Optical System and Detection Range Analysis of Synthetic Aperture Ladar
-
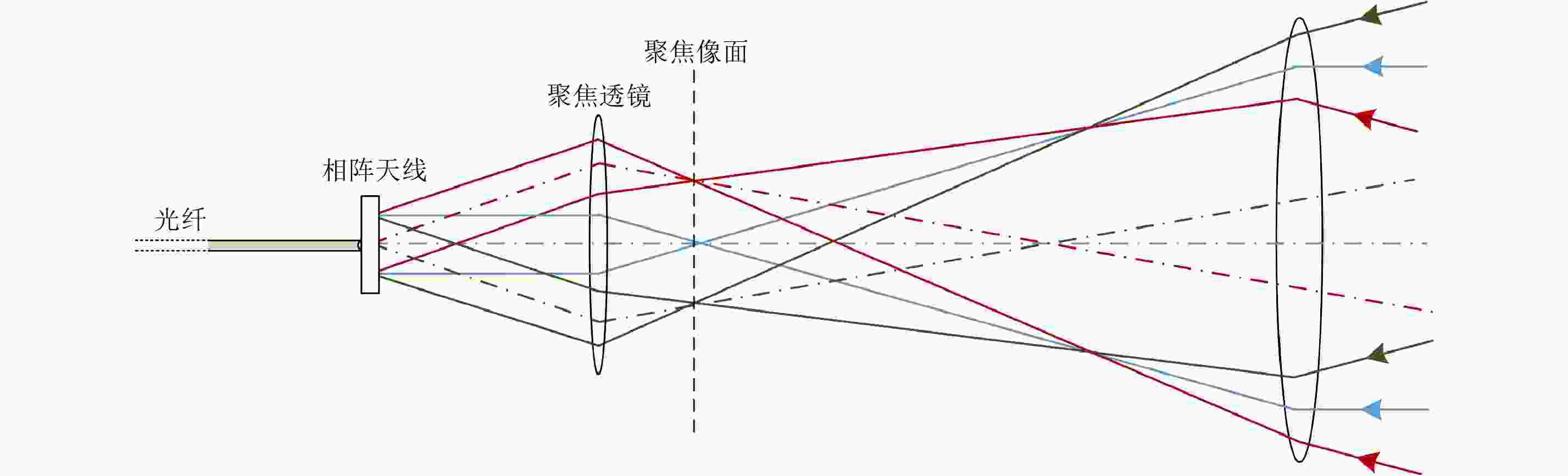
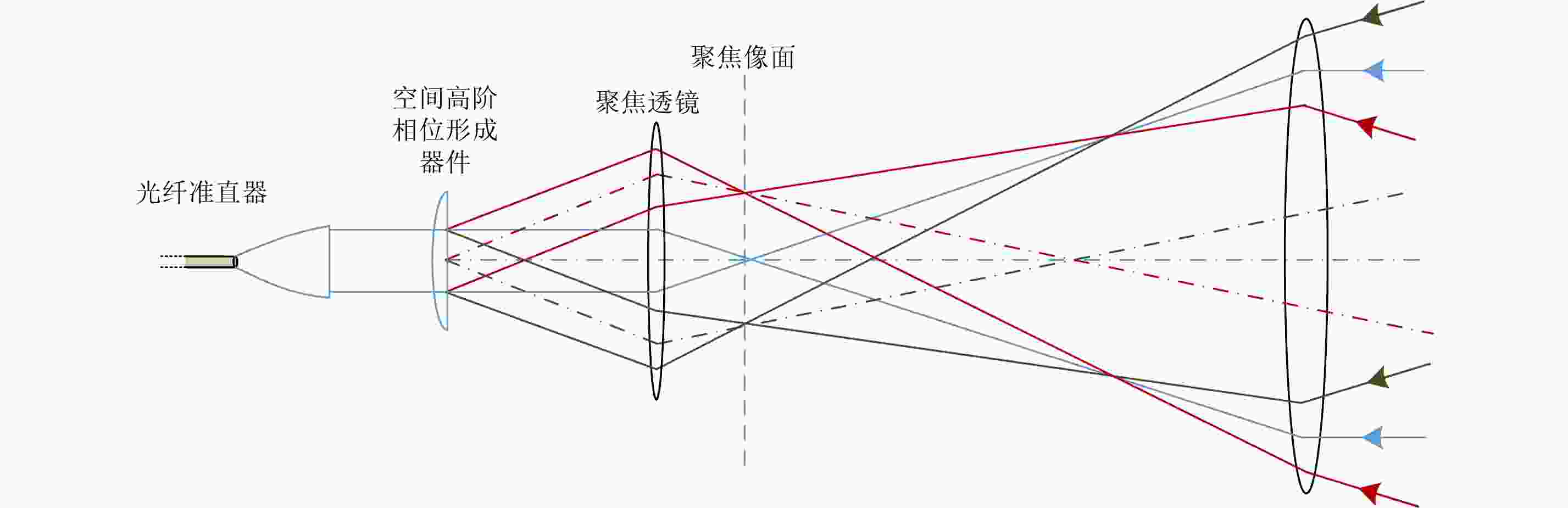
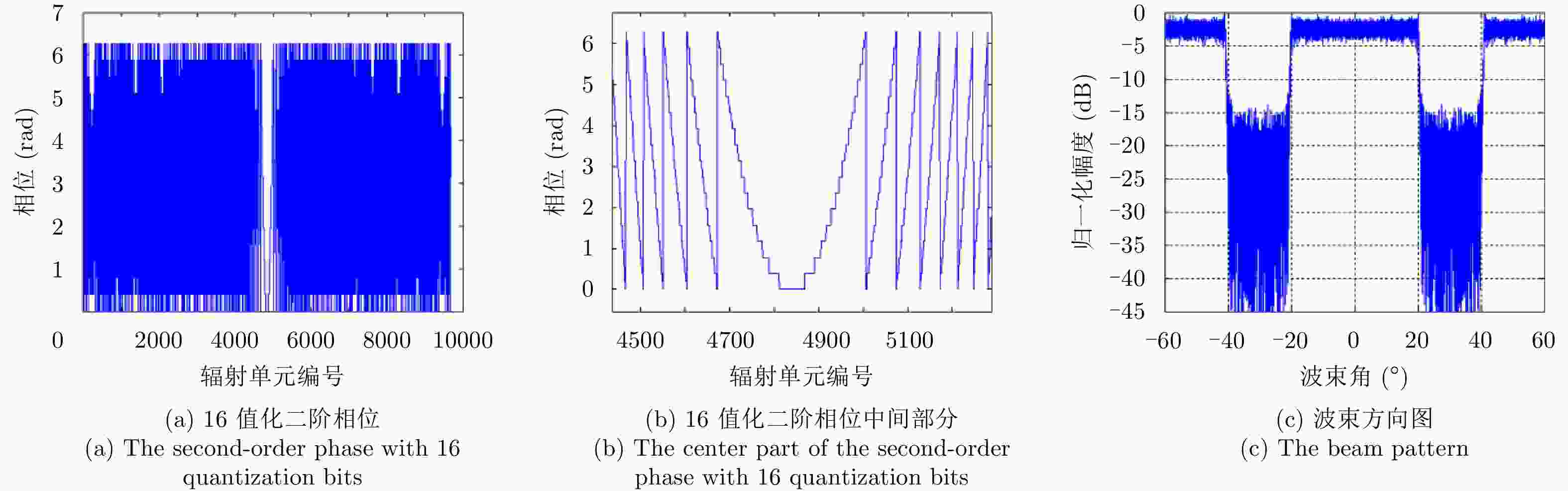
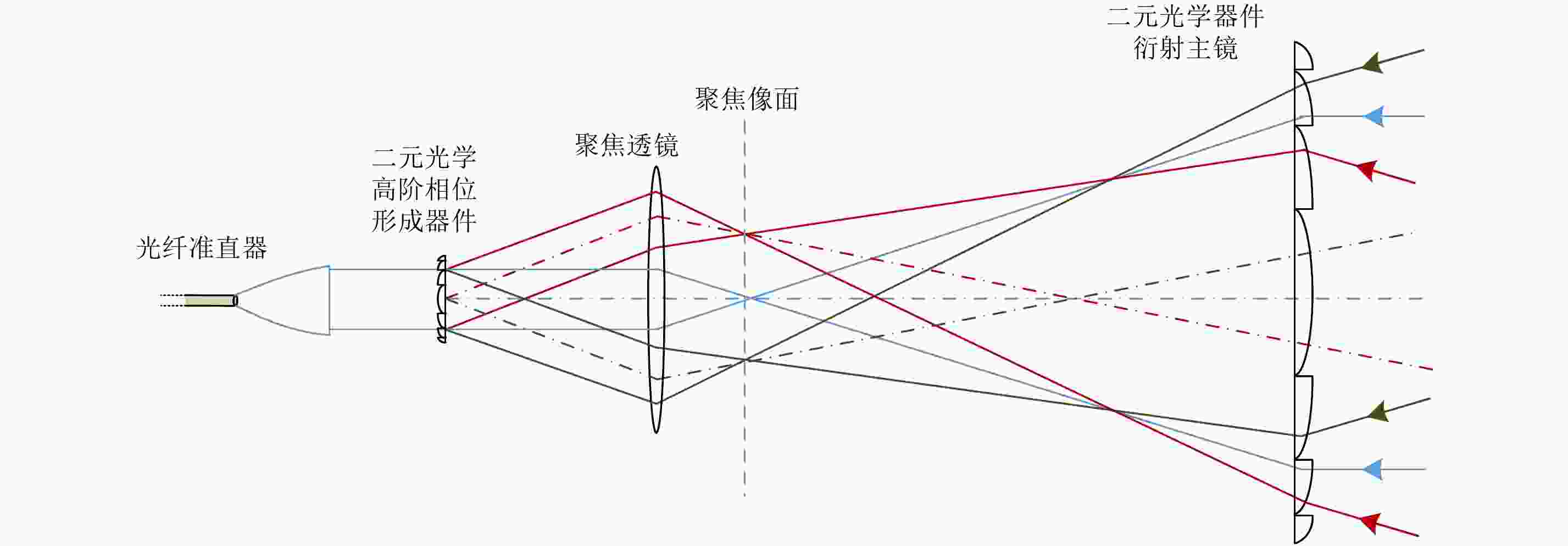
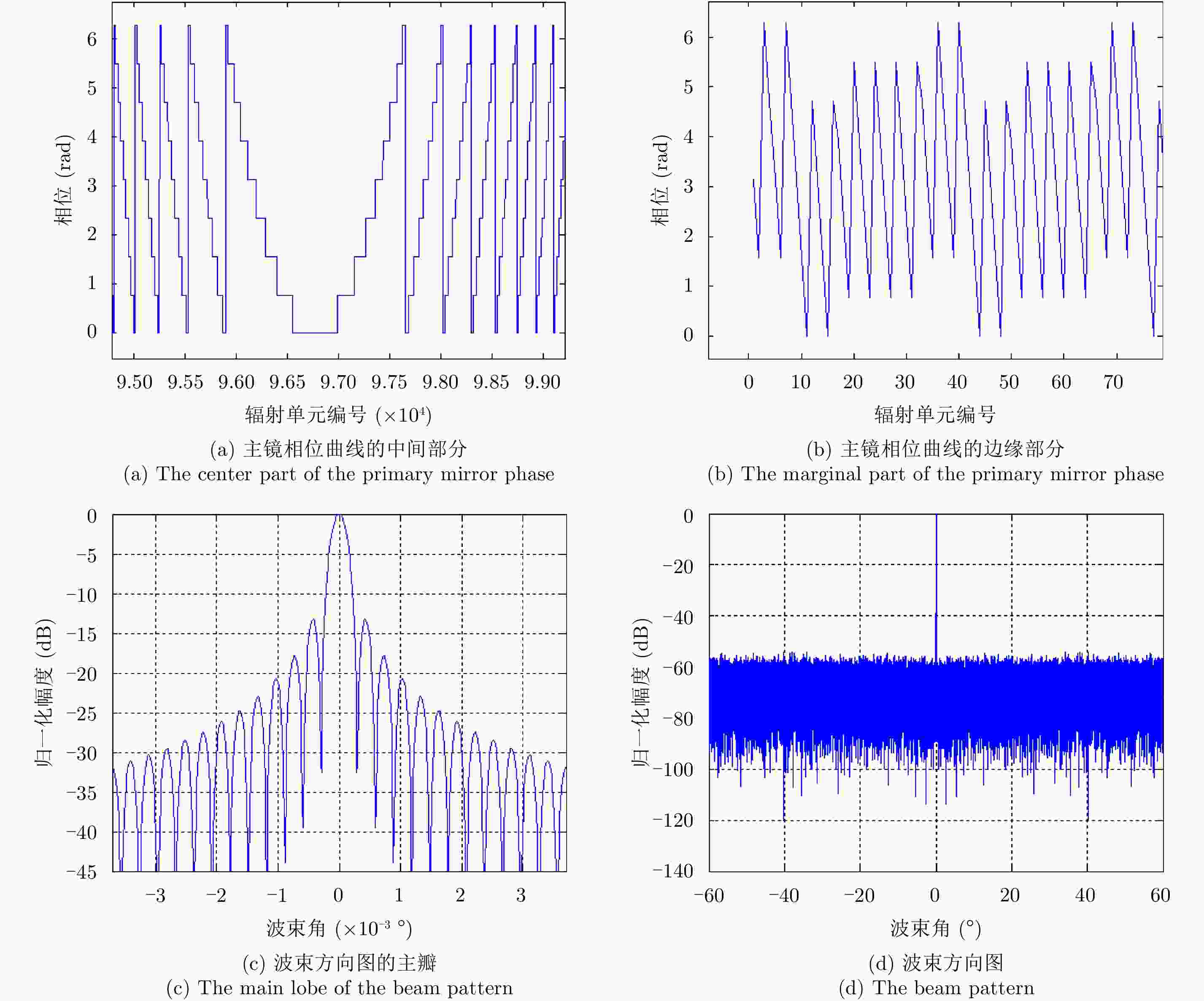
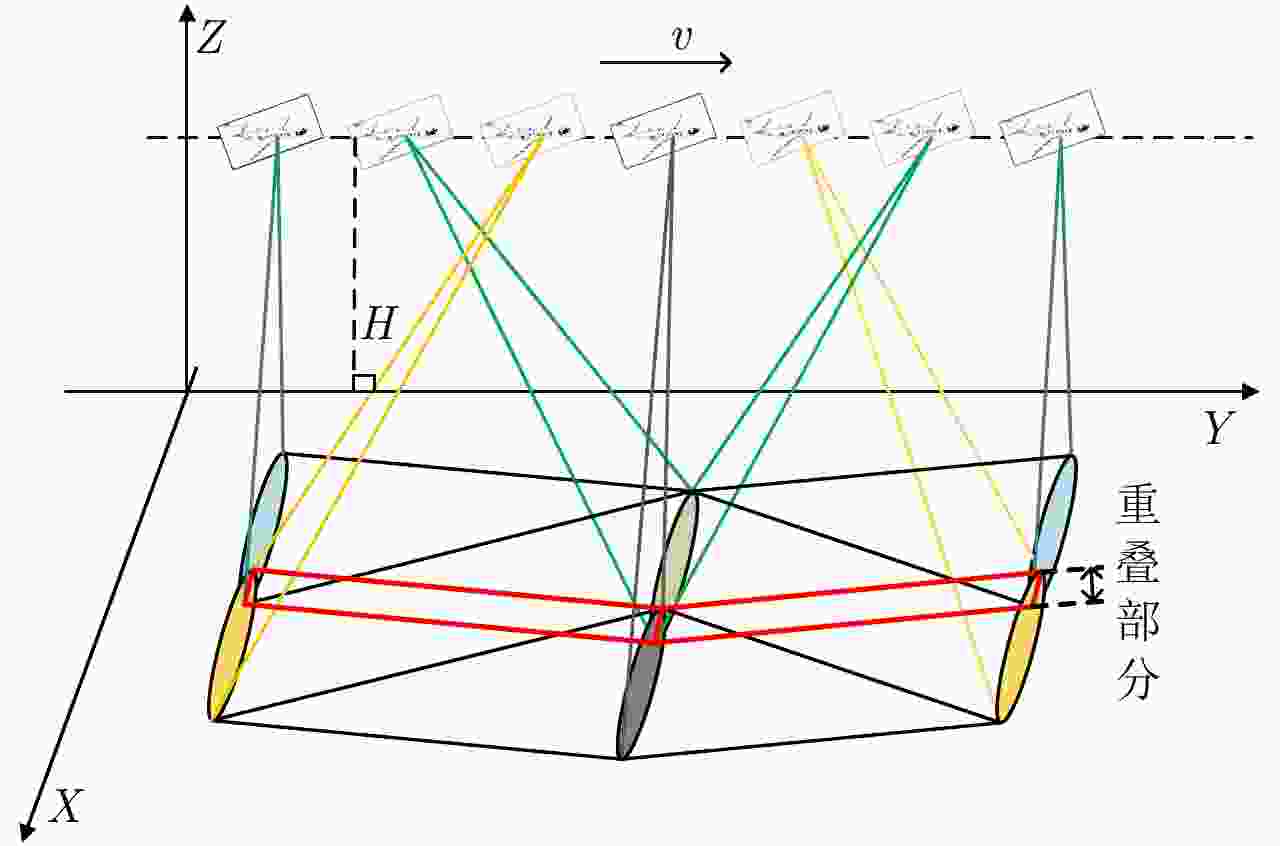
摘要: 该文对合成孔径激光雷达(Synthetic Aperture Ladar, SAL)光学系统和作用距离进行了分析。根据SAL成像特点,提出了SAL使用非成像衍射光学系统的概念,并引入相控阵模型对其性能进行分析。通过在压缩光路中馈源和主镜两处使用二元光学器件,在口径300 mm条件下将2°接收视场信号收入光纤,对所需的相位参数和对应的波束方向图进行了计算仿真。给出了SAL作用距离方程,分析了相干探测和信号积累增益,明确了SAL具有良好的微弱信号探测能力的结论。针对实际应用需求,给出了一个远距离高分辨率机载SAL系统参数和工作模式。5 cm分辨率时,在连续条带成像模式下,其作用距离可达5 km,幅宽可达1.5 km;在滑动聚束成像模式下,作用距离可达10 km,幅宽可达1 km。Abstract: Optical system and detection range of Synthetic Aperture Ladar (SAL) are analyzed. According to the imaging characteristics of SAL, the concept that SAL uses non-imaging diffractive optical system are proposed, meanwhile, the phased array model is introduced to analyze its performance. In the condition of using binary optical element on the feeder and primary mirror, the phaser parameters and beam pattern are presented using simulation. The signal of 2° view field is introduced into fiber with the 300 mm aperture telescope and compressed optical path. The radar detection range equation of SAL is introduced, coherent detection and signal accumulation gain are analyzed, the conclusion is SAL has good ability of detecting weak signal. Aiming at application requirement, system parameters and working modes of airborne SAL are given with high resolution and long detection range. With 5 cm resolution, the airborne SAL can achieve 5 km detection range with 1.5 km swath in strip-map imaging mode and 10 km detection range with 1 km swath in sliding spotlight imaging mode.
-
表 1 机载SAL条带成像模式扫描参数
Table 1. Scanning parameters of airborne SAL with strip-map imaging model
序号 雷达位置 扫描时间(s) 顺轨扫描范围(°) 顺轨扫描角速度(°/s) 交轨扫描范围(°) 交轨扫描角速度(°/s) 1 
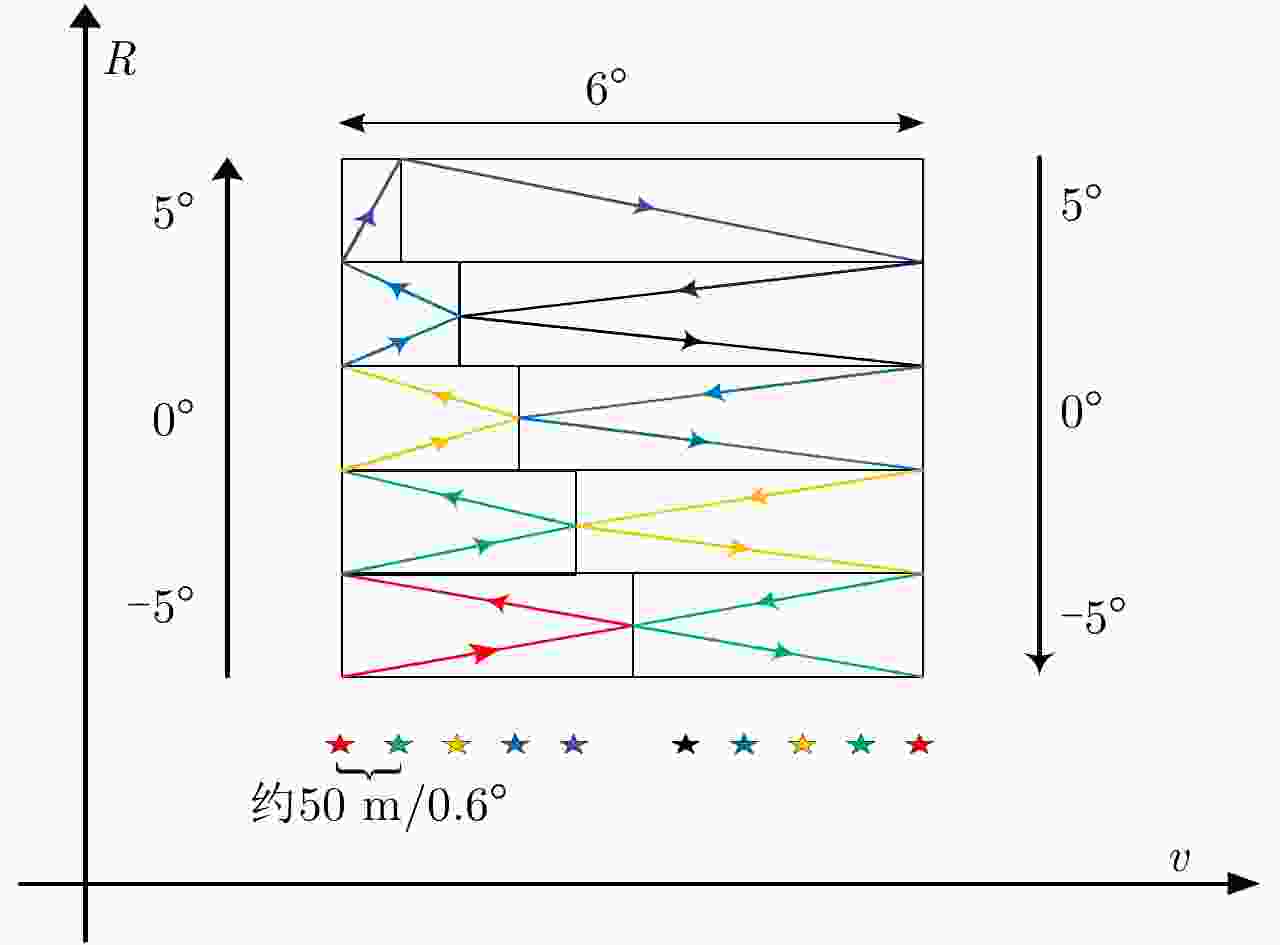
0 $ \to $1 $0\to 2.7\to - 0.6$ 6.0 $ - 5\to - 3$ 2 2 1 $ \to $2 $ - 0.6\to 1.5\to - 1.2$ 4.8 $ - 3\to - 1$ 2 3 2 $ \to $3 $ - 1.2\to 0.3\to - 1.8$ 3.6 $ - 1\to 1$ 2 4 3 $ \to $4 $ - 1.8\to - 0.9\to - 2.4$ 2.4 $1\to 3$ 2 5 4 $ \to $6 $ - 2.4\to - 2.1\to 2.6$ 2.5 $3\to 5\to 3$ 2 6 6 $ \to $7 $2.6\to - 2.7\to 1.8$ 9.8 $3\to 1$ 2 7 7 $ \to $8 $1.8\to - 2.7\to 1.2$ 8.4 $1\to - 1$ 2 8 8 $ \to $9 $1.2\to - 2.7\to 0.6$ 6.8 $ - 1\to - 3$ 2 9 9 $ \to $10 $0.6\to - 2.7\to 0$ 6.0 $ - 3\to - 5$ 2 表 2 作用距离5 km机载SAL系统参数
Table 2. System parameters of airborne SAL with 5 km detection range
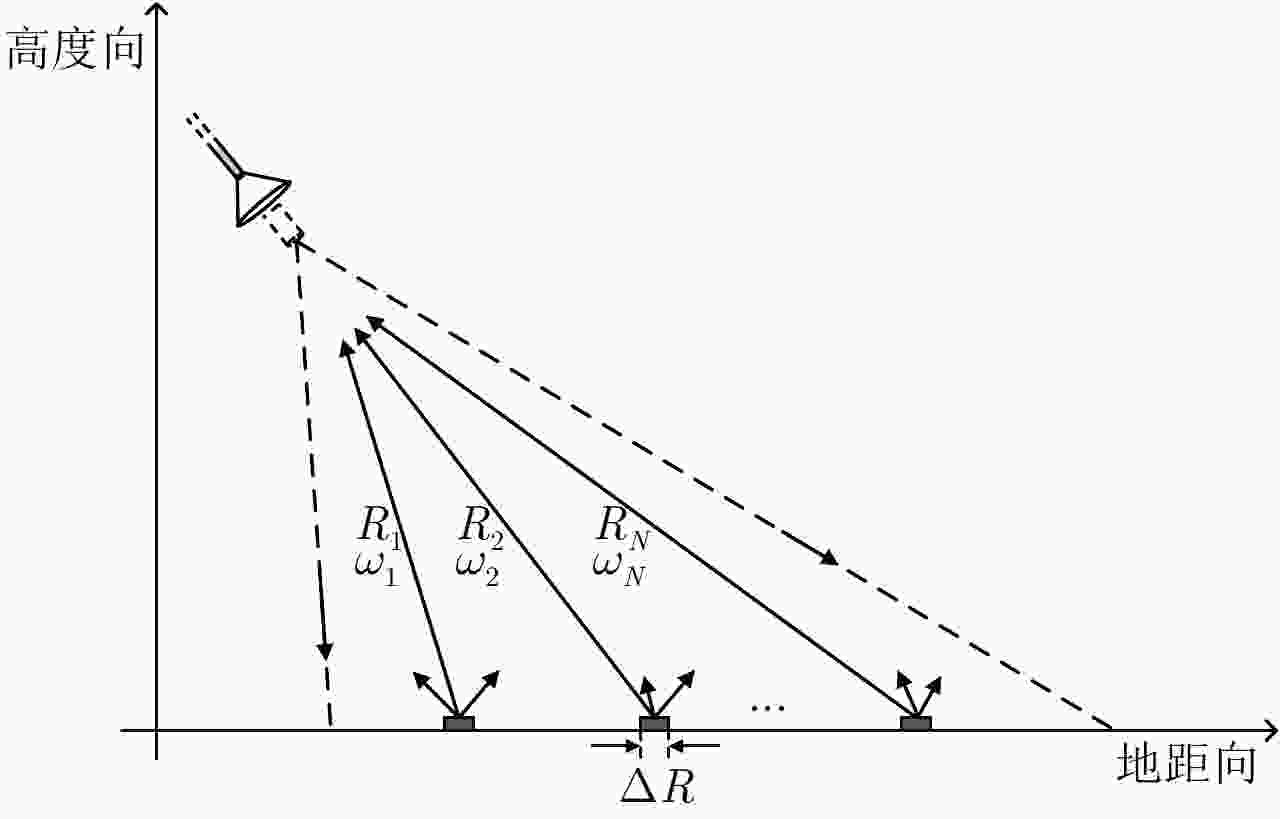
参数 数值 参数 数值 飞行高度 $H$(km) 2.5 飞行速度 $v$(m/s) 50 平均入射角 $\theta $(°) 60 脉冲重复频率(kHz) 50 顺轨/交轨波束宽度 ${\theta _{\rm{a}}}$, ${\theta _{\rm{c}}}$(mrad) 0.3, 35.0 目标散射系数 ${\sigma _0}$ 0.1 地距向瞬时幅宽 $\Delta R$(m) 350 距离/方位分辨率 ${\rho _{\rm{r}}}$, ${\rho _{\rm{a}}}$(m) 0.05, 0.05 顺轨/交轨扫描范围 $\Delta {\theta _{\rm{c}}}$, $\Delta {\theta _{\rm{a}}}$(°) $ \pm 3$, $ \pm 5$ 双程大气损耗 ${\eta _{{\rm{ato}}}}$ 0.4 最近/最远斜距 $R$(km) 4.35, 5.92 接收望远镜口径 $D$(mm) 300 顺轨/交轨扫描角速度大小 ${\omega _{\rm{a}}}$, ${\omega _{\rm{c}}}$ 如表1所示 发射光学系统损耗 ${\eta _{\rm{t}}}$ 0.9 顺轨/交轨扫描周期 ${T_{\rm{a}}}$, ${T_{\rm{c}}}$ 如表1所示 接收光学系统损耗 ${\eta _{\rm{r}}}$ 0.8 地距向扫描幅宽(km) 1.5 匹配损耗 ${\eta _{\rm{m}}}$ 0.5 激光波长 $\lambda $(μm) 1.55 其他光学损耗 ${\eta _{{\rm{oth}}}}$ 0.8 发射峰值功率 ${P_{\rm{t}}}$(W) 400 量子效率 ${\eta _{\rm{D}}}$ 0.5 脉冲宽度 ${T_{\rm{p}}}$(μs) 5 电子学系统损耗 ${\eta _{{\rm{ele}}}}$ 0.5 信号带宽 ${B_{\rm{r}}}$(GHz) 4 电子学噪声系数 ${F_{\rm{n}}}$(dB) 3 目标后向散射立体角 $\varOmega $ ${\rm{{{π}} }}$ 图像信噪比 ${{\rm SNR}_{\min }}$(条带模式)(dB) 10.3 表 3 作用距离10 km机载SAL系统参数
Table 3. System parameters of airborne SAL with 10 km detection range
参数 数值 参数 数值 飞行高度 $H$(km) 3.3 目标散射系数 ${\sigma _0}$ 0.1 入射角(°) 70 距离/方位分辨率 ${\rho _{\rm{r}}}$, ${\rho _{\rm{a}}}$(m) 0.05, 0.05 顺轨/交轨波束宽度 ${\theta _{\rm{a}}}$, ${\theta _{\rm{c}}}$(mrad) 0.3, 35.0 双程大气损耗 ${\eta _{{\rm{ato}}}}$ 0.25 最近/最远斜距 $R$(km) 9.21, 10.13 接收望远镜口径 $D$(mm) 300 地距向瞬时幅宽(km) 1 发射光学系统损耗 ${\eta _{\rm{t}}}$ 0.9 飞行速度 $v$(m/s) 50 接收光学系统损耗 ${\eta _{\rm{r}}}$ 0.8 激光波长 $\lambda $(μm) 1.55 匹配损耗 ${\eta _{\rm{m}}}$ 0.5 发射峰值功率 ${P_{\rm{t}}}$(W) 400 其他光学损耗 ${\eta _{{\rm{oth}}}}$ 0.8 脉冲宽度 ${T_{\rm{p}}}$(μs) 5 量子效率 ${\eta _{\rm{D}}}$ 0.5 脉冲重复频率(kHz) 50 电子学系统损耗 ${\eta _{{\rm{ele}}}}$ 0.5 信号带宽 ${B_{\rm{r}}}$(GHz) 4 电子学噪声系数 ${F_{\rm{n}}}$(dB) 3 目标后向散射立体角 $\varOmega $ ${\rm{{{π}} }}$ 图像信噪比 ${{\rm SNR}_{\min }}$(滑动聚束模式)(dB) 10 -
[1] Krause B W, Buck J, Ryan C, et al.. Synthetic aperture ladar flight demonstration[C]. Proceedings of 2011 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Baltimore, MD, USA, 2011. [2] 李道京, 张清娟, 刘波, 等. 机载合成孔径激光雷达关键技术和实现方案分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 143–151. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13021Li Dao-jing, Zhang Qing-juan, Liu Bo, et al. Key technology and implementation scheme analysis of air-borne synthetic aperture ladar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 143–151. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13021 [3] Liu L R. Coherent and incoherent synthetic-aperture imaging ladars and laboratory-space experimental demonstrations[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(4): 579–599. DOI: 10.1364/AO.52.000579 [4] Zhao Z L, Huang J Y, Wu S D, et al. Experimental demonstration of tri-aperture differential synthetic aperture ladar[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 389: 181–188. DOI: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.12.024 [5] Li G Z, Wang N, Wang R, et al. Imaging method for airborne SAL data[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(5): 351–353. DOI: 10.1049/el.2016.4205 [6] 卢智勇, 周煜, 孙建峰, 等. 机载直视合成孔径激光成像雷达外场及飞行实验[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(1): 0110001. DOI: 10.3788/CJL201744.0110001Lu Zhi-yong, Zhou Yu, Sun Jian-feng, et al. Airborne down-looking synthetic aperture imaging ladar field experiment and its flight testing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(1): 0110001. DOI: 10.3788/CJL201744.0110001 [7] 李道京, 杜剑波, 马萌. 合成孔径激光雷达的研究现状与天基应用展望[C]. 钱学森实验室首届空间技术未来发展及应用学术会, 北京, 2014: 18–20. [8] 田芊, 廖延彪, 孙利群. 工程光学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006: 35–38.Tian Qian, Liao Yan-biao, and Sun Li-qun. Engineering Optics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2006: 35–38. [9] 杜剑波, 李道京, 马萌, 等. 基于干涉处理的机载合成孔径激光雷达振动估计和成像[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(9): 0910003. DOI: 10.3788/CJL201643.0910003Du Jian-bo, Li Dao-jing, Ma Meng, et al. Vibration estimation and imaging of airborne synthetic aperture ladar based on interferometry processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(9): 0910003. DOI: 10.3788/CJL201643.0910003 [10] 伍洋. 射电望远镜天线相控阵馈源技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2013: 9–21.Wu Yang. Research on the phased array feed technology for the radio telescope[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2013: 9–21. [11] Yaacobi A, Sun J, Moresco M, et al. Integrated phased array for wide-angle beam steering[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(15): 4575–4578. DOI: 10.1364/OL.39.004575 [12] Sun J, Timurdogan E, Yaacobi A, et al. Large-scale nanophotonic phased array[J]. Nature, 2013, 493(7431): 195–199. DOI: 10.1038/nature11727 [13] 聂光. 光波导相控阵扫描光束优化方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2015: 25–33.Nie Guang. Study on beam optimization method for optical waveguide phased array[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2015: 25–33. [14] 周高杯, 宋红军, 邓云凯. 基于波束空间的SAR阵列天线波束展宽方法[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2011, 45(12): 2252–2258. DOI: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2011.12.028Zhou Gao-bei, Song Hong-jun, and Deng Yun-kai. Investigation of SAR array antenna beam broadening based on beam pattern space[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science) , 2011, 45(12): 2252–2258. DOI: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2011.12.028 [15] 任波, 赵良波, 朱富国. 高分三号卫星C频段多极化有源相控阵天线系统设计[J]. 航天器工程, 2017, 26(6): 68–74. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2017.06.011Ren Bo, Zhao Liang-bo, and Zhu Fu-guo. Design of C-band multi-polarized active phased array antenna system for GF-3 satellite[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2017, 26(6): 68–74. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2017.06.011 [16] 王帅, 孙华燕, 郭惠超, 等. APD阵列单脉冲三维成像激光雷达的发展与现状[J]. 激光与红外, 2017, 47(4): 389–398. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.04.001Wang Shuai, Sun Hua-yan, Guo Hui-chao, et al. Development and status of single pulse 3D imaging lidar based on APD array[J]. Laser&Infrared, 2017, 47(4): 389–398. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.04.001 [17] Skolnik M I and Wang Jun. Radar Handbook[M]. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2003: 9–10. [18] Pioneers in Photonic Technology. GAEA-2 10 megapixel phase only spatial light modulator (Reflective)[EB/OL]. https://holoeye.com/spatial-light-modulators/gaea-4k-phase-only-spatial-light-modulator/?from=singlemessage&isappinstalled=0 [19] 金国藩. 二元光学[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1998: 88–140.Jin Guo-fan. Binary Optics[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1998: 88–140. [20] 焦建超, 苏云, 王保华, 等. 地球静止轨道膜基衍射光学成像系统的发展与应用[J]. 国际太空, 2016(6): 49–55Jiao Jian-chao, Su Yun, Wang Bao-hua, et al. Development and application of GEO membrane based diffraction optical imaging system[J]. Space International, 2016(6): 49–55 [21] 舒嵘, 徐之海. 激光雷达成像原理与运动误差补偿方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 8–10.Shu Rong and Xu Zhihai. Imaging Thesis and Moving Comprehension of Ladar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 8–10. [22] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 105–115.Bao Zheng, Xing Meng-dao, and Wang Tong. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2015: 105–115. [23] Barber Z W and Dahl J R. Synthetic aperture ladar imaging demonstrations and information at very low return levels[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(24): 5531–5537. DOI: 10.1364/AO.53.005531 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: