A Single-bit Multiplexing Array Signal Transceiver Framework for Low-cost Lightweight Radar
-
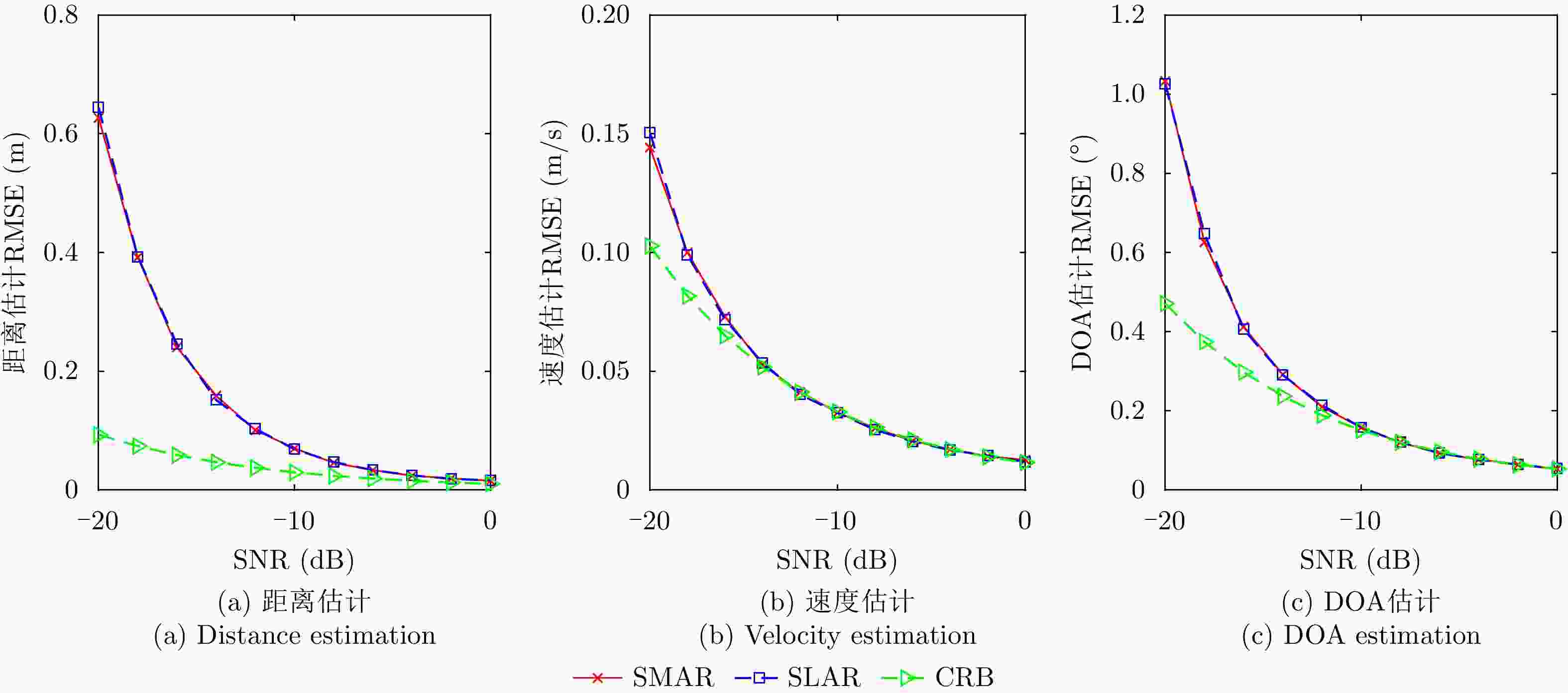
摘要: 面向低成本轻量级雷达的应用需求,该文提出了一种联合单比特采样量化和时分复用接收机的雷达信号收发框架。首先,通过介绍该框架的工作原理,阐述其在节省接收机数量方面的优势。从雷达资源配置的角度,分析了单比特采样量化在该框架中的重要性,并提出了该框架可利用时间换空间,获得比经典线性调频连续波雷达更好的探测性能。接着,推导了雷达测距、测速和测角公式,以及目标参数估计的克拉美罗界。在此基础上,验证了该框架的性能优势,同时也给出了其稳定工作的信噪比条件。最后,利用一种基于单比特二维多重信号分类的速度维配对算法,验证了该框架获取目标原理的正确性,以及性能分析的可靠性。Abstract: This paper proposes a radar signal transceiver framework that combines single-bit sampling and time division multiplexing receivers to satisfy the application requirements of low-cost lightweight radars. Firstly, this paper explains the advantages of saving the number of receivers by introducing the working principle of the framework. From the perspective of radar resource allocation, the importance of single-bit sampling in this framework was analyzed; additionally, the proposed framework can achieve better performance than a classical linear frequency modulation continuous wave radar using time and space exchange. Subsequently, the formulas for range, velocity and angle measurement were derived, along with the Cramér-Rao bound for estimating target parameters. Accordingly, the performance advantages of the proposed framework were verified, and the signal-to-noise ratio conditions for its stable operation were determined. Finally, this paper verifies the accuracy of the target acquisition principle of the proposed framework and the reliability of the performance analysis by using a velocity dimensional pairing algorithm based on single-bit two-dimensional multiple signal classification.
-
表 1 不同收发框架需要收发机的数量
Table 1. Number of transceivers required for different frameworks
收发框架类型 发射机数量(个) 接收机数量(个) SIMO 1 12 TDM-MIMO 1 6 SMA-MIMO 1 2 表 2 不同雷达类型的参数
Table 2. Parameters of different radar types
案例名 接收机数量 阵元数量M CPI (ms) 脉冲重复周期(μs) 脉冲个数P 脉冲宽度(μs) ADC采样频率(MHz) 单周期采样点数L TMLR 1 1 1.2 97.4026 12 97.4026 0.6844 66 SMAR-2 1 2 1.2 97.4026 12 48.7013 1.3689 66 SMAR-4 1 4 1.2 97.4026 12 24.3506 2.7378 66 SMAR-8 1 8 1.2 97.4026 12 12.1753 5.4756 66 SMAR-16 1 16 1.2 97.4026 12 6.0877 10.9511 66 SLAR-2 2 2 1.2 97.4026 12 48.7013 1.3689 66 SLAR-4 4 4 1.2 97.4026 12 24.3506 2.7378 66 SLAR-8 8 8 1.2 97.4026 12 12.1753 5.4756 66 SLAR-16 16 16 1.2 97.4026 12 6.0877 10.9511 66 -
[1] LIANG Junli, ZHANG Xuan, SO H C, et al. Sparse array beampattern synthesis via alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(5): 2333–2345. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2811778 [2] WANG Xiangrong, ABOUTANIOS E, and AMIN M G. Thinned array beampattern synthesis by iterative soft-thresholding-based optimization algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(12): 6102–6113. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2364048 [3] CHEN Kesong, YUN Xiaohua, HE Zishu, et al. Synthesis of sparse planar arrays using modified real genetic algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2007, 55(4): 1067–1073. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2007.893375 [4] FENG Lifang, CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, et al. Beampattern synthesis via the constrained subarray layout optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(1): 182–194. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3008652 [5] ZHANG Ruoyu, SHIM B, and WU Wen. Direction-of-arrival estimation for large antenna arrays with hybrid analog and digital architectures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 72–88. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3119768 [6] QIN Si, ZHANG Y D, and AMIN M G, et al. Generalized coprime array configurations for direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(6): 1377–1390. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2393838 [7] PAL P and VAIDYANATHAN P P. Nested arrays: A novel approach to array processing with enhanced degrees of freedom[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(8): 4167–4181. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2049264 [8] BARAL A B and TORLAK M. Joint Doppler frequency and direction of arrival estimation for TDM MIMO automotive radars[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 980–995. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3073572 [9] HU Xueyao, LI Yang, LU Man, et al. A multi-carrier-frequency random-transmission chirp sequence for TDM MIMO automotive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3672–3685. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2900357 [10] HONG Lang and HONG S. Systems and methods for virtual aperature radar tracking[P]. US, EP3746809A4, 2021. [11] LEE M S and KIM Y H. Design and performance of a 24-GHz switch-antenna array FMCW radar system for automotive applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2010, 59(5): 2290–2297. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2010.2045665 [12] FANG Jun, LIU Yumeng, LI Hongbin, et al. One-bit quantizer design for multisensor GLRT fusion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 257–260. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2243144 [13] 黄广佳, 程旭, 饶彬, 等. 基于广义Rao检验的单/多比特MIMO雷达运动目标检测方法[J/OL]. 系统工程与电子技术, 1–12. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2422.TN.20230201.1510.001.html, 2023.HUANG Guangjia, CHENG Xu, RAO Bin, et al. One/multi-bit MIMO radar detection of a moving target based on generalized Rao test[J/OL]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 1–12. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2422.TN.20230201.1510.001.html, 2023. [14] CHENG Xu, CIUONZO D, ROSSI P S, et al. Multi-bit & sequential decentralized detection of a noncooperative moving target through a generalized Rao test[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2021, 7: 740–753. doi: 10.1109/TSIPN.2021.3126930 [15] CHENG Xu, CIUONZO D, and ROSSI P S. Multibit decentralized detection through fusing smart and dumb sensors based on Rao test[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1391–1405. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2936777 [16] WANG Xueqian, LI Gang, and VARSHNEY P K. Distributed detection of weak signals from one-bit measurements under observation model uncertainties[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(3): 415–419. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2892196 [17] LI Chengxi, HE You, WANG Xueqian, et al. Distributed detection of sparse stochastic signals via fusion of 1-bit local likelihood ratios[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(12): 1738–1742. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2945193 [18] LI Chengxi, LI Gang, and VARSHNEY P K. Distributed detection of sparse stochastic signals with 1-bit data in tree-structured sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 2963–2976. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2988598 [19] XIAO Yuhang, RAMÍREZ D, SCHREIER P J, et al. One-bit target detection in collocated MIMO radar and performance degradation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(9): 9363–9374. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3178285 [20] REN Jiaying, ZHANG Tianyi, LI Jian, et al. Sinusoidal parameter estimation from signed measurements via majorization-minimization based RELAX[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(8): 2173–2186. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2899804 [21] STOICA P, SHANG Xiaolei, and CHENG Yuanbo. The Cramér-Rao bound for signal parameter estimation from quantized data [Lecture Notes][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2022, 39(1): 118–125. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2021.3116532 [22] FENG Lifang, HUANG Lei, LI Qiang, et al. An off-grid iterative reweighted approach to one-bit direction of arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(6): 8134–8139. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3239003 [23] BAR-SHALOM O and WEISS A J. DOA estimation using one-bit quantized measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(3): 868–884. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2002.1039405 [24] HUANG Xiaodong and LIAO Bin. One-bit MUSIC[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(7): 961–965. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2913452 [25] CHEN Xinzhu, HUANG Lei, ZHOU Hanfei, et al. One-bit digital beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(1): 555–567. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3181257 [26] FU Haoyu and CHI Yuejie. Quantized spectral compressed sensing: Cramer-Rao bounds and recovery algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(12): 3268–3279. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2827326 [27] ZAYYANI H, HADDADI F, and KORKI M. Double detector for sparse signal detection from one-bit compressed sensing measurements[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(11): 1637–1641. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2613898 [28] SHANG Xiaolei, LI Jian, and STOICA P. Weighted SPICE algorithms for range-Doppler imaging using one-bit automotive radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 1041–1054. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3071601 [29] ZAHABI S J, NAGHSH M M, MODARRES-HASHEMI M, et al. One-bit compressive radar sensing in the presence of clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(1): 167–185. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2916532 [30] ZHANG Rong, LI Changheng, LI Jian, et al. Range estimation and range-Doppler imaging using signed measurements in LFMCW radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3531–3550. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2907395 [31] JIN Benzhou, ZHU Jiang, WU Qihui, et al. One-bit LFMCW radar: Spectrum analysis and target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(4): 2732–2750. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2978374 [32] AMERI A, BOSE A, LI Jian, et al. One-bit radar processing with time-varying sampling thresholds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(20): 5297–5308. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2939086 [33] XI Feng, XIANG Yijian, ZHANG Zhen, et al. Joint angle and Doppler frequency estimation for MIMO radar with one-bit sampling: A maximum likelihood-based method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(6): 4734–4748. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3000841 [34] CHENG Ziyang, HE Zishu, and LIAO Bin. Target detection performance of collocated MIMO radar with one-bit ADCs[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(12): 1832–1836. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2951496 [35] XI Feng, XIANG Yijian, CHEN Shengyao, et al. Gridless parameter estimation for one-bit MIMO radar with time-varying thresholds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1048–1063. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2970343 [36] LIU Bingfan, CHEN Baixiao, and YANG Minglei. Parameter estimation and CRB analysis of 1-bit colocated MIMO radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2021, 15(6): 592–604. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12076 [37] 张国鑫, 易伟, 孔令讲. 基于1比特量化的大规模MIMO雷达系统直接定位算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 970–981. doi: 10.12000/JR21062ZHANG Guoxin, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Direct position determination for massive MIMO system with one-bit quantization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 970–981. doi: 10.12000/JR21062 [38] 王峥. 单比特压缩感知雷达成像关键技术的研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2021.WANG Zheng. One-bit compressed sensing radar imaging research on key technologies[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2021. [39] 赵博, 黄磊, 周汉飞, 等. 基于单频时变阈值的1-bit SAR成像方法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 446–454. doi: 10.12000/JR18036ZHAO Bo, HUANG Lei, ZHOU Hanfei, et al. 1-bit SAR imaging method based on single-frequency time-varying threshold[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 446–454. doi: 10.12000/JR18036 [40] ZHAO Bo, HUANG Lei, and BAO Weimin. One-bit SAR imaging based on single-frequency thresholds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 7017–7032. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2910284 [41] ZHAO Bo, HUANG Lei, LI Jian, et al. Deceptive SAR jamming based on 1-bit sampling and time-varying thresholds[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(3): 939–950. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2793247 [42] VAN VLECK J H and MIDDLETON D. The spectrum of clipped noise[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1966, 54(1): 2–19. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1966.4567 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: