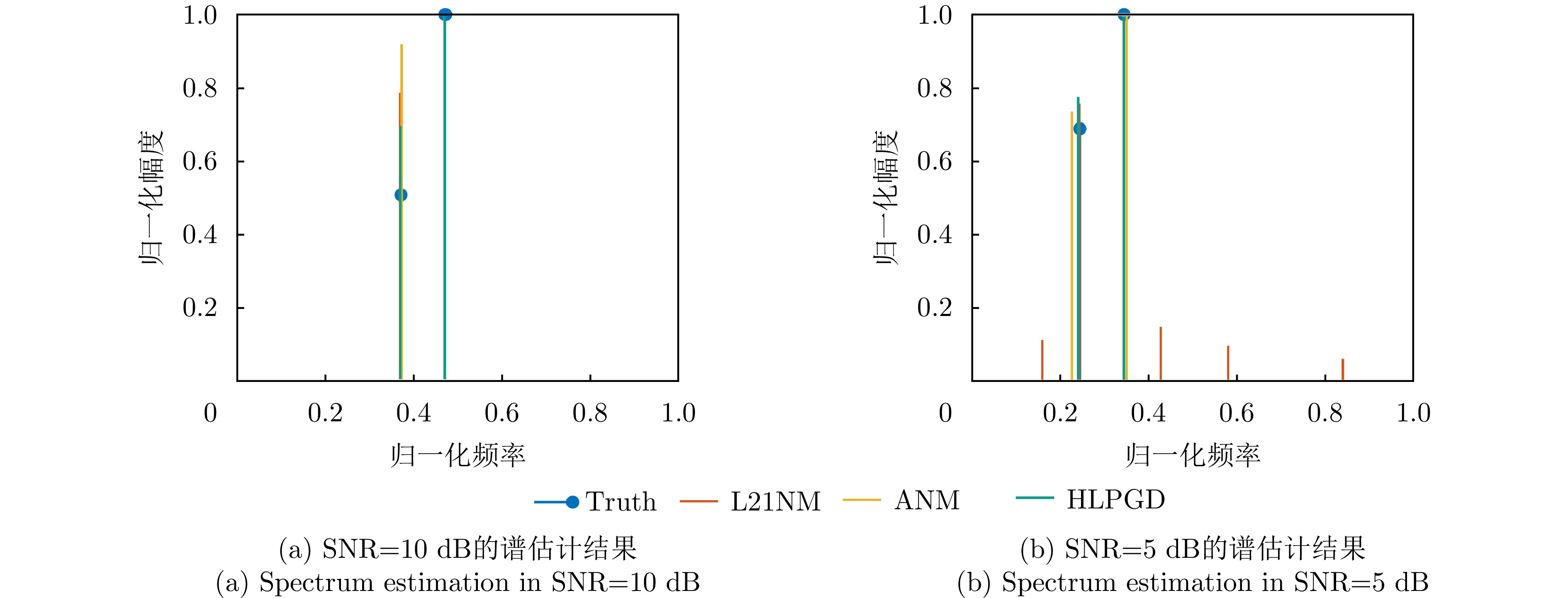
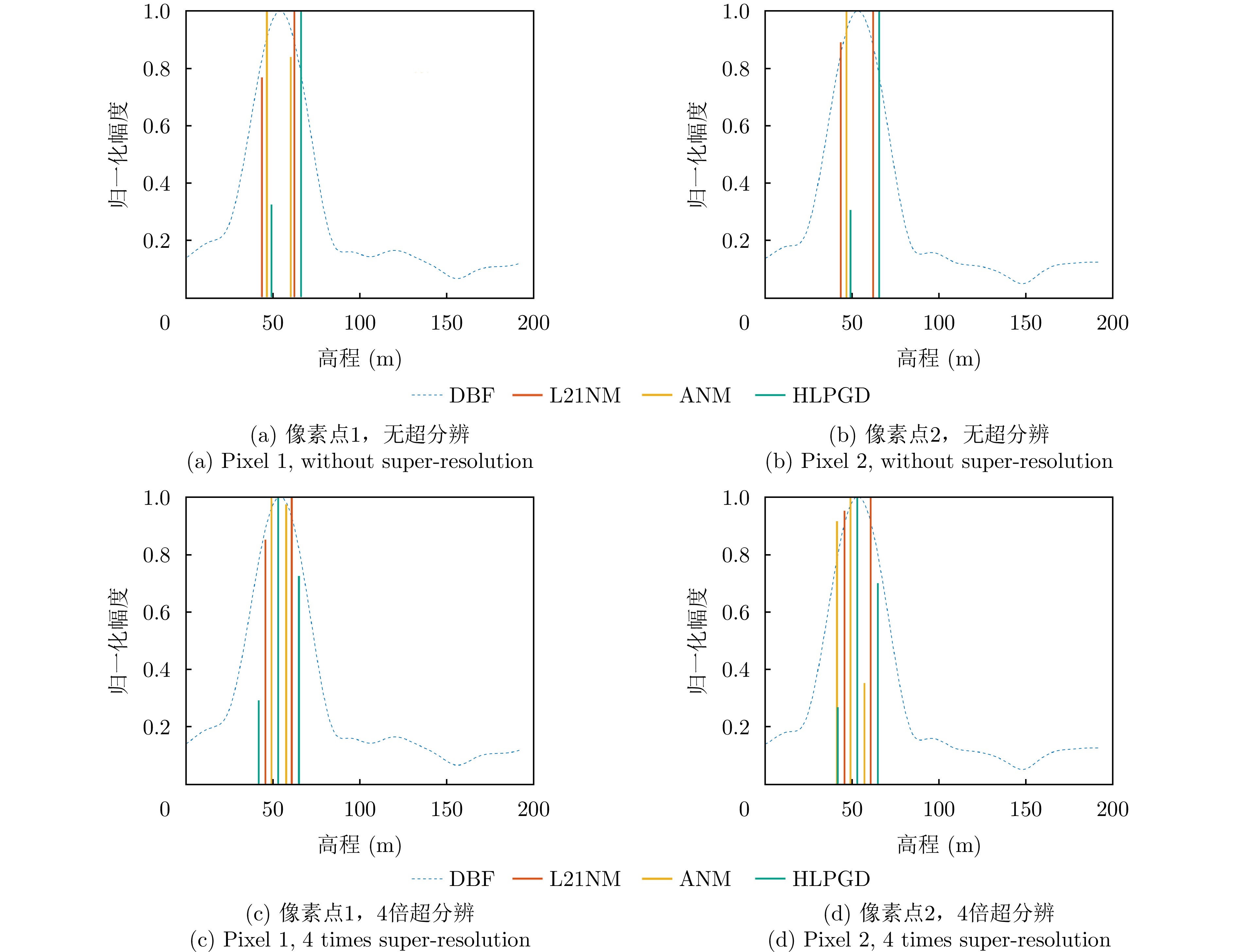
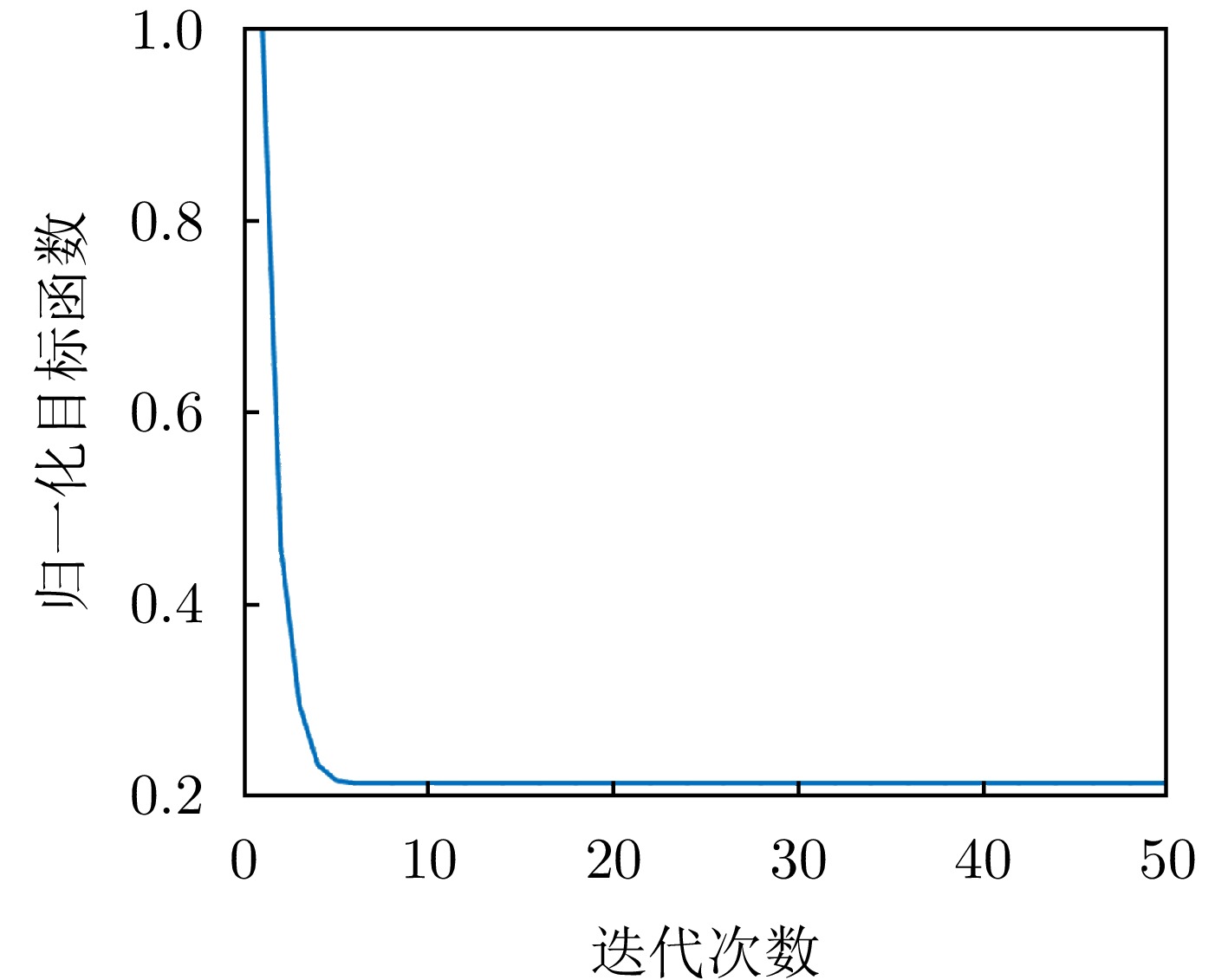
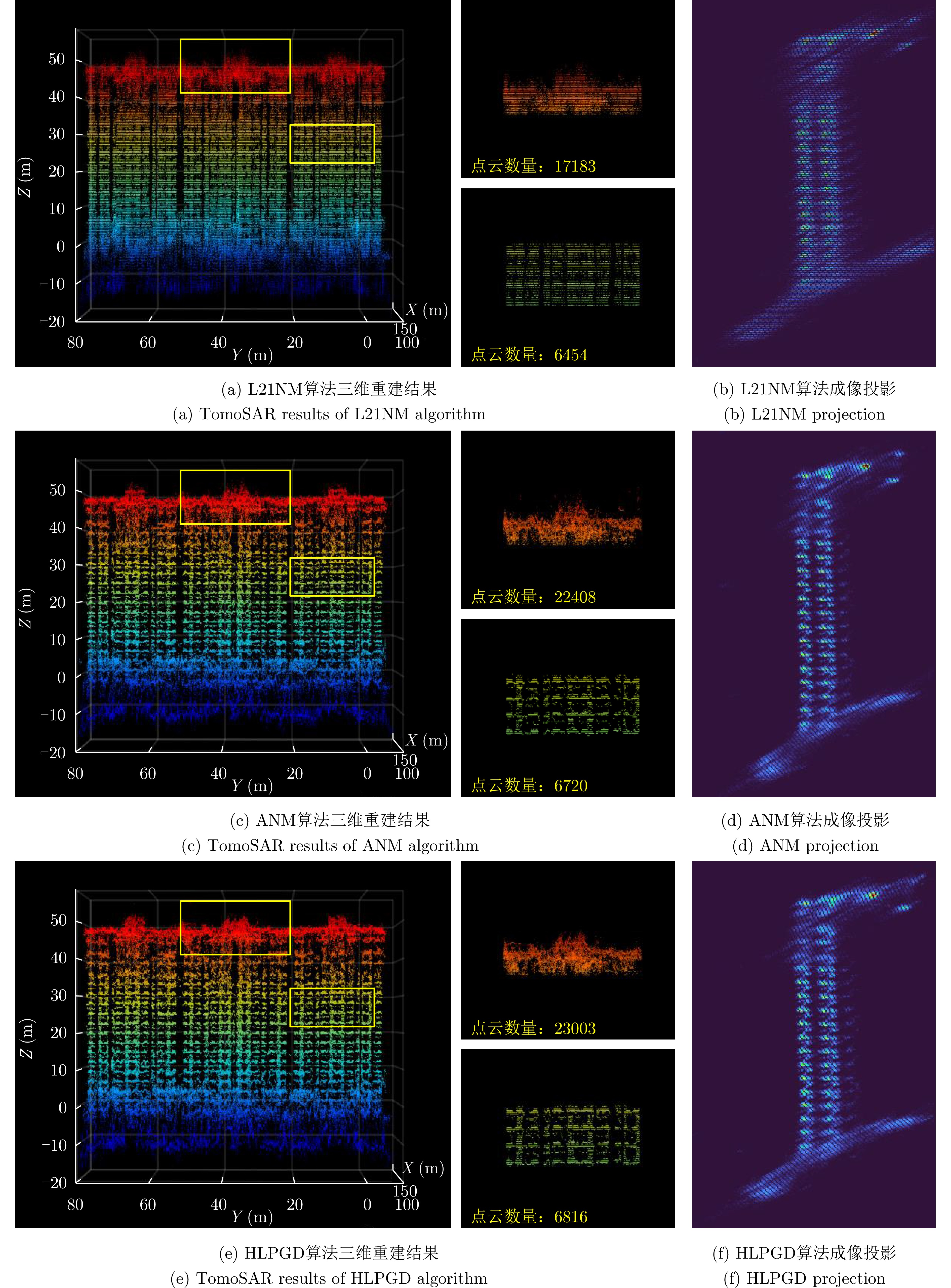
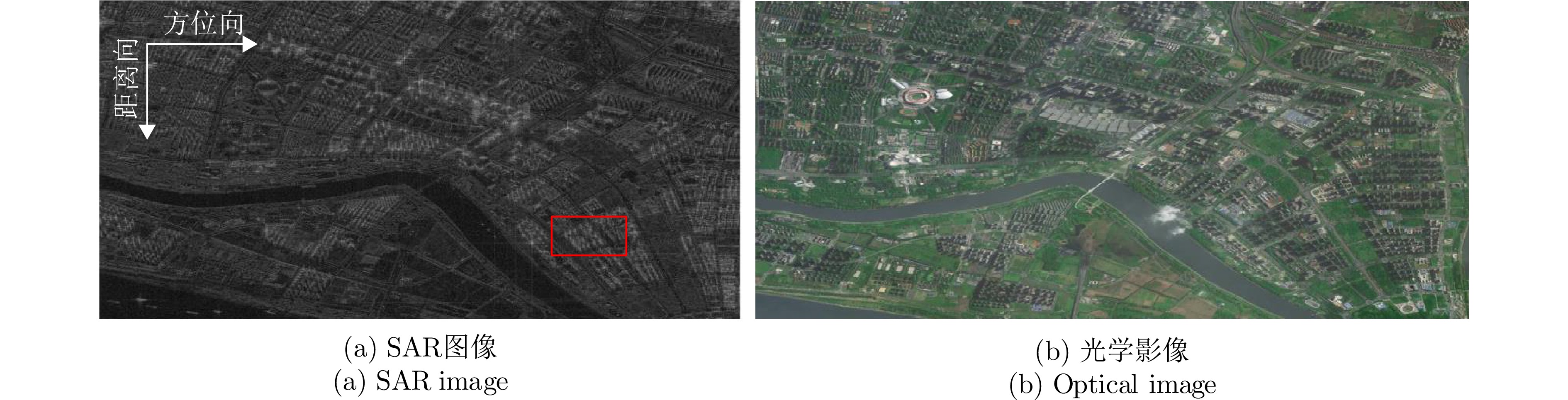
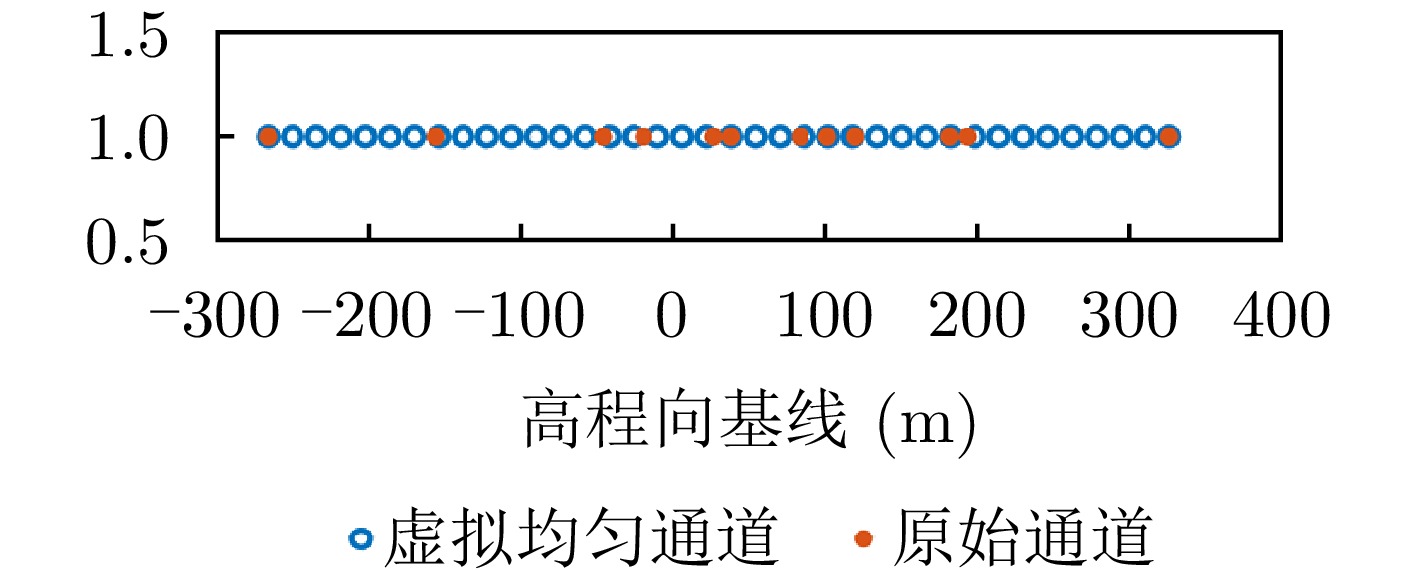
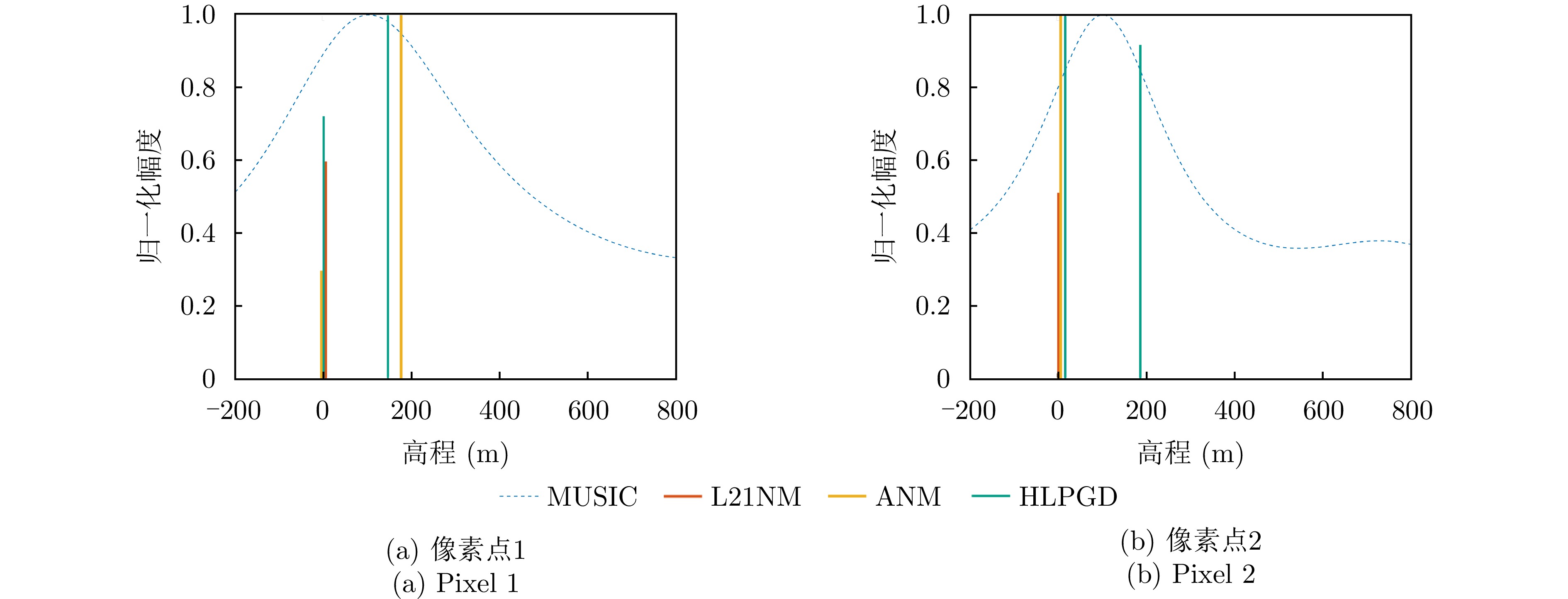
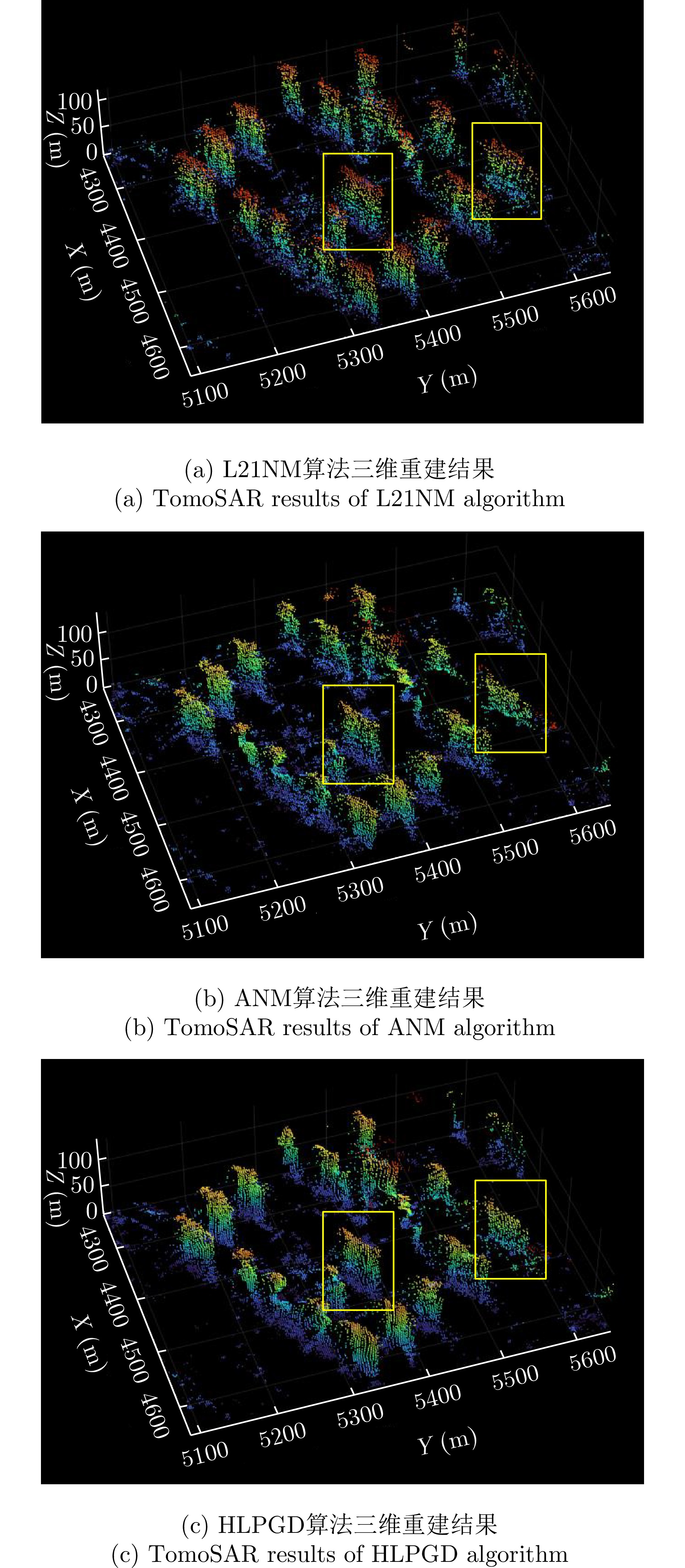
| [1] |
FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, and SERAFINO F. Three-dimensional multipass SAR focusing: Experiments with long-term spaceborne data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(4): 702–714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.843567. |
| [2] |
REIGBER A, MOREIRA A, and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Hamburg, Germany, 1999: 44–46. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1999.773395. |
| [3] |
FORNARO G and SERAFINO F. Imaging of single and double scatterers in urban areas via SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(12): 3497–3505. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.881748. |
| [4] |
丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像——从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090. DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090. |
| [5] |
WANG Chaodong, LI Zhongyu, HAI Yu, et al. Multistatic TomoSAR 3-D imaging technique via matrix completion for structured targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5215716. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3563481. |
| [6] |
毕辉, 金双, 王潇, 等. 基于高分三号SAR数据的城市建筑高分辨率高维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 40–51. doi: 10.12000/JR21113. BI Hui, JIN Shuang, WANG Xiao, et al. High-resolution high-dimensional imaging of urban building based on GaoFen-3 SAR data[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 40–51. doi: 10.12000/JR21113. |
| [7] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2050487. |
| [8] |
ZHU Xiaoxinag and BAMLER R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098. |
| [9] |
RAMBOUR C, DENIS L, TUPIN F, et al. Introducing spatial regularization in SAR tomography reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8600–8617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2921756. |
| [10] |
YANG Zai and XIE Lihua. On gridless sparse methods for line spectral estimation from complete and incomplete data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3139–3153. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2420541. |
| [11] |
LI Yuanxin and CHI Yuejie. Off-the-grid line spectrum denoising and estimation with multiple measurement vectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(5): 1257–1269. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2496294. |
| [12] |
杜邦, 仇晓兰, 张柘, 等. 基于扰动的结合Off-grid目标的层析SAR三维成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 62–70. doi: 10.12000/JR21093. DU Bang, QIU Xiaolan, ZHANG Zhe, et al. L1 minimization with perturbation for Off-grid tomographic SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 62–70. doi: 10.12000/JR21093. |
| [13] |
CANDÈS E J and FERNANDEZ-GRANDA C. Towards a mathematical theory of super-resolution[J]. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 2014, 67(6): 906–956. doi: 10.1002/cpa.21455. |
| [14] |
CHI Yuejie and FERREIRA DA COSTA M. Harnessing sparsity over the continuum: Atomic norm minimization for superresolution[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(2): 39–57. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2019.2962209. |
| [15] |
YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(1): 38–43. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2222378. |
| [16] |
TANG Gongguo, BHASKAR B N, SHAH P, et al. Compressed sensing off the grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(11): 7465–7490. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2277451. |
| [17] |
WANG Xiao and XU Feng. Tomographic SAR inversion by atomic-norm minimization—the gridless compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5239113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3223524. |
| [18] |
WANG Xiao and XU Feng. Efficient ADMM algorithm for atomic norm minimization in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5211415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3395510. |
| [19] |
GAO Silin, WANG Wenlong, WANG Muhan, et al. A robust super-resolution gridless imaging framework for UAV-borne SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5210917. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3393972. |
| [20] |
ZHANG Bangjie, XU Gang, YU Hanwen, et al. Array 3-D SAR tomography using robust gridless compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5205013. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3259980. |
| [21] |
LIU Minkun, WANG Yan, DING Zegang, et al. Atomic norm minimization based fast off-grid tomographic SAR imaging with nonuniform sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5203517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3358863. |
| [22] |
SHAO Mingxiao, ZHANG Zhe, LI Jie, et al. TADCG: A novel gridless tomographic SAR imaging approach based on the alternate descent conditional gradient algorithm with robustness and efficiency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5201213. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3345454. |
| [23] |
ZHANG Shuai, HAO Yingshuai, WANG Meng, et al. Multichannel Hankel matrix completion through nonconvex optimization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(4): 617–632. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2827299. |
| [24] |
CHEN Yuxin and CHI Yuejie. Robust spectral compressed sensing via structured matrix completion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(10): 6576–6601. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2014.2343623. |
| [25] |
CAI Jianfeng, WANG Tianming, and WEI Ke. Spectral compressed sensing via projected gradient descent[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2018, 28(3): 2625–2653. doi: 10.1137/17M1141394. |
| [26] |
LI Jinsheng, CUI Wei, and ZHANG Xu. Projected gradient descent for spectral compressed sensing via symmetric Hankel factorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 1590–1606. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3378004. |
| [27] |
仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 彭凌霄, 等. SARMV3D-1.0: SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112. QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112. |
| [28] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang, GE Nan, and SHAHZAD M. Joint sparsity in SAR tomography for urban mapping[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1498–1509. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2469646. |
| [29] |
XU Gang, ZHANG Bangjie, YU Hanwen, et al. Sparse synthetic aperture radar imaging from compressed sensing and machine learning: Theories, applications, and trends[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2022, 10(4): 32–69. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2022.3218801. |
| [30] |
杨磊, 王腾腾, 陈英杰, 等. 低秩矩阵补全高分辨SAR成像特征重建[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(8): 2965–2974. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220992. YANG Lei, WANG Tengteng, CHEN Yingjie, et al. Feature reconstruction of high resolution SAR imagery based on low rank matrix completion[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(8): 2965–2974. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220992. |
| [31] |
MAO Sihan and CHEN Jinchi. Blind super-resolution of point sources via projected gradient descent[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 4649–4664. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3209006. |
| [32] |
VU T and RAICH R. On asymptotic linear convergence of projected gradient descent for constrained least squares[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 4061–4076. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3192142. |
| [33] |
RAO B D and HARI K V S. Performance analysis of Root-MUSIC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(12): 1939–1949. doi: 10.1109/29.45540. |
| [34] |
BUDILLON A and SCHIRINZI G. GLRT based on support estimation for multiple scatterers detection in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1086–1094. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2494376. |
| [35] |
任烨仙, 徐丰. 若干层析SAR成像方法在解叠掩性能上的对比分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 71–82. doi: 10.12000/JR21139. REN Yexian and XU Feng. Comparative experiments on separation performance of overlapping scatterers with several tomography imaging methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 71–82. doi: 10.12000/JR21139. |
| [36] |
姬昂, 裴昊, 张邦杰, 等. 阵列SAR高分辨三维成像与点云聚类研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5): 2087–2094. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231223. JI Ang, PEI Hao, ZHANG Bangjie, et al. Research on high-resolution 3D imaging and point cloud clustering of array SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(5): 2087–2094. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231223. |
| [37] |
任子帅, 张照, 高雨欣, 等. 基于自适应高程约束的TomoSAR三维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(5): 1056–1068. doi: 10.12000/JR23111. REN Zishuai, ZHANG Zhao, GAO Yuxin, et al. Three-dimensional imaging of tomographic SAR based on adaptive elevation constraint[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(5): 1056–1068. doi: 10.12000/JR23111. |
| [38] |
LI Tao, TANG Xinming, ZHANG Xiang, et al. First application demonstrations of Lu Tan-1 SAR satellites[C]. 2023 SAR in Big Data Era (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 2023: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/BIGSARDATA59007.2023.10294711. |
| [39] |
XU Gang, CHEN Yuzhi, JI Ang, et al. 3-D high-resolution imaging and array calibration of ground-based millimeter-wave MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2024, 72(8): 4919–4931. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2024.3352406. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: