Performance Analysis on ISAR Imaging of Space Targets
-
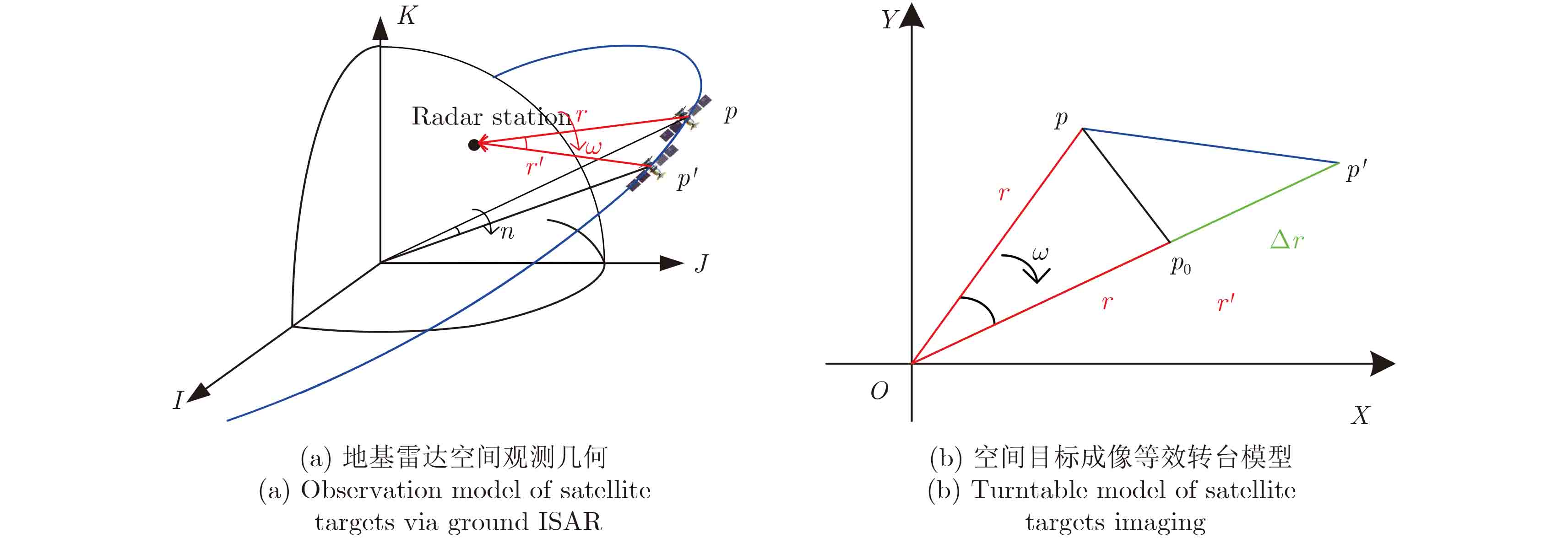
摘要: 空间目标逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)成像的方位维相干积累增益取决于目标运动状态信息,关于目标运动分析的缺失将直接影响空间目标ISAR观测中成像质量的预估与系统参数的设计。该文提出根据空间目标轨道参数计算其相对雷达视线运动状态,推导一定相干积累角ISAR成像的方位相干积累简化公式,实现基于相干积累角的ISAR成像时间段选择,可有效保证成像方位分辨率;同时详细分析目标轨道高度等参数对ISAR系统回波接收功率、成像质量的影响,为空间目标ISAR成像雷达体制设计提供了设计依据。理论推导和仿真实验均验证了空间目标ISAR成像中随着目标轨道高度升高,单次回波信噪比降低的损失可通过方位相干积累增益的提升实现部分弥补。该文工作可为空间目标ISAR成像体制和处理设计提供了理论基础和指标设计依据。Abstract: Usually, in traditional Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) systems design and mode selection for space satellite targets, coherent integration gain in azimuth direction hardly can be analyzed, which depends on target’s motion. In this study, we combine the target orbit parameters to determine its motion relative to radar and deduce coherent integration equation in ISAR imaging to realize the selection of imaging intervals based on coherent integration, which can ensure the resolution in azimuth direction. Meanwhile, we analyze the influence of target orbit altitude to echo power and imaging Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) that provides a new indicator for space observation ISAR systems design. The result of simulation experiment illustrates that with target orbit altitude increasing, coherent integration gain in azimuth direction of large-angular observation offsets the decreasing of imaging SNR in a degree, which provides a brand-new perspective for space observation ISAR systems and signal processing design.
-
表 1 实验ISAR系统主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of ISAR system
参数 数值 载频 16.7 GHz 带宽 1 GHz 方位向分辨率 0.18 m 距离向分辨率 0.15 m 脉冲重复频率 200 Hz 表 2 实验地基ISAR观测站位置
Table 2. Position parameters of radar sites
地点 经纬度 库尔勒 41.5°N, 86.8°E 北京 39.9°N, 116.4°E 西安 31.1°N, 108.4°E 表 3 不同轨道高度图像质量评价
Table 3. Comparison result of imaging quality at different heights
轨道高度(km) 成像时间(s) 脉冲积累数 TNR 脉冲积累数/TNR 791 9.94 1988 6.82 291.58 1200 12.40 2484 8.61 288.58 1800 16.82 3364 11.45 293.80 -
[1] Xing Mengdao and Bao Zheng. High-resolution ISAR imaging of high speed moving targets[C].IEE Proceedings- Radar,Sonar and Navigation, 2005, 152(2): 58–67. [2] Bai Xueru, Xing Mengdao, Zhou Feng,et al.. High-resolution 3D imaging of spinning space debris[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(7): 2352–2362. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2010854. [3] 王琦. 空间目标 ISAR 成像的研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10701-2010038216.htmWang Qi. Study of ISAR imaging for space targets[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10701-2010038216.htm [4] 王洋, 金胜, 黄璐. 空间目标双基地雷达ISAR成像技术研究[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2015, 13(5): 485–495. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDKJ201505008.htmWang Yang, Jin Sheng, and Huang Lu. Bistatic radar ISAR imaging of space target[J].Radar Science and Technology, 2015, 13(5): 485–495. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDKJ201505008.htm [5] 王珊, 季伟, 陈娟, 等. 基于运动目标检测的多脉冲相干积累算法[J]. 机械与电子, 2010, 9: 490–491. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJXX201009377.htmWang Shan, Ji Wei, Chen Juan,et al.. Coherent integration algorithm of high velocity moving target[J].Science and Technology Information, 2010, 9: 490–491. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJXX201009377.htm [6] 庞存锁, 张南, 侯慧玲. 高速微弱目标长时间积累对雷达方程的影响[J]. 火控雷达技术, 2015, 44(1): 7–9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKLD201501002.htmPang Cunsuo, Zhang Nan, and Hou Huilin. Radar equation for high-speed weak target during long time integration[J].Fire Control Radar Technology, 2015, 44(1): 7–9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKLD201501002.htm [7] 李亮, 洪峻, 明峰, 等. 电离层时空变化对中高轨SAR成像质量的影响分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(4): 915–922. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00859.Li Liang, Hong Jun, Ming Feng,et al.. Study on ionospheric effects induced by spatio-temporal variability on medium-earth-orbit SAR imaging quality[J].Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(4): 915–922. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00859. [8] 黄小红, 文贡坚. L波段雷达电离层高速运动目标ISAR成像补偿方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 12(37): 2971–2976. DOI: 10.999/JEIT150646.Huang Xiaohong and Wen Gongjian. Compensating method of L-band radar ISAR imaging for ionosphereic target with high-velocity[J].Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 12(37): 2971–2976. DOI: 10.999/ JEIT150646. [9] 袁孝康. 合成孔径雷达方程[J]. 上海航天, 2002, 3: 1–5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SHHT200203000.htmYuan Xiaokang. Synthetic aperture radar equation[J].Aerospace Shanghai, 2002, 3: 1–5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SHHT200203000.htm [10] 范录宏. 逆合成孔径雷达成像与干扰技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2006. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10614-2007051031.htmFan Luhong. Research on imaging and jamming of inverse synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2006. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10614-2007051031.htm [11] 许然. 提高雷达成像质量的若干新体制和新方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2015. http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis_Y2954050.aspxXu Ran. Study on new systems and techniques for improving radar imaging performances[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2015. http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis_Y2954050.aspx [12] Cao X, Su F, Sun H,et al.. Space debris observation via space-based ISAR imaging[C]. International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Guilin, China, April 18–21, 2007: 1–5. [13] Skolnik MI. Radar Handbook (Second edition)[M]. New York: Mcgraw-Hall Publishing Company, 1990. [14] 张云彬, 张永生. 近圆轨道遥感卫星星下点轨迹的计算[J]. 测绘学院学报, 2001, 18(4): 257–259.Zhang Yunbin and Zhang Yongsheng. Calculation of sub-satellite track of remote sensing satellite in nearly round orbit[J].Journal of Institute of Surveying and Mapping, 2001, 18(4): 257–259. [15] 任锴. 导航卫星精密定轨理论与方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 信息工程大学, 2015.Ren Kai. Research on theory and methodology of precise orbit determination of navigation satellites[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], PLA Information Engineering University, 2015. [16] 黄艳, 张永利, 刘志铭. 一种基于点目标的雷达影像质量评价方法[J]. 测绘工程, 2012, 21(1): 30–34.Huang Yan, Zhang Yongli, and Liu Zhiming. A method of SAR image quality evaluation based on pinpoint target[J].Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2012, 21(1): 30–34. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: