-
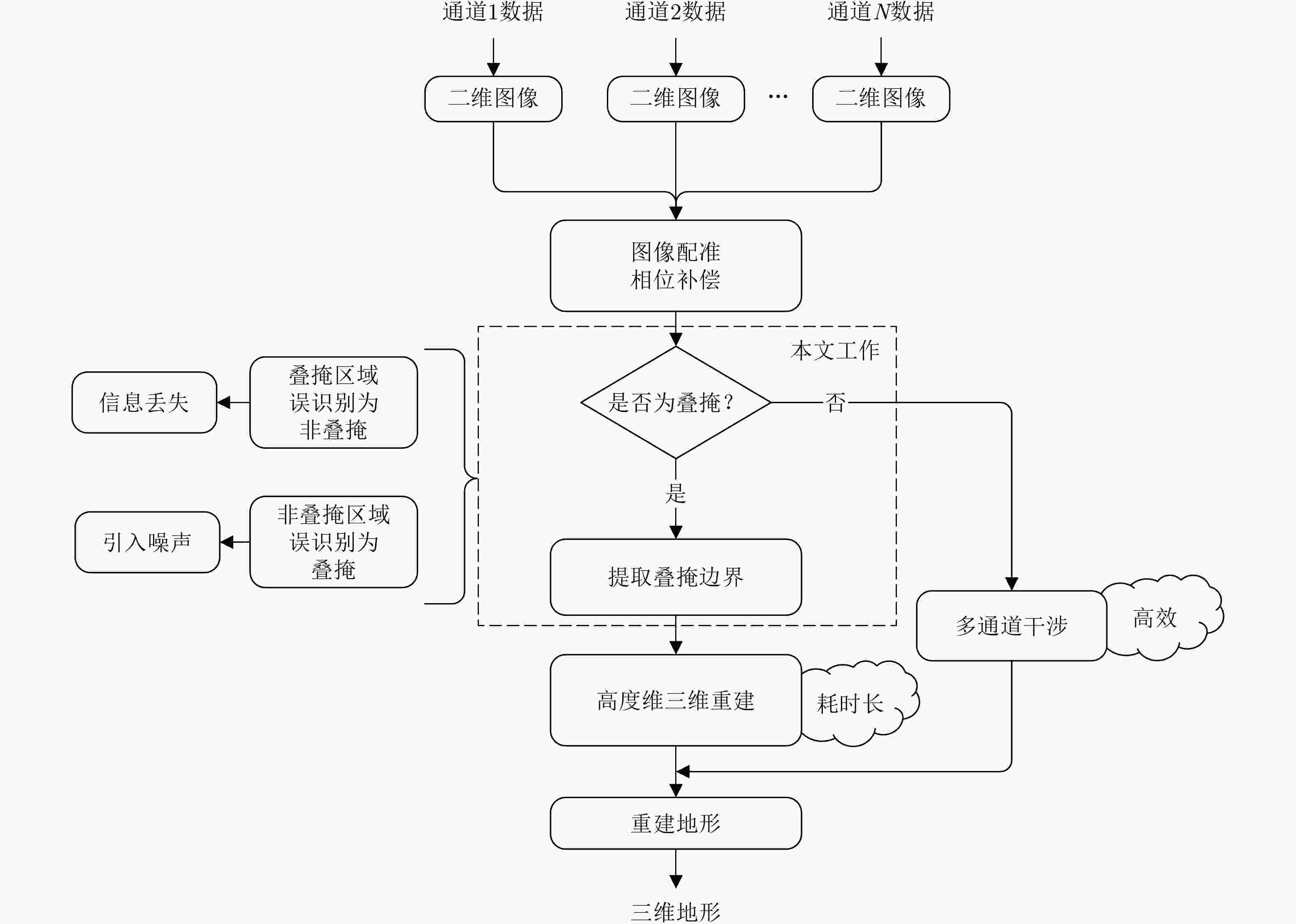
摘要: 建筑物叠掩检测在城市三维合成孔径雷达(3D SAR)成像流程中是至关重要的步骤,其不仅影响成像效率,还直接影响最终成像的质量。目前,用于建筑物叠掩检测的算法往往难以提取远距离全局空间特征,也未能充分挖掘多通道SAR数据中关于叠掩的丰富特征信息,导致现有叠掩检测算法的精确度无法满足城市3D SAR成像的要求。为此,该文结合Vision Transformer (ViT)模型和卷积神经网络(CNN)的优点,提出了一种基于深度学习的SAR城市建筑区域叠掩精确检测方法。ViT模型能够通过自注意力机制有效提取全局特征和远距离特征,同时CNN有着很强的局部特征提取能力。此外,该文所提方法还基于专家知识增加了用于挖掘通道间叠掩特征和干涉相位叠掩特征的模块,提高算法的准确率与鲁棒性,同时也能够有效地减轻模型在小样本数据集上的训练压力。最后在该文构建的机载阵列SAR数据集上测试,实验结果表明,该文所提算法检测准确率达到94%以上,显著高于其他叠掩检测算法。
-
关键词:
- 深度学习 /
- 专家知识 /
- 3D SAR成像 /
- 建筑区域叠掩检测 /
- Vision Transformer模型
Abstract: Building layover detection is a crucial step in the 3D Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging process in urban areas. It affects imaging efficiency and directly influences the final image quality. Currently, algorithms used for layover detection struggle to extract long-range global spatial characteristics and fail to fully exploit the rich features of layover in multi-channel SAR data. To address the issue of insufficient accuracy in existing layover detection algorithms to meet the requirements of urban 3D SAR imaging, this paper proposes a deep learning-powered SAR urban layover detection method that combines the advantages of the Vision Transformer (ViT) model and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The ViT model can efficiently extract global and long-range features through a self-attention mechanism, whereas the CNN has strong local feature extraction capabilities. Furthermore, the proposed method in this paper incorporates a module for investigating inter-channel layover features and interferometric phase layover features based on expert knowledge, which improves the accuracy and robustness of the algorithm while effectively decreasing the training pressure on the model in small-sample datasets. Finally, the proposed algorithm is tested on a self-built airborne array SAR dataset, and experimental findings revealed that the proposed algorithm achieves a detection accuracy of >94%, which is significantly higher than other layover detection algorithms, completely revealing the effectiveness of this method. -
表 1 机载SAR参数
Table 1. The parameters of airborne SAR
参数 数值 飞行高度 5 km 飞行速度 80 m/s 波段 Ku 入射角 40° 分辨率 0.3 m 表 2 本文方法与传统方法对比实验结果
Table 2. Comparison experiment results between the proposed method and traditional methods
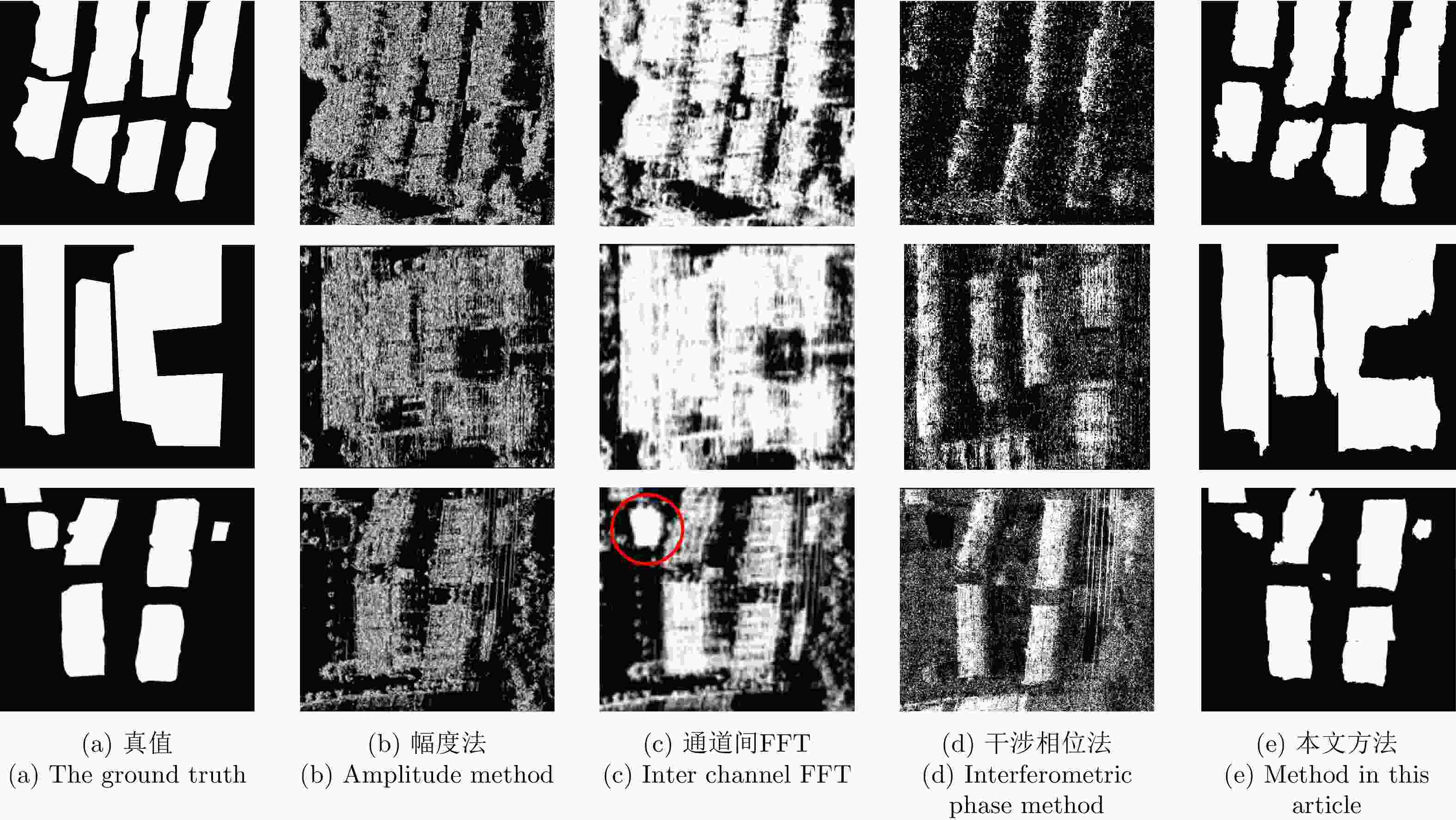
实验方法 准确率 精准度 召回率 虚警率 漏警率 幅度法 0.7285 0.6041 0.5912 0.3959 0.4088 通道间FFT 0.7820 0.6295 0.8231 0.3705 0.1769 干涉相位法 0.6502 0.4506 0.4311 0.5494 0.5689 本文方法 0.9443 0.7619 0.8699 0.2380 0.1300 表 3 本文方法与其他深度学习算法对比实验结果
Table 3. Comparison experiment results between the proposed method and other deep learning methods
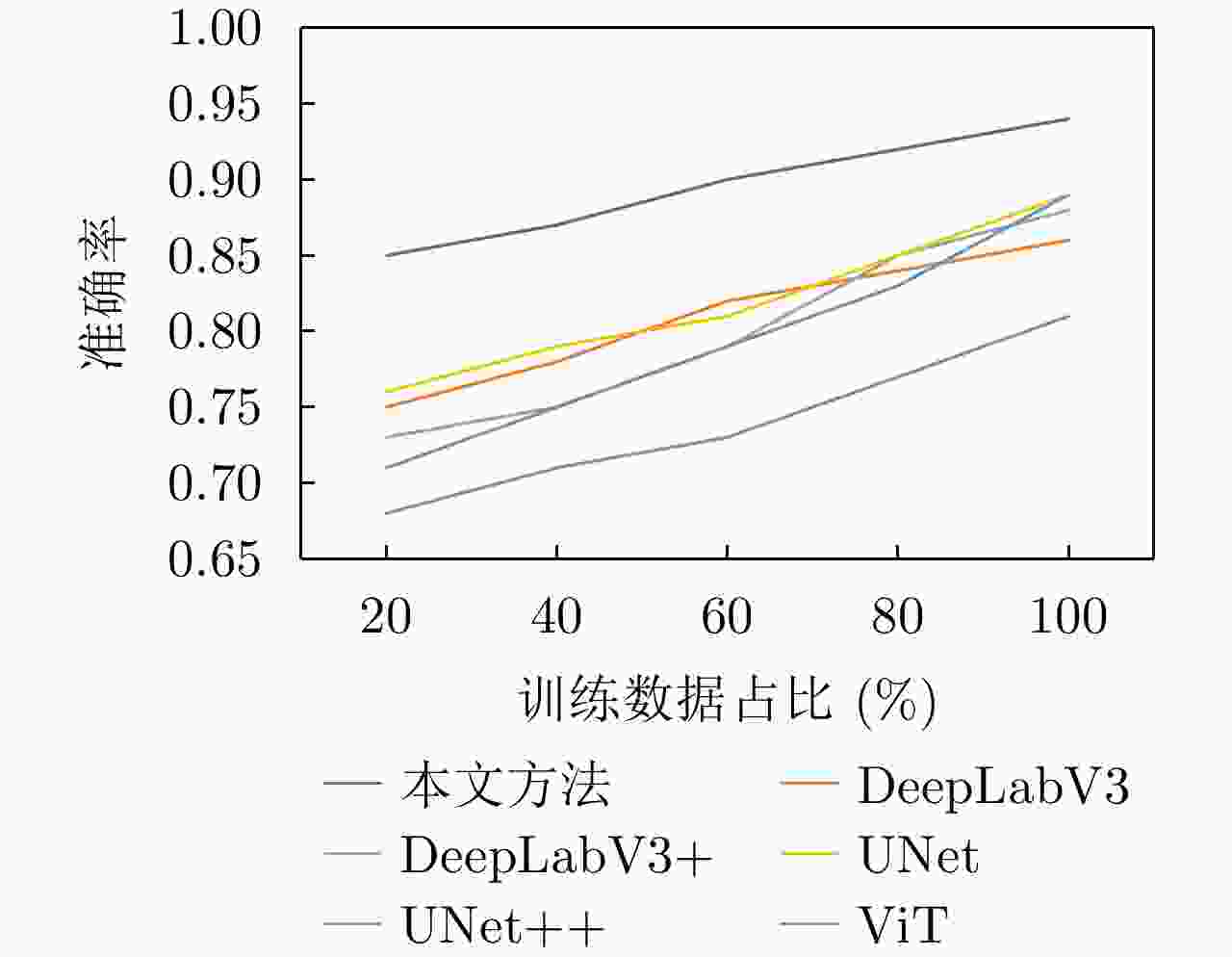
实验方法 准确率 精准度 召回率 虚警率 漏警率 参数量(M) UNet 0.8976 0.7463 0.8391 0.2537 0.1609 7.8 UNet++ 0.8963 0.7481 0.8382 0.2519 0.1618 9.8 DeepLabV3 0.8614 0.7112 0.7933 0.2688 0.1767 15.3 DeepLabV3+ 0.8831 0.7434 0.8291 0.2566 0.1709 15.6 ViT 0.8091 0.6331 0.6783 0.3668 0.3216 8.6 本文方法 0.9443 0.7619 0.8699 0.2380 0.1300 10.0 表 4 消融实验结果
Table 4. Results of ablation experiments
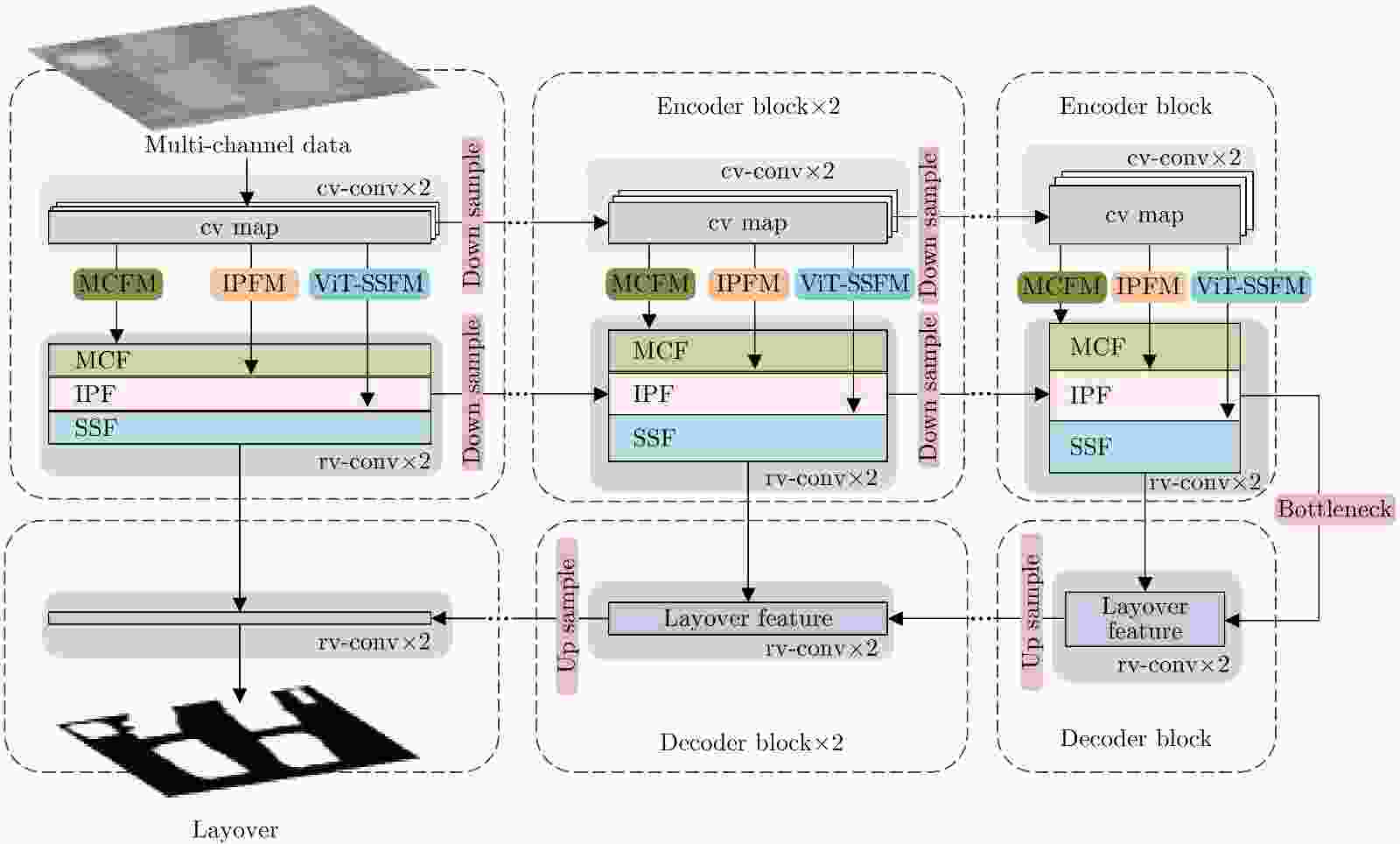
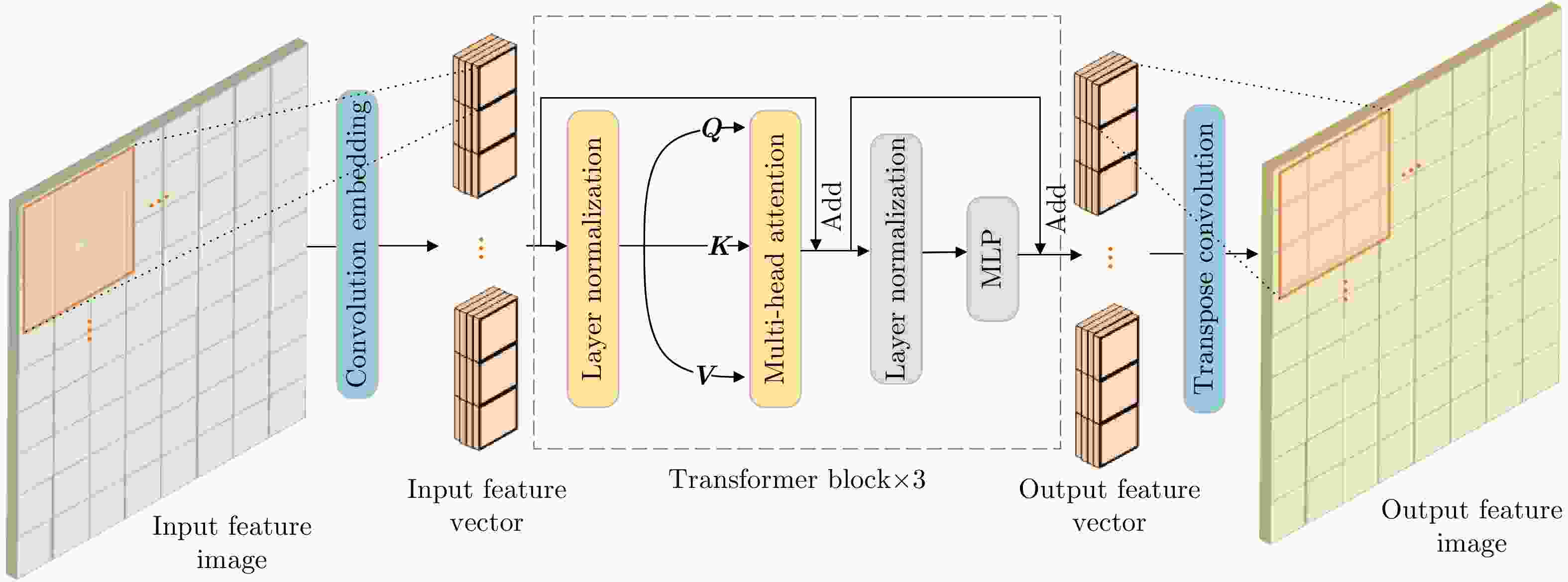
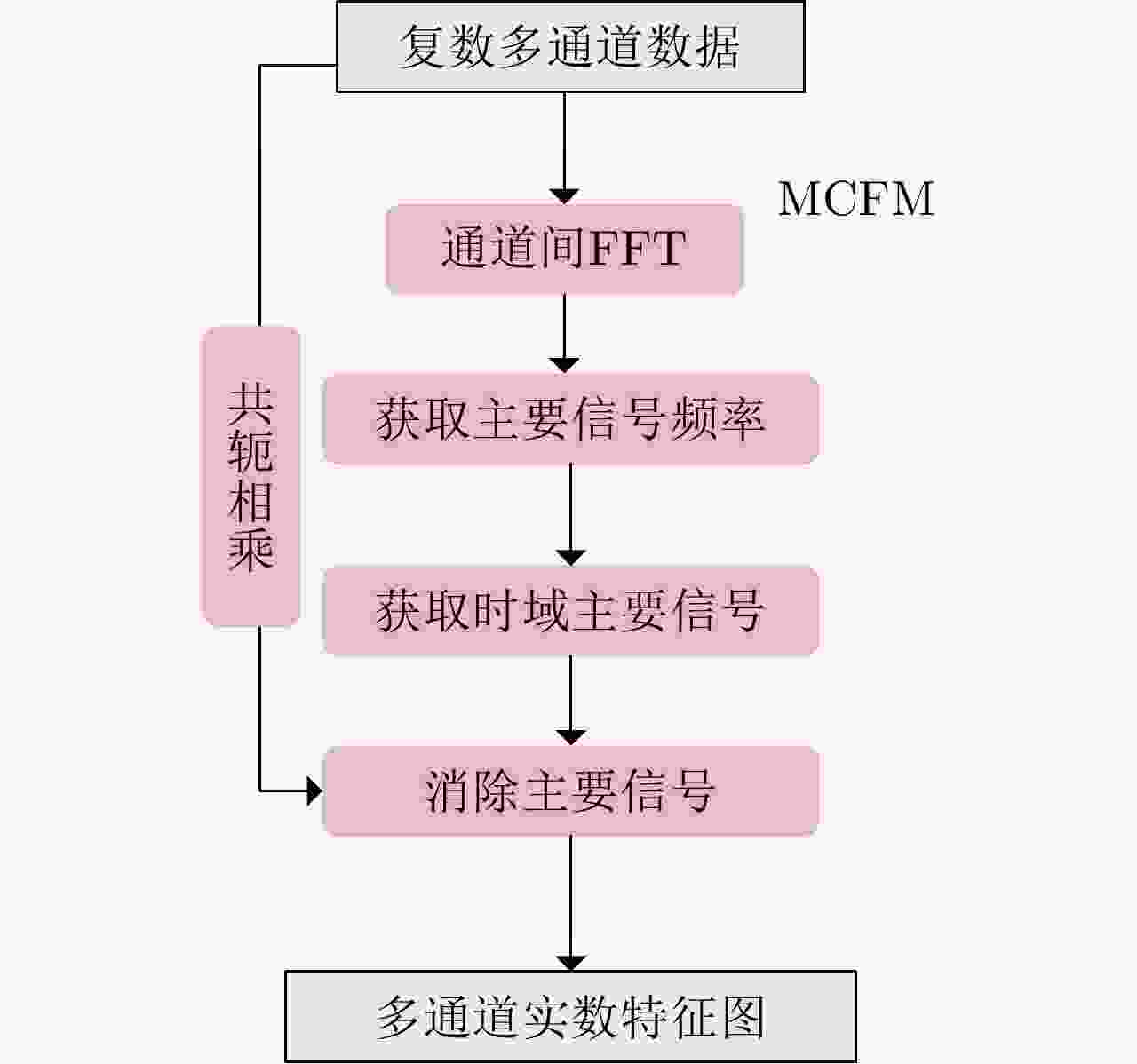
ViT-SSFM MCFM IPFM 准确率 精准度 召回率 × × × 0.8891 0.7263 0.8173 √ × × 0.9346 0.7512 0.8294 × √ √ 0.9162 0.7387 0.8516 √ √ √ 0.9443 0.7619 0.8699 -
[1] FU Kun, ZHANG Yue, SUN Xian, et al. A coarse-to-fine method for building reconstruction from HR SAR layover map using restricted parametric geometrical models[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 2004–2008. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2621054 [2] CHENG Kou, YANG Jie, SHI Lei, et al. The detection and information compensation of SAR layover based on R-D model[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2009, Guilin, China, 2009: 1–3. [3] 彭学明, 王彦平, 谭维贤, 等. 基于跨航向稀疏阵列的机载下视MIMO 3D-SAR三维成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(4): 943–949. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00720PENG Xueming, WANG Yanping, TAN Weixian, et al. Airborne downward-looking MIMO 3D-SAR imaging algorithm based on cross-track thinned array[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 943–949. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00720 [4] 郭睿, 臧博, 彭树铭, 等. 高分辨InSAR中的城市高层建筑特征提取[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2019, 46(4): 137–143. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2019.04.019GUO Rui, ZANG Bo, PENG Shuming, et al. Extraction of features of the urban high-rise building from high resolution InSAR data[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2019, 46(4): 137–143. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2019.04.019 [5] 田方, 扶彦, 刘辉, 等. 多输入多输出下视阵列SAR姿态角误差分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2020, 45(9): 65–71, 110. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2020.09.011TIAN Fang, FU Yan, LIU Hui, et al. Attitude angle error analysis of MIMO downward-looking array SAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2020, 45(9): 65–71, 110. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2020.09.011 [6] 冯荻. 高分辨率SAR建筑目标三维重建技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2016: 75–99.FENG Di. Research on three-dimensional reconstruction of buildings from high-resolution SAR data[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2016: 75–99. [7] 韩晓玲, 毛永飞, 王静, 等. 基于多基线InSAR的叠掩区域高程重建方法[J]. 电子测量技术, 2012, 35(4): 66–70, 85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2012.04.019HAN Xiaoling, MAO Yongfei, WANG Jing, et al. DEM reconstruction method in layover areas based on multi-baseline InSAR[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2012, 35(4): 66–70, 85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2012.04.019 [8] SOERGEL U, THOENNESSEN U, BRENNER A, et al. High-resolution SAR data: New opportunities and challenges for the analysis of urban areas[J]. IEE Proceedings – Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(3): 294–300. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045088 [9] PRATI C, ROCCA F, GUARNIERI A M, et al. Report on ERS-1 SAR interferometric techniques and applications[J]. ESA Study Contract Report, 1994: 3–7439. [10] WILKINSON A J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry: A model for the joint statistics in layover areas[C]. The 1998 South African Symposium on Communications and Signal Processing-COMSIG’98 (Cat. No. 98EX214), Rondebosch, South Africa, 1998: 333–338. [11] CHEN Wei, XU Huaping, and LI Shuang. A novel layover and shadow detection method for InSAR[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), Beijing, China, 2013: 441–445. [12] WU H T, YANG J F, and CHEN F K. Source number estimator using Gerschgorin disks[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Adelaide, Australia, 1994: IV/261–IV/264. [13] WU Yunfei, ZHANG Rong, and ZHAN Yibing. Attention-based convolutional neural network for the detection of built-up areas in high-resolution SAR images[C]. IGARSS 2018–2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 4495–4498. [14] WU Yunfei, ZHANG Rong, and LI Yue. The detection of built-up areas in high-resolution SAR images based on deep neural networks[C]. The 9th International Conference on Image and Graphics, Shanghai, China, 2017: 646–655. [15] CHEN Jiankun, QIU Xiaolan, DING Chibiao, et al. CVCMFF Net: Complex-valued convolutional and multifeature fusion network for building semantic segmentation of InSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5205714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3068124 [16] 崔紫维. 基于Transformer框架的地基SAR边坡监测相位分类方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北方工业大学, 2022: 1–63.CUI Ziwei. Phase classification method of ground-based SAR slope monitoring based on transformer framework[D]. [Master dissertation], North China University of Technology, 2022: 1–63. [17] 李文娜, 张顺生, 王文钦. 基于Transformer网络的机载雷达多目标跟踪方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 469–478. doi: 10.12000/JR22009LI Wenna, ZHANG Shunsheng, and WANG Wenqin. Multitarget-tracking method for airborne radar based on a transformer network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 469–478. doi: 10.12000/JR22009 [18] AZAD R, AL-ANTARY M T, HEIDARI M, et al. TransNorm: Transformer provides a strong spatial normalization mechanism for a deep segmentation model[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 108205–108215. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3211501 [19] DONG Hongwei, ZHANG Lamei, and ZOU Bin. Exploring vision transformers for polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5219715. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3137383 [20] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 2021: 1–20. [21] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A, et al. Spatial transformer networks[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 2017–2025. [22] 张潋钟. SAR图像舰船目标快速检测识别技术[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022.ZHANG Lianzhong. Fast detection and recognition of ship targets in SAR images[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022. [23] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [24] LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002. [25] HOCHREITER S, BENGIO Y, FRASCONI P, et al. Gradient Flow in Recurrent Nets: The Difficulty of Learning Long-term Dependencies[M]. KOLEN J F, KREMER S C. A Field Guide to Dynamical Recurrent Neural Networks. New York: Wiley-IEEE Press, 2001: 401–403. [26] 王万良, 王铁军, 陈嘉诚, 等. 融合多尺度和多头注意力的医疗图像分割方法[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2022, 56(9): 1796–1805. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2022.09.013WANG Wanliang, WANG Tiejun, CHEN Jiacheng, et al. Medical image segmentation method combining multi-scale and multi-head attention[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Engineering Science, 2022, 56(9): 1796–1805. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2022.09.013 [27] BASELICE F, FERRAIOLI G, and PASCAZIO V. DEM reconstruction in layover areas from SAR and auxiliary input data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 253–257. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2011287 [28] WANG Bin, WANG Yanping, HONG Wen, et al. Application of spatial spectrum estimation technique in multibaseline SAR for layover solution[C]. 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008: III-1139–III-1142. [29] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline l-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873 [30] FORNARO G, SERAFINO F, and SOLDOVIERI F. Three-dimensional focusing with multipass SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(3): 507–517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.809934 [31] GUILLASO S and REIGBER A. Scatterer characterisation using polarimetric SAR tomography[C]. 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Korea (South), 2005: 2685–2688. [32] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318–327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: