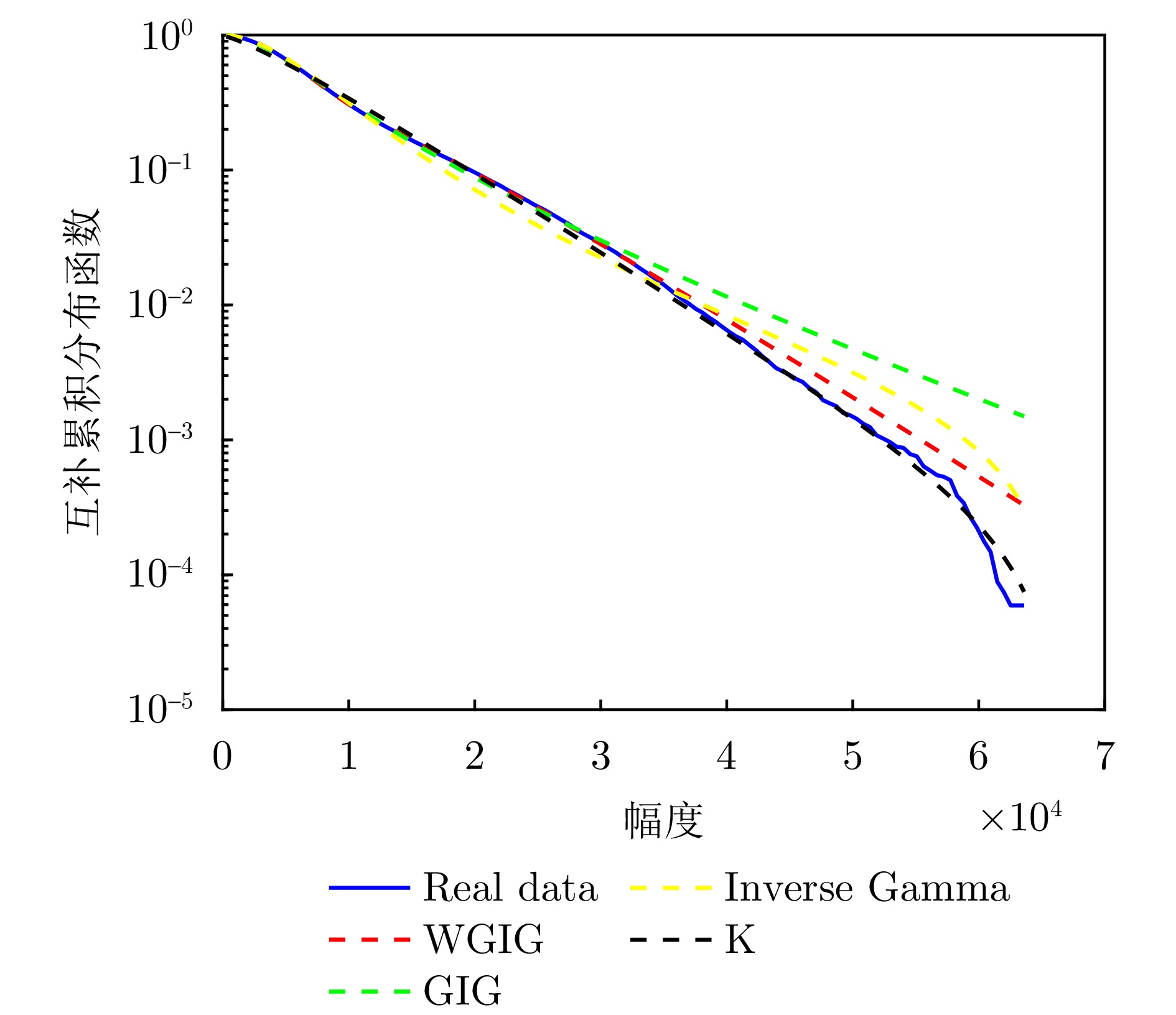
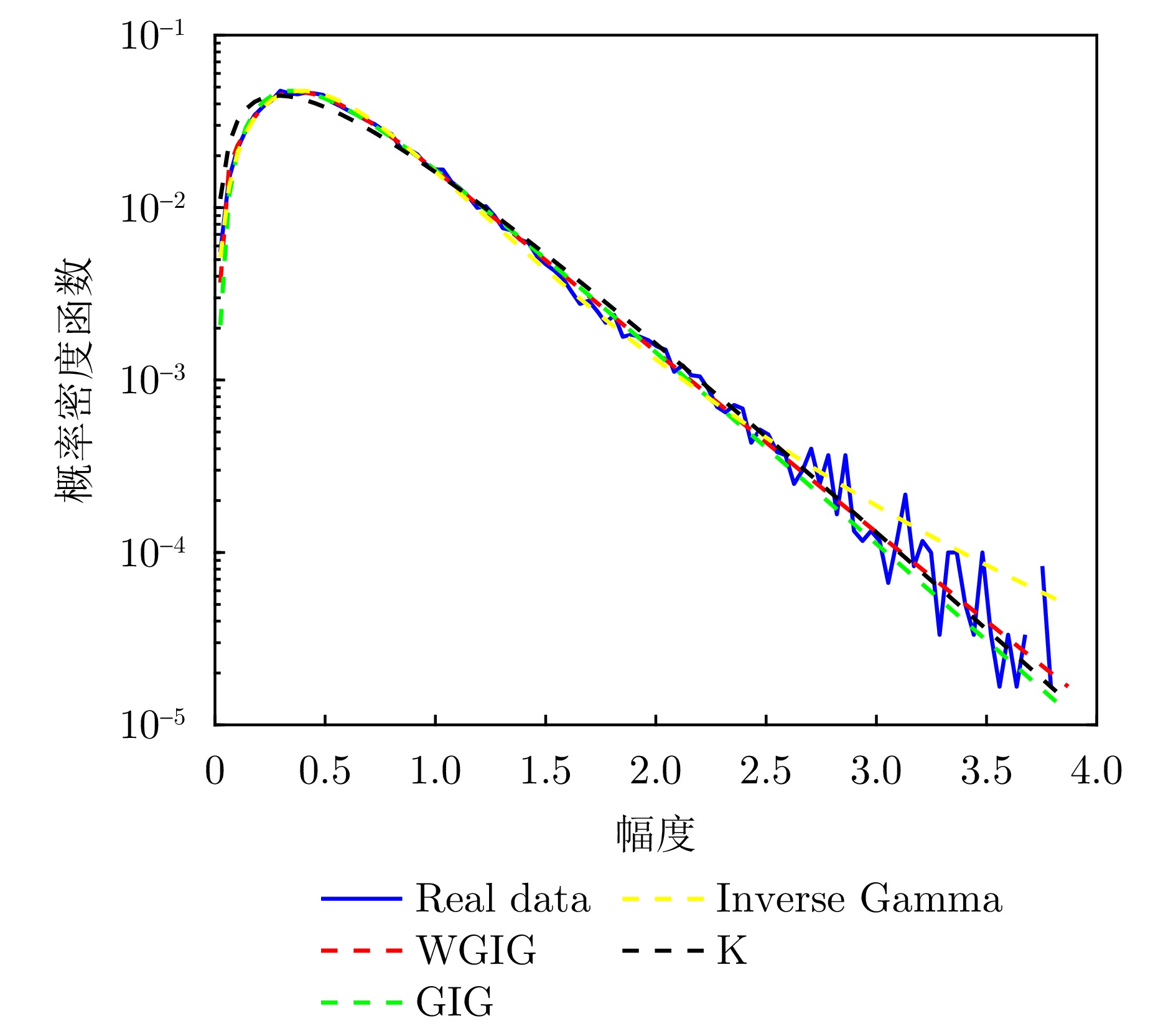
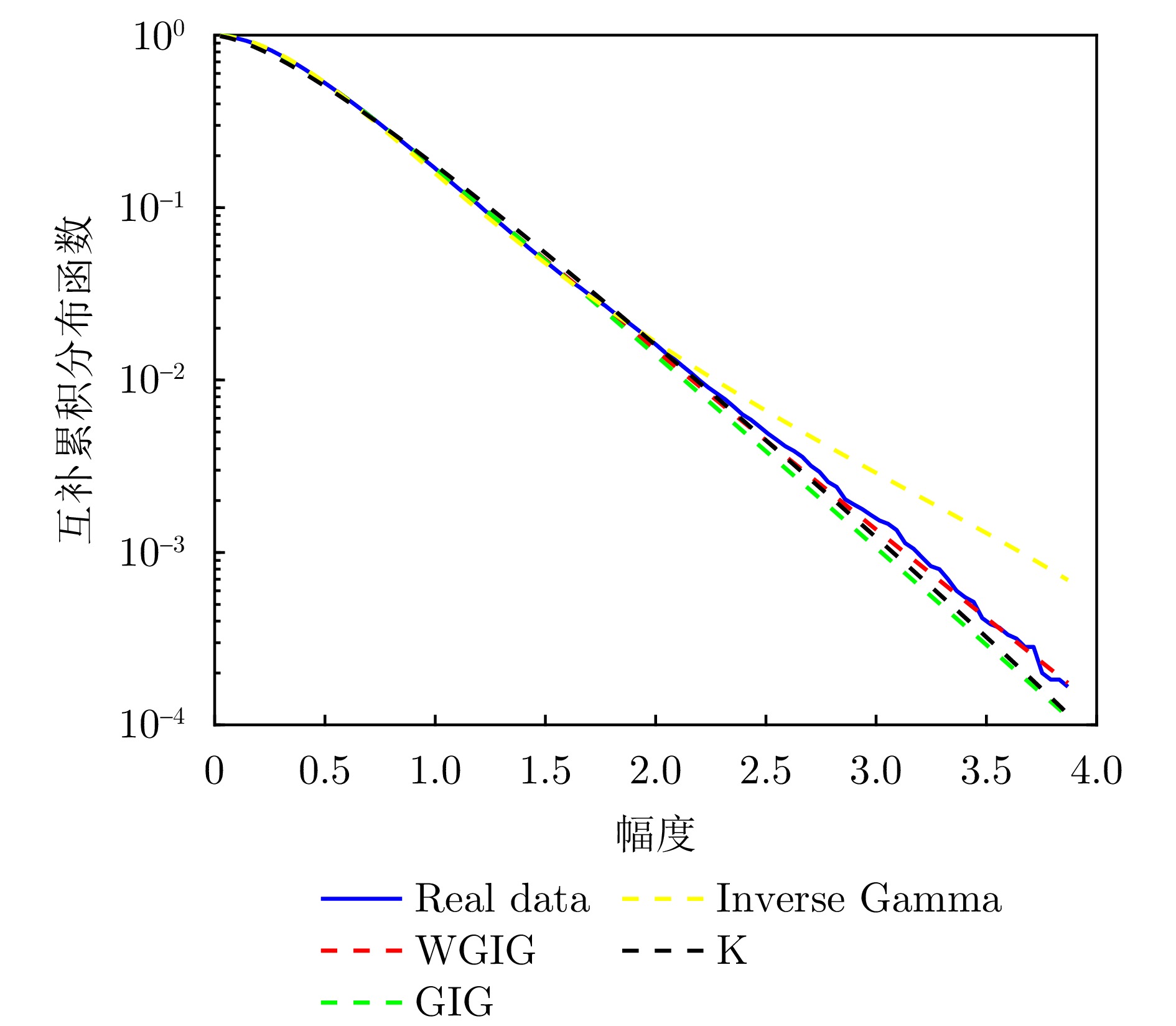
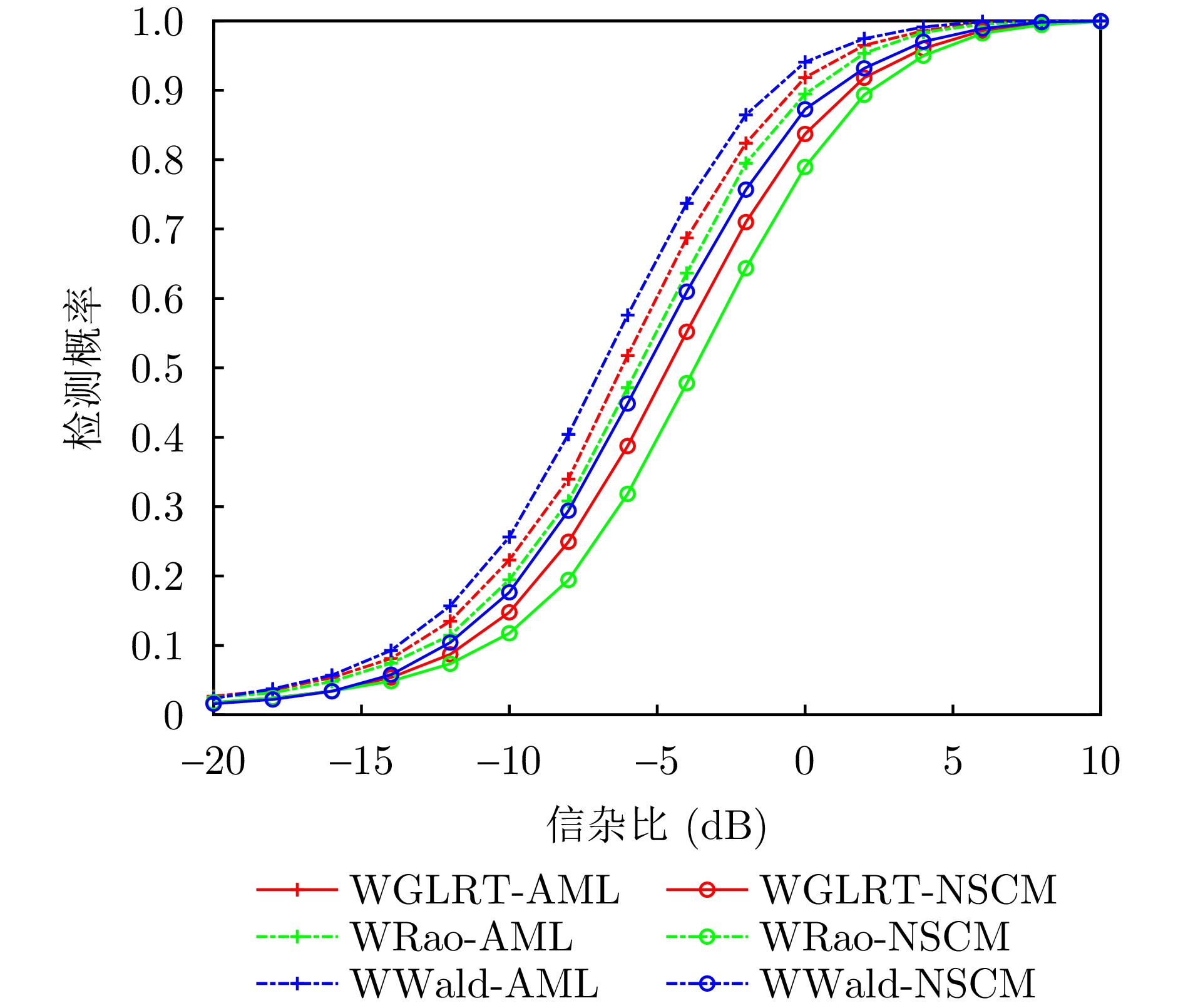
| [1] |
BANDIERA F, DE MAIO A, GRECO A S, et al. Adaptive radar detection of distributed targets in homogeneous noise plus subspace interference[C]. Conference Record of the Thirty-Ninth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2005: 765–769. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2005.1599856. |
| [2] |
LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, HAO Chengpeng, et al. Multichannel adaptive signal detection: Basic theory and literature review[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(2): 121301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3211-8. |
| [3] |
LIU Weijian, XIE Wenchong, LIU Jun, et al. Adaptive double subspace signal detection in Gaussian background—Part I: Homogeneous environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(9): 2345–2357. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2309556. |
| [4] |
HUGHES P K. A high-resolution radar detection strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1983, AES-19(5): 663–667. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1983.309368. |
| [5] |
GRECO M, GINI F, and RANGASWAMY M. Non-stationarity analysis of real X-band clutter data at different resolutions[C]. 2006 IEEE Radar Conference, Verona, USA, 2006: 44–50. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631774. |
| [6] |
GINI F and GRECO M. Texture modelling, estimation and validation using measured sea clutter data[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2002, 149(3): 115–124. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20020272. |
| [7] |
RANGASWAMY M. Spherically invariant random processes for modeling non-Gaussian radar clutter[C]. The 27th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 1993: 1106–1110. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.1993.342399. |
| [8] |
ZOU Pengjia, CHANG Siyuan, and SHUI Penglang. Compound-Gaussian clutter model with Weibull-distributed textures and parameter estimation[J] Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(16): 2912. doi: 10.3390/rs16162912. |
| [9] |
XU Shuwen, SHUI Penglang, and CAO Yunhe. Adaptive range-spread maneuvering target detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2015, 36: 46–56. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2014.09.010. |
| [10] |
CONTE E, DI BISCEGLIE M, LONGO M, et al. Canonical detection in spherically invariant noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1995, 43(2/4): 347–353. doi: 10.1109/26.380053. |
| [11] |
HE You, JIAN Tao, SU Feng, et al. Novel range-spread target detectors in non-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 1312–1328. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545191. |
| [12] |
JIANG Qing, WU Yuntao, LIU Weijian, et al. Subspace-based distributed target detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2023, 140: 104141. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2023.104141. |
| [13] |
许述文, 石星宇, 水鹏朗. 复合高斯杂波下抑制失配信号的自适应检测器[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 326–334. doi: 10.12000/JR19030. XU Shuwen, SHI Xingyu, and SHUI Penglang. An adaptive detector with mismatched signals rejection in compound Gaussian clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 326–334. doi: 10.12000/JR19030. |
| [14] |
YANG Yong, XIAO Shunping, WANG Xuesong, et al. Performance analysis of radar detection for correlated Gamma fluctuating targets in K distributed sea clutter[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2018, 79: 136–141. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2018.05.001. |
| [15] |
SHANG Xiuqin, SONG Hongjun, WANG Yu, et al. Adaptive detection of distributed targets in compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse gamma texture[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2012, 22(6): 1024–1030. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2012.05.002. |
| [16] |
WANG Qing, ZHOU Xuan, LIU Weijian, et al. Adaptive detection of point targets in compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse gamma texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 3967–3978. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3374715. |
| [17] |
丁昊, 王国庆, 刘宁波, 等. 逆Gamma纹理背景下两类子空间目标的自适应检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR16088. DING Hao, WANG Guoqing, LIU Ningbo, et al. Adaptive detectors for two types of subspace targets in an inverse Gamma textured background[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR16088. |
| [18] |
GAO Yongchan, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. A persymmetric GLRT for adaptive detection in compound-Gaussian clutter with random texture[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(6): 615–618. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2259232. |
| [19] |
OLLILA E, TYLER D E, KOIVUNEN V, et al. Compound-Gaussian clutter modeling with an inverse Gaussian texture distribution[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2012, 19(12): 876–879. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2221698. |
| [20] |
GAO Yongchan, LIAO Guisheng, and ZHU Shengqi. Adaptive signal detection in compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[C]. 2013 14th International Radar Symposium, Dresden, Germany, 2013: 935–940.
|
| [21] |
XUE Jian, XU Shuwen, and SHUI Penglang. Knowledge-based target detection in compound Gaussian clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 95: 102590. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2019.102590. |
| [22] |
XUE Jian, XU Shuwen, LIU Jun, et al. Model for non-Gaussian sea clutter amplitudes using generalized inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(6): 892–896. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2886782. |
| [23] |
GUO Hongzhi, WANG Zhihang, HE Zishu, et al. Persymmetric adaptive subspace detection in compound Gaussian sea clutter with generalized inverse Gaussian texture[J]. Signal Processing, 2024, 216: 109300. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2023.109300. |
| [24] |
XUE Jian, MA Manshan, LIU Jun, et al. Wald- and Rao-based detection for maritime radar targets in sea clutter with lognormal texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5119709. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3217615. |
| [25] |
XUE Jian, FAN Zhen, XU Shuwen, et al. Persymmetric adaptive radar target detection in CG-LN sea clutter using complex parameter suboptimum tests[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5111211. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3330865. |
| [26] |
XUE Jian, FAN Zhen, and XU Shuwen. Adaptive coherent detection for maritime radar range-spread targets in correlated heavy-tailed sea clutter with lognormal texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3505805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3397850. |
| [27] |
CHEN Xiaolin, LIU Kai, ZHANG Zhibo, et al. Mixture texture model with weighted generalized inverse Gaussian distribution for target detection[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2024, 154: 104677. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2024.104677. |
| [28] |
LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, LIU Tao, et al. Detector design and performance analysis for target detection in subspace interference[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 618–622. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3270080. |
| [29] |
TANG Peiqin, XU Zhenyu, XU Hong, et al. Distributed target detection based on gradient test in deterministic subspace interference[J]. Signal Processing, 2025, 227: 109673. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2024.109673. |
| [30] |
TANG Peiqin, WANG Yongliang, LIU Weijian, et al. A tunable detector for distributed target detection in the situation of signal mismatch[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 151–155. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2961838. |
| [31] |
SUN Mengru, LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, et al. Complex parameter Rao, Wald, Gradient, and Durbin tests for multichannel signal detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 117–131. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3132485. |
| [32] |
XIAO Daipeng, LIU Weijian, CHEN Hui, et al. An adaptive radar target detection method based on alternate estimation in power heterogeneous clutter[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(13): 2508. doi: 10.3390/rs16132508. |
| [33] |
LI Na, YANG Haining, CUI Guolong, et al. Adaptive two-step Bayesian MIMO detectors in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 161: 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.03.008. |
| [34] |
WANG Zhihang, HE Zishu, HE Qin, et al. Persymmetric range-spread targets detection in compound Gaussian sea clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8018305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3101369. |
| [35] |
ABRAMOWITZ M and STEGUN I A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions: With Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables[M]. New York: Dover Publications, 1965: 375–376.
|
| [36] |
DEVROYE L. Random variate generation for the generalized inverse Gaussian distribution[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2014, 24(2): 239–246. doi: 10.1007/s11222-012-9367-z. |
| [37] |
ATKINSON A C. The simulation of generalized inverse Gaussian and hyperbolic random variables[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing, 1982, 3(4): 502–515. doi: 10.1137/0903033. |
| [38] |
TANG Peiqin, PENG Xinyu, XU Hong, et al. Durbin tests for distributed target detection in deterministic subspace interference and noise[J]. Signal Processing, 2025, 234: 110009. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2025.110009. |
| [39] |
LIU Weijian, WANG Yongliang, and XIE Wenchong. Fisher information matrix, Rao test, and Wald test for complex-valued signals and their applications[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 94: 1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.06.032. |
| [40] |
GUO Qiang, LIU Lichao, HUANG Shuai, et al. Adaptive detectors for mismatched subspace target in clutter with lognormal texture[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2024, 154: 104692. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2024.104692. |
| [41] |
GINI F and GRECO M. Covariance matrix estimation for CFAR detection in correlated heavy tailed clutter[J]. Signal Processing, 2002, 82(12): 1847–1859. doi: 10.1016/S0165-1684(02)00315-8. |
| [42] |
CUI Yufeng, WANG Yongliang, LIU Weijian, et al. A tunable adaptive detector for distributed targets when signal mismatch occurs[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(4): 873–878. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2023.000029. |
| [43] |
刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089. LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089. |
| [44] |
刘宁波, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取年度进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011. LIU Ningbo, DING Hao, HUANG Yong, et al. Annual progress of the sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011. |
| [45] |
关键, 刘宁波, 王国庆, 等. 雷达对海探测试验与目标特性数据获取——海上目标双极化多海况散射特性数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 456–469. doi: 10.12000/JR23029. GUAN Jian, LIU Ningbo, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting radar experiment and target feature data acquisition for dual polarization multistate scattering dataset of marine targets[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 456–469. doi: 10.12000/JR23029. |
| [46] |
LI Dongfang, ZHAO Zhiqin, and ZHAO Yanwen. Analysis of experimental data of IPIX radar[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Computational Electromagnetics, Chengdu, China, 2018: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/COMPEM.2018.8496687. |
| [47] |
XU Xiaoke. Low observable targets detection by joint fractal properties of sea clutter: An experimental study of IPIX OHGR datasets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(4): 1425–1429. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2041144. |
| [48] |
MEZACHE A, SAHED M, and LAROUSSI T. K-distribution parameters estimation based on the Nelder-Mead algorithm in presence of thermal noise[C]. 2009 International Conference on Advances in Computational Tools for Engineering Applications, Beirut, Lebanon, 2009: 553–558. doi: 10.1109/ACTEA.2009.5227861. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: