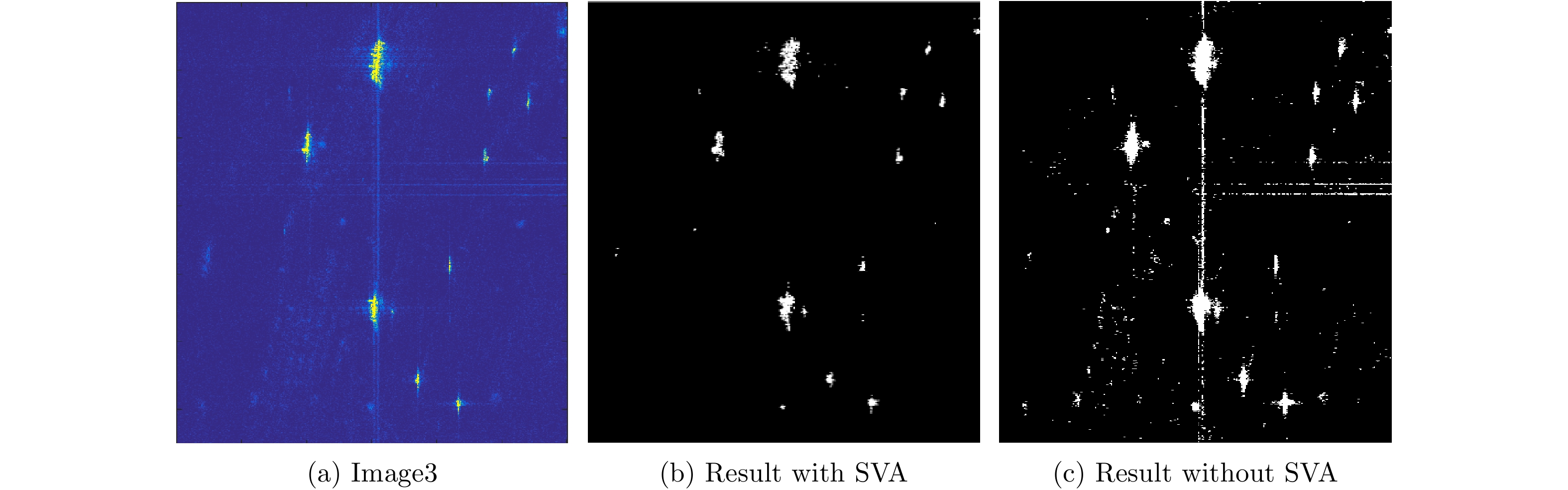
| [1] |
FAWZY Z M, EL-SAMIE F E A, and FOUAD M. Processing of synthetic aperture radar data using frequency modulated signals[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2019, 107(2): 1061–1076. doi: 10.1007/s11277-019-06317-x |
| [2] |
KERR D E. Propagation of Short Radio Waves[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1951.
|
| [3] |
MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 |
| [4] |
HARRIS F J. On the use of windows for harmonic analysis with the discrete Fourier transform[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1978, 66(1): 51–83. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1978.10837 |
| [5] |
STANKWITZ H C, DALLAIRE R J, and FIENUP J R. Nonlinear apodization for sidelobe control in SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1995, 31(1): 267–279. doi: 10.1109/7.366309 |
| [6] |
王一丁, 纪慧波, 洪峻. 变量切趾技术在SAR/ISAR图像处理中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2003, 25(12): 1622–1627.
WANG Yiding, JI Huibo, and HONG Jun. Application of apodization method in SAR/ISAR processing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2003, 25(12): 1622–1627.
|
| [7] |
SMITH B H. Generalization of spatially variant apodization to noninteger nyquist sampling rates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2000, 9(6): 1088–1093. doi: 10.1109/83.846250 |
| [8] |
CASTILLO-RUBIO C, LLORENTE-ROMANO S, and BURGOS-GARCIA M. Robust SVA method for every sampling rate condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(2): 571–580. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4285354 |
| [9] |
NI Chong, WANG Yanfei, XU Xianghui, et al. A SAR sidelobe suppression algorithm based on modified spatially variant apodization[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2010, 53(9): 2542–2551. doi: 10.1007/s11431-010-4035-z |
| [10] |
LIU Min, LI Zhou, and LIU Lu. A novel sidelobe reduction algorithm based on two-dimensional sidelobe correction using D-SVA for squint SAR images[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 783. doi: 10.3390/s18030783 |
| [11] |
El-DARYMLI K, MCGUIRE P, POWER D, et al. Target detection in synthetic aperture radar imagery: A state-of-the-art survey[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2013, 7(7): 071598.
|
| [12] |
ZHAO Bo, CHEN Li, ZHOU Xiaoyang, et al. Target detection from SAR images based on wavelet transform de-noise and improved CFAR[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7495, MIPPR 2009: Automatic Target Recognition and Image Analysis, Yichang, China, 2009: 749539.
|
| [13] |
KAPLAN L M. Improved SAR target detection via extended fractal features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(2): 436–451. doi: 10.1109/7.937460 |
| [14] |
XING X W, CHEN Z L, ZOU H X, et al. A fast algorithm based on two-stage CFAR for detecting ships in SAR images[C]. The 2009 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Shanxi, China, 2010.
|
| [15] |
SMITH M E and VARSHNEY P K. VI-CFAR: A novel CFAR algorithm based on data variability[C]. 1997 IEEE National Radar Conference, Syracuse, USA, 1997.
|
| [16] |
GANDHI P P and KASSAM S A. Analysis of CFAR processors in nonhomogeneous background[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1988, 24(4): 427–445. doi: 10.1109/7.7185 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work.jpg)





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: