Scattering Properties of Electromagnetic Waves from Randomly Oriented Rough Metal Plate in the Lower Terahertz Region
-
摘要: 该文提出了一种高效混合近似算法计算太赫兹频段无限薄金属板的电磁散射特性。在太赫兹低频段,金属目标可以被视为具有微粗糙表面的理想导体,散射场可以分为相干场和非相干场。该文采用物理光学法结合截断劈增量长度绕射系数法和微扰法来计算金属板的电磁散射分布。基于蒙特卡洛方法,分别利用多层快速多极子和提出的混合算法计算太赫兹低频段金属板的雷达散射截面,仿真结果表明该文提出的混合算法能够高效快速地给出太赫兹低频段金属板的电磁散射特性。
-
关键词:
- 太赫兹散射 /
- 物理光学 /
- 截断劈增量长度绕射系数法 /
- 微扰法 /
- 雷达散射截面
Abstract: An efficient hybrid algorithm is proposed to analyze the electromagnetic scattering properties of an infinitely thin metal plate in the lower terahertz (THz) frequency region. In this region, the metal plate can be viewed as a perfect electrically conductive object with a marginally rough surface. Hence, the THz scattered field from the metal plate can be divided into coherent and incoherent parts. The physical optics and truncated-wedge incremental-length diffraction coefficients methods are used to compute the coherent part, whereas the small perturbation method is used to compute the incoherent part. Then, the radar cross section of the rough metal plate surface is computed by the multilevel fast multipole and proposed hybrid algorithms. The numerical results show that the proposed algorithm has a good accuracy when rapidly simulating the scattering properties in the lower THz region. -
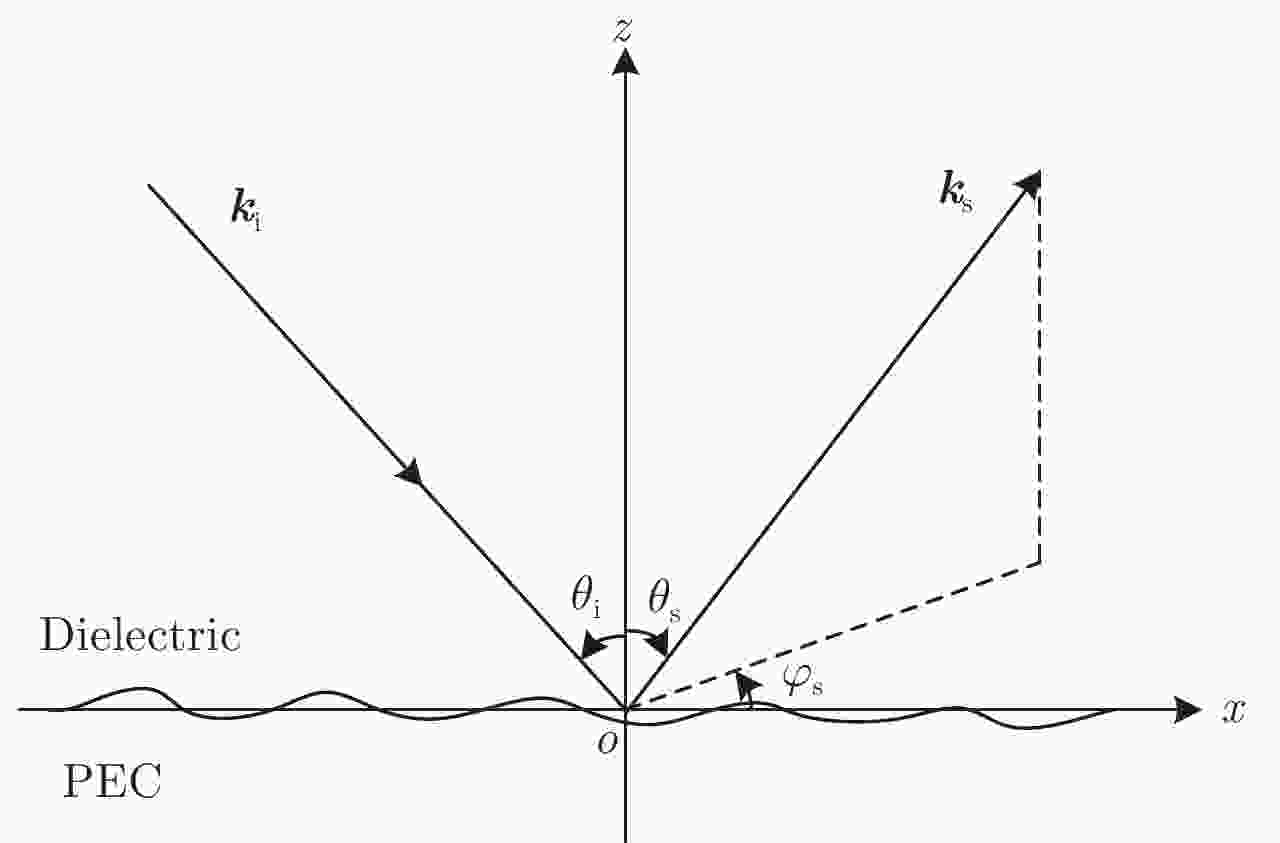
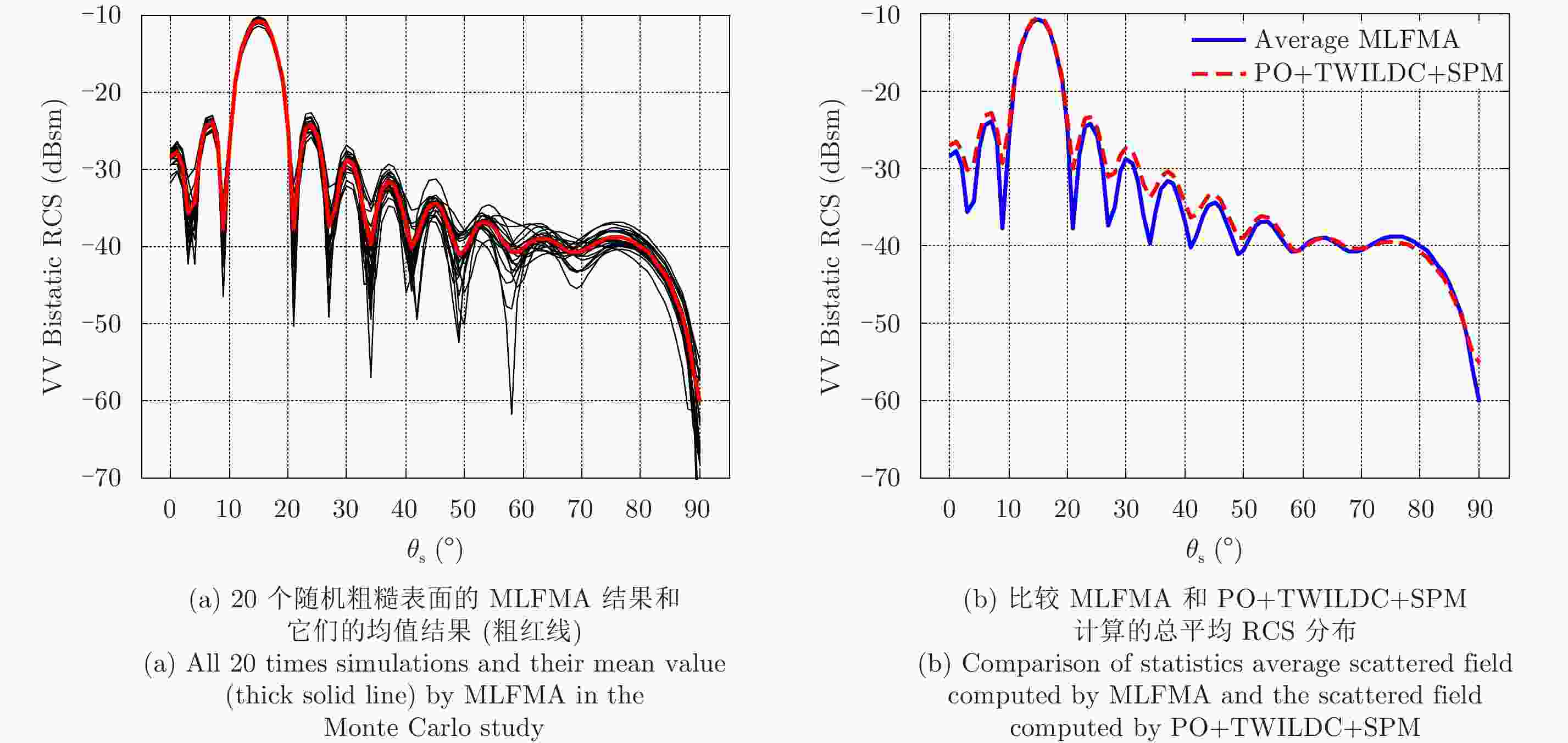
图 6 双站VV极化RCS结果分布(300 GHz)。角度设置为
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =15°,${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =180°,${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =0°,${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =0°~90°共91个点Figure 6. Bistatic VV-polarization RCS of the infinitely thin rough PEC plate at 300 GHz. The incident direction is given by
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =15° and${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =180°. The observation angle is from${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =0° to${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =90° with 91 points, in which${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =0°图 7 双站HH极化RCS结果分布(300 GHz)。角度设置为
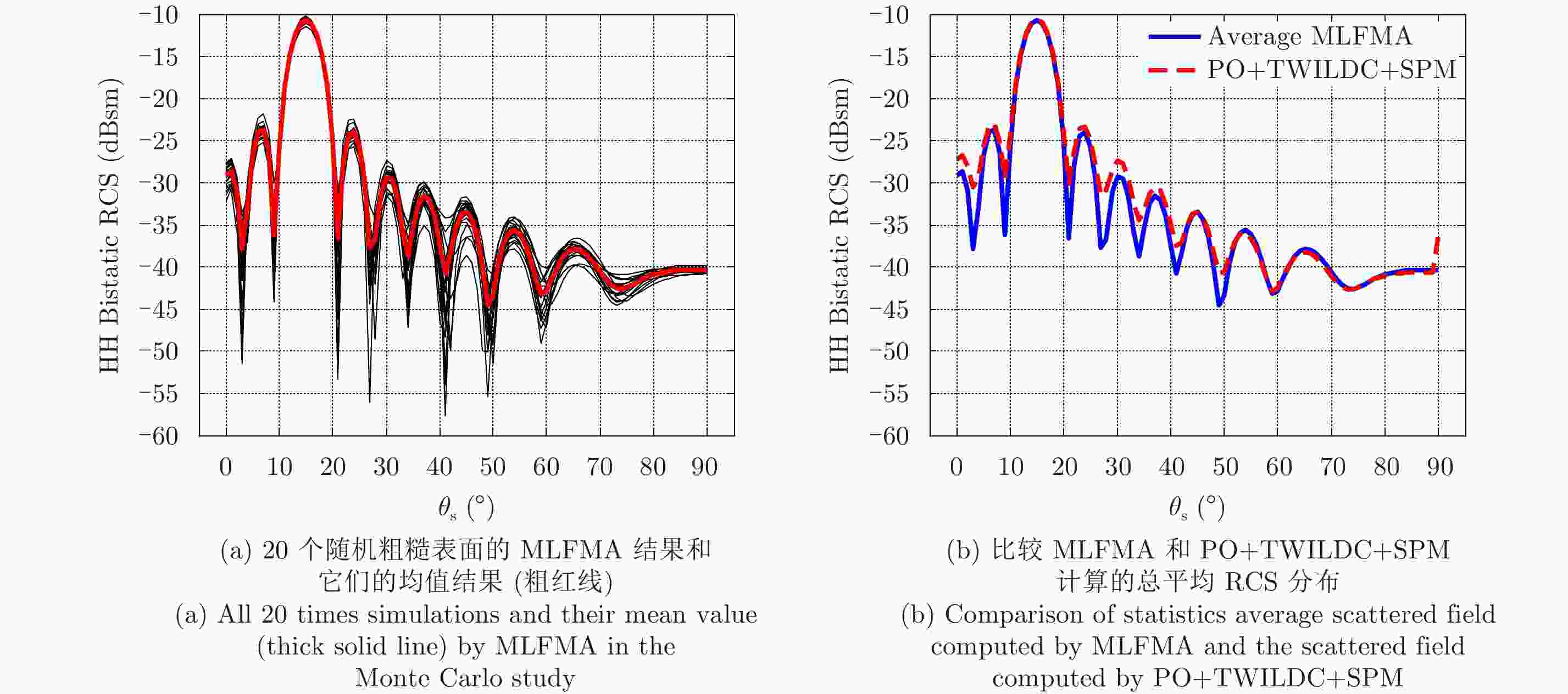
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =15°,${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =180°,${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =0°,${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =0°~90°共91个点Figure 7. Bistatic HH-polarization RCS of the infinitely thin rough PEC plate at 300 GHz. The incident direction is given by
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =15° and${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =180°. The observation angle is from${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =0° to${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =90° with 91 points, in which${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =0°图 8 双站VV极化RCS结果分布(300 GHz)。角度设置为
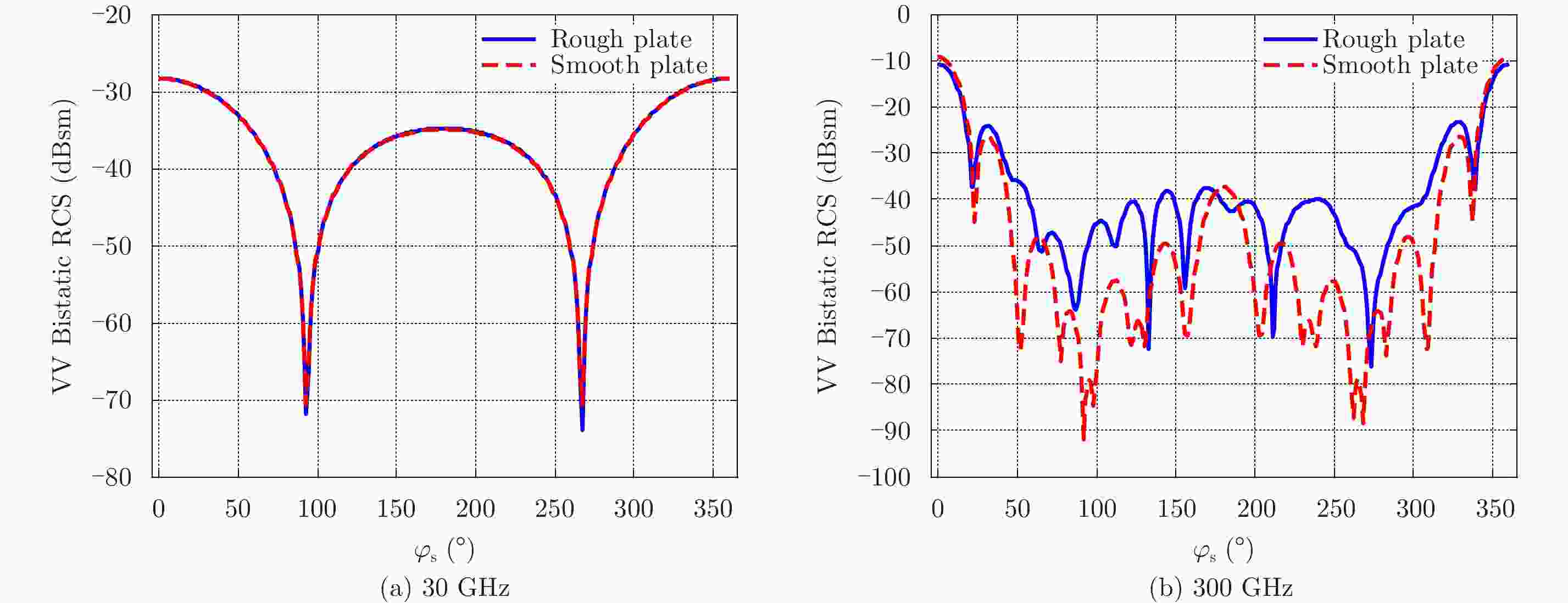
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =15°,${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =180°,${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =15°,${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =0°~360°共361个点Figure 8. Bistatic VV-polarization RCS of the infinitely thin rough PEC plate at 300 GHz. The incident direction is given by
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =15° and${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =180°. The observation angle is from${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =0° to${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =360° with 361 points, in which${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =15°图 9 双站HH极化RCS结果分布(300 GHz)。角度设置为
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =15°,${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =180°,${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =15°,${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =0°~360°共361个点Figure 9. Bistatic HH-polarization RCS of the infinitely thin rough PEC plate at 300 GHz. The incident direction is given by
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =15° and${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =180°. The observation angle is from${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =0° to${\varphi _{\rm{s}}}$ =360° with 361 points, in which${\theta _{\rm{s}}}$ =15°图 10 单站VV极化RCS结果分布(300 GHz)。角度设置为
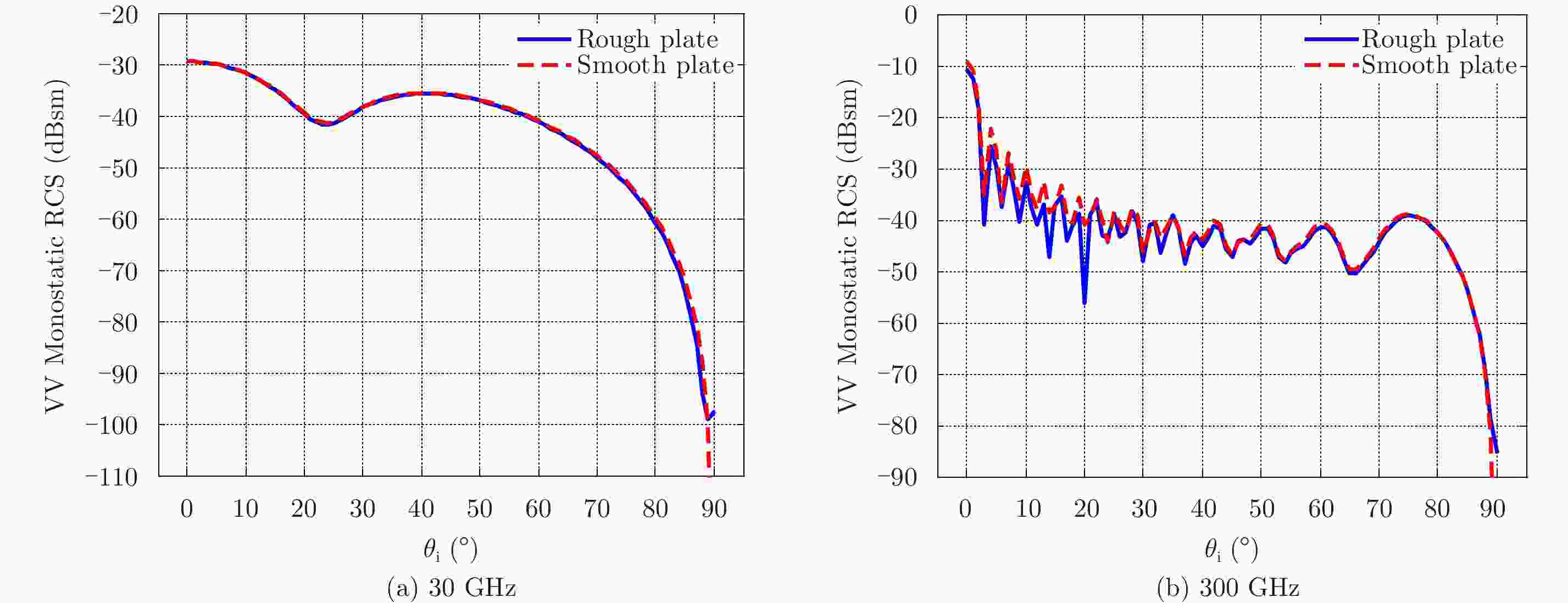
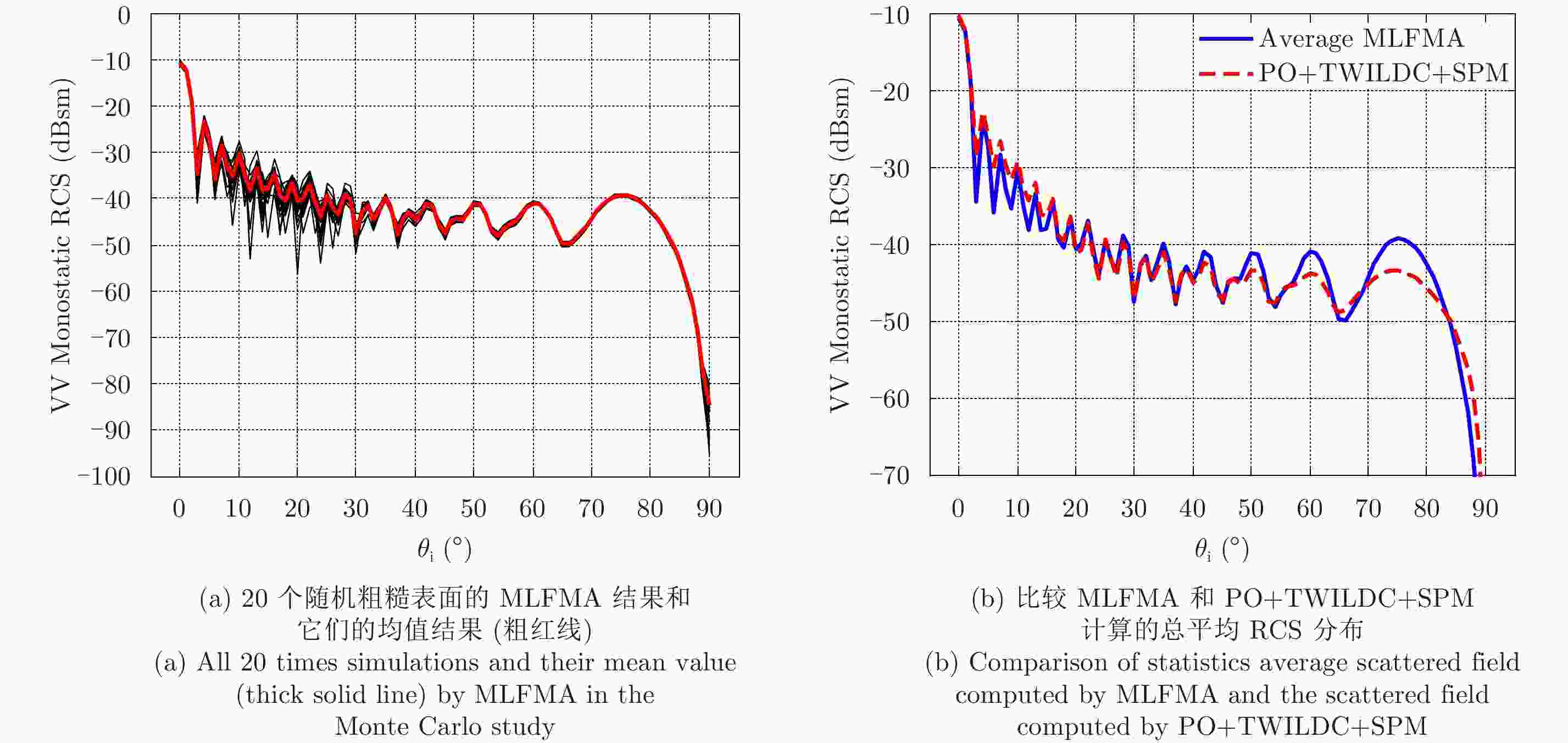
${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =0°,${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =0°~90°共91个点Figure 10. Monostatic VV-polarization RCS of the PEC infinitely thin rough plate at 300 GHz. The observation angle is from
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =0° to${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =90° with 91 points, in which${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =0°图 11 单站HH极化RCS结果分布(300 GHz)。角度设置为
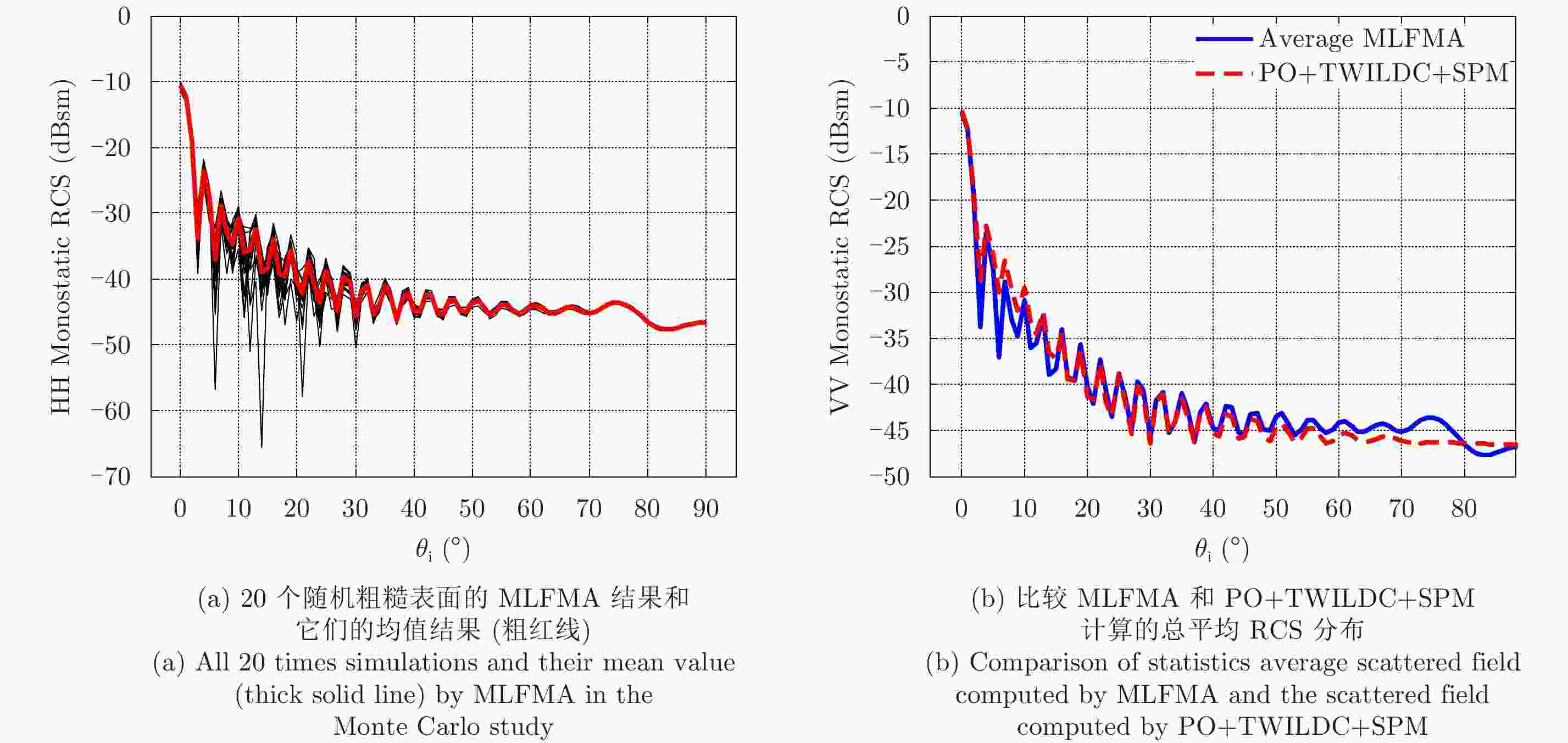
${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =0°,${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =0°~90°共91个点Figure 11. Monostatic HH-polarization RCS of the PEC infinitely thin rough plate at 300 GHz. The observation angle is from
${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =0° to${\theta _{\rm{i}}}$ =90° with 91 points, in which${\varphi _{\rm{i}}}$ =0° -
[1] 许景周, 张希成. 太赫兹科学技术和应用[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2007.Xu Jing-zhou and Zhang Xi-cheng. Terahertz Science Technology and Application[M]. Beijing, China: Peking University Press, 2007. [2] 王瑞君, 王宏强, 庄钊文, 等. 太赫兹雷达技术研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2013, 50(4): 040001Wang Rui-jun, Wang Hong-qiang, Zhuang Zhao-wen, et al. Research progress of terahertz radar technology[J]. Laser&Optoelectronics Progress, 2013, 50(4): 040001 [3] Cooper K B, Dengler R J, Llombart N, et al. Penetrating 3-D imaging at 4-and 25-m range using a submillimeter-wave radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2008, 56(12): 2771–2778. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2008.2007081 [4] Li Z, Cui T J, Zhong X J, et al. Electromagnetic scattering characteristics of PEC targets in the terahertz regime[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2009, 51(1): 39–50. DOI: 10.1109/MAP.2009.4939018 [5] Zhong X J, Cui T J, Li Z, et al. Terahertz-wave scattering by perfectly electrical conducting objects[J]. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 2007, 21(15): 2331–2340. DOI: 10.1163/156939307783134443 [6] Wu Z S. IR laser backscattering from an arbitrarily shaped dielectric object with rough surface[J]. Journal of Electronics(China) , 1993, 10(4): 298–306. DOI: 10.1007/BF02783158 [7] Ruck G T, Barrick D E, Stuart W D, et al.. Radar Cross Section Handbook[M]. New York: Plenum Press, 1970, Ch.9. [8] Ulaby F T, Moore R K, and Fung A K. Microwave Remote Sensing, vol. II[M]. Boston, USA: Artech House, 1978, Ch.12. [9] Johansen P M. Uniform physical theory of diffraction equivalent edge currents for truncated wedge strips[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1996, 44(7): 989–995. DOI: 10.1109/8.504306 [10] Wu Z S and Cui S M. Bistatic scattering by arbitrarily shaped objects with rough surface at optical and infrared frequencies[J]. International Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 1992, 13(4): 537–549. DOI: 10.1007/BF01010711 [11] Thorsos E I. The validity of the Kirchhoff approximation for rough surface scattering using a Gaussian roughness spectrum[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1988, 83(1): 78–92. DOI: 10.1121/1.396188 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: