Small Target Detection in Sea Clutter Background Based on Tsallis Entropy of Doppler Spectrum
-
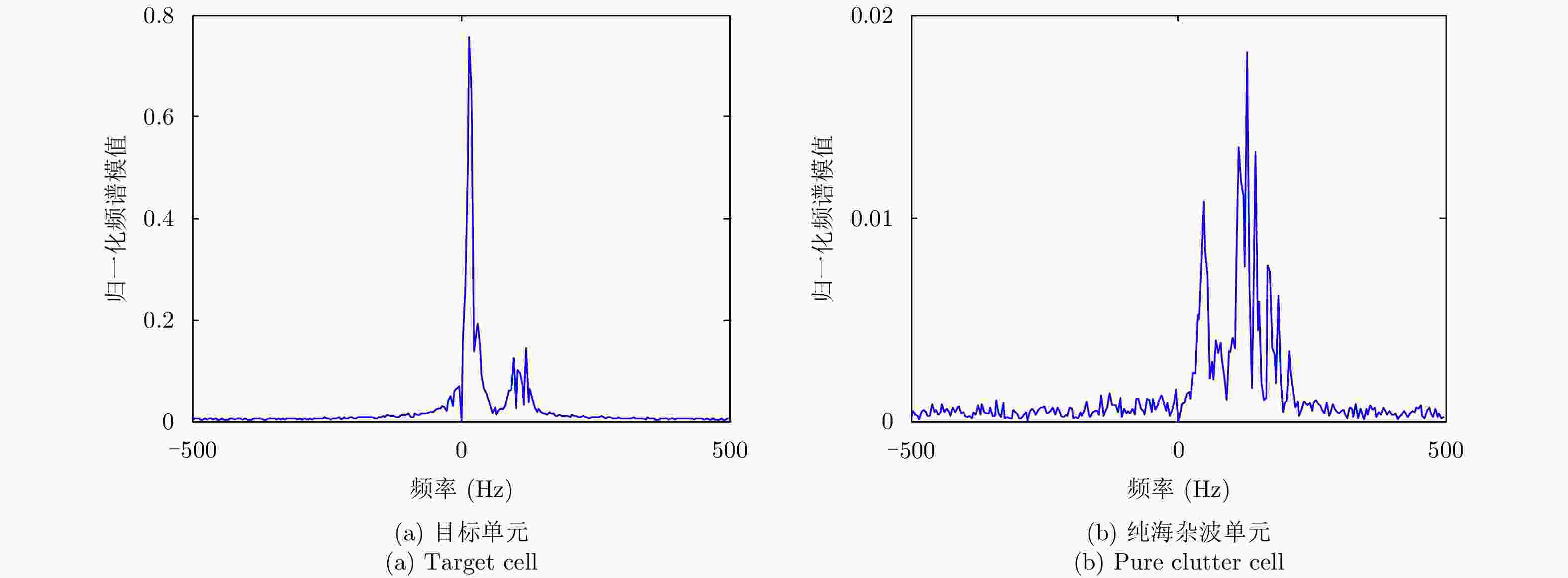
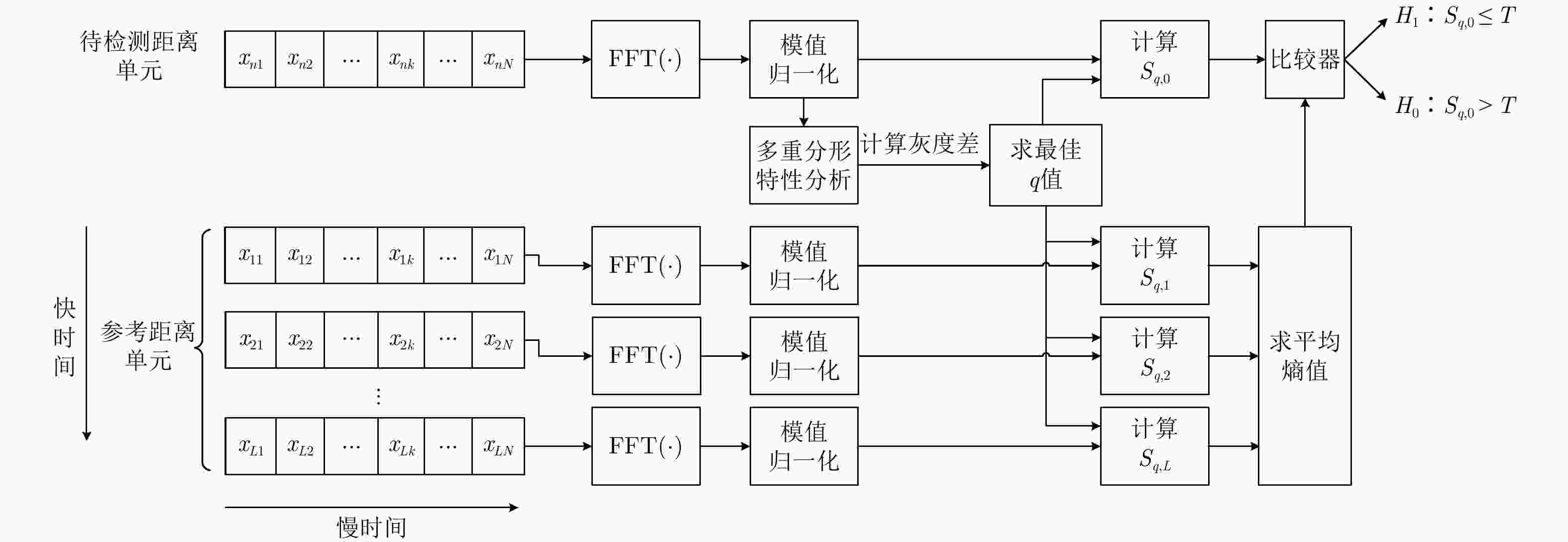
摘要: 根据海杂波和目标多普勒谱的聚集性差异,可以用熵特征来检测海杂波背景下的小目标,然而常用的香农熵仅仅是统计学角度的宏观量值,并不能反映出海杂波的非线性特性。非广延熵是香农熵的推广,可以描述海杂波已被证实的多重分形特性。该文首先给出了非广延熵与分形维数的关系,然后结合有目标单元回波的多普勒谱较纯杂波单元回波的多普勒谱聚集性更强以及海杂波回波具有多重分形特性的特点,提出了基于多普勒谱非广延熵的海杂波背景下的小目标检测方法,最后通过实测数据进行实验比较,验证了该文算法的有效性,在观测时间较短的情况下,与现有的多重分形频域Hurst指数方法和基于香农熵的方法相比,该文算法具有更好的检测性能。Abstract: According to the different concentration levels of Doppler spectrum between sea clutter and target, small target in sea clutter background can be detected using Shannon entropy. However, Shannon entropy is merely a special case of Tsallis entropy and cannot reflect the multifractality of sea clutter. In this paper, the relation between Tsallis entropy and the generalized fractal dimension is first presented, and then the Doppler spectrum’s concentrative level and multifractality of sea clutter are combined; finally an algorithm for detecting small target in sea clutter background based on Tsallis entropy of Doppler spectrum rather than of Shannon entropy is proposed. By comparison via IPIX dataset, the detection’s performance of Tsallis entropy is better than that of Shannon entropy and Hurst exponent as per short observations.
-
Key words:
- Sea clutter /
- Target detection /
- Doppler spectrum /
- Tsallis entropy /
- Multifractality
-
表 1 1993年IPIX雷达数据主要参数说明
Table 1. Description of the data sets of IPIX radar database in 1993
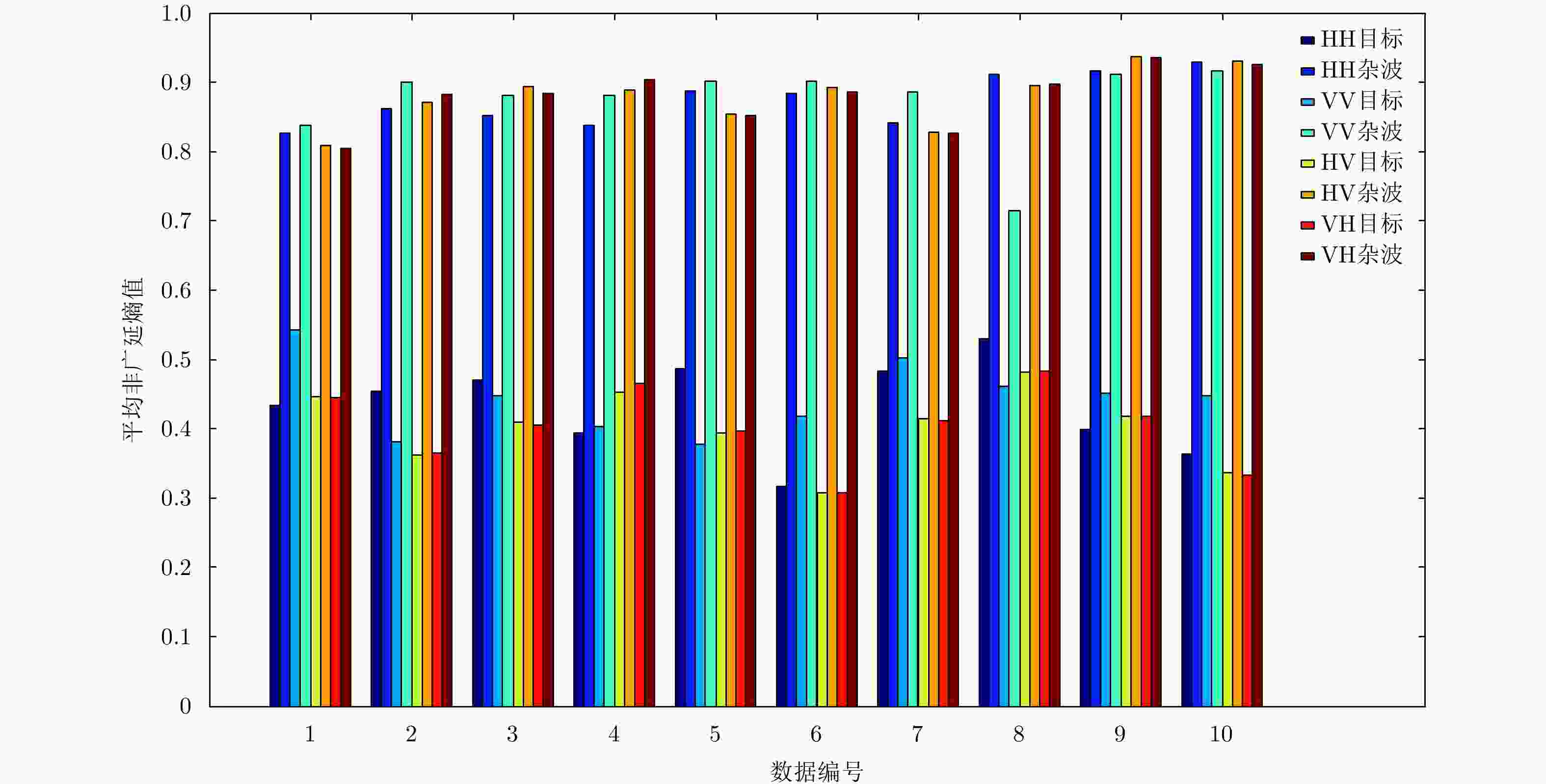
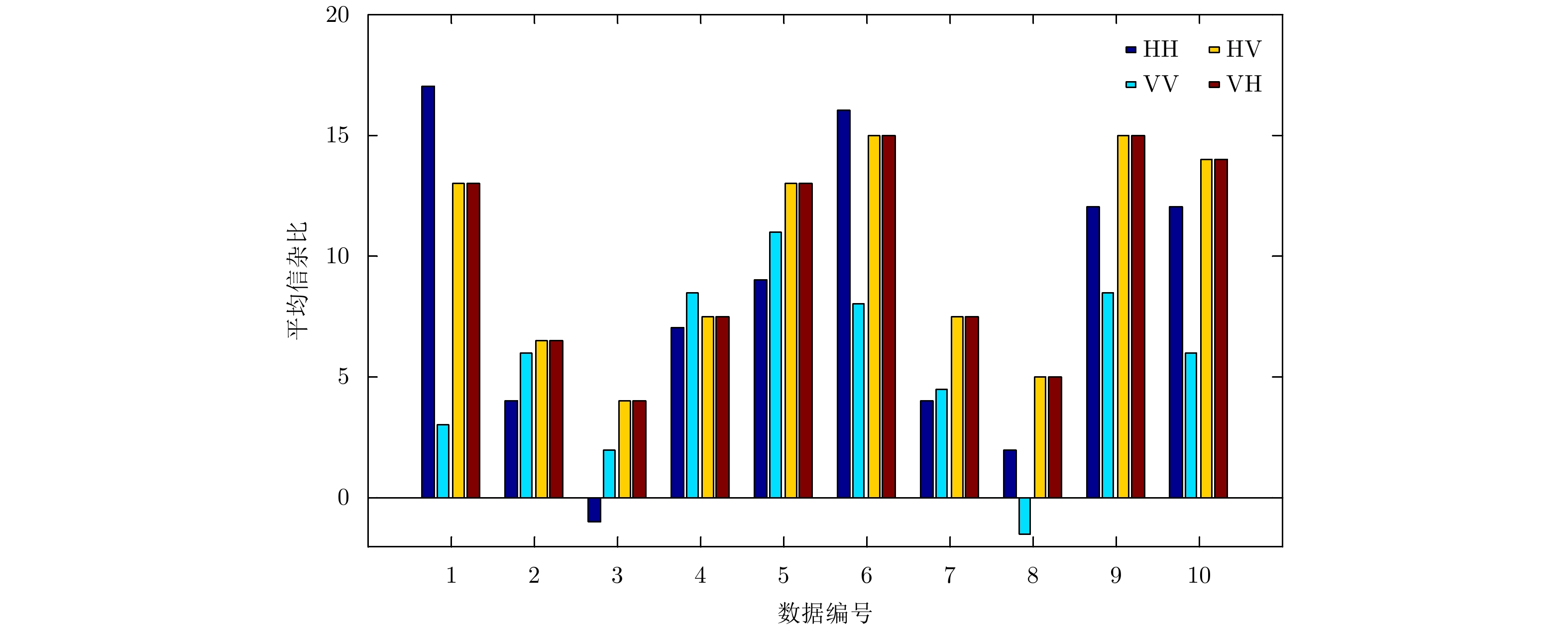
数据编号 目标所在单元 受目标影响单元 风速(km/h) 浪高(m) #17 9 8:11 9 2.2 #26 7 6:8 9 1.1 #30 7 6:8 19 0.9 #31 7 6:9 19 0.9 #40 7 5:8 9 1.0 #54 8 7:10 20 0.7 #280 8 7:10 10 1.6 #310 7 6:9 33 0.9 #311 7 6:9 33 0.9 #320 7 6:9 28 0.9 表 2 全部单元多普勒谱非广延熵值
Table 2. Tsallis entropy of Doppler spectrum of all the cells
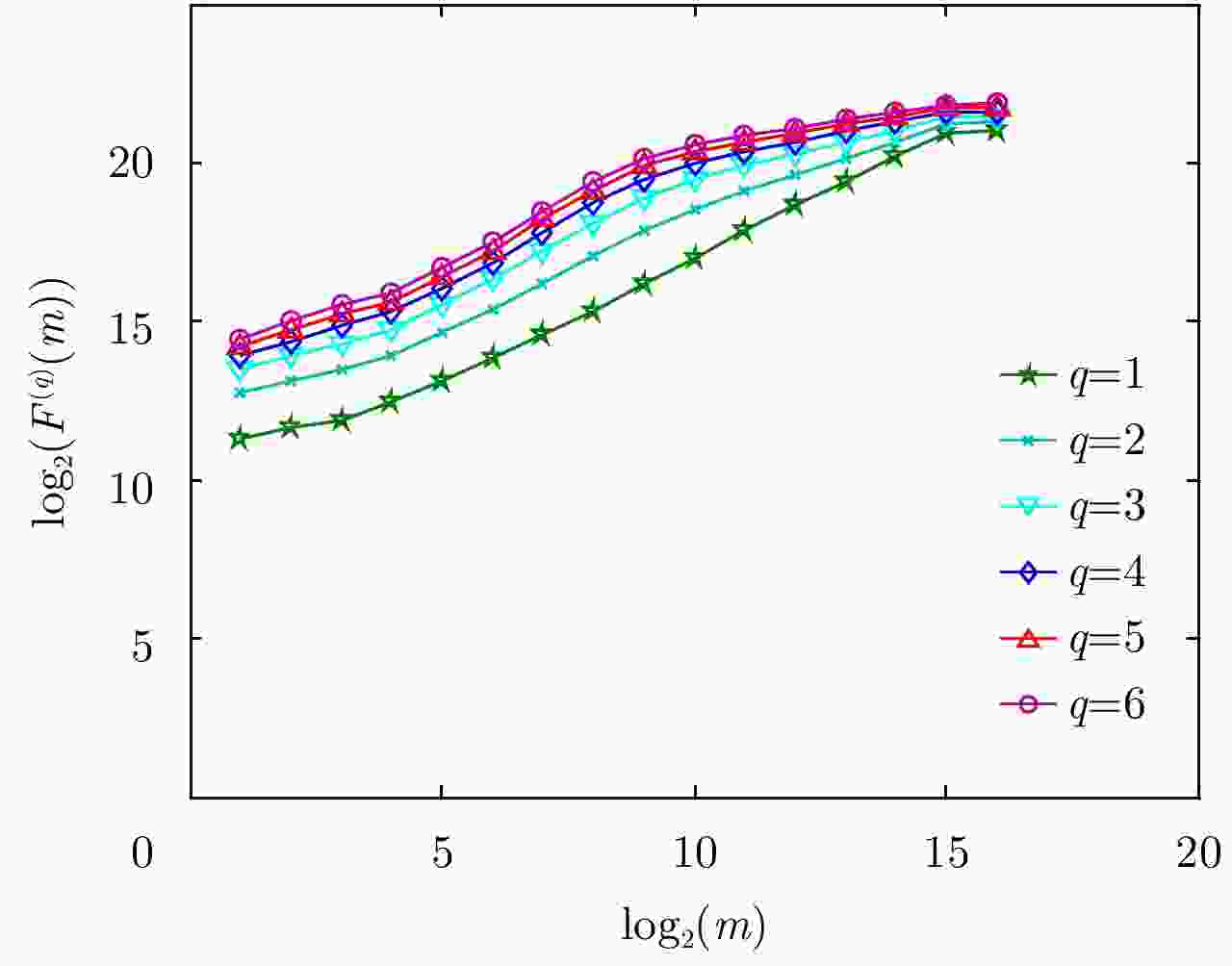
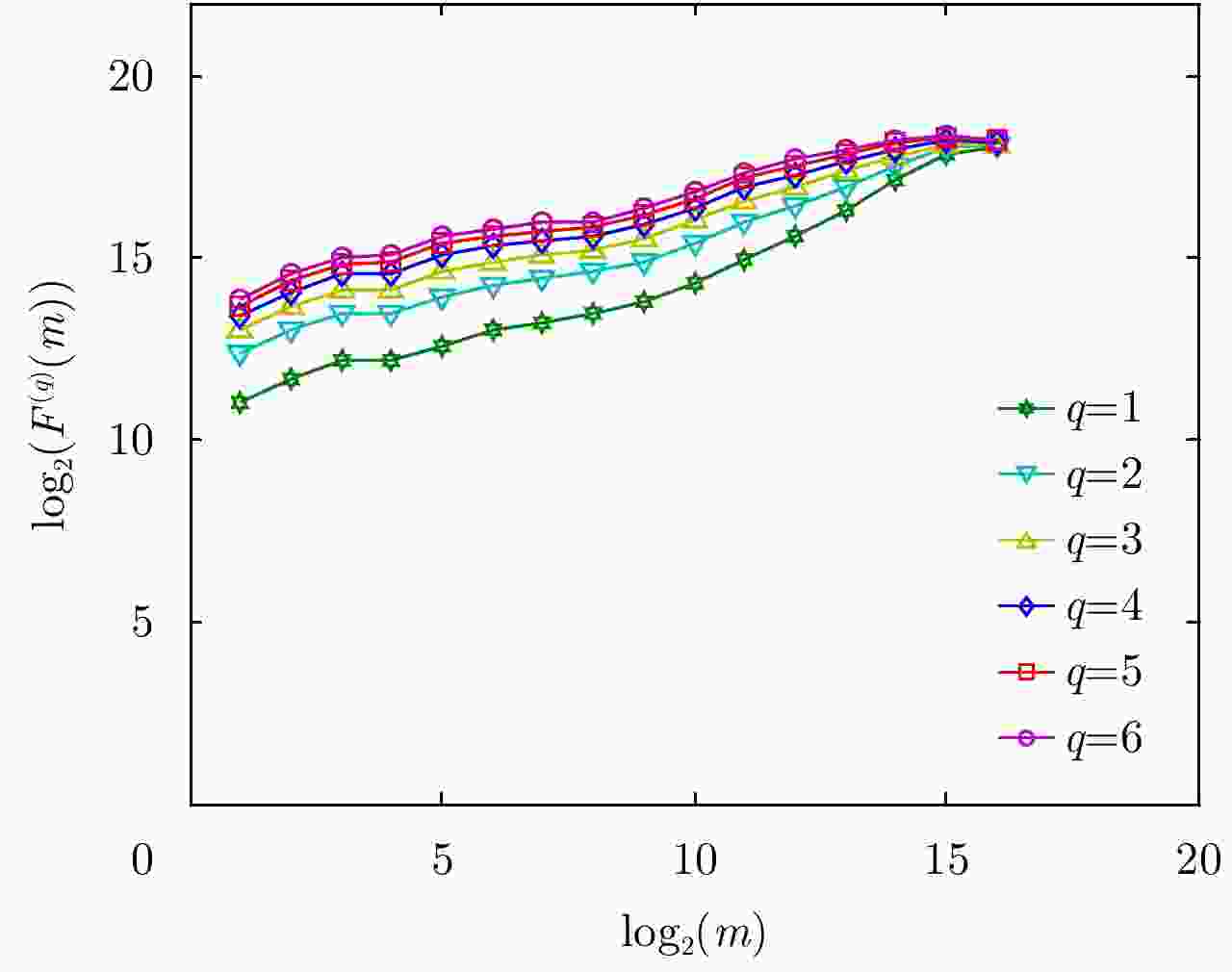
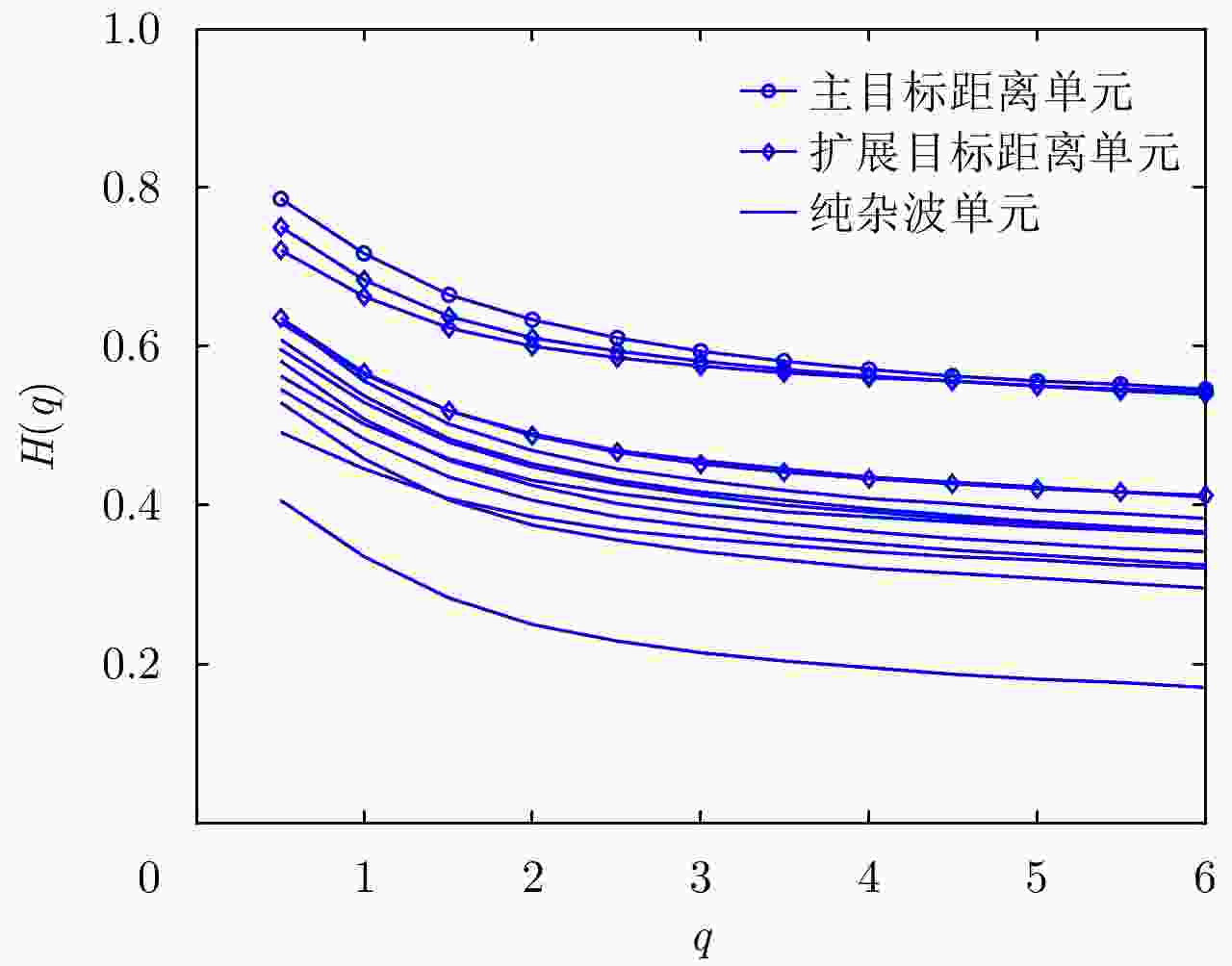
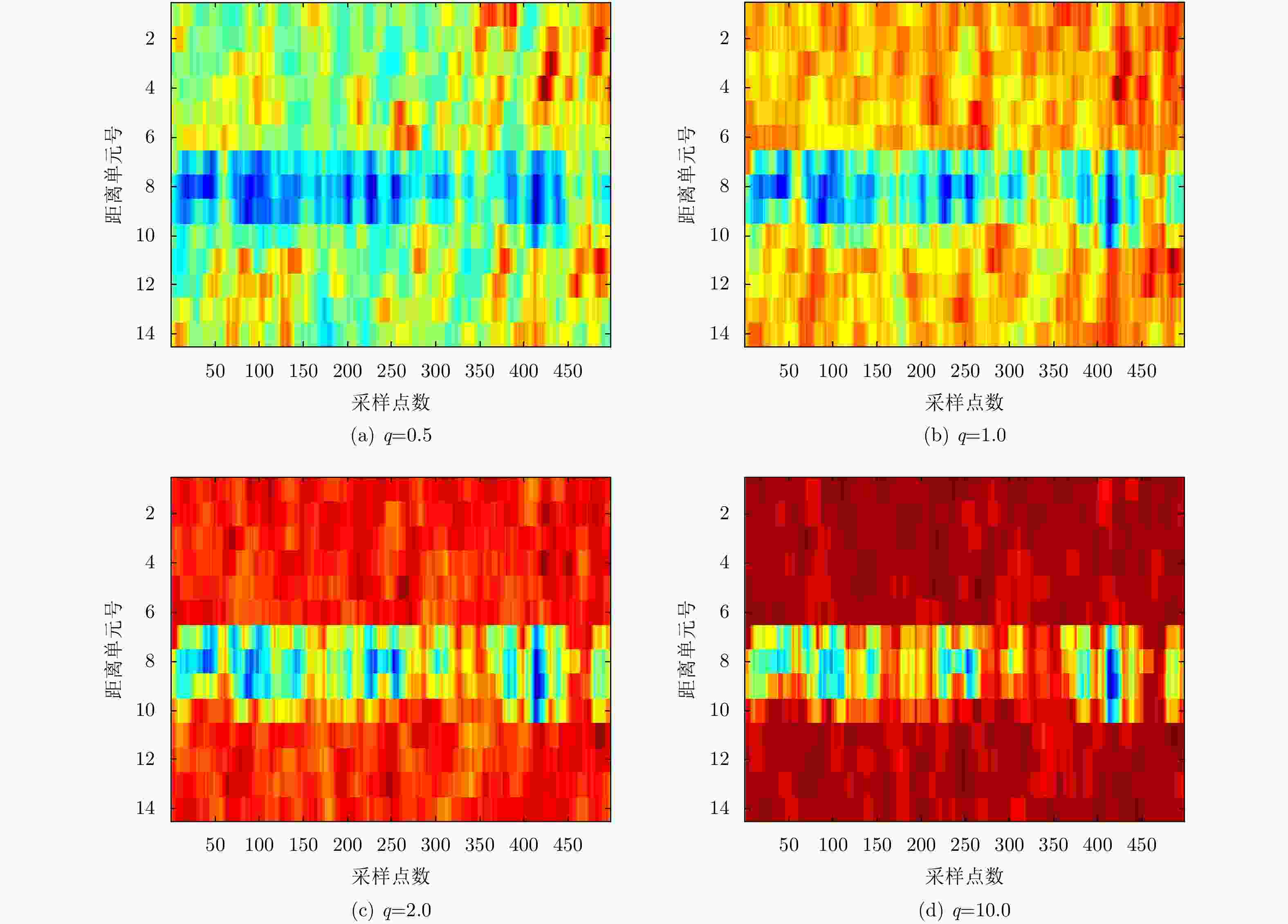
距离单元号 $q = 0.5$ $q = 1.0$ $q = 2.0$ $q = 3.0$ $q = 4.0$ $q = 5.0$ 1 0.7992 0.8919 0.9387 0.9564 0.9674 0.9748 2 0.7966 0.8851 0.9355 0.9553 0.9672 0.9751 3 0.7994 0.8768 0.9311 0.9533 0.9662 0.9744 4 0.8147 0.8757 0.9228 0.9449 0.9591 0.9687 5 0.8216 0.8727 0.9167 0.9392 0.9542 0.9647 6 0.8177 0.8707 0.9180 0.9418 0.9571 0.9674 7 0.6705 0.6834 0.7165 0.7511 0.7805 0.8045 8 0.6025 0.6017 0.6330 0.6725 0.7064 0.7343 9 0.6429 0.6522 0.6827 0.7191 0.7505 0.7760 10 0.7458 0.7839 0.8224 0.8526 0.8760 0.8939 11 0.8080 0.8668 0.9123 0.9368 0.9530 0.9642 12 0.8152 0.8717 0.9153 0.9372 0.9519 0.9623 13 0.8081 0.8635 0.9131 0.9382 0.9541 0.9647 14 0.8043 0.8671 0.9177 0.9419 0.9570 0.9672 表 3 不同FFT点数下最佳q值
Table 3. The best q values of different FFT points
数据编号 64 128 256 512 #280HH 6 3 3 2 #280VV 5 3 2 1 #280HV 4 3 2 2 #310HH 3 2 1 2 #310VV 8 3 3 3 #310HV 3 2 2 1 #311HH 3 2 1 1 #311VV 5 3 2 1 #311HV 3 2 1 1 表 4 不同
$\text{q}$ 值下算法的检测概率(%)Table 4. Detection probability of the proposed algorithm of different
$\text{q}$ values (%)数据编号 $q$取值 ${P_f}$ ${10^{ - 3}}$ ${10^{ - 2}}$ ${10^{ - 1}}$ HH VV HV HH VV HV HH VV HV #280 q = 1 82.09 90.14 96.78 85.92 92.56 98.19 92.76 95.37 100 q = 2 90.54 91.95 97.18 93.56 95.77 98.79 95.98 98.79 100 q = 3 92.15 93.56 96.38 94.16 98.19 98.39 96.58 99.40 100 q = 10 82.49 89.94 89.54 89.74 95.77 92.35 96.58 99.40 98.99 #310 q = 1 94.16 13.26 92.15 96.58 30.38 95.37 98.19 62.17 97.79 q = 2 95.98 24.35 94.16 97.99 50.91 97.38 98.79 75.86 98.39 q = 3 92.56 40.44 92.76 97.59 54.53 97.18 98.59 77.06 99.40 q = 10 68.61 42.45 78.27 92.15 55.33 85.51 98.39 72.03 99.20 #311 q = 1 100 98.59 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 q = 2 100 99.20 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 q = 3 100 98.59 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 q = 10 96.78 80.48 97.59 98.79 80.93 100 100 99.60 100 表 5 3种算法的检测概率(%)
Table 5. Detection probability of the three algorithms (%)
序列长度 方法 ${P_{\rm f}}$ ${10^{ - 3}}$ ${10^{ - 2}}$ ${10^{ - 1}}$ 27 频域Hurst指数法 1.00 16.30 46.20 q = 1(香农熵) 58.97 69.57 79.48 q = 3(非广延熵) 72.94 78.49 88.21 28 频域Hurst指数法 8.50 21.30 35.80 q = 1(香农熵) 82.09 85.92 92.76 q = 3(非广延熵) 92.15 94.16 96.58 29 频域Hurst指数法 15.50 32.80 43.10 q = 1(香农熵) 82.16 84.23 90.04 q = 3(非广延熵) 88.38 95.44 97.51 210 频域Hurst指数法 52.90 63.80 78.90 q = 1(香农熵) 61.95 80.53 93.81 q = 3(非广延熵) 89.38 98.23 100 表 6 观测时间为0.064 s所提方法检测概率(%)
Table 6. Detection probability when observation time is 0.064 s (%)
数据编号 ${10^{ - 3}}$ ${10^{ - 2}}$ ${10^{ - 1}}$ #280HH 35.51 46.83 61.53 #280VV 38.07 47.47 59.42 #280HV 54.60 62.12 74.13 #310HH 45.01 52.23 66.99 #310VV 9.64 15.69 30.99 #310HV 45.15 54.06 67.34 #311HH 82.29 89.52 95.52 #311VV 64.24 74.03 86.08 #311HV 85.98 93.31 97.15 表 7 观测时间为0.128 s所提方法检测概率(%)
Table 7. Detection probability when observation time is 0.128 s(%)
数据编号 ${10^{ - 3}}$ ${10^{ - 2}}$ ${10^{ - 1}}$ #280HH 73.64 78.49 88.31 #280VV 72.15 78.10 85.73 #280HV 88.21 92.37 95.24 #310HH 80.57 88.80 95.24 #310VV 31.62 38.75 58.97 #310HV 83.25 91.97 97.42 表 8 观测时间为0.032 s所提方法检测概率(%)
Table 8. Detection probability when observation time is 0.032 s (%)
数据编号 ${10^{ - 3}}$ ${10^{ - 2}}$ ${10^{ - 1}}$ #311HH 32.08 40.55 53.25 #311VV 15.54 23.45 34.94 #311HV 40.36 48.35 59.76 -
[1] FARINA A and STUDER F A. A review of CFAR detection techniques in radar systems[J]. Microware Journal, 1986, 29(5): 115, 116, 118. [2] 丁昊, 董云龙, 刘宁波, 等. 海杂波特性认知研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069DING Hao, DONG Yunlong, LIU Ningbo, et al. Overview and prospects of research on sea clutter property cognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069 [3] HAYKIN S, CURRIE B W, and KESLER S B. Maximum-entropy spectral analysis of radar clutter[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1982, 70(9): 953–962. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1982.12426 [4] 刘劲, 王雪, 刘宏伟. 基于多普勒谱特征的海杂波背景下小目标检测[J]. 现代雷达, 2008, 30(11): 63–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2008.11.016LIU Jin, WANG Xue, and LIU Hongwei. Small target detection in sea clutter background based on Doppler spectrum characteristics[J]. Modern Radar, 2008, 30(11): 63–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2008.11.016 [5] SHUI Penglang, LI Dongchen, and XU Shuwen. Tri-feature-based detection of floating small targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1416–1430. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120657 [6] DUK V, ROSENBERG L, and NG B W H. Target detection in sea-clutter using stationary wavelet transforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1136–1146. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2667558 [7] HAYKIN S, BAKKER R, and CURRIE B W. Uncovering nonlinear dynamics-the case study of sea clutter[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2002, 90(5): 860–881. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2002.1015011 [8] LO T, LEUNG H, LITVA J, et al. Fractal characterisation of sea-scattered signals and detection of sea-surface targets[J]. IEE Proceedings F - Radar and Signal Processing, 1993, 140(4): 243–250. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1993.0034 [9] 孙康, 金钢, 朱晓华. 基于波动分析的海上小目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(4): 882–887. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00927SUN Kang, JIN Gang, and ZHU Xiaohua. Small target detection within sea clutter based on the fluctuation analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(4): 882–887. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00927 [10] GAN D and SHOUHONG Z. Detection of sea-surface radar targets based on multifractal analysis[J]. Electronics Letters, 2000, 36(13): 1144–1145. doi: 10.1049/el:20000800 [11] 刘宁波, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 基于频域多尺度Hurst指数的海杂波中目标检测方法[J]. 电子学报, 2013, 41(3): 424–431. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.03.002LIU Ningbo, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Target detection within sea clutter based on multi-scale Hurst exponent in frequency domain[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(3): 424–431. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.03.002 [12] 刘宁波, 黄勇, 关键, 等. 实测海杂波频域分形特性分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(4): 929–935. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.11.1146.2011.00856LIU Ningbo, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al. Fractal analysis of real sea clutter in frequency domain[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 929–935. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.11.1146.2011.00856 [13] 刘宁波, 关键, 王国庆, 等. 基于海杂波FRFT谱多尺度Hurst指数的目标检测方法[J]. 电子学报, 2013, 41(9): 1847–1853. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.09.029LIU Ningbo, GUAN Jian, WANG Guoqing, et al. Target detection within sea clutter based on multi-scale Hurst exponent in FRFT domain[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(9): 1847–1853. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.09.029 [14] 陈小龙, 刘宁波, 宋杰, 等. 海杂波FRFT域分形特征判别及动目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(4): 823–830. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00486CHEN Xiaolong, LIU Ningbo, SONG Jie, et al. Fractal feature discriminant of sea clutter in FRFT domain and moving target detection algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2011, 33(4): 823–830. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00486 [15] LUO Feng, ZHANG Danting, and ZHANG Bo. The fractal properties of sea clutter and their applications in maritime target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1295–1299. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2237750 [16] FAN Yifei, LUO Feng, LI Ming, et al. Weak target detection in sea clutter background using local-multifractal spectrum with adaptive window length[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(7): 835–842. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0286 [17] FAN Yifei, LUO Feng, LI Ming, et al. Fractal properties of autoregressive spectrum and its application on weak target detection in sea clutter background[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(8): 1070–1077. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0473 [18] TSALLIS C, PLASTINO A R, and ZHENG W M. Power-law sensitivity to initial conditions—New entropic representation[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 1997, 8(6): 885–891. doi: 10.1016/S0960-0779(96)00167-1 [19] TSALLIS C and BRIGATTI E. Nonextensive statistical mechanics: A brief introduction[J]. Continuum Mechanics and Thermodynamics, 2004, 16(3): 223–235. doi: 10.1007/s00161-004-0174-4 [20] FURUICHI S. On uniqueness theorems for Tsallis entropy and Tsallis relative entropy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2005, 51(10): 3638–3645. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.855606 [21] 曹克非, 王参军. Tsallis熵与非广延统计力学[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 27(6): 514–520. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7971.2005.06.011CAO Kefei and WANG Canjun. Tsallis entropy and nonextensive statistical mechanics[J]. Journal of Yunnan University, 2005, 27(6): 514–520. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7971.2005.06.011 [22] BUNTE C and LAPIDOTH A. Maximum Rényi entropy rate[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2016, 62(3): 1193–1205. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2016.2521364 [23] 范一飞, 罗丰, 李明, 等. 海杂波AR谱多重分形特性及微弱目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(2): 455–463. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150581FAN Yifei, LUO Feng, LI Ming, et al. The multifractal properties of AR spectrum and weak target detection in sea clutter background[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(2): 455–463. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150581 [24] STEIN D W J. Detection of random signals in Gaussian mixture noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1995, 41(6): 1788–1801. doi: 10.1109/18.476307 [25] SHI Sainan and SHUI Penglang. Sea-surface floating small target detection by one-class classifier in time-frequency feature space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(11): 6395–6411. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2838260 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: