Polarimetric Calibration and Insect Orientation Estimation of High-resolution Fully Polarimetric Entomological Radar
-
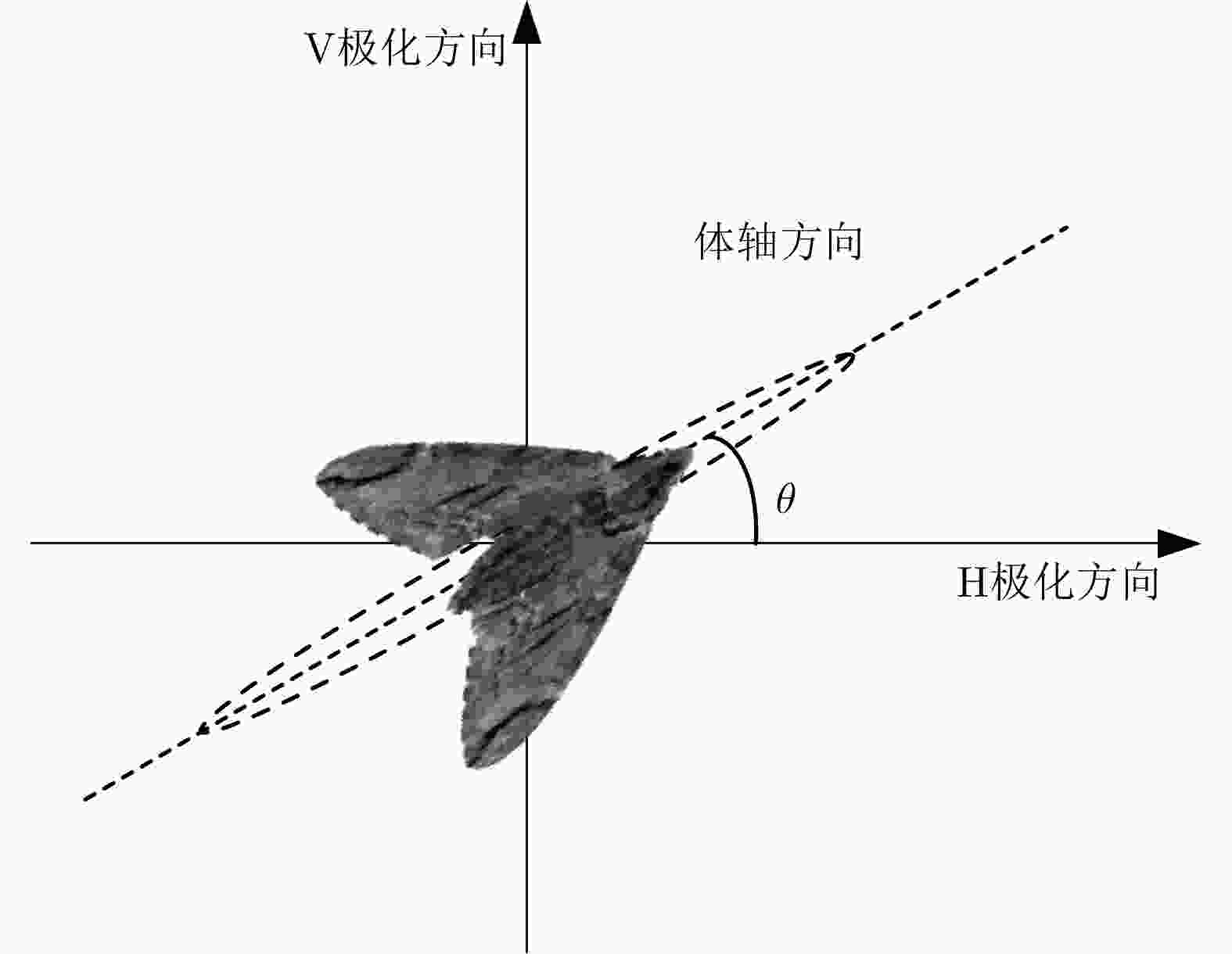
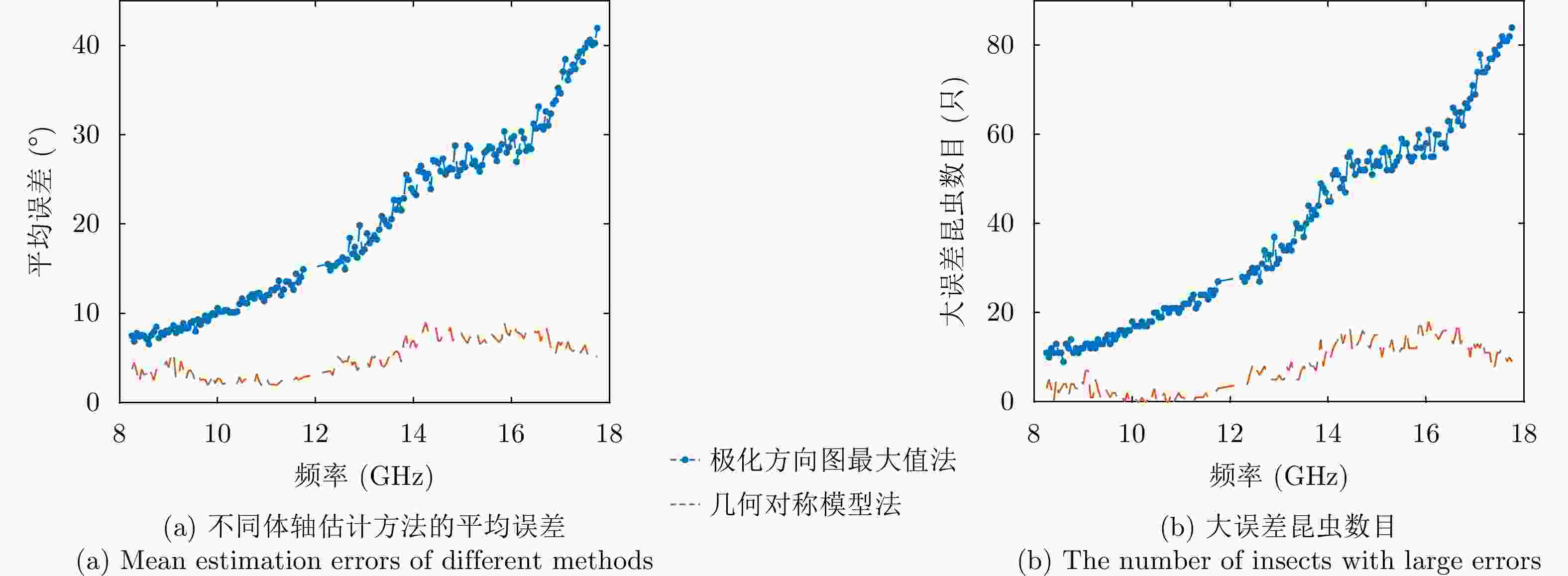
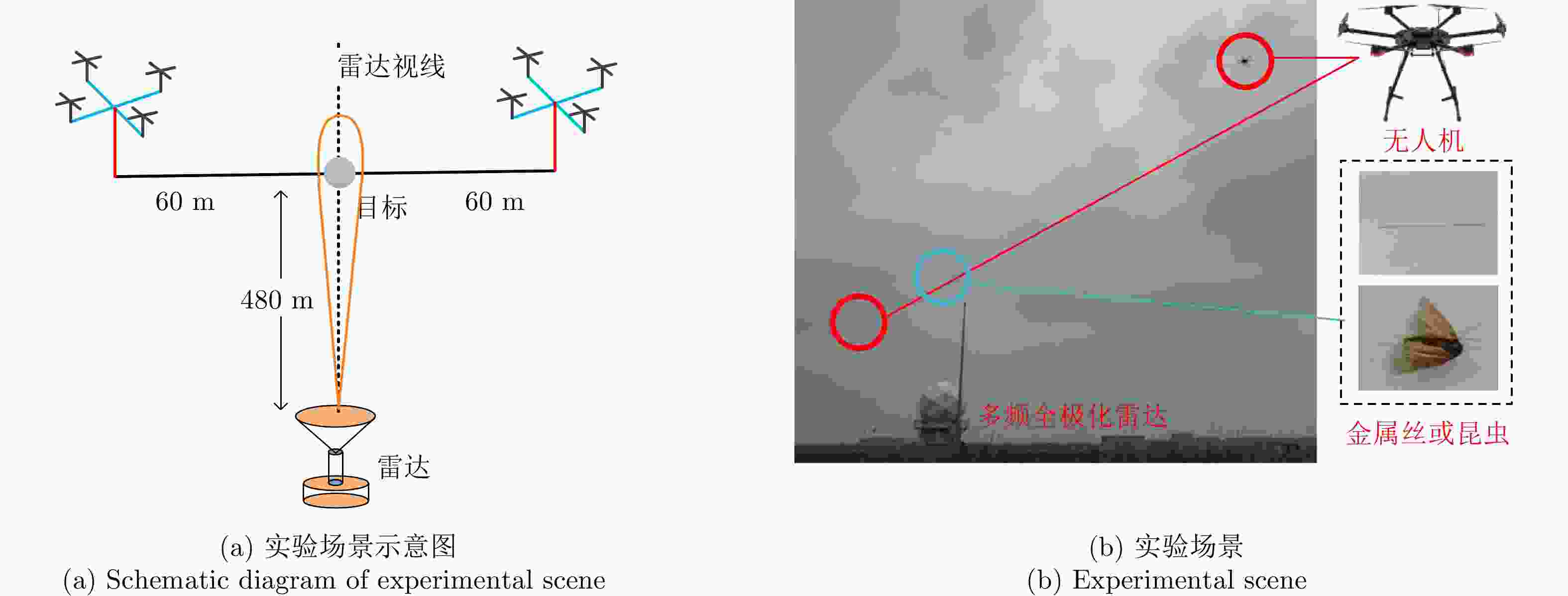
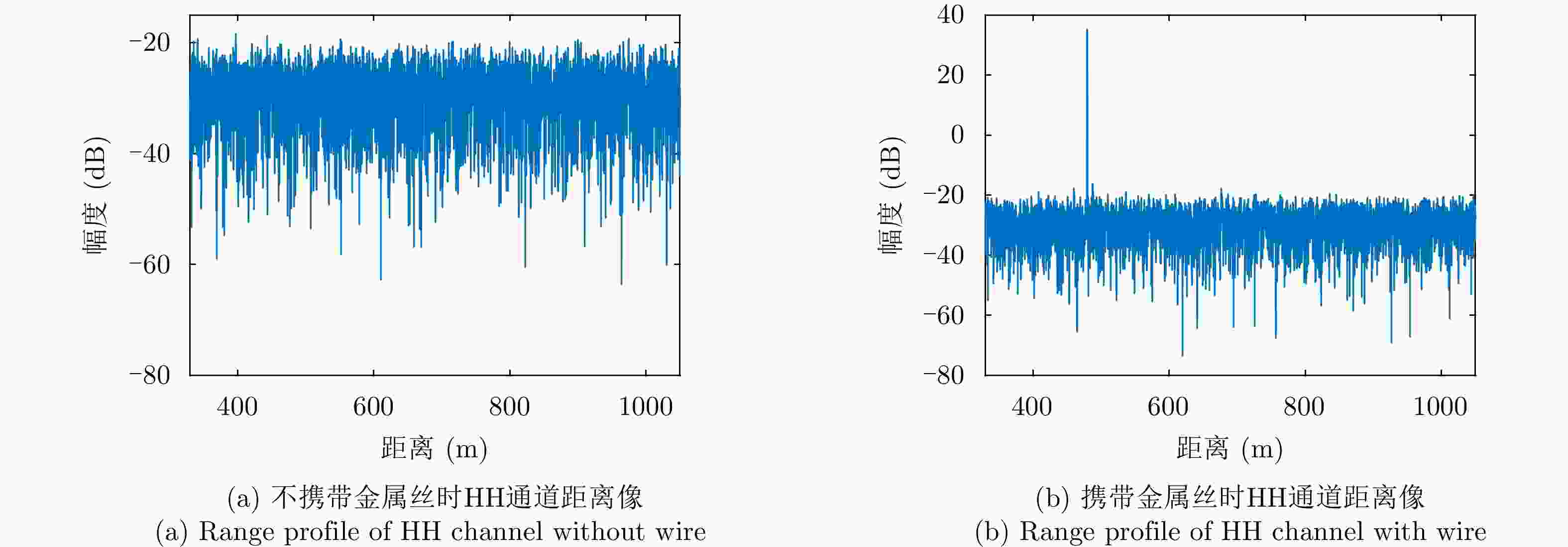
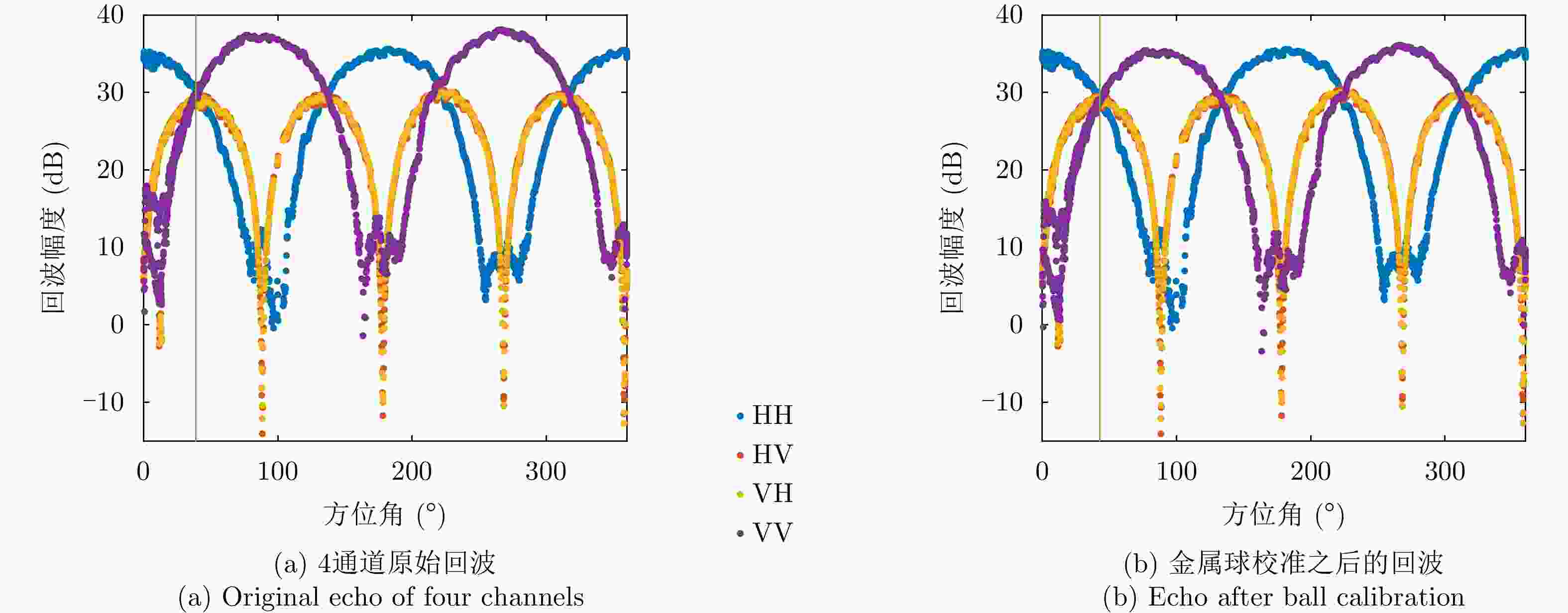
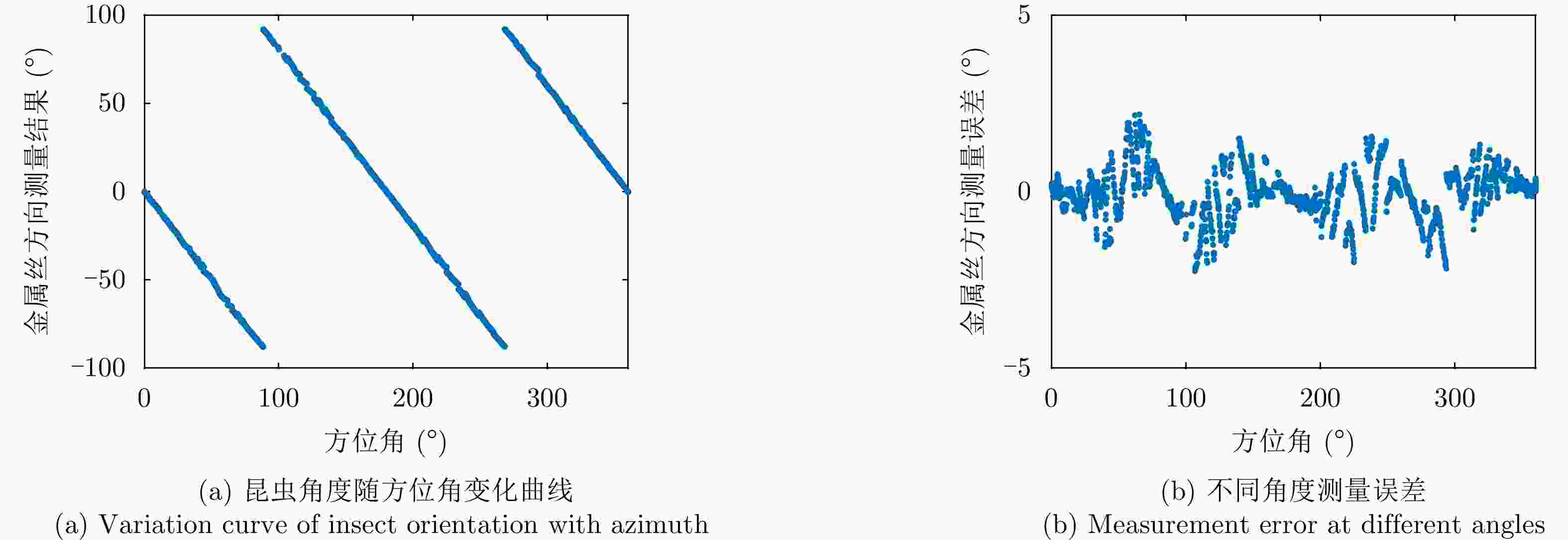
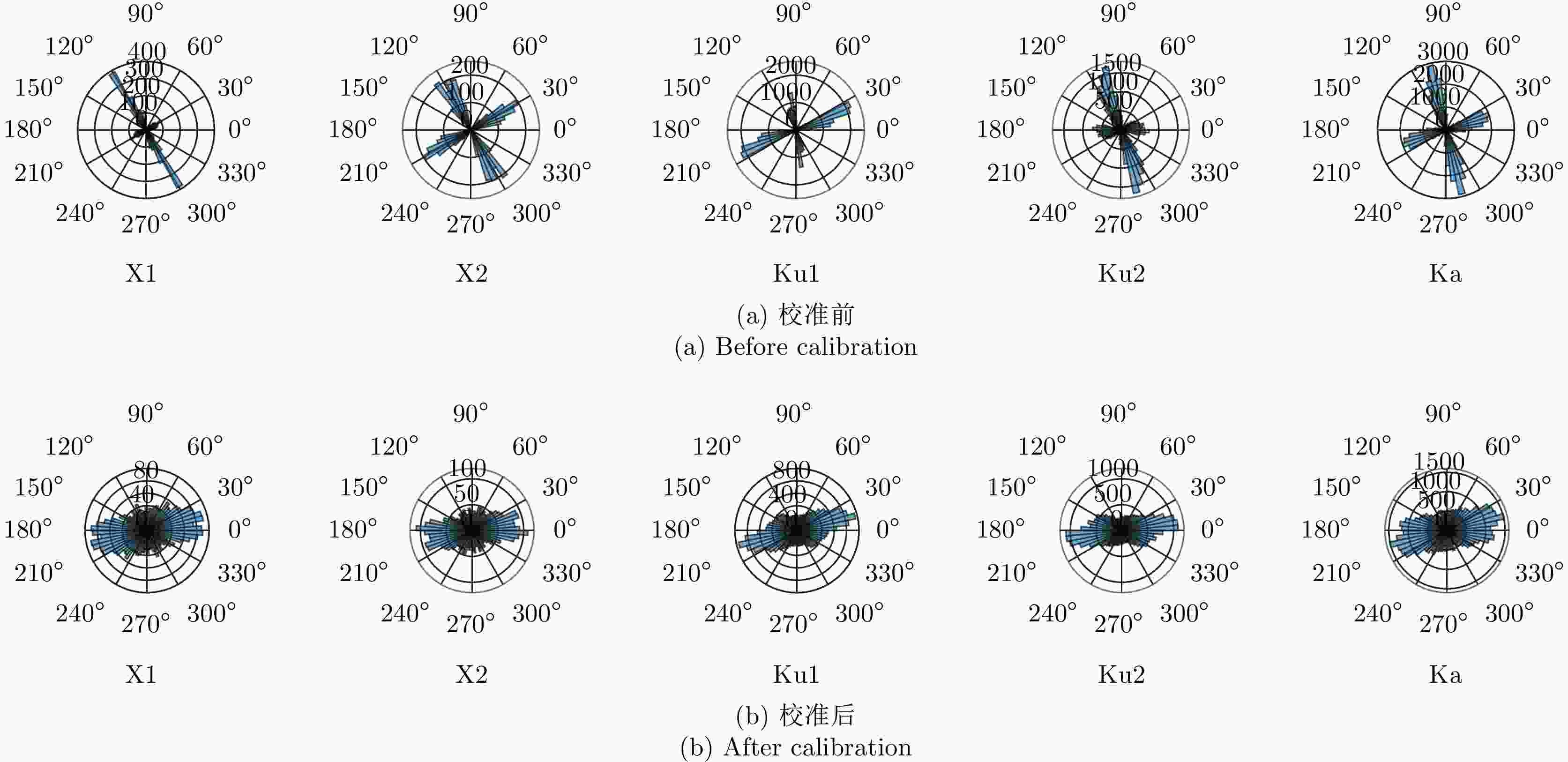
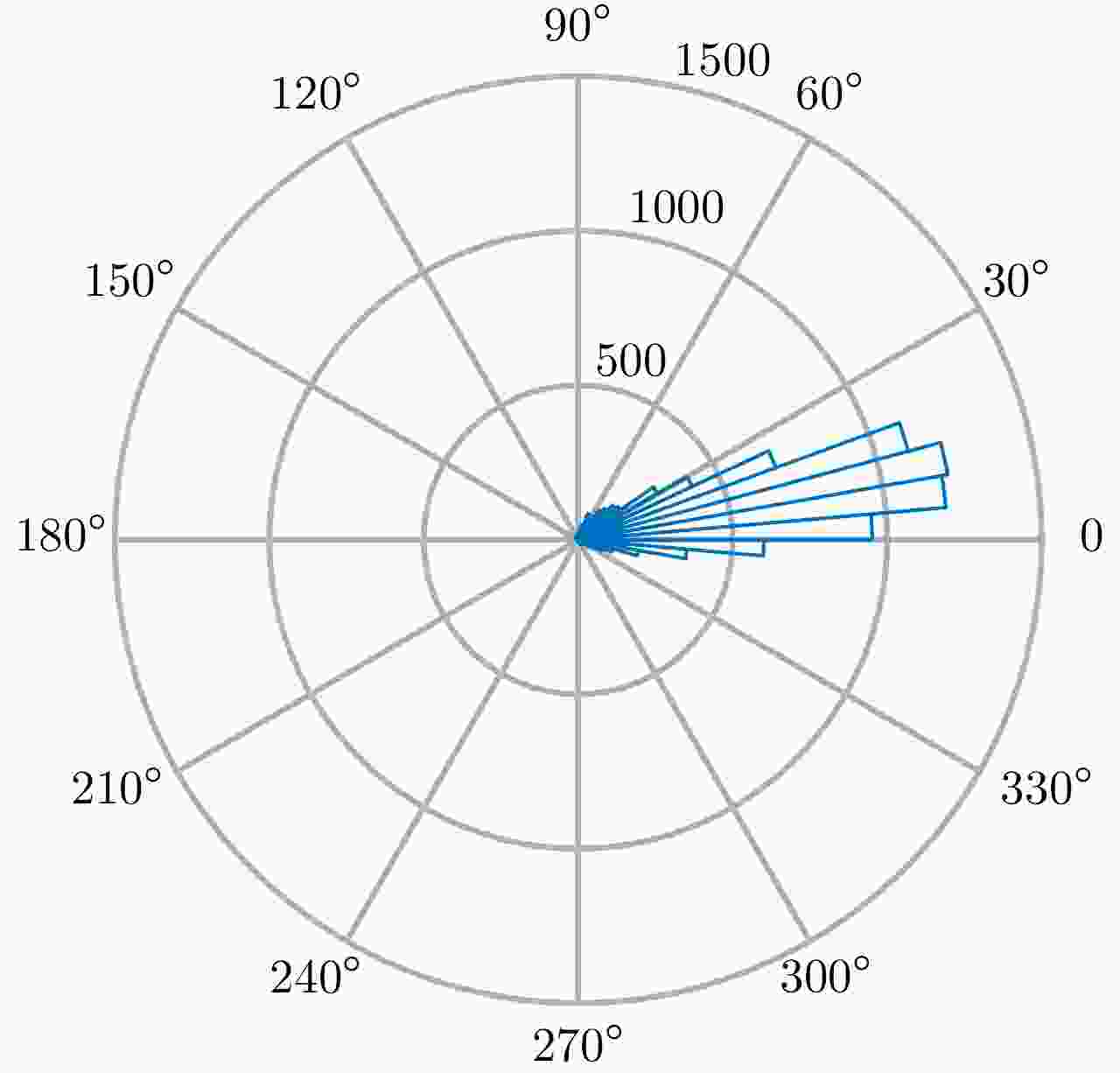
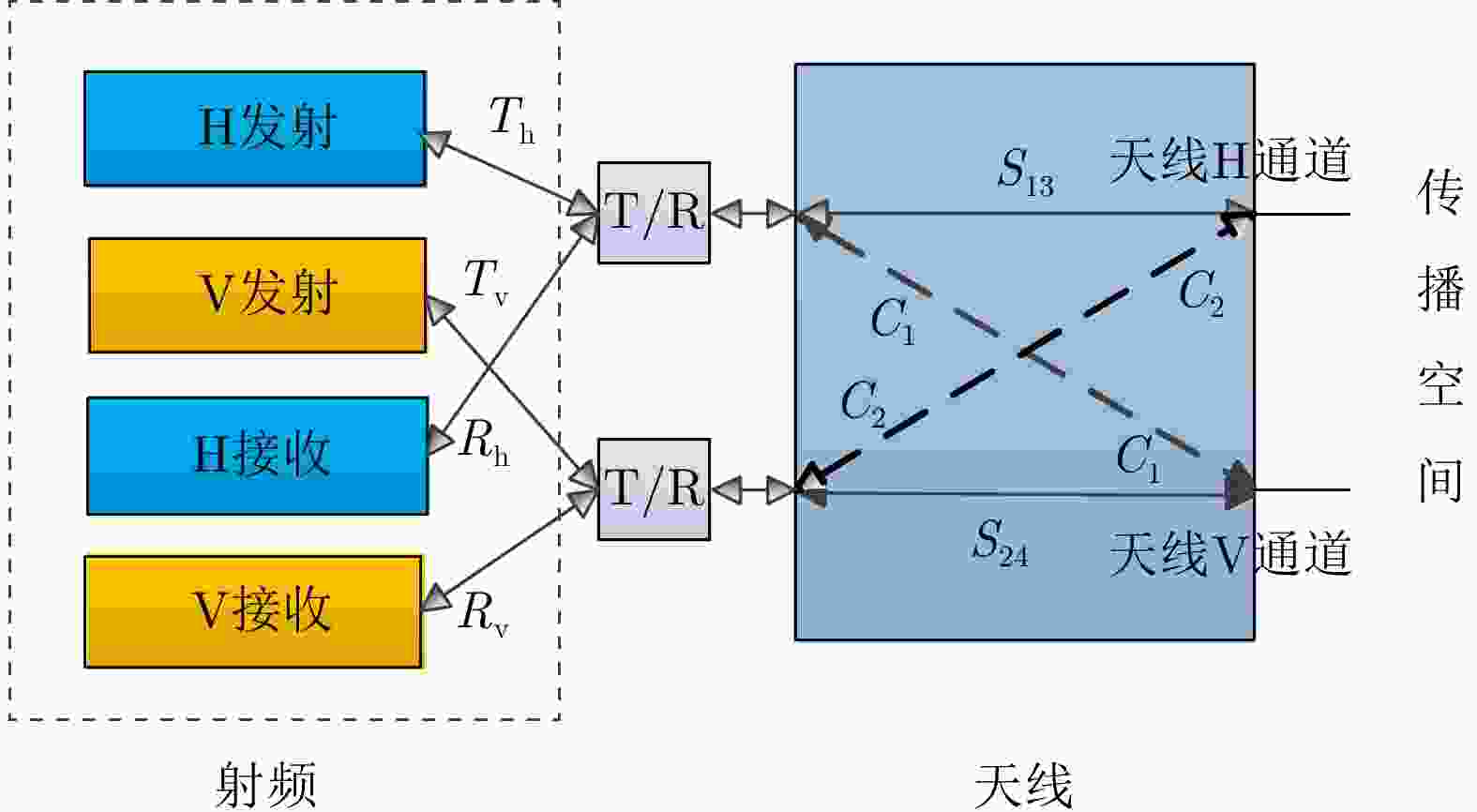
摘要: 迁飞性虫害突发性强、危害范围广,严重威胁国家粮食安全。昆虫雷达是监测昆虫迁飞的最有效手段,可为迁飞虫害预警防控提供关键信息支撑。传统昆虫雷达通过低分辨波形、旋转线极化天线等方式,实现昆虫体重、体轴方向等生物学参数测量。新型昆虫雷达采用调频步进频高分辨波形、瞬时全极化体制,可大幅提升昆虫生物学参数测量精度。但是,在传统极化测量误差之外,调频步进频成像会给不同极化通道引入新的乘性误差分量,导致极化通道间不一致更加复杂,必须进行高精度极化校准。针对以上问题,该文结合调频步进频波形特点对全极化测量模型进行了优化,并设计了一种基于松姿态约束下双定标体(金属球和金属丝)联合的高分辨全极化雷达极化校准方法,补偿了系统通道间不一致对极化信息测量的影响;在此基础上,进一步提出了基于生物对称模型的昆虫体轴方向估计方法,解析推导分析了极化通道间交叉串扰对体轴方向估计的影响机制。最后,利用多频全极化雷达(X, Ku, Ka)进行了极化校准和昆虫轴向测量实验,实测昆虫体轴方向测量误差优于3°,验证了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: Migratory pests are sudden outbreaks and widespread, putting national food security at risk. Entomological radar is most effective segment in monitoring insect migration, providing critical information for early warning and pest control. Traditional entomological radar can measure biological parameters such as mass and orientation using a low-resolution waveform and rotating linear polarization antenna. The new entomological radar uses a stepped chirp high-resolution waveform and instantaneous fully polarimetric system, which can considerably improve the accuracy of measuring insect biological data. However, in addition to the traditional polarization measurement errors, the stepped chirp waveform introduces new multiplicative error components to different polarization channels, resulting in a more complex imbalance between polarization channels, which requires high-precision polarization calibration. In response to the above issues, the fully polarimetric measurement model is optimized according to the characteristics of the high-resolution system, and a high-resolution system polarization error estimation method based on a sphere and a wire is proposed in this study, which can complete polarization calibration under the loose constraint of the calibrator attitude and compensate for the influence of channel inconsistency on polarization information measurement; additionally, an insect orientation estimation method based on a biological symmetry model is proposed, and the mechanism of cross-talk between polarization channels on orientation estimation is analyzed analytically. Finally, multifrequency high-resolution fully polarimetric radar (X, Ku, Ka) is used for polarimetric calibration and insect orientation measurement experiments, and the measurement error of orientation is less than 3°, which verified the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 不同交叉串扰时昆虫体轴方向估计误差
Table 1. Orientation estimation error under different cross-talk
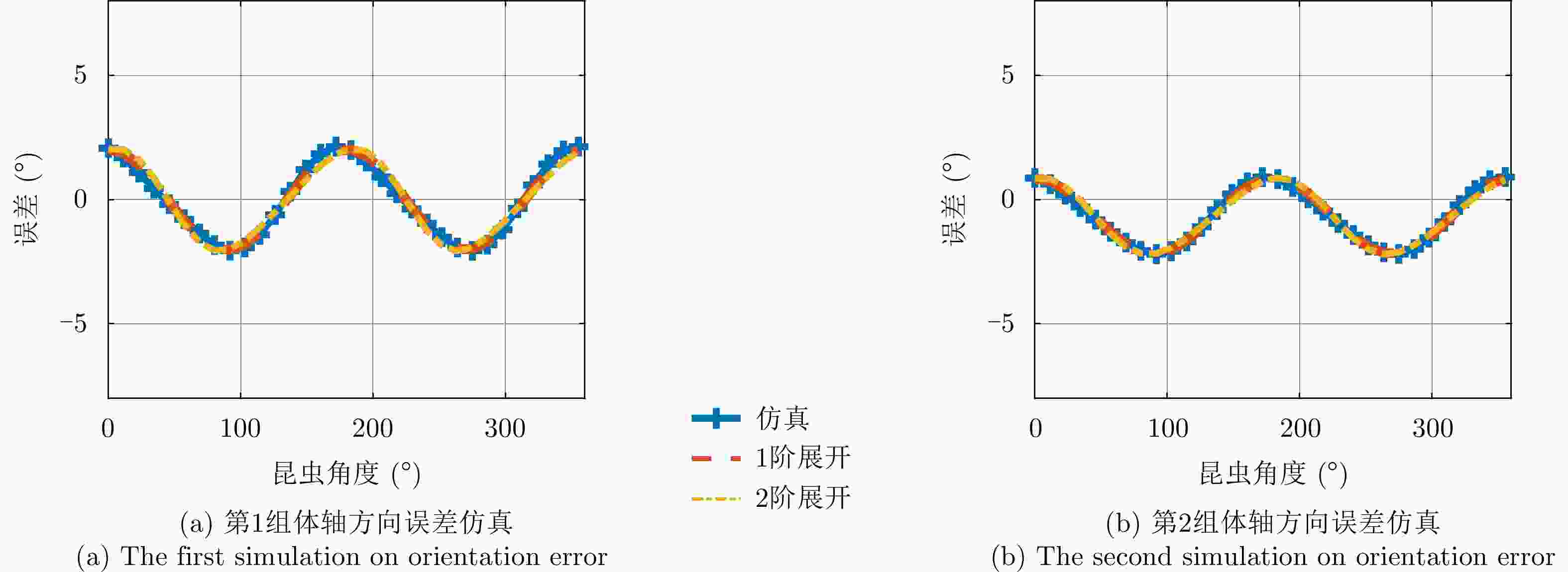
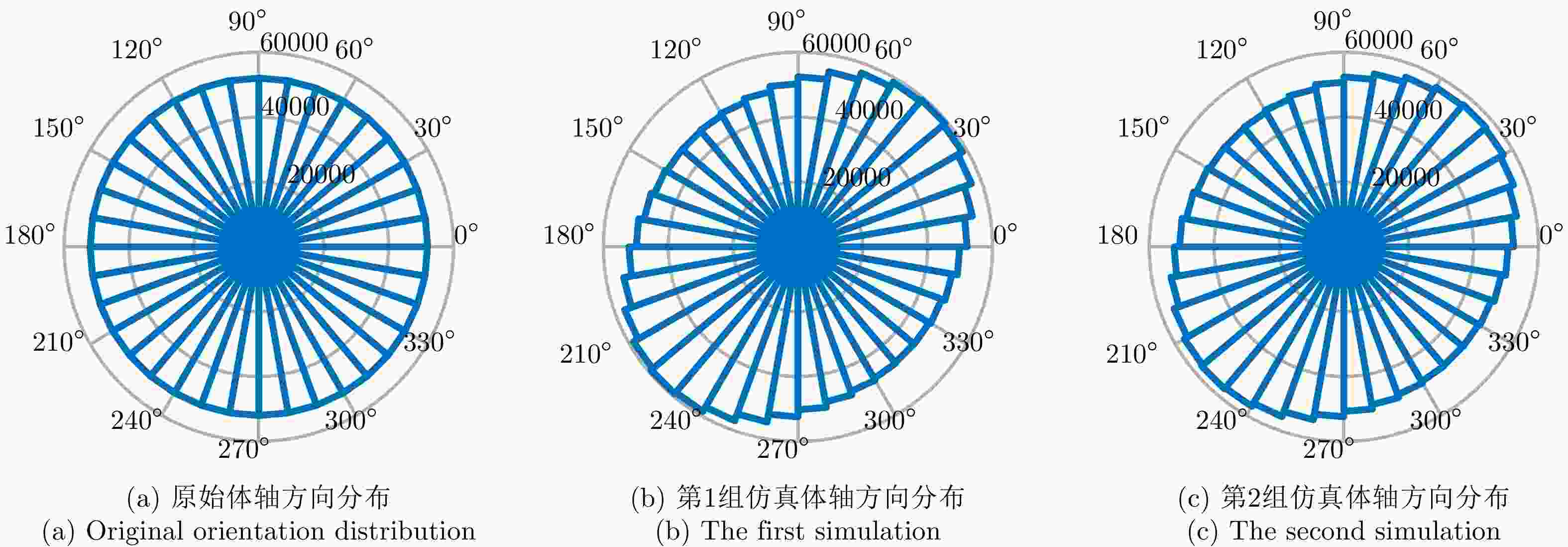
编号 交叉串扰${C_1}$ 交叉串扰${C_2}$ 体轴估计误差均值(°) 体轴估计误差标准差(°) 体轴估计误差最大值(°) 第1组 $0.055{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{j}}\pi /8}}$ $0.055{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{j}}\pi /8} }$ 8.9e-05 2.28 4.39 第2组 $0.055{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{j}}\pi /8}}$ ${C_1}/2$ –0.66 1.71 3.87 第3组 $0.055{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{j}}\pi /8}}$ $0.055{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{j}}\pi /16}}$ 0.08 2.46 4.74 表 2 多频全极化雷达参数
Table 2. The parameters of multi-frequency fully polarimetric radar
雷达参数 数值 雷达参数 数值 子频段带宽 1 GHz 距离分辨率 0.2 m(汉明窗) 中心频率 X1: 9.5 GHz; X2: 11.5 GHz; Ku1: 15.5 GHz;
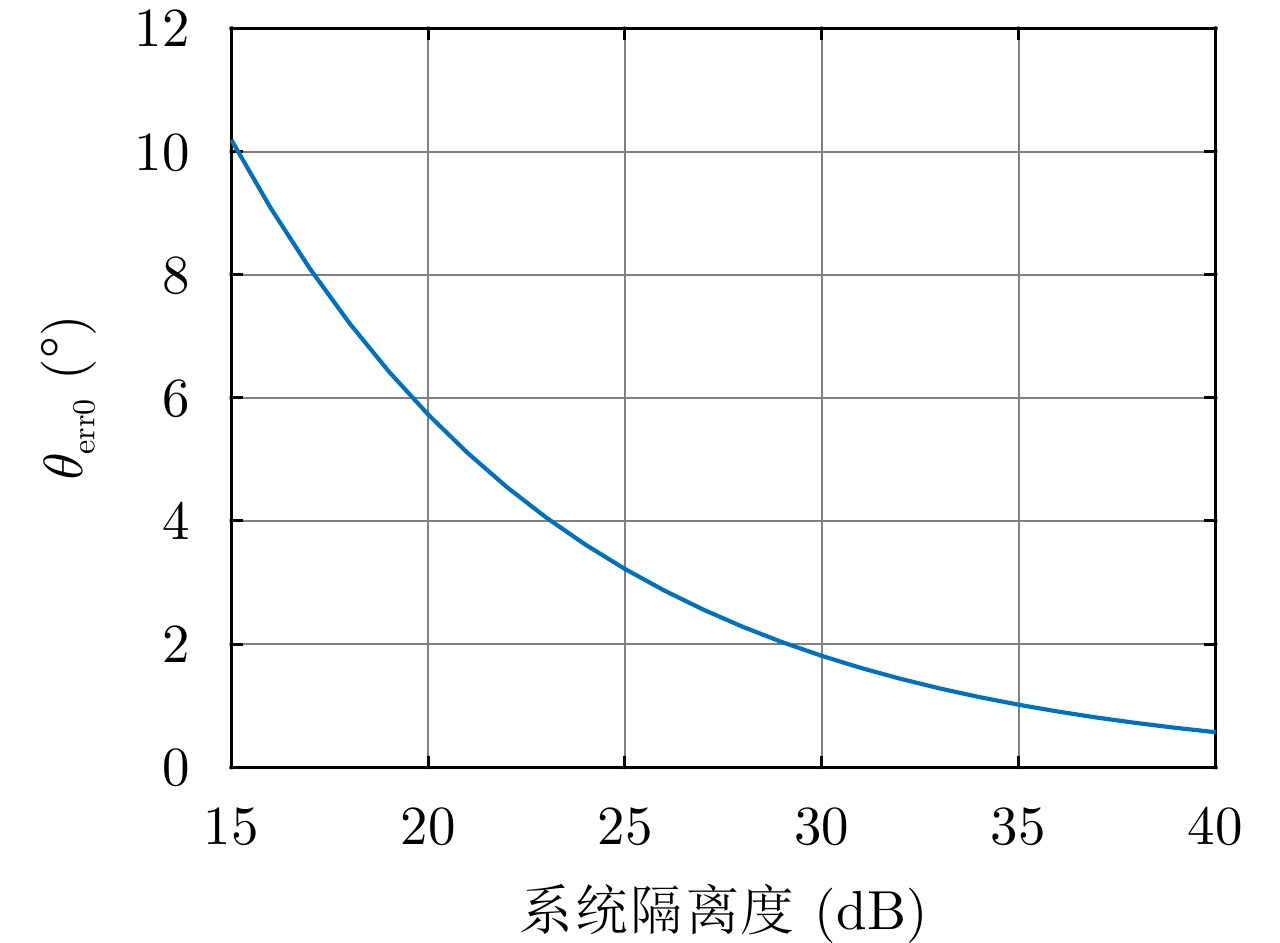
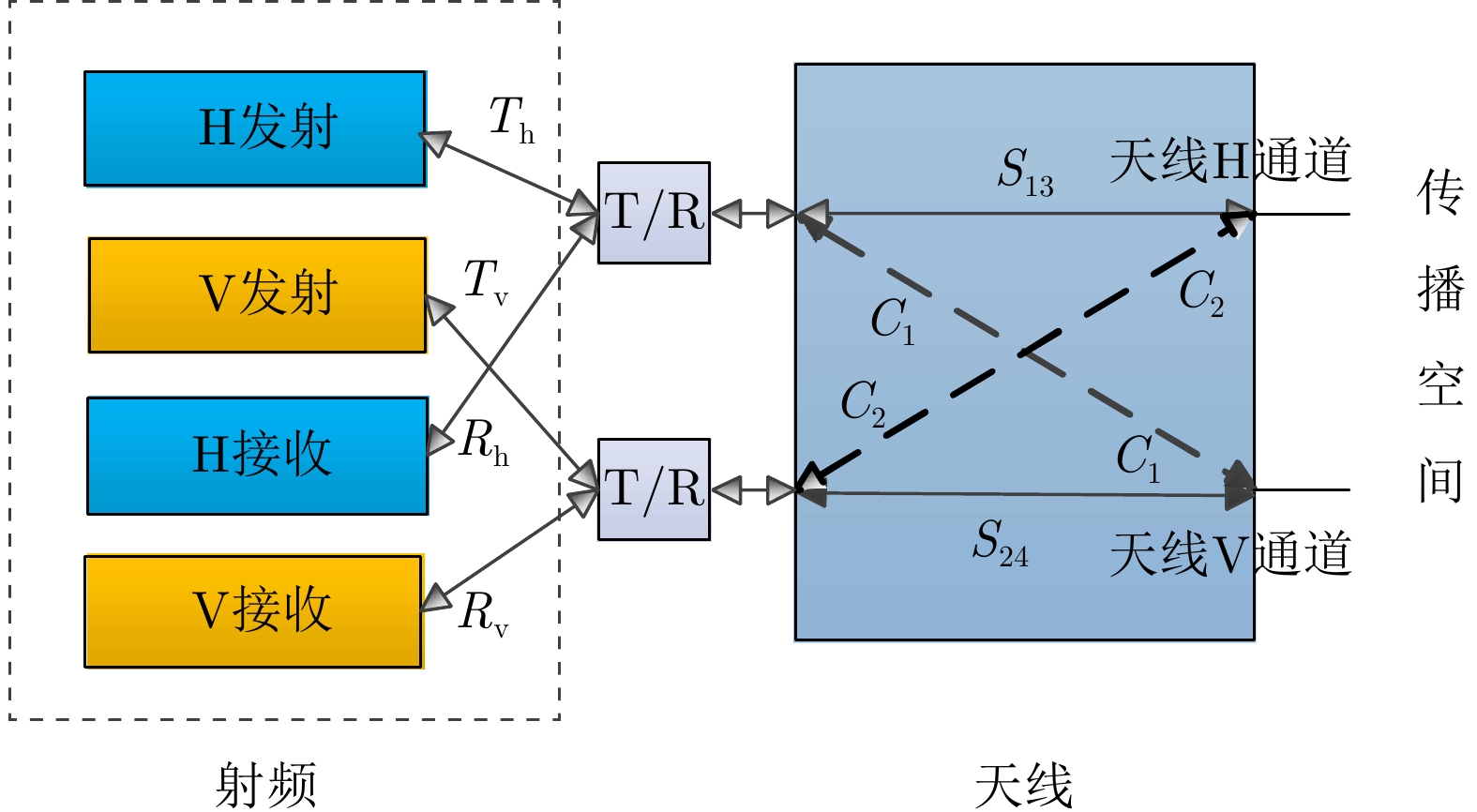
Ku2: 17.5 GHz; Ka: 35 GHz同频段不同通道间隔离度 >25 dB (3 dB波束宽度内) 天线形式 X, Ku, Ka 3波段共口径反射面天线 主反射面直径 2400 mm 3 dB波束宽度 X频段:<1.1°;Ku频段:<0.6°;Ka频段:<0.35° 天线增益 X频段:>42 dB;Ku频段:
>46 dB;Ka频段:>52 dB波形体制 调频步进频(每个子频段10个跳频点) 脉冲宽度(实际) 0.4 μs 跳频间隔 100 MHz 子跳频点信号带宽 125 MHz 脉冲重复周期 20 μs 探测距离 300~1350 m 峰值功率 X频段:≥580 W;Ku频段:≥100 W;
Ka频段:≥20 W表 3 不同频段昆虫体轴方向测量误差
Table 3. Measurement error of insect orientation in different frequencies
昆虫高度(m) 频段 角度估计误差均值(°) 角度估计误差标准差(°) 角度估计误差最大值(°) 480 X1 –0.077 0.83 2.70 X2 –0.063 0.88 2.54 Ku1 –0.089 0.95 2.88 Ku2 –0.093 1.01 2.90 Ka –0.130 1.31 2.98 440 X1 0.025 0.75 1.57 X2 0.038 0.87 1.84 Ku1 0.091 0.94 2.28 Ku2 0.097 0.91 2.33 Ka 0.190 1.38 2.80 400 X1 0.001 0.76 1.32 X2 0.077 0.92 1.94 Ku1 0.099 1.09 1.98 Ku2 0.108 1.21 2.01 Ka 0.210 1.44 2.55 -
[1] HU Gao, LIM K S, HORVITZ N, et al. Mass seasonal bioflows of high-flying insect migrants[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6319): 1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.aah4379 [2] WANG Rui, HU Cheng, LIU Changjiang, et al. Migratory insect multifrequency radar cross sections for morphological parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(6): 3450–3461. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2884926 [3] HU Cheng, LI Weidong, WANG Rui, et al. Insect biological parameter estimation based on the invariant target parameters of the scattering matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 6212–6225. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2904869 [4] HU Cheng, LI Wenji, WANG Rui, et al. Accurate insect orientation extraction based on polarization scattering matrix estimation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(10): 1755–1759. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2733719 [5] SMITH A D, RILEY J R, and GREGORY R D. A method for routine monitoring of the aerial migration of insects by using a vertical-looking radar[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B:Biological Sciences, 1993, 340(1294): 393–404. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1993.0081 [6] BEERWINKLE K R, WITZ J A, and SCHLEIDER P G. An automated, vertical looking, X-band radar system for continuously monitoring aerial insect activity[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 1993, 36(3): 965–970. doi: 10.13031/2013.28423 [7] DRAKE V A, CHAPMAN J W, LIM K S, et al. Ventral-aspect radar cross sections and polarization patterns of insects at X band and their relation to size and form[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 38(18): 5022–5044. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2017.1320453 [8] LONG Teng, HU Cheng, WANG Rui, et al. Entomological radar overview: System and signal processing[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2020, 35(1): 20–32. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2019.2955575 [9] LI Chao, LI Yongzhen, YANG Yong, et al. Moving target’s scattering matrix estimation with a polarimetric radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(8): 5540–5551. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2966905 [10] UNAL C M H, NIEMEIJER R J, VAN SINTTRUYEN J S, et al. Calibration of a polarimetric radar using a rotatable dihedral corner reflector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(4): 837–845. doi: 10.1109/36.298011 [11] 崔兴超, 粟毅, 陈思伟. 融合极化旋转域特征和超像素技术的极化SAR舰船检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 35–48. doi: 10.12000/JR20147CUI Xingchao, SU Yi, and CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric SAR ship detection based on polarimetric rotation domain features and superpixel technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 35–48. doi: 10.12000/JR20147 [12] 杨汝良, 戴博伟, 李海英. 极化合成孔径雷达极化层次和系统工作方式[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 132–142. doi: 10.12000/JR16013YANG Ruliang, DAI Bowei, and LI Haiying. Polarization hierarchy and system operating architecture for polarimetric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 132–142. doi: 10.12000/JR16013 [13] 安孟昀, 殷加鹏, 黄建开, 等. 一种双极化气象雷达自适应谱极化滤波方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 408–417. doi: 10.12000/JR21199AN Mengyun, YIN Jiapeng, HUANG Jiankai, et al. Adaptive spectral polarization filter design for dual-polarization weather radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 408–417. doi: 10.12000/JR21199 [14] SARABANDI K and ULABY F T. A convenient technique for polarimetric calibration of single-antenna radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1990, 28(6): 1022–1033. doi: 10.1109/36.62627 [15] GAU J R J and BURNSIDE W D. New polarimetric calibration technique using a single calibration dihedral[J]. IEE Proceedings - Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation, 1995, 142(1): 19–25. doi: 10.1049/ip-map:19951544 [16] DAI Huanyao, CHANG Yuliang, DAI Dahai, et al. Calibration method of phase distortions for cross polarization channel of instantaneous polarization radar system[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 21(2): 211–218. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4132.2010.02.007 [17] YU Teng, LI Muyang, LI Weidong, et al. Polarimetric calibration technique for a fully polarimetric entomological radar based on antenna rotation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(7): 1551. doi: 10.3390/rs14071551 [18] HUANG Peikang, NING Chao, XU Xiaojian, et al. Solution for polarimetric radar cross section measurement and calibration[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 25(2): 211–216. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2014.00025 [19] 何密, 李永祯, 王雪松, 等. 基于Pauli基分解的极化校准算法[J]. 宇航学报, 2011, 32(12): 2589–2595. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2011.12.018HE Mi, LI Yongzhen, WANG Xuesong, et al. A polarimetric calibration algorithm based on Pauli-basis decomposition[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2011, 32(12): 2589–2595. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2011.12.018 [20] 何密. 同时极化测量体制雷达的校准方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2014.HE Mi. Study on calibration methods for simultaneous measurement polarimetric radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2014. [21] ZENG Tao, MAO Cong, HU Cheng, et al. Grating lobes suppression method for stepped frequency GB-SAR system[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 25(6): 987–995. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2014.00113 [22] ALDHOUS A C. An investigation of the polarisation dependence of insect radar cross sections at constant aspect[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Cranfield University, 1989. [23] CAMERON W L and LEUNG L K. Feature motivated polarization scattering matrix decomposition[C]. IEEE International Conference on Radar, Arlington, USA, 1990: 549–557. [24] HU Cheng, LI Muyang, LI Weidong, et al. A data-driven polarimetric calibration method for entomological radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5114014. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3178108 [25] HU Cheng, LI Weidong, WANG Rui, et al. Discrimination of parallel and perpendicular insects based on relative phase of scattering matrix eigenvalues[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(6): 3927–3940. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2959622 [26] 罗佳. 天线空域极化特性及应用[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2008.LUO Jia. Application and analysis of spatial polarization characteristics for antenna[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2008. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: