-
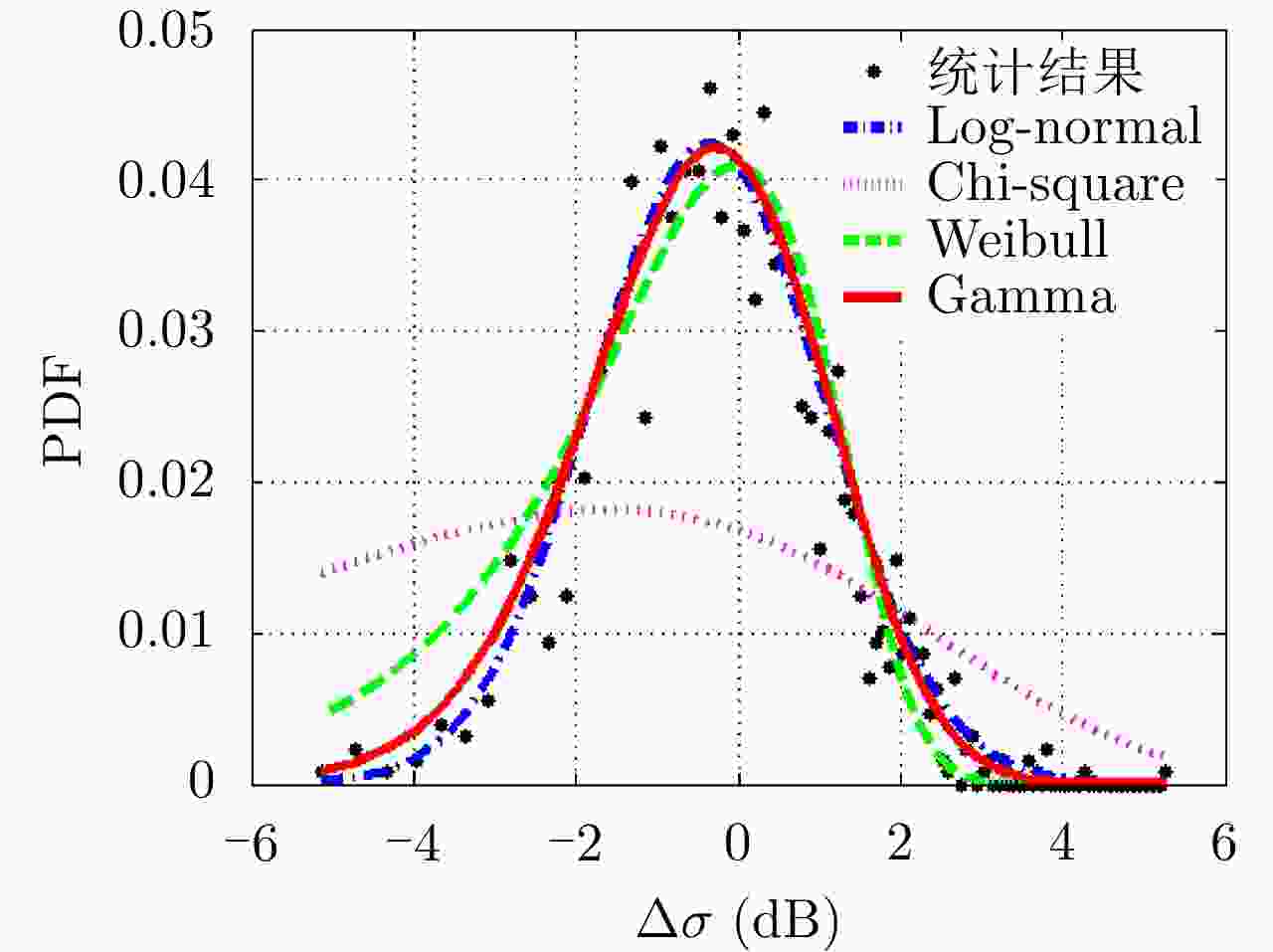
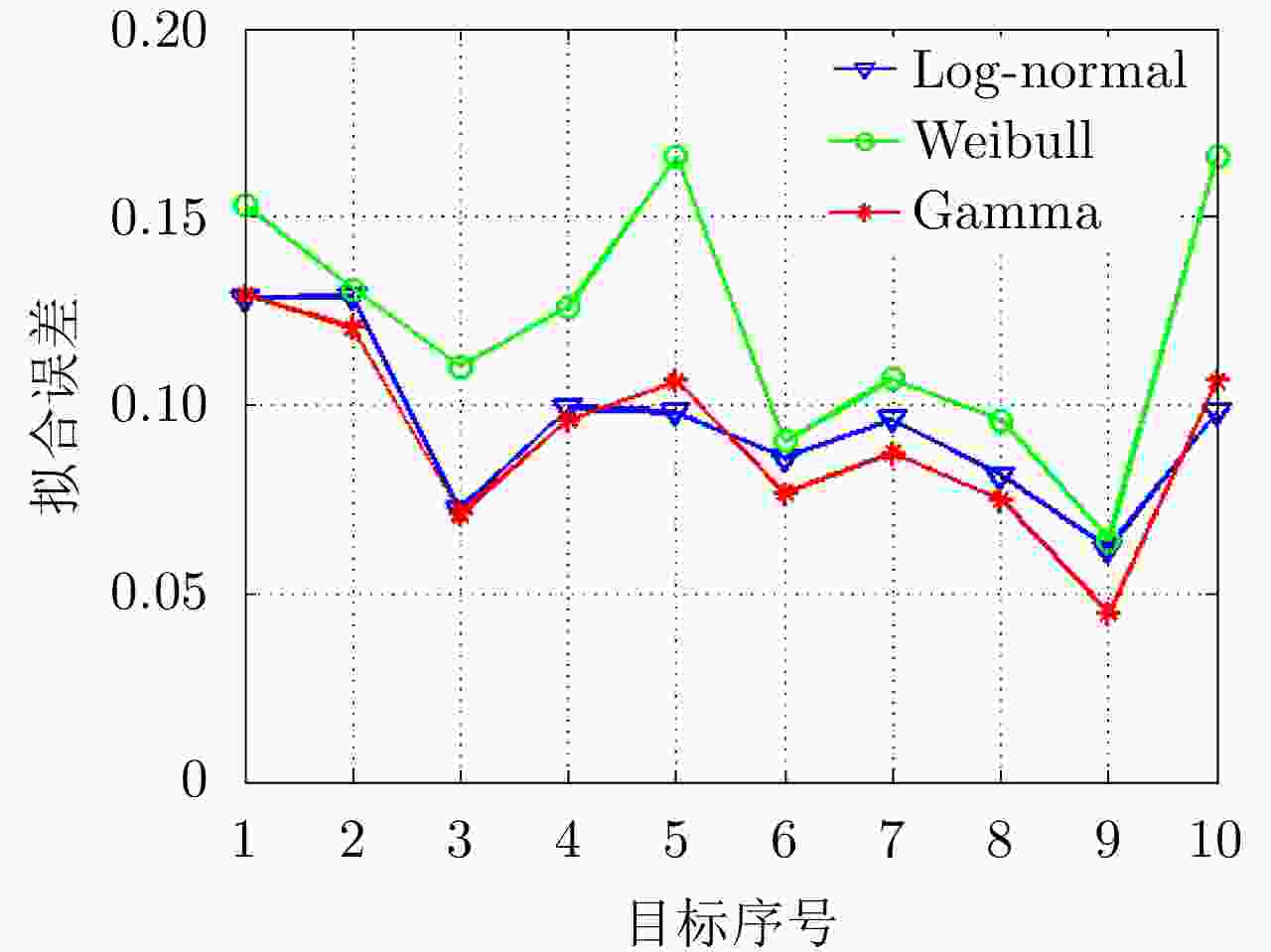
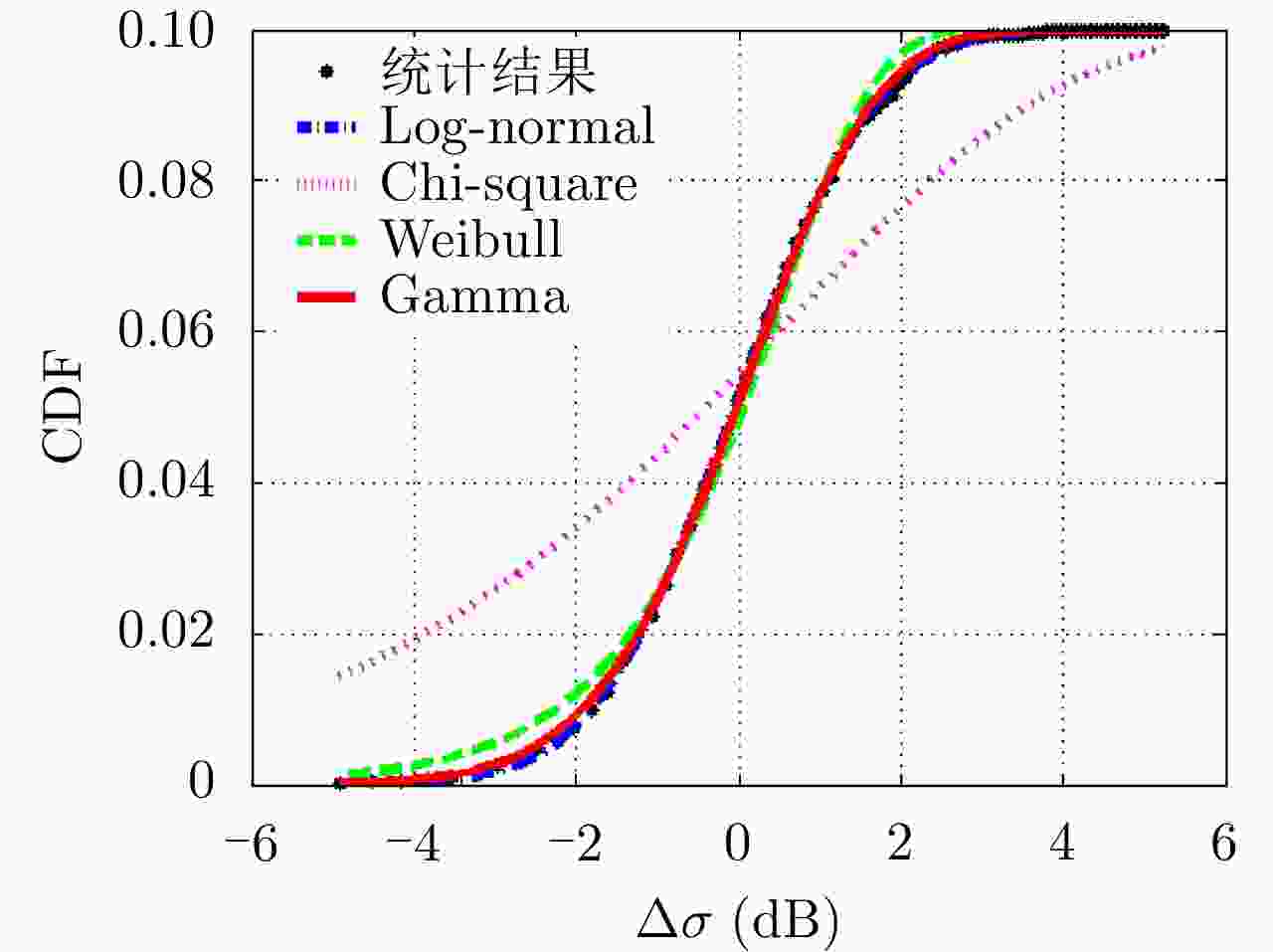
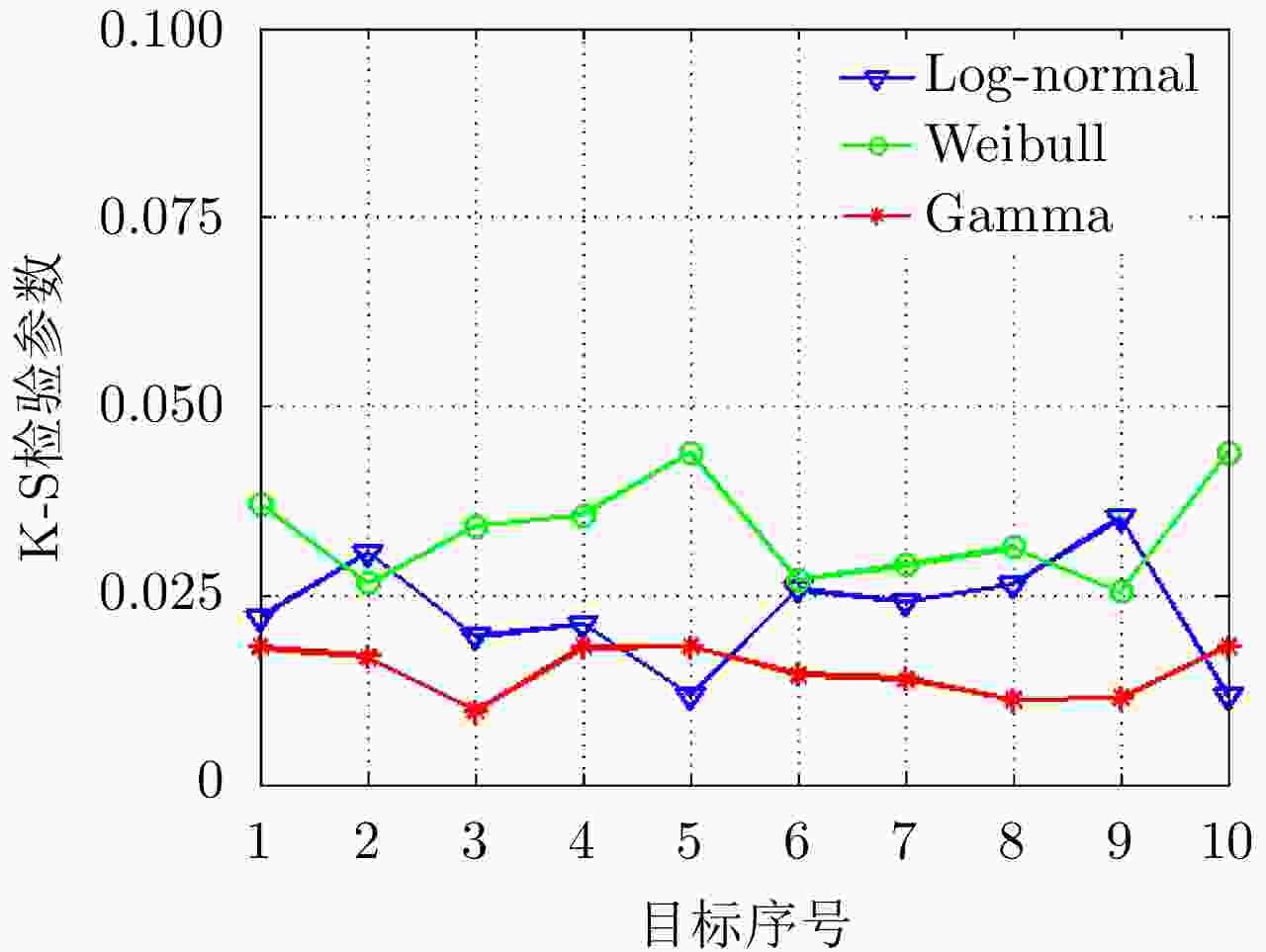
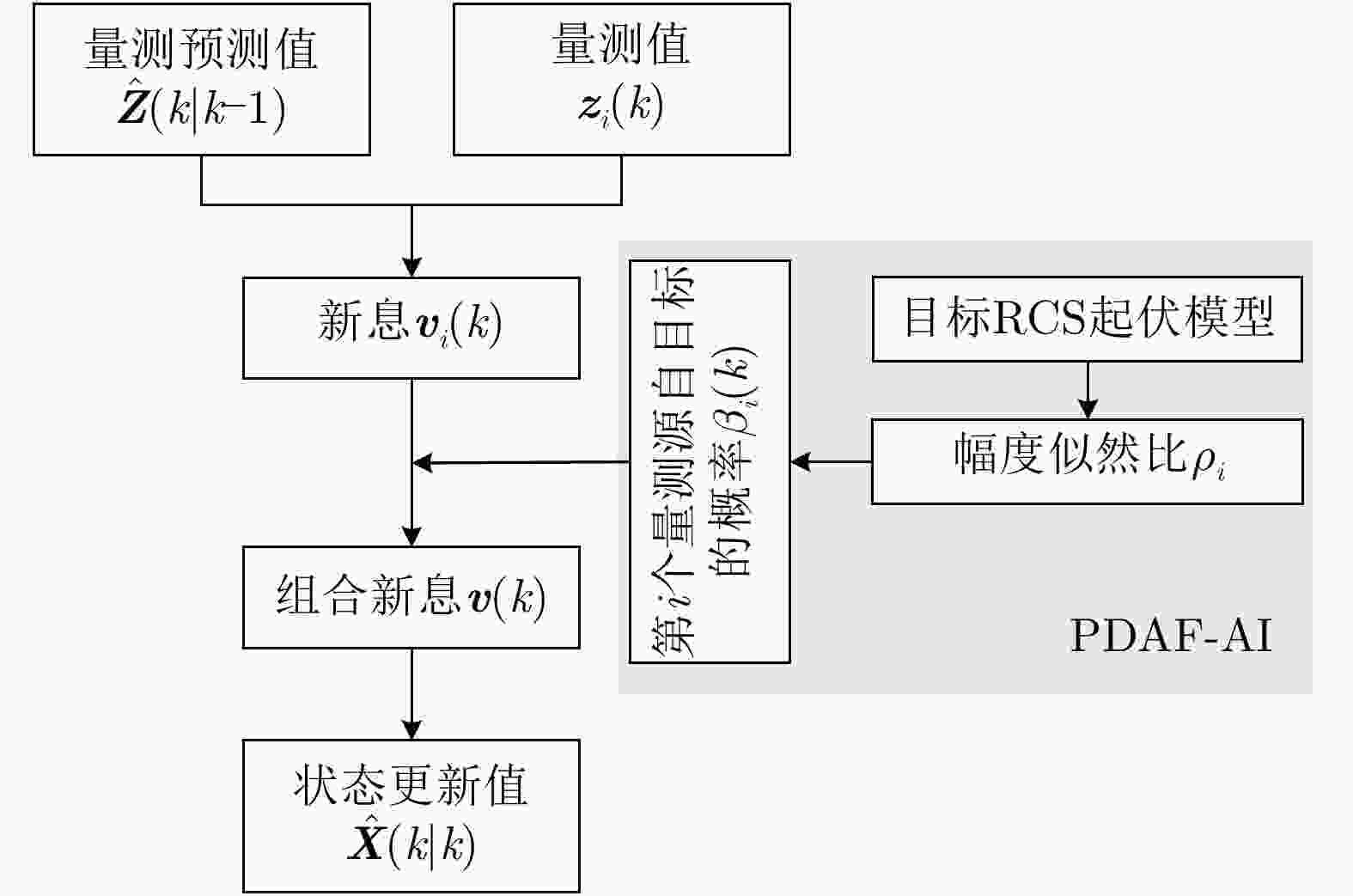
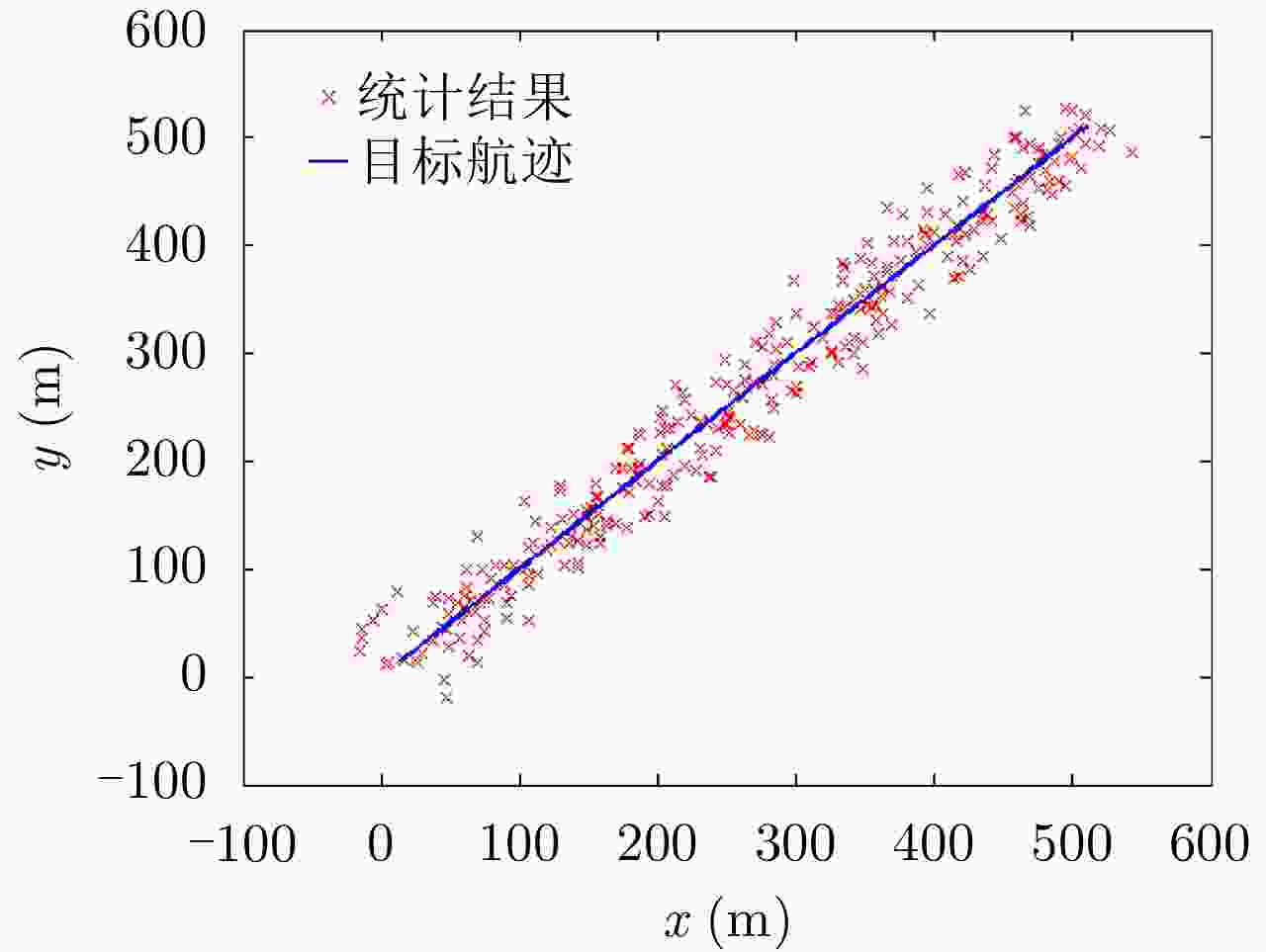
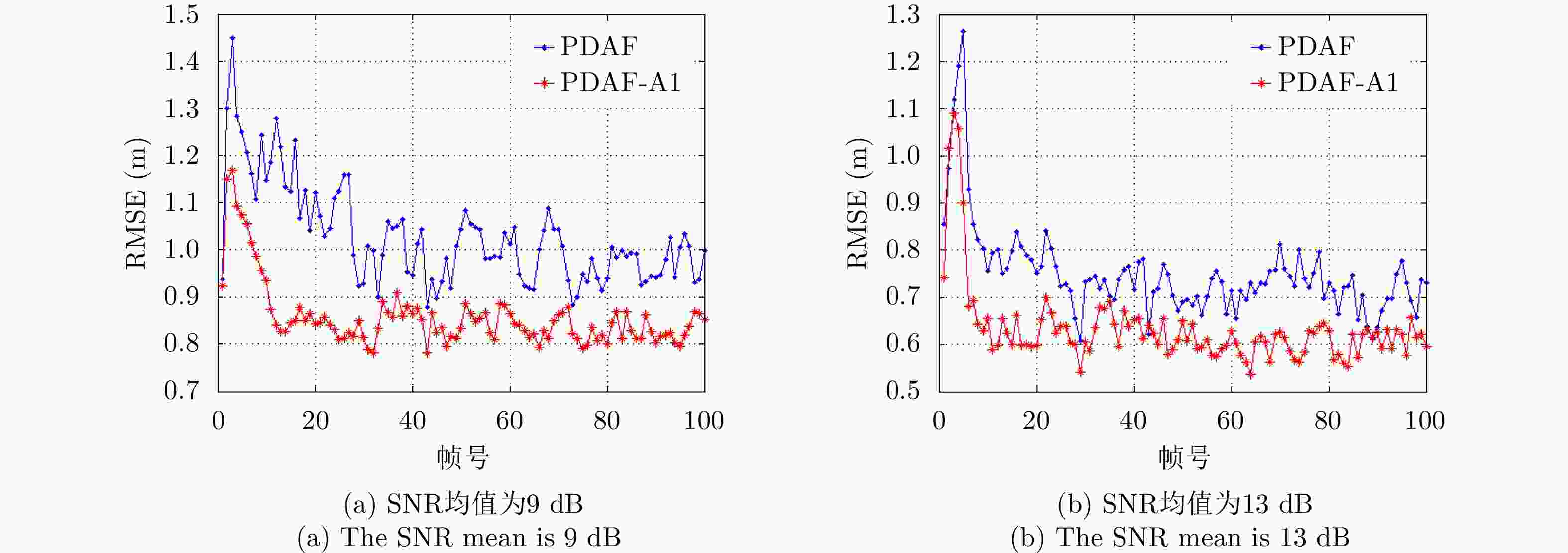
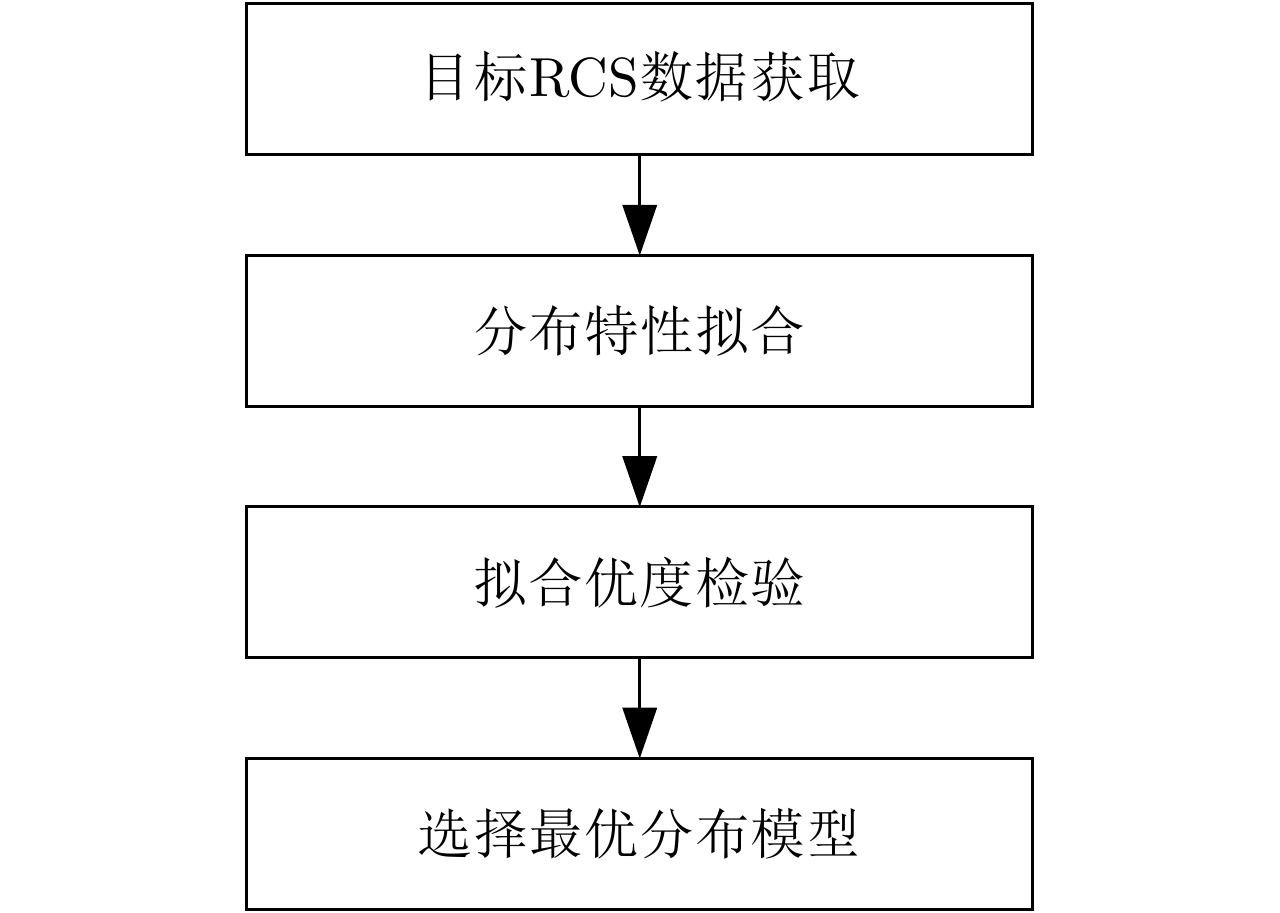
摘要: 害虫迁飞具有规模大、突发性强的特点,会导致病虫害异地大爆发,粮食产量下降,造成重大的经济损失。昆虫雷达是监测迁飞性害虫的一种有效手段。昆虫目标的雷达散射截面积(RCS)较小,回波能量弱,在保证高检测率的同时会带来高虚警率问题,进而导致在目标跟踪的数据关联环节,易受虚假量测的影响出现关联错误。幅度特征辅助跟踪算法利用目标与噪声点迹的幅度差异,可以有效提高目标与噪声的识别度,改善跟踪性能,但是其需要已知目标的RCS起伏模型作为先验信息来计算幅度似然比。因此,该文基于Ku波段高分辨昆虫雷达外场实测昆虫回波数据,分析了昆虫目标的RCS起伏特性,得出Gamma分布可以较好地拟合昆虫目标的RCS统计分布,并将其作为先验信息,推导出Gamma起伏目标在高斯白噪声背景下的幅度似然比。通过在不同信噪比、不同量测噪声及不同起伏模型参数下的仿真结果及性能指标分析,验证了相比于概率数据互联滤波算法(PDAF)算法,目标RCS特征辅助的跟踪算法可以有效提高昆虫目标的跟踪精度。Abstract: Pest migration has the characteristics of large scale and strong suddenness, which will lead to the outbreaks of pests and diseases, the decline of grain yield, and considerable economic losses. Entomological radar is an effective means of monitoring migratory pests. However, the Radar Cross Section (RCS) of an insect target is small, whereas the echo power is weak. High detection probability will result in a high false alarm probability. In the data association step of target tracking, the association error occurs due to the influence of false measurement. By utilizing the amplitude difference between the target and noise, the amplitude information-assisted tracking algorithm can effectively improve the recognition degree toward the target and noise and improve the tracking performance. However, the RCS fluctuation model of the target is needed as prior information to calculate the amplitude likelihood ratio. Therefore, in this paper, the insect RCS fluctuating characteristics are analyzed based on Ku-band entomological radar experiment data. The results show that gamma distribution can fit well the RCS probability distribution of the insect target. On this basis, we derive the amplitude likelihood ratio of the gamma fluctuation target in Gaussian white-noise background. By analyzing the simulation results and performance under different signal-to-noise ratios, measurement noises, and fluctuation model parameters, compared with probabilistic data association filter, the RCS feature-aided tracking algorithm can effectively improve the insect target tracking accuracy.
-
Key words:
- Entomological radar /
- Target tracking /
- Radar Cross Section fluctuating /
- Feature aided
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 目标RCS起伏模型 伽马分布 杂波点幅度模型 瑞利分布 起伏模型参数1 Ω=1.8, v=2.0 起伏模型参数2 Ω=2.0, v=3.2 杂波密度$\lambda $ 0.00004 SNR 9 dB, 13 dB 虚警概率 10–4 扫描间隔T 1 s 跟踪步数 100 波门尺寸 16 过程噪声方差$\sigma _p^2$ 0.01 m2 量测噪声标准差$\sigma _R^{}$ 1 m 蒙特卡洛仿真次数 500 航迹丢失判别$m$ 7帧 第1门限${T_1}$ 1 m 第2门限${T_2}$ 5 m 表 2 不同量测噪声下均方根误差均值改善值
Table 2. The improvement of the root mean square error under different measurement noises
量测噪声标准差(m) SNR(dB) 均方根误差均值改善(m) 1 9 0.14 13 0.11 3 9 0.53 13 0.42 5 9 1.17 13 0.96 表 3 不同起伏参数下有效航迹改善率
Table 3. The improvement probability of effective track underdifferent fluctuation parameters
SNR(dB) 参数1(%) 参数2(%) 9 7.1 8.3 10 6.7 7.4 11 5.9 6.5 12 4.3 5.0 13 2.5 3.1 14 1.9 2.1 15 1.6 1.8 -
[1] CHAPMAN J W, DRAKE V A, and REYNOLDS D R. Recent insights from radar studies of insect flight[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2011, 56: 337–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-120709-144820 [2] LERRO D and BAR-SHALOM Y. Automated tracking with target amplitude information[C] Proceedings of 1990 American Control Conference, San Diego, USA, 1990: 2875–2880. doi: 10.23919/ACC.1990.4791244. [3] LERRO D and BAR-SHALOM Y. Interacting multiple model tracking with target amplitude feature[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1993, 29(2): 494–509. doi: 10.1109/7.210086 [4] BREKKE E, HALLINGSTAD O, and GLATTETRE J. Tracking small targets in heavy-tailed clutter using amplitude information[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2010, 35(2): 314–329. doi: 10.1109/joe.2010.2044670 [5] 陈振兴. 基于知识辅助的弱目标跟踪算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2013.CHEN Zhenxing. Research of knowledge-aided dim target tracking algorithm[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2013. [6] 夏玫. 基于雷达辅助知识的微弱目标跟踪算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2015.XIA Mei. Research on radar auxiliary knowledge aided dim target tracking algorithm[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015. [7] 汪兵. 非独立同分布起伏目标建模与检测算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017.WANG Bing. Research on modeling and the detection algorithm of non-ⅡD fluctuating targets[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017. [8] 黄坦. 雷达目标动态RCS特性对探测的影响研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2014.HUANG Tan. Research on the influence of target dynamic RCS characteristics on radar detection[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2014. [9] HOBBS S E, ALLSOPP K, and WOLF W. Signal analysis for an entomological radar with a vertical nutating beam[R]. College of Aeronautics Report 9919, 2003. [10] DOWDY P C. RCS probability distribution function modeling of a fluctuating target[C]. Proceedings of 1991 IEEE National Radar Conference, Los Angeles, USA, 1991. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1991.114752. [11] 何友, 修建娟, 关欣. 雷达数据处理及应用[M]. 3版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2013: 147–151.HE You, XIU Jianjuan, and GUAN Xin. Radar Data Processing with Applications[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2013: 147–151. [12] 理查兹, 邢孟道, 王彤, 李真芳, 译. 雷达信号处理基础[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2008: 253–254.RICHARDS M A, XING Mengdao, WANG Tong, LI Zhenfang, translation. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2008: 253–254. [13] GRADSHTEYN I S and RYZHIK I M. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products[M]. 7th ed. San Diego: Academic Press, 2007: 1157–1160. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: