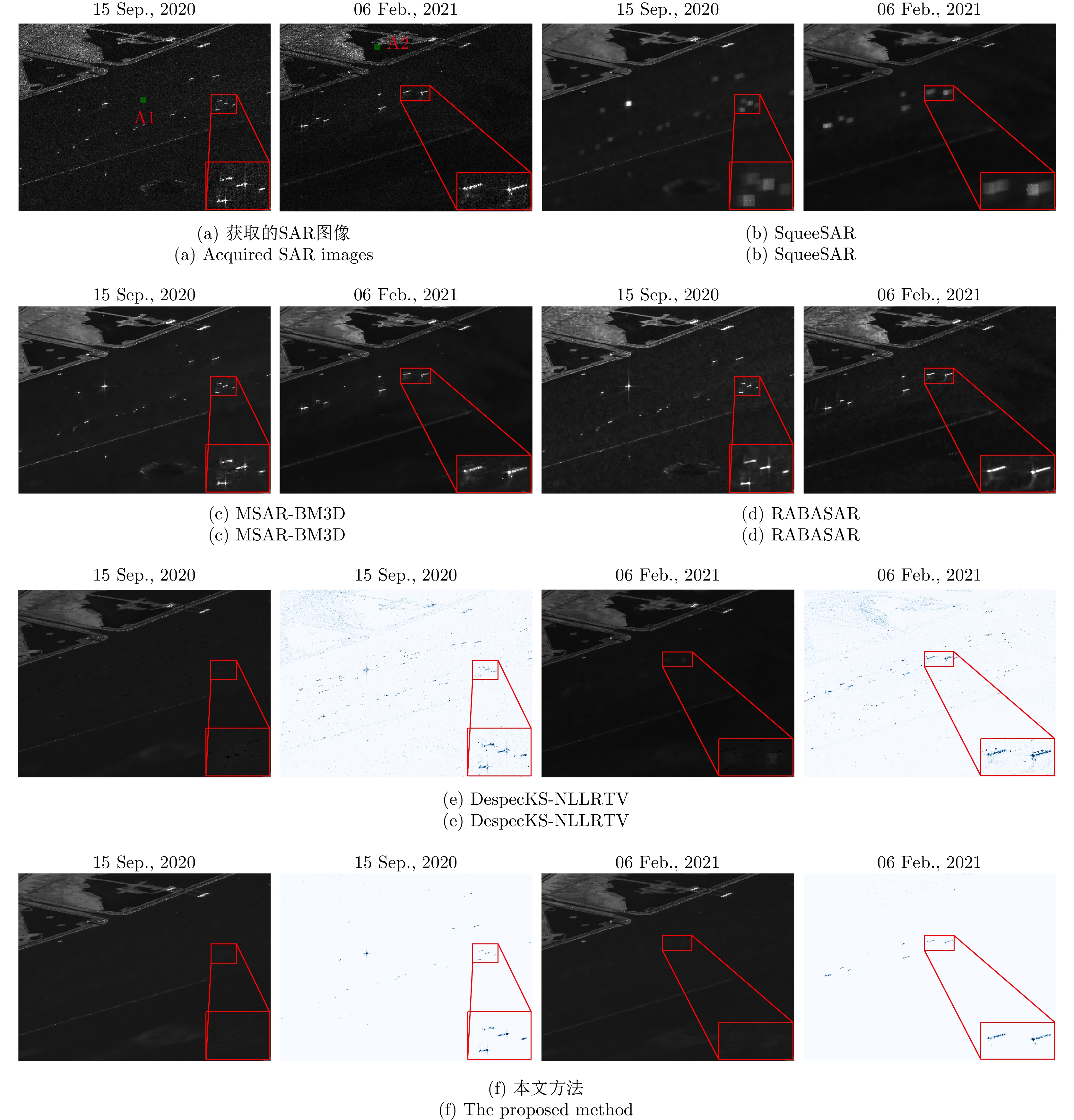
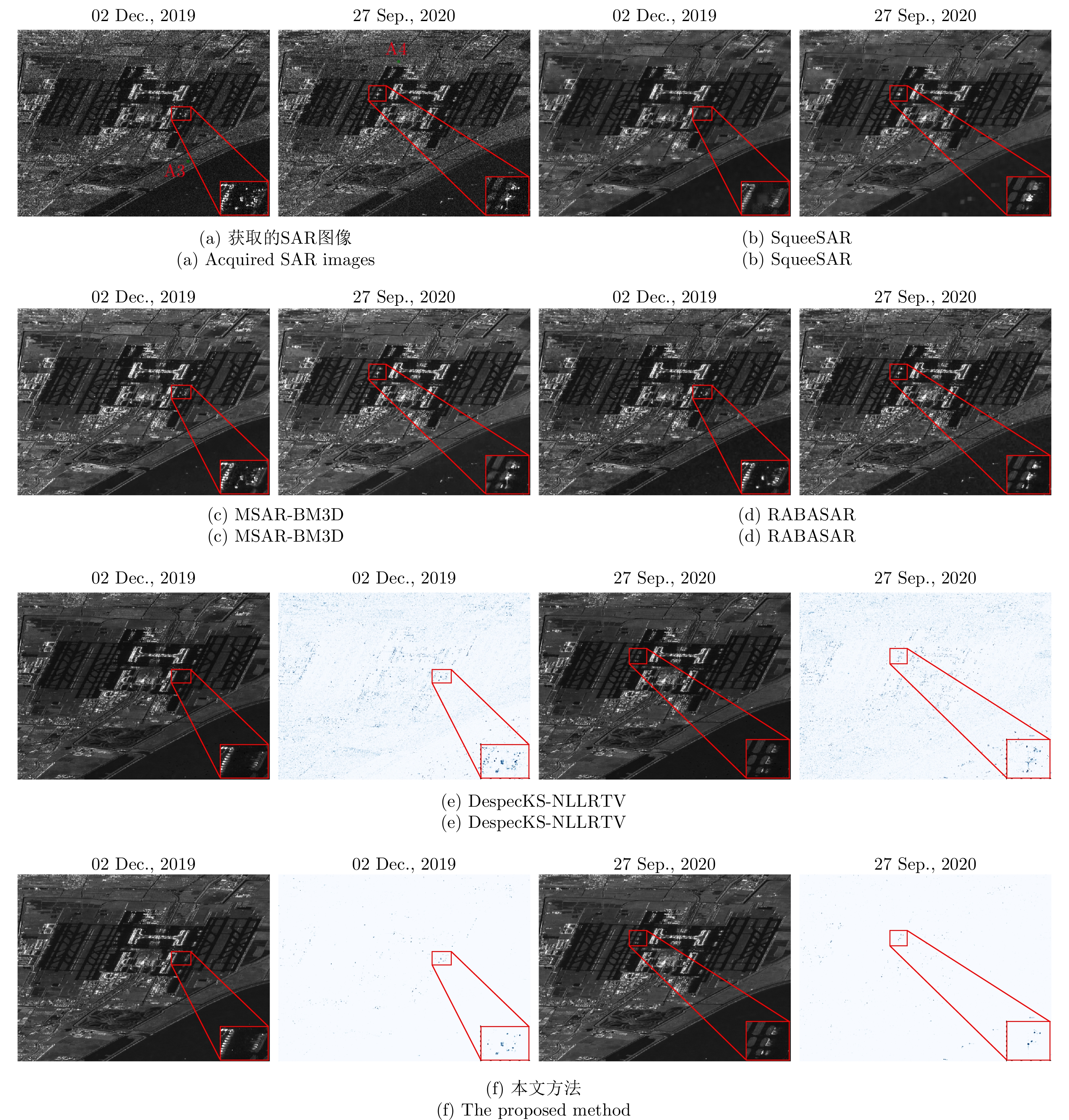
| [1] |
MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 |
| [2] |
DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 |
| [3] |
陈杰, 杨威, 王亚敏, 等. 高时相星载序贯SAR图像运动目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 1048–1060. doi: 10.12000/JR22184CHEN Jie, YANG Wei, WANG Yamin, et al. Moving target monitoring algorithm based on high-frame-rate SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 1048–1060. doi: 10.12000/JR22184 |
| [4] |
XUE Feiyang, LV Xiaolei, DOU Fangjia, et al. A review of time-series interferometric SAR techniques: A tutorial for surface deformation analysis[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2020, 8(1): 22–42. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2956165 |
| [5] |
徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130 |
| [6] |
ARGENTI F, LAPINI A, BIANCHI T, et al. A tutorial on speckle reduction in synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(3): 6–35. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2277512 |
| [7] |
VASILE G, TROUVE E, LEE J S, et al. Intensity-driven adaptive-neighborhood technique for polarimetric and interferometric SAR parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(6): 1609–1621. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.864142 |
| [8] |
LEE J S, GRUNES M R, and GRANDI G D. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering and its implication for classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2363–2373. doi: 10.1109/36.789635 |
| [9] |
BIOUCAS-DIAS J M and FIGUEIREDO M A T. Multiplicative noise removal using variable splitting and constrained optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(7): 1720–1730. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2045029 |
| [10] |
DALSASSO E, YANG Xiangli, DENIS L, et al. SAR image despeckling by deep neural networks: From a pre-trained model to an end-to-end training strategy[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(16): 2636. doi: 10.3390/rs12162636 |
| [11] |
XIONG Kai, ZHAO Guanghui, WANG Yingbin, et al. SPB-Net: A deep network for SAR imaging and despeckling with downsampled data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(11): 9238–9256. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3034102 |
| [12] |
MOLINI A B, VALSESIA D, FRACASTORO G, et al. Speckle2Void: Deep self-supervised SAR despeckling with blind-spot convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5204017. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3065461 |
| [13] |
DELEDALLE C A, DENIS L, POGGI G, et al. Exploiting patch similarity for SAR image processing: The nonlocal paradigm[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 69–78. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2311305 |
| [14] |
XU Gang, GAO Yandong, LI Jinwei, et al. InSAR phase denoising: A review of current technologies and future directions[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2020, 8(2): 64–82. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2955120 |
| [15] |
QUEGAN S, LE TOAN T, YU Jiongjiong, et al. Multitemporal ERS SAR analysis applied to forest mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(2): 741–753. doi: 10.1109/36.842003 |
| [16] |
TROUVE E, CHAMBENOIT Y, CLASSEAU N, et al. Statistical and operational performance assessment of multitemporal SAR image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(11): 2519–2530. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817270 |
| [17] |
SU Xin, DELEDALLE C A, TUPIN F, et al. Two-step multitemporal nonlocal means for synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6181–6196. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2295431 |
| [18] |
FERRETTI A, FUMAGALLI A, NOVALI F, et al. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(9): 3460–3470. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2124465 |
| [19] |
CHIERCHIA G, EL GHECHE M, SCARPA G, et al. Multitemporal SAR image despeckling based on block-matching and collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(10): 5467–5480. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2707806 |
| [20] |
PARRILLI S, PODERICO M, ANGELINO C V, et al. A nonlocal SAR image denoising algorithm based on LLMMSE wavelet shrinkage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(2): 606–616. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2161586 |
| [21] |
ZHAO Weiying, DELEDALLE C A, DENIS L, et al. Ratio-based multitemporal SAR images denoising: RABASAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(6): 3552–3565. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2885683 |
| [22] |
BAIER G, HE Wei, and YOKOYA N. Robust nonlocal low-rank SAR time series despeckling considering speckle correlation by total variation regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(11): 7942–7954. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2985400 |
| [23] |
CHAMBOLLE A and POCK T. A first-order primal-dual algorithm for convex problems with applications to imaging[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2011, 40(1/2): 120–145. doi: 10.1007/s10851-010-0251-1 |
| [24] |
BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 |
| [25] |
FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 |
| [26] |
DELEDALLE C A, DENIS L, TABTI S, et al. MuLoG, or how to apply Gaussian denoisers to multi-channel SAR speckle reduction?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4389–4403. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2713946 |
| [27] |
WANG Yilun, YANG Junfeng, YIN Wotao, et al. A new alternating minimization algorithm for total variation image reconstruction[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2008, 1(3): 248–272. doi: 10.1137/080724265 |
| [28] |
PARIKH N and BOYD S. Proximal algorithms[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Optimization, 2014, 1(3): 127–239. doi: 10.1561/2400000003 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: