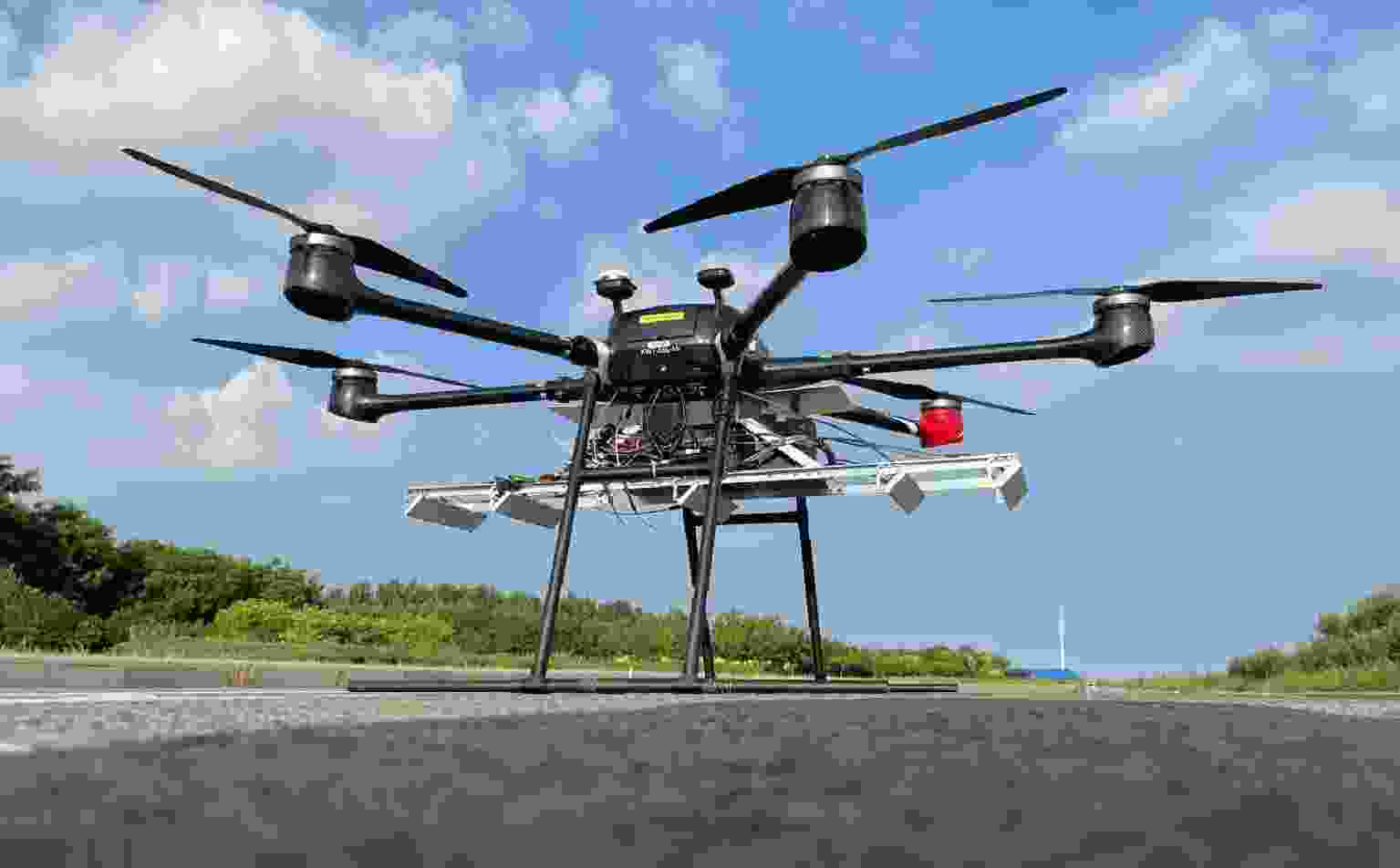
Microwave Vision Three-dimensional SAR Experimental System and Full-polarimetric Data Processing Method(in English)
-
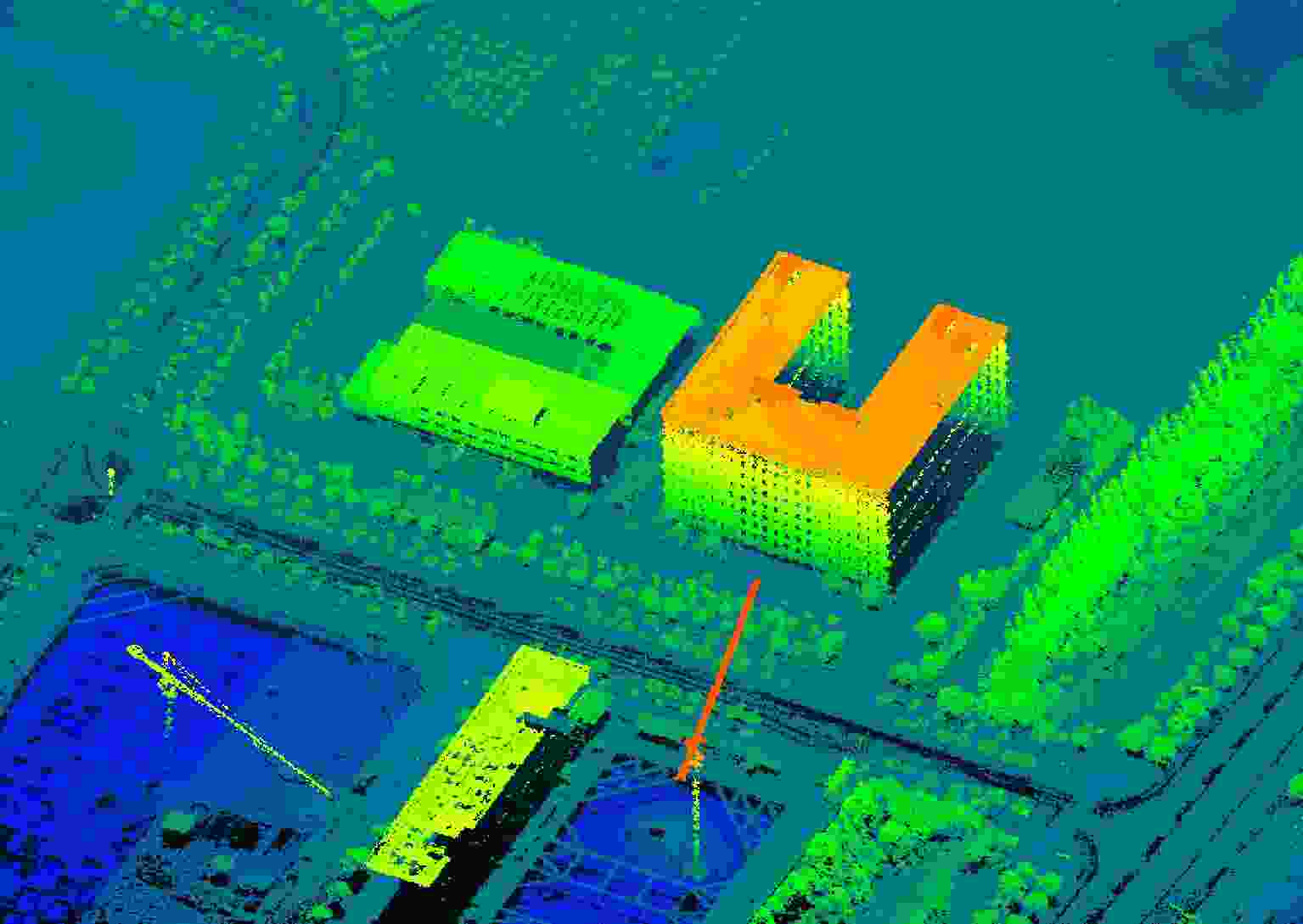
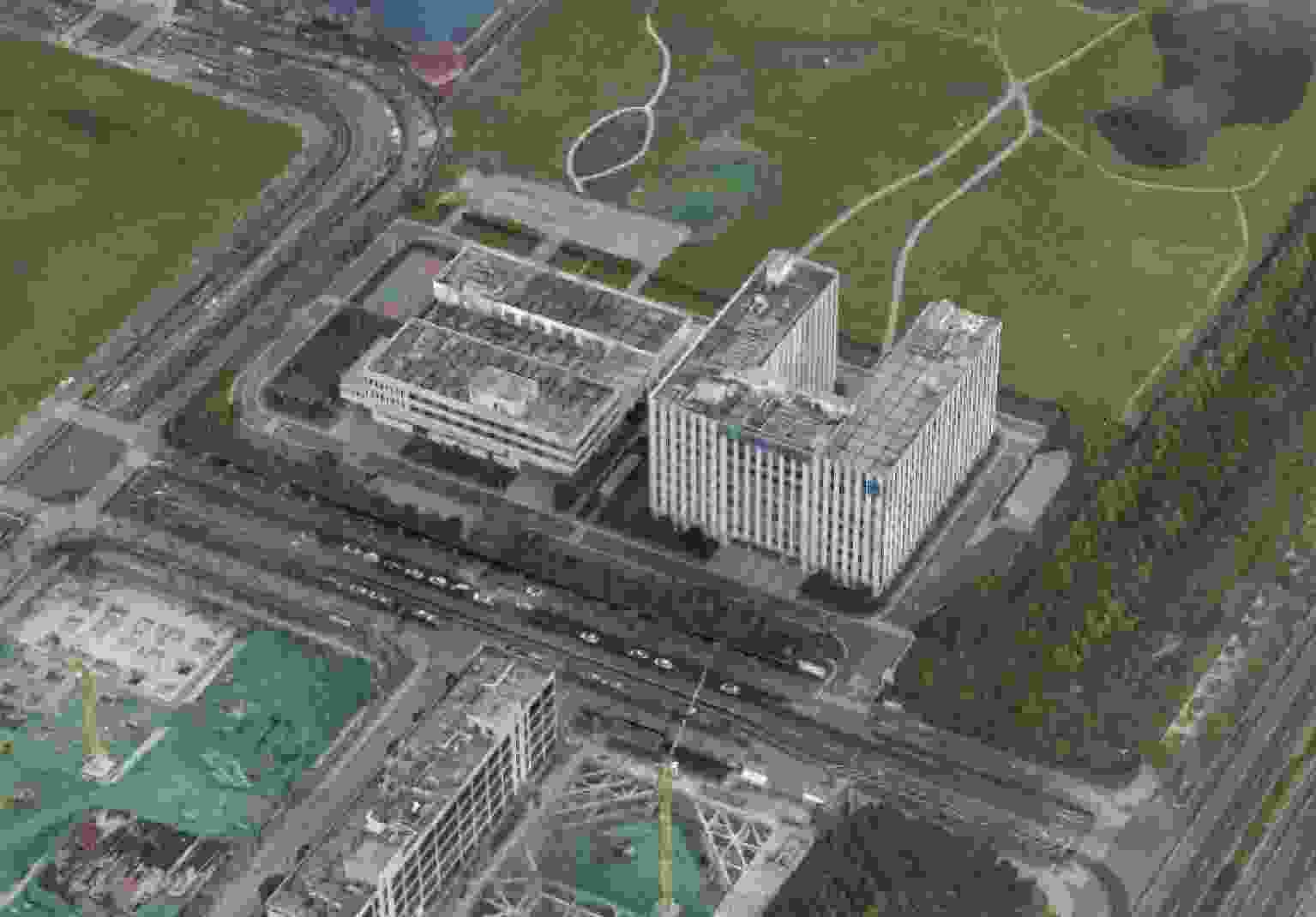
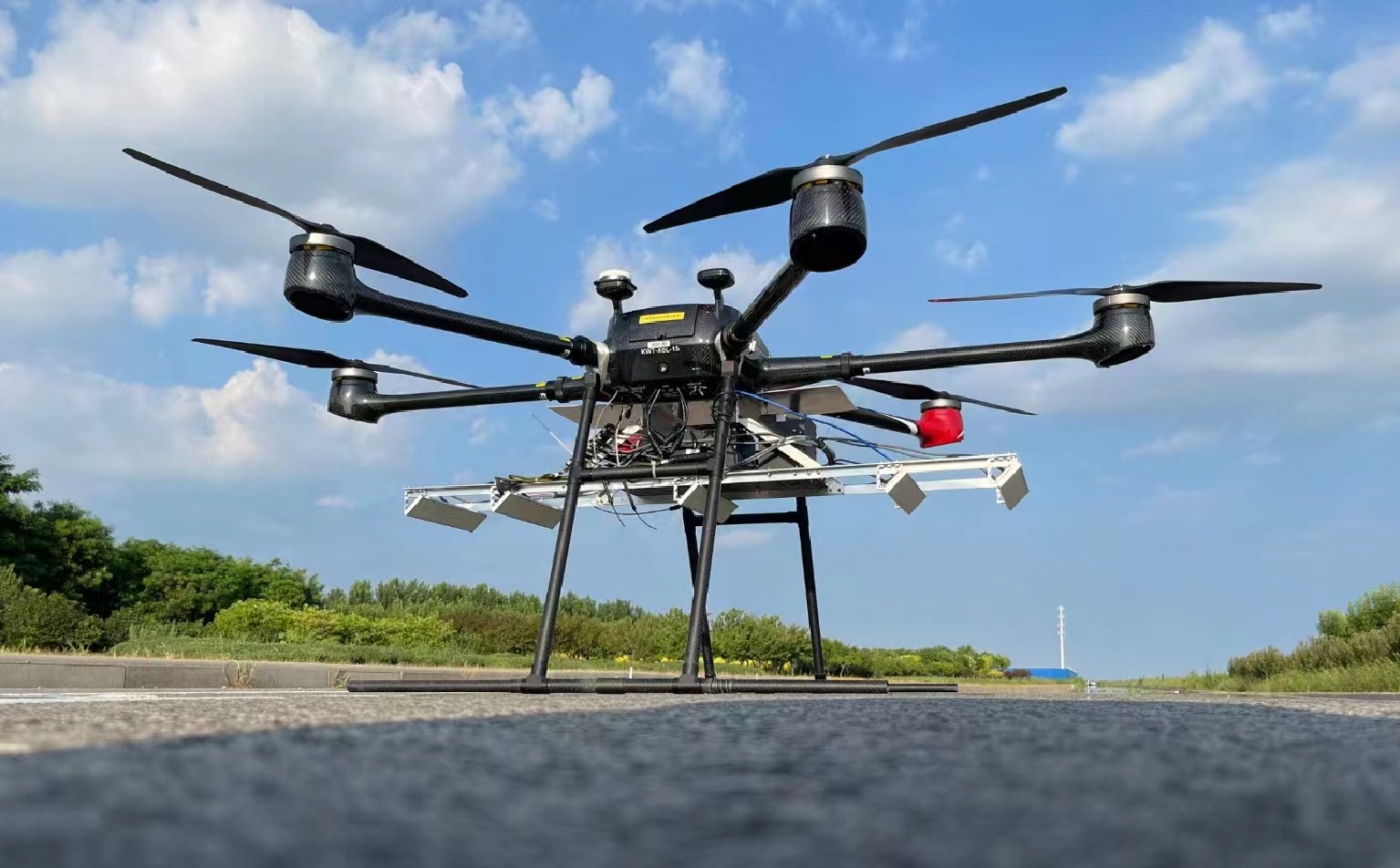
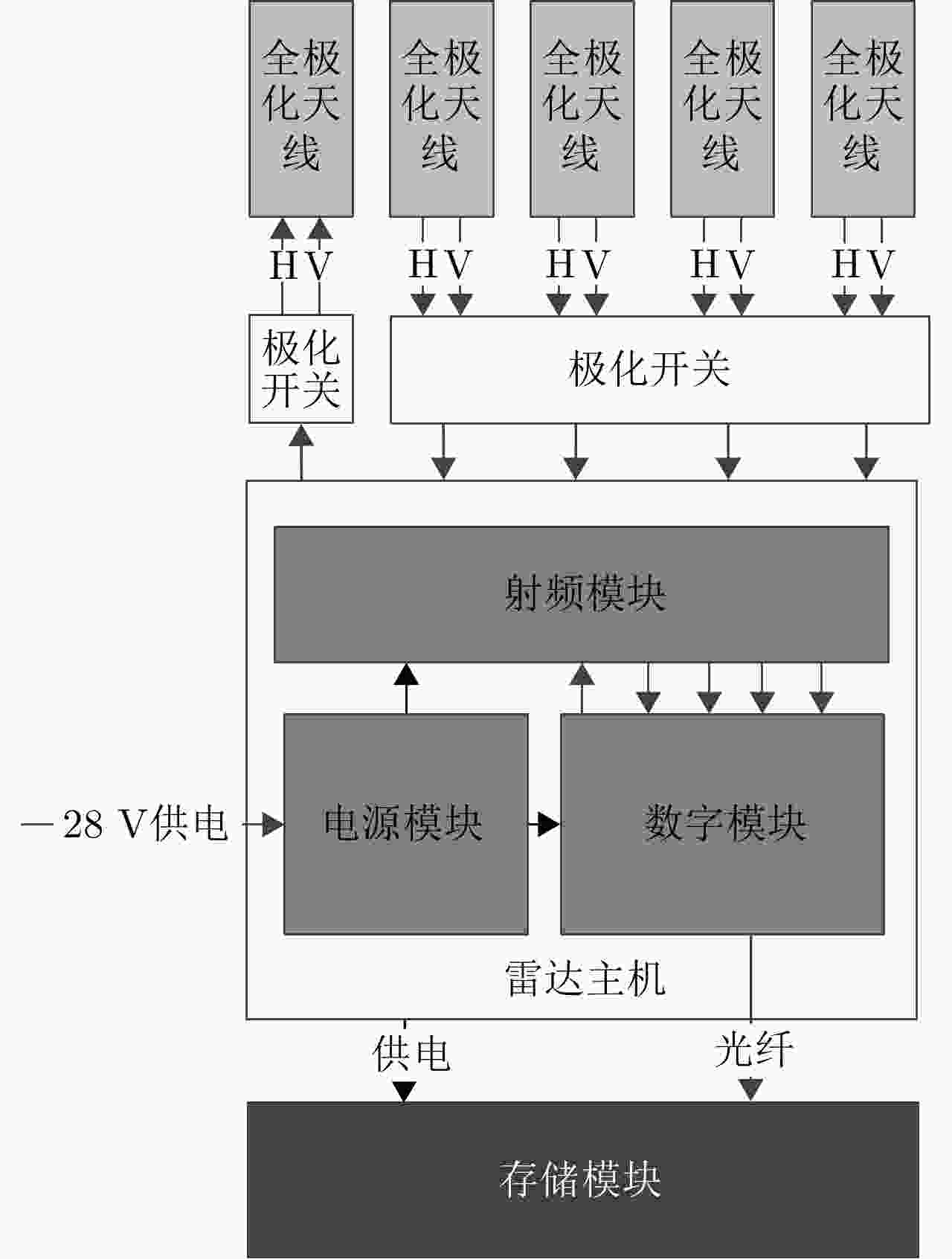
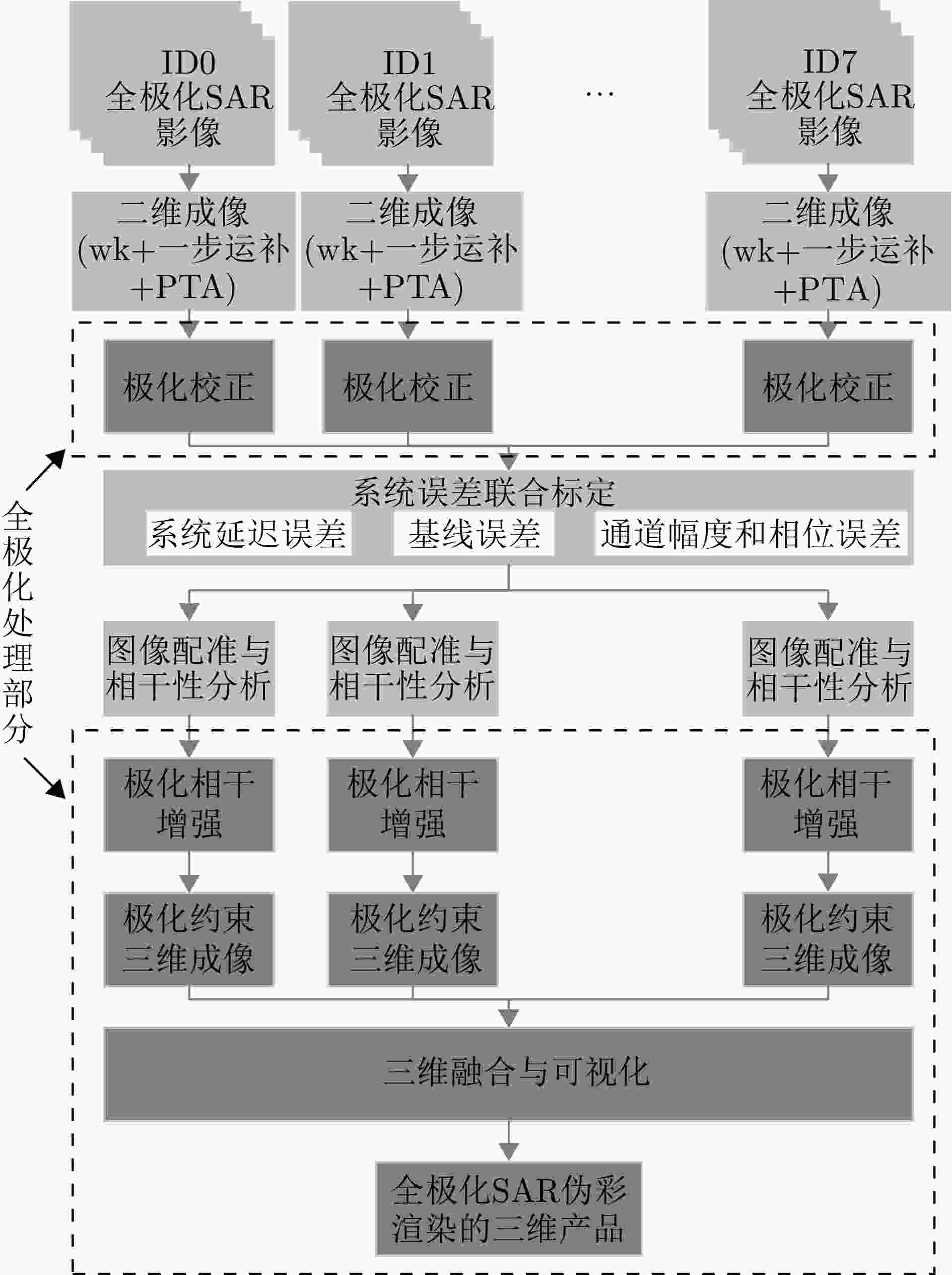
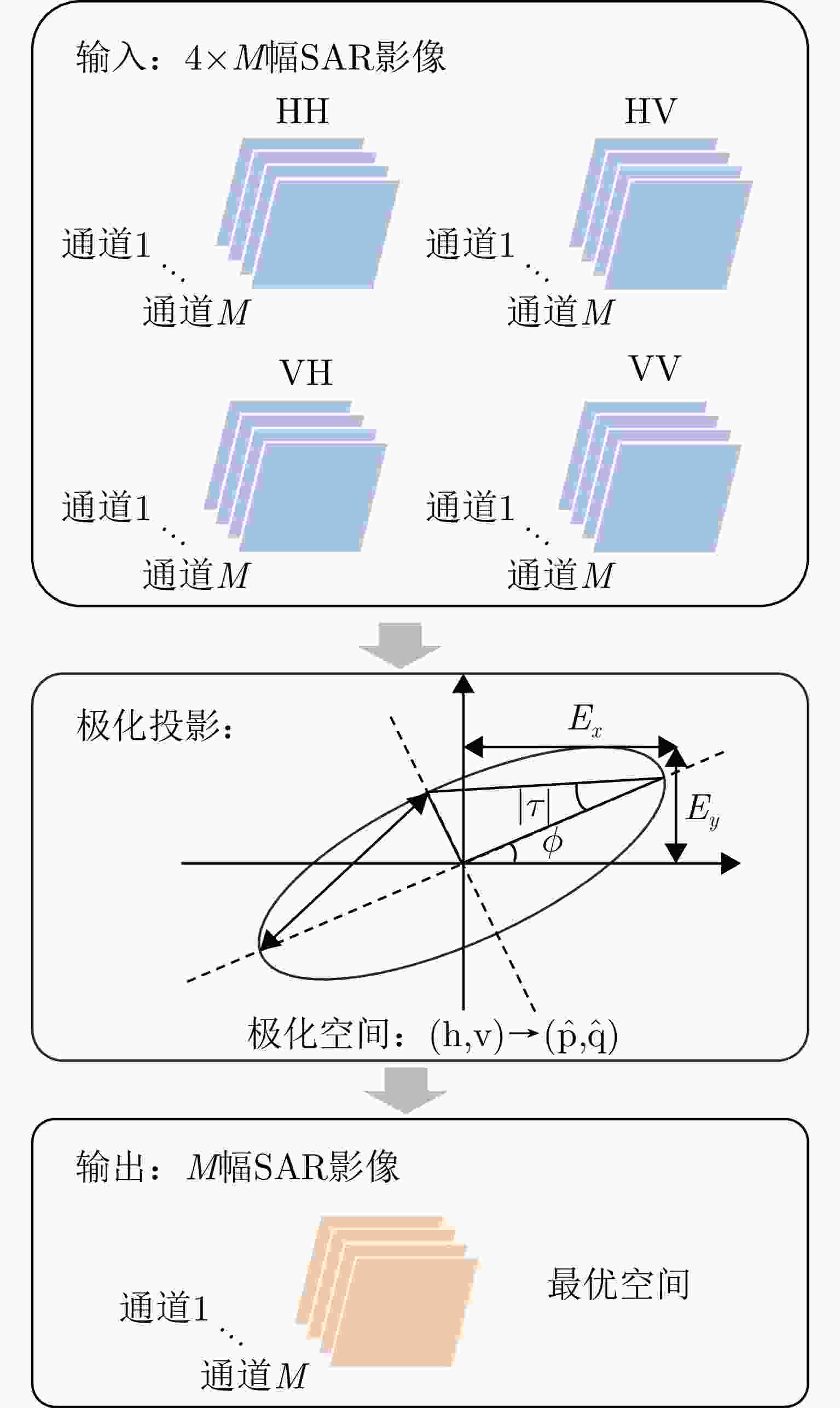
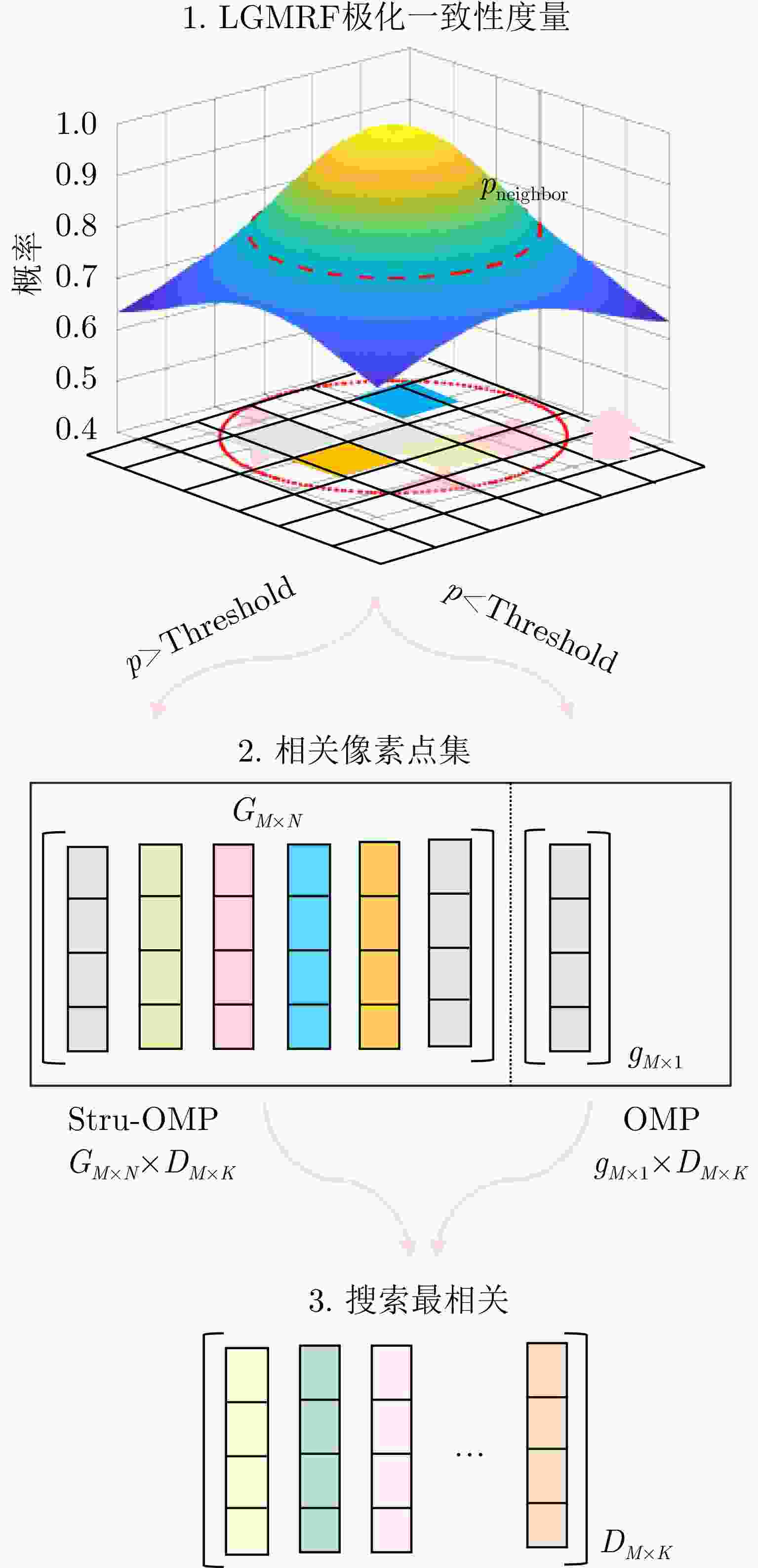
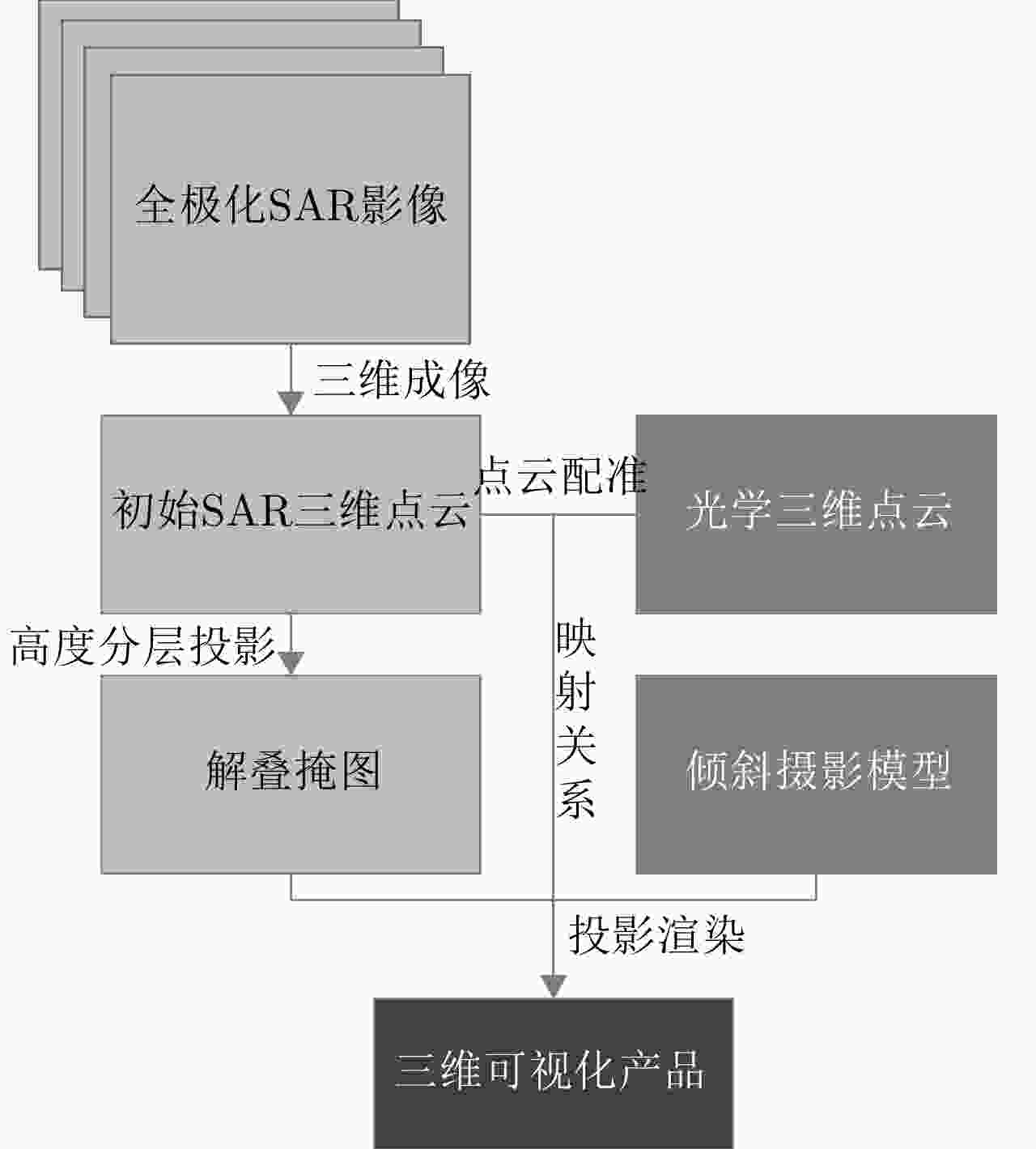
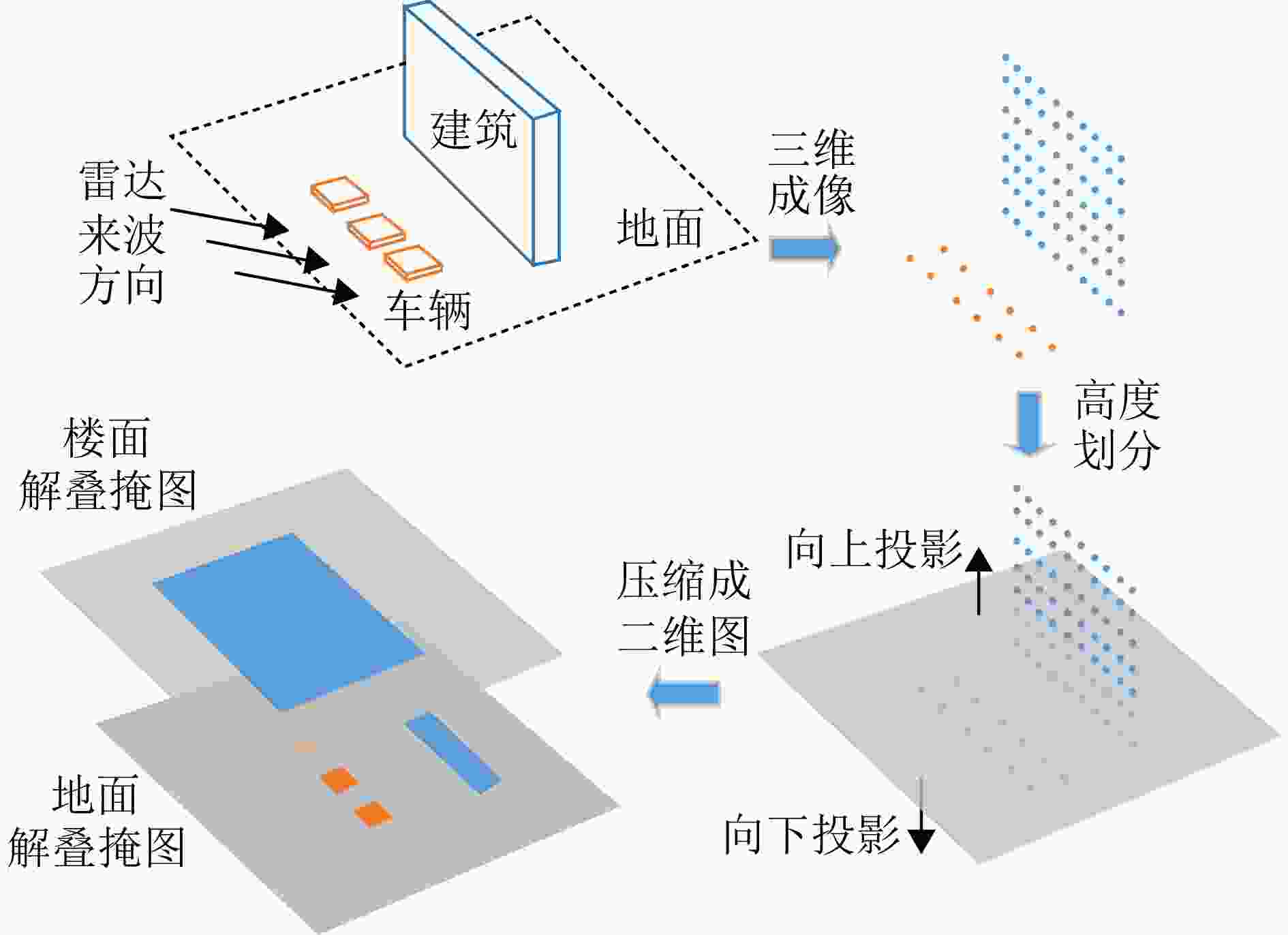
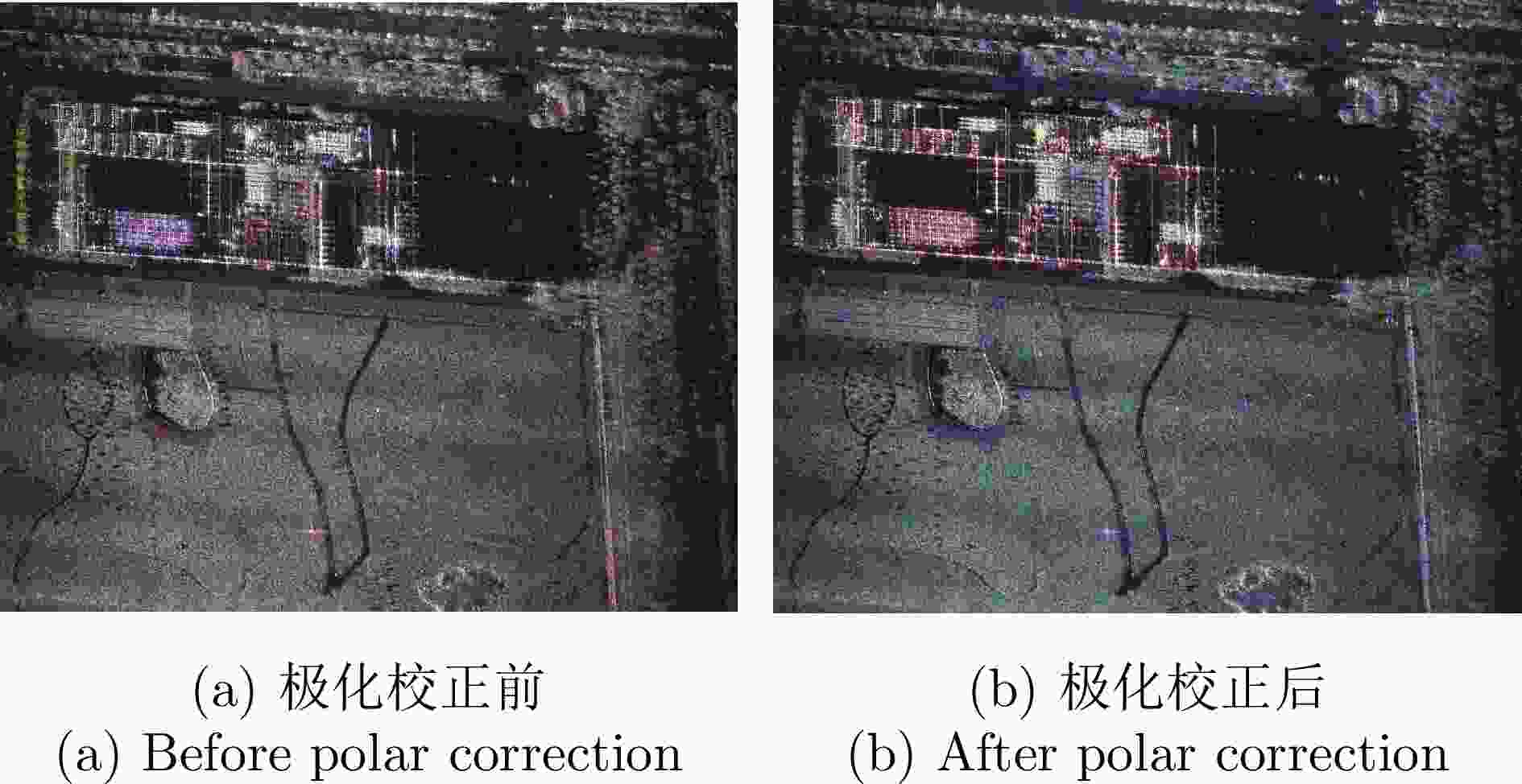
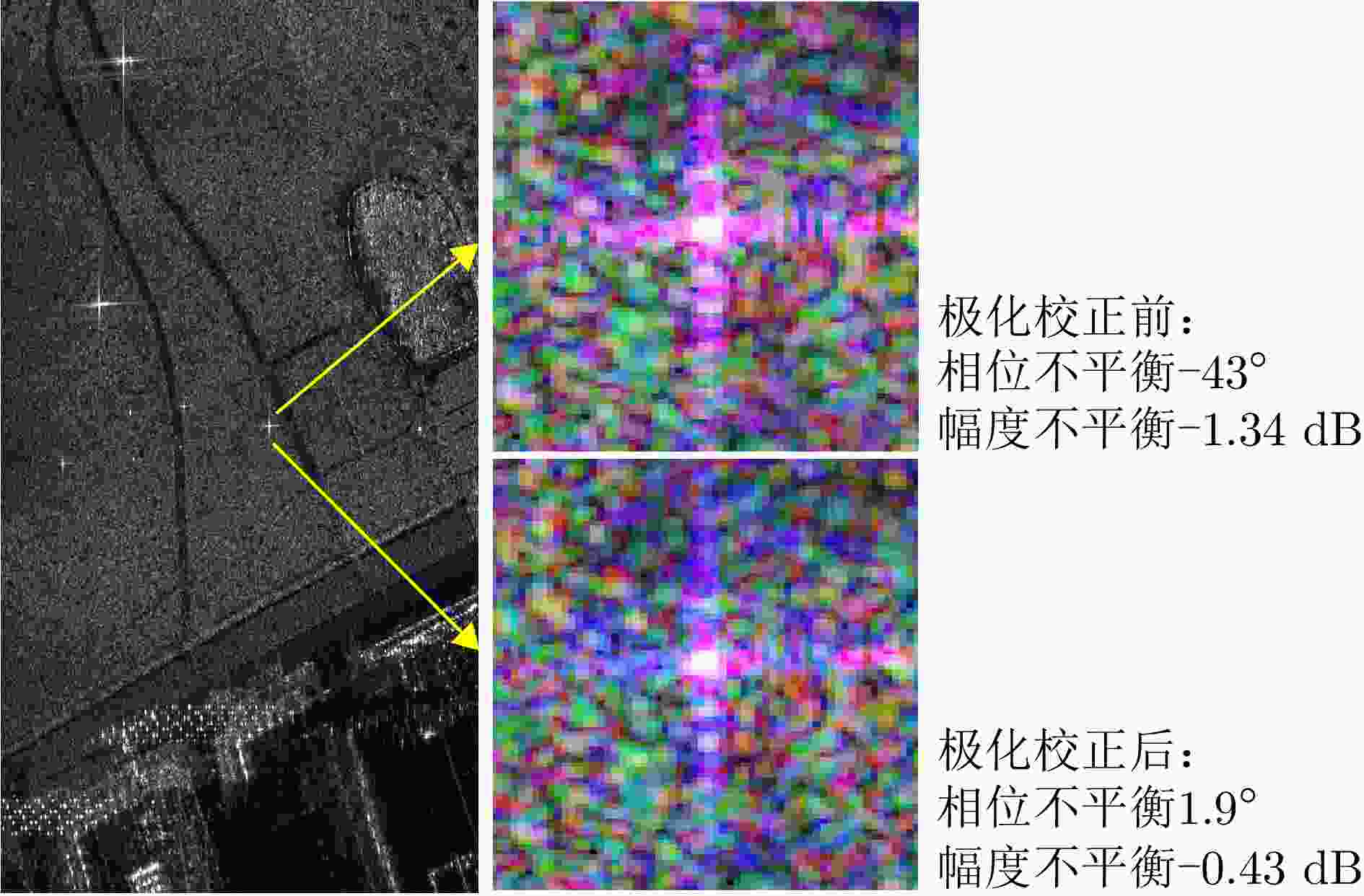
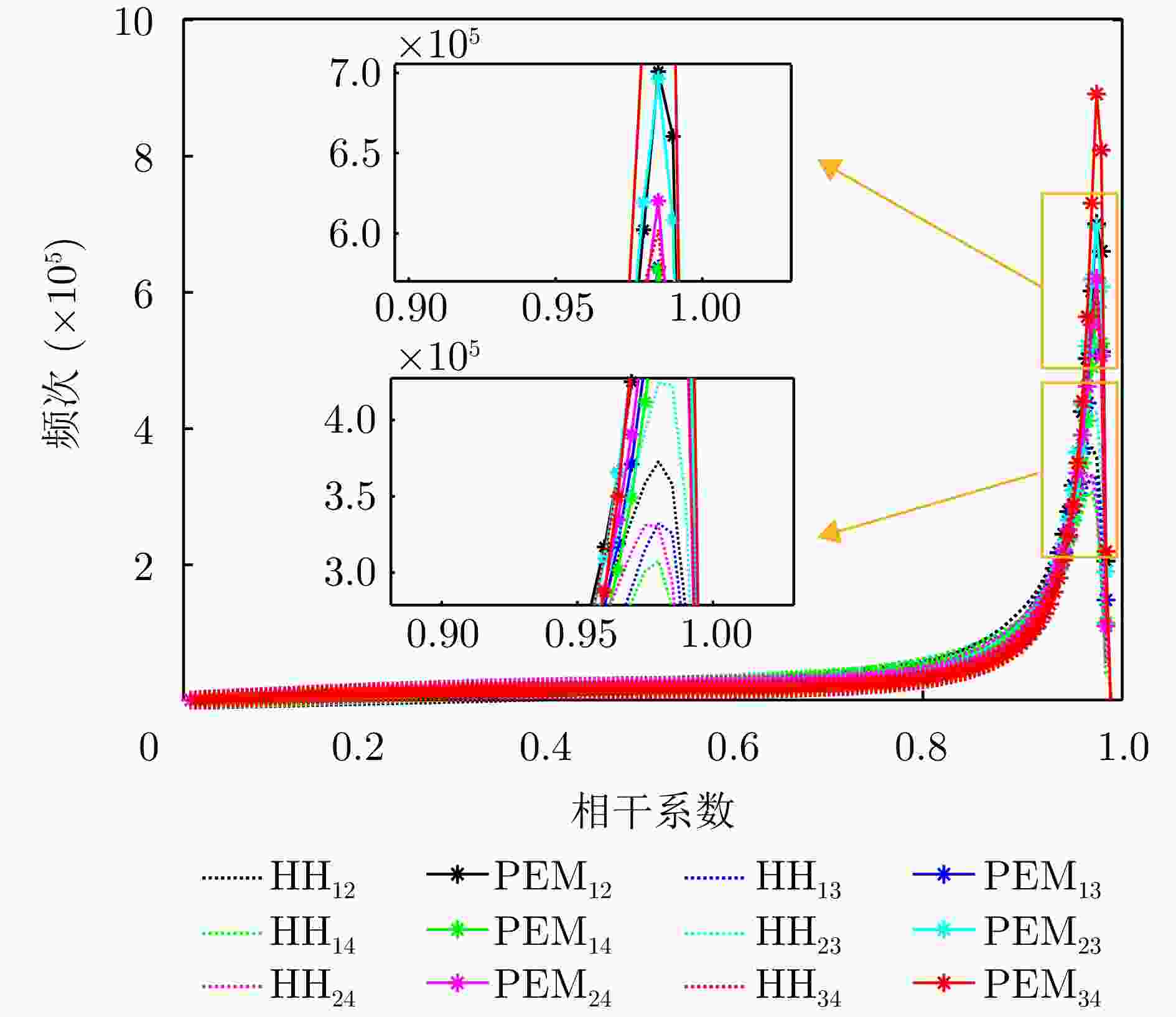
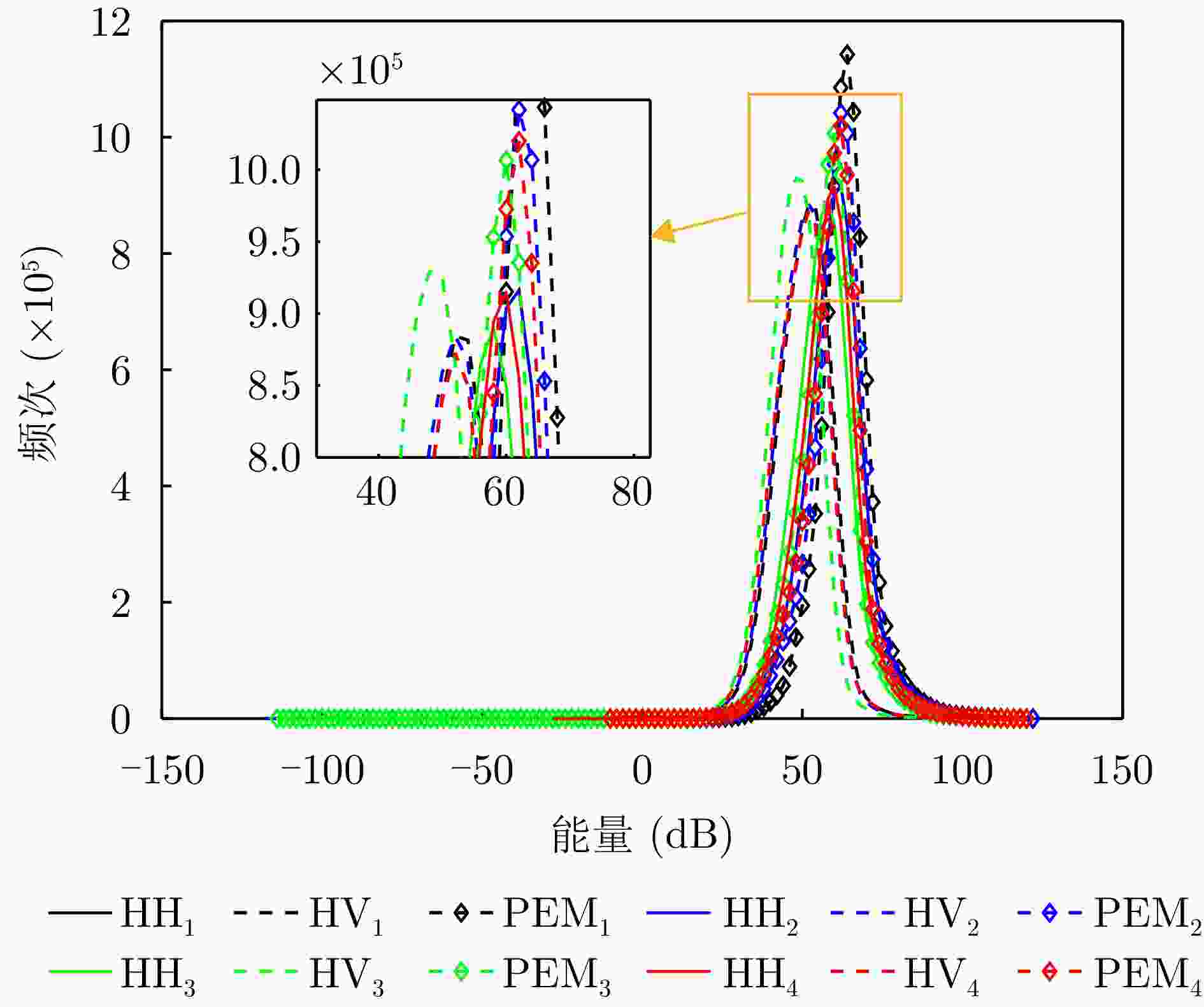
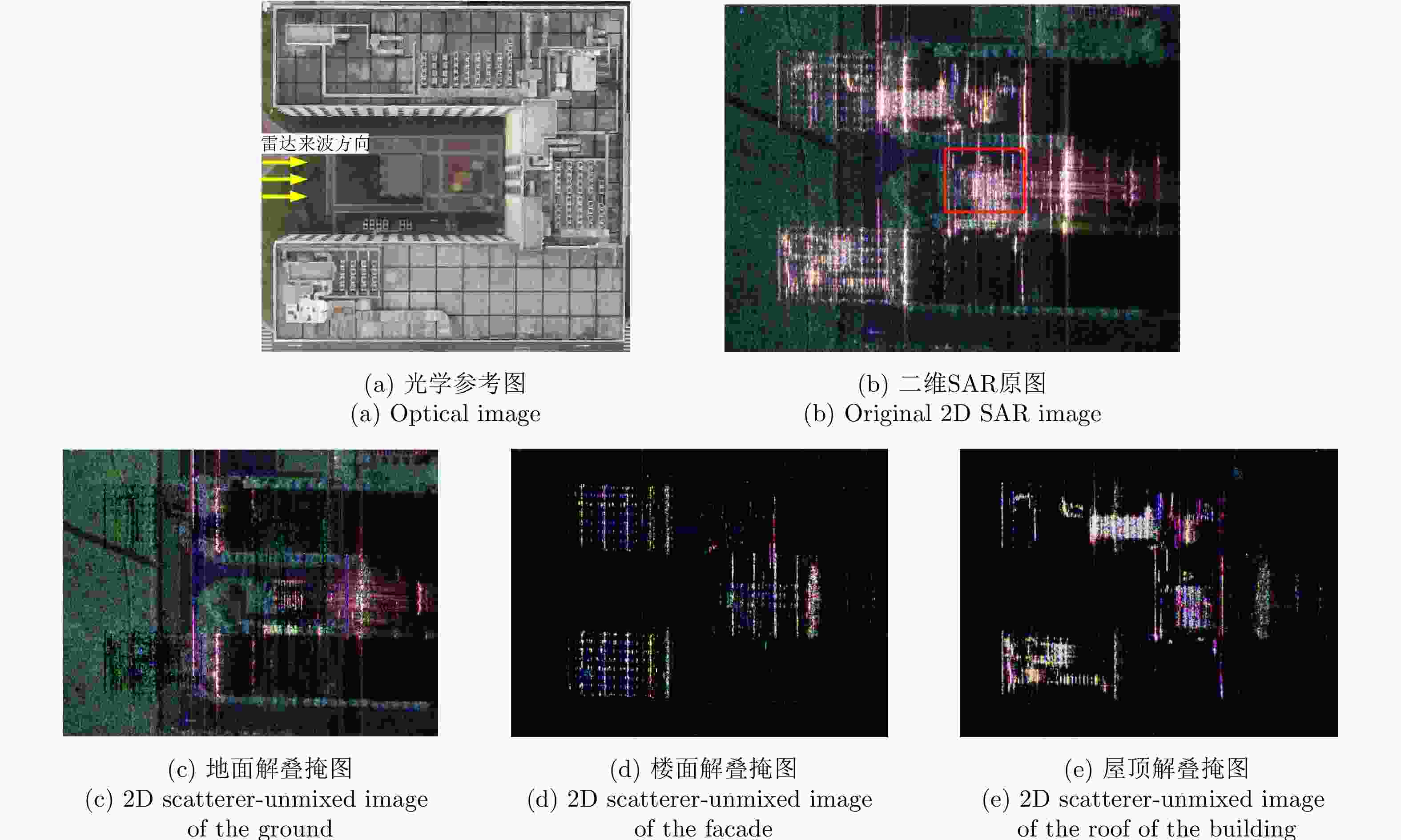
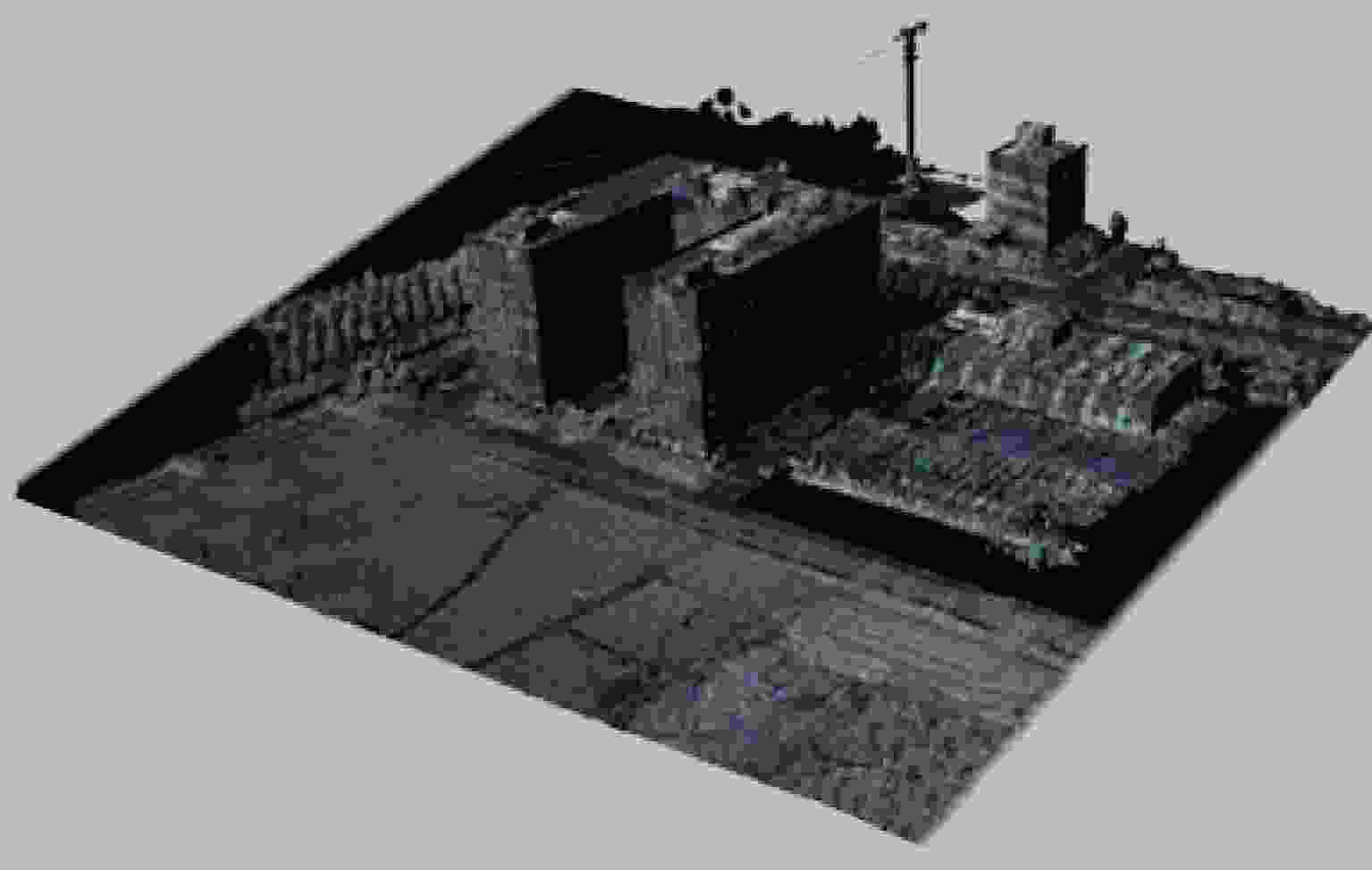
摘要: 三维合成孔径雷达在测绘制图、防灾减灾等诸多领域有应用潜力,已经成为SAR的重要研究方向。为减少三维SAR的观测次数或天线阵元数量,推动三维SAR的应用和发展,中国科学院空天信息创新研究院牵头研制了微波视觉三维SAR实验系统,旨在为微波视觉SAR三维成像提供实验平台和数据。该文针对微波视觉三维SAR实验系统及其全极化数据处理方法进行介绍,涵盖了极化校正、极化相干增强、极化约束三维成像、三维融合可视化等全流程的关键步骤。基于发布的SAR微波视觉三维成像全极化数据集,给出了三维成像结果示例,验证了微波视觉三维SAR实验系统的全极化性能以及处理方法的有效性。该文发布的数据集将为SAR三维成像研究提供良好的数据条件。Abstract: Three-Dimensional (3D) Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) holds great potential for applications in fields such as mapping and disaster management, making it an important research focus in SAR technology. To advance the application and development of 3D SAR, especially by reducing the number of observations or antenna array elements, the Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, (AIRCAS) has pioneered the development of the full-polarimetric Microwave Vision 3D SAR (MV3DSAR) experimental system. This system is designed to serve as an experimental platform and a source of data for microwave vision SAR 3D imaging studies. This study introduces the MV3DSAR experimental system along with its full-polarimetric SAR data set. It also proposes a set of full-polarimetric data processing scheme that covers essential steps such as polarization correction, polarization coherent enhancement, microwave vision 3D imaging, and 3D fusion visualization. The results from the 3D imaging data set confirm the full-polarimetric capabilities of the MV3DSAR experimental system and validate the effectiveness of the proposed processing method. The full-polarimetric unmanned aerial vehicle -borne array interferometric SAR data set, released through this study, offers enhanced data resources for advancing 3D SAR imaging research.
-
Key words:
- SAR 3D imaging /
- Microwave vision /
- Polarimetric array interference SAR /
- UAV-borne SAR /
- Multiview
-
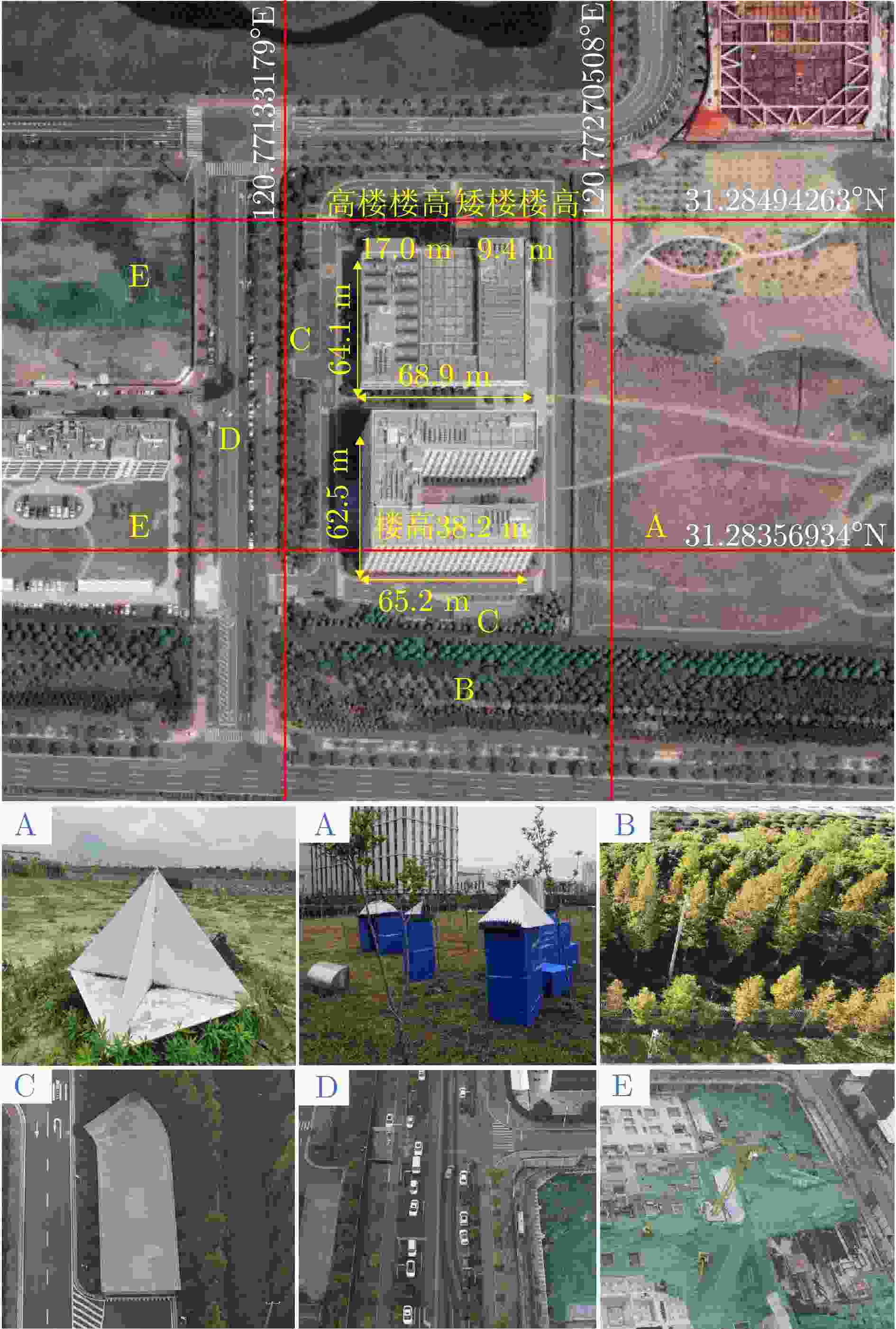
表 1 全极化Ku-SAR载荷参数
Table 1. Parameters of full-polarimetric Ku-SAR payload
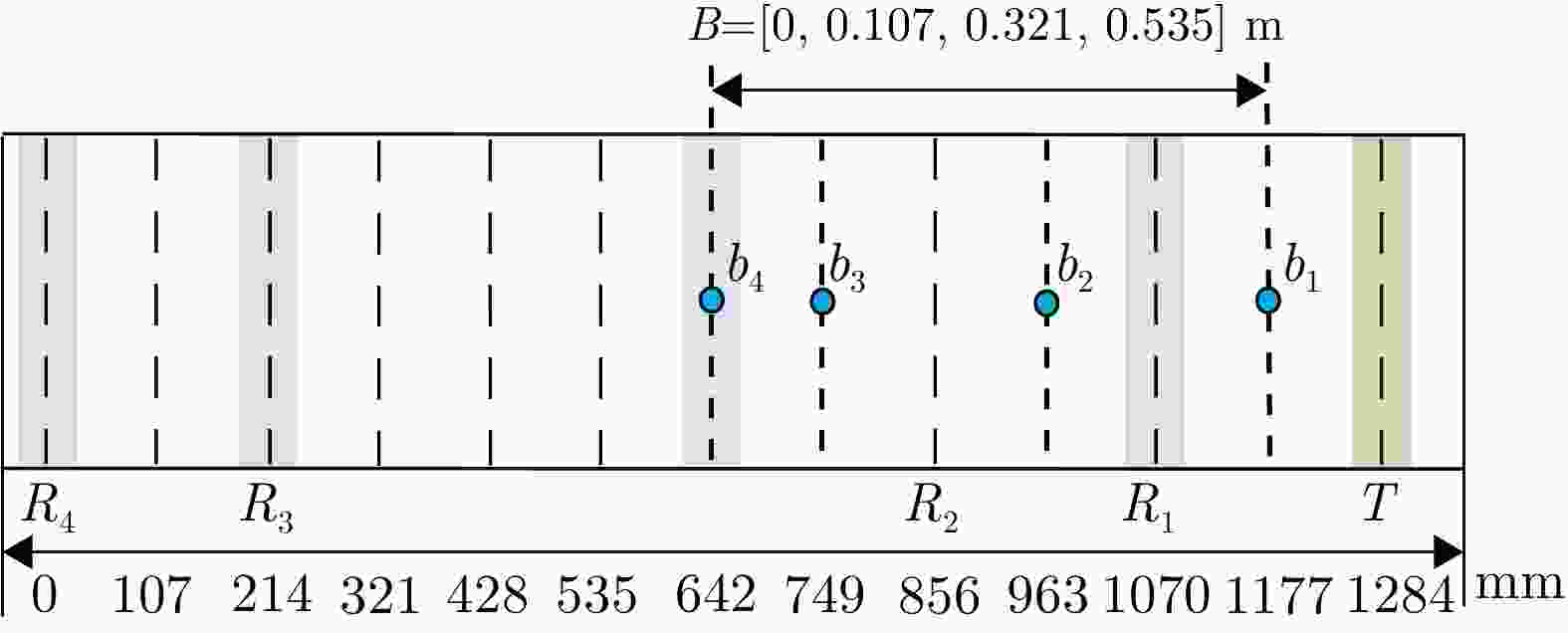
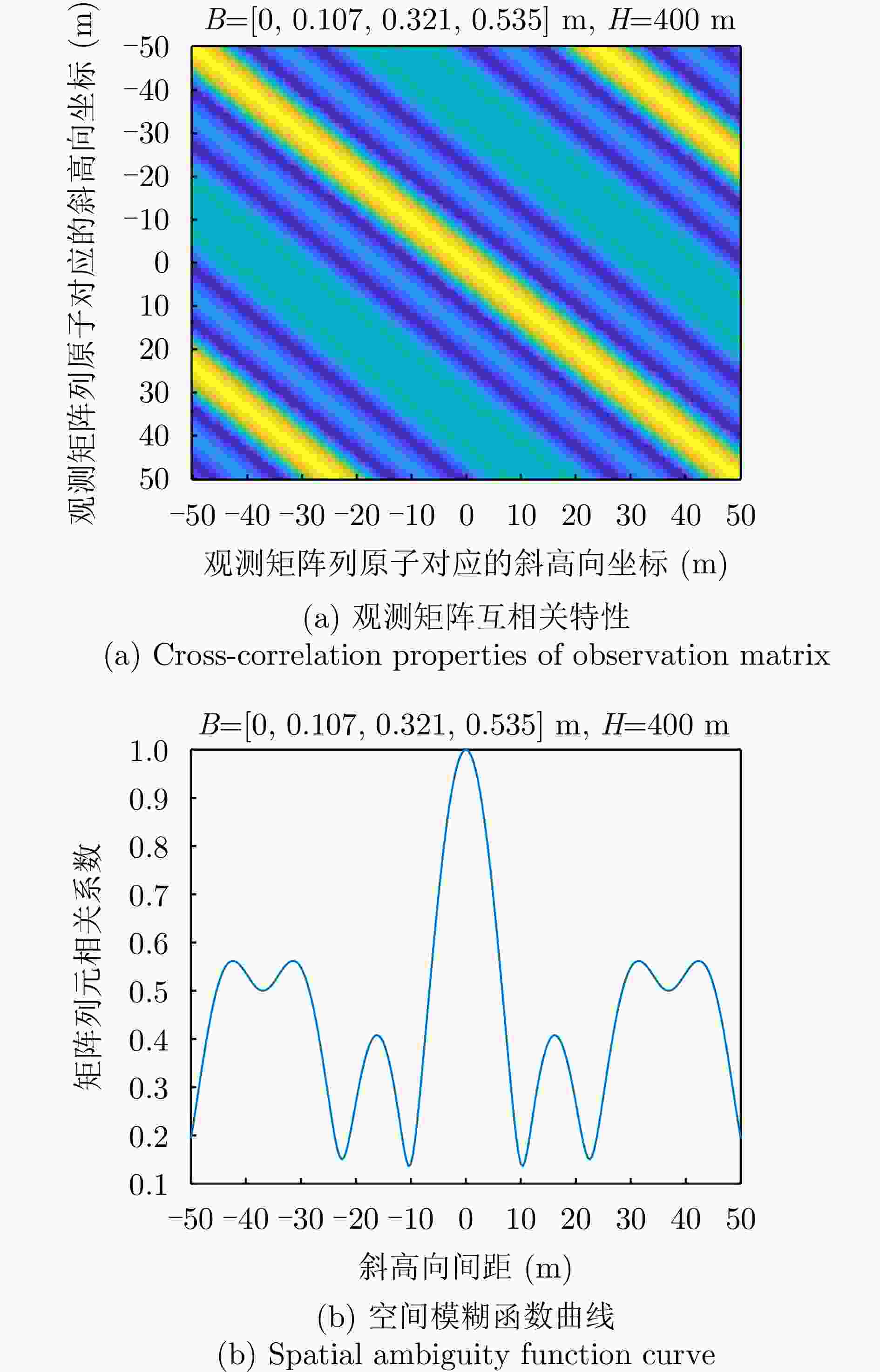
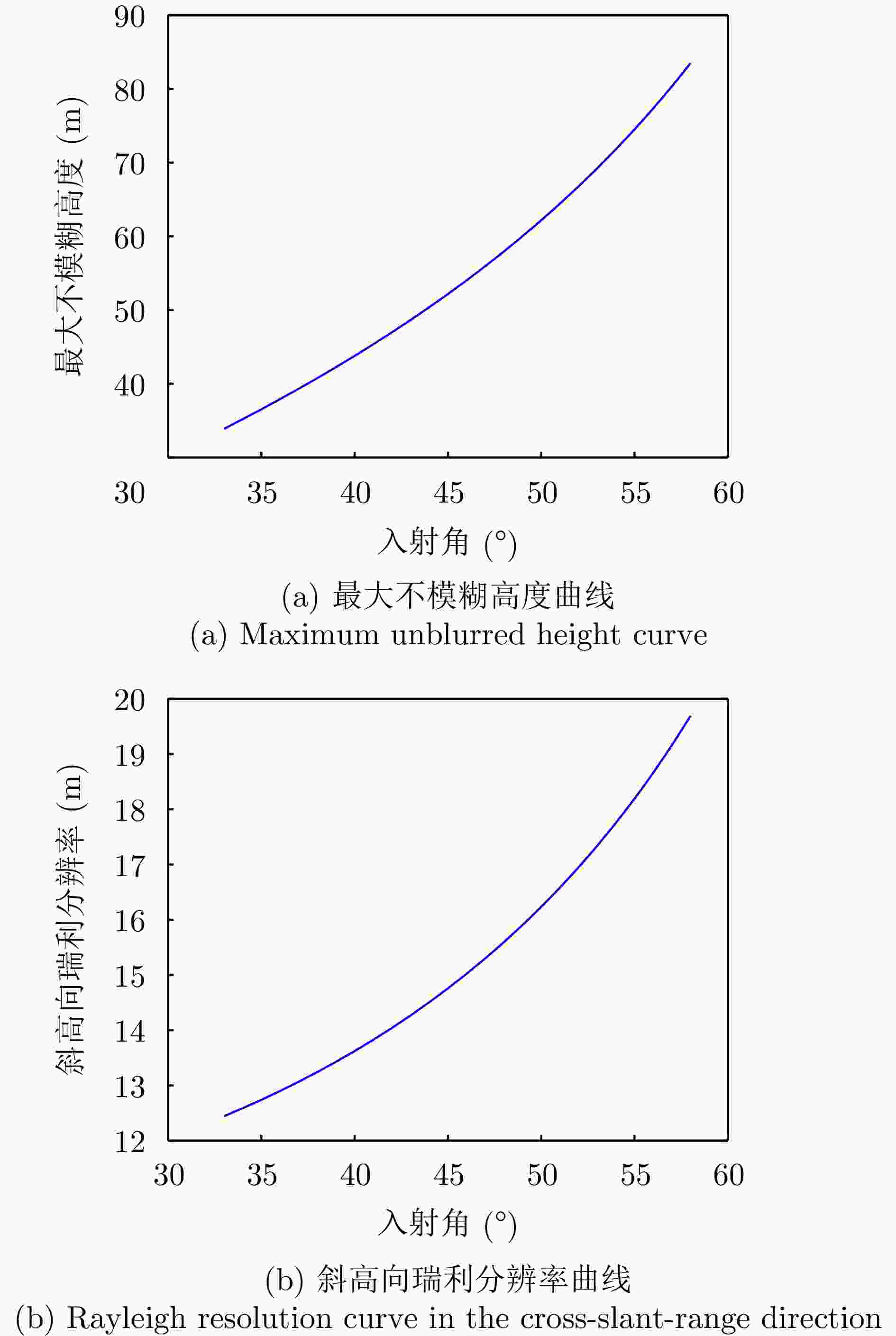
序号 参数名称 参数值或内容 1 中心频率 15.2 GHz 2 信号形式 调频连续波(FMCW) 3 极化方式 HH/HV/VH/VV 4 信号带宽 1200 MHz 5 天线尺寸(单通道) 0.05 m(俯仰)×0.32 m(方位) 6 每个极化的阵列通道数 4 7 分辨率 优于0.2 m×0.2 m 8 天线波束宽度 方位≥4° 俯仰≥24° 9 天线极化隔离度 优于25 dB 10 通道相位不平衡稳定度 ±5° (10 min内) 11 通道幅度不平衡稳定度 ±0.2 dB (10 min内) 12 中心视角 45° 13 NESZ 不大于–30 dB (最远
作用距离3.6 km)14 Ku-SAR重量 主机、存储、电池、天线、结构等
一共5.7 kg表 2 三维重建精度对比
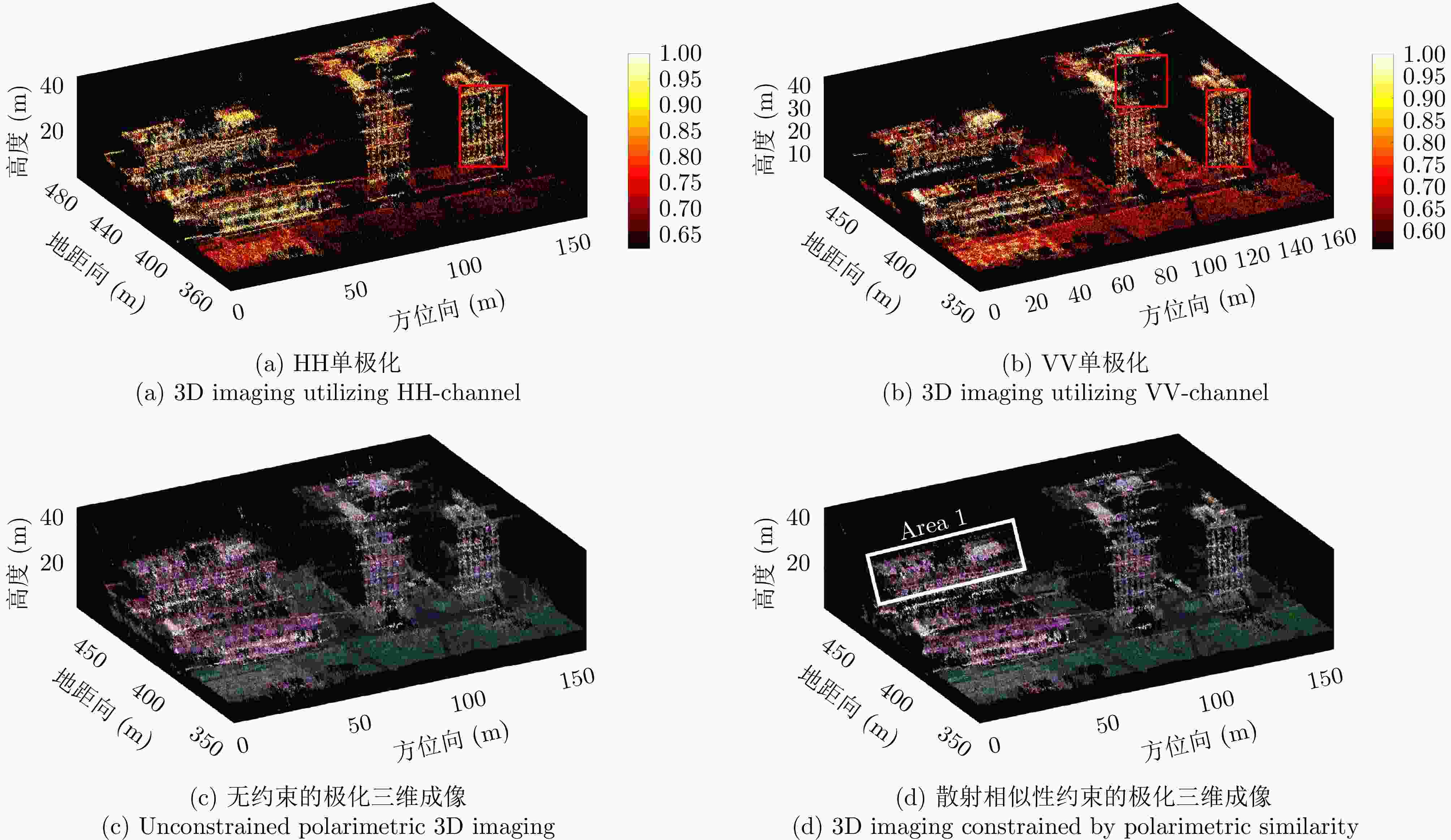
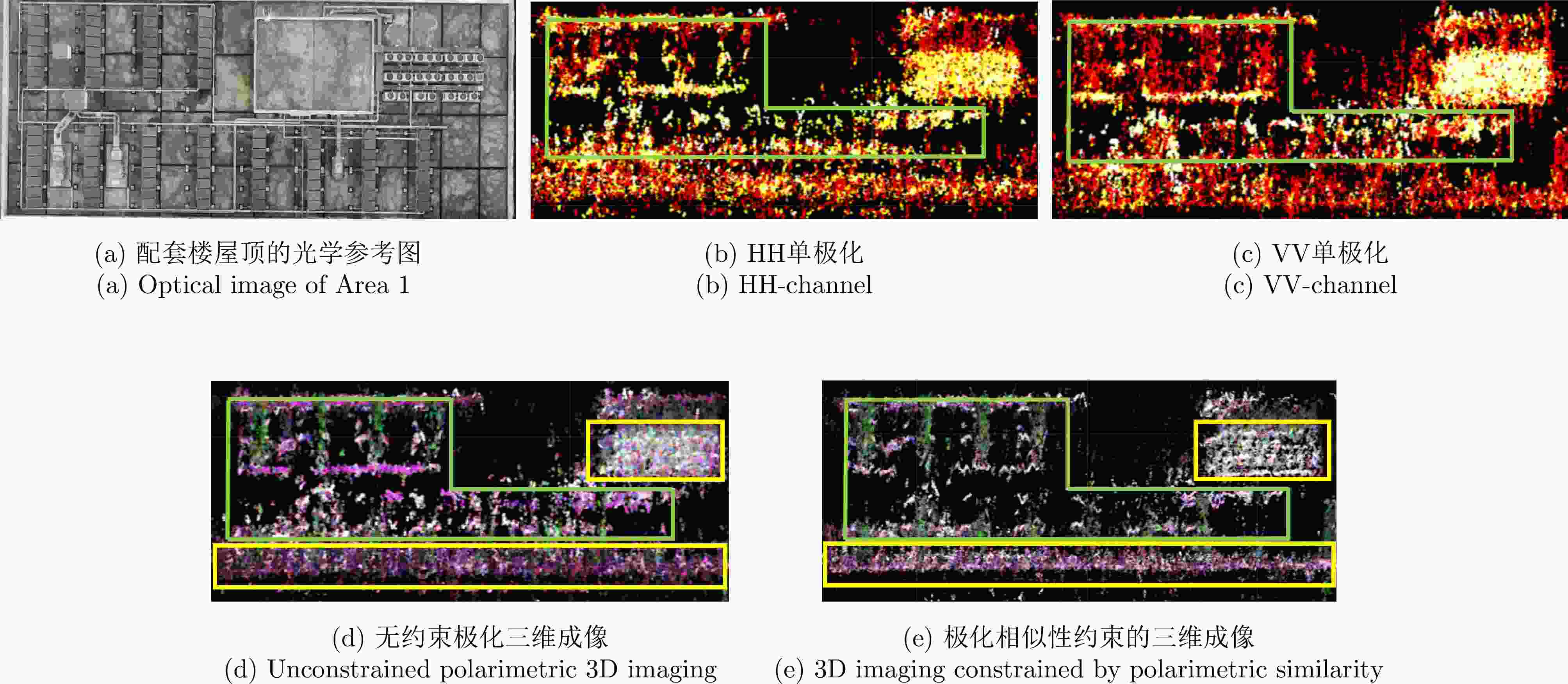
Table 2. Comparison of 3D reconstruction accuracy
三维成像方法 点云三维重建精度(m) HH单极化 1.51 VV单极化 1.46 无约束的全极化 1.36 极化相似性约束的全极化 0.93 表 1 Parameters of full-polarimetric Ku-SAR payload
Number Name Value / Content 1 Center frequency 15.2 GHz 2 Signal form FMCW 3 Polarization HH/HV/VH/VV 4 Bandwidth 1200 MHz5 Antenna size (1 Channel) 0.05 m (pitch) ×
0.32 m (azimuth)6 Number of array channels 4 7 Resolution Better than 0.2 m × 0.2 m 8 Antenna beamwidth Azimuth: ≥4°
Pitch: ≥24°9 Polarization isolation of antenna Better than 25 dB 10 Phase imbalance between channels ±5° (within 10 min) 11 Amplitude imbalance between channels ±0.2 dB
(within 10 min)12 Central angle of view 45° 13 NESZ Not more than –30 dB
(maximum operating
distance: 3.6 km)14 Total weight 5.7 kg 表 2 Comparison of 3D reconstruction accuracy
3D Imaging Methods 3D Reconstruction Accuracy (m) HH single-polarimetric 3D imaging 1.51 VV single-polarimetric 3D imaging 1.46 Unconstrained polarimetric 3D imaging 1.36 3D imaging constrained by polarimetric similarity 0.93 -
[1] KNAELL K K and CARDILLO G P. Radar tomography for the generation of three-dimensional images[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1995, 142(2): 54–60. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19951791. [2] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098. [3] TEBALDINI S, NAGLER T, ROTT H, et al. Imaging the internal structure of an alpine glacier via L-band airborne SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(12): 7197–7209. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2597361. [4] HUANG Yue, FERRO-FAMIL L, and REIGBER A. Under-foliage object imaging using SAR tomography and polarimetric spectral estimators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(6): 2213–2225. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2171494. [5] FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, and SERAFINO F. Three-dimensional multipass SAR focusing: Experiments with long-term spaceborne data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(4): 702–714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.843567. [6] 张福博. 阵列干涉SAR三维重建信号处理技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2015.ZHANG Fubo. Research on signal processing of 3-D reconstruction in linear array synthetic aperture radar interferometry[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. [7] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873. [8] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183. [9] ZHU Xiaoxiang, GE Nan, and SHAHZAD M. Joint sparsity in SAR tomography for urban mapping[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1498–1509. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2469646. [10] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像——从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090.DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090. [11] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 杨振礼, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR关键技术及实验系统初步进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027.QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, YANG Zhenli, et al. Key technology and preliminary progress of microwave vision 3D SAR experimental system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027. [12] JIAO Zekun, DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Urban 3D imaging using airborne TomoSAR: Contextual information-based approach in the statistical way[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 170: 127–141. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.10.013. [13] JIAO Zekun, QIU Xiaolan, DONG Shuhang, et al. Preliminary exploration of geometrical regularized SAR tomography[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 201: 174–192. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.05.019. [14] 朱庆涛, 殷君君, 曾亮, 等. 基于邻域一致性的极化SAR图像仿射配准[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 49–60. doi: 10.12000/JR20120.ZHU Qingtao, YIN Junjun, ZENG Liang, et al. Polarimetric SAR image affine registration based on neighborhood consensus[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 49–60. doi: 10.12000/JR20120. [15] 仇晓兰, 罗一通, 程遥, 等. SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集-3.0[EB/OL]. 雷达学报. https://radars.ac.cn/web/data/getData?newsColumnId=1cbc9f2d-f2ee-4748-9972-748c007f697f, 2024.QIU Xiaolan, LUO Yitong, CHENG Yao, et al. SAR microwave vision 3D imaging Dataset 3.0[EB/OL]. Journal of Radars. https://radars.ac.cn/web/data/getData?newsColumnId=2f2748db-10ef-4ad0-bcc4-f087ce59b6f8&pageType=en, 2024. [16] 徐牧, 王雪松, 肖顺平. 基于改善极化相似性的极化SAR目标增强新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(5): 1047–1051. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00754.XU Mu, WANG Xuesong, and XIAO Shunping. Target enhancement in POL-SAR imagery based on the improvement of polarization characteristics similarity[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2008, 30(5): 1047–1051. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00754. [17] JIANG Sha, QIU Xiaolan, HAN Bing, et al. A quality assessment method based on common distributed targets for GF-3 polarimetric SAR data[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 807. doi: 10.3390/s18030807. [18] LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009. doi: 10.1201/9781420054989. [19] SONG Shujie, QIU Xiaolan, and SHANGGUAN Songtao. Study on the three dimension imaging methods of fully-polarised array InSAR[C]. IET International Radar Conference, Chongqing, China, 2023: 2999–3003. doi: 10.1049/icp.2024.1571. [20] SONG Shujie and QIU Xiaolan. A sparse Bayesian learning 3d imaging methodology based on polarimetric energy maximum in urban area for pol-array-insar[C]. IGARSS Conference, 2024, Athens, Greece, 2024. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10641994. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: