A Distributed Asynchronous Recursive Filtering Fusion Algorithm via DP-TBD
-
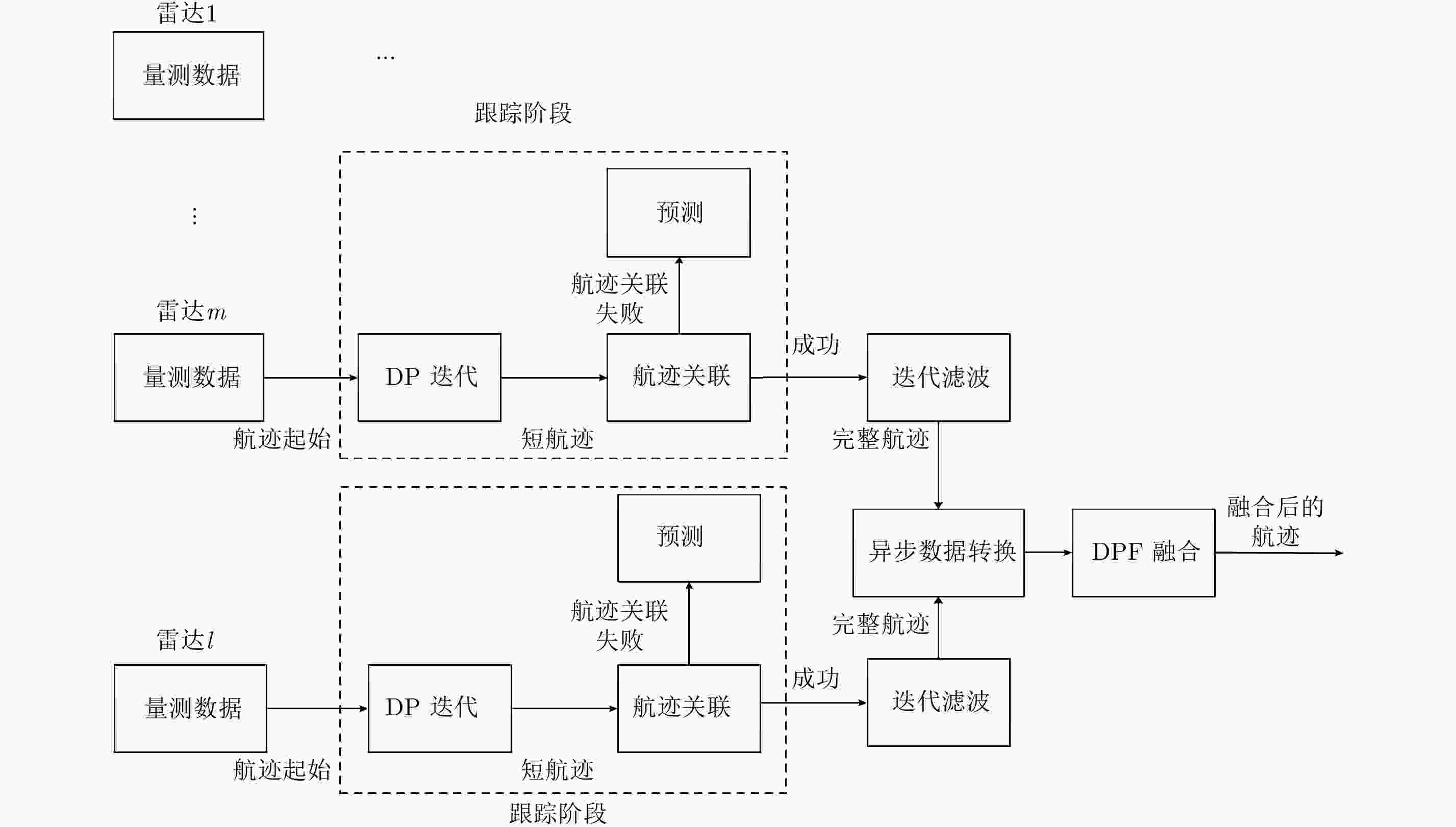
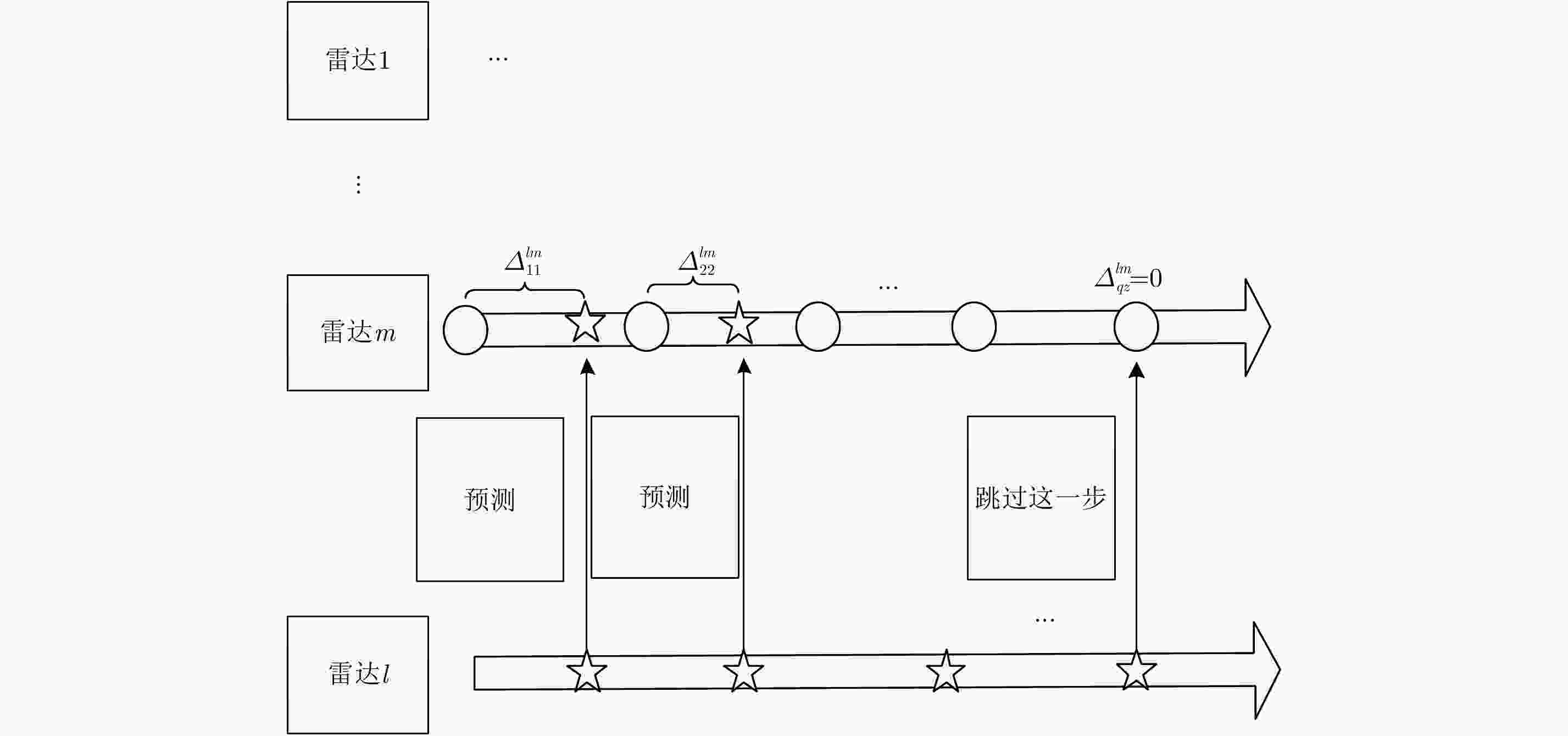
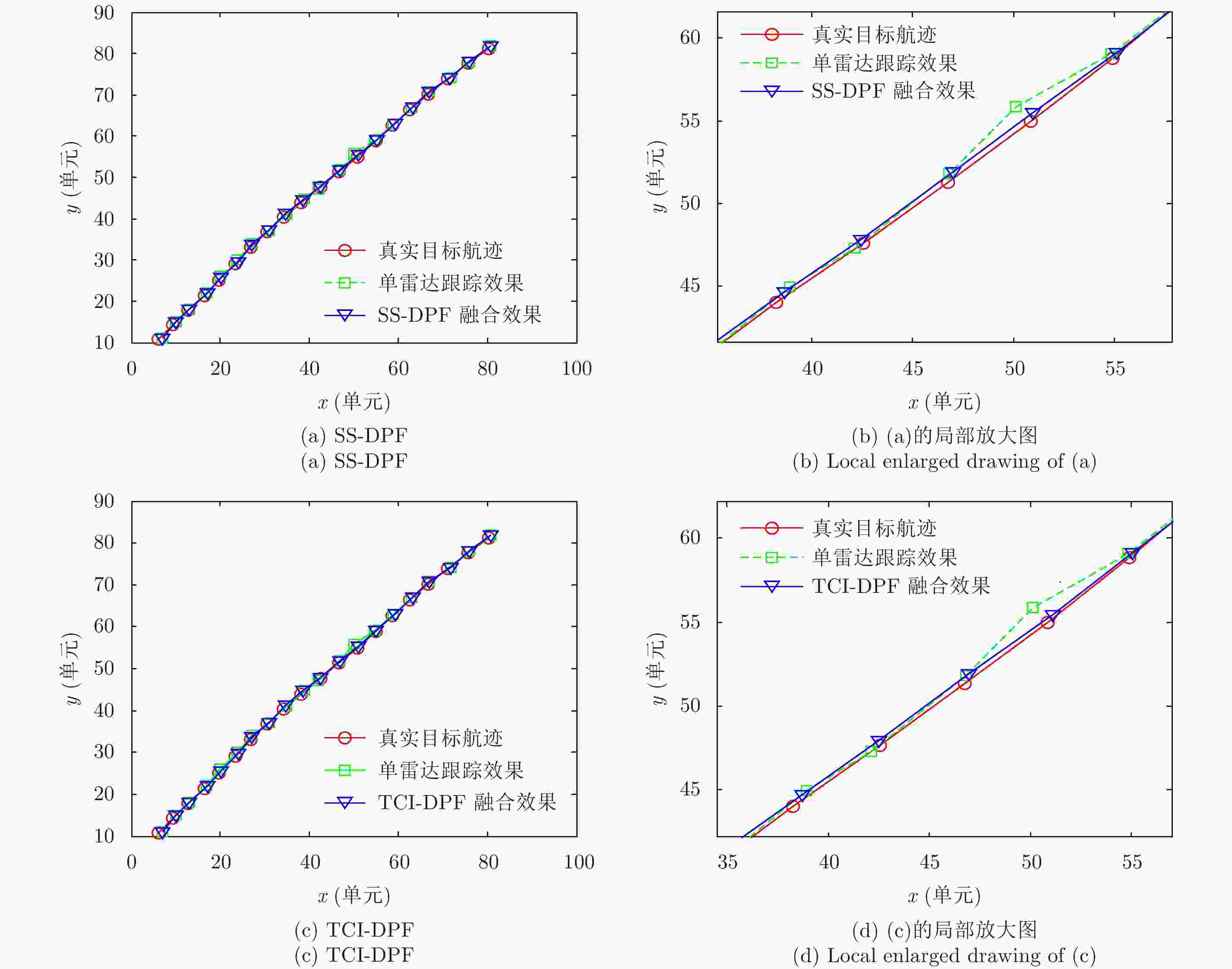
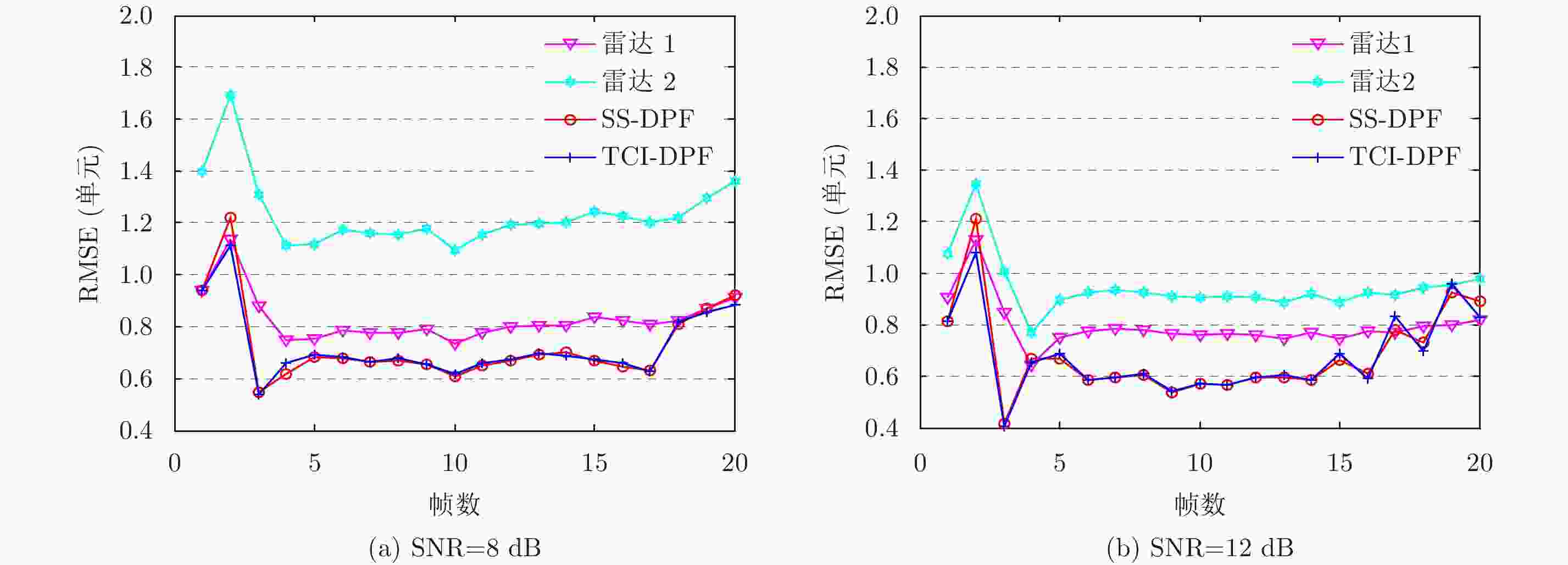
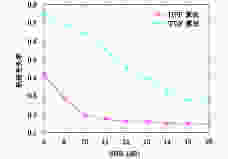
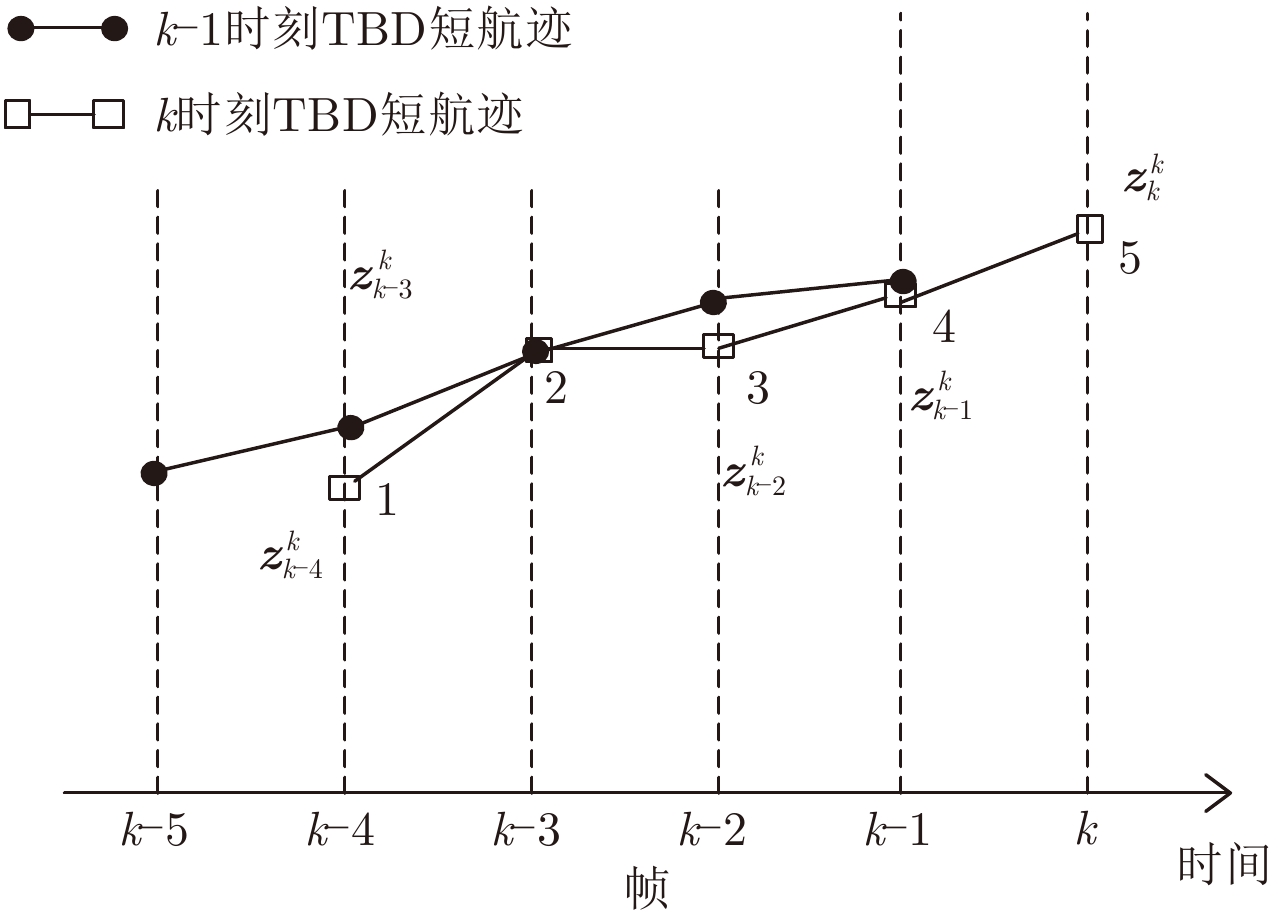
摘要: 该文主要运用检测前跟踪动态规划(Dynamic Programming-Track Before Detect)算法解决目标跟踪问题。动态规划(Dynamic Programming, DP)是一种通过对量测空间栅格化处理,然后对离散的量测空间中所有可能的物理路径进行遍历的算法。然而,该算法提供的是一种未经滤波和平滑的点迹序列。随着实际战争环境日益复杂,基于单雷达的DP-TBD算法在信噪比(SNR)较低时跟踪效果不佳。此外,由于DP-TBD算法没有状态误差协方差矩阵,因此无法将不同雷达的点迹序列进行融合。而且由于通信时延和不同的采样周期,不同雷达的数据往往是异步的。为了解决以上问题,该文提出了一种基于DP-TBD的分布式异步迭代滤波融合算法(DynamicProgramming Fuison, DPF)。该算法分为两步,第1步提出了一种迭代滤波方法对DP点迹进行处理;第2步将不同雷达获得的异步状态估计转化为同步的,接着利用几种分布式的融合方法来获取融合之后的状态估计。仿真结果说明,和单雷达相比,该融合算法可以有效提升目标跟踪的性能,同时,该算法也可以降低航迹丢失率和计算量。Abstract: In this paper, we address target tracking problems by the use of multiple sensors via the Dynamic Programming (DP)-based Track-Before-Detect (TBD) method. Generally, DP-TBD is a grid-based method that estimates target trajectories by searching all the physically admissible paths in a determinate discrete state space. However, this multi-frame detection algorithm provides plot sequences without filtering or smoothing. With the growing complexity of the battle field environment, single radar based on DP-TBD cannot achieve satisfactory results when the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) is low. Besides, it is very difficult to fuse plot sequences from different radars because they contain no state error covariance matrix. Furthermore, various radars always contain asynchronous data due to the diversity of sampling times and communication delays. To alleviate these problems, we propose a distributed asynchronous recursive filtering fusion (Dynamic Programming Fuison, DPF) algorithm based on DP-TBD, which is divided into two steps. In the first step, we propose an iterative filter algorithm via DP-TBD. Then, we convert the asynchronous evaluation data into synchronous data and implement several distributed fusion algorithms to estimate the target state. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can correctly estimate target trajectories and significantly enhance tracking accuracy compared to solo radar. In addition, this algorithm can decrease the track loss rate and calculation burden.
-
表 1 DPF算法和CDPF算法一次DP迭代的执行时间(s)
Table 1. One time execution time of DPF algorithm and CDPF algorithm (s)
参数 DPF算法 CDPF算法 传感器1的跟踪时间 4.07 0.052 传感器2的跟踪时间 3.661 0.043 融合时间 0.1 7.74 -
[1] Bar-Shalom Y and Li Xiao-rong. Multitarget-Multisensor Tracking: Principles and Techniques[M]. Storrs, CT: YBS, 1995. [2] Bar-Shalom Y and Blair W D. Multitarget-Multisensor Tracking: Applications and Advances, Vol. III[M]. Norwood, MA: Artech House, 2000. [3] Bar-Shalom Y, Daum F, and Huang J. The probabilistic data association filter[J]. IEEE Control Systems, 2009, 29(6): 82–100. DOI: 10.1109/MCS.2009.934469 [4] Davey S J and Rutten M G. A comparison of three algorithms for tracking dim targets[C]. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Information, Decision and Control, Adelaide, Australia, 2007: 342–347. [5] Barniv Y. Dynamic programming solution for detecting dim moving targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1985, AES-21(1): 144–156. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.1985.310548 [6] Barniv Y and Kella O. Dynamic programming solution for detecting dim moving targets part II: Analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1987, AES-23(6): 776–788. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.1987.310914 [7] Arnold J, Shaw S W, and Pasternack H. Efficient target tracking using dynamic programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1993, 29(1): 44–56. DOI: 10.1109/7.249112 [8] Tonissen S M and Evans R J. Peformance of dynamic programming techniques for Track-Before-Detect[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1996, 32(4): 1440–1451. DOI: 10.1109/7.543865 [9] Johnston L A and Krishnamurthy V. Performance analysis of a dynamic programming track before detect algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(1): 228–242. DOI: 10.1109/7.993242 [10] Yi Wei, Morelande M R, Kong Ling-jiang, et al. An efficient multi-frame track-before-detect algorithm for multi-target tracking[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(3): 421–434. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2256415 [11] Buzzi S, Lops M, Venturino L, et al. Track-before-detect procedures in a multi-target environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(3): 1135–1150. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4655369 [12] Wallace W R. The use of track-before-detect in pulse-Doppler radar[C]. Proceedings of RADAR 2002, Edinburgh, UK, 2002: 315–319. [13] Buzzi S, Lops M, and Venturino L. Track-before-detect procedures for early detection of moving target from airborne radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(3): 937–954. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1541440 [14] Orlando D, Ricci G, and Bar-Shalom Y. Track-before-detect algorithms for targets with Kinematic constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(3): 1837–1849. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5937268 [15] Grossi E, Lops M, and Venturino L. A Novel dynamic programming algorithm for Track-Before-Detect in radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(10): 2608–2619. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2251338 [16] Yi Wei, Kong Ling-jiang, and Yang Jian-yu. Thresholding process based dynamic programming Track-before-detect algorithm[J]. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 2013, E96.B(1): 291–300. DOI: 10.1587/transcom.E96.B.291 [17] Liu Rui, Yi Wei, Kong Ling-jiang, et al.. Recursive filtering for target tracking in multi-frame Track-Before-Detect[C]. Proceedings of the 2014 17th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Salamanca, Spain, 2014: 1–6. [18] Fang Zi-cheng, Yi Wei, and Kong Ling-jiang. A tracking approach for low observable target using plot-sequences of multi-frame detection[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 19th International Conference on Information Fusion, Heidelberg, Germany, 2016: 1427–1433. [19] Govaers F, Rong Yang, Chee L H, et al. Track-before-detect in distributed sensor applications[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2011, 2011: 20. DOI: 10.1186/1687-6180-2011-20 [20] Gao Xin-bo, Chen Jin-guang, Tao Da-cheng, et al. Multi-sensor centralized fusion without measurement noise covariance by variational Bayesian approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(1): 718–727. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5705702 [21] Ma Jing and Sun Shu-li. Centralized fusion estimators for multisensor systems with random sensor delays, multiple packet dropouts and uncertain observations[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2013, 13(4): 1228–1235. DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2012.2227995 [22] Zhai Yan, Yeary M B, Havlicek J P, et al. A new centralized sensor fusion-tracking methodology based on particle filtering for power-aware systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2008, 57(10): 2377–2387. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2008.919009 [23] Mohammadi A and Asif A. Distributed particle filter implementation with intermittent/irregular consensus convergence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(10): 2572–2587. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2245123 [24] Zhao Tong and Nehorai A. Distributed sequential Bayesian estimation of a diffusive source in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(4): 1511–1524. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2006.889975 [25] Üney M, Clark D E, and Julier S J. Distributed fusion of PHD filters via exponential mixture densities[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(3): 521–531. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2257162 [26] Guo Yun-fei, Zeng Ze-bing, and Zhao Shang-yu. An amplitude association dynamic programming TBD algorithm with multistatic radar[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 35th Chinese Control Conference, Chengdu, China, 2016: 5076–5079. [27] Talebi H and Hemmatyar A. Asynchronous track-to-track fusion by direct estimation of time of sample in sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2014, 14(1): 210–217. DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2013.2281394 [28] Hu Yanyan, Duan Zhansheng, and Zhou Donghua. Estimation fusion with general asynchronous multi-rate sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(4): 2090–2102. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5595618 [29] Yan L P, Liu B S, and Zhou D H. Asynchronous multirate multisensor information fusion algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(3): 1135–1146. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4383603 [30] Wang Yi-min and Li X R. Distributed estimation fusion with unavailable cross-correlation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(1): 259–278. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6129634 [31] Julier S J. An empirical study into the use of chernoff information for robust, distributed fusion of Gaussian mixture models[C]. Proceedings of the 2006 9th IEEE International Conference on Information Fusion, Florence, Italy, 2006: 1–8. [32] Aprile A, Grossi E, Lops M, et al.. An application of Track-Before-Detect to sea-clutter rejection: Experimental results based on real data[C]. Proceedings of the 2014 11th European Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2014: 505–508. [33] Li Yang-yang, Wang Jing-he, Yi Wei, et al.. A centralized asynchronous fusion algorithm for sensors with different resolution via DP-TBD[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 922–927. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: