Mainlobe Blanket Interference Suppression with PEPC-MIMO Radar via Low-rank Matrix Decomposition
-
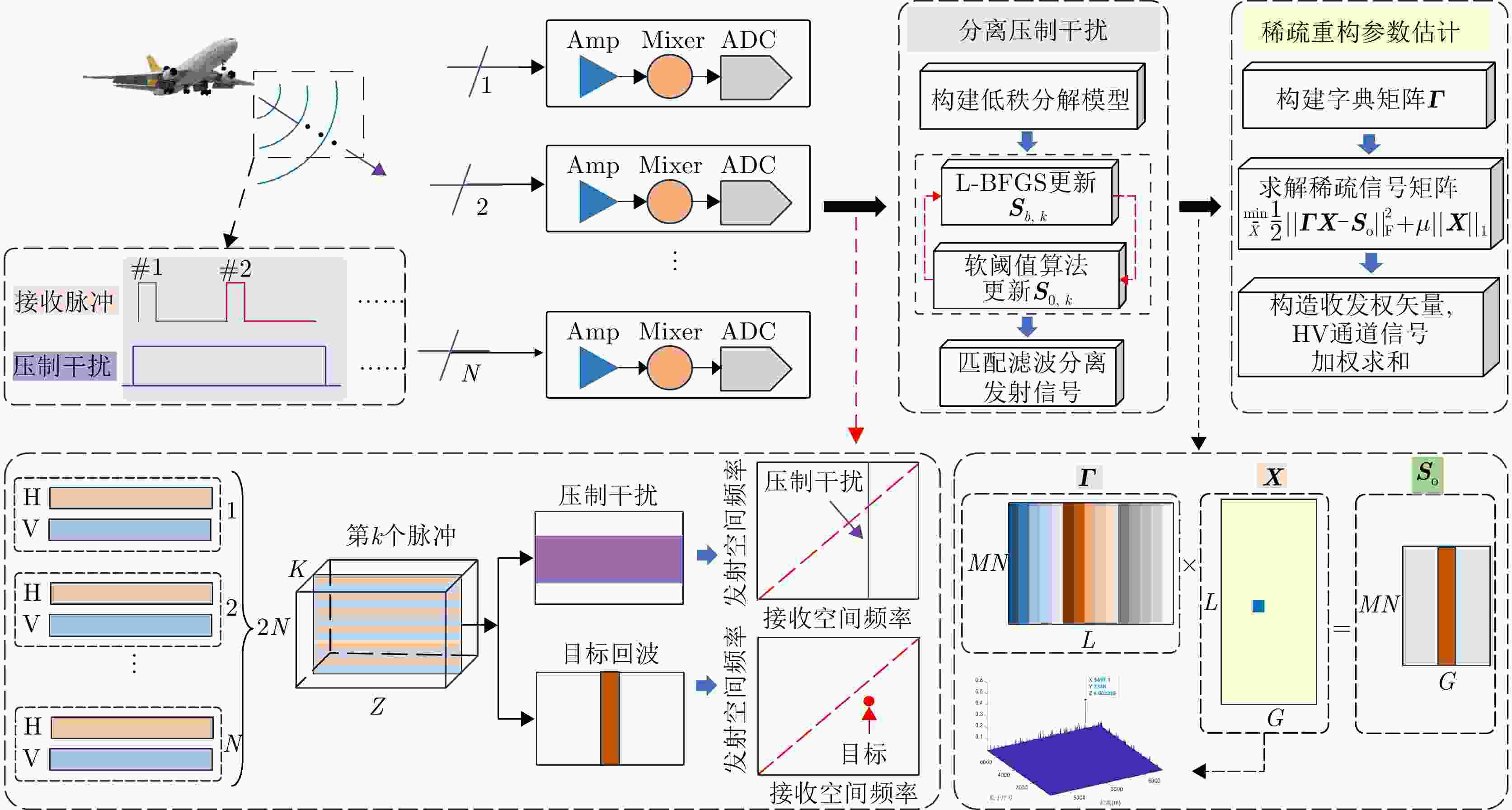
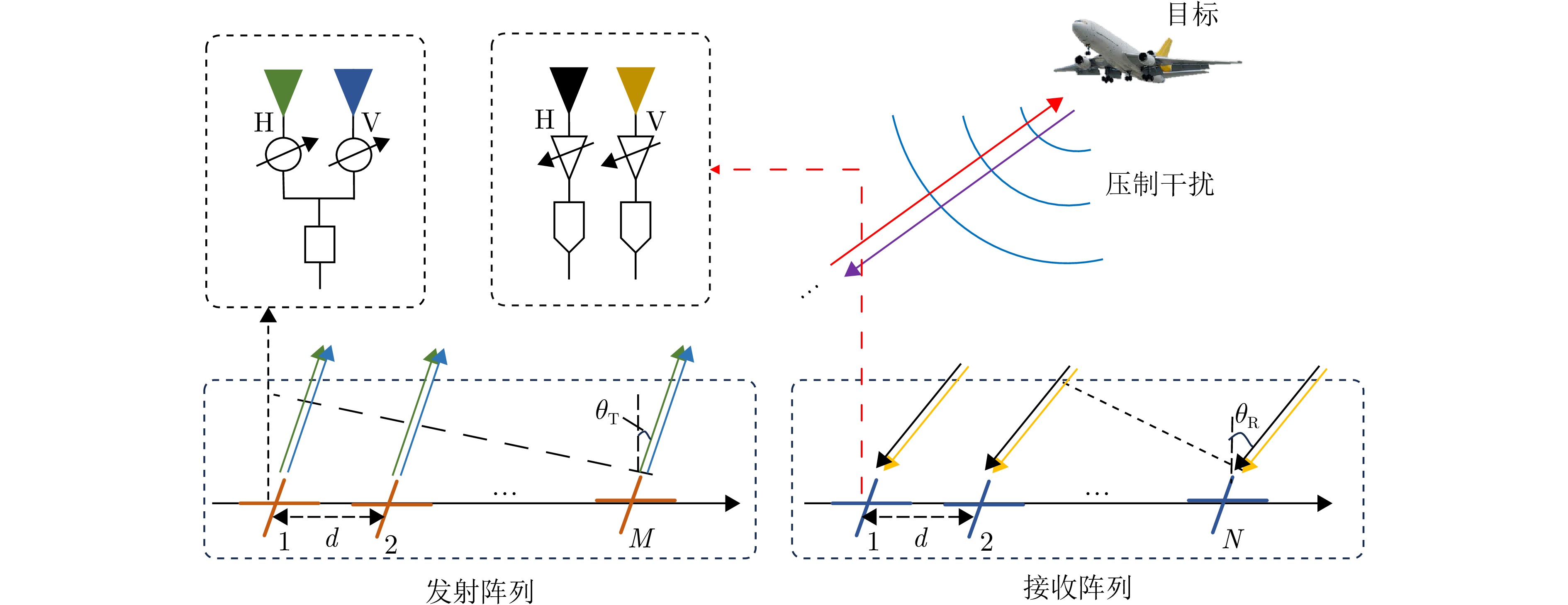
摘要: 阵元-脉冲编码( EPC-MIMO)雷达通过在发射阵元和脉冲间引入相位编码,可实现主瓣欺骗干扰抑制,但仍然无法应对主瓣压制干扰的威胁。对此,该文在EPC-MIMO雷达中加入极化调制,研究了极化阵元-脉冲编码(PEPC-MIMO)雷达体制下的主瓣压制干扰抑制方法。具体而言,基于主值成分追踪(SPCP)分解框架,利用压制干扰在空间-极化联合域的低秩特性,将主瓣压制干扰抑制问题转化为一个“低秩+稀疏”模型的优化问题。随后,利用L-BFGS-AO算法进行迭代求解,实现目标回波和主瓣压制干扰的精准分离。进一步地,提出了一种基于稀疏重构的PEPC-MIMO雷达参数估计方法用于估计目标回波信号的发射角度、接收角度以及目标距离模糊区,从而构造最优的波束形成权矢量对各通道信号进行加权求和。仿真实验验证了所提方法在无先验知识前提下抑制主瓣压制干扰方面的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 极化阵元-脉冲编码雷达 /
- 主瓣压制干扰抑制 /
- 矩阵低秩分解 /
- 稀疏重构 /
- 参数估计
Abstract: By applying phase coding in transmit elements and pulses, the Element-Pulse Coding Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (EPC-MIMO) radar can effectively suppress mainlobe deceptive interference. However, this approach remains ineffective against mainlobe blanket interference. To address this drawback, this paper investigates the mainlobe blanket interference suppression using a Polarization Element-Pulse Coding Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (PEPC-MIMO) radar system. Specifically, within the framework of stable principal component pursuit decomposition, the interference suppression problem is formulated as a “low-rank + sparse” optimization model by exploiting the low-rank structure of the received signal in the joint time-space-polarization domain. The resulting optimization problem is solved iteratively using a Limited-memory Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno-based Alternating Optimization (L-BFGS-AO) algorithm, thereby enabling accurate separation of target echoes from mainlobe blanket interference. Furthermore, a sparse reconstruction-based parameter estimation method is proposed to estimate the target’s transmit angle, receive angle, and range ambiguity region. These estimates are then used to construct optimal receive weight vectors for the weighted summation of signals across channels. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in suppressing mainlobe blanket interference without requiring prior knowledge of the interference. -
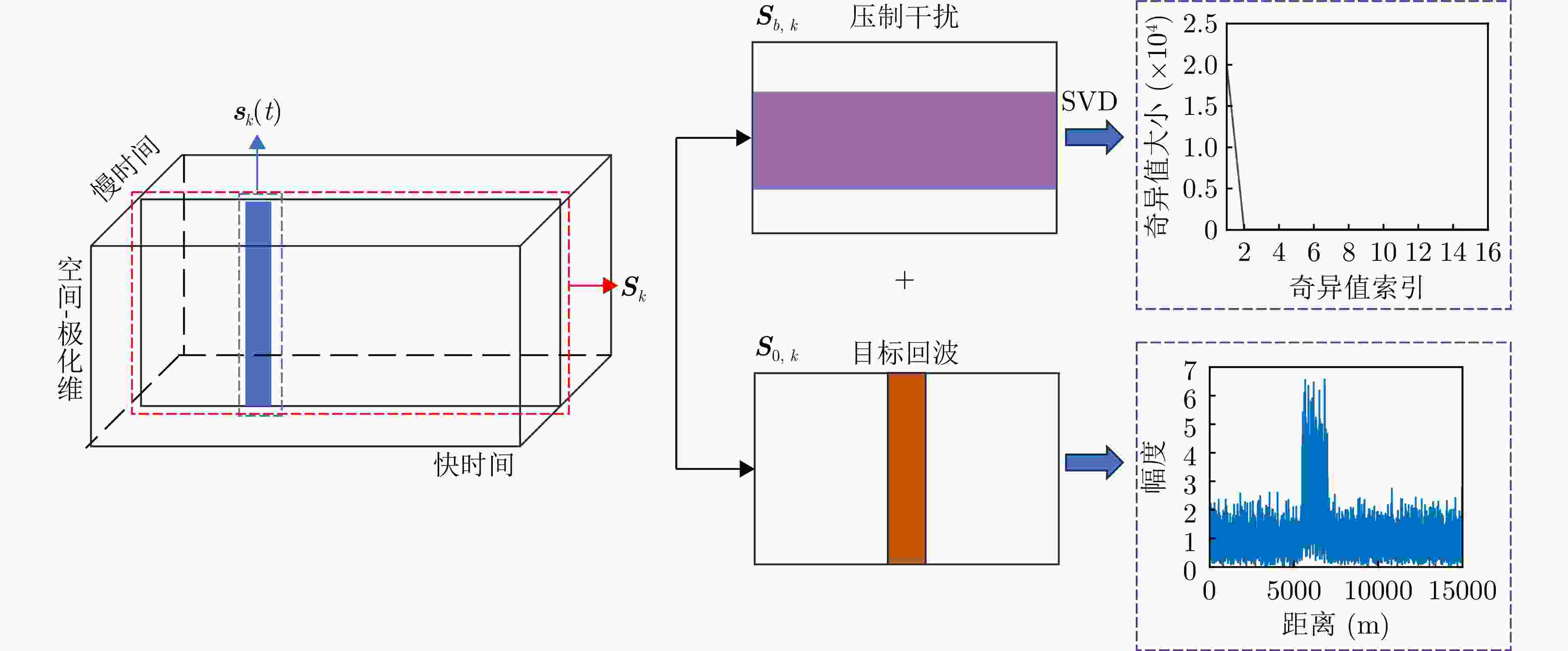
1 基于L-BFGS-AO的主瓣压制干扰分离算法
1. Separation of blanket interference suppression based on L-BFGS-AO algorithm
输入:第k个脉冲接收信号$ {\boldsymbol{S}}_{k} $, $ {c}_{1} $, $ {c}_{2} $, $ \delta $ 初始化:$ i=1 $, $ \boldsymbol{R}_{k}^{(i)} $, $ \boldsymbol{V}_{k}^{(i)} $, $ \boldsymbol{S}_{0,k}^{(i)} $,U,最大迭代次数I while $ i\text{ < }I $ 1. 计算梯度$ \nabla \boldsymbol{R}_{k}^{(i)} $, $ \nabla \boldsymbol{V}_{k}^{(i)} $; 2. 将变量和梯度分别矢量化,得到$ \boldsymbol{r}_{k}^{(i)} $和$ \nabla \boldsymbol{f}_{k}^{(i)} $,并计算变量
增量$ \boldsymbol{c}_{k}^{(i-1)} $和梯度增量$ \boldsymbol{y}_{k}^{(i-1)} $;3. 初始化$ {\boldsymbol{a}}^{(i-1)}=\nabla \boldsymbol{f}_{k}^{(i)} $,若$ i\leq \text{U} $,令$ {U}_{0}=i $,否则令
$ {U}_{0}=U $;4. for $ u=(i-1)\colon (i-{U}_{0}) $ 5. $ {\eta }_{u}={\left(\boldsymbol{c}_{k}^{(u)}\right)}^{\text{T}}{\boldsymbol{a}}^{(u)}/{\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{k}^{(u)}\right)}^{\text{T}}\boldsymbol{c}_{k}^{(u)} $; 6. $ {\boldsymbol{a}}^{(u-1)}={\boldsymbol{a}}^{(u)}-{\eta }_{u}\boldsymbol{y}_{k}^{(u)} $; 7. end 8. $ {\boldsymbol{b}}^{(i-{{U}_{0}})}={\boldsymbol{a}}^{(u-1)} $ 9. for $ u=(i-{U}_{0})\colon (i-1) $ 10. $ {\beta }_{u}={\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{k}^{(u)}\right)}^{\text{T}}{\boldsymbol{b}}^{(u)}/{\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{k}^{(u)}\right)}^{\text{T}}\boldsymbol{c}_{k}^{(u)} $; 11. $ {\boldsymbol{b}}^{(u+1)}={\boldsymbol{b}}^{(u)}+\boldsymbol{c}_{k}^{(u)}\left({\eta }_{u}-{\beta }_{u}\right) $; 12. end 13. $ \boldsymbol{d}_{k}^{(i)}=-{\boldsymbol{b}}^{(u+1)} $; 14. 更新$ \boldsymbol{r}_{k}^{(i+1)} = \boldsymbol{r}_{k}^{(i)} + \alpha _{k}^{(i)}\boldsymbol{d}_{k}^{(i)} $,计算得到$ \boldsymbol{R}_{k}^{(i+1)} $和$ \boldsymbol{V}_{k}^{(i+1)} $; 15. 计算
$ \boldsymbol{S}_{0,k}^{(i+1)}=\text{sign}\left(\boldsymbol{Z}_{k}^{(i+1)}\right)\odot \max \left(\left| \boldsymbol{Z}_{k}^{(i+1)}\right| -\dfrac{{\lambda }_{\text{s}}}{2},0\right) $;16. if $ \left| f\left(\boldsymbol{R}_{k}^{(i+1)},\boldsymbol{V}_{k}^{(i+1)},\boldsymbol{S}_{0,k}^{(i+1)}\right)- f\left(\boldsymbol{R}_{k}^{(i)},\boldsymbol{V}_{k}^{(i)},\boldsymbol{S}_{0,k}^{(i)}\right)\right| $
$ \leq \delta $ then17. 令$ \boldsymbol{S}_{0,k}^{(\ast )}=\boldsymbol{S}_{0,k}^{(i)} $,停止迭代; 18. end 19.$ i=i+1 $; end while 输出:$ \boldsymbol{S}_{0,k}^{(\ast )} $ 表 1 PEPC-MIMO雷达系统仿真参数
Table 1. System parameters of PEPC-MIMO radar
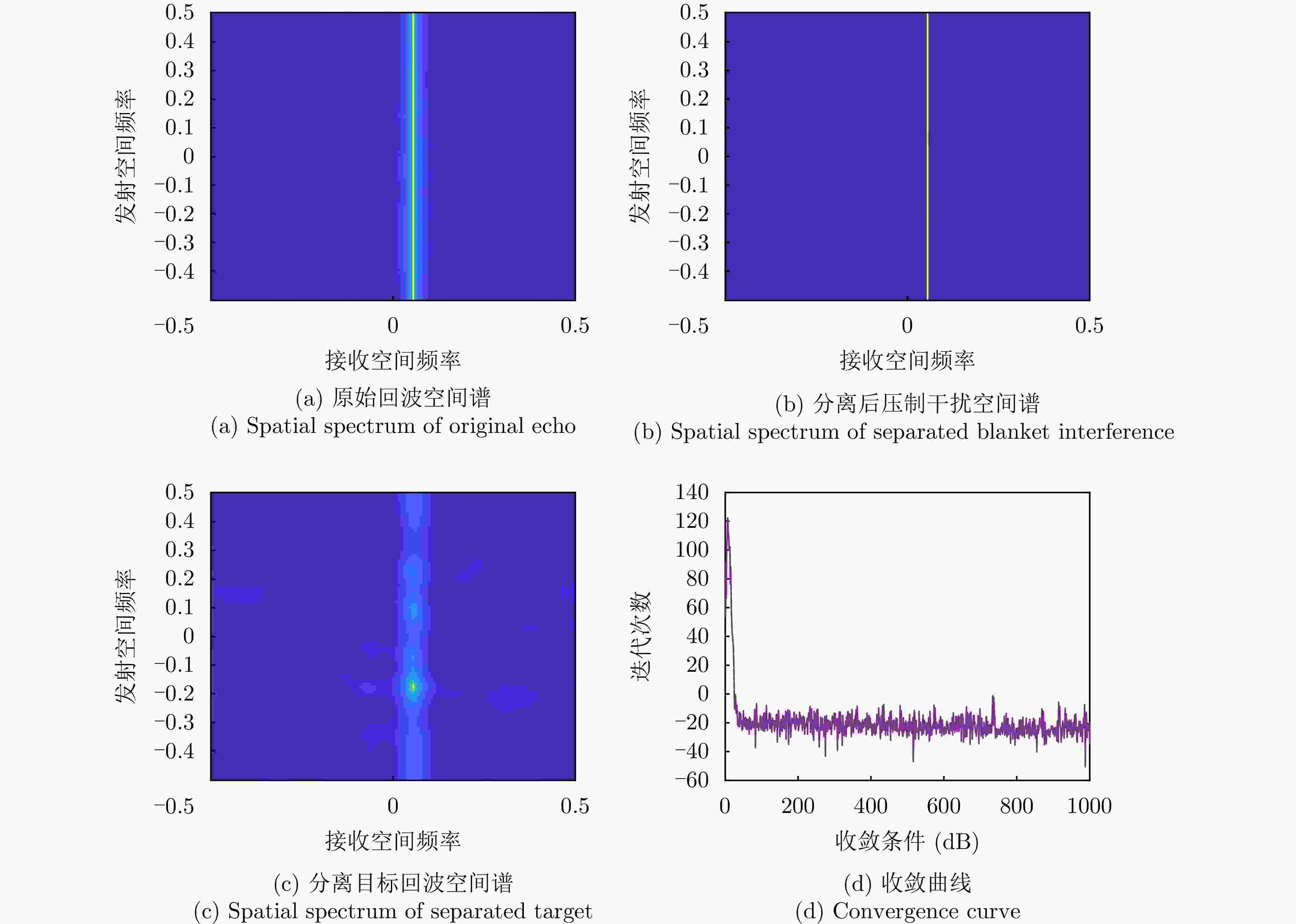
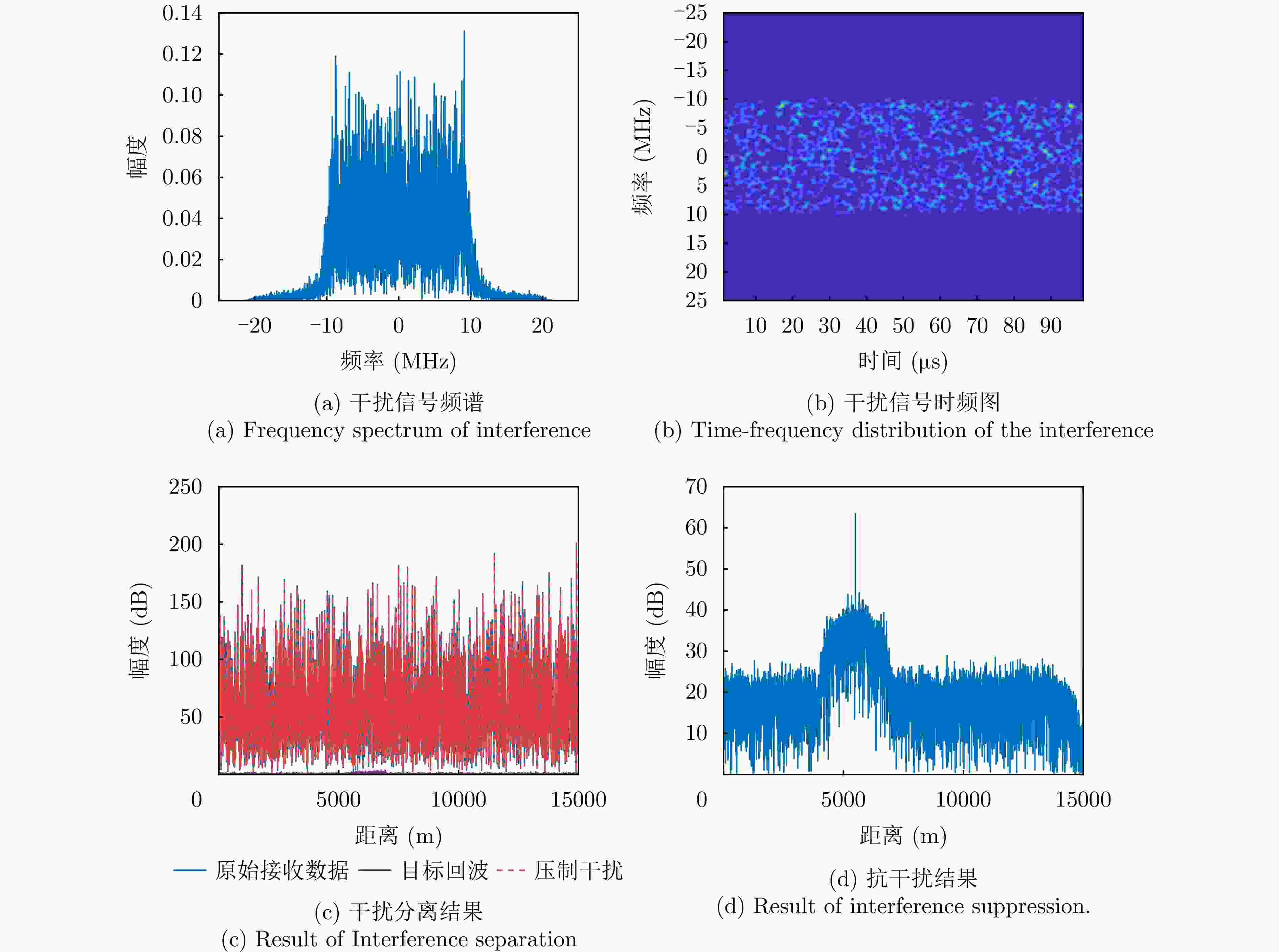
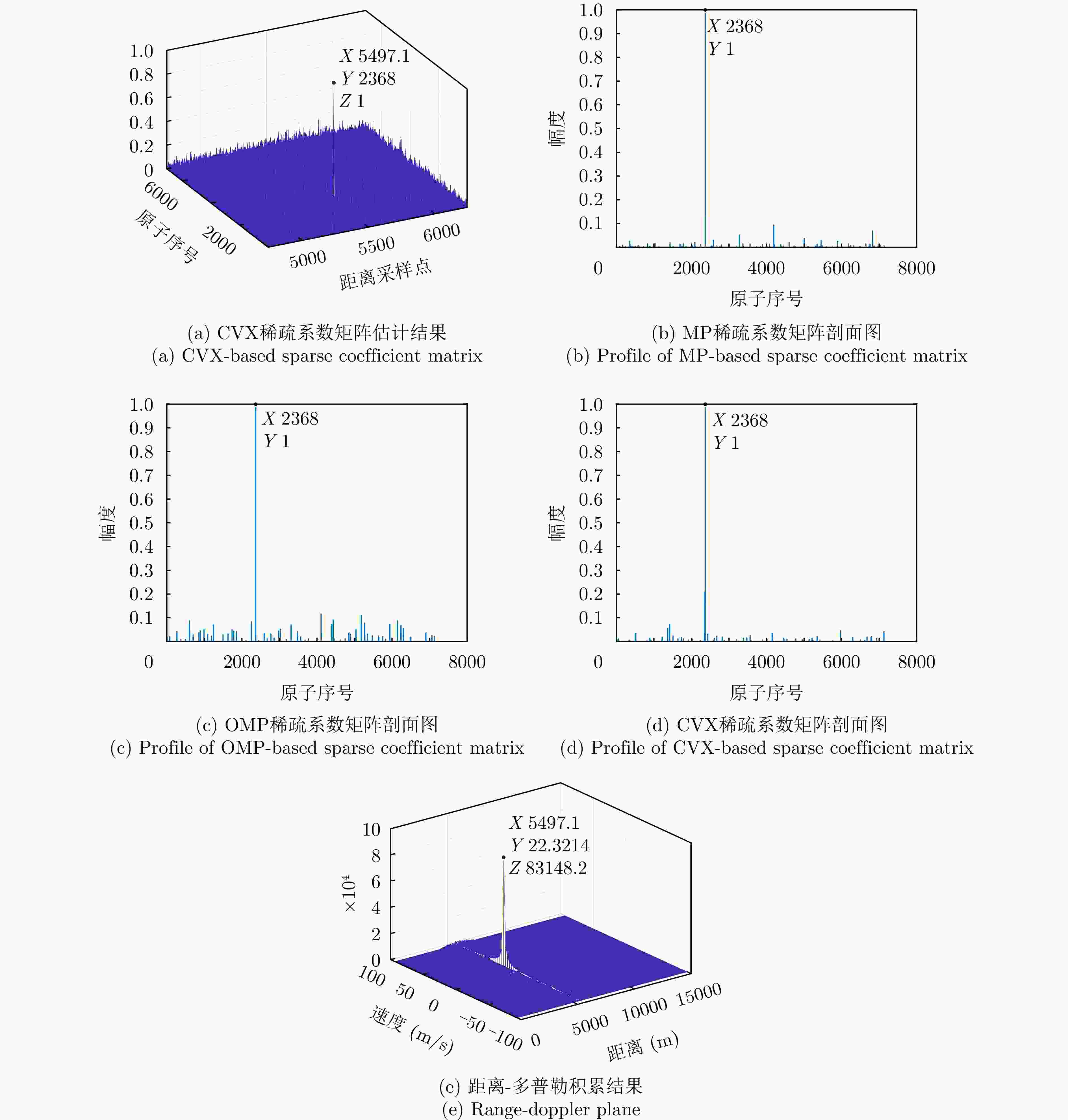
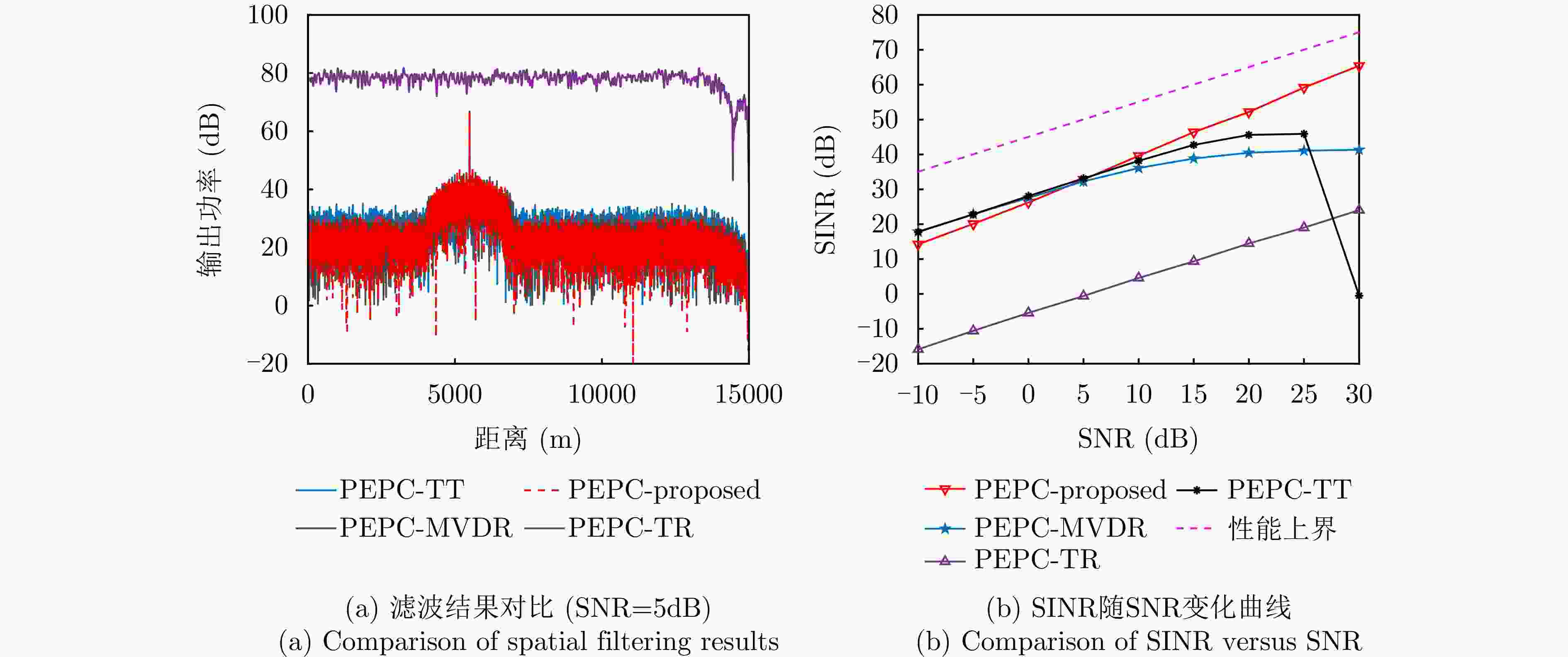
参数 数值 参数 数值 发射阵元数M 8 接收阵元数N 8 载频$ {f}_{0} $ 8 GHz 脉冲重复频率$ {f}_{{\mathrm{r}}} $ 10 kHz 脉冲数K 64 发射编码系数$ \gamma $ 0.125 采样率 50 MHz 脉宽$ {T}_{{\mathrm{p}}} $ 10 μs 表 2 目标干扰仿真参数
Table 2. Parameters of true and false targets
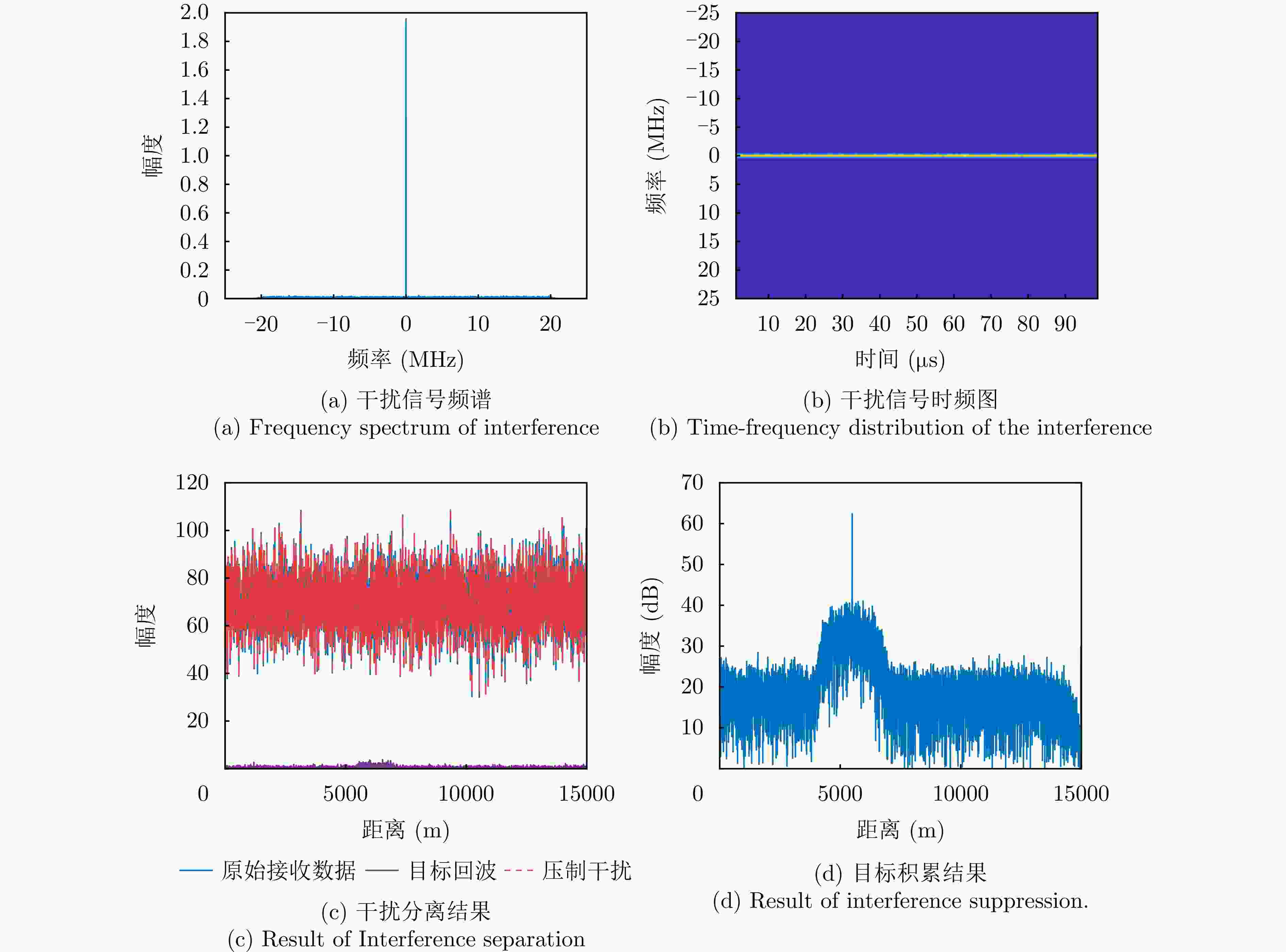
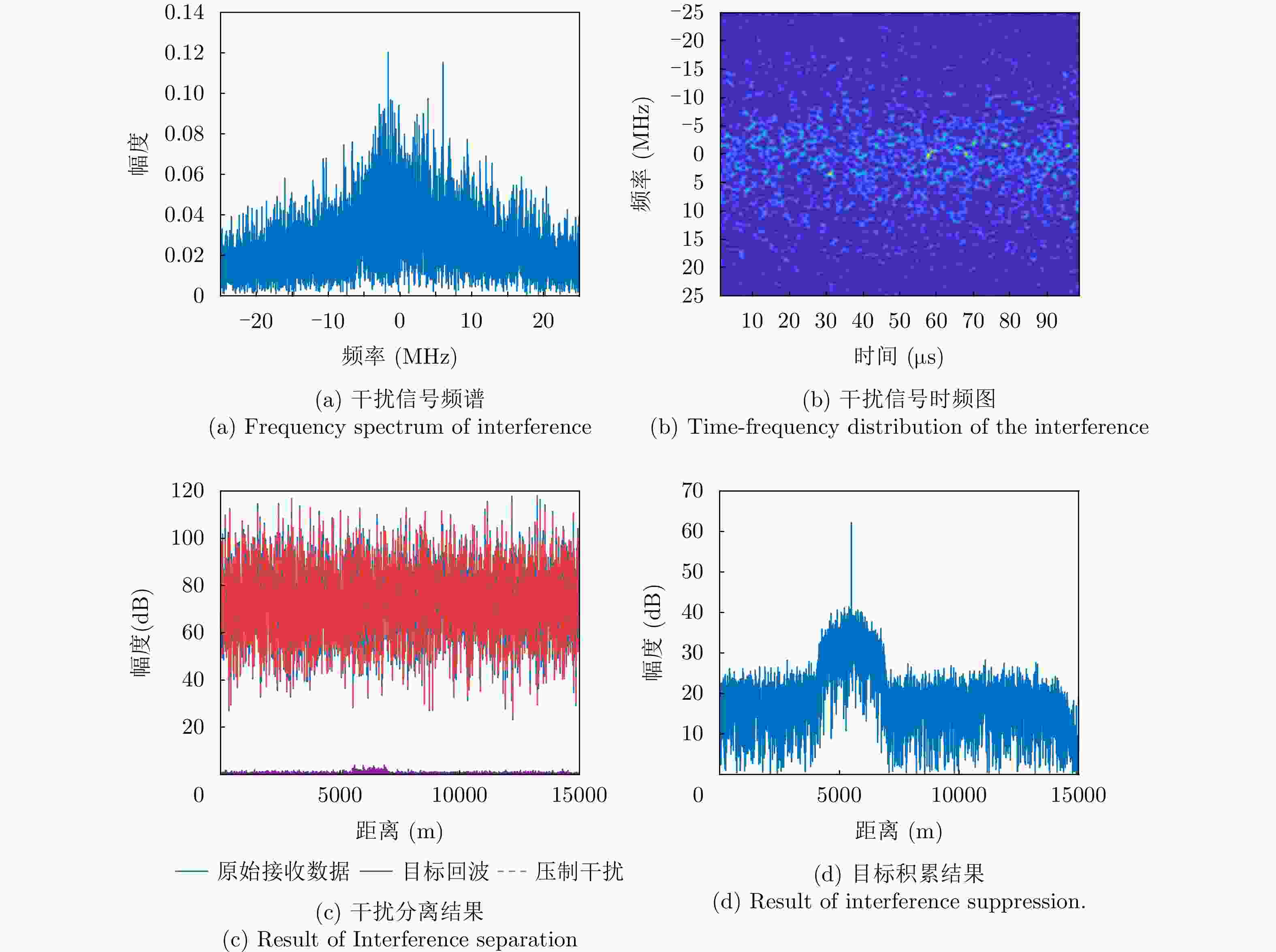
参数 目标 主瓣压制干扰 发射角度(°) 13 \ 接收角度(°) 10 10 SNR/JNR (dB) 5 40 目标速度(m/s) 20 \ 主值距离(km) 5.5 \ 脉冲延迟数 3 \ 极化参数$ \left(\vartheta ,{\gamma }_{{\mathrm{s}}}\right) $ (60°, 45°) (45°, 0) -
[1] SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Radar maritime target detection via spatial-temporal feature attention graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5102615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3358862. [2] HE Xiaoyang, CHEN Xiaolong, DU Xiaolin, et al. Maritime target radar detection and tracking via DTNet transfer learning using multi-frame images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(5): 836. doi: 10.3390/rs17050836. [3] YE Xinzhe, XUE Wei, CHEN Xiaolong, et al. Cauchy kernel-based AEKF for UAV target tracking via digital ubiquitous radar under the sea-air background[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3506605. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3402687. [4] ZHAO Haonan, ZHANG Zhimin, QIAO Kai, et al. Demonstration of MIMO-SAR echo separation scheme for improved OFDM waveforms with airborne X-band DBF-SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4015205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3449391. [5] WEI Tiantian, ZHANG Yongwei, LU Pingping, et al. An improved echo separation scheme with OFDM chirp waveforms for spaceborne MIMO SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4002805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3356729. [6] 全英汇, 方文, 沙明辉, 等. 频率捷变雷达波形对抗技术现状与展望[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(11): 3126–3136. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.11.QUAN Yinghui, FANG Wen, SHA Minghui, et al. Present situation and prospects of frequency agility radar wave form countermeasures[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3126–3136. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.11. [7] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 魏文强, 等. 认知智能雷达抗干扰技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191.CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, WEI Wenqiang, et al. An overview of antijamming methods and future works on cognitive intelligent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191. [8] 孟昊宇, 杨小鹏, 高升, 等. 基于特征值斜投影的主瓣干扰抑制方法[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(2): 439–444. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.02.025.MENG Haoyu, YANG Xiaopeng, GAO Sheng, et al. Main lobe interference suppression method based on eigenvalue oblique projection[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(2): 439–444. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.02.025. [9] 王荣清, 谢旌阳, 田彪, 等. 联合干扰感知与参数估计的抗间歇采样转发干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(6): 1337–1354. doi: 10.12000/JR24153.WANG Rongqing, XIE Jingyang, TIAN Biao, et al. Integrated jamming perception and parameter estimation method for anti-interrupted sampling repeater jamming[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(6): 1337–1354. doi: 10.12000/JR24153. [10] 张孟达, 余颖菲. 一种改进的盲源分离抗主瓣干扰方法[J]. 火控雷达技术, 2024, 53(3): 34–38. doi: 10.19472/j.cnki.1008-8652.2024.03.006.ZHANG Mengda and YU Yingfei. An improved method for jamming supression based on blind source separation[J]. Fire Control Radar Technology, 2024, 53(3): 34–38. doi: 10.19472/j.cnki.1008-8652.2024.03.006. [11] ZHANG Shiyuan, LU Xingyu, YU Jintao, et al. Clutter suppression for radar via deep joint sparse recovery network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3500205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3332035. [12] 张嘉翔, 张凯翔, 梁振楠, 等. 一种基于深度强化学习的频率捷变雷达智能频点决策方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 227–239. doi: 10.12000/JR23197.ZHANG Jiaxiang, ZHANG Kaixiang, LIANG Zhennan, et al. An intelligent frequency decision method for a frequency agile radar based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 227–239. doi: 10.12000/JR23197. [13] WANG Junxu, ZHANG Lei, MENG Zhichao, et al. General RFI suppression with sidelobe cancellation filtering for dual-polarization SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 4012005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3321321. [14] MATTINGLY R G, MARTONE A F, and METCALF J G. Techniques for mitigating the impact of intra-CPI waveform agility[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radar Systems, 2024, 2: 24–40. doi: 10.1109/TRS.2023.3343192. [15] LAN Lan, ROSAMILIA M, AUBRY A, et al. FDA-MIMO transmitter and receiver optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 1576–1589. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3366438. [16] LAN Lan, MARINO A, AUBRY A, et al. GLRT-based adaptive target detection in FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 597–613. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3028485. [17] LAN Lan, ROSAMILIA M, AUBRY A, et al. Single-snapshot angle and incremental range estimation for FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 3705–3718. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3083591. [18] 兰岚, 许京伟, 朱圣棋, 等. 波形分集阵列雷达抗干扰进展[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(6): 1437–1451. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.06.01.LAN Lan, XU Jingwei, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Advances in anti-jamming using waveform diverse array radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(6): 1437–1451. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.06.01. [19] FANG Yunfei, ZHU Shengqi, LIAO Bin, et al. Target localization with bistatic MIMO and FDA-MIMO dual-mode radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(1): 952–964. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3333829. [20] LAN, Lan, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Mainlobe deceptive jammer suppression using element-pulse coding with MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 182: 107955. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107955. [21] GAO Jie, ZHU Shengqi, LAN Lan, et al. Joint deceptive jammer and clutter suppression via 3-D-ANM with EPC-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 1487–1504. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3456755. [22] QIU Zizhou, LIAO Zhipeng, XU Jingwei, et al. Range-ambiguous clutter suppression for space-based early warning radar using vertical FDA and horizontal EPC[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3502905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3260996. [23] 唐波, 张玉, 张浩. 基于交替投影的MIMO雷达信号盲分离算法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(9): 2092–2097. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.09.006.TANG Bo, ZHANG Yu, and ZHANG Hao. Blind separation of MIMO radar signals based on alternating projection[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(9): 2092–2097. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.09.006. [24] JIA Yuheng, LI Jianan, WU Wenhui, et al. Semi-supervised symmetric non-negative matrix factorization with low-rank tensor representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2025, 35(2): 1534–1547. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3471877. [25] SONG Meiping, ZHANG Xiao, LI Lan, et al. A tensor-based go decomposition method for hyperspectral anomaly detection[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 4584–4600. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3525743. [26] LAN Lan, ZHANG Yitao, XU Jingwei, et al. Suppressing mainlobe deceptive jammers via two-low-rank matrix decomposition in FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 2885–2898. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3480030. [27] CHEN Xuezhi, HUANG Yan, YU Xutao, et al. A RFI mitigation approach for spaceborne SAR using homologous interference knowledge at coastal regions[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 5990–6006. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3530473. [28] LOU Mingyue, AN Hongyang, ZUO Haowen, et al. Feature-enhanced low-rank and sparse decomposition network for SAR RFI suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5210517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3564509. [29] DRIGGS D, BECKER S, and ARAVKIN A. Adapting regularized low-rank models for parallel architectures[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2019, 41(1): A163–A189. doi: 10.1137/17M1147342. [30] BYRD R H, LU Peihuang, NOCEDAL J, et al. A limited memory algorithm for bound constrained optimization[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 1995, 16(5): 1190–1208. doi: 10.1137/0916069. [31] 肖炯, 唐波, 王海. 互耦条件下基于稀疏重构的MIMO雷达角度估计[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(5): 1123–1133. doi: 10.12000/JR24061.XIAO Jiong, TANG Bo, and WANG Hai. Sparse reconstruction-based direction of arrival estimation for MIMO radar in the presence of unknown mutual coupling[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(5): 1123–1133. doi: 10.12000/JR24061. [32] XIAO Jiong and TANG Bo. Hyperparameter free sparse estimation for wideband multiple-input-multiple-output radar direction finding without secondary data[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2024, 18(12): 2552–2563. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12658. [33] 关中意. 基于多维域特征的雷达有源干扰识别方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2024. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2024.003610.GUAN Zhongyi. Study of active radar jamming recognition method based on multidimensional features[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2024. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2024.003610. [34] MALLAT S G and ZHANG Zhifeng. Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1993, 41(12): 3397–3415. doi: 10.1109/78.258082. [35] TROPP J A and GILBERT A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12): 4655–4666. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108. [36] LAN Lan, ZHANG Yitao, LIAO Ruiqian, et al. Mainlobe deceptive jammer mitigation with multipath in EPC-MIMO radar exploiting matrix decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(10): 14674–14688. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3403147. [37] OSELEDETS I V. Tensor-train decomposition[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2011, 33(5): 2295–2317. doi: 10.1137/090752286. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: