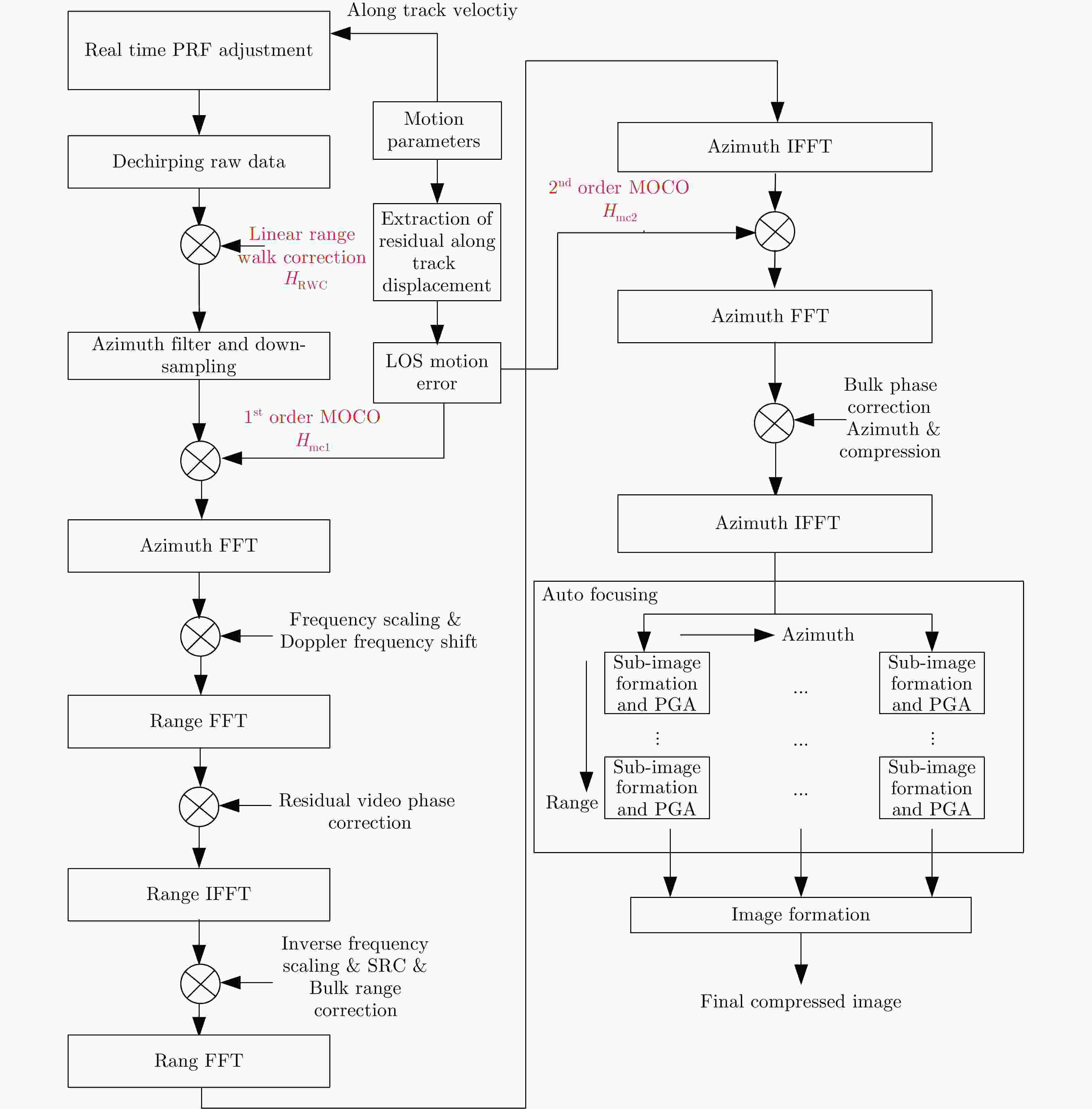
Modification and Compensation of the Line-of-Sight Motion Error for Multirotor UAV SAR
-
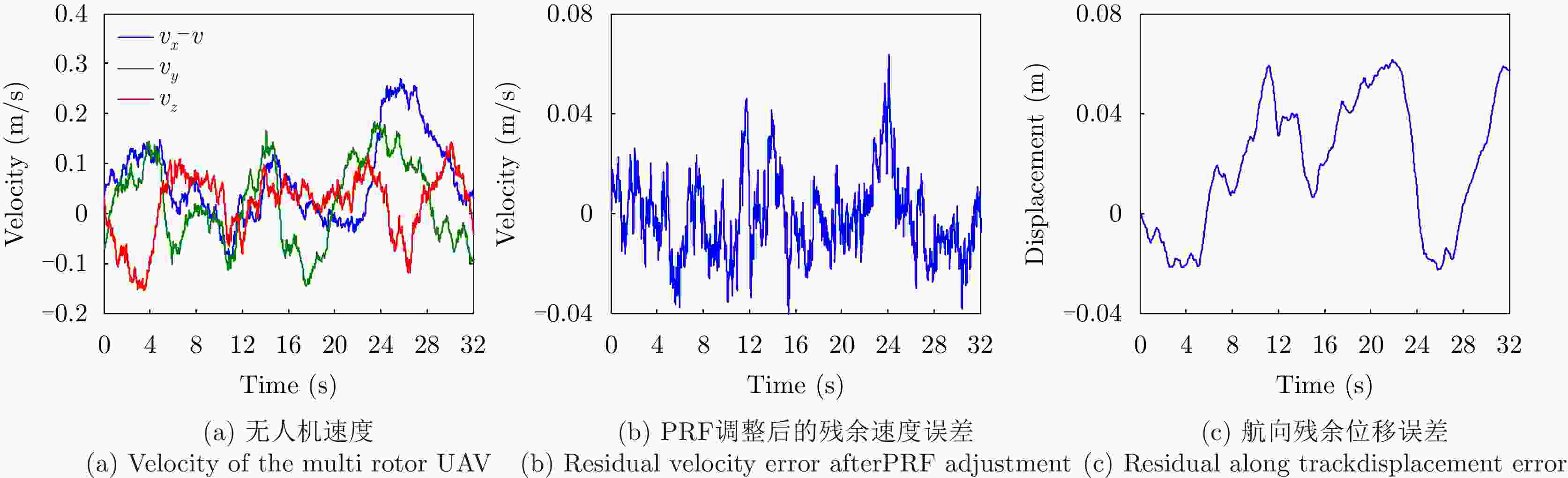
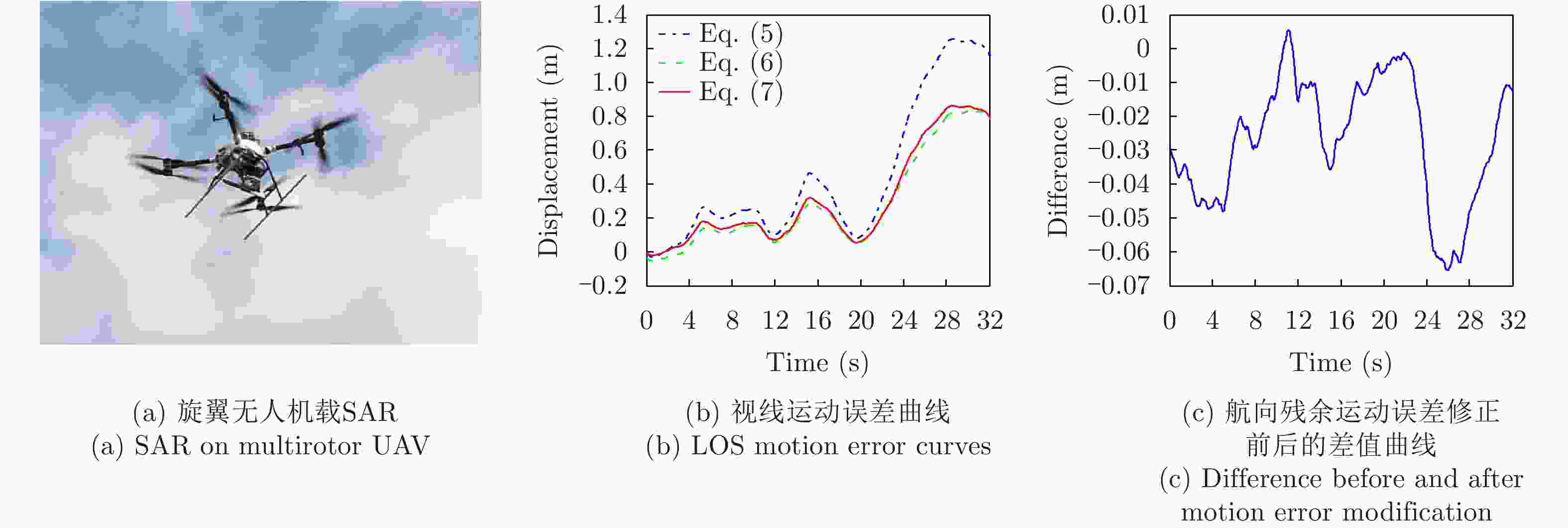
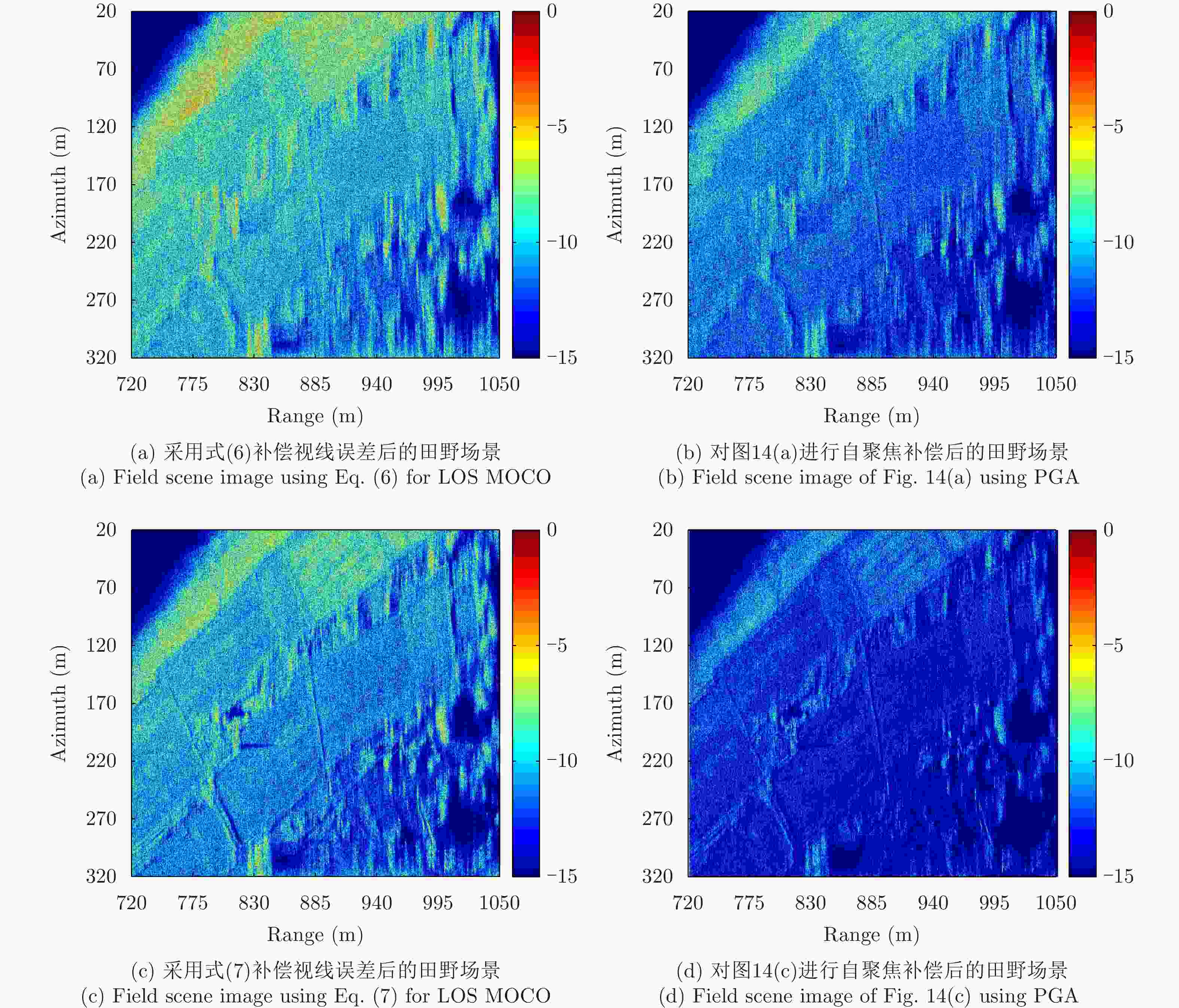
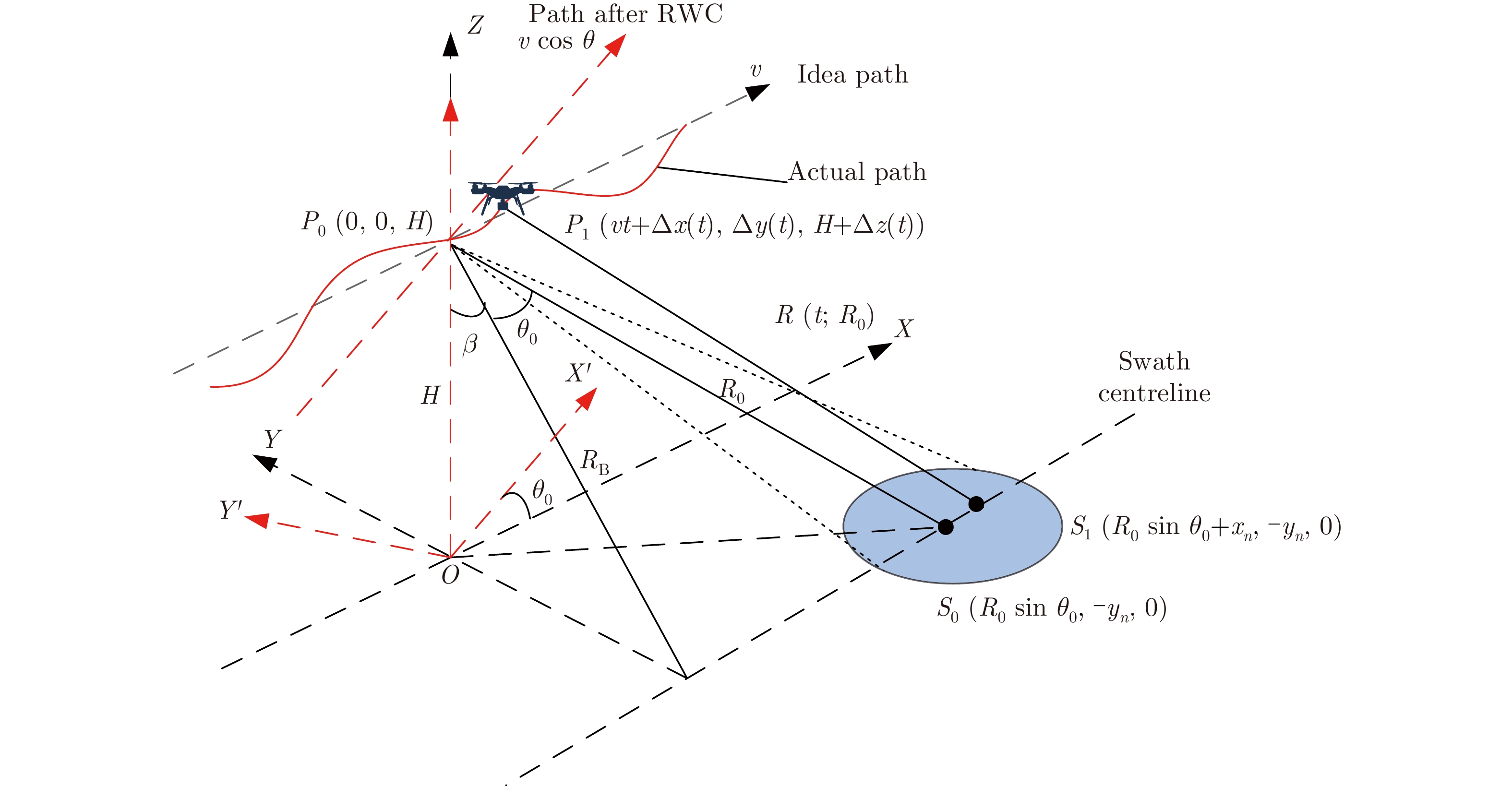
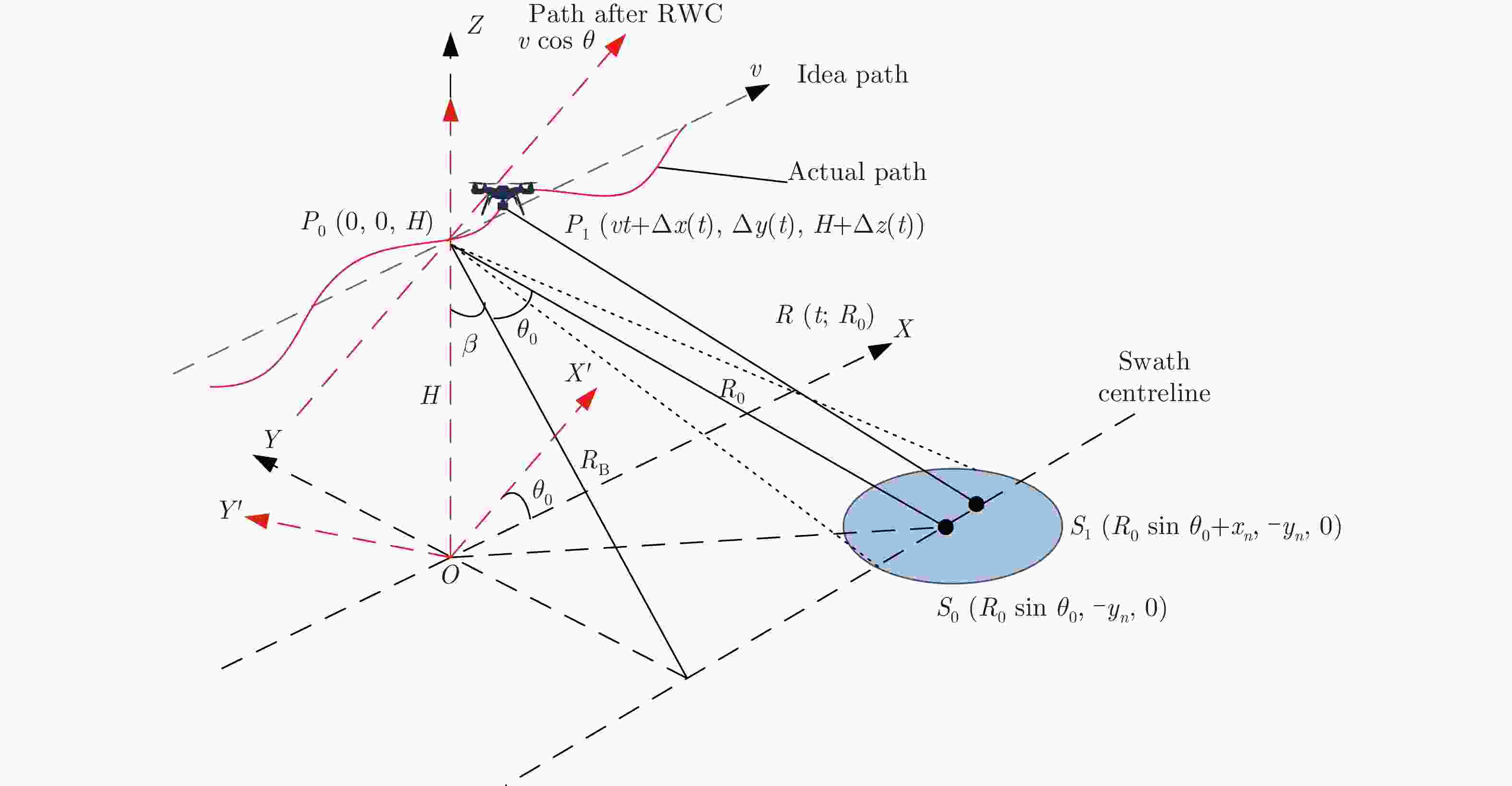
摘要: 多旋翼无人机体积小、重量轻、成本低,但由于飞行航迹极不稳定,成像信号处理难度很大。基于惯导数据实时调整脉冲重复频率(PRF)可预先补偿航向位移误差,但是,其残余误差在高波段合成孔径雷达(SAR)斜视成像时不能忽略。为此,利用位移实测值与理想值间的差异提取残余航向位移误差,修正了斜视成像几何下的视线运动误差,改进了传统的1阶、2阶视线误差补偿因子,并基于成对回波理论分析了旋翼无人机正弦位移误差的幅度和频率容限。仿真和实测数据验证了所提方法在大斜视成像时可减小视线运动误差约一个数量级,显著提高多旋翼无人机载SAR成像的性能。Abstract: The multirotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) has the advantages of small size, light weight, and low cost. However, imaging signal processing is complicated due to the extremely unstable flight path. Real-time adjustment of pulse repetition frequency based on inertial navigation data can compensate for the along-track displacement error in advance, but the residual error cannot be ignored for highly squinted high-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR). Therefore, the residual along-track displacement error is extracted based on the difference between the measured displacement value and the ideal one, and then the Line-of-Sight (LOS) motion error of the squint imaging geometry is modified. The traditional first-order and second-order LOS error compensation factors are improved, and the tolerance of the amplitude and frequency of the sinusoidal displacement error of a multirotor UAV is analyzed based on paired echo theory. Simulation and flight experiments verify that the proposed method can reduce the LOS motion error by an order of magnitude in large squint imaging and significantly improve the imaging performance of the squinted SAR of a multirotor UAV.
-
表 1 雷达系统仿真实验参数
Table 1. Experimental parameters of radar systems
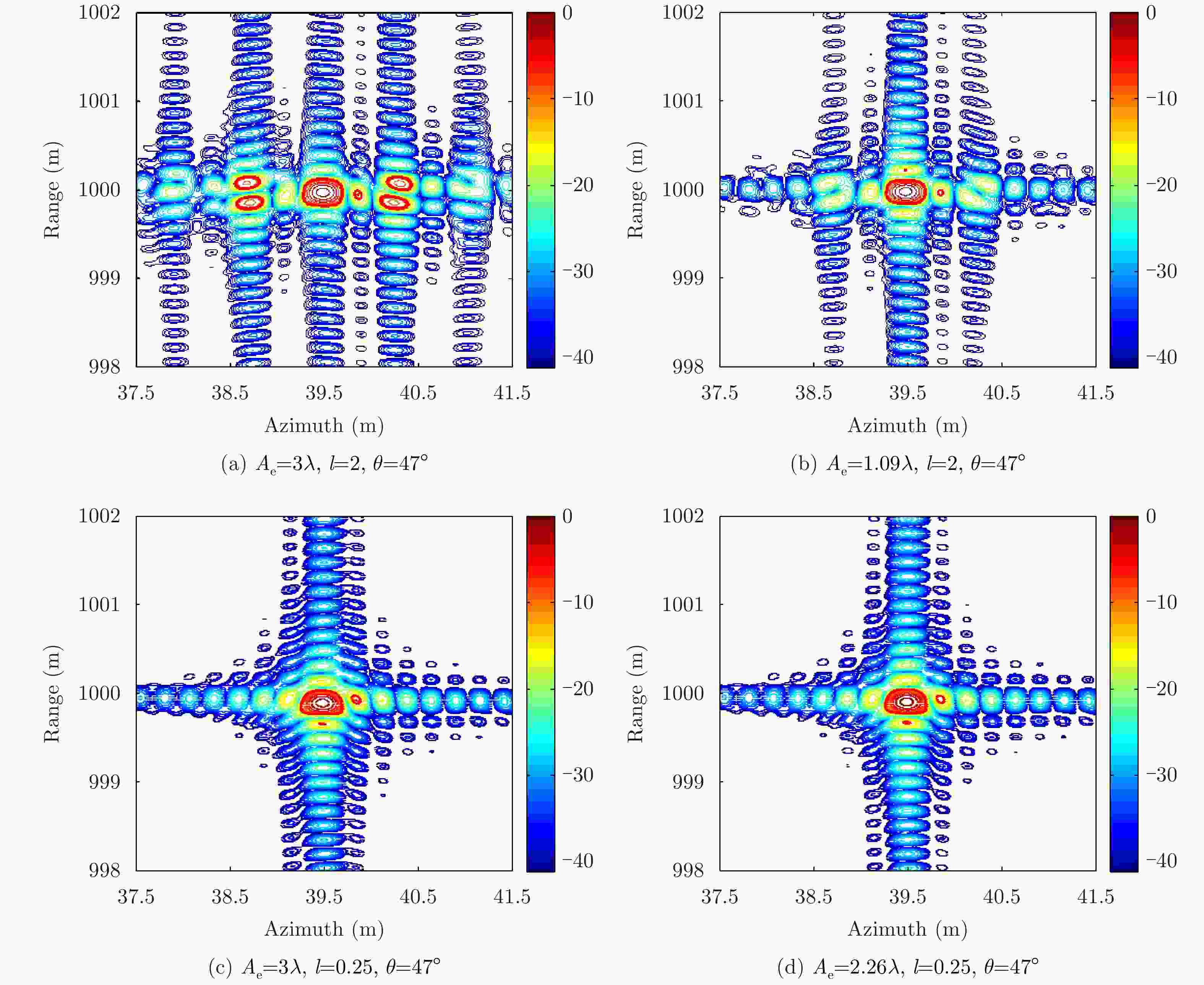
参数 数值 参数 数值 信号带宽 900 MHz 平台飞行速度 10 m/s 雷达中心频率 15 GHz 距离向采样率 10 MHz 信号时宽 400 μs 场景中心斜距 1 km 去调频参考斜距 1 km 成像斜视角 10°/47° 参考脉冲重复频率PRF 2 kHz 方位向点数(抽样后) 2048 距离向点数 4096 平台飞行高度 200 m 表 2 图11中点目标成像性能指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of image performance of the point target in Fig. 11
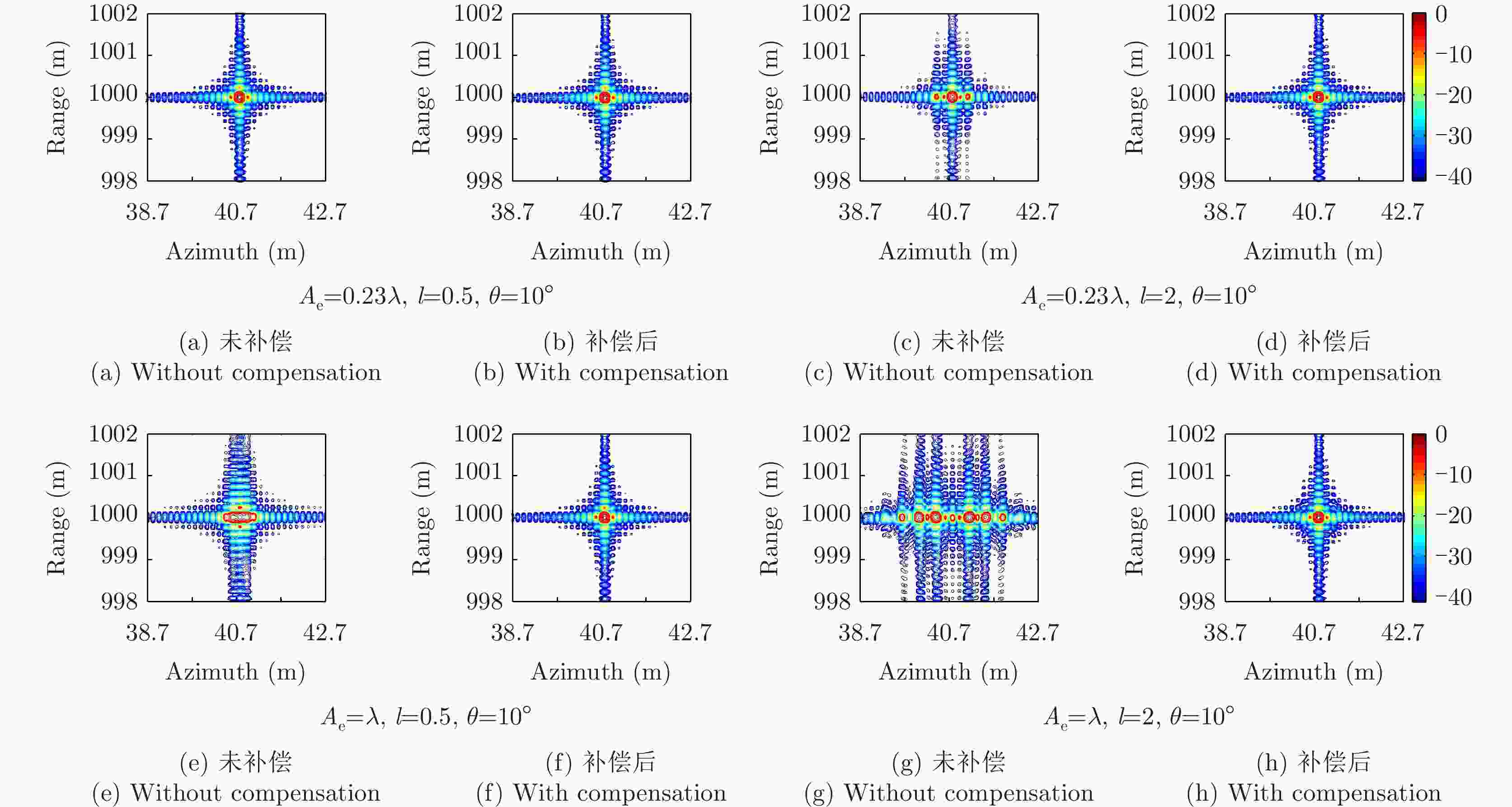
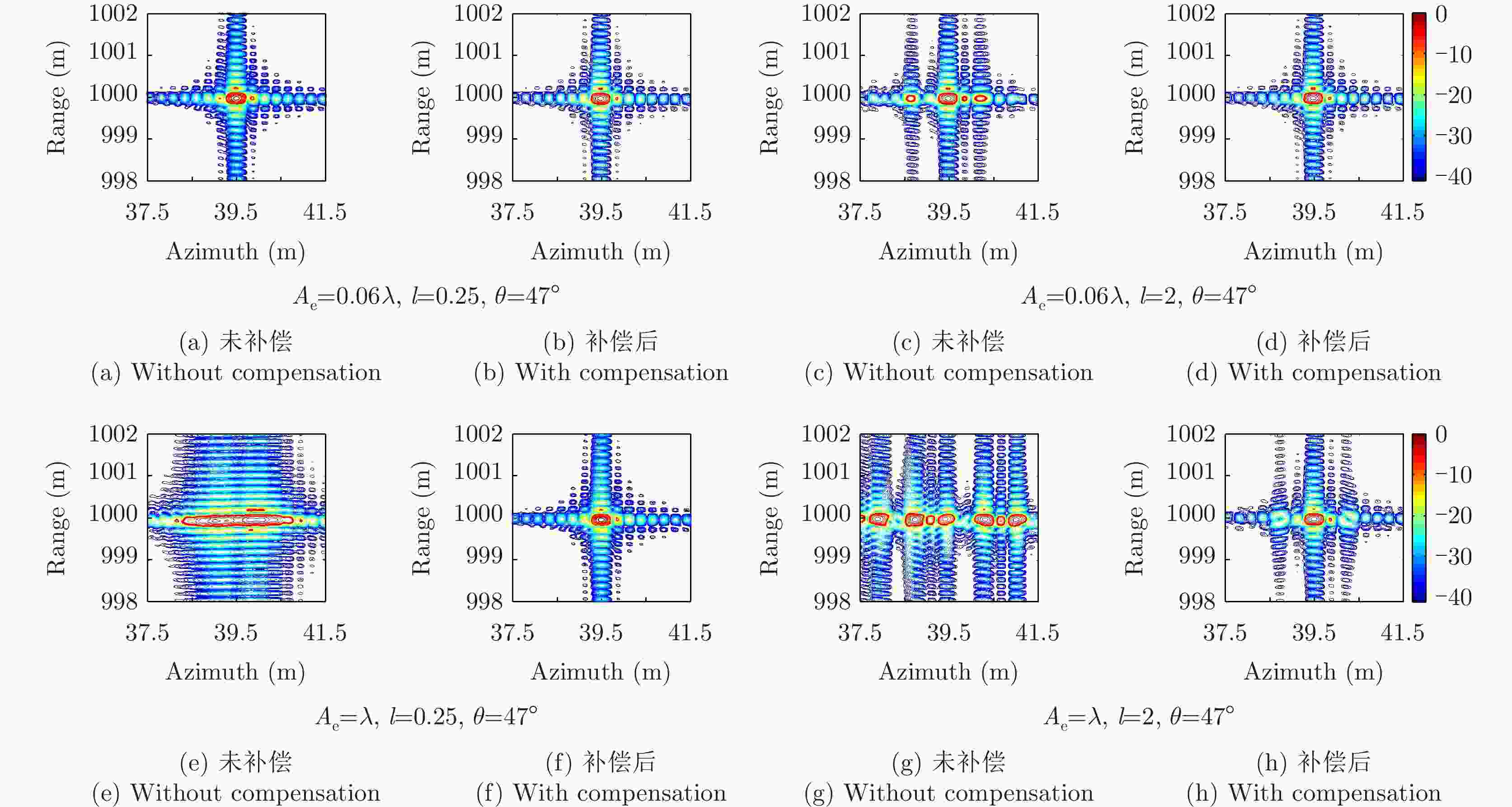
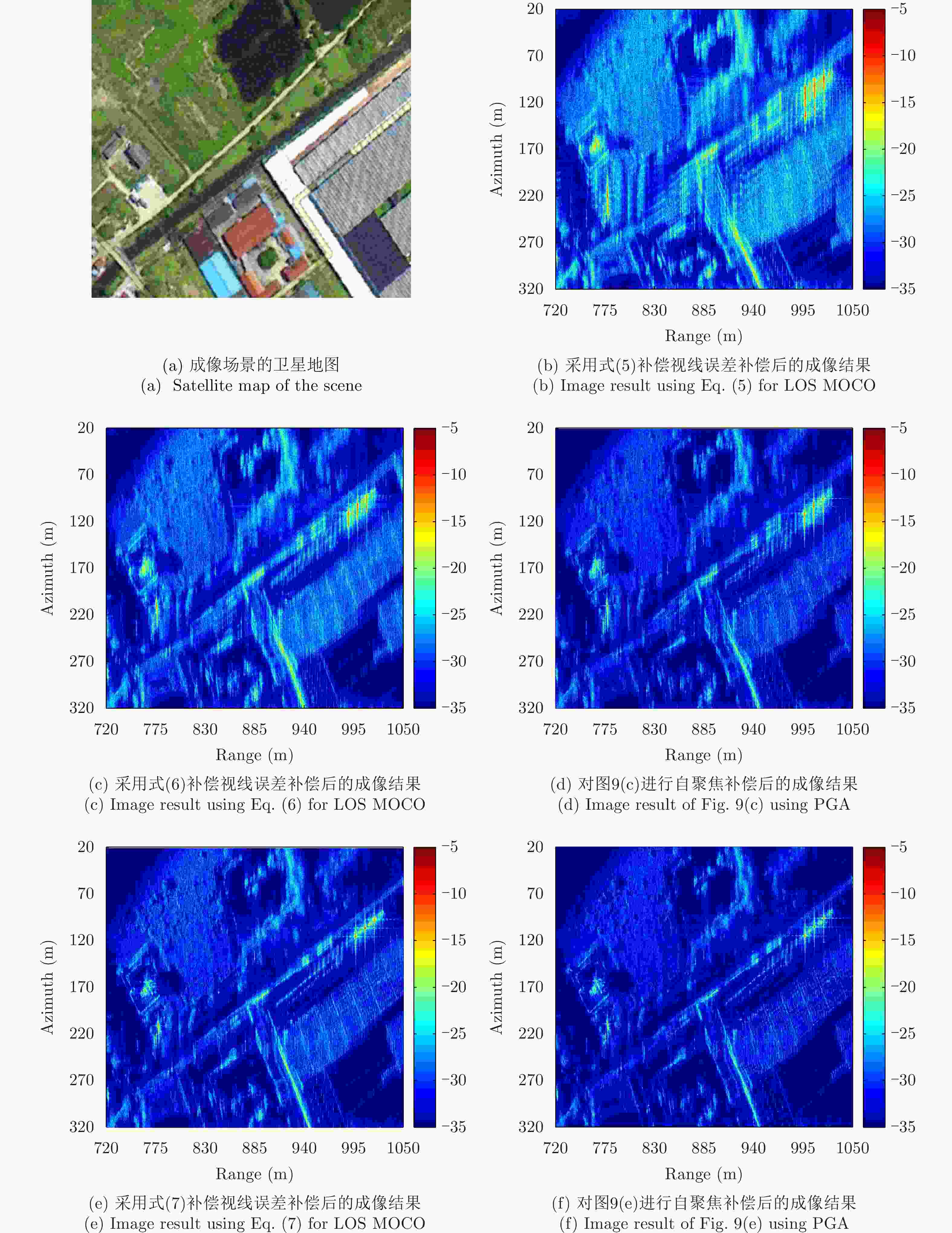
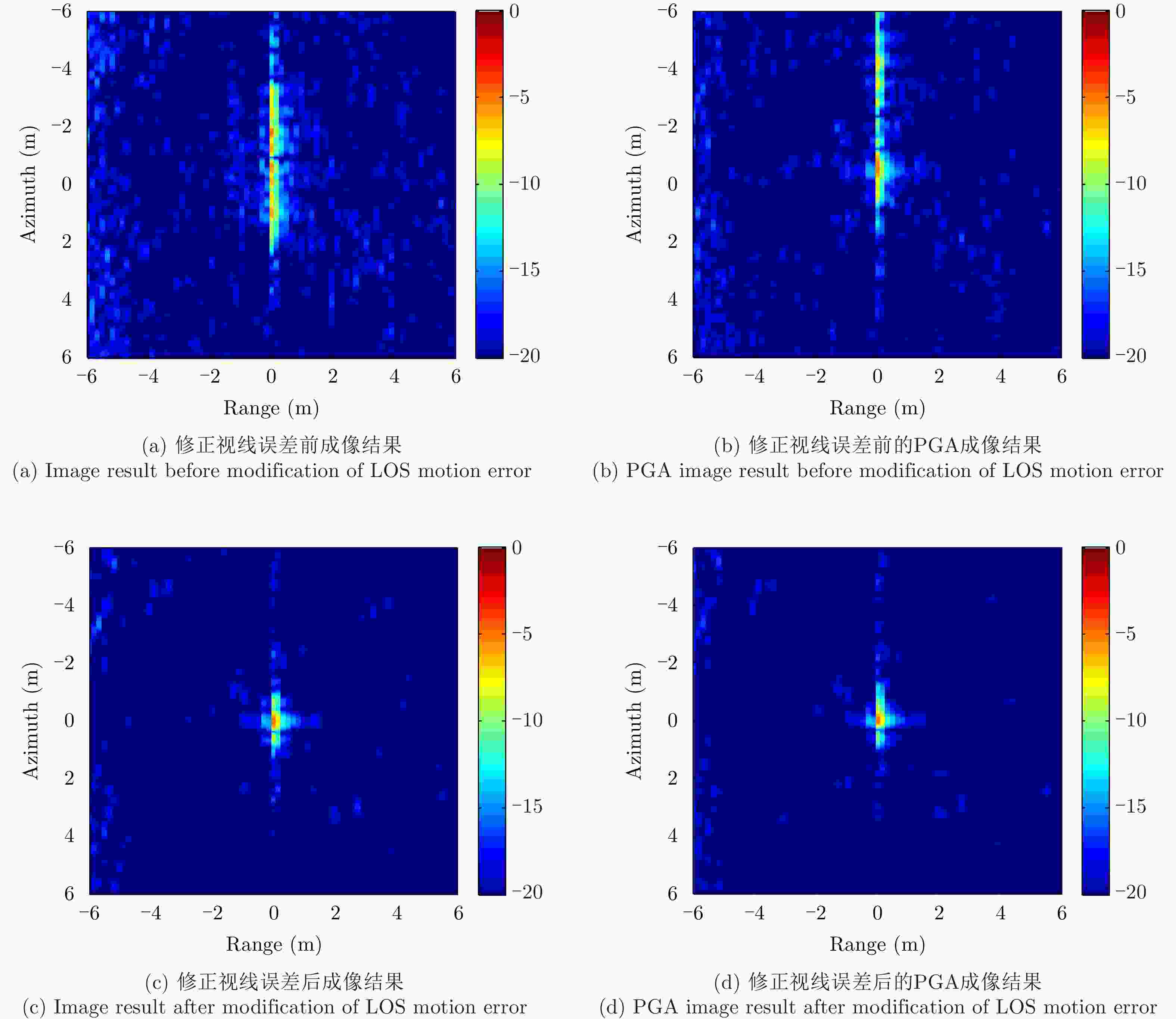
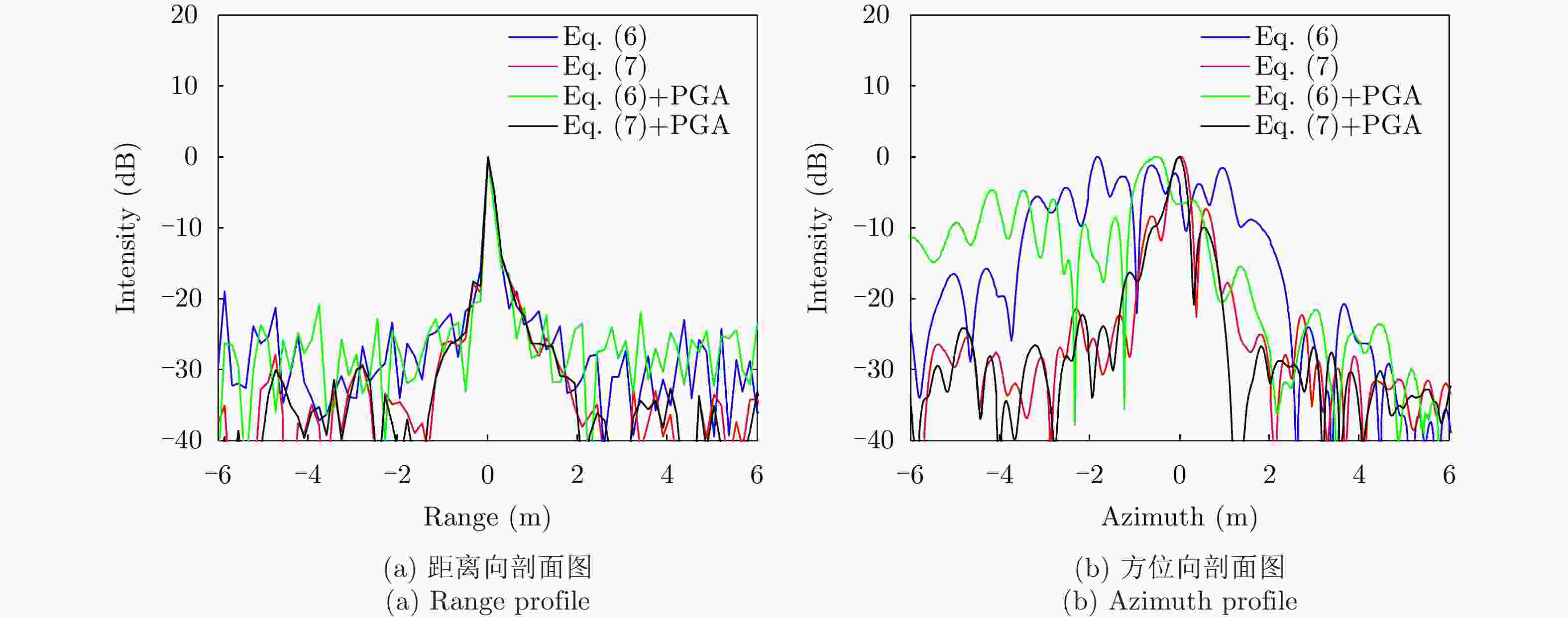
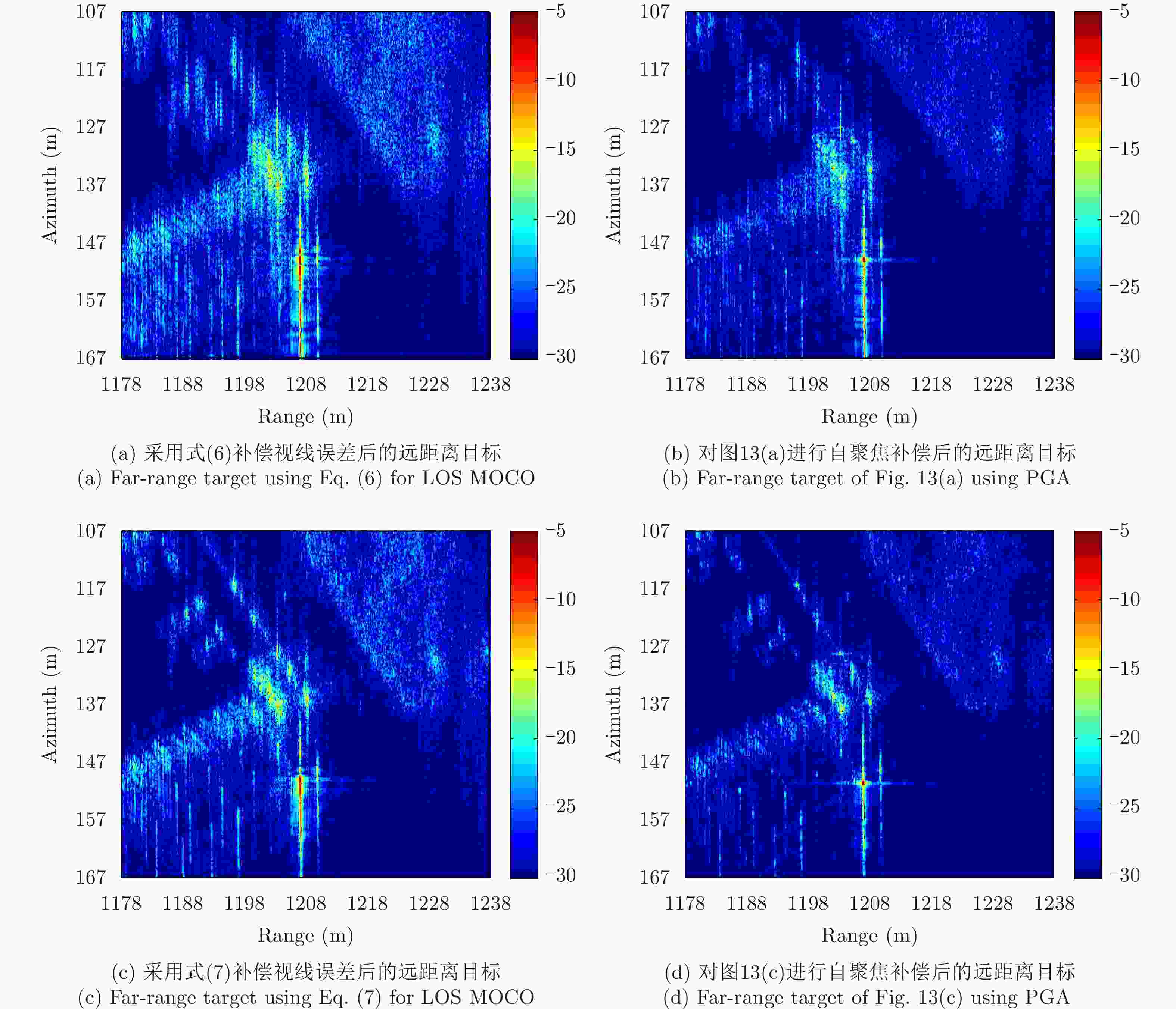
运动误差补偿方法 距离分辨率(m) 方位分辨率(m) 距离向PSLR(dB) 方位向PSLR(dB) 距离向ISLR(dB) 方位向ISLR(dB) 视线误差修正前 0.2151 0.8976 –18.8341 –2.5750 –11.9464 4.6462 视线误差修正前+PGA 0.2140 0.6586 –21.2475 –6.2690 –12.7365 1.3083 视线误差修正后 0.2151 0.3409 –17.9402 –7.0802 –14.0103 –2.6761 视线误差修正+PGA 0.2182 0.3276 –17.6637 –10.0202 –14.2019 –3.1933 -
[1] ZHOU Song, YANG Lei, ZHAO Lifan, et al. Quasi-polar-based FFBP algorithm for miniature UAV SAR imaging without navigational data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7053–7065. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2017.2739133 [2] HU Xianyang, MA Changzheng, HU Ruizhi, et al. Imaging for small UAV-borne FMCW SAR[J]. Sensors, 2018, 19(1): 87. doi: 10.3390/s19010087 [3] YI Tianzhu, HE Zhihua, HE Feng, et al. Generalized nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for high-resolution highly squint SAR imaging[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(11): 2568. doi: 10.3390/s17112568 [4] 邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102 [5] BERIZZI F, MARTORELLA M, CACCIAMANO A, et al. A contrast-based algorithm for synthetic range-profile motion compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 3053–3062. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002576 [6] MANCILL C E and SWIGER J M. A map drift autofocus technique for correcting higher order SAR phase error[C]. 27th Annual Tri-Service Radar Symposium Record, Monterey, USA, 1981: 391–400. [7] HUANG Yan, LIU Feiyang, CHEN Zhanye, et al. An improved map-drift algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(11): 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3011973 [8] XING Mengdao, JIANG Xiuwei, WU Renbiao, et al. Motion compensation for UAV SAR based on raw radar data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(8): 2870–2883. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2015657 [9] DE MACEDO K A C, SCHEIBER R, and MOREIRA A. An autofocus approach for residual motion errors with application to airborne repeat-pass SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 3151–3162. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.924004 [10] ZHANG Lei, SHENG Jialian, XING Mengdao, et al. Wavenumber-domain autofocusing for highly squinted UAV SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2012, 12(5): 1574–1588. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2011.2175216 [11] ZHANG Lei, QIAO Zhijun, XING Mengdao, et al. A robust motion compensation approach for UAV SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3202–3218. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2180392 [12] XIONG Tao, XING Mengdao, WANG Yong, et al. Minimum-entropy-based autofocus algorithm for SAR data using chebyshev approximation and method of series reversion, and its implementation in a data processor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1719–1728. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2013.2253781 [13] SU Y A, LIU Weixian, FENG Hongchuan, et al. Study of multi-rotor UAV SAR processing[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, USA, 2017: 226–232. [14] 邢涛, 胡庆荣, 李军, 等. 机载毫米波SAR垂直航向运动补偿分析与比较[J]. 火控雷达技术, 2016, 45(1): 13–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8652.2016.01.003XING Tao, HU Qingrong, LI Jun, et al. Analysis and comparison of airborne MMW SAR vertical course motion compensation[J]. Fire Control Radar Technology, 2016, 45(1): 13–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8652.2016.01.003 [15] 黎涛, 付耀文, 张健丰, 等. 多旋翼无人机载SAR视线向运动误差补偿方法[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(3): 491–501. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.03.006LI Tao, FU Yaowen, ZHANG Jianfeng, et al. A method of line-of-sight motion error compensation for multi-rotor UAV SAR[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(3): 491–501. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.03.006 [16] 邢涛, 李军, 胡庆荣, 等. 毫米波小斜视SAR垂直航向运动分析与补偿[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2016, 43(1): 127–132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2016.01.023XING Tao, LI Jun, HU Qingrong, et al. Cross-track motion analysis and compensation of millimeter wave small squint SAR[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2016, 43(1): 127–132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2016.01.023 [17] SU Hao, WEI Shunjun, ZHANG Xiaoling, et al. Efficient autofocus of small multi-rotor UAV SAR by minimum entropy BP algorithm[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 7356–7359. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0625 [18] BEZVESILNIY O O, GOROVYI I M, and VAVRIV D M. Autofocusing SAR images via local estimates of flight trajectory[J]. International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies, 2016, 8(6): 881–889. doi: 10.1017/S1759078716000180 [19] SHEN Wei, HE Xueli, MAO Xinhua, et al. An autofocus algorithm for multi-rotor UAV SAR[C]. International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Phuket, Thailand, 2017: 1–2. [20] FORNARO G. Trajectory deviations in airborne SAR: Analysis and compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(3): 997–1009. doi: 10.1109/7.784069 [21] GU Chengfei, CHANG Wenge, LI Xiangyang, et al. A new distortion correction method for FMCW SAR real-time imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(3): 429–433. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2647962 [22] 曾朝阳, 王辉. W波段UAV MISAR实时成像运动补偿方法[J]. 上海航天(中英文), 2020, 37(1): 63–69, 100. doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.1006-1630.2020.01.009ZENG Zhaoyang and WANG Hui. The motion compensation method for W-band UAV MISAR real-time imaging[J]. Aerospace Shanghai (Chinese &English) , 2020, 37(1): 63–69, 100. doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.1006-1630.2020.01.009 [23] 贾高伟, 常文革. 高分辨率UAV SAR的三维运动误差分离与补偿[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2014, 36(4): 71–76. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201404013JIA Gaowei and CHANG Wenge. Three-dimensional motion error correction for unmanned aerial vehicle synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2014, 36(4): 71–76. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201404013 [24] CARIS M, STANKO S, PALM S, et al. Synthetic aperture radar at millimeter wavelength for UAV surveillance applications[C]. 2015 IEEE 1st International Forum on Research and Technologies for Society and Industry Leveraging a better tomorrow (RTSI), Turin, Italy, 2015: 349–352. [25] STANKO S, JOHANNES W, SOMMER R, et al. Millimeterwave radar for SAR on UAVs with real-time image display[C]. 2011 12th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Leipzig, Germany, 2011: 507–511. [26] SUN B M, KENNEY R H, YEARY M B, et al. An up-sampled particle filter fusion technique and its application in synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Microwaves, 2022, 2(1): 108–122. doi: 10.1109/JMW.2021.3123531 [27] 张雨轮, 张涛, 李涛, 等. 基于惯导的机载斜视SAR运动补偿研究[J]. 火控雷达技术, 2014, 43(1): 18–21, 41. doi: 10.19472/j.cnki.1008-8652.2014.01.005ZHANG Yulun, ZHANG Tao, LI Tao, et al. Study on IMU based motion compensation for airborne squint SAR[J]. Fire Control Radar Technology, 2014, 43(1): 18–21, 41. doi: 10.19472/j.cnki.1008-8652.2014.01.005 [28] LIANG Yujie, LIANG Yi, ZHANG Gang, et al. A modified design method of pulse repetition frequency for synthetic aperture radar system based on the single point equivalent squint model[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2021, 15(7): 748–759. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12081 [29] TSUNODA S I, PACE F, STENCE J, et al. Lynx: A high-resolution synthetic aperture radar[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 3704, Radar Sensor Technology IV, Orlando, USA, 1999: 20–27. [30] 李建阳, 常文革, 李悦丽. UWB SAR实时PRF调整[J]. 现代雷达, 2009, 31(4): 34–37. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2009.04.008LI Jianyang, CHANG Wenge, and LI Yueli. Real time adjustment of PRF in UWB SAR[J]. Modern Radar, 2009, 31(4): 34–37. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2009.04.008 [31] LIANG Yi, LI Guofei, ZHANG Gang, et al. A nonparametric paired echo suppression method for helicopter-borne SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(12): 2080–2084. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2962175 [32] KLAUDER J R, PRICE A C, DARLINGTON S, et al. The theory and design of chirp radars[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 1960, 39(4): 745–808. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1960.tb03942.x [33] 张澄波. 合孔径雷达: 原理、系统分析与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 140–152.ZHANG Chengbo. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Principles, System Analyses, Applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989: 140–152. [34] 沈永欢, 梁在中, 许履瑚, 等. 实用数学手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1992: 668–672.SHEN Yonghuan, LIANG Zaizhong, XU Lvhu, et al. Handbook of Practical Mathematics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1992: 668–672. [35] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Norwood: Artech House, 2005: 60. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: