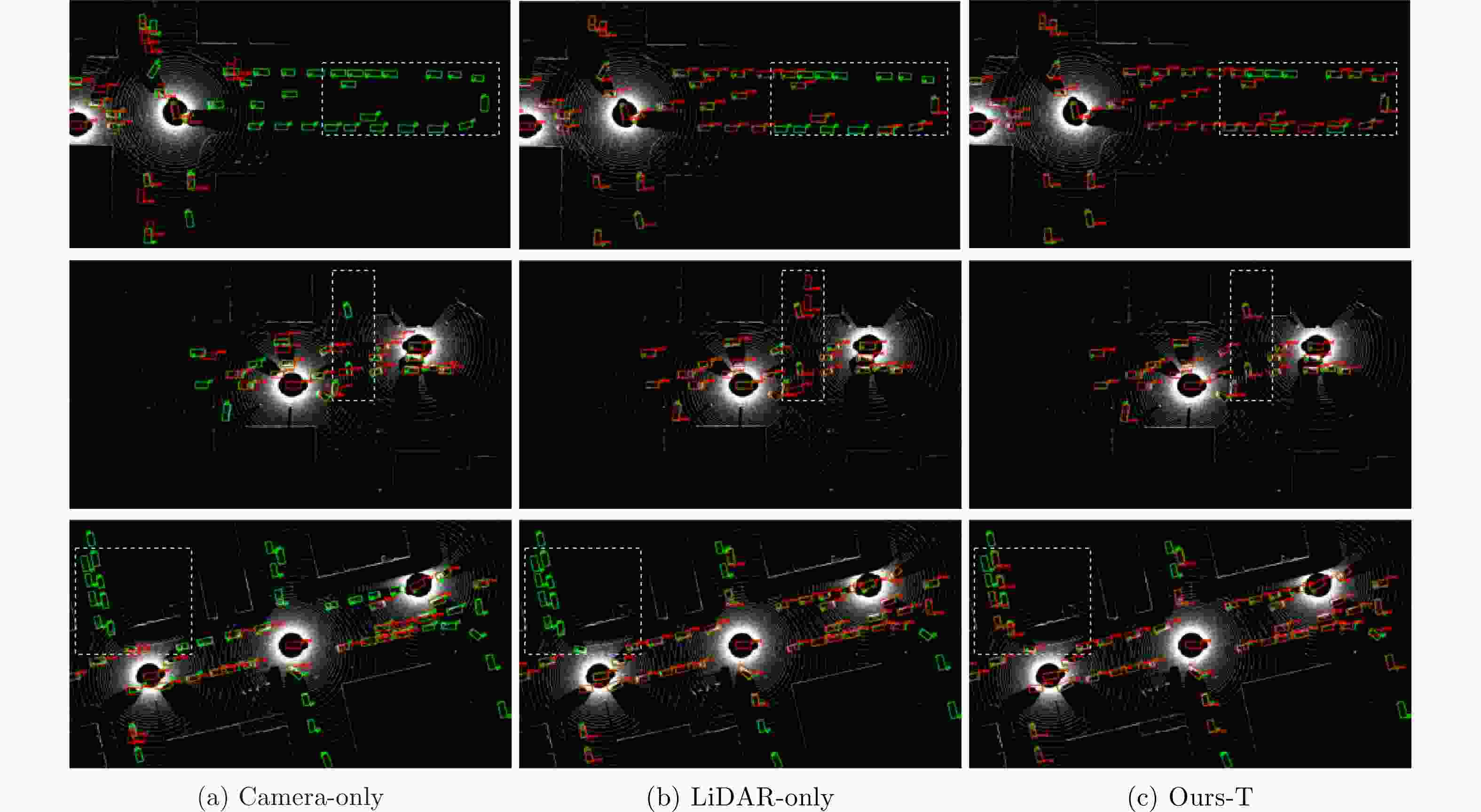
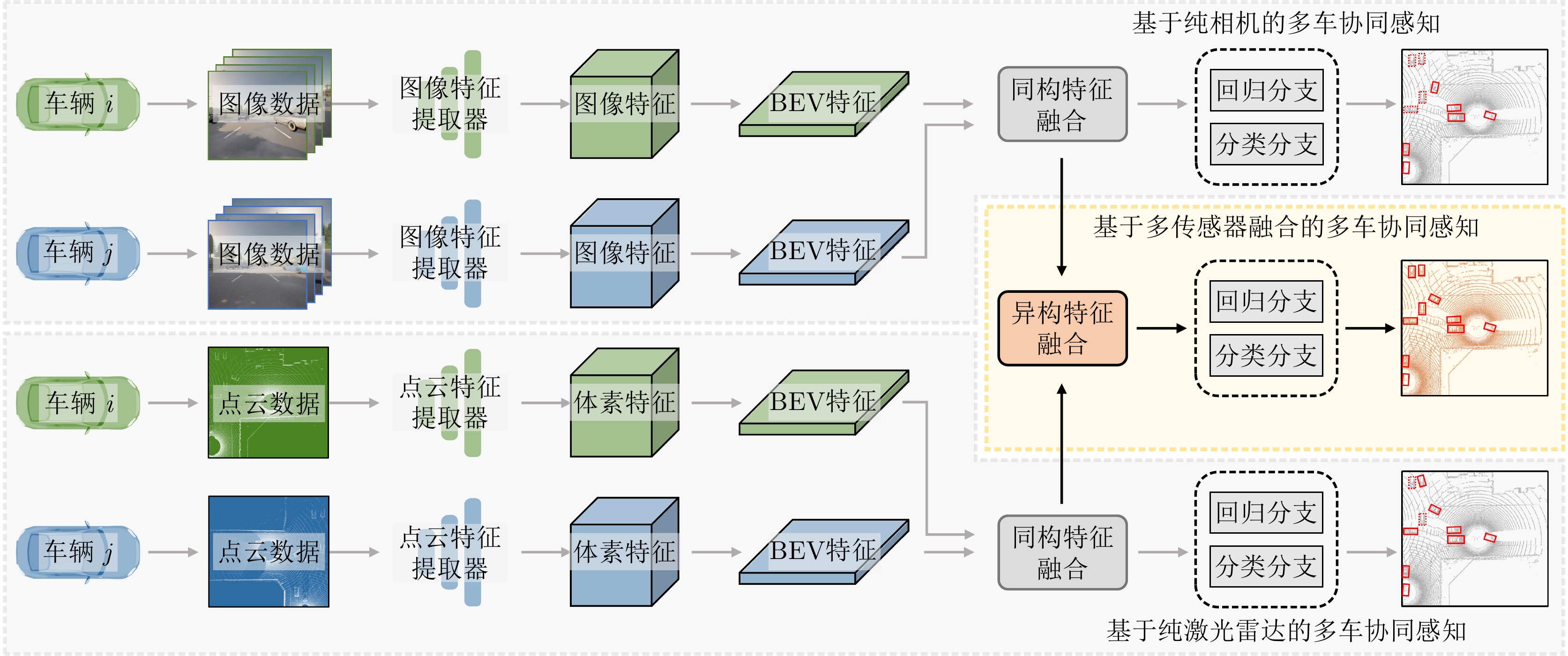
-
摘要: 该文提出了一种新的多模态协同感知框架,通过融合激光雷达和相机传感器的输入来增强自动驾驶感知系统的性能。首先,构建了一个多模态融合的基线系统,能有效地整合来自激光雷达和相机传感器的数据,为后续研究提供了可比较的基准。其次,在多车协同环境下,探索了多种流行的特征融合策略,包括通道级拼接、元素级求和,以及基于Transformer的融合方法,以此来融合来自不同类型传感器的特征并评估它们对模型性能的影响。最后,使用大规模公开仿真数据集OPV2V进行了一系列实验和评估。实验结果表明,基于注意力机制的多模态融合方法在协同感知任务中展现出更优越的性能和更强的鲁棒性,能够提供更精确的目标检测结果,从而增加了自动驾驶系统的安全性和可靠性。Abstract: This paper proposes a novel multimodal collaborative perception framework to enhance the situational awareness of autonomous vehicles. First, a multimodal fusion baseline system is built that effectively integrates Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) point clouds and camera images. This system provides a comparable benchmark for subsequent research. Second, various well-known feature fusion strategies are investigated in the context of collaborative scenarios, including channel-wise concatenation, element-wise summation, and transformer-based methods. This study aims to seamlessly integrate intermediate representations from different sensor modalities, facilitating an exhaustive assessment of their effects on model performance. Extensive experiments were conducted on a large-scale open-source simulation dataset, i.e., OPV2V. The results showed that attention-based multimodal fusion outperforms alternative solutions, delivering more precise target localization during complex traffic scenarios, thereby enhancing the safety and reliability of autonomous driving systems.
-
表 1 与SOTA算法的综合性能对比(%)
Table 1. Comprehensive performance comparison with SOTA algorithms (%)
算法 Default Culver city AP@0.5 AP@0.7 AP@0.5 AP@0.7 No Fusion 67.9 60.2 55.7 47.1 Early Fusion 89.1 80.0 82.9 69.6 Late Fusion 85.8 78.1 79.9 66.8 V2VNet[7] 89.7 82.2 86.8 73.3 Cooper[5] 89.1 80.0 82.9 69.6 F-Cooper[6] 88.7 79.1 84.5 72.9 AttFuse[8] 89.9 81.1 85.4 73.6 CoBEVT[15] 91.4 86.2 85.9 77.3 Ours-S 89.5 82.6 86.7 76.4 Ours-C 91.1 85.0 87.0 78.1 Ours-T 91.4 85.2 88.6 78.8 表 2 所提算法不同异构模态场景下的性能对比(%)
Table 2. Performance comparison of the proposed algorithm under different heterogeneous modal scenarios (%)
算法 Default Culver city AP@0.5 AP@0.7 AP@0.5 AP@0.7 Camera-only 43.9 28.1 19.0 8.6 LiDAR-only 90.9 82.9 85.9 75.4 Hybrid-C 70.7 58.1 58.9 44.5 Hybrid-L 87.8 78.6 76.6 63.6 表 1 Comprehensive performance comparison with SOTA algorithms (%)
Method Default Culver City AP@0.5 AP@0.7 AP@0.5 AP@0.7 No Fusion 67.9 60.2 55.7 47.1 Early Fusion 89.1 80.0 82.9 69.6 Late Fusion 85.8 78.1 79.9 66.8 V2VNet [ 7] 89.7 82.2 86.8 73.3 Cooper [ 5] 89.1 80.0 82.9 69.6 F-Cooper [ 6] 88.7 79.1 84.5 72.9 AttFuse [ 8] 89.9 81.1 85.4 73.6 CoBEVT [ 15] 91.4 86.2 85.9 77.3 Ours-S 89.5 82.6 86.7 76.4 Ours-C 91.1 85.0 87.0 78.1 Ours-T 91.4 85.2 88.6 78.8 表 2 Performance comparison of the proposed algorithm under different heterogeneous modal scenarios (%)
Method Default Culver City AP@0.5 AP@0.7 AP@0.5 AP@0.7 Camera-only 43.9 28.1 19.0 8.6 LiDAR-only 90.9 82.9 85.9 75.4 Hybrid-C 70.7 58.1 58.9 44.5 Hybrid-L 87.8 78.6 76.6 63.6 -
[1] LIU Si, GAO Chen, CHEN Yuan, et al. Towards vehicle-to-everything autonomous driving: A survey on collaborative perception[EB/OL]. https://arxiv:abs/2308.16714, 2023. [2] HAN Yushan, ZHANG Hui, LI Huifang, et al. Collaborative perception in autonomous driving: Methods, datasets, and challenges[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2023, 15(6): 131–151. doi: 10.1109/MITS.2023.3298534. [3] REN Shunli, CHEN Siheng, and ZHANG Wenjun. Collaborative perception for autonomous driving: Current status and future trend[C]. 2021 5th Chinese Conference on Swarm Intelligence and Cooperative Control, Singapore, Singapore, 2023: 682–692. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-3998-3_65. [4] 上官伟, 李鑫, 柴琳果, 等. 车路协同环境下混合交通群体智能仿真与测试研究综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2022, 22(3): 19–40. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2022.03.002.SHANGGUAN Wei, LI Xin, CHAI Linguo, et al. Research review on simulation and test of mixed traffic swarm in vehicle-infrastructure cooperative environment[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2022, 22(3): 19–40. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2022.03.002. [5] CHEN Qi, TANG Sihai, YANG Qing, et al. Cooper: Cooperative perception for connected autonomous vehicles based on 3D point clouds[C]. 2019 IEEE 39th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Dallas, USA, 2019: 514–524. doi: 10.1109/ICDCS.2019.00058. [6] CHEN Qi, MA Xu, TANG Sihai, et al. F-cooper: Feature based cooperative perception for autonomous vehicle edge computing system using 3D point clouds[C]. 4th ACM/IEEE Symposium on Edge Computing, Arlington, USA, 2019: 88–100. doi: 10.1145/3318216.3363300. [7] WANG T H, MANIVASAGAM S, LIANG Ming, et al. V2VNet: Vehicle-to-vehicle communication for joint perception and prediction[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 605–621. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_36. [8] XU Runsheng, XIANG Hao, XIA Xin, et al. OPV2V: An open benchmark dataset and fusion pipeline for perception with vehicle-to-vehicle communication[C]. 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, USA, 2022: 2583–2589. doi: 10.1109/ICRA46639.2022.9812038. [9] XU Runsheng, XIANG Hao, TU Zhengzhong, et al. V2x-ViT: Vehicle-to-everything cooperative perception with vision transformer[C]. 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 107–124. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19842-7_7. [10] LI Yiming, REN Shunli, WU Pengxiang, et al. Learning distilled collaboration graph for multi-agent perception[C]. 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Virtual Online, 2021: 29541–29552. [11] LI Yiming, ZHANG Juexiao, MA Dekun, et al. Multi-robot scene completion: Towards task-agnostic collaborative perception[C]. 6th Conference on Robot Learning, Auckland, New Zealand, 2023: 2062–2072. [12] QIAO Donghao and ZULKERNINE F. Adaptive feature fusion for cooperative perception using LiDAR point clouds[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2023: 1186–1195. doi: 10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00124. [13] ZHANG Zijian, WANG Shuai, HONG Yuncong, et al. Distributed dynamic map fusion via federated learning for intelligent networked vehicles[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 2021: 953–959. doi: 10.1109/ICRA48506.2021.9561612. [14] WANG Binglu, ZHANG Lei, WANG Zhaozhong, et al. CORE: Cooperative reconstruction for multi-agent perception[C]. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 8710–8720. [15] XU Runsheng, TU Zhengzhong, XIANG Hao, et al. CoBEVT: Cooperative bird’s eye view semantic segmentation with sparse transformers[C]. 6th Conference on Robot Learning, Auckland, New Zealand, 2022: 989–1000. [16] HU Yue, LU Yifan, XU Runsheng, et al. Collaboration helps camera overtake LiDAR in 3D detection[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 9243–9252. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00892. [17] 党相卫, 秦斐, 卜祥玺, 等. 一种面向智能驾驶的毫米波雷达与激光雷达融合的鲁棒感知算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR21036.DANG Xiangwei, QIN Fei, BU Xiangxi, et al. A robust perception algorithm based on a radar and LiDAR for intelligent driving[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR21036. [18] CHEN Xiaozhi, MA Huimin, WAN Ji, et al. Multi-view 3D object detection network for autonomous driving[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6526–6534. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.691. [19] VORA S, LANG A H, HELOU B, et al. PointPainting: Sequential fusion for 3d object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 4603–4611. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00466. [20] LIANG Tingting, XIE Hongwei, YU Kaicheng, et al. BEVFusion: A simple and robust LiDAR-camera fusion framework[C]. 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 10421–10434. [21] LIU Zhijian, TANG Haotian, AMINI A, et al. BEVFusion: Multi-task multi-sensor fusion with unified bird’s-eye view representation[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 2023: 2774–2781. doi: 10.1109/ICRA48891.2023.10160968. [22] JIAO Yang, JIE Zequn, CHEN Shaoxiang, et al. MSMDFusion: Fusing LiDAR and camera at multiple scales with multi-depth seeds for 3D object detection[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 21643–21652. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.02073. [23] PRAKASH A, CHITTA K, and GEIGER A. Multi-modal fusion transformer for end-to-end autonomous driving[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 7073–7083. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00700. [24] XIANG Hao, XU Runsheng, and MA Jiaqi. HM-ViT: Hetero-modal vehicle-to-vehicle cooperative perception with vision transformer[EB/OL]. https://arxiv: abs/2304.10628, 2023. [25] READING C, HARAKEH A, CHAE J, et al. Categorical depth distribution network for monocular 3D object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 8551–8560. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00845. [26] LANG A H, VORA S, CAESAR H, et al. PointPillars: Fast encoders for object detection from point clouds[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 12689–12697. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.01298. [27] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [28] 郭帅, 陈婷, 王鹏辉, 等. 基于角度引导Transformer融合网络的多站协同目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 516–528. doi: 10.12000/JR23014.GUO Shuai, CHEN Ting, WANG Penghui, et al. Multistation cooperative radar target recognition based on an angle-guided transformer fusion network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 516–528. doi: 10.12000/JR23014. [29] XU Runsheng, GUO Yi, HAN Xu, et al. OpenCDA: An open cooperative driving automation framework integrated with co-simulation[C]. 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, USA, 2021: 1155–1162. doi: 10.1109/ITSC48978.2021.9564825. [30] DOSOVITSKIY A, ROS G, CODEVILLA F, et al. CARLA: An open urban driving simulator[C]. 1st Annual Conference on robot learning, Mountain View, USA, 2017: 1–16. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: