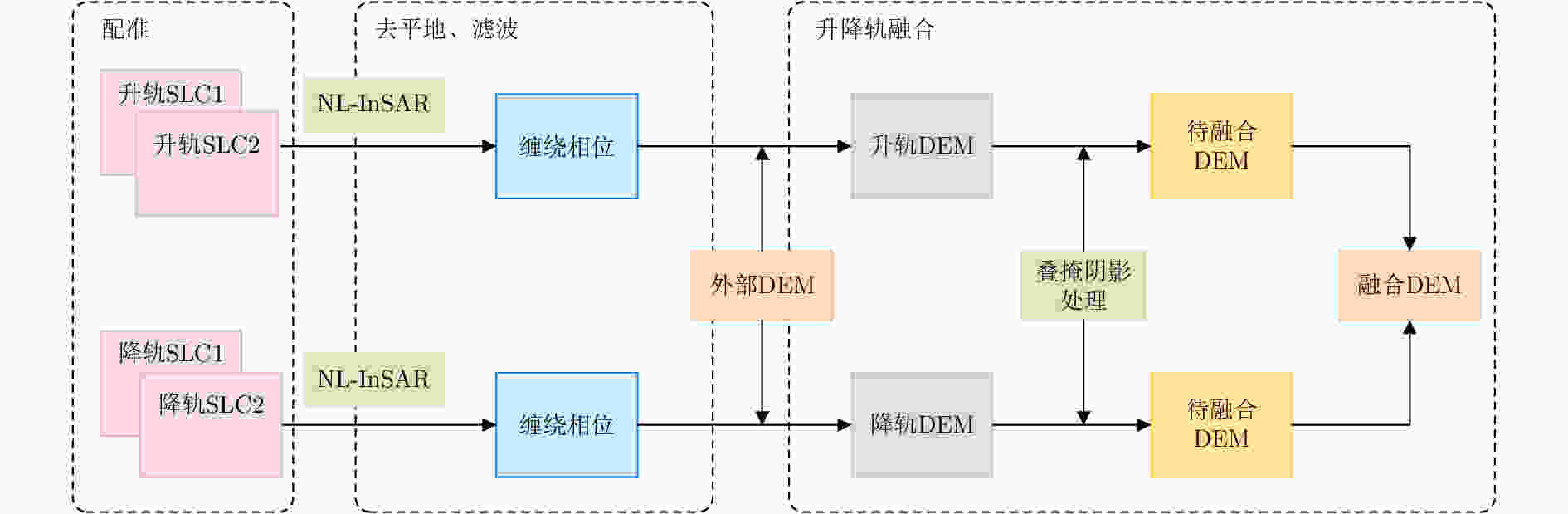
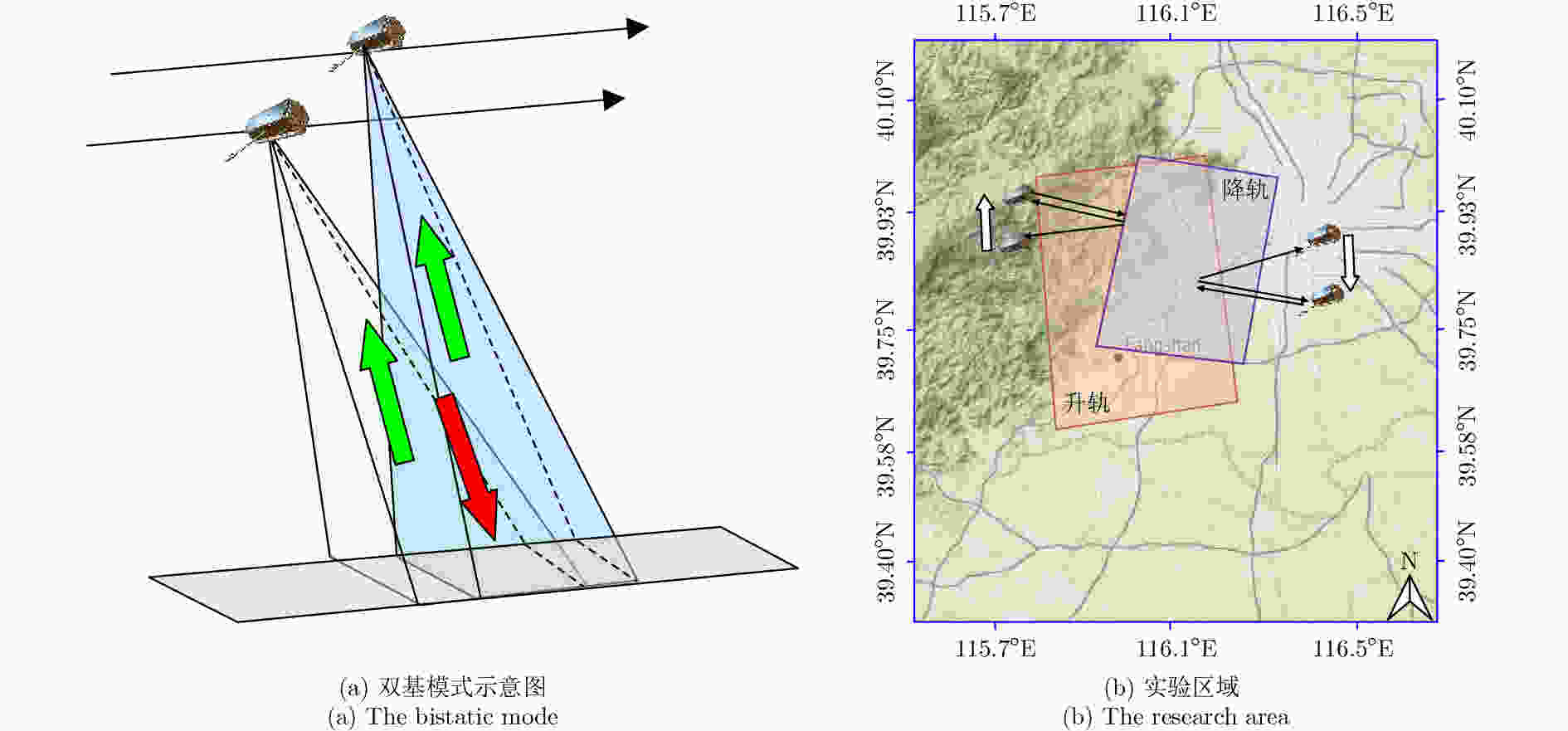
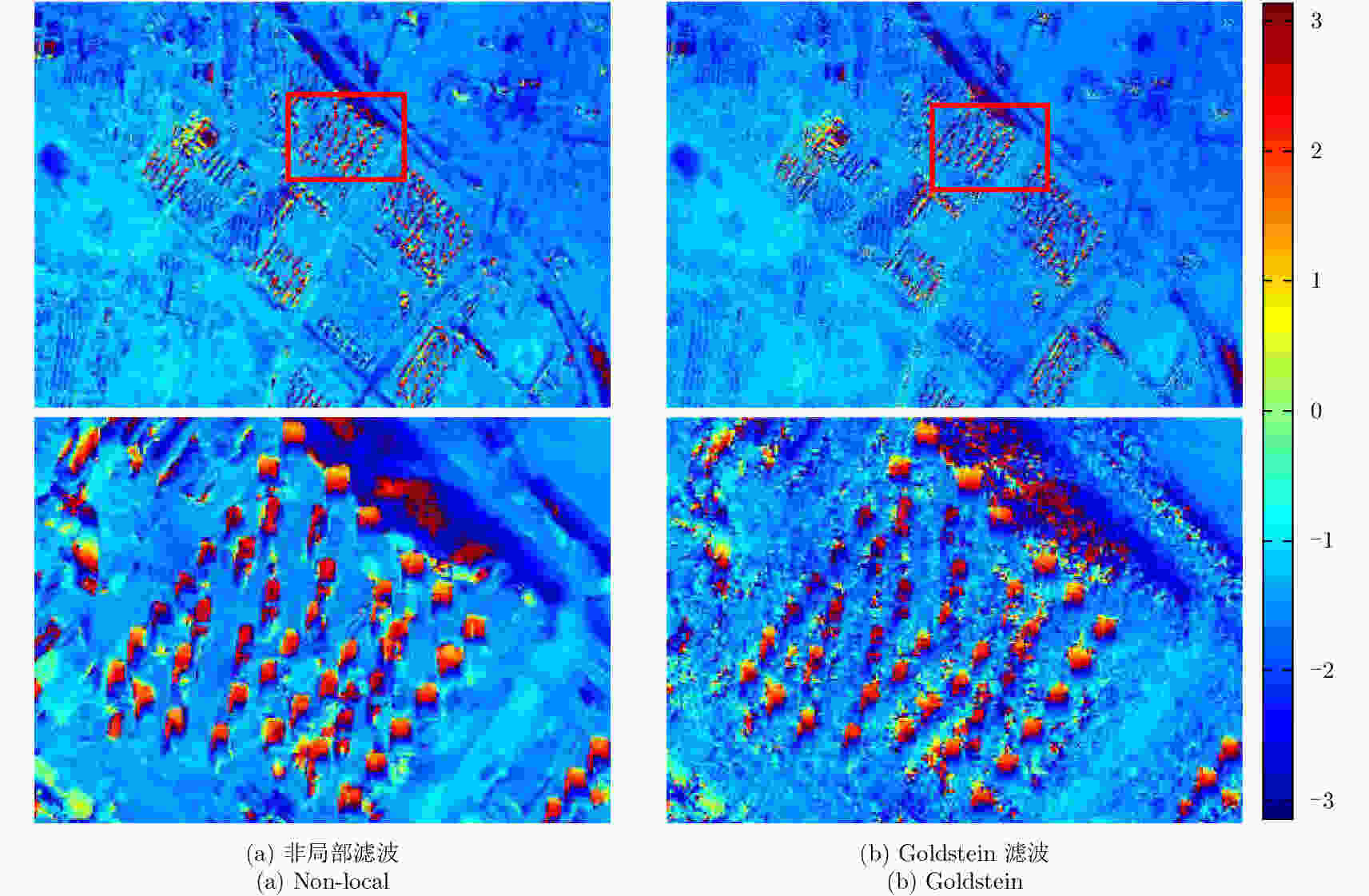
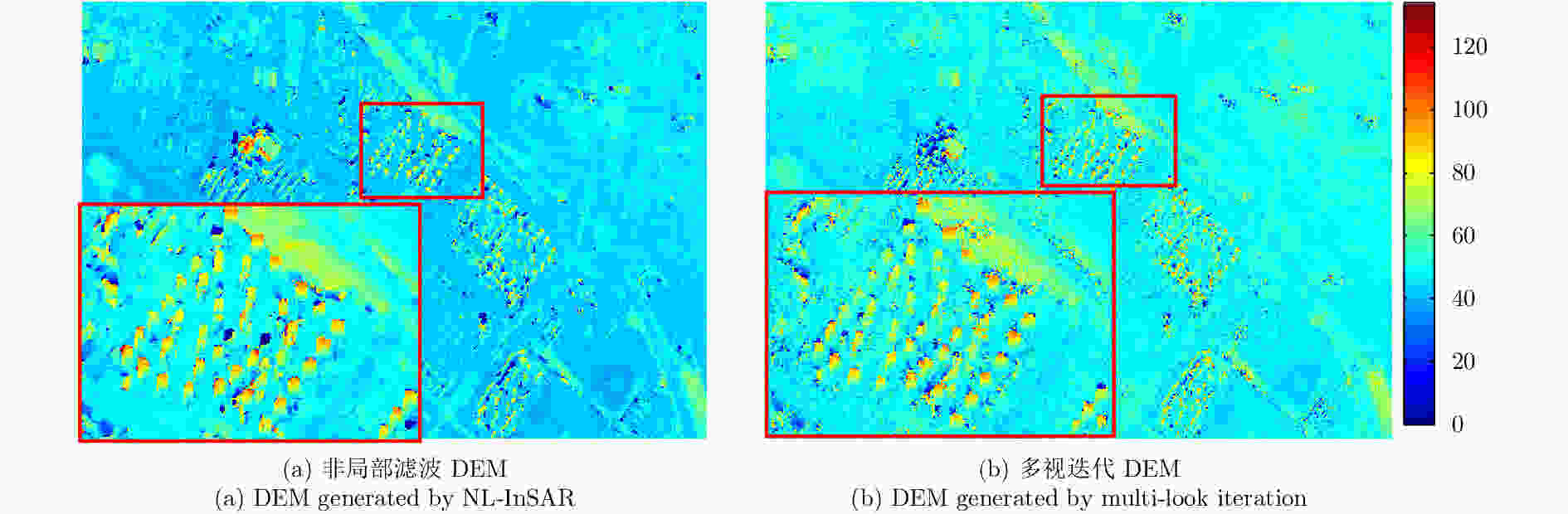
A High Precision DEM Generation Method Based on Ascending and Descending Pass TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X BiSAR Data
-
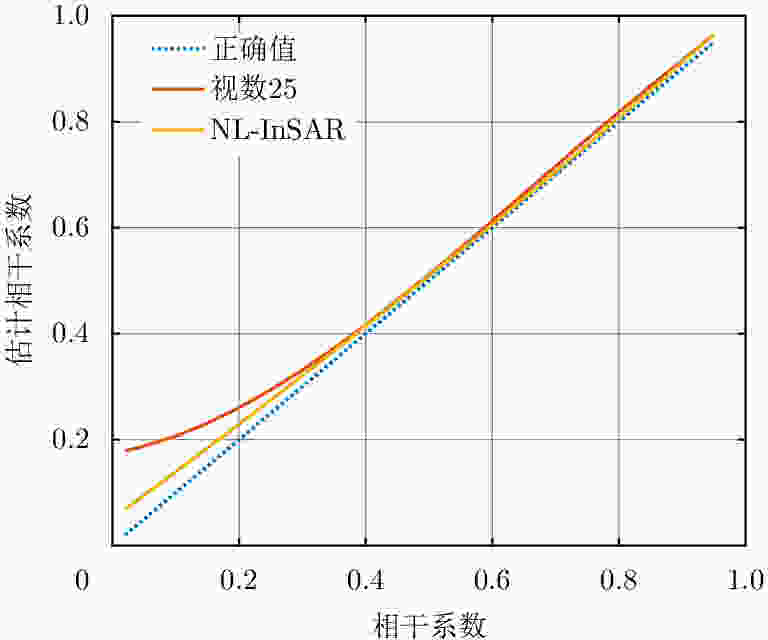
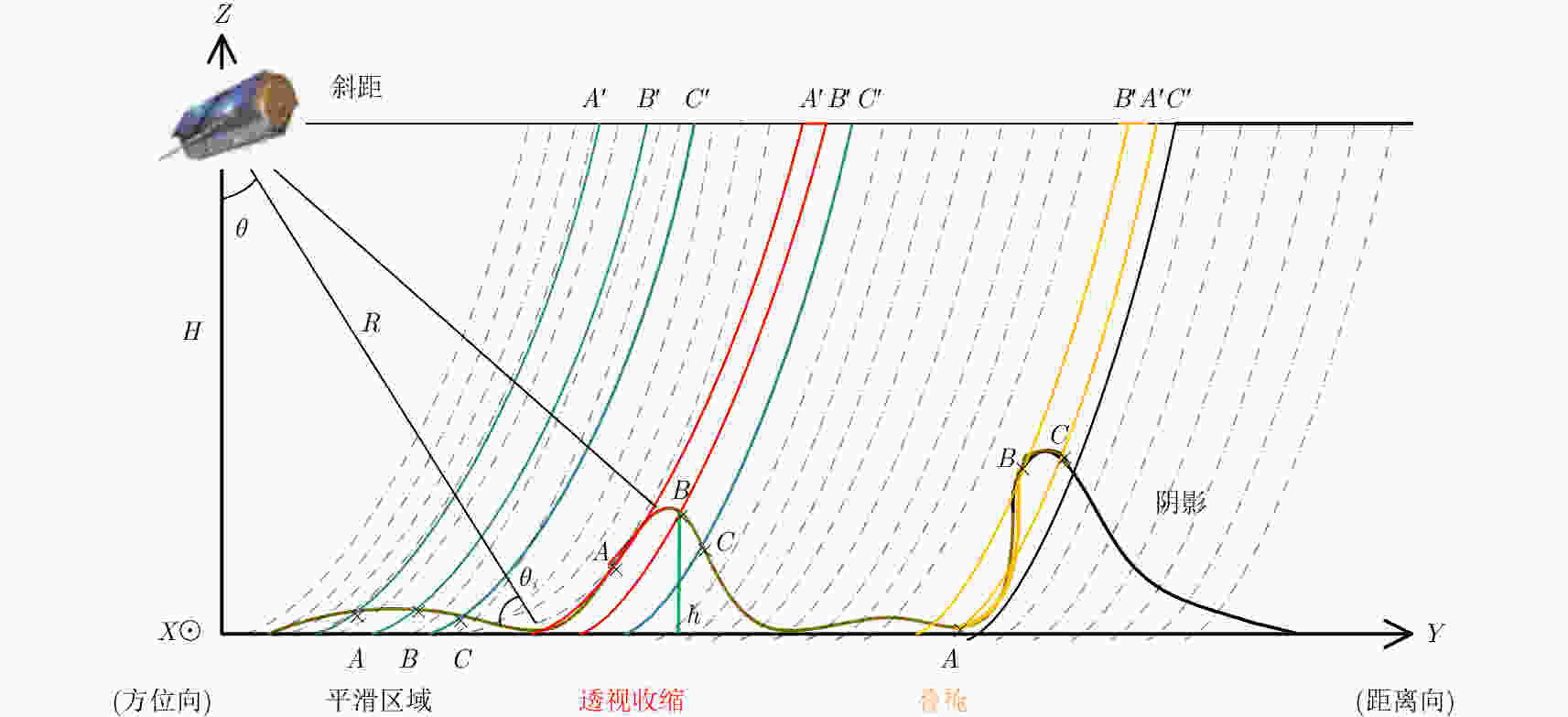
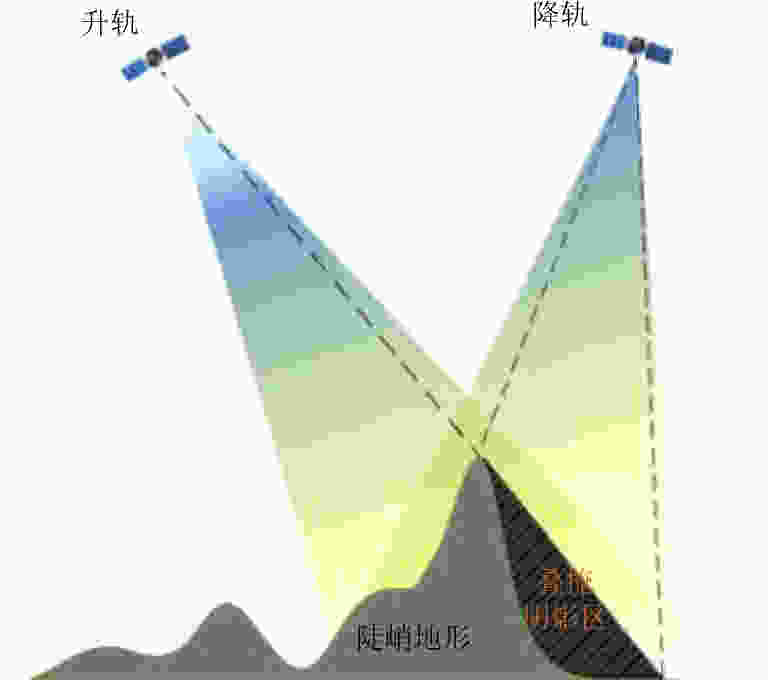
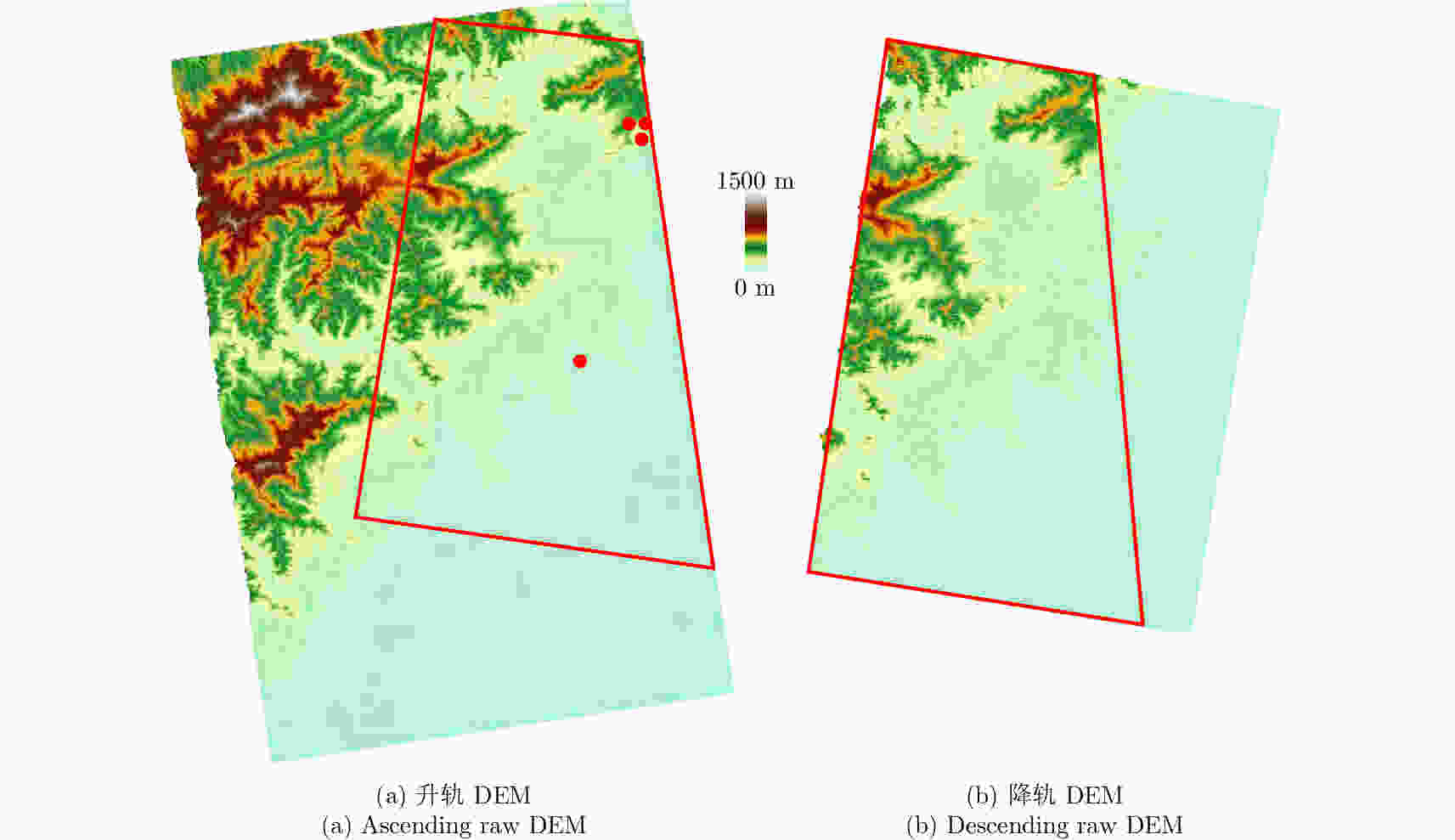
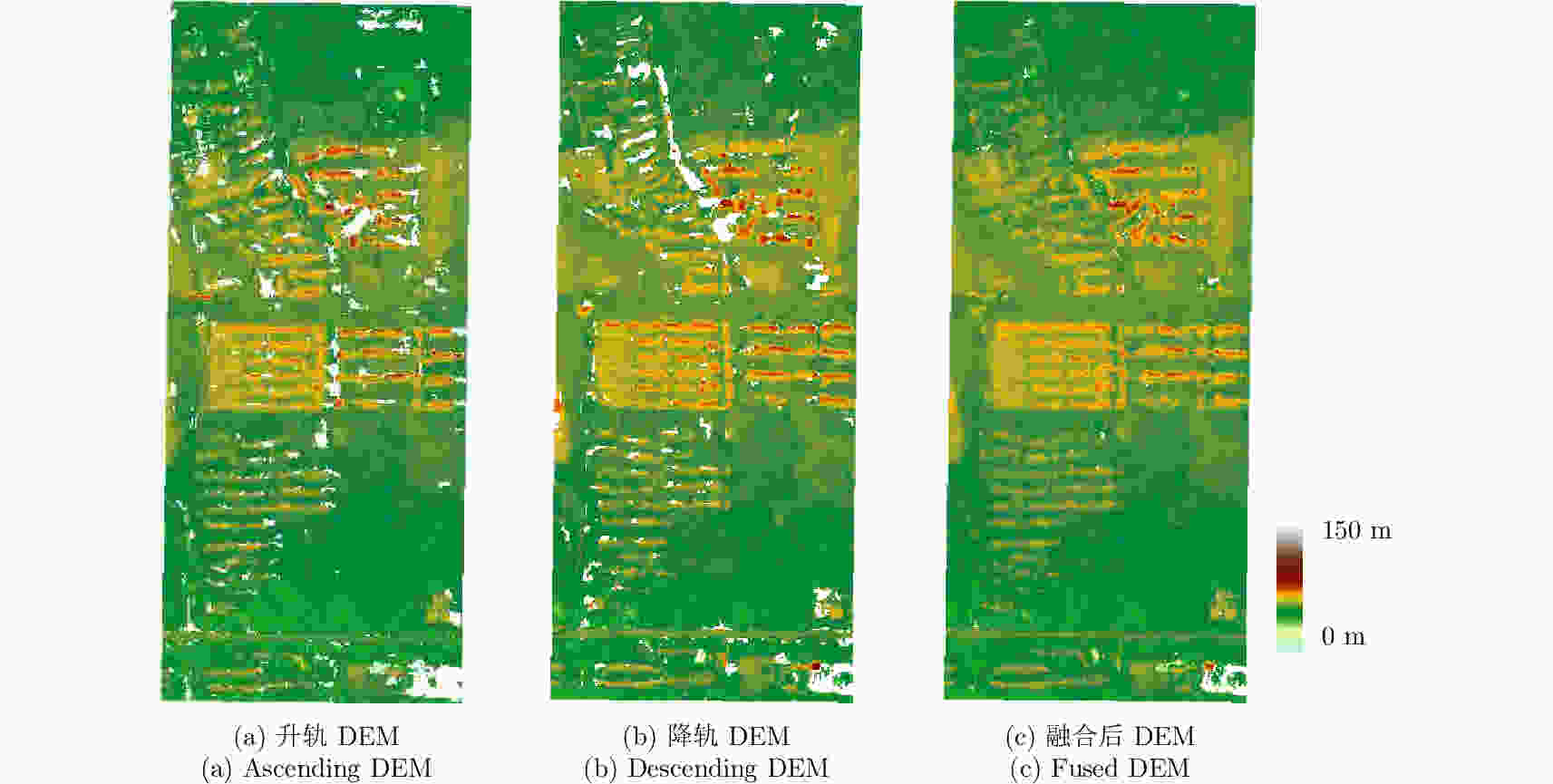
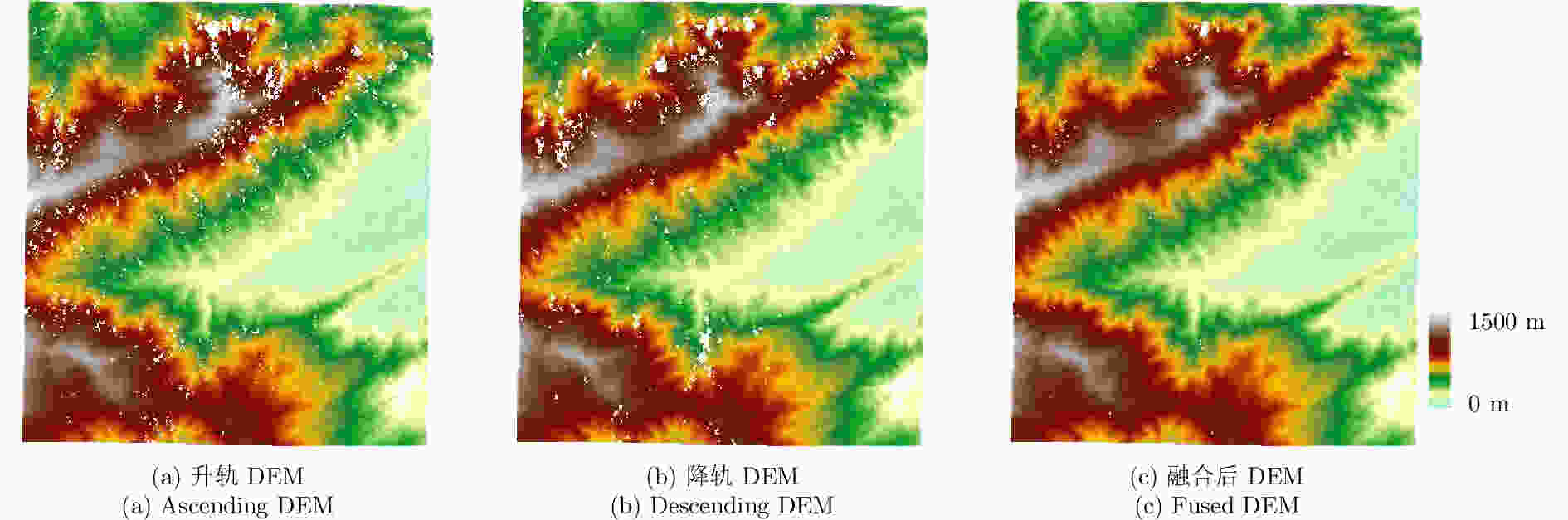
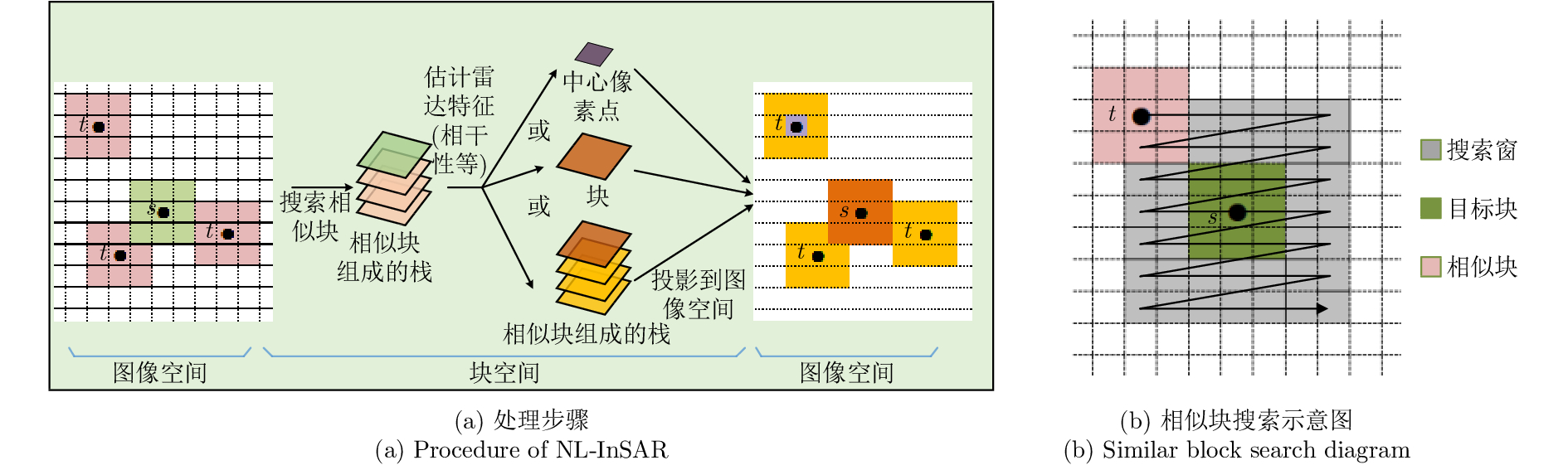
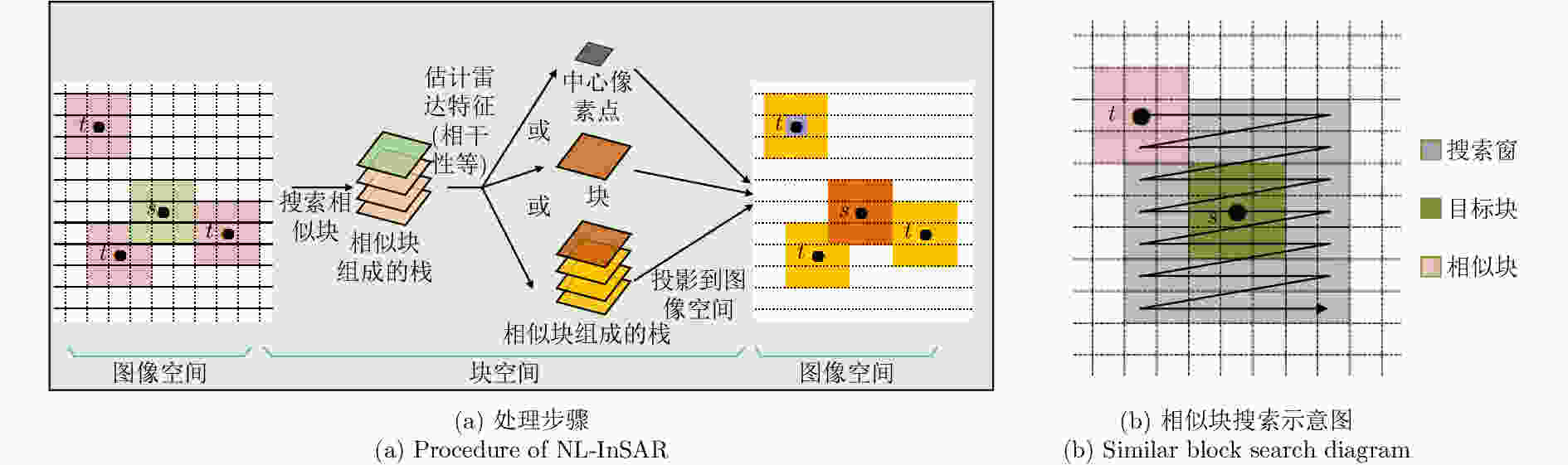
摘要: 该文基于TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X (TSX/TDX)双基升降轨数据,首先采用非局部干涉(NonLocal Interferometric SAR, NL-InSAR)相位滤波分别得到单航过升轨和降轨模式下的高分辨率DEM。在此基础上,基于NL-InSAR估计得到的较准确相干系数,提出一种升降轨DEM融合方法,恢复SAR侧视成像造成的几何畸变,提高DEM重建精度。该文采用两幅北京地区的TSX/TDX升降轨干涉对进行融合处理,结果表明,在地形复杂地区的叠掩和阴影等无效区域,融合之后的DEM无效点数明显减少。经统计,融合后无效点数比例由升轨、降轨的4.93%和4.52%降低到1.34%。同时,融合DEM的精度相比于升轨的6.74 m提高了8.7%、相比于降轨的6.67 m提高了9.6%,融合后高程精度达到6.09 m。Abstract: A method for fine resolution and high precision Digital Elevation Model (DEM) generation using ascending and descending pass TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X (TSX/TDX) datasets is proposed in this study. First, the NonLocal Interferometric SAR (NL-InSAR) can effectively generate ascending and descending pass raw DEMs. On this basis, the coherence well recovered by NL-InSAR is used to fusion the raw DEMs to further improve the accuracy and reduce the invalids caused by layover and shadows. This method was used to process the TSX/TDX data obtained in Beijing. The number of invalid points of DEM after fusion decreased significantly. Statistics result shows that it decreased from 4.93% in ascending raw DEM and 4.52% in descending raw DEM to 1.34% in the fusion DEM. At the same time, the accuracy of the fusion DEM increased by 9.6% compared to 6.67 m in the descending raw DEM and 8.7% compared to 6.74 m in the ascending raw DEM, reaching 6.09 m.
-
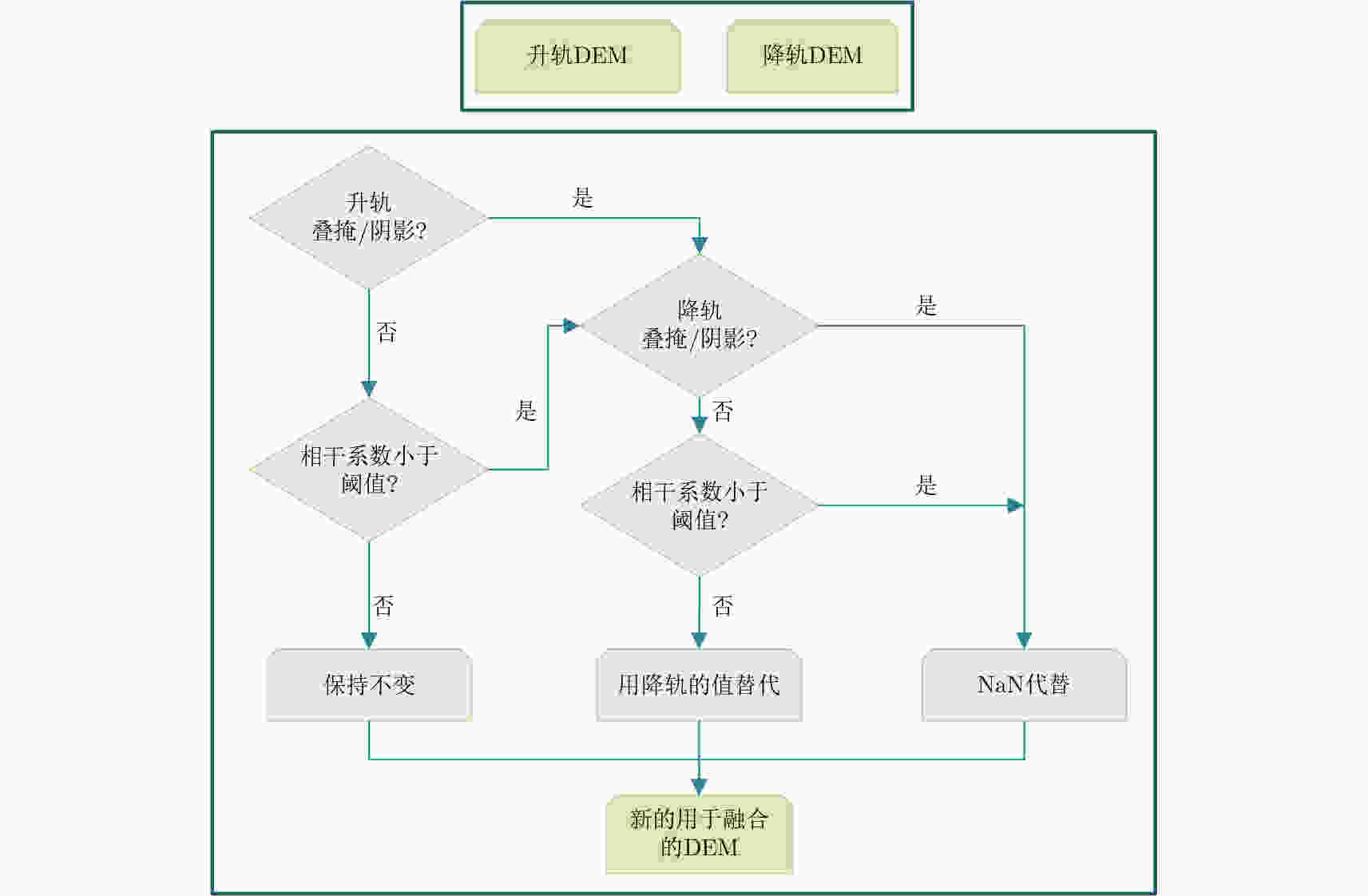
表 1 升降轨DEM融合处理表
Table 1. Logic table for ascending and descending pass TanDEM-X raw DEMs fusion
升轨叠掩
/阴影降轨叠掩
/阴影升轨相干系数
小于阈值降轨相干系数
小于阈值融合DEM 1 1 – – 无效值 1 0 – 1 无效值 1 0 – 0 降轨h 0 1 1 – 无效值 0 1 0 – 升轨h 0 0 0 1 升轨h 0 0 1 0 降轨h 0 0 0 0 加权 0 0 1 1 无效值 表 2 数据集
Table 2. Datasets
数据类型 时间 轨道 垂直基线(m) 入射角(°) 模糊高度(m) TDX/TSX 2014-08-19 升轨 104.27 43.34 73.31 TDX/TSX 2014-04-07 降轨 89.22 45.86 93.21 表 3 缺失区域统计表
Table 3. Statistics table of invalids
处理方法 无效点比例(%) 升轨 4.93 降轨 4.52 融合 1.34 表 4 与SRTM DEM对比高程残差统计表(SRTM)
Table 4. Comparison of height difference with respect to SRTM DEM
处理方法 山区 平地 升轨DEM (m) 13.55 7.37 降轨DEM (m) 12.80 6.81 融合后DEM (m) 11.56 6.61 表 5 高程精度
Table 5. Accuracy of different DEMs
序号 纬度(°) 经度(°) 控制点高程值(m) 升轨DEM (m) 降轨DEM (m) 融合DEM (m) 高程值 误差 高程值 误差 高程值 误差 1 39.787079N 116.386766E 36.46 46.19 9.73 47.61 11.15 46.42 9.96 2 39.946029N 116.180640E 80.67 78.64 –2.03 75.55 –5.12 77.28 –3.39 3 39.936176N 116.163946E 83.03 76.40 –6.63 81.13 –1.90 80.00 –3.03 4 39.933121N 116.158557E 90.82 96.75 5.93 95.70 4.88 96.15 5.33 均方根误差 6.74 6.67 6.09 -
[1] 蒋厚军. 高分辨率星载InSAR技术在DEM生成及更新中的应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 武汉大学, 2012: 1–2Jiang Hou-jun. High-resolution spaceborne SAR interferometry for DEM generation and updating[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Wuhan University, 2012: 1–2 [2] Farr T G and Kobrick M. Shuttle radar topography mission produces a wealth of data[J]. Eos,Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2000, 81(48): 583–585. DOI: 10.1029/EO081i048p00583 [3] Krieger G, Moreira A, Fiedler H, et al. TanDEM-X: A satellite formation for high-resolution SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3317–3341. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.900693 [4] 邓云凯, 王宇. 先进双基SAR技术研究(英文)[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14026Deng Yunkai and Wang Robert. Exploration of advanced bistatic SAR experiments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14026 [5] Rizzoli P, Bräutigam B, Kraus T, et al. Relative height error analysis of TanDEM-X elevation data[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2012, 73: 30–38. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2012.06.004 [6] Rizzoli P, Martone M, Gonzalez C, et al. Generation and performance assessment of the global TanDEM-X digital elevation model[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 132: 119–139. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.08.008 [7] Martone M, Rizzoli P, Wecklich C, et al. The global forest/non-forest map from TanDEM-X interferometric SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 205: 352–373. [8] Zhu X X, Lachaise M, Adam F, et al.. Beyond the 12 m TanDEM-X DEM[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 2014: 390–393 [9] 斯奇, 王宇, 邓云凯, 等. 一种基于最大后验框架的聚类分析多基线干涉SAR高度重建算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 640–652. DOI: 10.12000/JR17043Si Qi, Wang Yu, Deng Yunkai, et al. A novel cluster-analysis algorithm based on MAP framework for multi-baseline InSAR height reconstruction[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 640–652. DOI: 10.12000/JR17043 [10] Gao X M, Liu Y L, Li T, et al. High precision DEM generation algorithm based on InSAR multi-look iteration[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(7): 741. DOI: 10.3390/rs9070741 [11] 杜亚男, 冯光财, 李志伟, 等. TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X获取高精度数字高程模型技术研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(9): 3089–3102Du Yanan, Feng Guangcai, Li Zhiwei, et al. Generation of high precision DEM from TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(9): 3089–3102 [12] Deledalle C A, Denis L, and Tupin F. NL-InSAR: Nonlocal interferogram estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(4): 1441–1452. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2076376 [13] 靳国旺, 徐青, 张红敏. 合成孔径雷达干涉测量[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2014: 169–183Jin Guo-wang, Xu Qing, and Zhang Hong-min. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry[M]. Beijing: National Defend Industry Press, 2014: 169–183 [14] 刘辉, 靳国旺, 张红敏, 等. DEM辅助的山区InSAR相位解缠[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2017, 34(2): 215–220. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2017.02.019Liu Hui, Jin Guo-wang, Zhang Hong-min, et al. Phase unwrapping assisted by DEM of InSAR for mountainous terrain[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2017, 34(2): 215–220. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2017.02.019 [15] Kropatsch W G and Strobl D. The generation of SAR layover and shadow maps from digital elevation models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1990, 28(1): 98–107. DOI: 10.1109/36.45752 [16] Carrasco D, Díaz J, and Broquetas A. Ascending-descending orbit combination SAR interferometry assessment[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd ERS Symposium, Florence, Italy, 1997: 1789–1794 [17] 赵争. 地形复杂区域InSAR高精度DEM提取方法[D]. [博士论文], 武汉大学, 2014Zhao Zheng. Methods on high-accuracy DEM extraction from interferometric SAR in sophisticated terrain areas[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Wuhan University, 2014 [18] Zhang X J, Zeng Q M, Jiao J, et al. Fusion of space-borne multi-baseline and multi-frequency interferometric results based on extended Kalman filter to generate high quality DEMs[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2016, 111: 32–44. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.11.005 [19] Deo R, Rossi C, Eineder M, et al. Framework for fusion of ascending and descending pass TanDEM-X raw DEMs[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(7): 3347–3355. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2431433 [20] Goodman N R. Statistical analysis based on a certain multivariate complex Gaussian distribution (an introduction)[J]. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1963, 34(1): 152–177. DOI: 10.1214/aoms/1177704250 [21] Deledalle C A, Denis L, Poggi G, et al. Exploiting patch similarity for SAR image processing: The nonlocal paradigm[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 69–78. DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2311305 [22] Seymour M S and Cumming I G. Maximum likelihood estimation for SAR interferometry[C]. Proceedings of 1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 1994, 4: 2272–2275 [23] 肖金群. 采用D-InSAR技术获取山区DEM的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中南大学, 2011: 9–10Xiao Jin-qun. DEM generation in mountainous area with differential InSAR technique[D]. [Master dissertation], Central South University, 2011: 9–10 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: