Moving Targets Detection with Low-bit Quantization in Distributed Radar on Moving Platforms
-
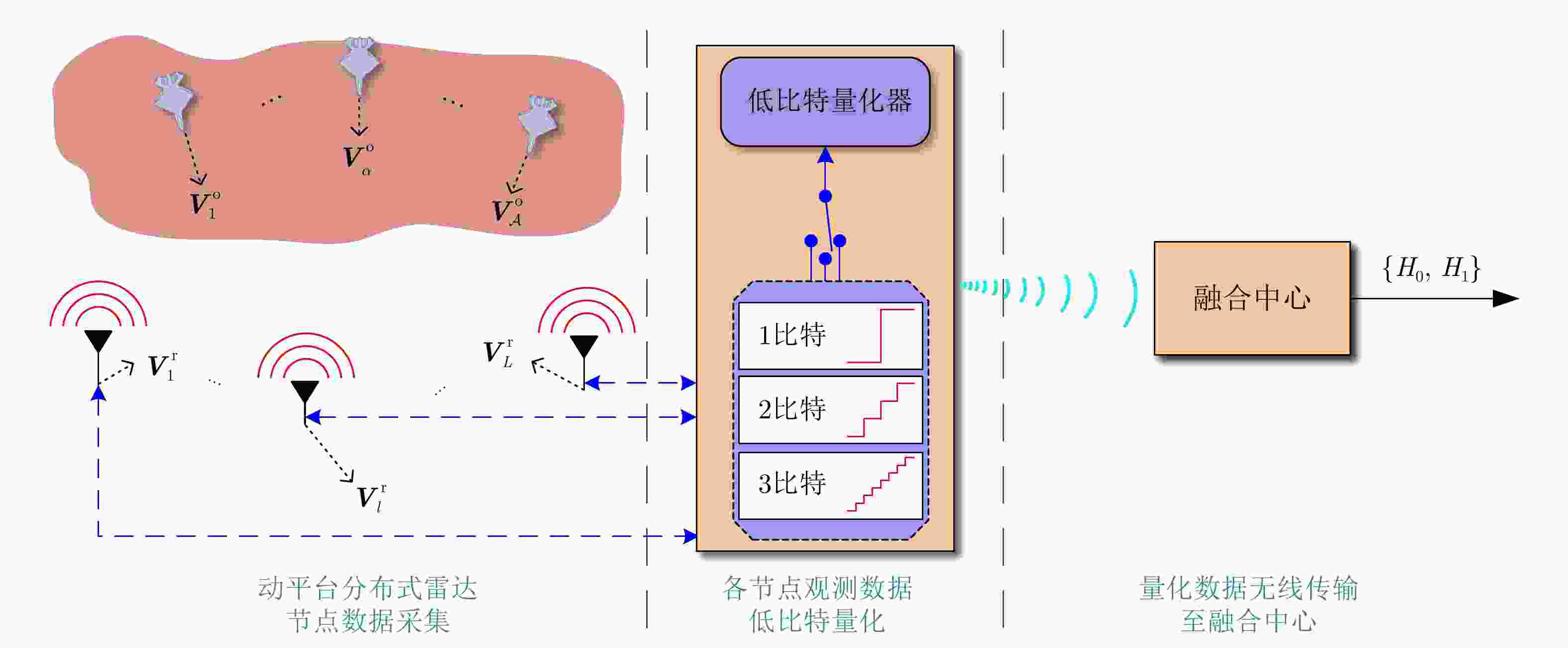
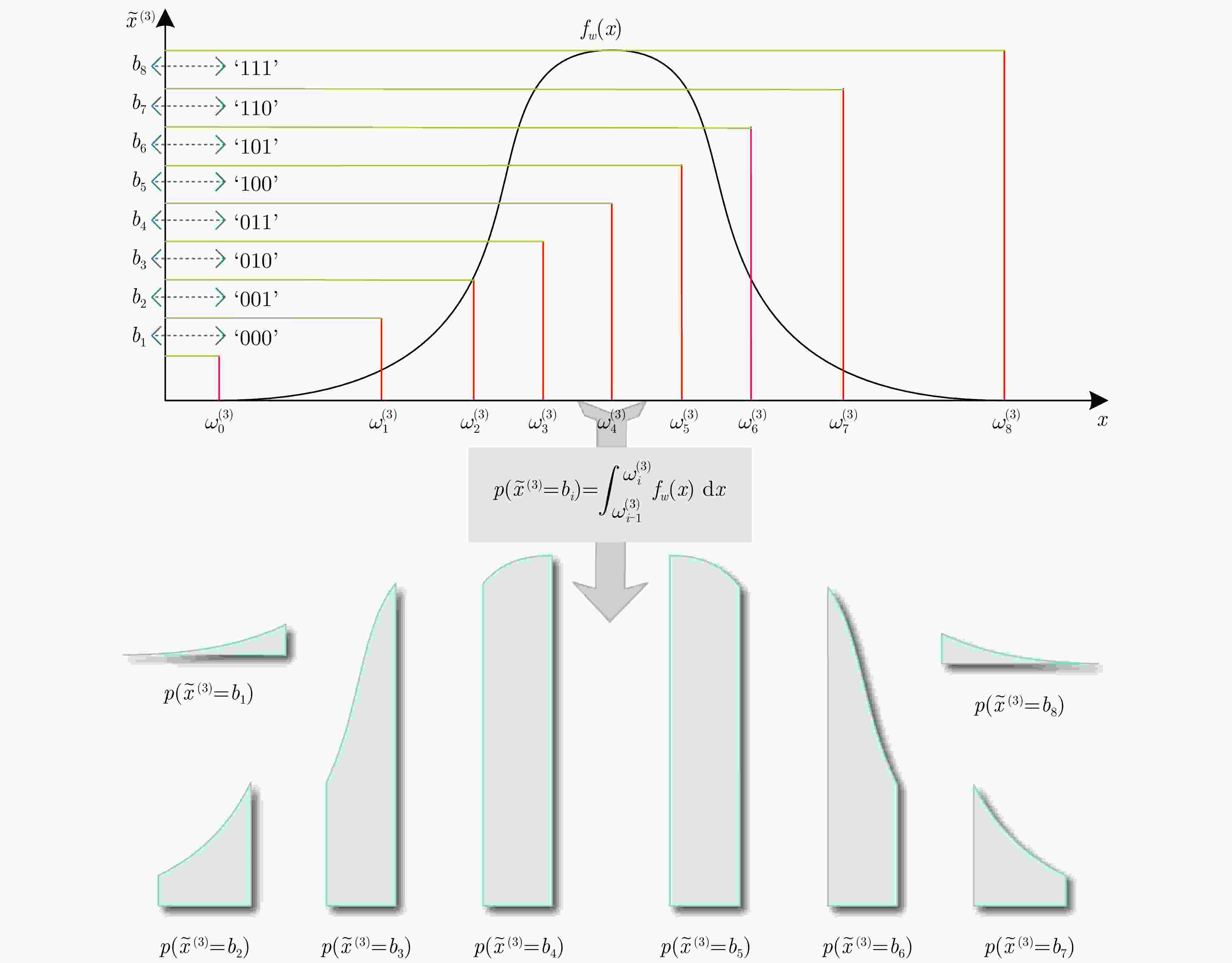
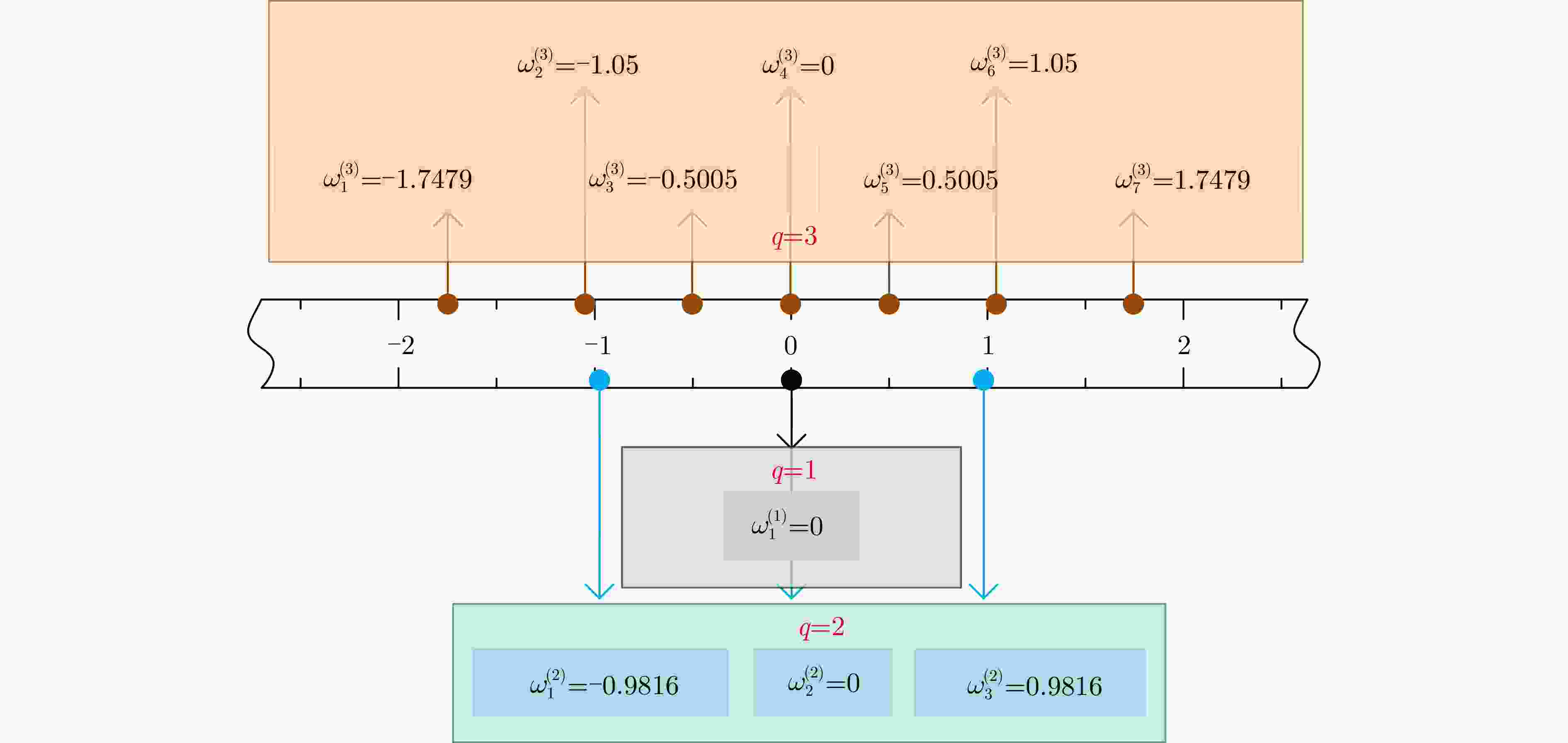
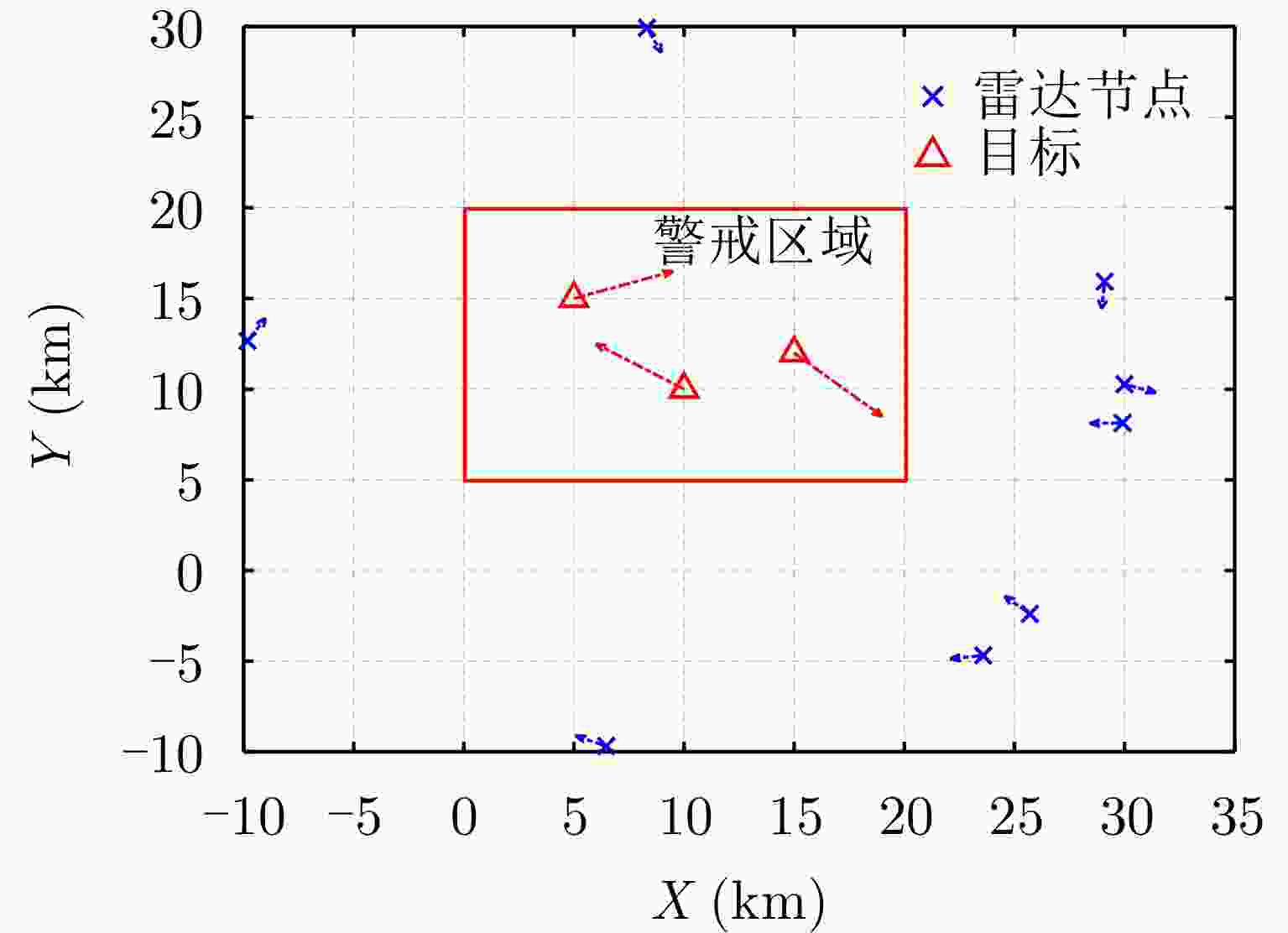
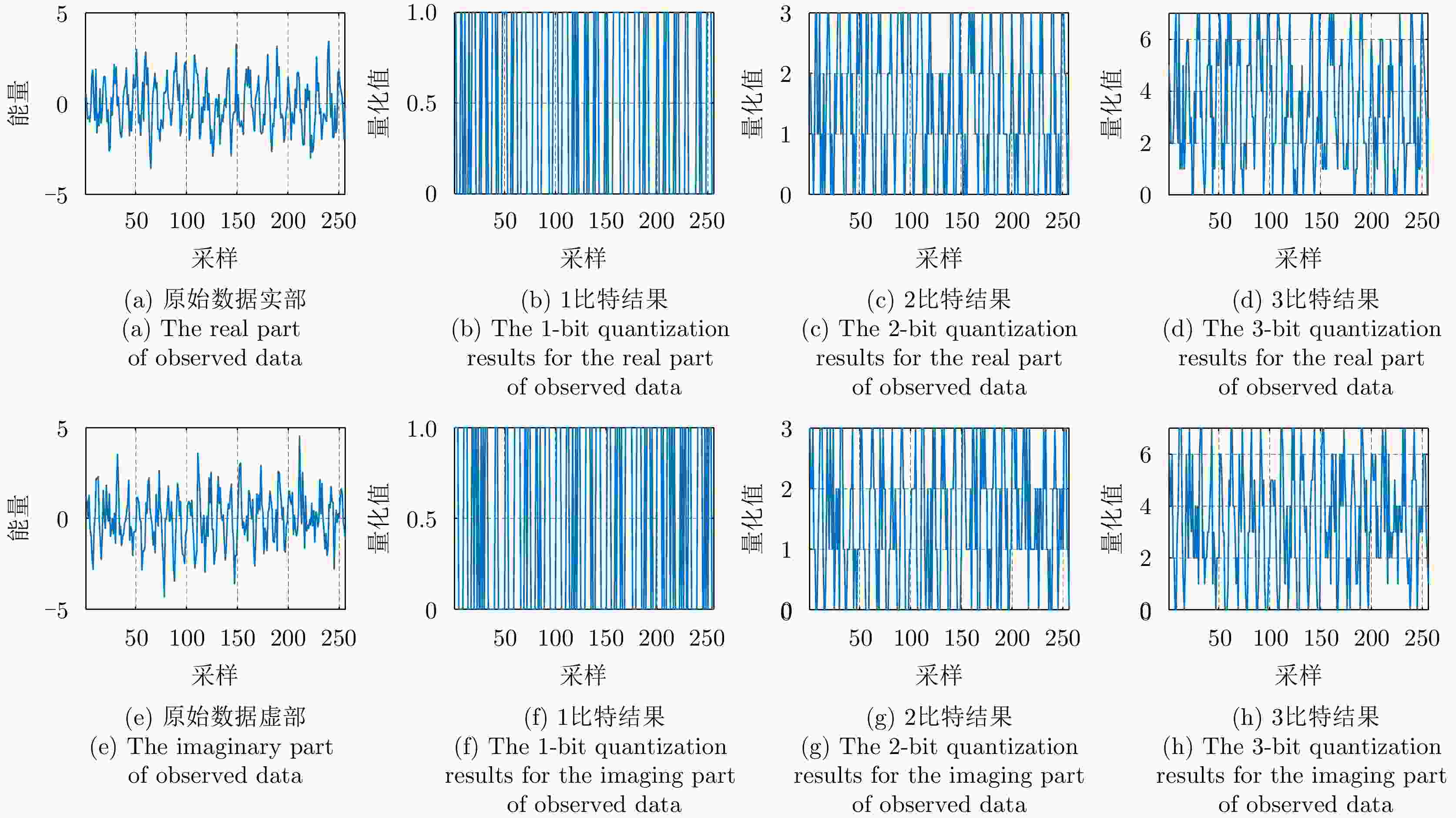
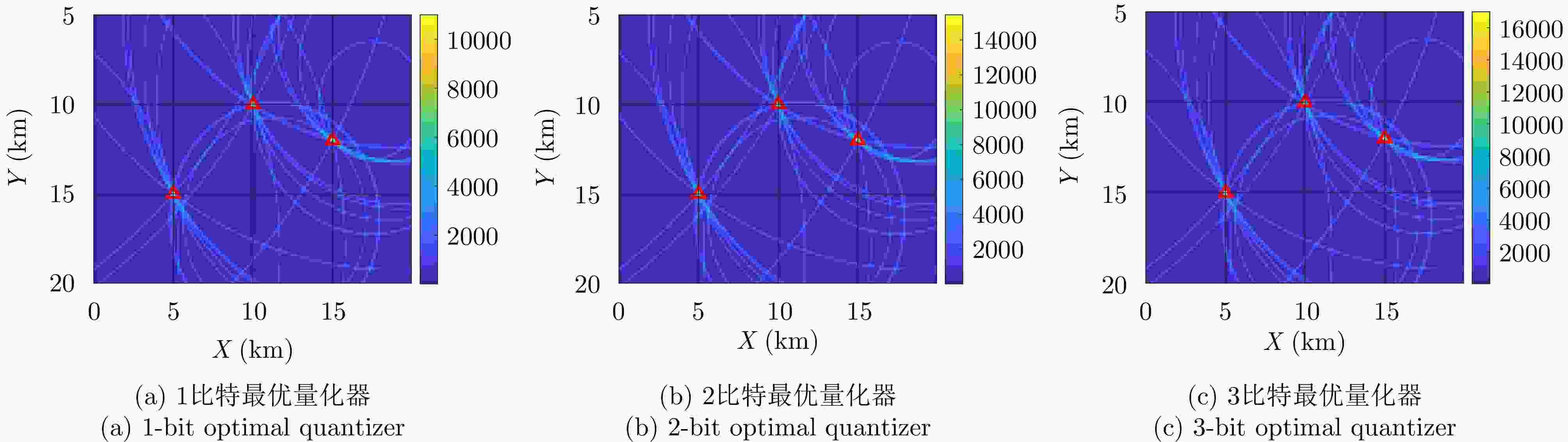
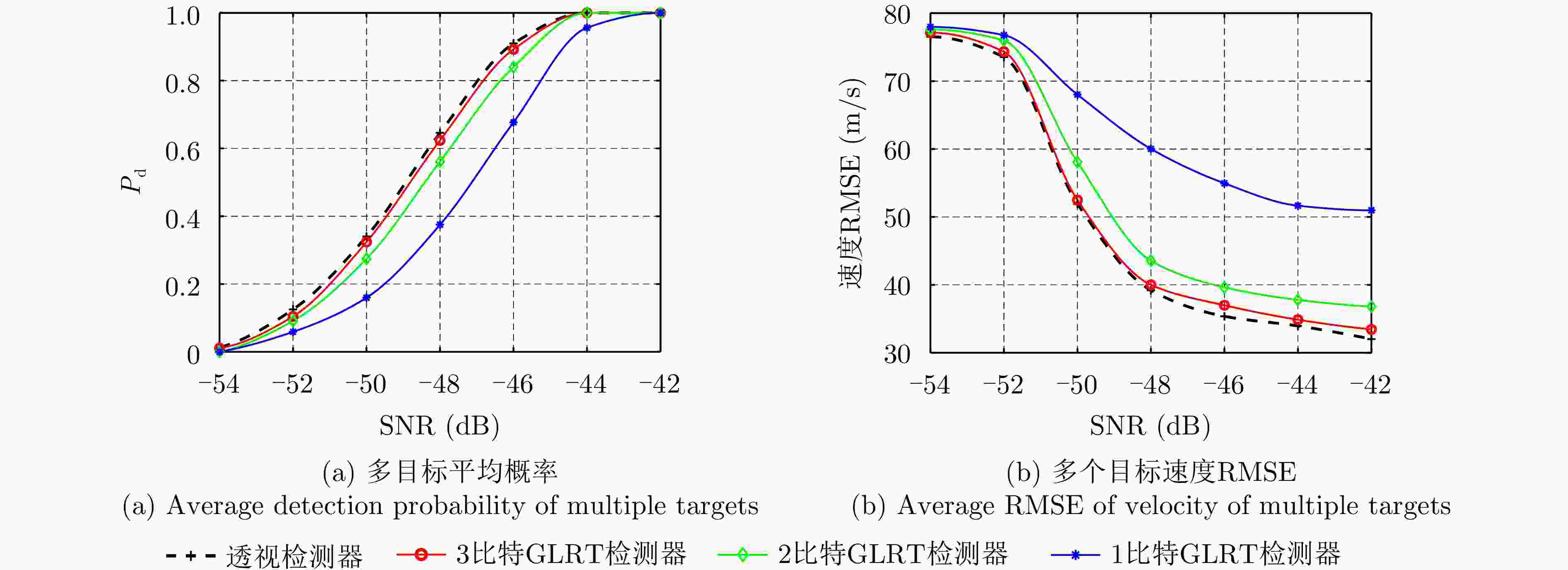
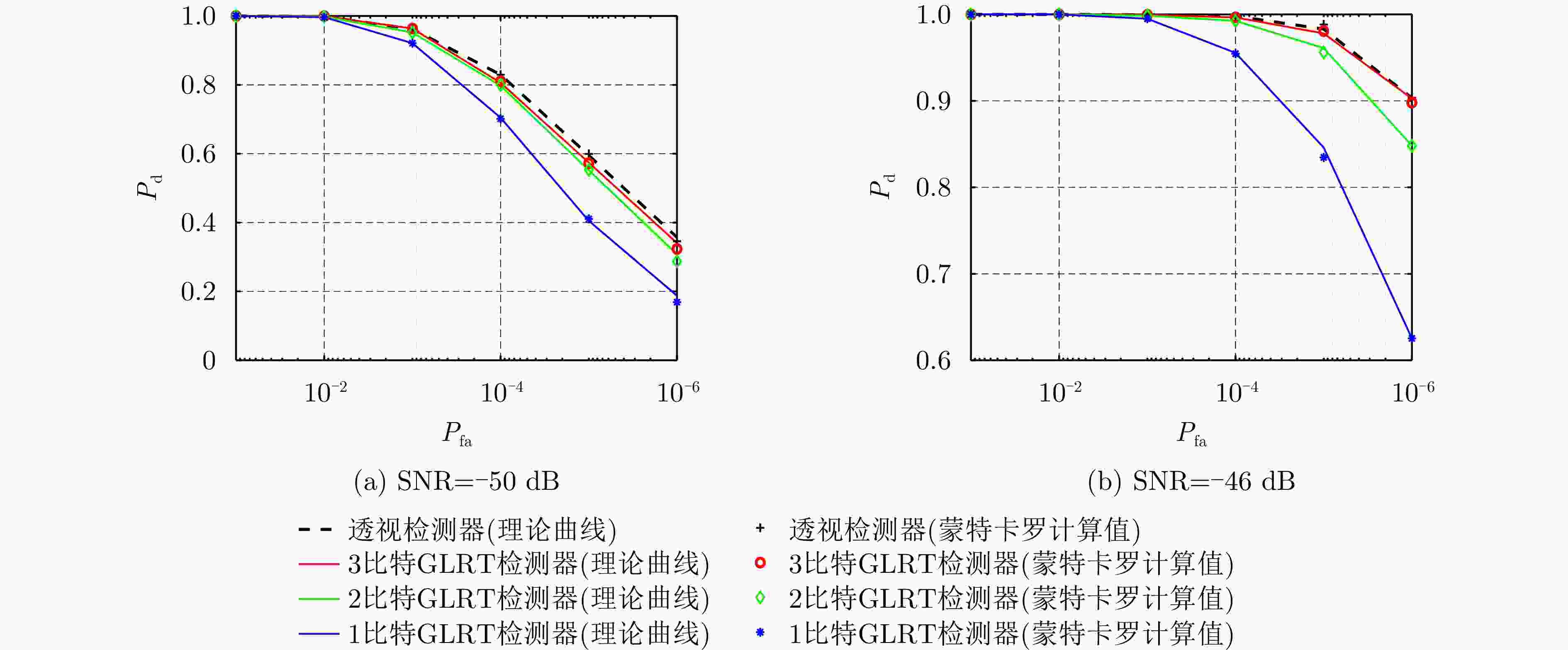
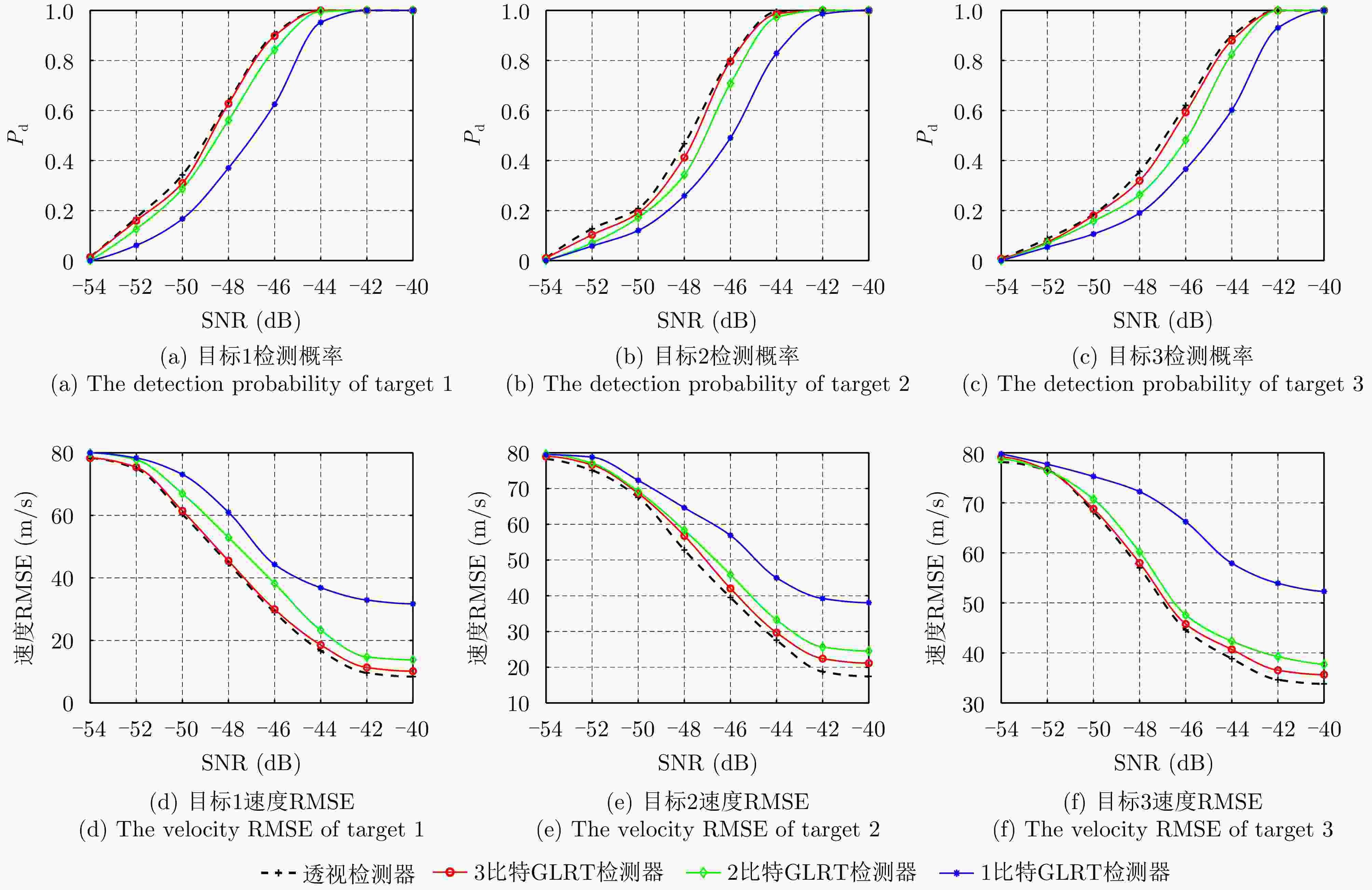
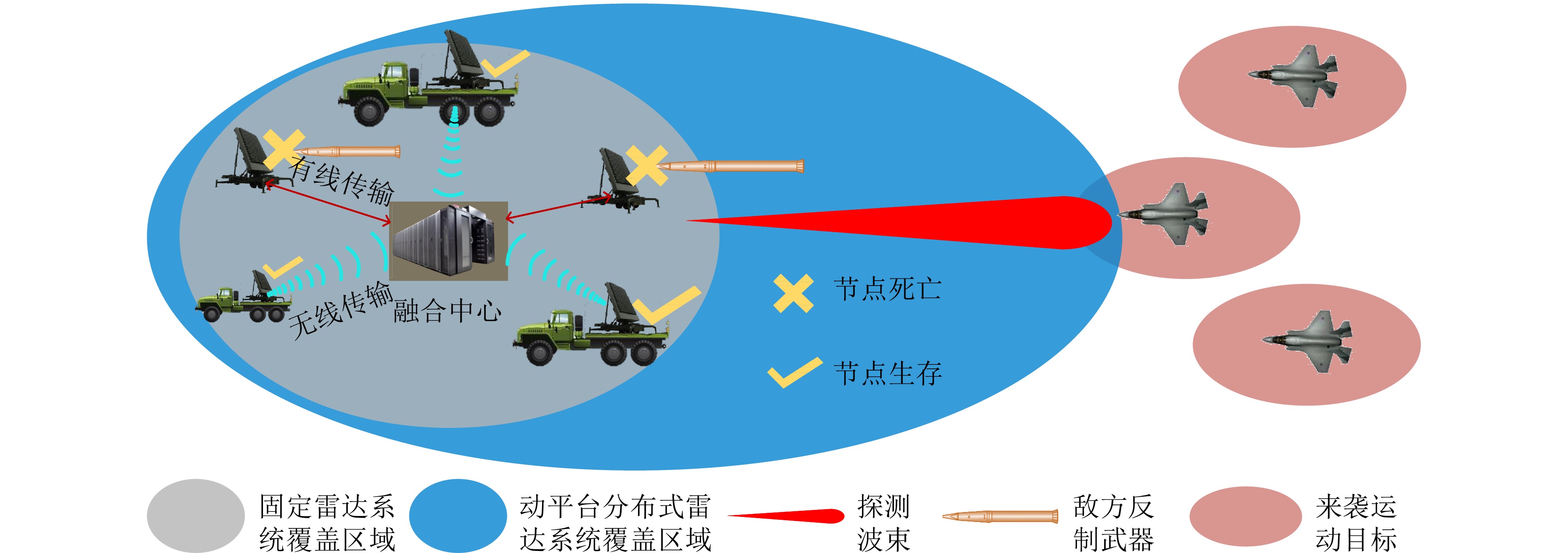
摘要: 动平台分布式雷达系统可有效提升系统的生存能力和探测性能,但运动平台之间通常采用无线传输方式,难以配备大通信带宽以传输完整的信号数据,给雷达系统的高性能检测带来极大挑战。由于低比特量化技术可显著降低分布式系统的通信传输代价和计算资源消耗,该文针对低信噪比弱信号环境下提出了动平台分布式雷达系统的低比特量化运动目标检测算法。首先,根据系统资源将各节点的多脉冲观测数据选择对应位数的低比特量化器进行量化,推导了关于量化器和多个目标状态的似然函数。其次,证明了低比特量化数据对应似然函数关于未知目标反射系数的凸性,并基于该特性设计了多普勒频移和反射系数的联合估计器。然后,针对探测区域中存在的多个状态未知目标设计了多目标检测器,推导了其恒虚警率门限。最后,通过推导系统的渐近性能设计了最优低比特量化器,在保证系统鲁棒性的同时有效提升了系统的检测性能。仿真实验分析了所提算法的检测与估计性能,结果证明了所提算法在低信噪比弱信号环境下的有效性,同时表明低比特量化数据可在仅占用低于20%通信带宽的基础上实现接近高精度(16比特量化)数据对应的检测和估计性能,且2比特量化策略可作为检测性能和雷达系统资源消耗的折中选择。Abstract: Distributed radar with moving platforms can enhance the survivability and detection performance of a system, however, it is difficult to equip these platforms with sufficient communication bandwidth to transmit high-precision observed data, posing a great challenge to the high-performance detection of a distributed radar system. Because low-bit quantization can effectively reduce the computation cost and resource consumption of distributed radar systems, in this paper, we investigate the high-performance detection of multiple moving targets using the distributed radar system on moving platforms by adopting the low-bit quantization strategy. First, according to system resources, multipulse observed data of each node may be quantized with a low-bit quantizer and the likelihood function relative to the quantizer and states of multiple targets are derived. Subsequently, based on the convexity of the likelihood function relative to the unknown reflection coefficients, a joint estimation algorithm is designed for the Doppler shifts and reflection coefficients. Then, a generalized likelihood ratio test based multi-target detector is designed for detecting multiple targets in the surveillance area with unknown states, and deriving the constant false alarm rate detection threshold. Finally, the optimal low-bit quantizer is designed by deriving the asymptotic detection performance of the system, which effectively improves the detection performance and ensures robustness. Simulation experiments are conducted to analyze the detection and estimation performance of the proposed algorithm, thereby demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm for weak signals, and showing that the low-bit quantized data can achieve detection and estimation performance close to that of the high-precision (16-bit quantization) data while consuming a complementary 20% of the communication bandwidth. Besides, according to the simulated results, the two-bit quantization strategy may be a trade-off between the detection performance and resource consumption of the distributed radar system.
-
1 基于BGDA的联合估计器设计
1. BGDA-based joint estimator design
输入:量化数据$ \widetilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}_l^{\left( q \right)} $,初始状态${\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( 0 \right) = {\left[ {\widetilde \alpha _{l\mathcal{G}}^{\text{R}},\widetilde \alpha _{l\mathcal{G}}^{\text{I}}} \right]^{\rm T} }$,学习率${\beta _l}$,容忍精度${\eta _l}$。 输出:第l个通道的检测统计量$ {\varLambda _{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}_l^{\left( q \right)}} \right) $,未知参数的估计$ \left( {\hat f_l^{\text{d}},{{\hat {\boldsymbol{\alpha}} }_{l\mathcal{G}}}} \right) $。 for $\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}} \in \left[ {f_{\min }^{\text{d}},f_{\max }^{\text{d}}} \right]$ 初始赋值:${\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right) \leftarrow {\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( 0 \right)$ while ${\left\| {\nabla {{\widetilde \ell }_1}\left( {\widetilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}_l^{\left( q \right)};\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}},{{\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right)} \right)} \right\|_2} > {\eta _l}$ ${\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right) \leftarrow {\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right) + \beta _l^{\rm T} \nabla {\widetilde \ell _1}\left( {\widetilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}_l^{\left( q \right)};\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}},{{\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right)} \right)$ end $ {\varLambda _{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}_l^{\left( q \right)};\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}},{{\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right)} \right) = {\widetilde \ell _1}\left( {\widetilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}_l^{\left( q \right)};\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}},{{\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right)} \right) $ end $ \left\{ \begin{gathered} \left( {\hat f_l^{\text{d}},{{\hat {\boldsymbol{\alpha}} }_{l\mathcal{G}}}} \right) = \mathop {\arg \max }\limits_{\left\{ {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}},{{\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right)} \right\}} \left\{ {{\varLambda _{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}_l^{\left( q \right)};\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}},{{\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right)} \right)} \right\} \\ {\varLambda _{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{Y}}_l}} \right) = \max \left\{ {{\varLambda _{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}_l^{\left( q \right)};\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}},{{\widetilde {\boldsymbol{\alpha }}}_{l\mathcal{G}}}\left( {\widetilde f_l^{\text{d}}} \right)} \right)} \right\} \\ \end{gathered} \right. $ -
[1] VISWANATHAN R and VARSHNEY P K. Distributed detection with multiple sensors Part I. Fundamentals[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1997, 85(1): 54–63. doi: 10.1109/5.554208. [2] CHONG C Y and KUMAR S P. Sensor networks: Evolution, opportunities, and challenges[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2003, 91(8): 1247–1256. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2003.814918. [3] REIBMAN A R and NOLTE L W. Optimal detection and performance of distributed sensor systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1987, AES-23(1): 24–30. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1987.313355. [4] CHAKRABARTY K, IYENGAR S S, QI Hairong, et al. Grid coverage for surveillance and target location in distributed sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2002, 51(12): 1448–1453. doi: 10.1109/TC.2002.1146711. [5] KAPLAN L M. Global node selection for localization in a distributed sensor network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 113–135. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603409. [6] ZHOU Shidong, ZHAO Ming, XU Xibin, et al. Distributed wireless communication system: A new architecture for future public wireless access[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2003, 41(3): 108–113. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2003.1186553. [7] SHI Qingjiang, HE Chen, CHEN Hongyang, et al. Distributed wireless sensor network localization via sequential greedy optimization algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(6): 3328–3340. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2045416. [8] 时晨光, 唐志诚, 周建江, 等. 非理想检测下多雷达网络节点选择与辐射资源联合优化分配算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(3): 565–583. doi: 10.12000/JR23081.SHI Chenguang, TANG Zhicheng, ZHOU Jianjiang, et al. Joint collaborative radar selection and transmit resource allocation in multiple distributed radar networks with imperfect detection performance[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 565–583. doi: 10.12000/JR23081. [9] 易伟, 袁野, 刘光宏, 等. 多雷达协同探测技术研究进展: 认知跟踪与资源调度算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 471–499. doi: 10.12000/JR23036.YI Wei, YUAN Ye, LIU Guanghong, et al. Recent advances in multi-radar collaborative surveillance: Cognitive tracking and resource scheduling algorithms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 471–499. doi: 10.12000/JR23036. [10] FISHLER E, HAIMOVICH A, BLUM R S, et al. Spatial diversity in radars-models and detection performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 823–838. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.862813. [11] HAIMOVICH A M, BLUM R S, and CIMINI L J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(1): 116–129. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4408448. [12] 闵涛, 王象, 肖顺平. 基于复数指示角差异的多基地雷达密集多目标存在性检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(4): 456–464. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13116.MIN Tao, WANG Xiang, and XIAO Shunping. Detection of multiple unresolved targets based on complex indicated angle difference using multistatic radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(4): 456–464. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13116. [13] ZHANG Shiyu, ZHOU Yu, SHA Minghui, et al. Moving multitarget detection using a multisite radar system with widely separated stations[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(11): 2660. doi: 10.3390/rs14112660. [14] LI Hongbin, WANG Zhe, LIU Jun, et al. Moving target detection in distributed MIMO radar on moving platforms[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1524–1535. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2467355. [15] 严俊坤, 白舸, 黄佳沁, 等. 多机雷达协同区域动态覆盖航迹优化方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 541–549. doi: 10.12000/JR22196.YAN Junkun, BAI Ge, HUANG Jiaqin, et al. Flight path optimization method for dynamic area coverage based on multi-aircraft radars[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 541–549. doi: 10.12000/JR22196. [16] CHEN Peng, ZHENG Le, WANG Xiaodong, et al. Moving target detection using colocated MIMO radar on multiple distributed moving platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(17): 4670–4683. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2714999. [17] 邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102.XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102. [18] HE Shaoming, SHIN H S, XU Shuoyuan, et al. Distributed estimation over a low-cost sensor network: A review of state-of-the-art[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 54: 21–43. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.06.026. [19] RIBEIRO A and GIANNAKIS G B. Bandwidth-constrained distributed estimation for wireless sensor networks-part I: Gaussian case[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 1131–1143. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.863009. [20] CIUONZO D, JAVADI S H, MOHAMMADI A, et al. Bandwidth-constrained decentralized detection of an unknown vector signal via multisensor fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2020, 6: 744–758. doi: 10.1109/TSIPN.2020.3037832. [21] 张国鑫, 易伟, 孔令讲. 基于1比特量化的大规模MIMO雷达系统直接定位算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 970–981. doi: 10.12000/JR21062.ZHANG Guoxin, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Direct position determination for massive MIMO system with one-bit quantization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 970–981. doi: 10.12000/JR21062. [22] FANG Jun, LIU Yumeng, LI Hongbin, et al. One-bit quantizer design for multisensor GLRT fusion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 257–260. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2243144. [23] RIBEIRO A and GIANNAKIS G B. Bandwidth-constrained distributed estimation for wireless sensor networks-part II: Unknown probability density function[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(7): 2784–2796. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.874366. [24] CIUONZO D, ROSSI P S, and WILLETT P. Generalized Rao test for decentralized detection of an uncooperative target[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(5): 678–682. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2686377. [25] 万环, 余显祥, 全智, 等. 基于交替方向惩罚法的低精度量化MIMO雷达恒模波形设计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 557–569. doi: 10.12000/JR22072.WAN Huan, YU Xianxiang, QUAN Zhi, et al. Constant modulus waveform design for low-resolution quantization MIMO radar based on an alternating direction penalty method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 557–569. doi: 10.12000/JR22072. [26] 赵博, 黄磊, 周汉飞, 等. 基于单频时变阈值的1-bit SAR成像方法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 446–454. doi: 10.12000/JR18036.ZHAO Bo, HUANG Lei, ZHOU Hanfei, et al. 1-bit SAR imaging method based on single-frequency time-varying threshold[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 446–454. doi: 10.12000/JR18036. [27] PAPADOPOULOS H C, WORNELL G W, and OPPENHEIM A V. Sequential signal encoding from noisy measurements using quantizers with dynamic bias control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2001, 47(3): 978–1002. doi: 10.1109/18.915654. [28] STOICA P, SHANG Xiaolei, and CHENG Yuanbo. The Cramér-Rao bound for signal parameter estimation from quantized data [lecture notes][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2022, 39(1): 118–125. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2021.3116532. [29] GAO Fei, GUO Lili, LI Hongbin, et al. Quantizer design for distributed GLRT detection of weak signal in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(14): 2032–2042. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2379279. [30] WANG Xueqian, LI Gang, and VARSHNEY P K. Detection of sparse stochastic signals with quantized measurements in sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(8): 2210–2220. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2903034. [31] WANG Xueqian, LI Gang, QUAN Chen, et al. Distributed detection of sparse stochastic signals with quantized measurements: The generalized Gaussian case[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(18): 4886–4898. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2932884. [32] CHENG Xu, CIUONZO D, ROSSI P S, et al. Multi-bit & sequential decentralized detection of a noncooperative moving target through a generalized Rao test[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2021, 7: 740–753. doi: 10.1109/TSIPN.2021.3126930. [33] AMERI A, BOSE A, LI Jian, et al. One-bit radar processing with time-varying sampling thresholds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(20): 5297–5308. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2939086. [34] CHENG Ziyang, HE Zishu, and LIAO Bin. Target detection performance of collocated MIMO radar with one-bit ADCs[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(12): 1832–1836. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2951496. [35] XIAO Yuhang, RAMÍREZ D, SCHREIER P J, et al. One-bit target detection in collocated MIMO radar and performance degradation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(9): 9363–9374. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3178285. [36] WANG Zhen, HE Qian, and BLUM R S. Target detection using quantized cloud MIMO radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 1–16. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3129364. [37] RICHARDS M A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing[M]. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education, 2014. [38] XU Luzhou, LI Jian, and STOICA P. Target detection and parameter estimation for MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(3): 927–939. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4655353. [39] KAY S and ZHU Zhenghan. The complex parameter Rao test[J]. IEEE Trans. Signal Process, 2016, 64(24): 6580–6588. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2613071. [40] YANG Shixing, YI Wei, JAKOBSSON A, et al. Weak signal detection with low-bit quantization in colocated MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023, 71: 447–460. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2023.3246233. [41] YANG Shixing, YI Wei, and JAKOBSSON A. Multitarget detection strategy for distributed MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5113516. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3175046. [42] CHAO Shuyuan, CHEN Baixiao, and LI Caicai. Grid cell based detection strategy for MIMO radar with widely separated subarrays[J]. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2012, 66(9): 741–751. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2012.01.006. [43] YANG Shixing, LAI Yangming, JAKOBSSON A, et al. Hybrid quantized signal detection with a bandwidth-constrained distributed radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 7835–7850. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3296344. [44] WERNER K and JANSSON M. DOA estimation and detection in colored noise using additional noise-only data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(11): 5309–5322. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.898758. [45] HE Qian, LEHMANN N H, BLUM R S, et al. MIMO radar moving target detection in homogeneous clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 1290–1301. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545189. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: