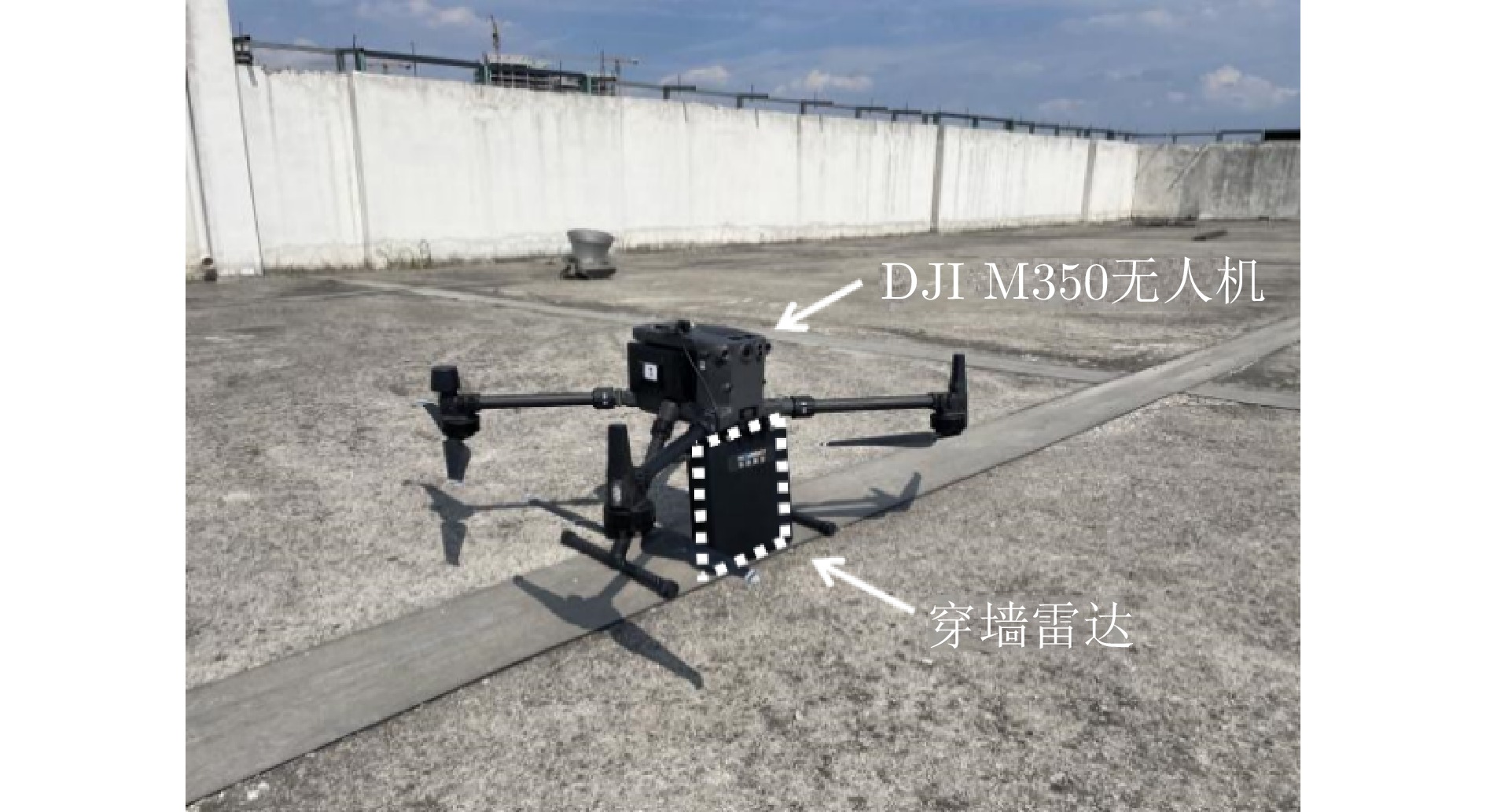
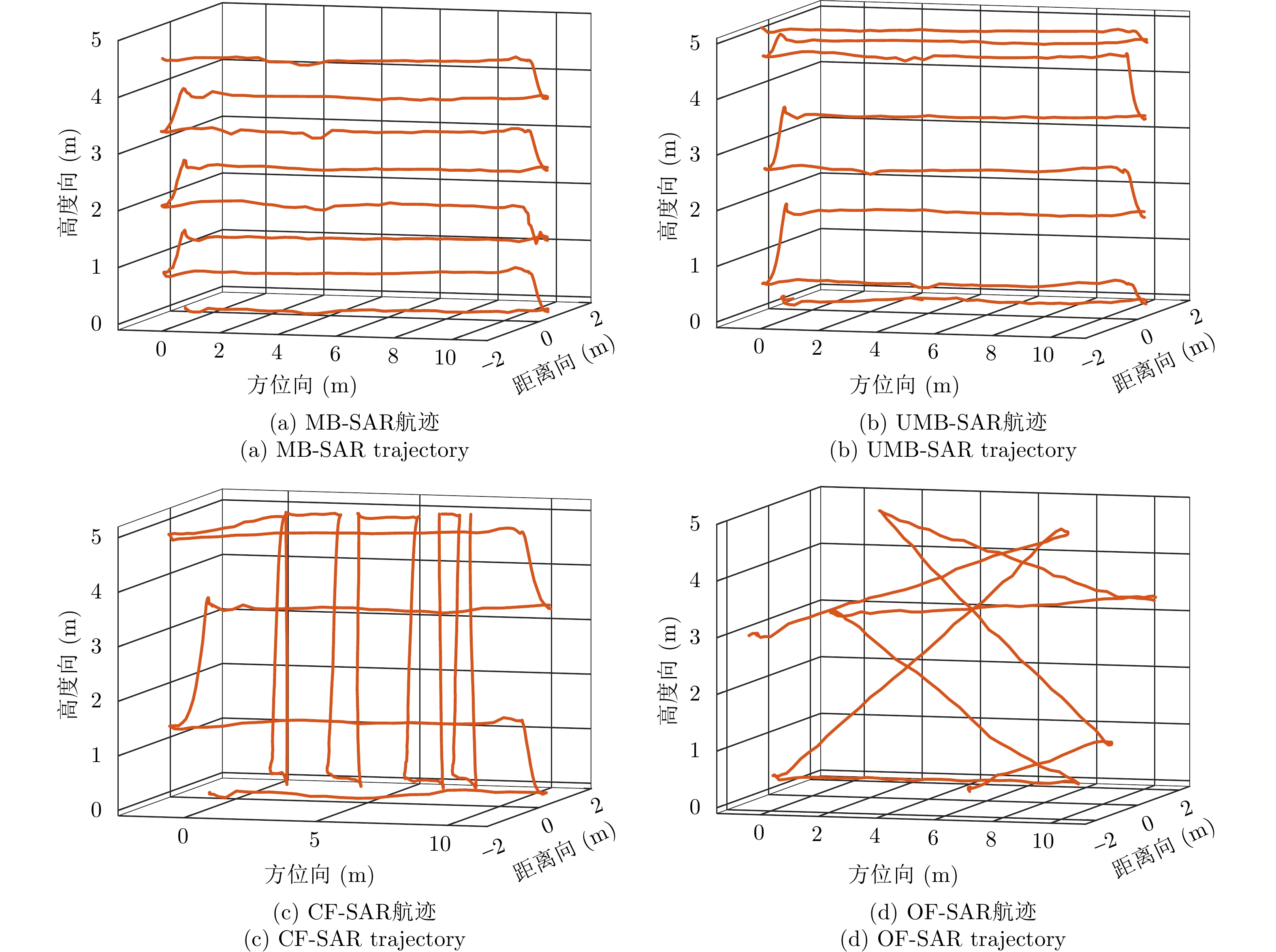
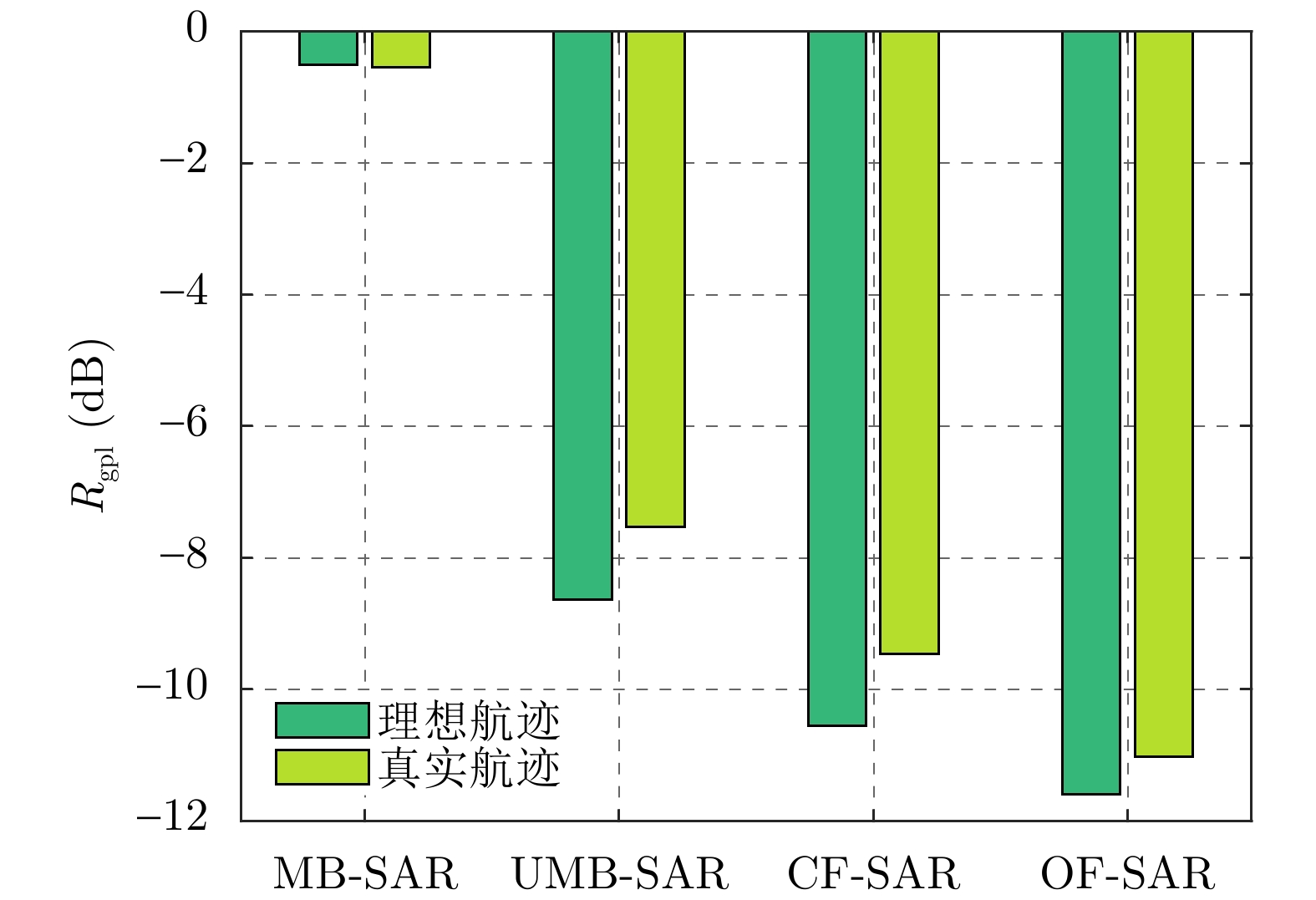
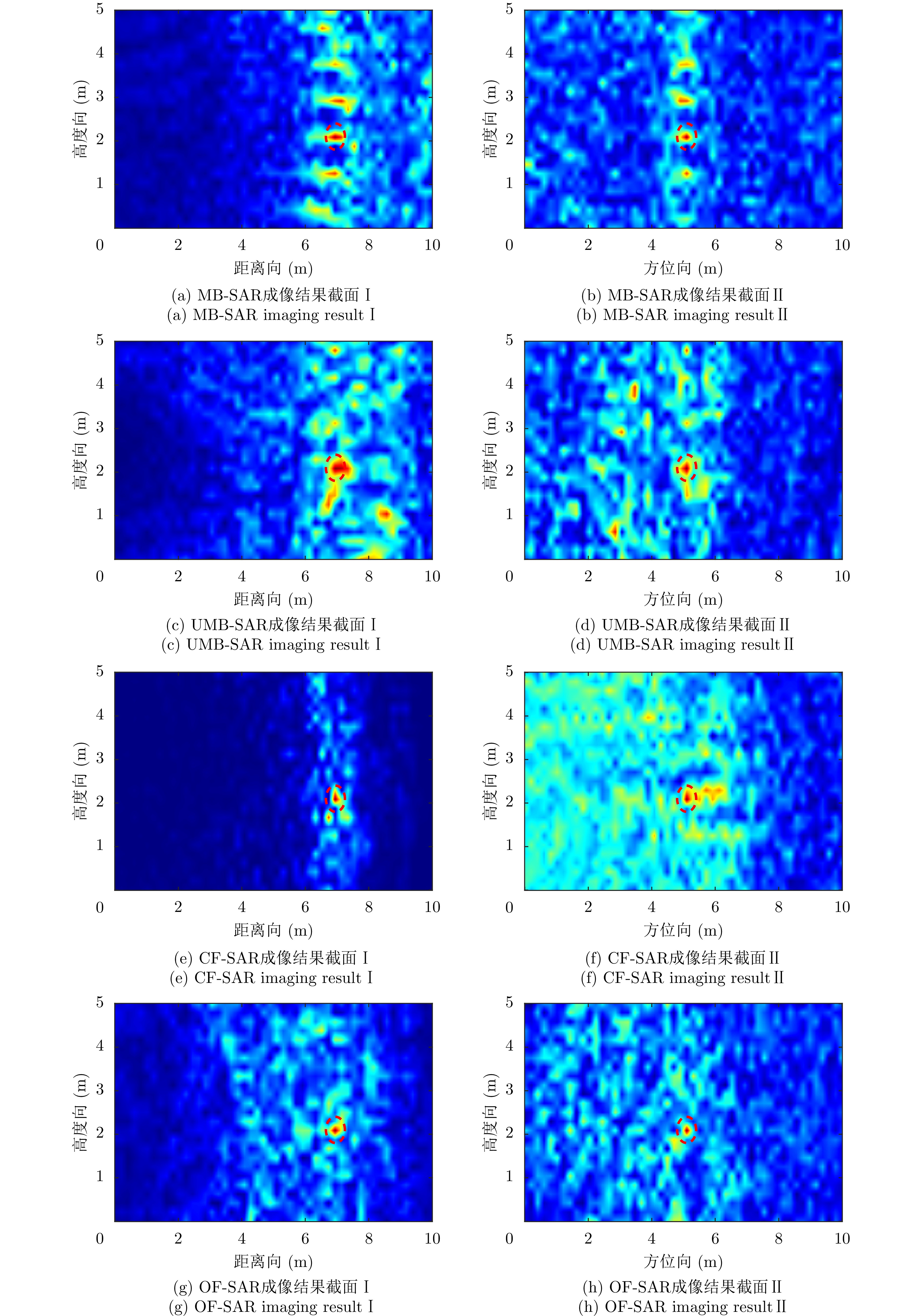
| [1] |
GAO Weicheng, YANG Xiaopeng, QU Xiaodong, et al. TWR-MCAE: A data augmentation method for through-the-wall radar human motion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5118617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3213748. |
| [2] |
YANG Xiaopeng, GAO Weicheng, QU Xiaodong, et al. A lightweight multiscale neural network for indoor human activity recognition based on macro and micro-Doppler features[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(24): 21836–21854. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3301519. |
| [3] |
金添, 宋勇平, 崔国龙, 等. 低频电磁波建筑物内部结构透视技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119. JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, CUI Guolong, et al. Advances on penetrating imaging of building layout technique using low frequency radio waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119. |
| [4] |
UNAL M, CALISKAN A, TURK A S, et al. Subsurface and through-wall SAR imaging techniques for ground penetrating radar[J]. Технология и Конструирование в Электронной Аппаратуре, 2013(6): 32–36. doi: 10.15222/tkea2013.6.32. |
| [5] |
WANG Yazhou and FATHY A E. Advanced system level simulation platform for three-dimensional UWB through-wall imaging SAR using time-domain approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(5): 1986–2000. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2011.2170694. |
| [6] |
SÉVIGNY P. Joint through-wall 3-D radar imaging and motion detection using a stop-and-go SAR trajectory[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485325. |
| [7] |
LIU Jiangang, JIA Yong, KONG Lingjiang, et al. MIMO through-wall radar 3-D imaging of a human body in different postures[J]. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 2016, 30(7): 849–859. doi: 10.1080/09205071.2016.1159996. |
| [8] |
KONG Lingjiang, CUI Guolong, YANG Xiaobo, et al. Three-dimensional human imaging for through-the-wall radar[C]. 2009 IEEE Radar Conference, Pasadena, USA, 2009: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2009.4976932. |
| [9] |
ZHAO Yikun, YANG Wenfu, LI Yinchuan, et al. Multi-path suppression algorithm for through-the-wall imaging[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(19): 5629–5633. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0126. |
| [10] |
FREY O and MEIER E. 3-D time-domain SAR imaging of a forest using airborne multibaseline data at L- and P-bands[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3660–3664. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2011.2128875. |
| [11] |
DOGARU T, PHELAN B, and LIAO Dahan. Imaging of buried targets using UAV-based, ground penetrating, synthetic aperture radar[C]. SPIE 11003, Radar Sensor Technology XXIII, Baltimore, USA, 2019. doi: 10.1117/12.2519116. |
| [12] |
ANDRE D, FAULKNER B, and FINNIS M. Low-frequency 3D synthetic aperture radar for the remote intelligence of building interiors[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(15): 984–987. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.1584. |
| [13] |
廖明生, 魏恋欢, 汪紫芸, 等. 压缩感知在城区高分辨率SAR层析成像中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031. LIAO Mingsheng, WEI Lianhuan, WANG Ziyun, et al. Compressive sensing in high-resolution 3D SAR tomography of urban scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031. |
| [14] |
ALISTARH C A, PODILCHAK S K, RE P D H, et al. Sectorized FMCW MIMO radar by modular design with non-uniform sparse arrays[J]. IEEE Journal of Microwaves, 2022, 2(3): 442–460. doi: 10.1109/jmw.2022.3165401. |
| [15] |
FENG Chen, YE Haojian, HONG Hong, et al. A hybrid algorithm for sparse antenna array optimization of MIMO radar[C]. 2022 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, Las Vegas, USA, 2022: 115–117. doi: 10.1109/RWS53089.2022.9719968. |
| [16] |
HARTMANN F and OSTERMANN J. Investigation of the effect of the flight path on the three dimensional locatability of targets[C]. 2021 7th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Bali, Indonesia, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/APSAR52370.2021.9688372. |
| [17] |
BROWN A and ANDERSON D. Trajectory optimization for high-altitude long-endurance UAV maritime radar surveillance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(3): 2406–2421. doi: 10.1109/taes.2019.2949384. |
| [18] |
DROZDOWICZ J and SAMCZYNSKI P. Drone-based 3D synthetic aperture radar imaging with trajectory optimization[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(18): 6990. doi: 10.3390/s22186990. |
| [19] |
SAEEDI J and FAEZ K. A back-projection autofocus algorithm based on flight trajectory optimization for synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 27(2): 411–431. doi: 10.1007/s11045-014-0308-1. |
| [20] |
JIAO Bowen, WANG Zuyi, and XU Li. Control strategy and flight trajectory optimization strategy based on improved De Casteljau’s algorithm for indoor drone[C]. 2021 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Kunming, China, 2021: 4633–4638. doi: 10.1109/CCDC52312.2021.9602413. |
| [21] |
LAHMERI M A, GHANEM W, KNILL C, et al. Trajectory and resource optimization for UAV synthetic aperture radar[C]. 2022 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2022: 897–903. doi: 10.1109/GCWkshps56602.2022.10008658. |
| [22] |
TASHTARIAN G and MAJEDI M S. Grating lobes reduction in linear arrays composed of subarrays using PSO[C]. 2019 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC), Istanbul, Turkey, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ISNCC.2019.8909108. |
| [23] |
INDU N, SINGH R P, CHOUDHARY H R, et al. Trajectory design for UAV-to-ground communication with energy optimization using genetic algorithm for agriculture application[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(16): 17548–17555. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2020.3046463. |
| [24] |
WANG Chuhan, LI Xiaolong, WANG Mingxing, et al. A stepwise optimization and control method for node location and path of airborne distributed MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(7): 1249–1265. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.07.007. |
| [25] |
WANG Xiaofeng, RUAN Yaduan, and ZHANG Xinggan. Accuracy improvement of high-resolution wide-swath spaceborne synthetic aperture radar imaging with low pule repetition frequency[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(15): 3811. doi: 10.3390/rs15153811. |
| [26] |
WARREN C, GIANNOPOULOS A, GRAY A, et al. A CUDA-based GPU engine for gprMax: Open source FDTD electromagnetic simulation software[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2019, 237: 208–218. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2018.11.007. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: