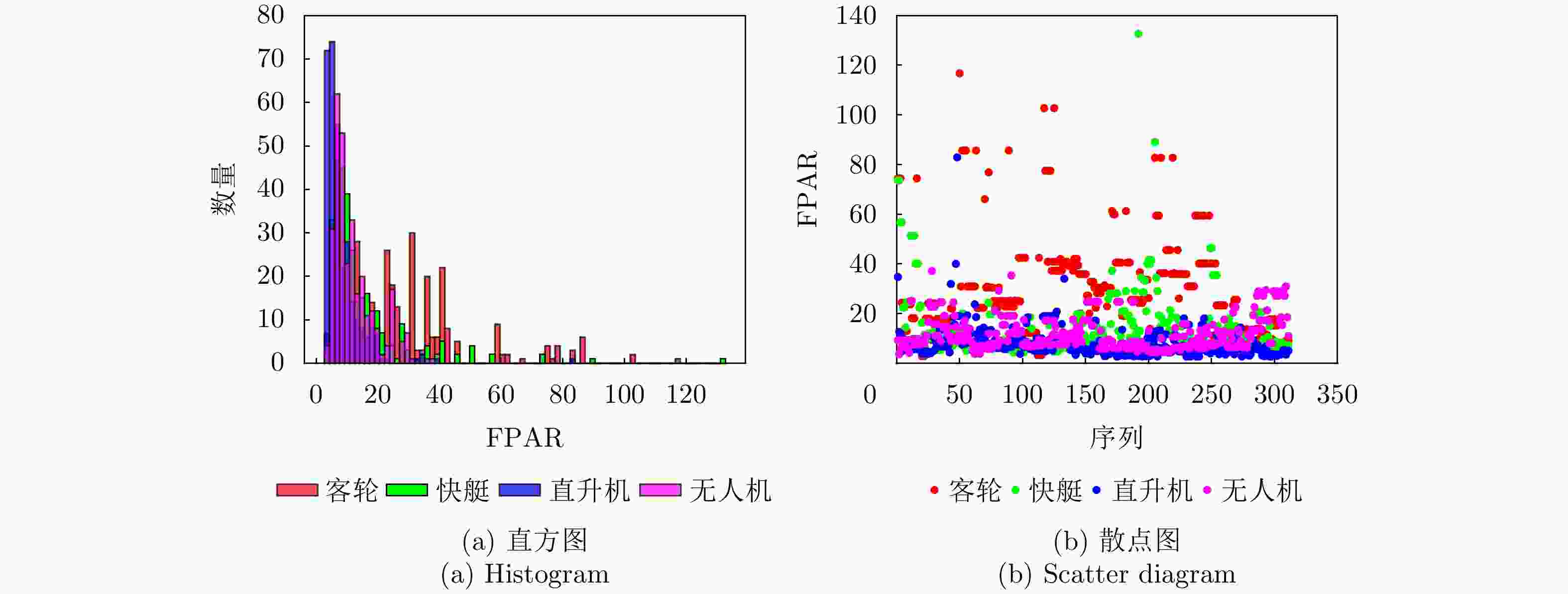
Table 5. Comparison of characteristic values of typical targets in the frequency-domain of sea and air
目标类型 频谱峰值与均值之比(FPAR) 直升机 2.63~82.96 无人机 3.66~37.13 快艇 3.00~132.71 客轮 2.91~116.79 表 6 海空典型目标的速度特征
Table 6. Speed characteristics of a typical target in the sea and air
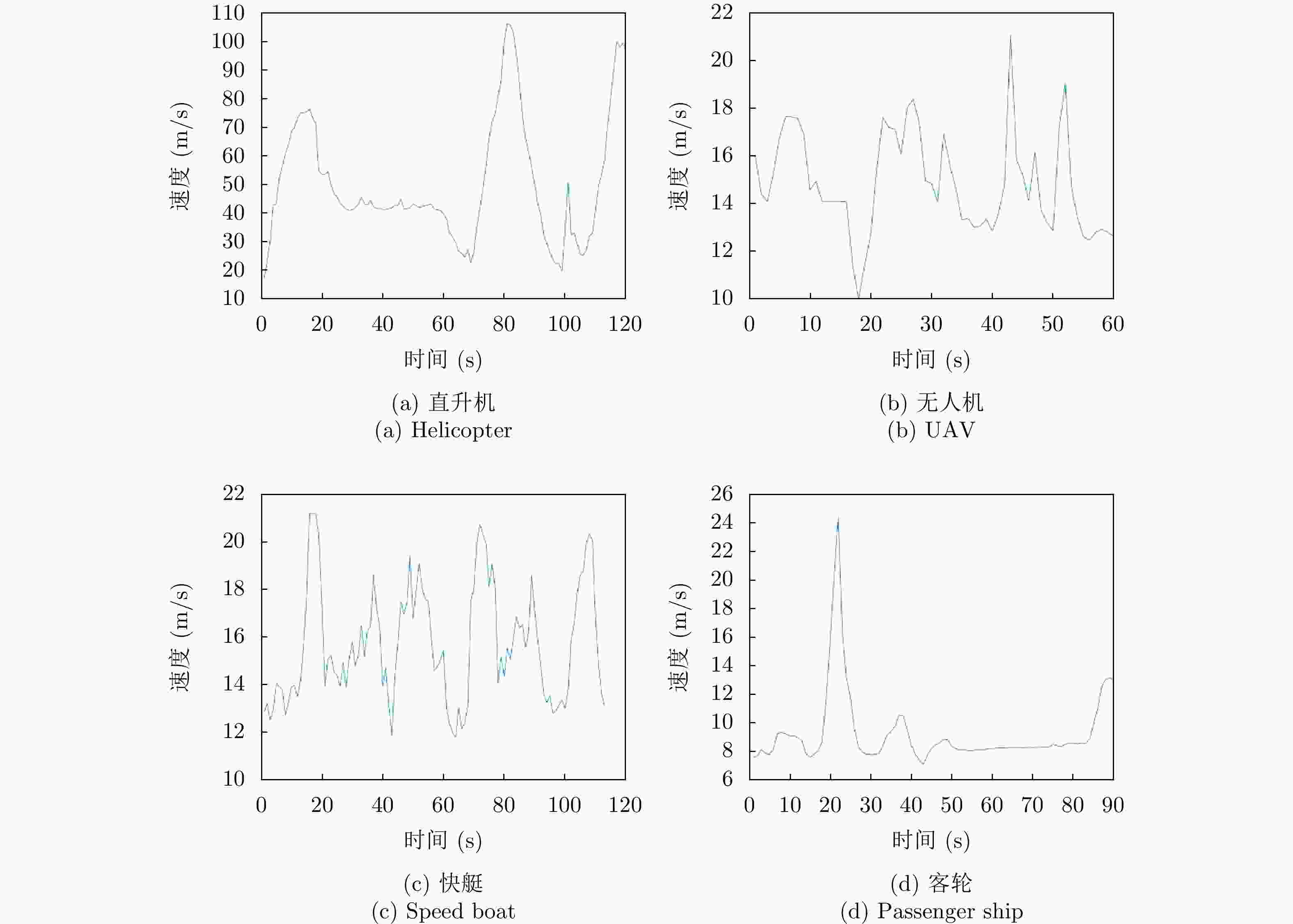
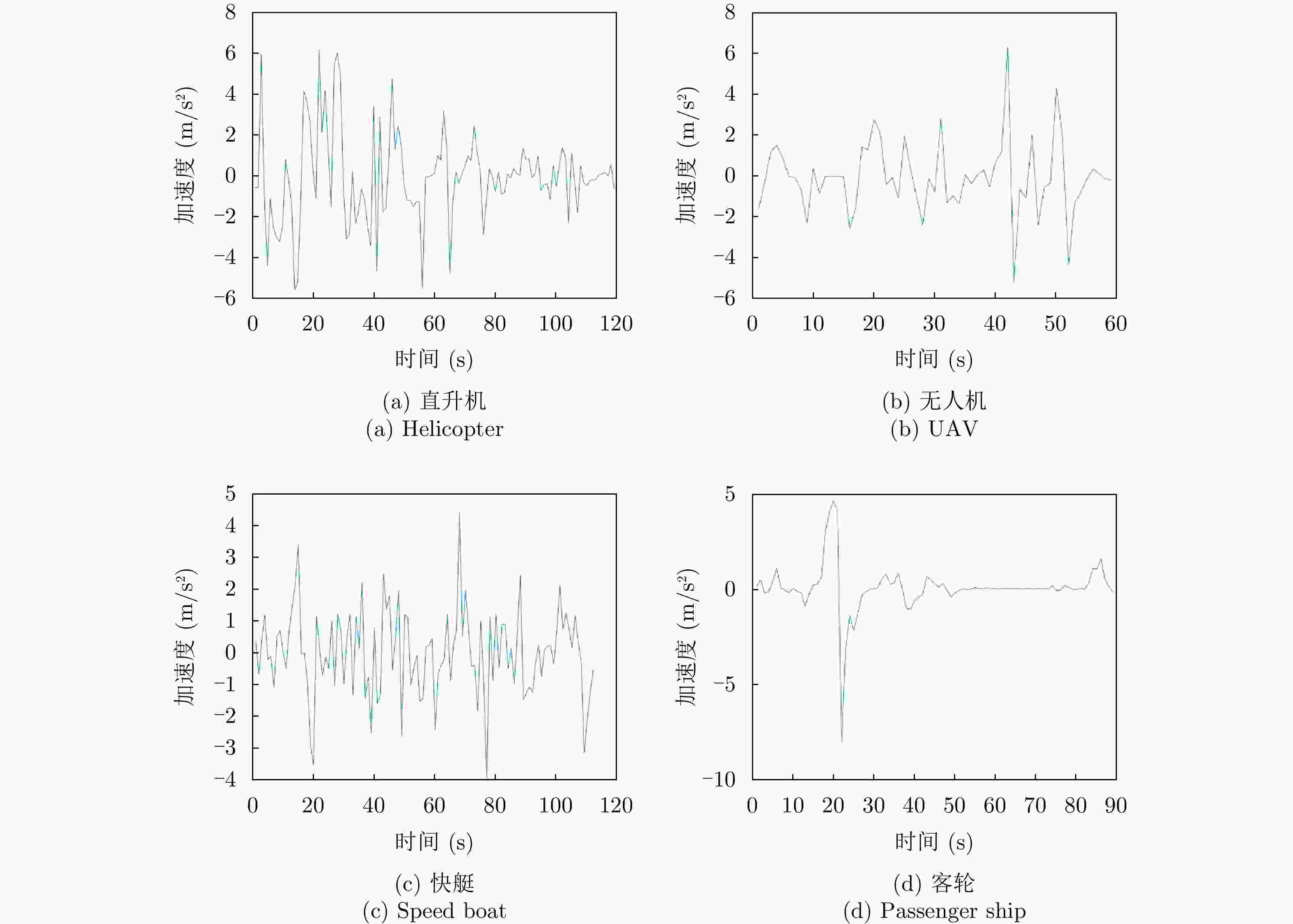
目标类型 速度变异系数 归一化加速度过零点数 直升机 0.21~0.45 0.15~0.37 无人机 0.13~0.19 0.25~0.45 快艇 0.10~0.30 0.10~0.40 客轮 0.28~0.72 0.03~0.32 表 7 海空典型目标航迹特征
Table 7. Typical target track characteristics in the sea and air
目标类型 航向差 航迹参数 直升机 2.95~13.97 0.65~0.94 无人机 7.25~13.30 0.80~0.97 快艇 6.09~13.87 0.70~0.97 客轮 9.75~14.37 0.26~0.65 表 8 被动雷达海空典型目标特征汇总
Table 8. Summary of typical target characteristics in the sea and air for passive radar
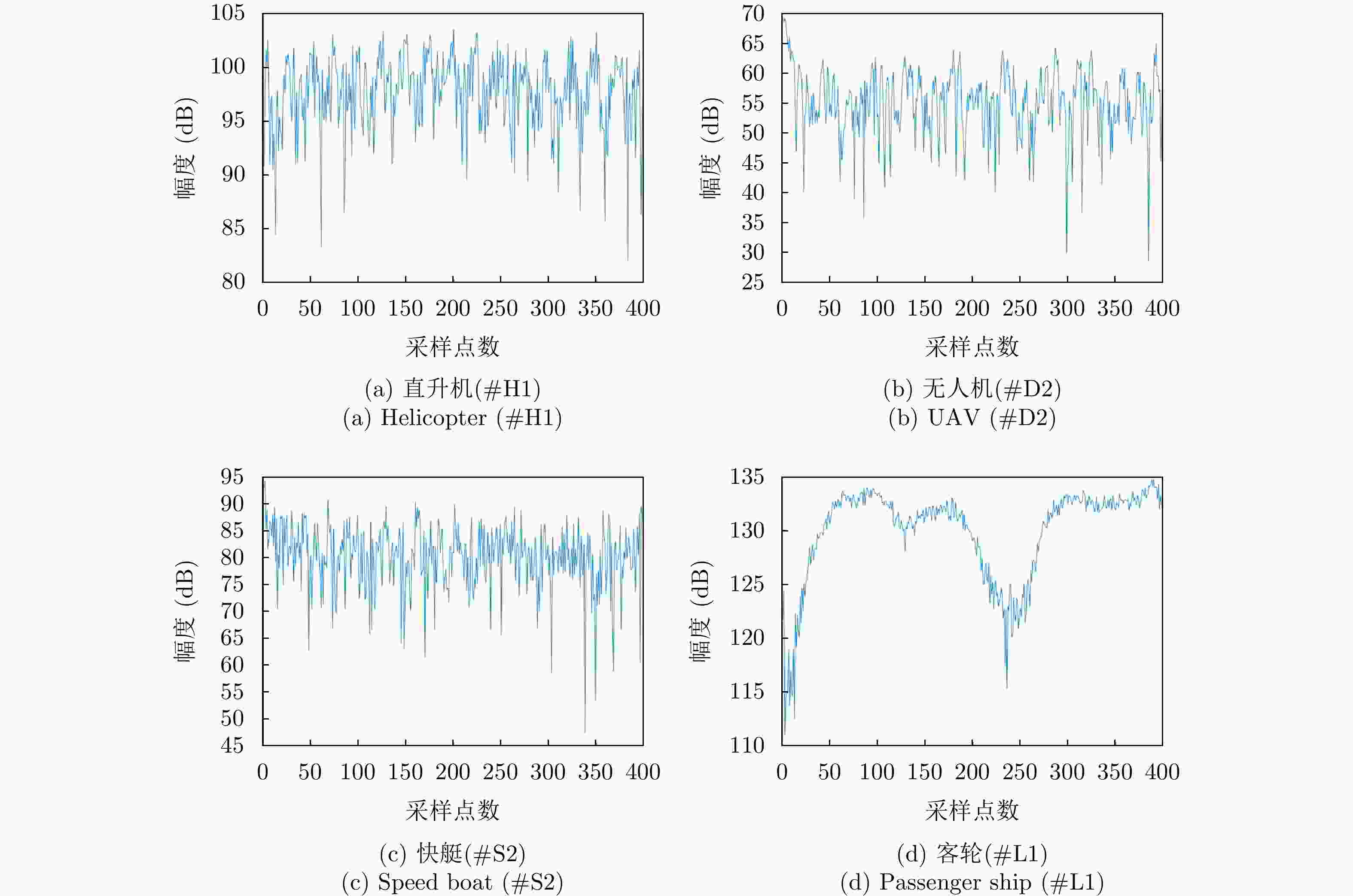
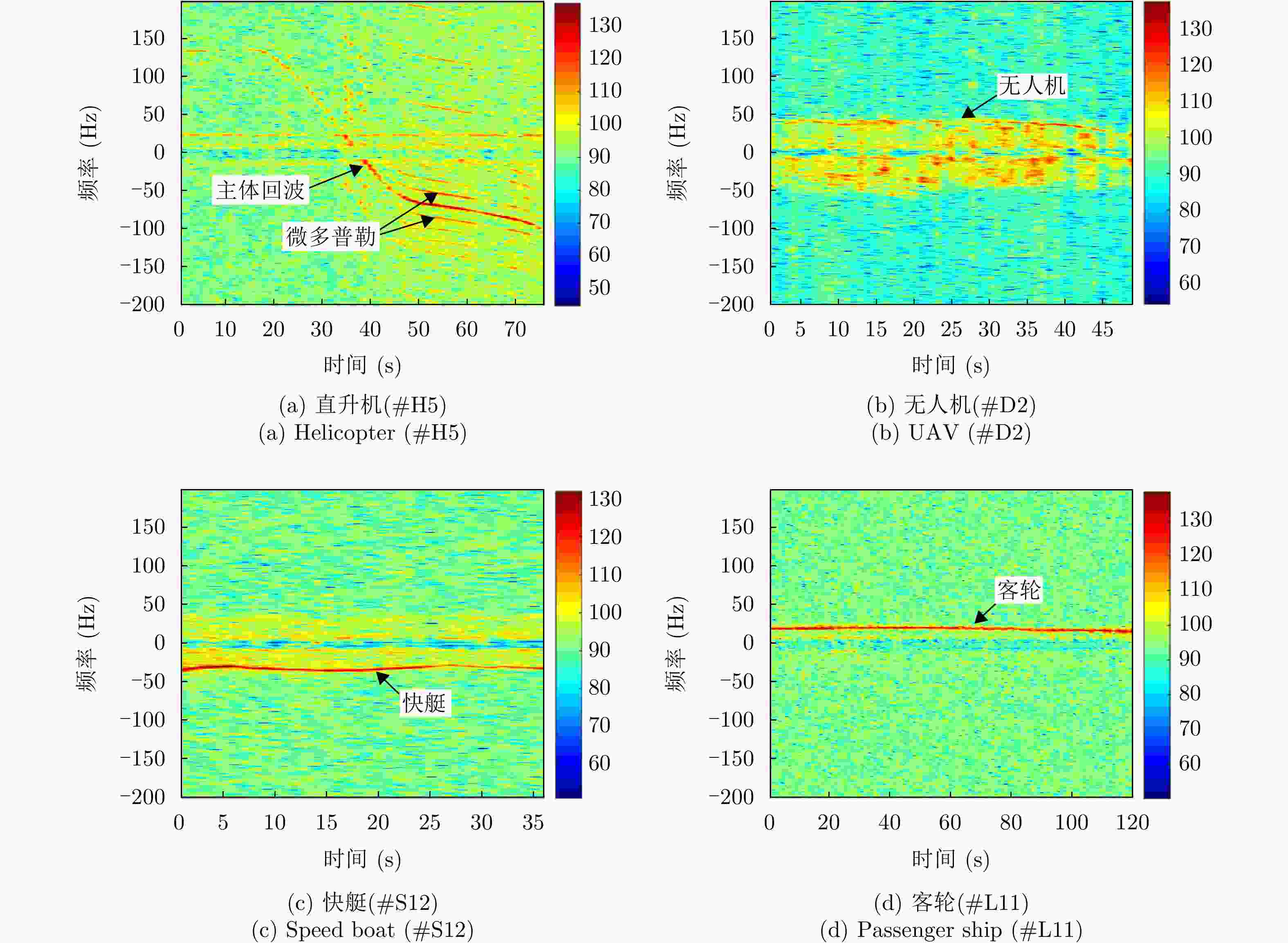
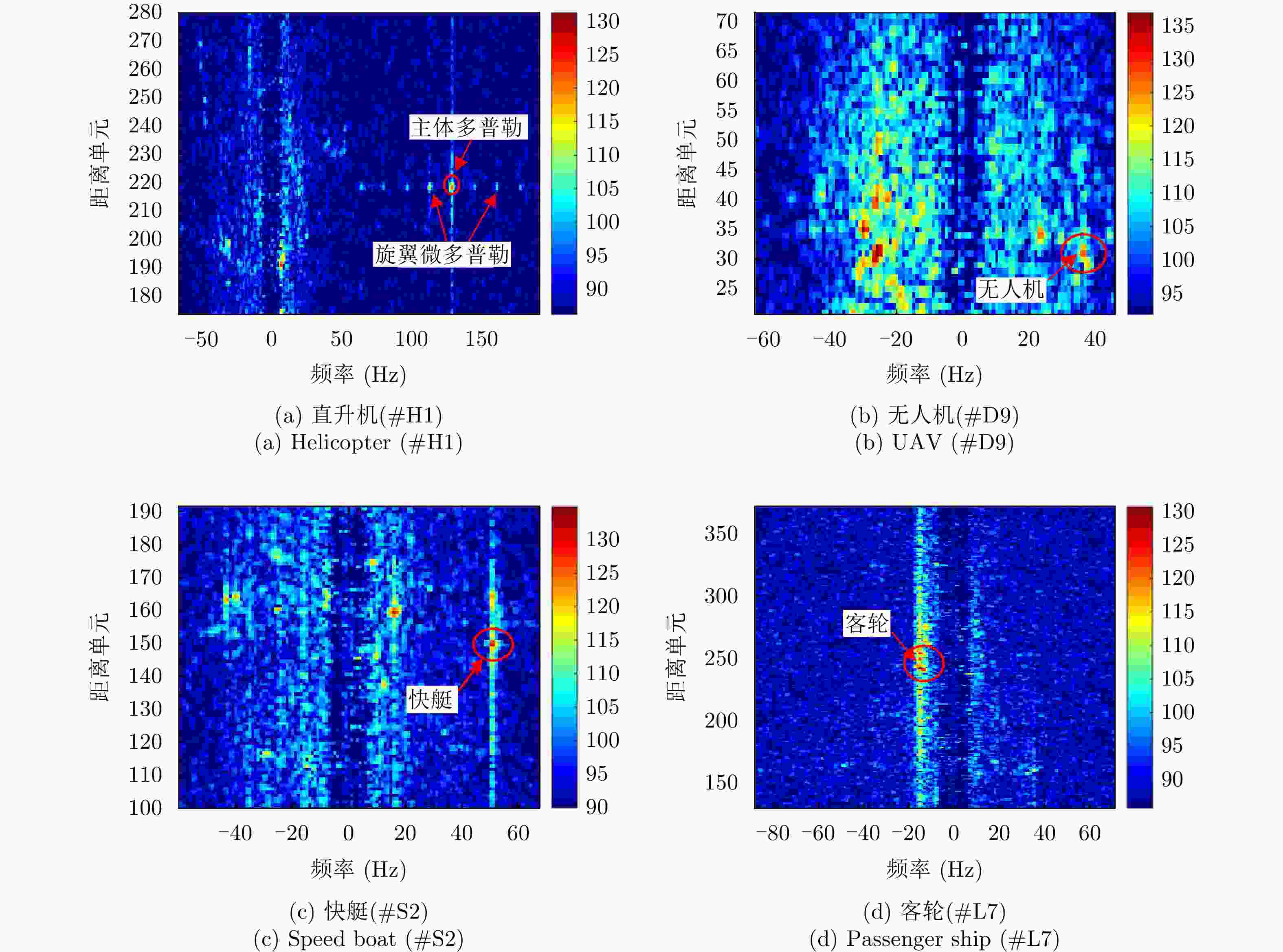
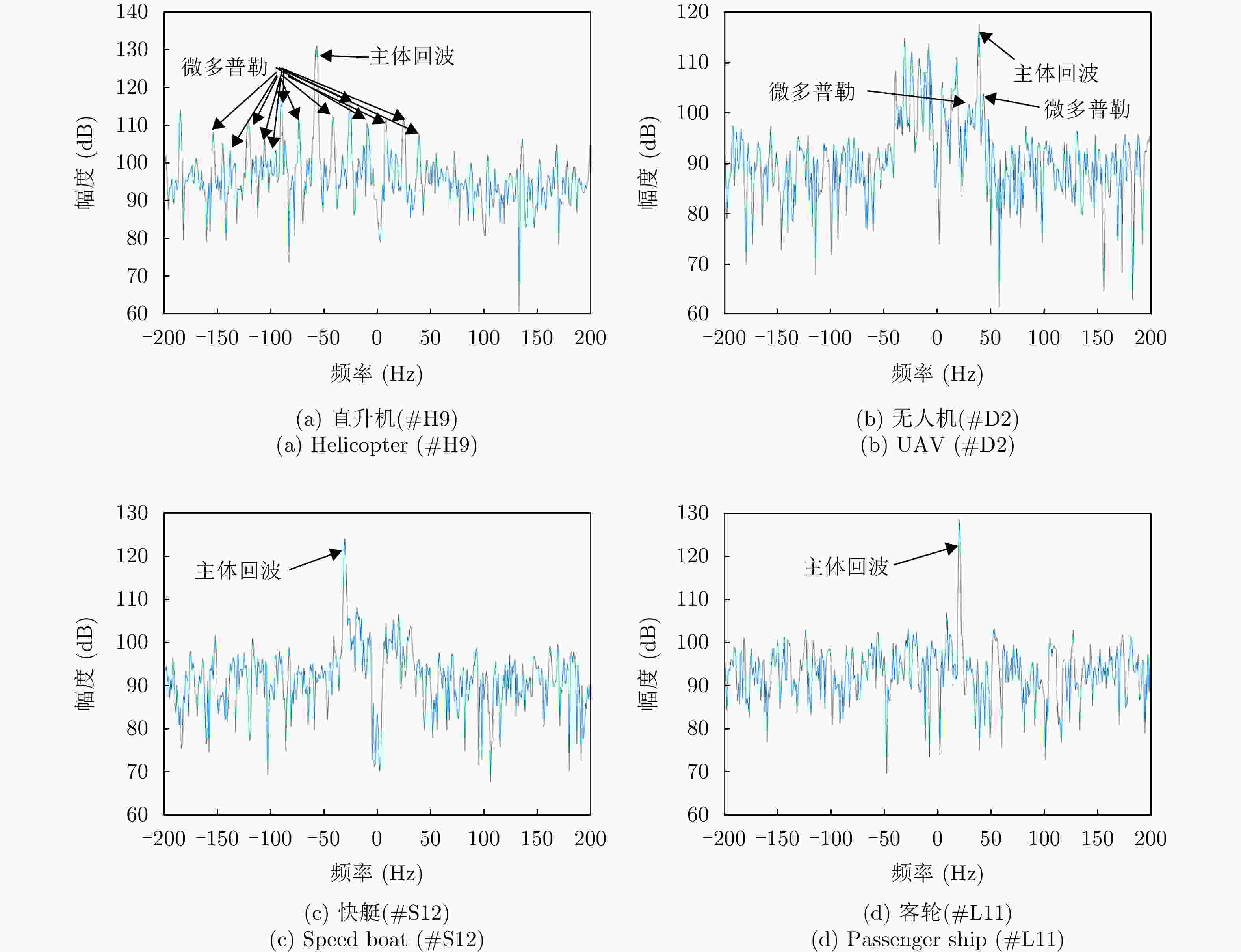
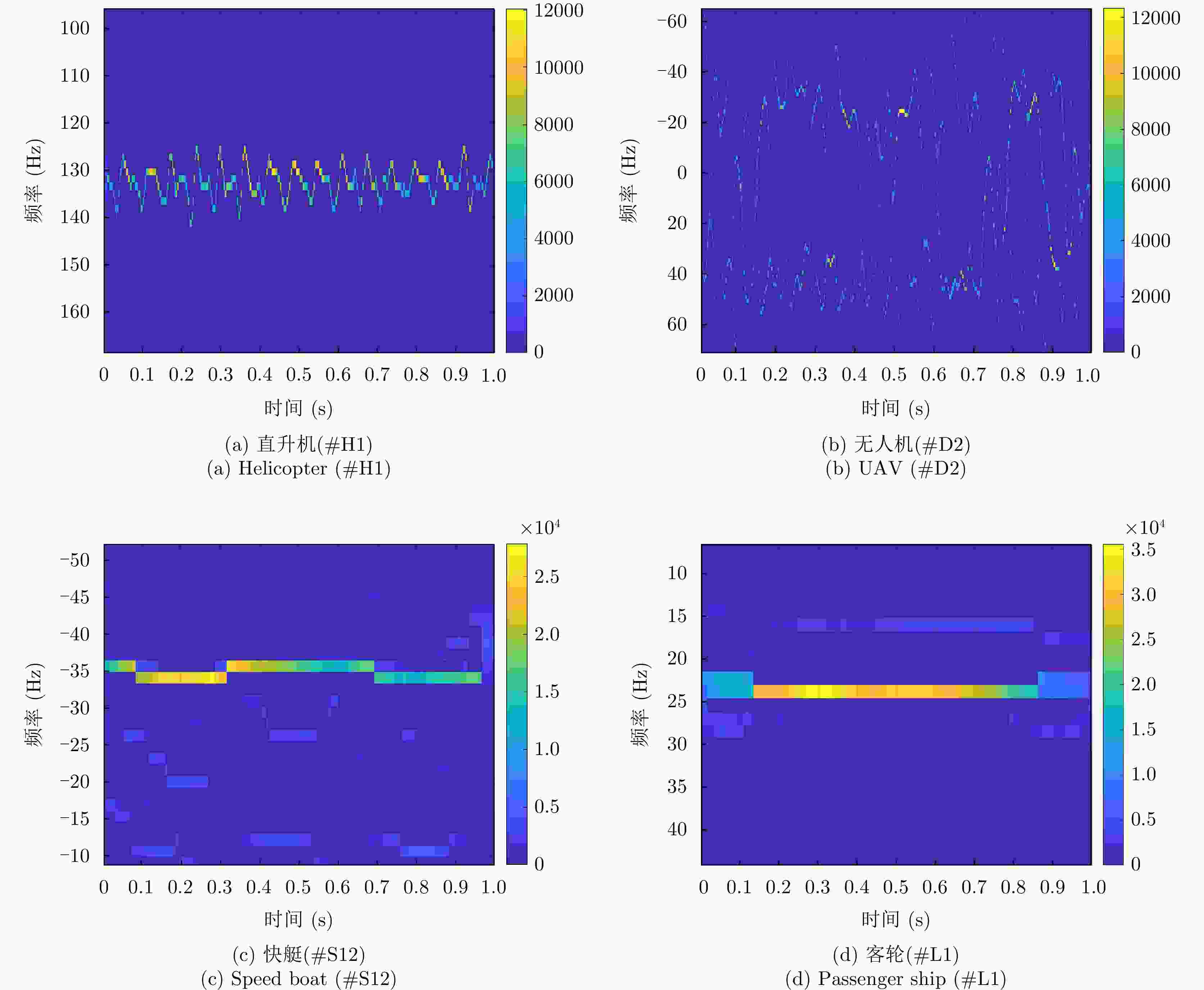
特征域 特征 结论 时域 时域回波图 直升机、客轮目标区别较大,快艇和无人机较相似 频域 多普勒瀑布图 帧间特征,表示目标的全局的特性,各目标区分度较大 距离多普勒图 直升机、无人机作为空中目标与海面有一定的高度,受海面影响小,距离扩展不明显或小,
而客轮和快艇目标受海面影响大,距离扩展明显多普勒谱图 直升机的微多普勒明显,无人机的微多普勒不明显,快艇的尖峰比客轮尖峰短且杂波影响比客轮更大 时频 时频图 直升机目标为正弦曲线,无人机目标与零频呈对称分布,能量较强的部分在正负频率交错呈现,
快艇略有曲折、杂波多,客轮为直线、杂波少运动 速度变异系数 对各目标有一定的区分能力,但有重叠部分 -
[1] 陈小龙, 南钊, 张海, 等. 飞鸟与旋翼无人机雷达微多普勒测量实验研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 2021, 36(5): 704–714. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2020192.CHEN Xiaolong, NAN Zhao, ZHANG Hai, et al. Experimental research on radar micro-Doppler of flying bird and rotor UAV[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2021, 36(5): 704–714. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2020192. [2] 陈小龙, 陈唯实, 饶云华, 等. 飞鸟与无人机目标雷达探测与识别技术进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068.CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Weishi, RAO Yunhua, et al. Progress and prospects of radar target detection and recognition technology for flying birds and unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068. [3] 何炜琨, 孙景波, 王晓亮, 等. 基于RSP-CFD方法的小型旋翼无人机微动特征提取[J]. 信号处理, 2021, 37(3): 399–408. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.03.010.HE Weikun, SUN Jingbo, WANG Xiaoliang, et al. Micro-motion feature extraction of micro-rotor UAV based on RSP-CFD method[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2021, 37(3): 399–408. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.03.010. [4] 李波, 岑宗骏, 汤俊. 一种基于信息积累的外辐射源目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 959–966. doi: 10.12000/JR20023.LI Bo, CEN Zongjun, and TANG Jun. A new method of target detection for passive radar based on information accumulation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 959–966. doi: 10.12000/JR20023. [5] 周子铂, 王彬彬, 张朝伟, 等. 基于迭代对消的外辐射源雷达目标检测方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2022, 20(5): 555–564. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.05.012.ZHOU Zibo, WANG Binbin, ZHANG Chaowei, et al. Target detection method based on iteration elimination in passive bistatic radar[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2022, 20(5): 555–564. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.05.012. [6] 苗铎, 杨东凯, 许志超, 等. GNSS外辐射源雷达低慢小目标探测概率[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(3): 657–664. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0271.MIAO Duo, YANG Dongkai, XU Zhichao, et al. Low-altitude, slow speed and small target detection probability of passive radar based on GNSS signals[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(3): 657–664. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0271. [7] 李宇倩, 易建新, 万显荣, 等. 外辐射源雷达直升机旋翼参数估计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(3): 313–319. doi: 10.12000/JR17125.LI Yuqian, YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, et al. Helicopter rotor parameter estimation method for passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 313–319. doi: 10.12000/JR17125. [8] 吴志东, 万显荣, 易建新. 外辐射源雷达探鸟实验初步研究[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2022, 23(3): 296–301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2022.03.007.WU Zhidong, WAN Xianrong, and YI Jianxin. Bird detection based on passive radar[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2022, 23(3): 296–301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2022.03.007. [9] LI Mingzhe and LI Xiaojiang. Detectability of maritime targets using passive radar based on satellite-borne illuminators[C]. 2019 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET), Chengdu, China, 2019: 273–276. doi: 10.1109/ELTECH.2019.8839324. [10] 谭文清, 宋杰, 庄敬敏, 等. 被动雷达海上目标探测实验研究[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2024, 22(1): 87–92, 103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2024.01.012.TAN Wenqing, SONG Jie, ZHUANG Jingmin, et al. Experimental study on maritime target detection of passive radar[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2024, 22(1): 87–92, 103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2024.01.012. [11] 王文兵, 李华, 梁龙. 基于微多普勒特征的外辐射源雷达目标识别方法[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2018, 33(5): 20–25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2018.05.005.WANG Wenbing, LI Hua, and LIANG Long. Identification of target in passive radar based on micro-Doppler features[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2018, 33(5): 20–25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2018.05.005. [12] 梁文斌, 谢跃雷. 多频段外辐射源无人机检测实验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(28): 12128–12135. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.28.12128.LIANG Wenbin and XIE Yuelei. Experimental research on multi-frequency external emitter UAV detection[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(28): 12128–12135. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.28.12128. [13] 施赛楠, 杨静, 王杰. 基于多域多维特征融合的海面小目标检测[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(12): 2099–2106. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.016.SHI Sainan, YANG Jing, and WANG Jie. Detection of sea-surface small target based on multi-domain and multi-dimensional feature fusion[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 2099–2106. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.016. [14] 邓振华, 陈小龙, 薛伟, 等. 海空背景下低慢小目标泛探雷达多域多维特征建模与分析[J]. 信号处理, 2024, 40(5): 801–814. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.05.001.DENG Zhenhua, CHEN Xiaolong, XUE Wei, et al. Multi-domain and multi-dimensional feature modeling and analysis of low, slow, and small targets via ubiquitous radar under sea and air background[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(5): 801–814. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.05.001. [15] 陈小龙, 袁旺, 杜晓林, 等. 多波段FMCW雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-FMCWR-1.0)及高分辨微动特征提取方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142.CHEN Xiaolong, YUAN Wang, DU Xiaolin, et al. Multiband FMCW radar LSS-target detection dataset (LSS-FMCWR-1.0) and high-resolution micromotion feature extraction method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142. [16] 万显荣, 易建新, 占伟杰, 等. 基于多照射源的被动雷达研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 939–958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143.WAN Xianrong, YI Jianxin, ZHAN Weijie, et al. Research progress and development trend of the multi-illuminator-based passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 939–958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143. [17] 支双双. 双基地雷达两种目标定位方法误差分析与仿真[J]. 西安工程大学学报, 2015, 29(2): 209–214. doi: 10.13338/j.issn.1674-649x.2015.02.015.ZHI Shuangshuang. Error analysis and simulation of two target location methods for bistatic radar[J]. Journal of Xi’an Polytechnic University, 2015, 29(2): 209–214. doi: 10.13338/j.issn.1674-649x.2015.02.015. [18] 陈志猛, 左燕, 王文光. 误差校正下外辐射雷达无源定位算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(3): 42–47. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.03.009.CHEN Zhimeng, ZUO Yan, and WANG Wenguang. Passive radar localization algorithm with bias registration[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(3): 42–47. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.03.009. [19] YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, CHENG Feng, et al. Deghosting for target tracking in single frequency network based passive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(4): 2655–2668. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.130424. [20] POON M W Y, KHAN R H, and LE-NGOC S. A singular value decomposition (SVD) based method for suppressing ocean clutter in high frequency radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1993, 41(3): 1421–1425. doi: 10.1109/78.205747. [21] 赵学智, 叶邦彦. 分量形成方式对奇异值分解信号处理效果的影响[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2011, 45(3): 368–374. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2011.03.015.ZHAO Xuezhi and YE Bangyan. The influence of formation manner of component on signal processing effect of singular value decomposition[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2011, 45(3): 368–374. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2011.03.015. [22] 丁昊, 朱晨光, 刘宁波, 等. 高海况条件下海面漂浮小目标特征提取与分析[J]. 海军航空大学学报, 2023, 38(4): 301–312. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2023.04.001.DING Hao, ZHU Chenguang, LIU Ningbo, et al. Feature extraction and analysis of small floating targets in high sea conditions[J]. Journal of Naval Aviation University, 2023, 38(4): 301–312. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2023.04.001. [23] YU Gang, WANG Zhonghua, and ZHAO Ping. Multisynchrosqueezing transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(7): 5441–5455. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2868296. [24] 张冰, 姜培刚, 林天然. 基于MSST和双通道CNN技术的变转速轴承故障诊断研究[J]. 机电工程, 2021, 38(9): 1145–1151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2021.09.009.ZHANG Bing, JIANG Peigang, and LIN Tianran. Varying speed bearing fault diagnosis based on MSST and two-channel CNN technique[J]. Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, 2021, 38(9): 1145–1151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2021.09.009. [25] VORONOVICH A G and ZAVOROTNY V U. Bistatic radar equation for signals of opportunity revisited[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 1959–1968. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2771253. [26] 陈小龙, 何肖阳, 邓振华, 等. 雷达微弱目标智能化处理技术与应用[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 501–524. doi: 10.12000/JR23160.CHEN Xiaolong, HE Xiaoyang, DENG Zhenhua, et al. Radar intelligent processing technology and application for weak target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 501–524. doi: 10.12000/JR23160. [27] LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, HAO Chengpeng, et al. Multichannel adaptive signal detection: Basic theory and literature review[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(2): 121301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3211-8. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: