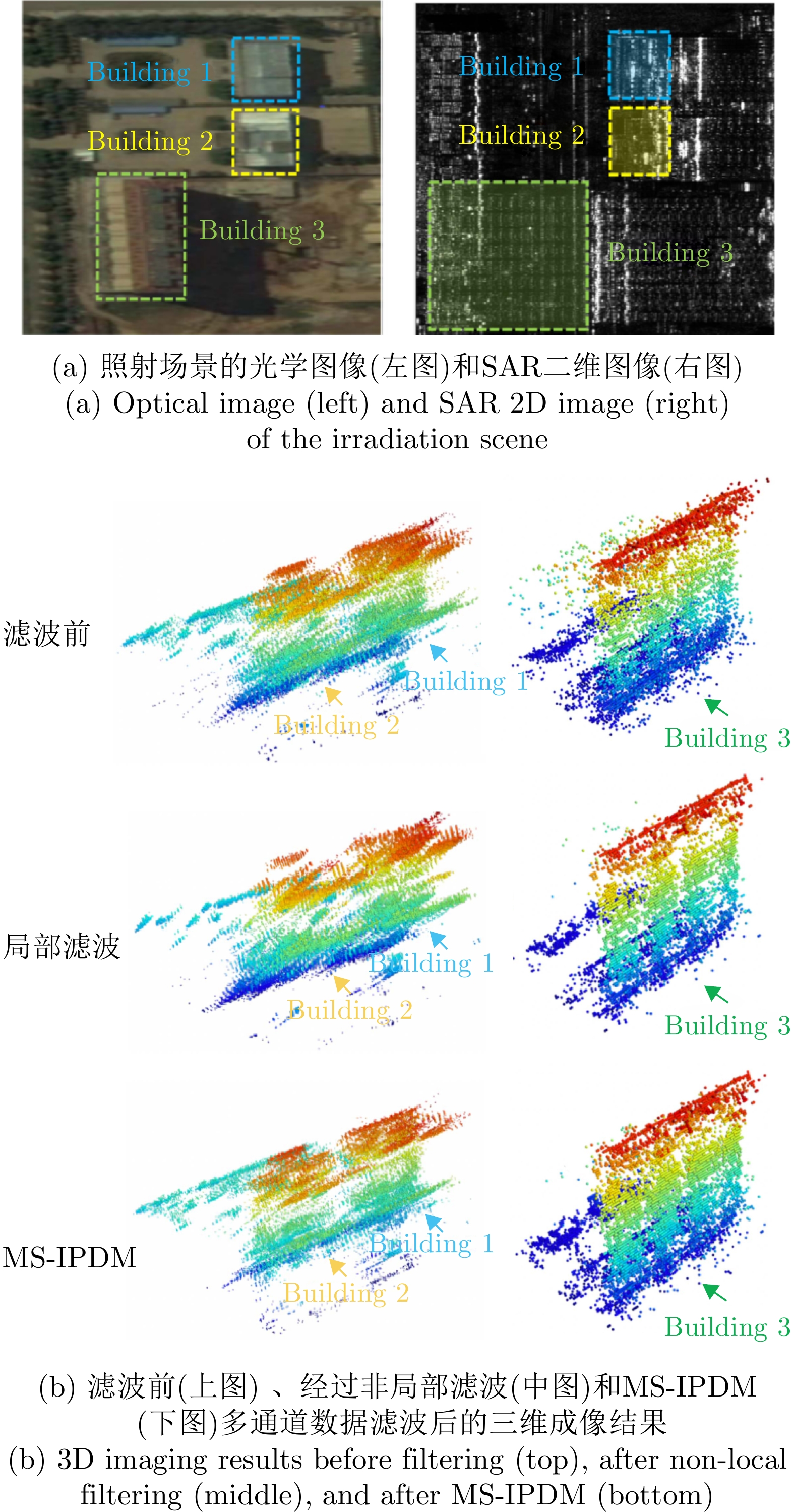
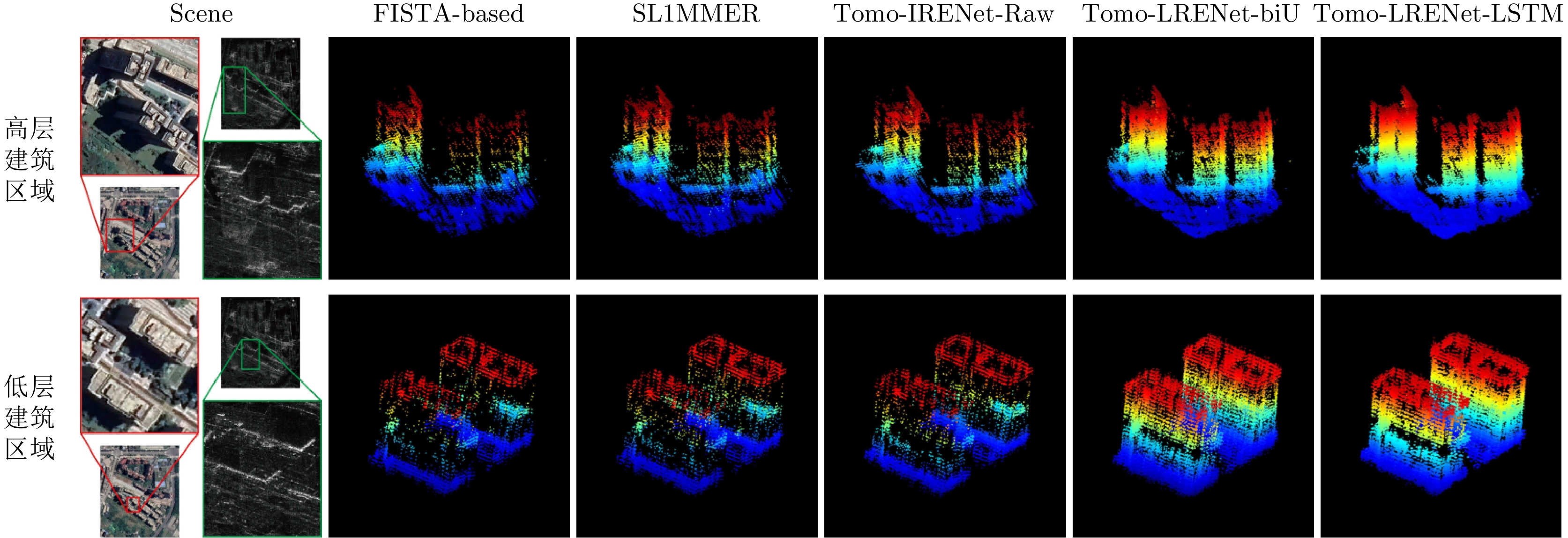
| [1] |
FORNARO G, SERAFINO F, and SOLDOVIERI F. Three-dimensional focusing with multipass SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(3): 507–517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.809934. |
| [2] |
NANNINI M, SCHEIBER R, HORN R, et al. First 3-D reconstructions of targets hidden beneath foliage by means of polarimetric SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(1): 60–64. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2160329. |
| [3] |
ANTONELLO G, CASAGLI N, FARINA P, et al. Ground-based SAR interferometry for monitoring mass movements[J]. Landslides, 2004, 1(1): 21–28. doi: 10.1007/s10346-003-0009-6. |
| [4] |
LIU Peiyao, ZHU Kaiwen, WANG Zhen, et al. Ground-based radar three-dimensional imaging for moon under sparse observations[C]. IET International Radar Conference (IRC 2023), Chongqing, China, 2023: 4183–4188. doi: 10.1049/icp.2024.1786. |
| [5] |
LI Liechen and LI Daojing. Sparse array SAR 3D imaging for continuous scene based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645. |
| [6] |
REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873. |
| [7] |
WANG Yan, DING Zegang, LI Linghao, et al. First demonstration of single-pass distributed SAR tomographic imaging with a P-band UAV SAR prototype[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5238618. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3221859. |
| [8] |
BUDILLON A, EVANGELISTA A, and SCHIRINZI G. SAR tomography from sparse samples[C]. 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009: IV-865–IV-868. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2009.5417514. |
| [9] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Very high resolution SAR tomography via compressive sensing[C]. 6th International Workshop on Advanced Optical Metrology on Fringe 2009, Frascati, Italy, 2009.
|
| [10] |
ZHAO Kexiang, BI Hui, and ZHANG Bingchen. SAR tomography method based on fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(5): 1019–1023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.05.11. |
| [11] |
WANG Xiao, XU Feng, and JIN Yaqiu. The iterative reweighted alternating direction method of multipliers for separating structural layovers in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(11): 1883–1887. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2694825. |
| [12] |
WANG Xiao and XU Feng. Tomographic SAR inversion by atomic-norm minimization-the gridless compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5239113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3223524. |
| [13] |
LIU Minkun, WAND Yan, DING Zegang, et al. Atomic norm minimization based fast off-grid tomographic SAR imaging with nonuniform sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5203517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3358863. |
| [14] |
ZHANG Siqian, ZHU Yutao, DONG Ganggang, et al. Truncated SVD-based compressive sensing for downward-looking three-dimensional SAR imaging with uniform/nonuniform linear array[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(9): 1853–1857. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2431254. |
| [15] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Demonstration of super-resolution for tomographic SAR imaging in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3150–3157. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2177843. |
| [16] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183. |
| [17] |
HUANG Yue, FERRO-FAMIL L, and REIGBER A. Under-foliage object imaging using SAR tomography and polarimetric spectral estimators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(6): 2213–2225. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2171494. |
| [18] |
SHI Yilei, ZHU Xiaoxiang, and BAMLER R. Nonlocal compressive sensing-based SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(5): 3015–3024. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2879382. |
| [19] |
RAMBOUR C, DENIS L, TUPIN F, et al. Introducing spatial regularization in SAR tomography reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8600–8617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2921756. |
| [20] |
LIN Bo, LI Chao, JI Yicai, et al. A millimeter-wave 3D imaging algorithm for MIMO synthetic aperture radar[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(13): 5979. doi: 10.3390/s23135979. |
| [21] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, SHI Jun, et al. 3-D SAR imaging via perceptual learning framework with adaptive sparse prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5202716. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3237660. |
| [22] |
HAN Dong, ZHOU Liangjiang, JIAO Zekun, et al. Efficient 3D image reconstruction of airborne TomoSAR based on back projection and improved adaptive ISTA[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 47399–47410. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3066984. |
| [23] |
KHALIL ALSMADI M, OMAR K B, NOAH S A, et al. Performance comparison of multi-layer perceptron (back propagation, delta rule and perceptron) algorithms in neural networks[C]. 2009 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference, Patiala, India, 2009: 296–299. doi: 10.1109/IADCC.2009.4809024. |
| [24] |
ZHOU Feiyan, JIN Linpeng, and DONG Jun. Review of convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(6): 1229–1251. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.01229. |
| [25] |
LIU Jianwei and SONG Zhiyan. Overview of recurrent neural networks[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(11): 2753–2768. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2021.1241. |
| [26] |
WANG Kunfeng, GOU Chao, DUAN Yanjie, et al. Generative adversarial networks: The state of the art and beyond[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 321–332. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.y000003. |
| [27] |
WU Chunxiao, ZHANG Zenghui, CHEN Longyong, et al. Super-resolution for MIMO array SAR 3-D imaging based on compressive sensing and deep neural network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 3109–3124. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3000760. |
| [28] |
SHEN Rong, WEI Shunjun, ZHOU Zichen, et al. Image enhancement of 3-D SAR via U-net framework[C]. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 947–950. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9884760. |
| [29] |
SERAFÍN-GARCÍA S A, NANNINI M, HÄNSCH R, et al. Deep-learning-based view interpolation toward improved TomoSAR focusing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4014205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3424195. |
| [30] |
KUMAR S V, SUN Xinyao, WANG Zheng, et al. A U-net approach for InSAR phase unwrapping and denoising[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(21): 5081. doi: 10.3390/rs15215081. |
| [31] |
ZENG Tianjiao, ZHAN Xu, REN Yu, et al. Exploring spatial feature regularization in deep-learning-based TomoSAR reconstruction: A preliminary study and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5201227. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3521278. |
| [32] |
LIU Liang, REN Yu, ZHANG Xiaoling, et al. Towards realistic TomoSAR reconstruction through light reconstruction and enhancement[C]. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Zhuhai, China, 2024: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICSIDP62679.2024.10869124. |
| [33] |
WANG Shihong, GUO Jiayi, ZHANG Yueting, et al. TomoSAR 3D reconstruction for buildings using very few tracks of observation: A conditional generative adversarial network approach[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(24): 5055. doi: 10.3390/rs13245055. |
| [34] |
WANG Mou, HU Yifei, WEI Shunjun, et al. Unsupervised 3D SAR imaging network based on generative adversary learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2025, 73(7): 4621–4636. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2025.3547742. |
| [35] |
QIAN Kun, WANG Yuanyuan, SHI Yilei, et al. Super-resolving SAR tomography using deep learning[C]. 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 4810–4813. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS47720.2021.9554165. |
| [36] |
GAO Jingkun, YE Yu, LI Shizhong, et al. Fast super-resolution 3D SAR imaging using an unfolded deep network[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICSIDP47821.2019.9173392. |
| [37] |
SHEN Rong, WEI Shunjun, WEN Yanbo, et al. A 3-D imaging method of building with TomoSAR based on DUADMM-net[C]. IGARSS 2023–2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 7933–7936. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10282080. |
| [38] |
LIU Changhao, WANG Yan, DING Zegang, et al. Analysis of deep learning 3-D imaging methods based on UAV SAR[C]. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 2951–2954. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9883292. |
| [39] |
BEBIS G and GEORGIOPOULOS M. Feed-forward neural networks[J]. IEEE Potentials, 1994, 13(4): 27–31. doi: 10.1109/45.329294. |
| [40] |
POPESCU M C, BALAS V E, PERESCU-POPESCU L, et al. Multilayer perceptron and neural networks[J]. WSEAS Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 2009, 8(7): 579–588. doi: 10.5555/1639537.1639542. |
| [41] |
WU Jianxin. Introduction to convolutional neural networks[J]. National Key Lab for Novel Software Technology, Nanjing University, China, 2017, 5(23): 495.
|
| [42] |
BUDILLON A, JOHNSY A C, SCHIRINZI G, et al. SAR tomography based on deep learning[C]. IGARSS 2019–2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 3625–3628. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8900616. |
| [43] |
LIU Changhao, WANG Yan, ZHANG Guangbin, et al. High resolution large elevation synthetic aperture tomographic SAR imaging with classifier-based imaging architecture[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 20666–20677. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3593845. |
| [44] |
OUYANG Depeng, ZHANG Yueting, GUO Jiayi, et al. MLC-net: A sparse reconstruction network for TomoSAR imaging based on multi-label classification neural network[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2025, 220: 85–99. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2024.11.018. |
| [45] |
ZENG Tao, LIU Minkun, WANG Yan, et al. Tomographic SAR imaging with large elevation aperture: A P-band small UAV demonstration[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(3): 132303. doi: 10.1007/s11432-021-3391-2. |
| [46] |
RANGAN S, SCHNITER P, and FLETCHER A K. Vector approximate message passing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2019, 65(10): 6664–6684. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2019.2916359. |
| [47] |
BREDIES K and LORENZ D A. Linear convergence of iterative soft-thresholding[J]. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 2008, 14(5): 813–837. doi: 10.1007/s00041-008-9041-1. |
| [48] |
BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016. |
| [49] |
TROPP J A and GILBERT A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12): 4655–4666. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108. |
| [50] |
WIPF D P and RAO B D. Sparse Bayesian learning for basis selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(8): 2153–2164. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.831016. |
| [51] |
GREGOR K and LECUN Y. Learning fast approximations of sparse coding[C]. The 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel: Omnipress, 2010: 399–406. doi: 10.5555/3104322.3104374. |
| [52] |
QIAN Kun, WANG Yuanyuan, SHI Yilei, et al. γ-net: Superresolving SAR tomographic inversion via deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4706116. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3164193. |
| [53] |
REN Yu, ZHANG Xiaoling, HU Yunqiao, et al. AETomo-Net: A novel deep learning network for tomographic SAR imaging based on multi-dimensional features[C]. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 3464–3467. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9884512. |
| [54] |
WANG Muhan, ZHANG Zhe, QIU Xiaolan, et al. ATASI-Net: An efficient sparse reconstruction network for tomographic SAR imaging with adaptive threshold[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 4701918. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3268132. |
| [55] |
MA Qian, HU Zhongyuan, WANG Chuxin, et al. An adaptive complex LISTA network exploiting Toeplitz structure for TomoSAR 3D reconstruction[C]. 2025 25th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Pylos, Greece, 2025: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/DSP65409.2025.11075068. |
| [56] |
QIAN Kun, WANG Yuanyuan, JUNG P, et al. Basis pursuit denoising via recurrent neural network applied to super-resolving SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4710015. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3221185. |
| [57] |
WANG Yan, LIU Changhao, ZHU Rui, et al. MAda-Net: Model-adaptive deep learning imaging for SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5202413. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3239405. |
| [58] |
LIU Changhao, WANG Yan, ZHANG Guangbin, et al. GITomo-Net: Geometry-independent deep learning imaging method for SAR tomography[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2025, 220: 608–620. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2025.01.004. |
| [59] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, SHI Jun, et al. CSR-Net: A novel complex-valued network for fast and precise 3-D microwave sparse reconstruction[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 4476–4492. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3014696. |
| [60] |
BECK A and TEBOULLE M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(1): 183–202. doi: 10.1137/080716542. |
| [61] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, LIANG Jiadian, et al. TPSSI-Net: Fast and enhanced two-path iterative network for 3D SAR sparse imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 7317–7332. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3104168. |
| [62] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, LIANG Jiadian, et al. RMIST-Net: Joint range migration and sparse reconstruction network for 3-D mmW imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5205117. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3068405. |
| [63] |
YANIK M E, WANG Dan, and TORLAK M. Development and demonstration of MIMO-SAR mmWave imaging testbeds[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 126019–126038. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3007877. |
| [64] |
LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J M and FORTUNY-GUASCH J. 3-D radar imaging using range migration techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2000, 48(5): 728–737. doi: 10.1109/8.855491. |
| [65] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, ZHOU Zichen, et al. CTV-Net: Complex-valued TV-driven network with nested topology for 3-D SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(4): 5588–5602. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3208252. |
| [66] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, LIANG Jiadian, et al. Lightweight FISTA-inspired sparse reconstruction network for mmW 3-D holography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211620. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3093307. |
| [67] |
DEL CAMPO G M, NANNINI M, and REIGBER A. Statistical regularization for enhanced TomoSAR imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 1567–1589. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2970595. |
| [68] |
FU Kun, ZHANG Yue, SUN Xian, et al. A coarse-to-fine method for building reconstruction from HR SAR layover map using restricted parametric geometrical models[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 2004–2008. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2621054. |
| [69] |
TIAN Ye, DING Chibiao, SHI Minan, et al. Layover detection using neural network based on expert knowledge[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(23): 6087. doi: 10.3390/rs14236087. |
| [70] |
田野, 丁赤飚, 张福博, 等. 一种基于深度学习的SAR城市建筑区域叠掩精确检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 441–455. doi: 10.12000/JR23033. TIAN Ye, DING Chibiao, ZHANG Fubo, et al. SAR building area layover detection based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 441–455. doi: 10.12000/JR23033. |
| [71] |
DUAN Haoxuan, LIU Yuzhou, ZHANG Hong, et al. Large-area urban TomoSAR method with limited a priori knowledge and a complex deep learning model[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2025, 139: 104521. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2025.104521. |
| [72] |
MUKHERJEE S, ZIMMER A, KOTTAYIL N K, et al. CNN-based InSAR denoising and coherence metric[C]. 2018 IEEE SENSORS, New Delhi, India, 2018: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICSENS.2018.8589920. |
| [73] |
LI Jie, XU Zhongqiu, LI Zhiyuan, et al. A CNN-based multichannel interferometric phase denoising method applied to TomoSAR imaging[C]. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 3448–3451. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9884475. |
| [74] |
LI Jie, XU Zhongqiu, LI Zhiyuan, et al. An unsupervised CNN-based multichannel interferometric phase denoising method applied to TomoSAR imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 3784–3796. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3263964. |
| [75] |
SHI Yilei, WANG Yuanyuan, ZHU Xiaoxiang, et al. Non-local SAR tomography for large-scale urban mapping[C]. IGARSS 2019–2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 5197–5200. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8897890. |
| [76] |
VITALE S, FERRAIOLI G, PASCAZIO V, et al. InSAR-MONet: Interferometric SAR phase denoising using a multiobjective neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5239814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3224303. |
| [77] |
ZHANG Qi, JIANG Houjun, and WANG Teng. A semi-supervised self-boosting learning method for InSAR phase denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5513916. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3568932. |
| [78] |
AGHABABAEI H, FERRAIOLI G, VITALE S, et al. A deep learning solution for phase screen estimation in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2025, 22: 4007605. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2025.3555441. |
| [79] |
ZHANG Siqian, DONG Ganggang, and KUANG Gangyao. Matrix completion for downward-looking 3-D SAR imaging with a random sparse linear array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 1994–2006. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2771826. |
| [80] |
ZHOU Siyan, LI Yanlei, ZHANG Fubo, et al. Automatic regularization of TomoSAR point clouds for buildings using neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(17): 3748. doi: 10.3390/s19173748. |
| [81] |
ERTIN E, AUSTIN C D, SHARMA S, et al. GOTCHA experience report: Three-dimensional SAR imaging with complete circular apertures[C]. Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XIV, Orlando, USA, 2007: 656802. doi: 10.1117/12.723245. |
| [82] |
MUPPALA A V, NASHASHIBI A Y, AFSHARI E, et al. Fast-Fourier time-domain SAR reconstruction for millimeter-wave FMCW 3-D imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2024, 72(12): 7028–7038. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2024.3406938. |
| [83] |
仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 彭凌霄, 等. SARMV3D-1.0: SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112. QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112. |
| [84] |
仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 杨振礼, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR关键技术及实验系统初步进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027. QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, YANG Zhenli, et al. Key technology and preliminary progress of microwave vision 3D SAR experimental system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027. |
| [85] |
仇晓兰, 罗一通, 宋舒洁, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR实验系统及其全极化数据处理方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(5): 941–954. doi: 10.12000/JR24137. QIU Xiaolan, LUO Yitong, SONG Shujie, et al. Microwave vision three-dimensional SAR experimental system and full-polarimetric data processing method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(5): 941–954. doi: 10.12000/JR24137. |
| [86] |
WEI Shunjun, ZHOU Zichen, WANG Mou, et al. 3DRIED: A high-resolution 3-D millimeter-wave radar dataset dedicated to imaging and evaluation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(17): 3366. doi: 10.3390/rs13173366. |
| [87] |
BI Hui, JIN Shuang, XU Weihao, et al. First three-dimensional imaging experiment of Chinese commercial SAR satellite Fucheng-1[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2025, 68(7): 177301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-024-4418-8. |
| [88] |
王岩, 刘常浩, 王昊泽, 等. DistUAV-Tomo3D-1.0: 分布式无人机雷达多发多收单航过层析三维成像数据集[J]. 信号处理, 2025, 41(8): 1436–1442. doi: 10.12466/xhcl.2025.08.012. WANG Yan, LIU Changhao, WANG Haoze, et al. DistUAV-Tomo3D-1.0: Distributed UAV radar multiple transmit-receive single-pass tomographic SAR 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2025, 41(8): 1436–1442. doi: 10.12466/xhcl.2025.08.012. |
| [89] |
焦润之, 邓嘉, 韩亚权, 等. 3DSARBuSim 1.0: 人造建筑高分辨星载SAR三维成像仿真数据集[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(7): 2681–2693. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230882. JIAO Runzhi, DENG Jia, HAN Yaquan, et al. 3DSARBuSim 1.0: High-resolution space borne SAR 3D imaging simulation dataset of man-made buildings[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(7): 2681–2693. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230882. |
| [90] |
WEI Lianhuan, FENG Qiuyue, LIU Shanjun, et al. Minimum redundancy array — a baseline optimization strategy for urban SAR tomography[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(18): 3100. doi: 10.3390/rs12183100. |
| [91] |
LI Ying, WANG Yan, DING Zegang, et al. Dual-frequency SAR tomography with long sparse non-uniform baseline in ground-based lunar mapping[C]. 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 2915–2918. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS47720.2021.9553160. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: