Target Tracking for Passive Bistatic Radar Based on Mutual Information Entropy and Improved PHD
-
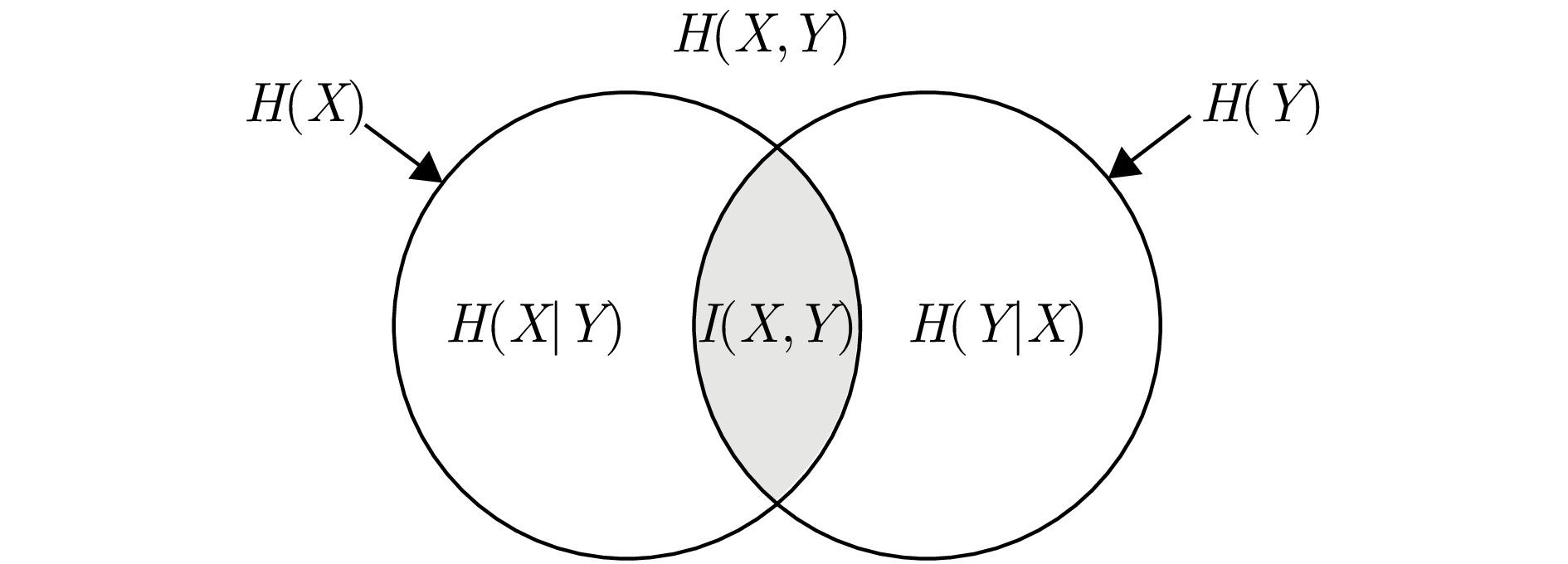
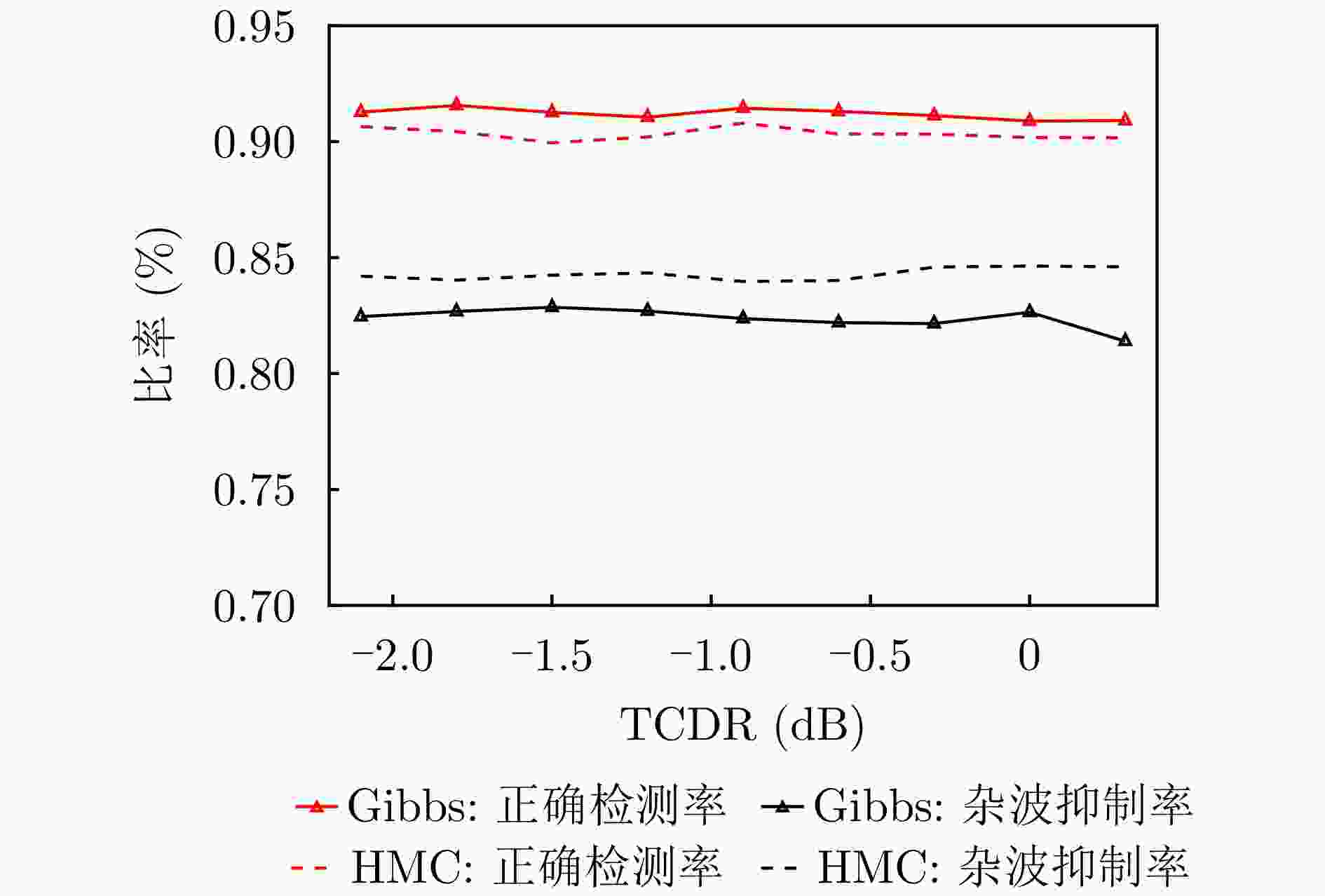
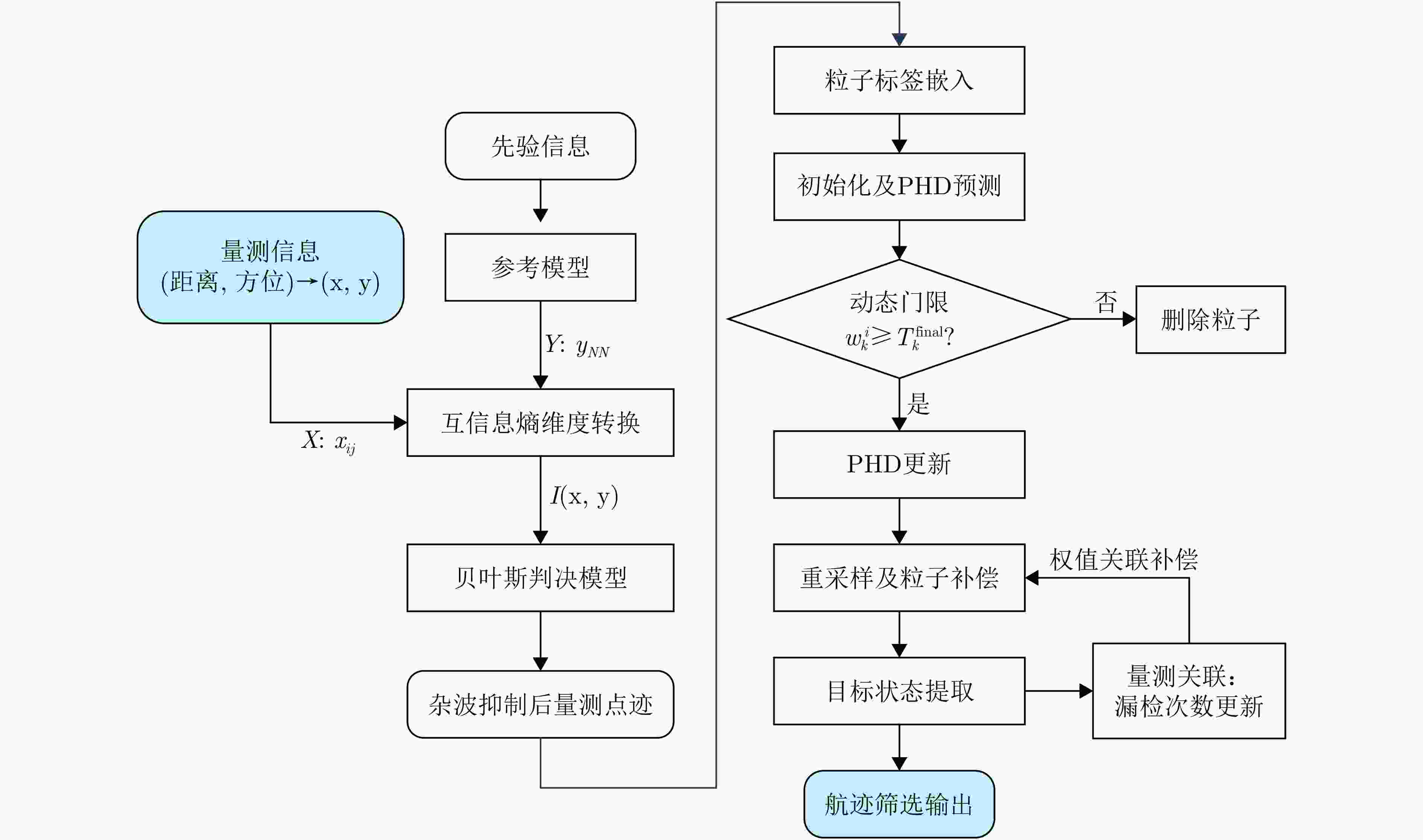
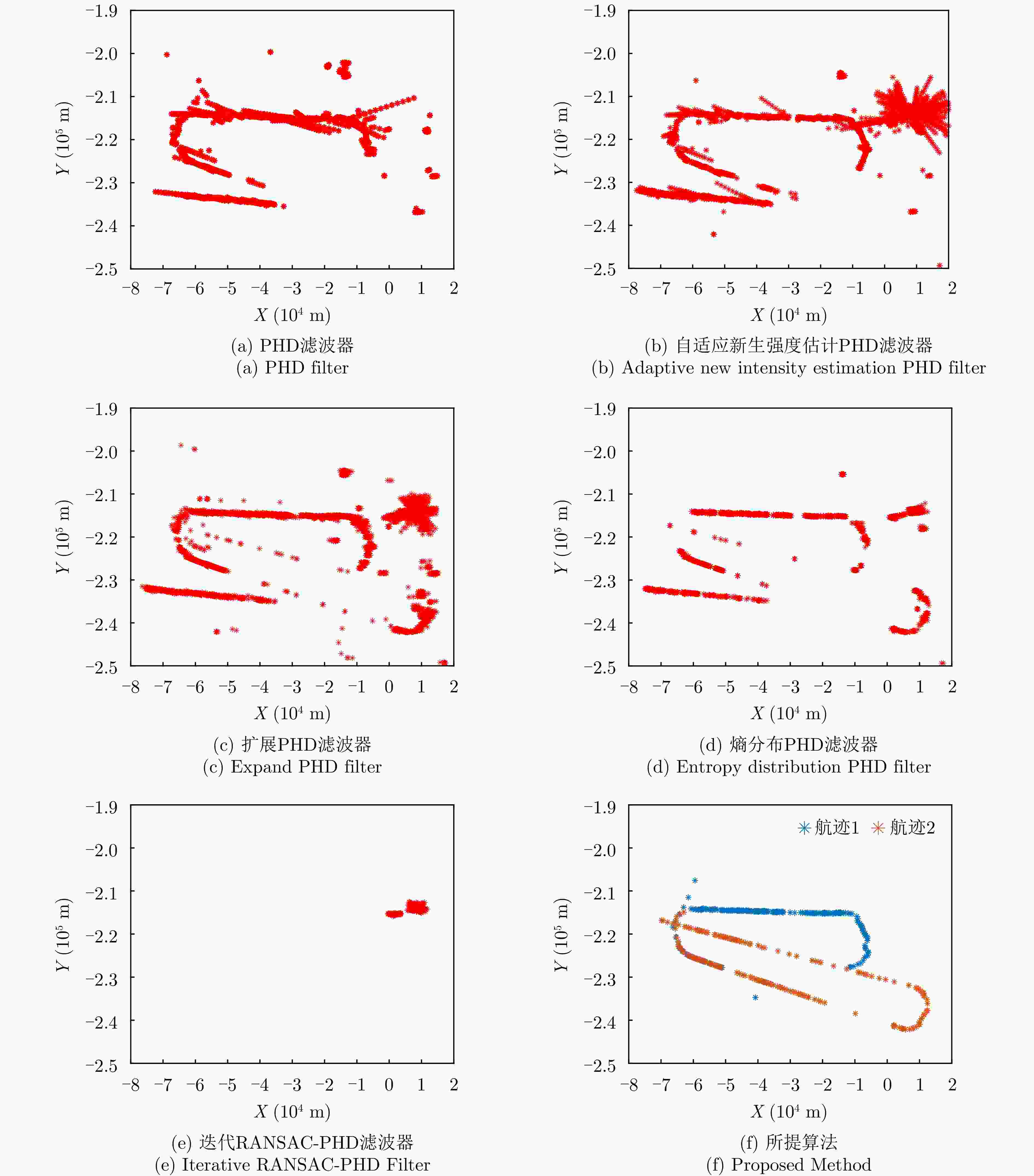
摘要: 针对非合作双基地雷达目标跟踪时主要面临的高杂波率、低检测概率等问题,该文提出了一种基于互信息熵和改进PHD滤波器的目标跟踪协同处理框架,首先将目标点和杂波点与参考模型间不同的统计相关程度量化为互信息熵值,基于互信息熵维特征完成杂波点迹筛除;其次通过动态权值补偿对经典PHD滤波器进行改进,减缓粒子权值归零过程的同时减少目标误删现象,解决低检测概率下点迹不连续且间隔随机给目标跟踪带来的点迹断联、目标丢失等问题。通过仿真实验验证了所提算法框架的有效性与性能,外场实测数据验证了所提方法在实际应用中可取得良好的目标跟踪结果。Abstract: This study proposes a processing framework based on Mutual Information Entropy (MIE) and an improved probability hypothesis density filter to address the key challenges—high clutter density and low detection probability—in Passive Bistatic Radar (PBR) target tracking. First, statistical differences in the correlation between target and clutter points, as well as between reference models, are quantified as mutual information entropy values, which are then used to eliminate clutter points. Second, the classical probability hypothesis density filter is improved through dynamic weight compensation, mitigating particle weight degeneration and reducing the deletion of false targets. This approach effectively resolves issues such as track fragmentation and target loss caused by discontinuous measurements with random intervals under low detection probability. The effectiveness of the proposed framework was verified through simulation experiments, and field test data demonstrated that the proposed method achieves good target-tracking performance in practical applications.
-
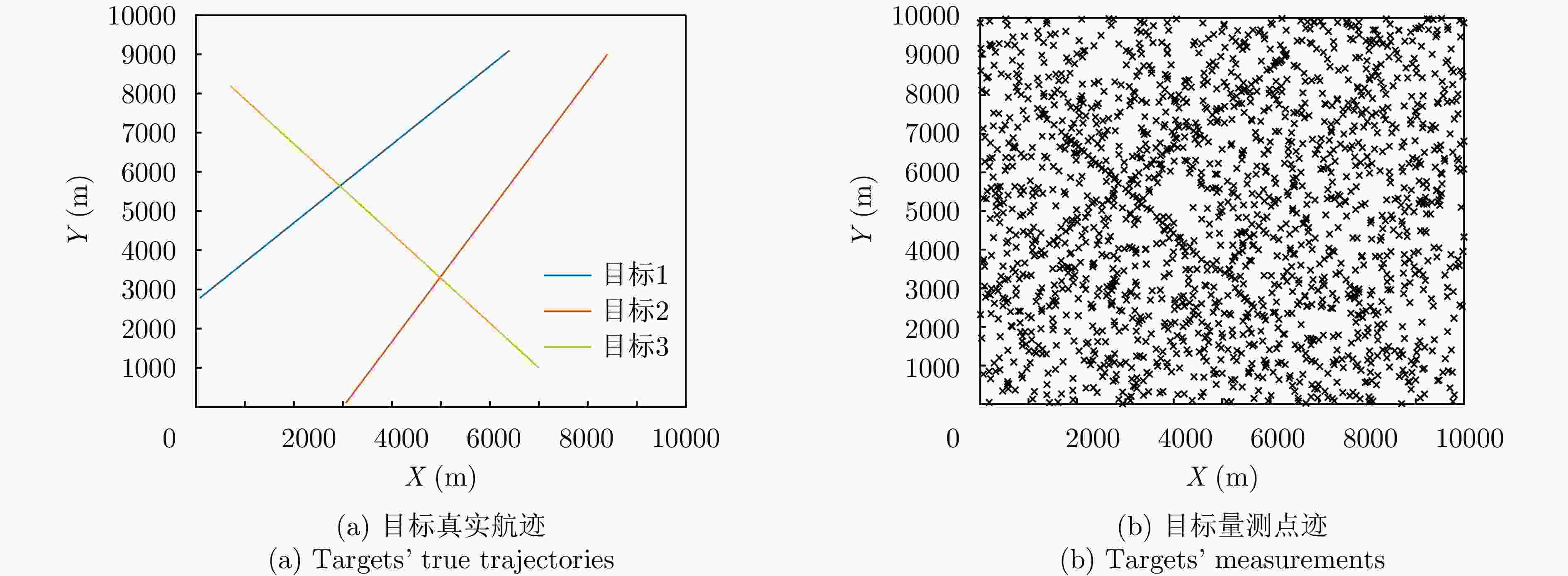
表 1 仿真目标参数设置
Table 1. Simulation parameter setting of target
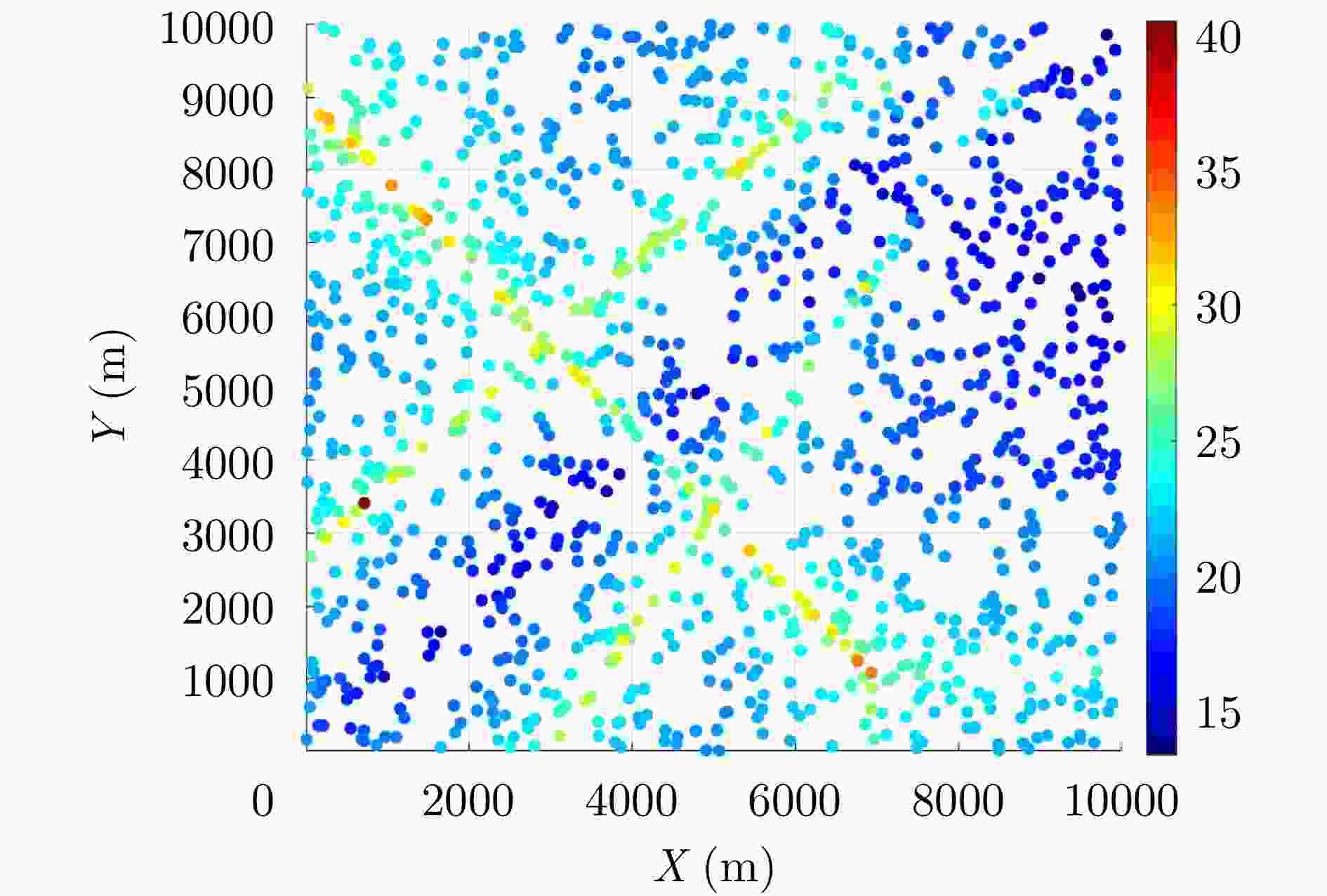
目标 起始位置(x,y) (m) 速度($ {v}_{x},{v}_{y} $) (m/s) 存活时间(s) 1 (0, 2700 )(80, 80) (0, 80) 2 ( 3000 , 0)(60, 100) (0, 90) 3 (0, 9000 )(70, –80) (10, 100) 表 2 仿真场景参数设置
Table 2. Simulation parameter setting of scenario
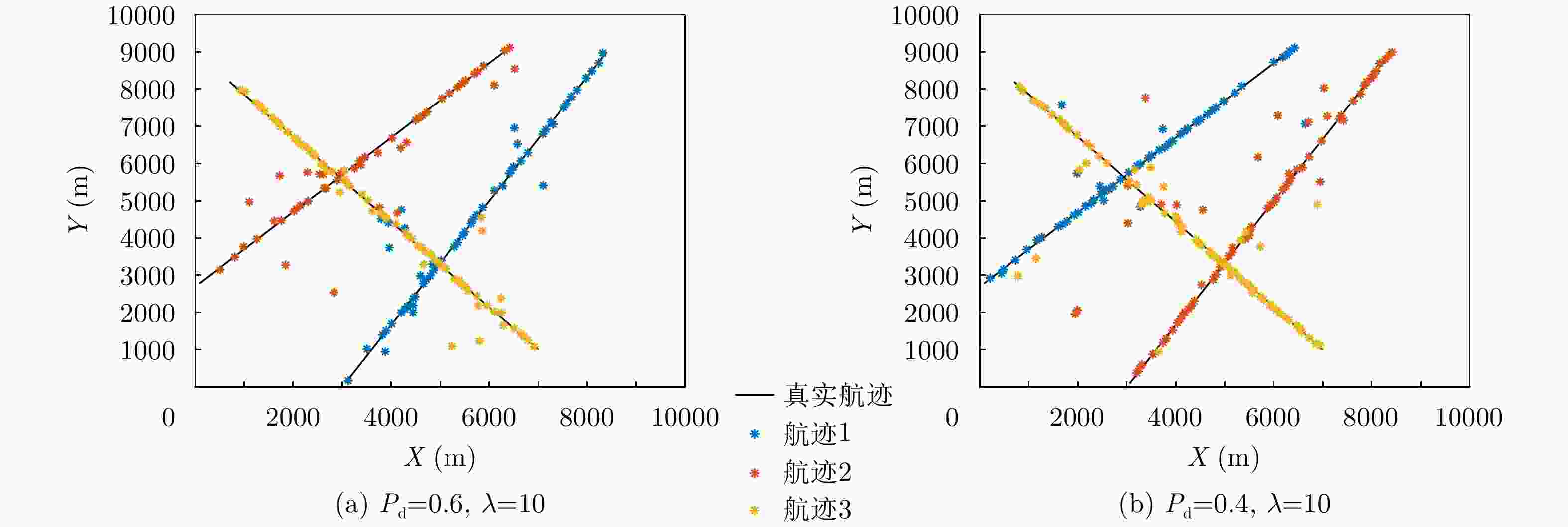
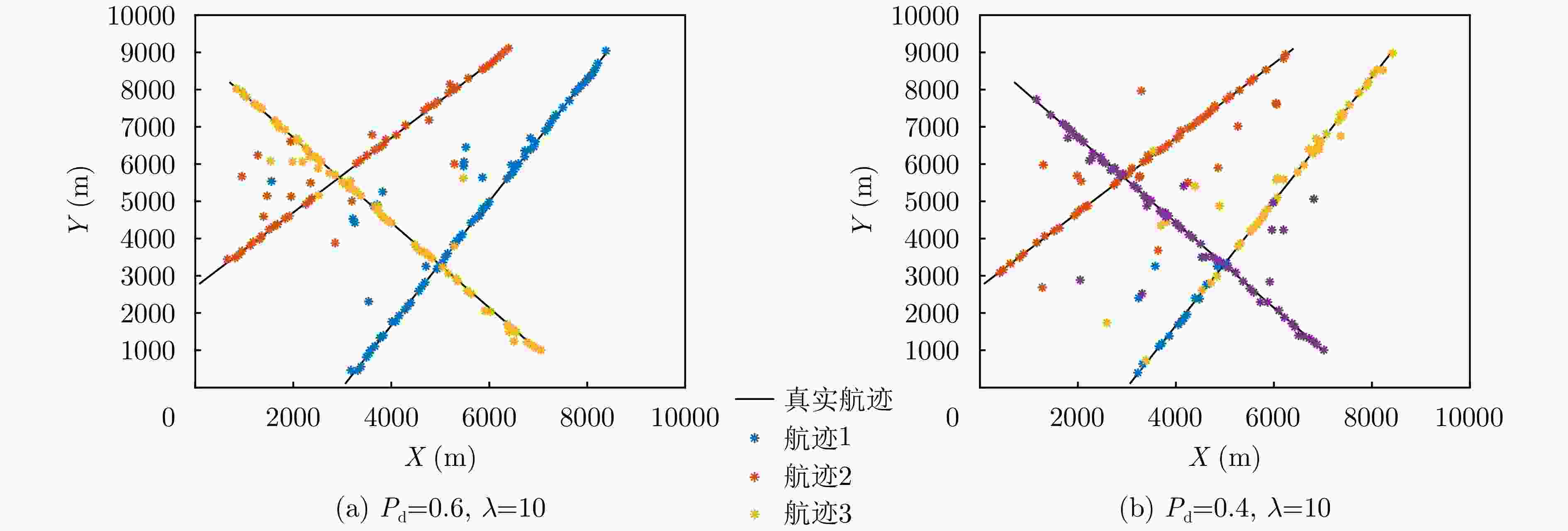
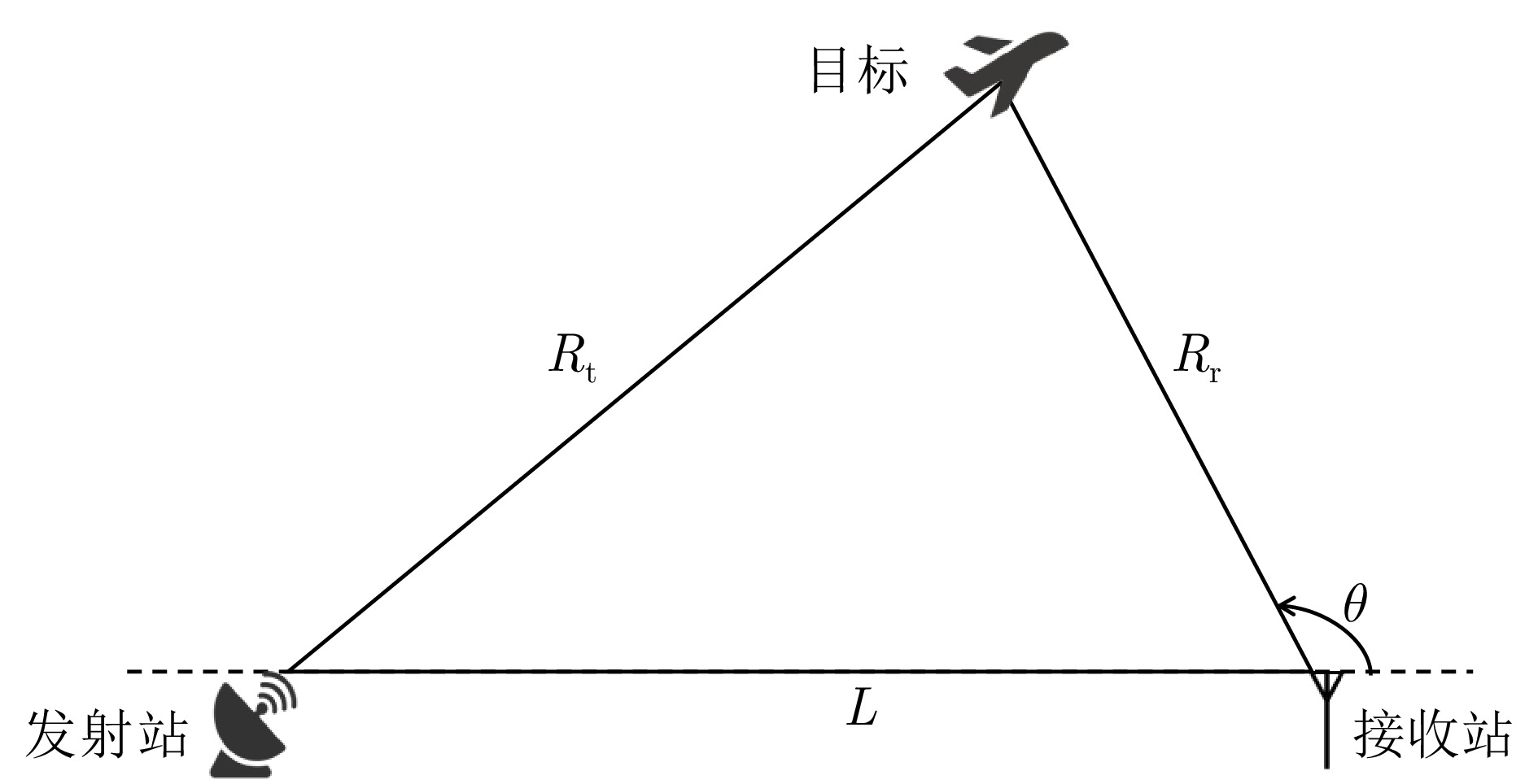
参数 数值 双基地基线距离 10 km 探测距离范围 [10 km, 60 km] 探测角度范围 [30°, 150°] 目标检测概率$ {P}_{{\mathrm{d}}} $ 0.5 泊松杂波均值$ \lambda $ 20 距离量测误差(精度) 30 m 角度量测误差(精度) 1° -
[1] COLONE F, FILIPPINI F, and PASTINA D. Passive radar: Past, present, and future challenges[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2023, 38(1): 54–69. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2022.3221685. [2] GRIFFITHS H D and BAKER C J. An Introduction to Passive Radar, Second Edition[M]. Artech House, 2022. [3] HORLBECK M, SCHEINER B, WEIGEL R, et al. Overview of passive radar and its receiver architectures to enhance safety in civil aviation: A comprehensive analysis of history, principles, and performance optimization strategies[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2024, 25(5): 53–71. doi: 10.1109/MMM.2024.3363991. [4] 万显荣, 易建新, 占伟杰, 等. 基于多照射源的被动雷达研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 939–958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143.WAN Xianrong, YI Jianxin, ZHAN Weijie, et al. Research progress and development trend of the multi-illuminator-based passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 939–958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143. [5] 刘智星, 杜思予, 吴耀君, 等. 脉间-脉内捷变频雷达抗间歇采样干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(2): 301–312. doi: 10.12000/JR22001.LIU Zhixing, DU Siyu, WU Yaojun, et al. Anti-interrupted sampling repeater jamming method for interpulse and intrapulse frequency-agile radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(2): 301–312. doi: 10.12000/JR22001. [6] 张迪. 复杂条件下雷达点迹处理方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.002930.ZHANG Di. Research on radar plot processing under complex conditions[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.002930. [7] 罗兴旺, 张伯彦, 刘嘉, 等. 雷达数据处理中的杂波抑制方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2016, 38(1): 37–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.01.07.LUO Xingwang, ZHANG Boyan, LIU Jia, et al. Researches on the method of clutter suppression in radar data processing[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(1): 37–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.01.07. [8] WANG Zhifei, YU Junpeng, and YANG Yuhao. False-alarm suppression with random forest by exploiting ambiguity features of targets[J]. Electronics Letters, 2022, 58(24): 917–919. doi: 10.1049/ell2.12642. [9] 彭笑冬, 刘长江. 炮位雷达中的虚警抑制处理[J]. 现代雷达, 2024, 46(12): 67–72. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2024.12.010.PENG Xiaodong and LIU Changjiang. False alarm suppression based on firefinder radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2024, 46(12): 67–72. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2024.12.010. [10] SUN Chunlin, MAO Xingpeng, TANG Zhibo, et al. Radar false alarm suppression based on target spatial temporal stationarity for UAV detecting[J]. Drones, 2024, 8(12): 699. doi: 10.3390/drones8120699. [11] 姚毅, 李建勋, 李增辉, 等. 基于分层贝叶斯的雷达真假点迹识别方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2018, 40(3): 53–57. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2018.03.012.YAO Yi, LI Jianxun, LI Zenghui, et al. Recognition solution of real and false radar trace point based on Bayesian hierarchical model[J]. Modern Radar, 2018, 40(3): 53–57. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2018.03.012. [12] WU Lin, WANG Fei, XU Yongjun, et al. A parallel implementation of hypothesis-oriented multiple hypothesis tracking[C]. 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Rustenburg, South Africa, 2020: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/FUSION45008.2020.9190459. [13] ANGLE R B, STREIT R L, and EFE M. A low computational complexity JPDA filter with superposition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 1031–1035. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3082040. [14] 毕文豪, 周杰, 张安, 等. 杂波环境下基于最大熵模糊聚类的JPDA算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(7): 1920–1927. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.07.02.BI Wenhao, ZHOU Jie, ZHANG An, et al. JPDA algorithm based on maximum entropy fuzzy clustering in clutter environment[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(7): 1920–1927. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.07.02. [15] 熊振宇, 崔亚奇, 熊伟, 等. 卫星与雷达位置数据自适应关联[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(1): 91–98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.01.12.XIONG Zhenyu, CUI Yaqi, XIONG Wei, et al. Adaptive association for satellite and radar position data[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(1): 91–98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.01.12. [16] GAO Chang, YAN Junkun, CHEN Bo, et al. Data association for maneuvering targets through a combined Siamese network and XGBoost model[J]. Signal Processing, 2023, 211: 109086. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2023.109086. [17] PENG Duo, XIE Kun, and LIU Mingshuo. Manoeuvre target tracking in wireless sensor networks using convolutional bi-directional long short-term memory neural networks and extended Kalman filtering[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(13): 4261. doi: 10.3390/s24134261. [18] 熊伟, 朱洪峰, 崔亚奇. 在线学习的循环自适应机动目标跟踪算法[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(5): 325250. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.25250.XIONG Wei, ZHU Hongfeng, and CUI Yaqi. Recurrent adaptive maneuvering target tracking algorithm based on online learning[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(5): 325250. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.25250. [19] 严灵杰, 顾杰, 姜余, 等. 基于随机有限集的多目标跟踪技术综述[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2024, 39(1): 81–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2024.01.013.YAN Lingjie, GU Jie, JIANG Yu, et al. Overview of multi-target tracking technology based on random finite set[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2024, 39(1): 81–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2024.01.013. [20] MAHLER R. “Statistics 102” for multisource-multitarget detection and tracking[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(3): 376–389. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2253084. [21] VO B N and MA W K. The Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4091–4104. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881190. [22] VO B N, SINGH S, and DOUCET A. Sequential Monte Carlo methods for multitarget filtering with random finite sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(4): 1224–1245. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1561884. [23] 曾雅俊, 王俊, 魏少明, 等. 分布式多传感器多目标跟踪方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 197–213. doi: 10.12000/JR22111.ZENG Yajun, WANG Jun, WEI Shaoming, et al. Review of the method for distributed multi-sensor multi-target tracking[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 197–213. doi: 10.12000/JR22111. [24] 王志伟, 刘永祥, 杨威, 等. 基于航迹概率假设密度的多传感器多目标跟踪[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(2): 526–533. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.02.17.WANG Zhiwei, LIU Yongxiang, YANG Wei, et al. Multi-sensor multi-target tracking with trajectory probability hypothesis density[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(2): 526–533. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.02.17. [25] LI Tiancheng, ELVIRA V, FAN Hongqi, et al. Local-diffusion-based distributed SMC-PHD filtering using sensors with limited sensing range[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(4): 1580–1589. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2882084. [26] MALAS J A and PASALA K M. Information theory based radar signature analysis[C]. 2007 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2007: 1–13. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2007.353066. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: