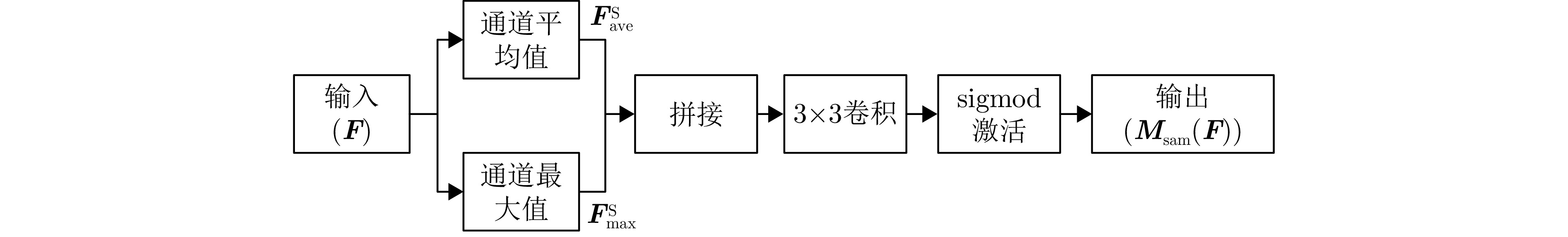
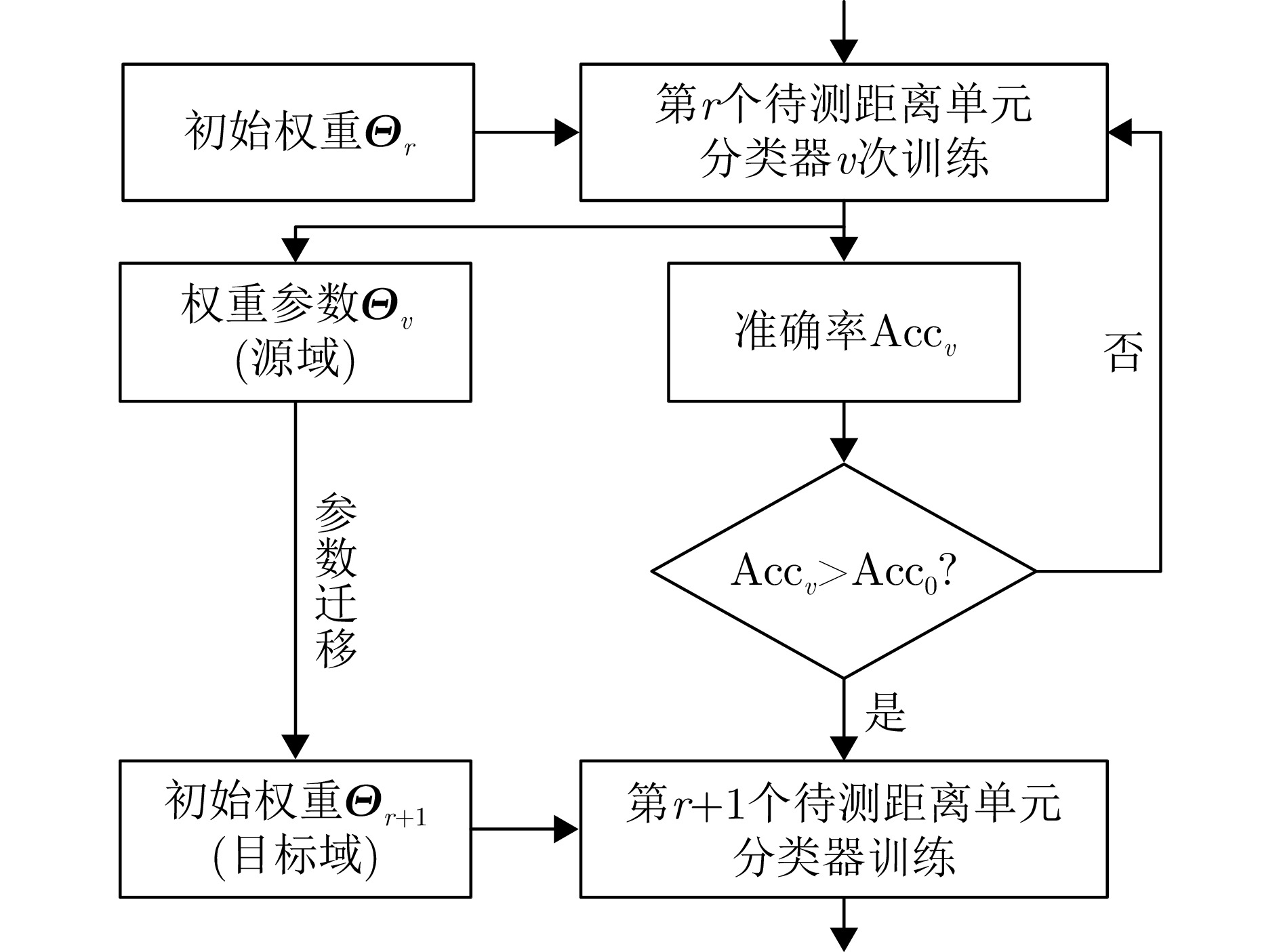
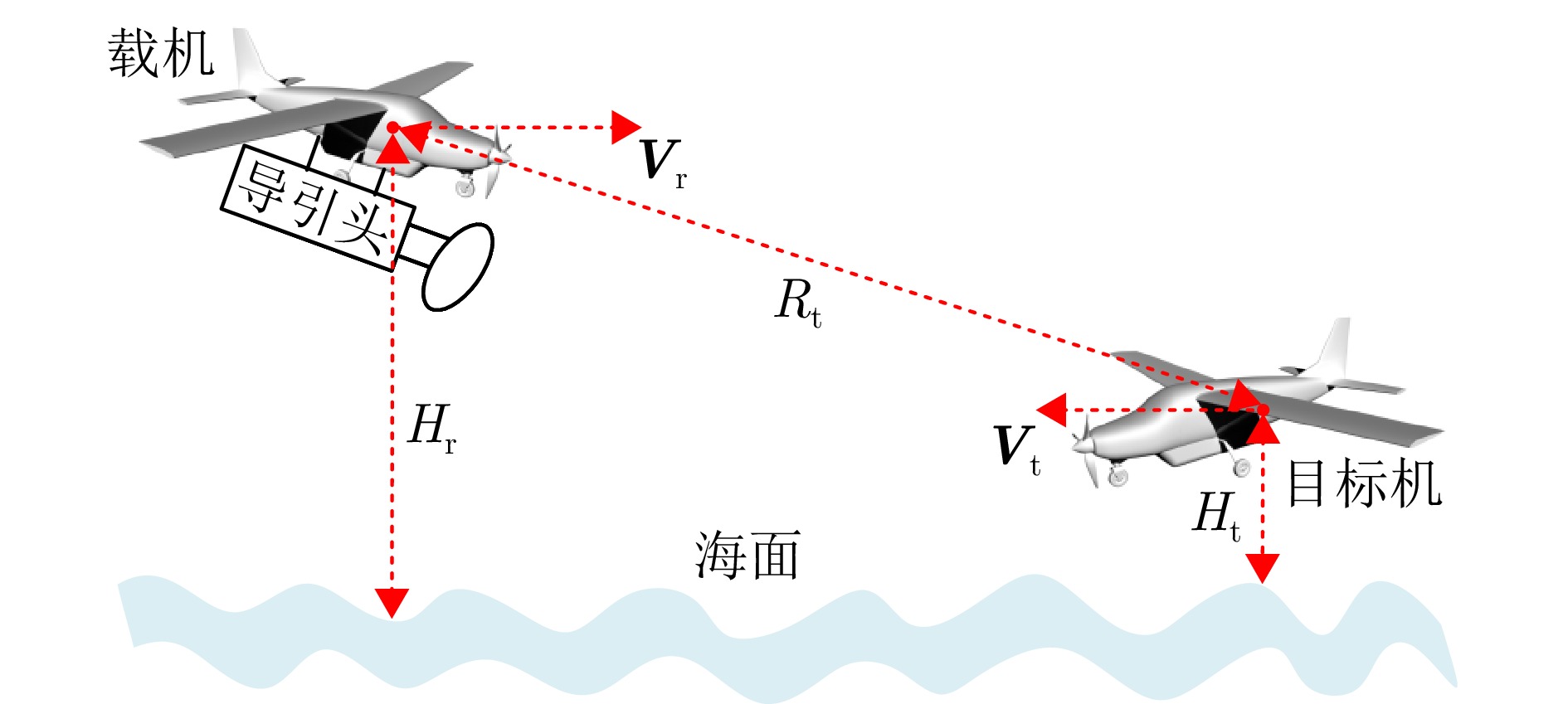
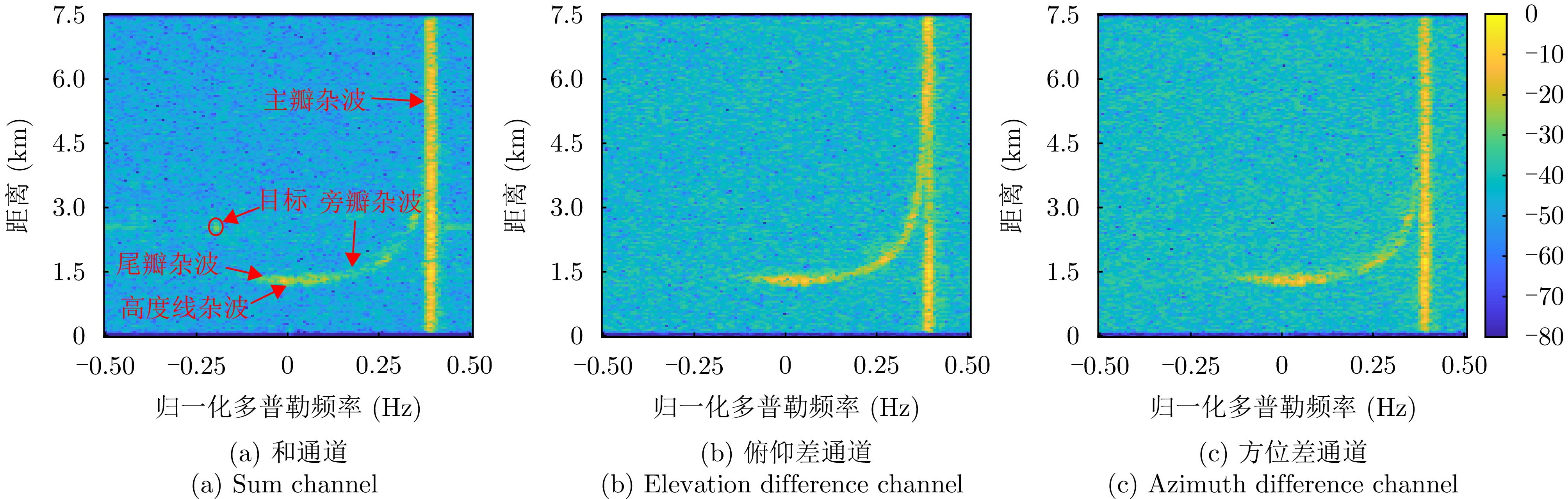
| [1] |
HUANG Penghui, YANG Hao, ZOU Zihao, et al. Multichannel clutter modeling, analysis, and suppression for missile-borne radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 3236–3260. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3147136. |
| [2] |
XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Research on STAP approach of forward looking array radar with high-velocity[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2013, 35(3): 509–515. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00992. |
| [3] |
MELVIN W L. A STAP overview[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2004, 19(1): 19–35. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2004.1263229. |
| [4] |
REED I S, MALLETT J D, and BRENNAN L E. Rapid convergence rate in adaptive arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1974, AES-10(6): 853–863. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1974.307893. |
| [5] |
SHI Jieming, CHENG Ziyang, LI Jun, et al. Pulse interval optimization for Doppler ambiguity clutter suppression in missile-borne STAP radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3506205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3371438. |
| [6] |
HE Songhua, HU Xia, and ZHANG Jun. Channel-level STAP method for lofty target detection of missile-borne wideband phased-array radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2016, 32(5): 528–535. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2016.05.004. |
| [7] |
XIONG Yuanyi, XIE Wenchong, WANG Yongliang, et al. Short-range nonstationary clutter suppression for airborne KA-STAP radar in complex terrain environment[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 2766–2776. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3522257. |
| [8] |
LI Jun’ao, LI Zhongyu, YANG Qing, et al. Efficient matrix sparse recovery STAP method based on Kronecker transform for BiSAR sea clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5103218. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3362844. |
| [9] |
WANG Xiangrong, ABOUTANIOS E, and AMIN M G. Reduced-rank STAP for slow-moving target detection by antenna-pulse selection[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(8): 1156–1160. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2390148. |
| [10] |
WANG Haihong, DUAN Keqing, SHEN Wei, et al. Reduced-dimensional STAP method for nonstationary clutter suppression in endfire array airborne radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(17): 27750–27762. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3429173. |
| [11] |
XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Clutter characteristic and suppression approach for missile-borne diving non-broadside array radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(8): 1631–1637. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.08.08. |
| [12] |
LI Haodong, LIAO Guisheng, and XU Jingwei. Robust adaptive clutter suppression approach for missile-borne radar with $\Sigma\Delta $-beam[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(2): 273–279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.02.08. |
| [13] |
EL KHATIB A, ASSALEH K, and MIR H. Learning-based space-time adaptive processing[C]. The 1st International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and their Applications (ICCSPA), Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2013: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICCSPA.2013.6487279. |
| [14] |
EL KHATIB A, ASSALEH K, and MIR H. Space-time adaptive processing using pattern classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(3): 766–779. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2385653. |
| [15] |
刘喆, 许晓晴. 基于支持向量机的动目标显示方法研究[C]. 第十四届全国雷达学术年会, 成都, 2017: 1–6.
LIU Zhe and XU Xiaoqing. Research on moving target indication method based on support vector machine[C]. The 14th National Radar Conference, Chengdu, China, 2017: 1–6.
|
| [16] |
LIU Zhe, HO D K C, XU Xiaoqing, et al. Moving target indication using deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 65651–65660. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2877018. |
| [17] |
LI Guifeng, TONG Ningning, FENG Weike, et al. Airborne radar moving target detection based on DenseNet[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University: Natural Science Edition, 2021, 22(2): 83–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2021.02.013. |
| [18] |
HOU Yunfei, ZHANG Yingnan, GUI Wenzhu, et al. CNN-based moving target detection for airborne radar with controllable false alarm module[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3508405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3438948. |
| [19] |
TAO Haihong, GUO Xiaoshuang, SUN Chenwei, et al. Dimensionality reduction of phased array and 4-channel monopulse angle measurement of sum and difference beams[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019, 39(1): 75–80. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.01.013. |
| [20] |
佘胜团. 毫米波单脉冲天线阵和低副瓣天线阵的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2006: 30–34.
SHE Shengtuan. Study of millimetre-wave monopulse antenna arrays and low paraflap antenna arrays[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2006: 30–34.
|
| [21] |
BROWN R D, SCHNEIBLE R A, WICKS M C, et al. STAP for clutter suppression with sum and difference beams[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36(2): 634–646. doi: 10.1109/7.845254. |
| [22] |
LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791. |
| [23] |
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386. |
| [24] |
SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 40–49.
|
| [25] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. |
| [26] |
HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243. |
| [27] |
ZHU Xizhou, CHENG Dazhi, ZHANG Zheng, et al. An empirical study of spatial attention mechanisms in deep networks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 6687–6696. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00679. |
| [28] |
SHAO Ling, ZHU Fan, and LI Xuelong. Transfer learning for visual categorization: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(5): 1019–1034. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2330900. |
| [29] |
陈一凡, 刘剑刚, 贾勇, 等. 基于仿真样本迁移学习的穿墙雷达高分辨成像方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 807–821. doi: 10.12000/JR24049. CHEN Yifan, LIU Jiangang, JIA Yong, et al. High-resolution imaging method for through-the-wall radar based on transfer learning with simulation samples[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 807–821. doi: 10.12000/JR24049. |
| [30] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026–1034. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.123. |
| [31] |
WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: