-
摘要: 目标检测与识别是高分辨合成孔径雷达(SAR)领域的热点问题。机场上飞机作为一种典型目标,其检测和识别有一定的独特性。该文回顾了SAR图像典型目标检测识别领域技术的发展过程,分析了SAR图像中飞机目标的散射机制及面临的技术难点,阐述了 SAR 飞机目标检测识别的系统流程、技术路线和关键科学问题,对基于传统与基于深度学习两个方面的飞机目标检测识别的研究进展进行了归纳总结,并讨论了各类方法的特点及存在的问题,展望了未来的发展趋势。该文认为如何将深度学习与目标电磁散射机理结合、提高网络或模型的泛化能力是提升SAR图像中目标检测识别精度的关键,并给出了一种基于散射信息与深度学习融合的飞机目标检测方法。Abstract: Target detection and recognition are popular issues in the field of high-resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR). As a typical target, aircraft detection and identification has certain uniqueness. This paper reviews the development of detection and recognition techniques for a typical target in SAR imagery, analyzes the scattering mechanism and technical difficulties of aircraft in SAR imagery, describes the system flow, technical routes, and key scientific problems of target aircraft detection and recognition in SAR imagery, summarizes the research progress from traditional methods to deep-learning-based methods for aircraft detection and recognition, discusses the characteristics and existing problems of various methods, and predicts the future development trend. This paper proposes that combining target electromagnetic scattering mechanism with deep convolutional neural network to improve the generalization capability of the model is the key to improve SAR detection and recognition performance. Moreover, this paper establishes an aircraft detection method based on the fusion of scattering information and deep convolutional neural network.
-
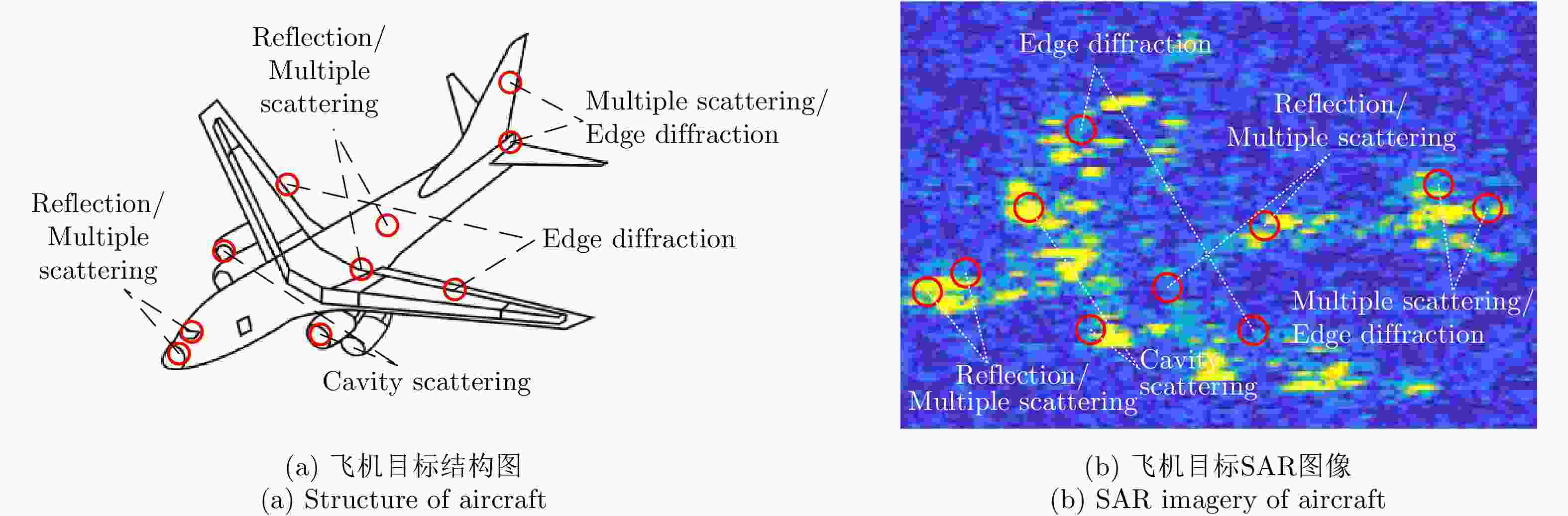
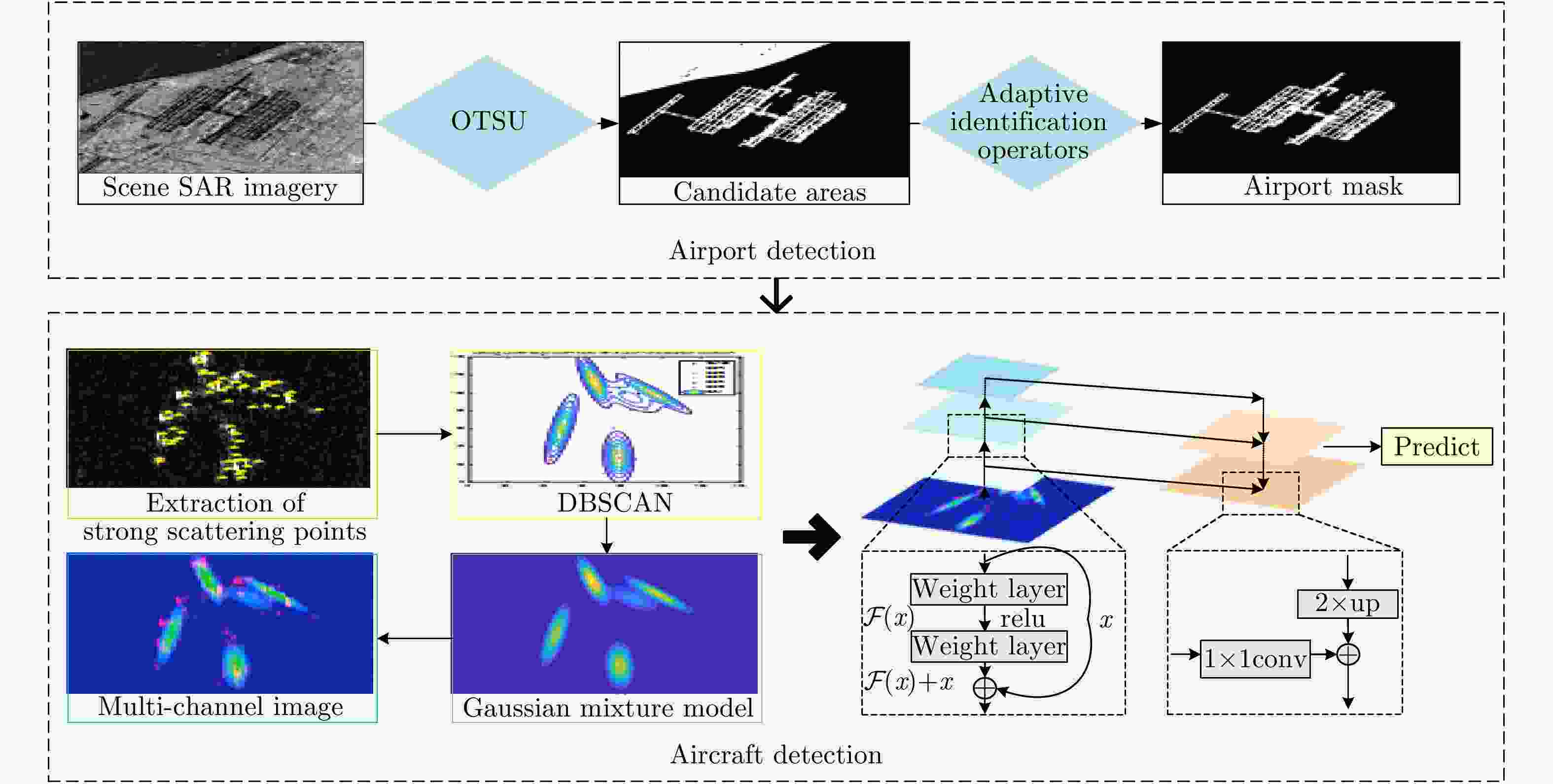
表 1 飞机各部件散射机理
Table 1. Scattering mechanism of each component
部件 散射机理 具体描述 机头 反射/多次散射 机头是由一系列结构组成的,驾驶舱与地面成二面角结构 机身 反射/多次散射 机身包含多种纵向和横向元件:大梁、桁条、隔框和蒙皮等;发动机与机翼成二面角结构 尾翼 多次散射/边缘绕射 尾翼分垂直尾翼和水平尾翼两部分,形成二面体或三面体结构 机翼 边缘绕射 机翼包括副翼、襟翼和缝翼等结构,包含丰富的边缘信息 动力装置 腔体散射 发动机有典型的空腔结构 表 2 机场检测算法效果论证
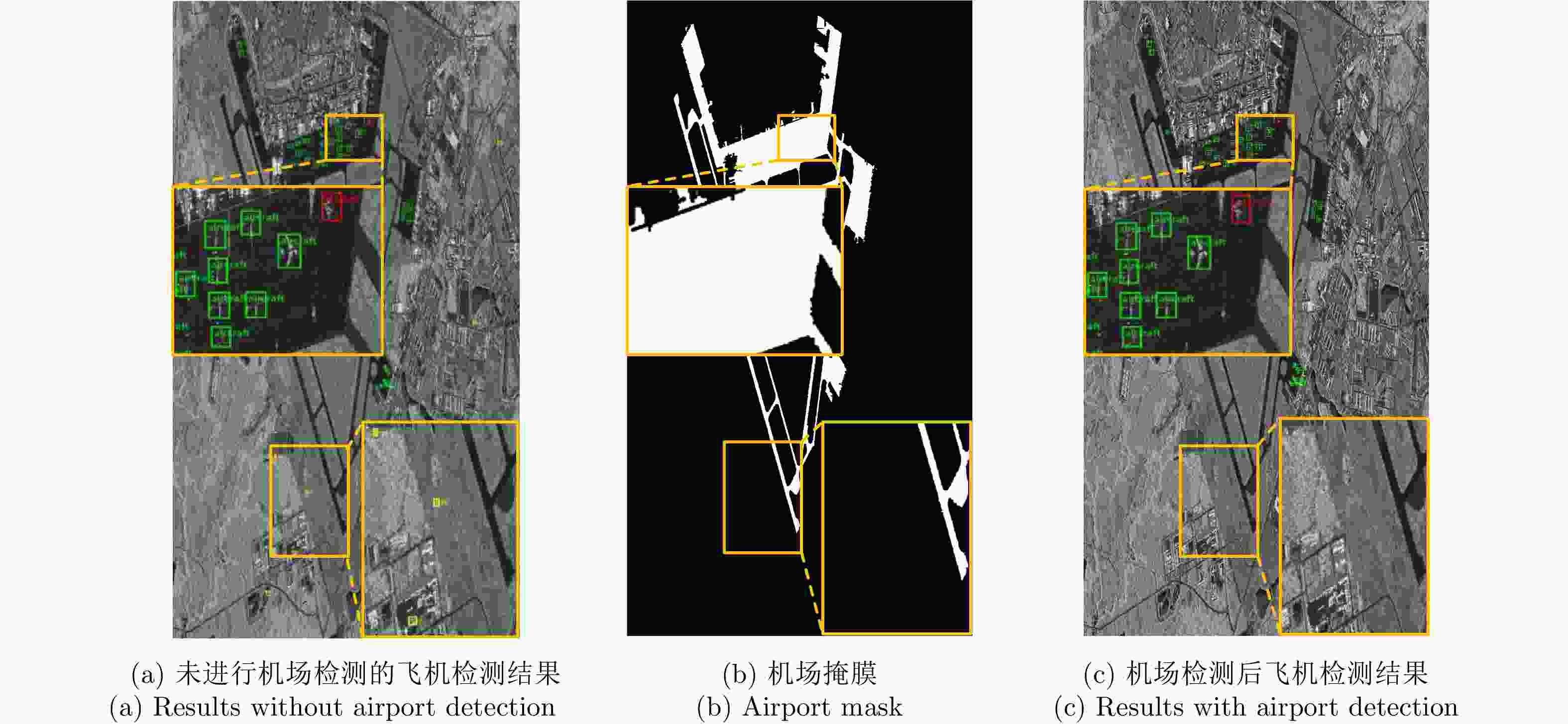
Table 2. Demonstration of airport detection algorithm effectiveness
算法 正确检测目标数目(个) 漏检目标数目(个) 虚警目标数目(个) 虚警率(%) 精确率(%) 未进行机场检测 580 28 103 15.1 84.9 进行机场检测 580 28 50 7.9 92.1 表 3 基于GF-3与TerraSAR-X卫星数据的散射信息增强效果对比
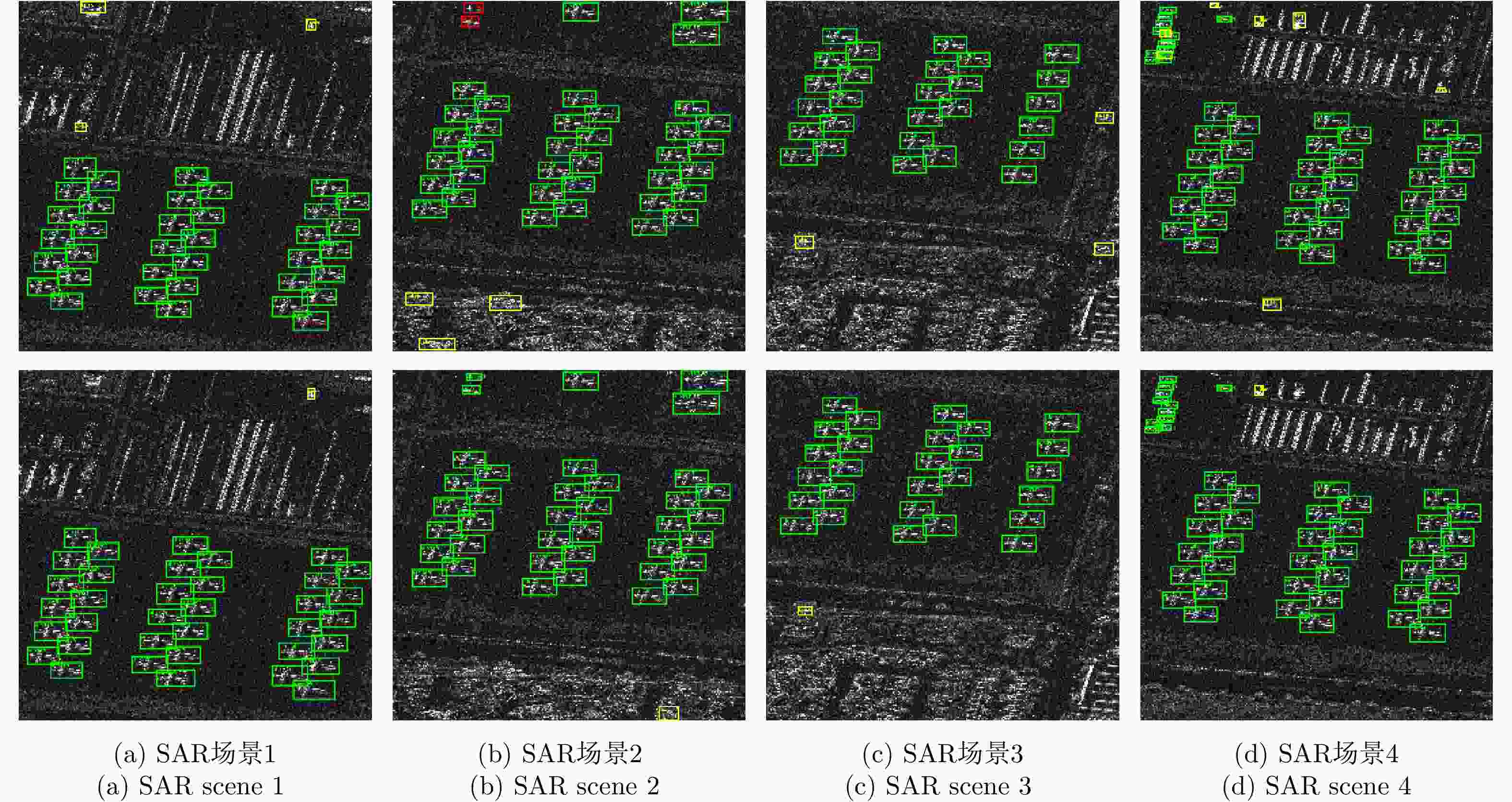
Table 3. Results of algorithm without/with scattering information enhancement based on GF-3 and TerraSAR-X data
算法 检测结果 GF-3 TerraSAR-X 合计 未进行散射信息增强特征金字塔算法 正检个数 429 133 562 漏检个数 42 4 46 虚警个数 53 14 67 虚警率(%) 11.0 9.5 10.7 召回率(%) 91.1 97.1 92.4 精确率(%) 89.0 90.5 89.3 散射信息增强特征金字塔算法 正检个数 445 135 580 漏检个数 26 2 28 虚警个数 43 7 50 虚警率(%) 8.8 4.9 7.9 召回率(%) 94.5 98.5 95.4 精确率(%) 91.2 95.1 92.1 表 4 SAR图像飞机目标检测识别算法对比
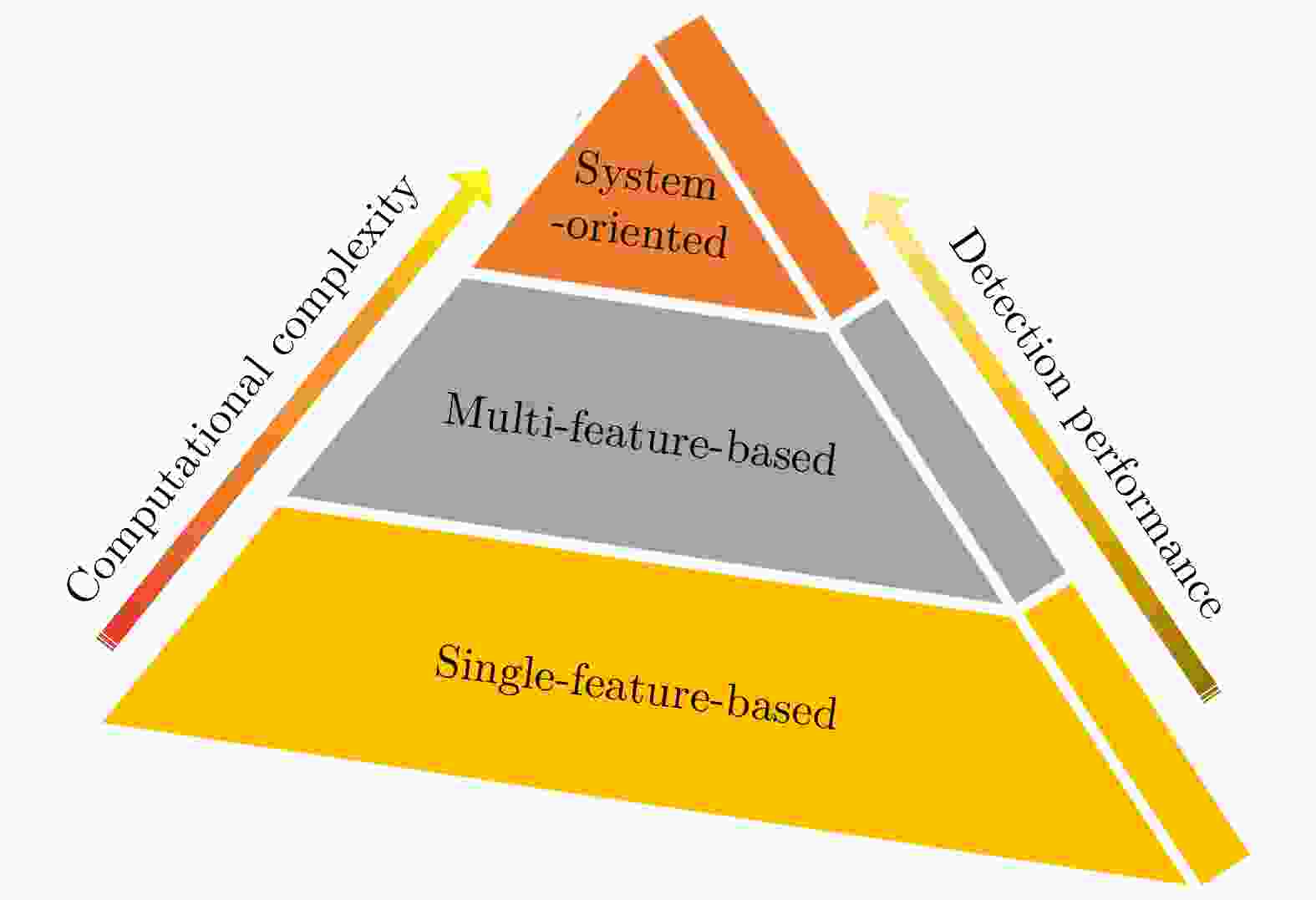
Table 4. Comparison of different aircraft detection and recognition methods in SAR imagery
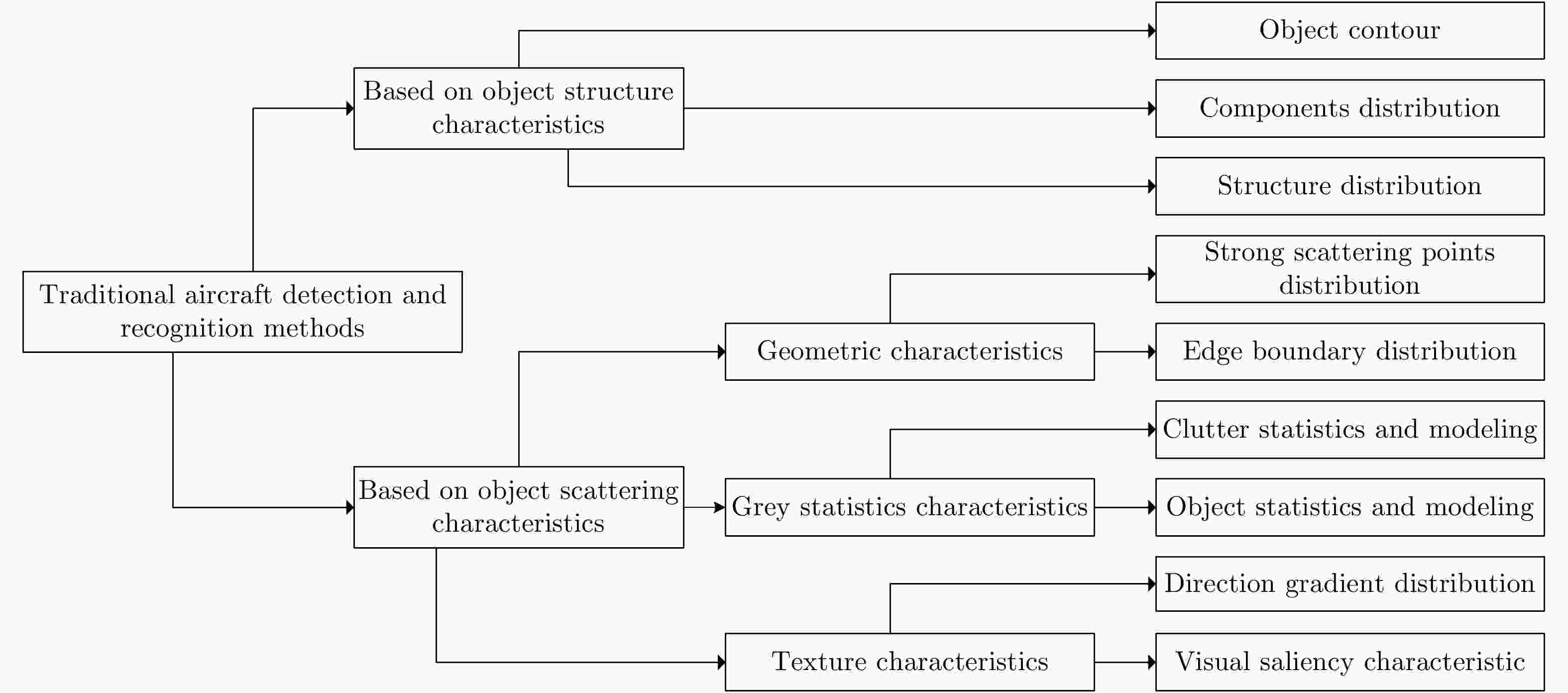
算法 具体分类 具有的优势 存在的问题 传统的方法 基于目标结构特征 算法的稳定性较好 需要先验信息,难以推广应用 基于目标散射特征 目标几何特征 算法的速度较快 容易受背景杂波干扰 灰度统计特征 算法的稳定性较好 建立统一的目标统计模型难度大 目标纹理特征 算法精度较高 鲁棒的目标局部纹理特征提取难度大 基于深度学习的方法 直接应用深度学习 算法的精度较高,算法速度较快 训练样本需求量大,网络泛化能力差 结合目标散射特征 算法的精度较高,稳定性较好 训练样本需求量大,训练过程较为复杂 -
[1] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [2] DUDGEON D E and LACOSS R T. An overview of automatic target recognition[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1993, 6(1): 3–10. [3] CUI Yi, ZHOU Guangyi, YANG Jian, et al. On the iterative censoring for target detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 641–645. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2098434 [4] 徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130 [5] CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720 [6] 高贵, 周蝶飞, 蒋咏梅, 等. SAR图像目标检测研究综述[J]. 信号处理, 2008, 24(6): 971–981. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.06.018GAO Gui, ZHOU Diefei, JIANG Yongmei, et al. Study on target detection in SAR image: A survey[J]. Signal Processing, 2008, 24(6): 971–981. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.06.018 [7] NOVAK L M, OWIRKA G J, BROWER W S, et al. The automatic target-recognition system in SAIP[J]. Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1997, 10(2): 187–201. [8] STEENSON B O. Detection performance of a mean-level threshold[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1968, AES-4(4): 529–534. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1968.5409020 [9] FINN H M and JOHNSON R S. Adaptive detection mode with threshold control as a function of spatially sampled clutter-level estimates[J]. RCA Review, 1968, 29(3): 414–464. [10] HANSEN V G. Constant false alarm rate processing in search radars[C]. 1973 IEEE International Radar Conference, London, UK, 1973: 325–332. [11] TRUNK G V. Range resolution of targets using automatic detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1978, AES-14(5): 750–755. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1978.308625 [12] KUTTIKKAD S and CHELLAPPA R. Non-Gaussian CFAR techniques for target detection in high resolution SAR images[C]. 1st IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Austin, USA, 1994: 910–914. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.1994.413444. [13] SMITH M E and VARSHNEY P K. VI-CFAR: A novel CFAR algorithm based on data variability[C]. 1997 IEEE National Radar Conference, Syracuse, USA, 1997: 263–268. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1997.588317. [14] 种劲松, 朱敏慧. SAR图像舰船及其尾迹检测研究综述[J]. 电子学报, 2003, 31(9): 1356–1360. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2003.09.020CHONG Jinsong and ZHU Minhui. Survey of the study on ship and wake detection in SAR imagery[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2003, 31(9): 1356–1360. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2003.09.020 [15] 王超, 张波, 温晓阳, 等. 基于雷达散射特性的高分辨率SAR图像自动目标识别[J]. 电波科学学报, 2004, 19(4): 422–426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2004.04.008WANG Chao, ZHANG Bo, WEN Xiaoyang, et al. Automatic target recognition in high resolution SAR image based on backscatter characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2004, 19(4): 422–426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2004.04.008 [16] 唐涛. 合成孔径雷达图像局部特征提取与应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2016: 36–63.TANG Tao. Research and application of local feature extraction in synthetic aperture radar imagery[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2016: 36–63. [17] AO Wei, XU Feng, LI Yongchen, et al. Detection and discrimination of ship targets in complex background from spaceborne ALOS-2 SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(2): 536–550. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2787573 [18] GAO Gui, OUYANG Kewei, LUO Yongbo, et al. Scheme of parameter estimation for generalized gamma distribution and its application to ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(3): 1812–1832. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2634862 [19] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, XING Xiangwei, et al. Area ratio invariant feature group for ship detection in SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(7): 2376–2388. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2820078 [20] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Ship detection based on complex signal kurtosis in single-channel SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6447–6461. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2906054 [21] WANG Xiaolong and CHEN Cuixia. Ship detection for complex background SAR images based on a multiscale variance weighted image entropy method[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(2): 184–187. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2633548 [22] ZHANG Xinzheng, QIN Jianhong, and LI Guojun. SAR Target classification using Bayesian compressive sensing with scattering centers features[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2013, 136: 385–407. doi: 10.2528/PIER12120705 [23] DONG Ganggang, WANG Na, and KUANG Gangyao. Sparse representation of monogenic signal: With application to target recognition in SAR images[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(8): 952–956. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2321565 [24] 宦若虹, 杨汝良. 基于小波域NMF特征提取的SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(3): 588–591.HUAN Ruohong and YANG Ruliang. Synthetic aperture radar images target recognition based on wavelet domain NMF feature extraction[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(3): 588–591. [25] 龙泓琳, 皮亦鸣, 曹宗杰. 基于非负矩阵分解的SAR图像目标识别[J]. 电子学报, 2010, 38(6): 1425–1429.LONG Honglin, PI Yimin, and CAO Zongjie. Non-negative matrix factorization for target recognition[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(6): 1425–1429. [26] 张新征, 谭志颖, 王亦坚. 基于多特征-多表示融合的SAR图像目标识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 492–502. doi: 10.12000/JR17078ZHANG Xinzheng, TAN Zhiying, and WANG Yijian. SAR target recognition based on multi-feature multiple representation classifier fusion[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 492–502. doi: 10.12000/JR17078 [27] 程建, 黎兰, 王海旭. 稀疏表示框架下的SAR目标识别[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2014, 43(4): 524–529. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2014.04.009CHENG Jian, LI Lan, and WANG Haixu. SAR target recognition under the framework of sparse representation[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2014, 43(4): 524–529. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2014.04.009 [28] 张锐, 洪峻, 明峰. 基于目标CSAR回波模型的SAR自动目标识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(1): 27–32. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00192ZHANG Rui, HONG Jun, and MING Feng. SAR ATR algorithm based on CSAR raw echo modeling[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(1): 27–32. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00192 [29] HE Chu, LI Shuang, LIAO Zixian, et al. Texture classification of PolSAR data based on sparse coding of wavelet polarization textons[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(8): 4576–4590. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2236338 [30] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [31] 郑远攀, 李广阳, 李晔. 深度学习在图像识别中的应用研究综述[J]. 计算机工程应用, 2019, 55(12): 20–36. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1903-0031ZHENG Yuanpan, LI Guangyang, and LI Ye. Survey of application of deep learning in image recognition[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(12): 20–36. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1903-0031 [32] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.81. [33] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [34] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.169. [35] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [36] DAI Jifeng, LI Yi, HE Kaiming, et al. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks[C]. The 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [37] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.106. [38] HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.322. [39] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91. [40] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]. 2017 IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6517–6525. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.690. [41] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. [42] FU Chengyang, LIU Wei, RANGA A, et al. DSSD: Deconvolutional single shot detector[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1701.06659, 2017. [43] LI Zuoxin and ZHOU Fuqiang. FSSD: Feature fusion single shot multibox detector[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1712.00960, 2017. [44] WANG Haipeng, CHEN Sizhe, XU Feng, et al. Application of deep-learning algorithms to MSTAR data[C]. 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Milan, Italy, 2015: 3743–3745. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2015.7326637. [45] WAGNER S A. SAR ATR by a combination of convolutional neural network and support vector machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(6): 2861–2872. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.160061 [46] AMRANI M and JIANG Feng. Deep feature extraction and combination for synthetic aperture radar target classification[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2017, 11(4): 042616. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.11.042616 [47] DENG Sheng, DU Lan, LI Chen, et al. SAR automatic target recognition based on euclidean distance restricted autoencoder[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(7): 3323–3333. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2670083 [48] WANG Zhaocheng, DU Lan, MAO Jiashun, et al. SAR target detection based on SSD with data augmentation and transfer learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(1): 150–154. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2867242 [49] HUANG Xiayuan, NIE Xiangli, WU Wei, et al. SAR target configuration recognition based on the biologically inspired model[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 234: 185–191. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.12.054 [50] LIN Zhao, JI Kefeng, KANG Miao, et al. Deep convolutional highway unit network for SAR target classification with limited labeled training data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(7): 1091–1095. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2698213 [51] ZHANG Fan, HU Chen, YIN Qiang, et al. Multi-aspect-aware bidirectional LSTM networks for synthetic aperture radar target recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2017(5): 26880–26891. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2773363 [52] GAO Fei, YANG Yue, WANG Jun, et al. A Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks (DCGANs)-based semi-supervised method for object recognition in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(6): 846. doi: 10.3390/rs10060846 [53] HUANG Yan, LIAO Guisheng, ZHANG Zhen, et al. SAR automatic target recognition using joint low-rank and sparse multiview denoising[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(10): 1570–1574. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2851146 [54] SHANG Ronghua, WANG Jiaming, JIAO Licheng, et al. SAR targets classification based on deep memory convolution neural networks and transfer parameters[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(8): 2834–2846. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2836909 [55] AN Quanzhi, PAN Zongxu, and YOU Hongjian. Ship detection in Gaofen-3 SAR images based on sea clutter distribution analysis and deep convolutional neural network[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 334. doi: 10.3390/s18020334 [56] 朱明明, 许悦雷, 马时平, 等. 改进区域卷积神经网络的机场检测方法[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(7): 0728001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0728001ZHU Mingming, XU Yuelei, MA Shiping, et al. Airport detection method with improved region-based convolutional neural network[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(7): 0728001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0728001 [57] XIE Jie, HE Nanjun, FANG Leyuan, et al. Scale-free convolutional neural network for remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6916–6928. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2909695 [58] 宋建社, 郑永安, 袁礼海. 合成孔径雷达图像理解与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 53–67.SONG Jianshe, ZHENG Yongan, and YUAN Lihai. Understanding and Applications of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 53–67. [59] ZHANG Tao, JI Jinsheng, LI Xiaofeng, et al. Ship detection from PolSAR imagery using the complete polarimetric covariance difference matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(5): 2824–2839. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2877821 [60] El-DARYMLI K, MCGUIRE P, POWER D, et al. Target detection in synthetic aperture radar imagery: A state-of-the-art survey[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2013, 7(1): 071598. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.7.071598 [61] 高君, 高鑫, 孙显. 基于几何特征的高分辨率SAR图像飞机目标解译方法[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2015, 34(8): 21–28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2015.08.008GAO Jun, GAO Xin, and SUN Xian. Geometrical features-based method for aircraft target interpretation in high-resolution SAR images[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2015, 34(8): 21–28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2015.08.008 [62] 林煜东. 复杂背景下的光学遥感图像目标检测算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西南交通大学, 2017: 24–47.LIN Yudong. Target detection in optical remote sensing images with complecated background[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017: 24–47. [63] CHEN Jiehong, ZHANG Bo, and WANG Chao. Backscattering feature analysis and recognition of civilian aircraft in TerraSAR-X images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 796–800. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2362845 [64] 郭倩, 王海鹏, 徐丰. 星载合成孔径雷达图像的飞机目标检测[J]. 上海航天, 2018, 35(6): 57–64. doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.1006-1630.2018.06.010GUO Qian, WANG Haipeng, and XU Feng. Aircraft target detection from spaceborne synthetic aperture radar image[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2018, 35(6): 57–64. doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.1006-1630.2018.06.010 [65] HU Xiangyun, SHEN Jiajie, SHAN Jie, et al. Local edge distributions for detection of salient structure textures and objects[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 466–470. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2210188 [66] LI Lu, DU Lan, and WANG Zhaocheng. Target detection based on dual-domain sparse reconstruction saliency in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(11): 4230–4243. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2874128 [67] DOU Fangzheng, DIAO Wenhui, SUN Xian, et al. Aircraft recognition in high resolution SAR images using saliency map and scattering structure features[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7729402. [68] FU Kun, DOU Fangzheng, LI Hengchao, et al. Aircraft recognition in SAR images based on scattering structure feature and template matching[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(11): 4206–4217. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2872018 [69] HE Chu, TU Mingxia, LIU Xinlong, et al. Mixture statistical distribution based multiple component model for target detection in high resolution SAR imagery[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2017, 6(11): 336. doi: 10.3390/ijgi6110336 [70] TAN Yihua, LI Qingyun, LI Yansheng, et al. Aircraft detection in high-resolution SAR images based on a gradient textural saliency map[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(9): 23071–23094. doi: 10.3390/s150923071 [71] 王思雨, 高鑫, 孙皓, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的高分辨率SAR图像飞机目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 195–203. doi: 10.12000/JR17009WANG Siyu, GAO Xin, SUN Hao, et al. An aircraft detection method based on convolutional neural networks in high-resolution SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 195–203. doi: 10.12000/JR17009 [72] DOU Fangzheng, DIAO Wenhui, SUN Xian, et al. Aircraft reconstruction in high-resolution SAR images using deep shape prior[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2017, 6(11): 330. doi: 10.3390/ijgi6110330 [73] HE Chu, TU Mingxia, XIONG Dehui, et al. Adaptive component selection-based discriminative model for object detection in high-resolution SAR imagery[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2018, 7(2): 72. doi: 10.3390/ijgi7020072 [74] AN Quanzhi, PAN Zongxu, LIU Lei, et al. DRBox-v2: An improved detector with rotatable boxes for target detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8333–8349. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2920534 [75] 赵丹新, 孙胜利. 基于ResNet的遥感图像飞机目标检测新方法[J]. 电子设计工程, 2018, 26(22): 164–168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2018.22.036ZHAO Danxin and SUN Shengli. A new method for target detection of remote sensing image based on ResNet. computer engineering and applications[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2018, 26(22): 164–168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2018.22.036 [76] ZHANG Linbin, LI Chuyin, ZHAO Lingjun, et al. A cascaded three-look network for aircraft detection in SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 11(1): 57–65. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2019.1681599 [77] HE Chu, TU Mingxia, XIONG Dehui, et al. A component-based multi-layer parallel network for airplane detection in SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(7): 1016. doi: 10.3390/rs10071016 [78] 谭振宇, 江刚武, 刘建辉. 一种结合非顶层特征图和自适应阈值的飞机目标检测算法[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2019, 36(4): 382–387.TAN Zhenyu, JIANG Gangwu, and LIU Jianhui. A combination of non-top-level feature maps and adaptive thresholds aircraft target detection algorithm[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2019, 36(4): 382–387. [79] LIN Zhao, JI Kefeng, LENG Xiangguang, et al. Squeeze and excitation rank faster R-CNN for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(5): 751–755. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2882551 [80] CUI Zongyong, LI Qi, CAO Zongjie, et al. Dense attention pyramid networks for multi-scale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8983–8997. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923988 [81] WEI Shunjun, SU Hao, MING Jing, et al. Precise and robust ship detection for high-resolution SAR imagery based on HR-SDNet[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(1): 167. doi: 10.3390/rs12010167 [82] ZHAO Yan, ZHAO Lingjun, LI Chuyin, et al. Pyramid attention dilated network for aircraft detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2981255 [83] GUO Qian, WANG Haipeng, and XU Feng. Aircraft detection in high-resolution SAR images using scattering feature information[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/APSAR46974.2019.9048502. [84] 徐丰, 金亚秋. 从物理智能到微波视觉[J]. 科技导报, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.10.004XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. From the emergence of intelligent science to the research of microwave vision[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.10.004 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: