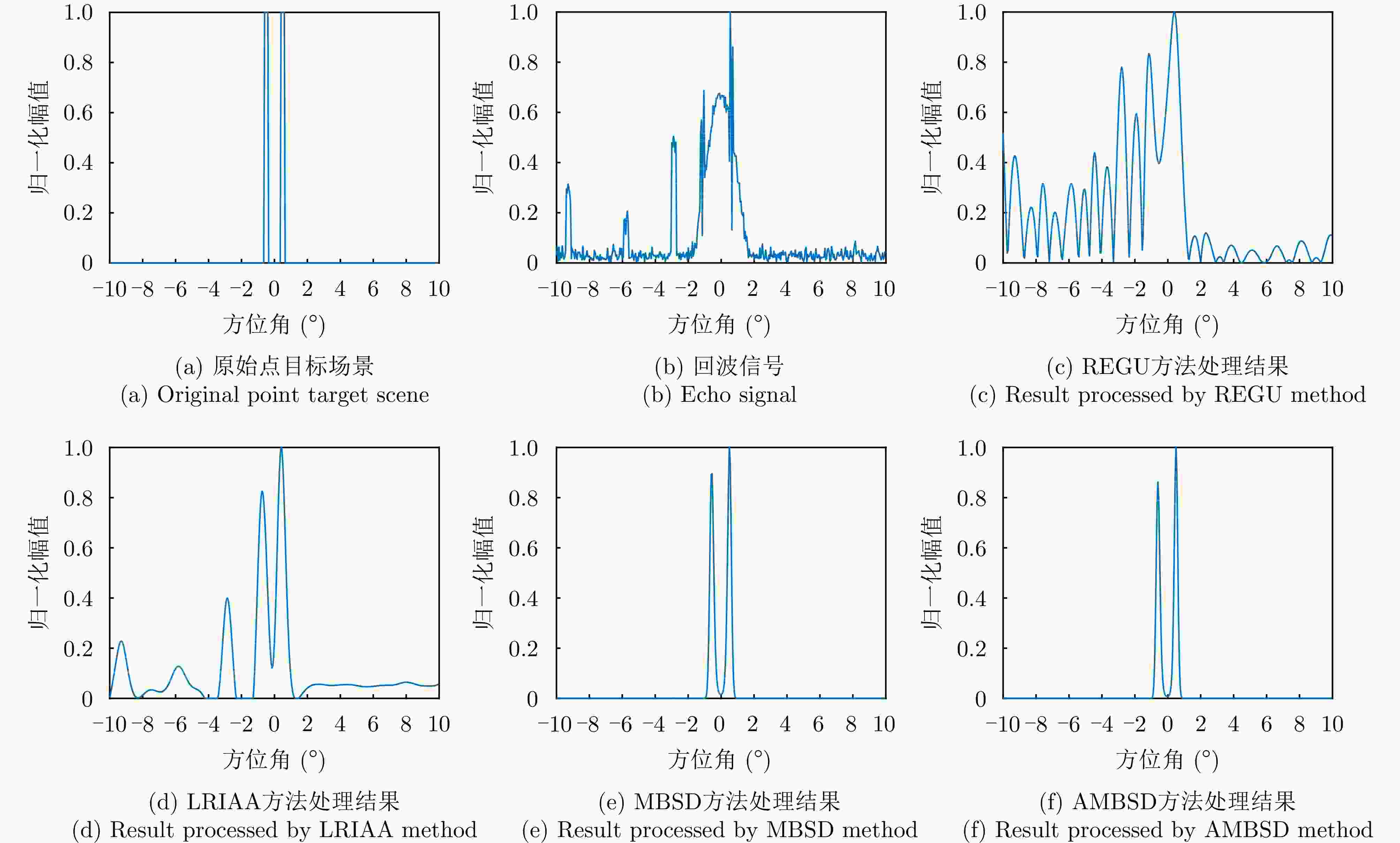
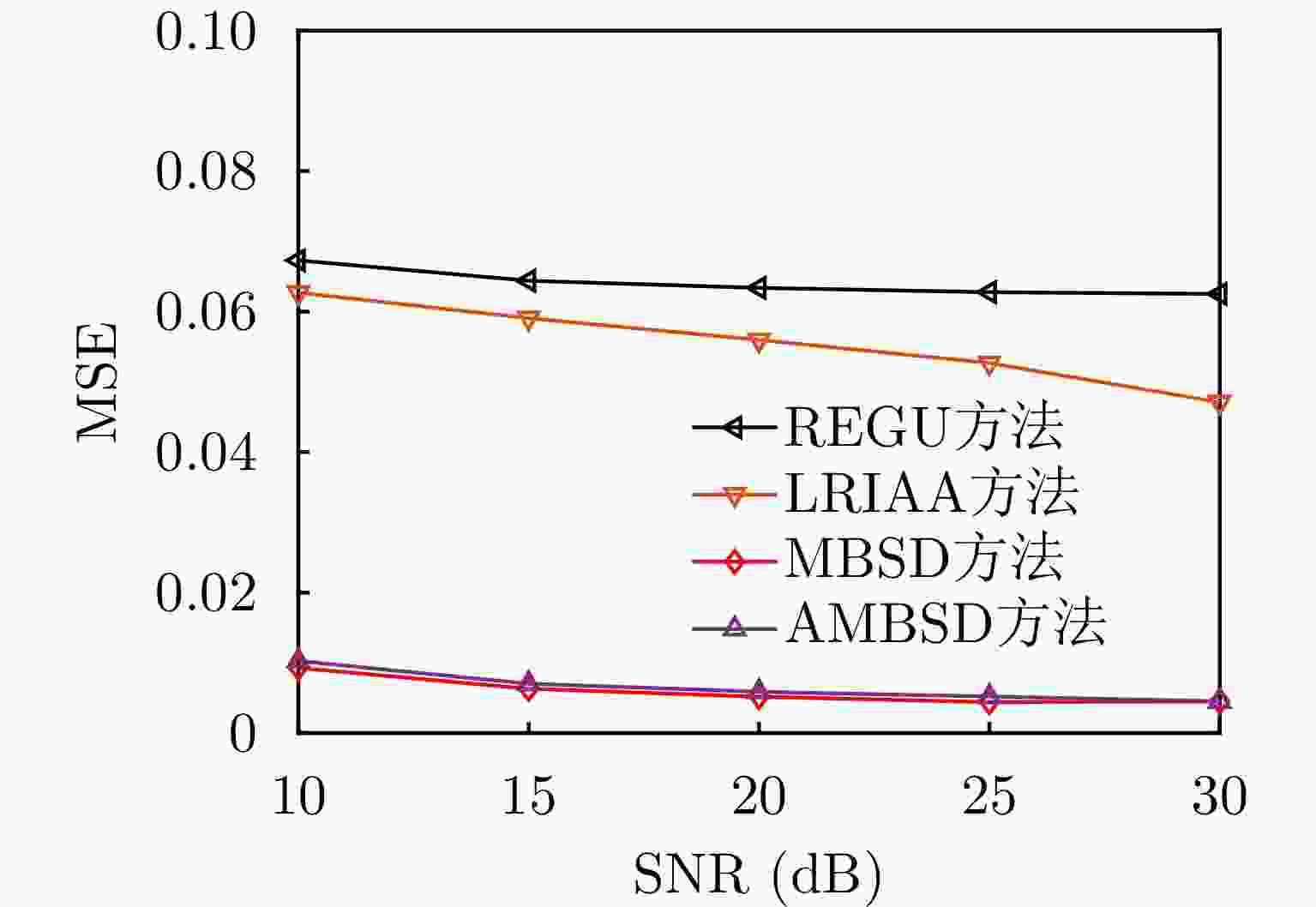
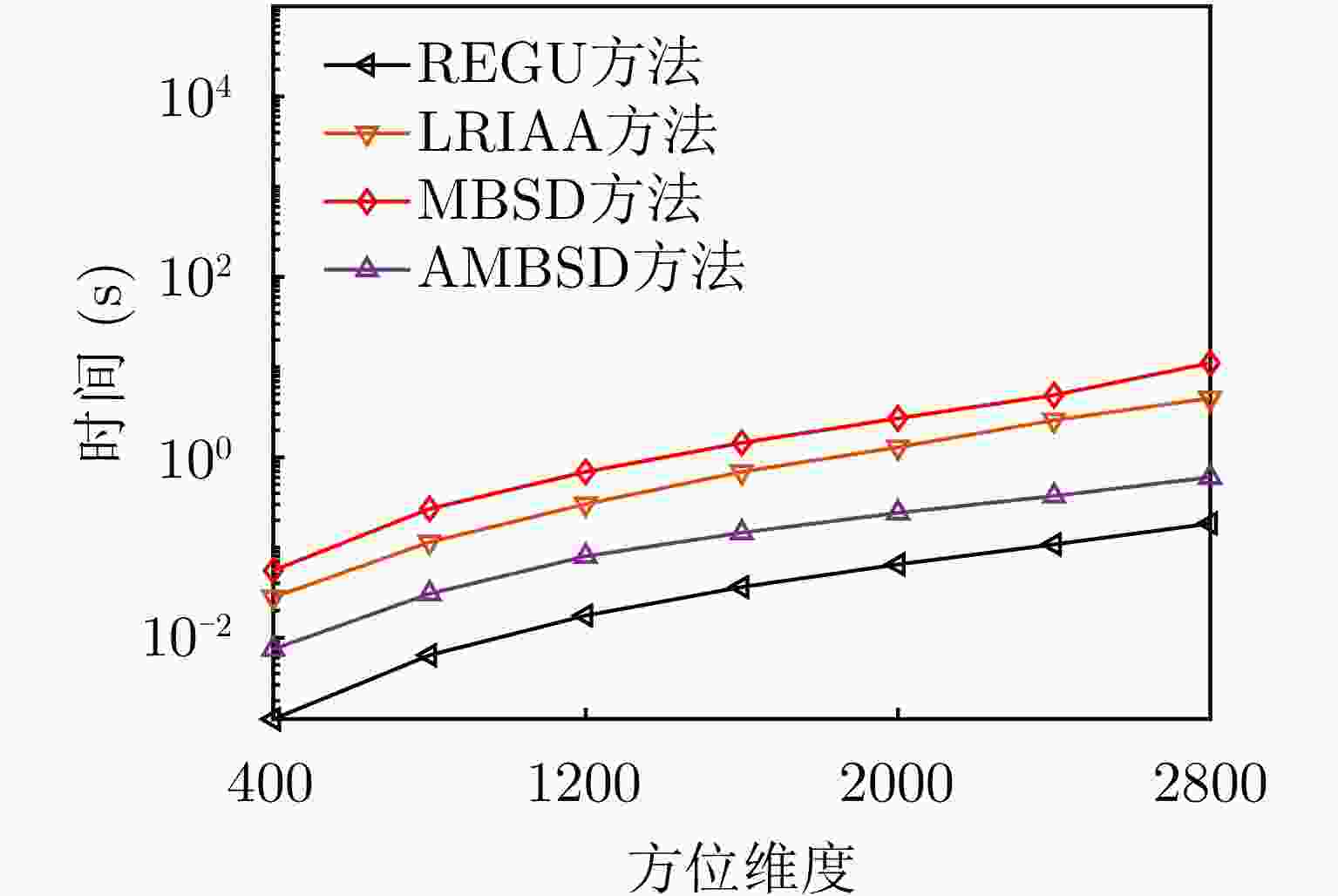
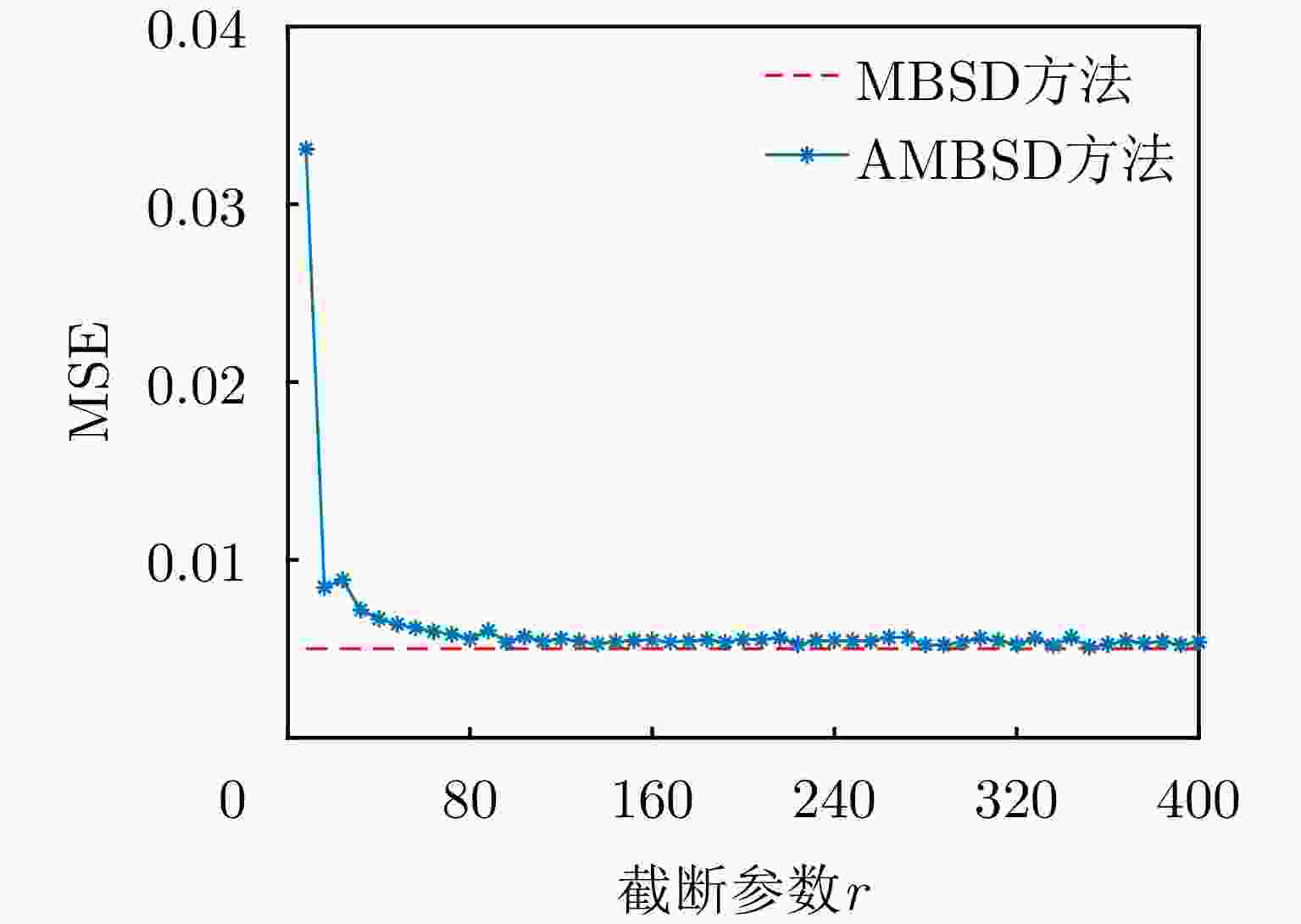
-
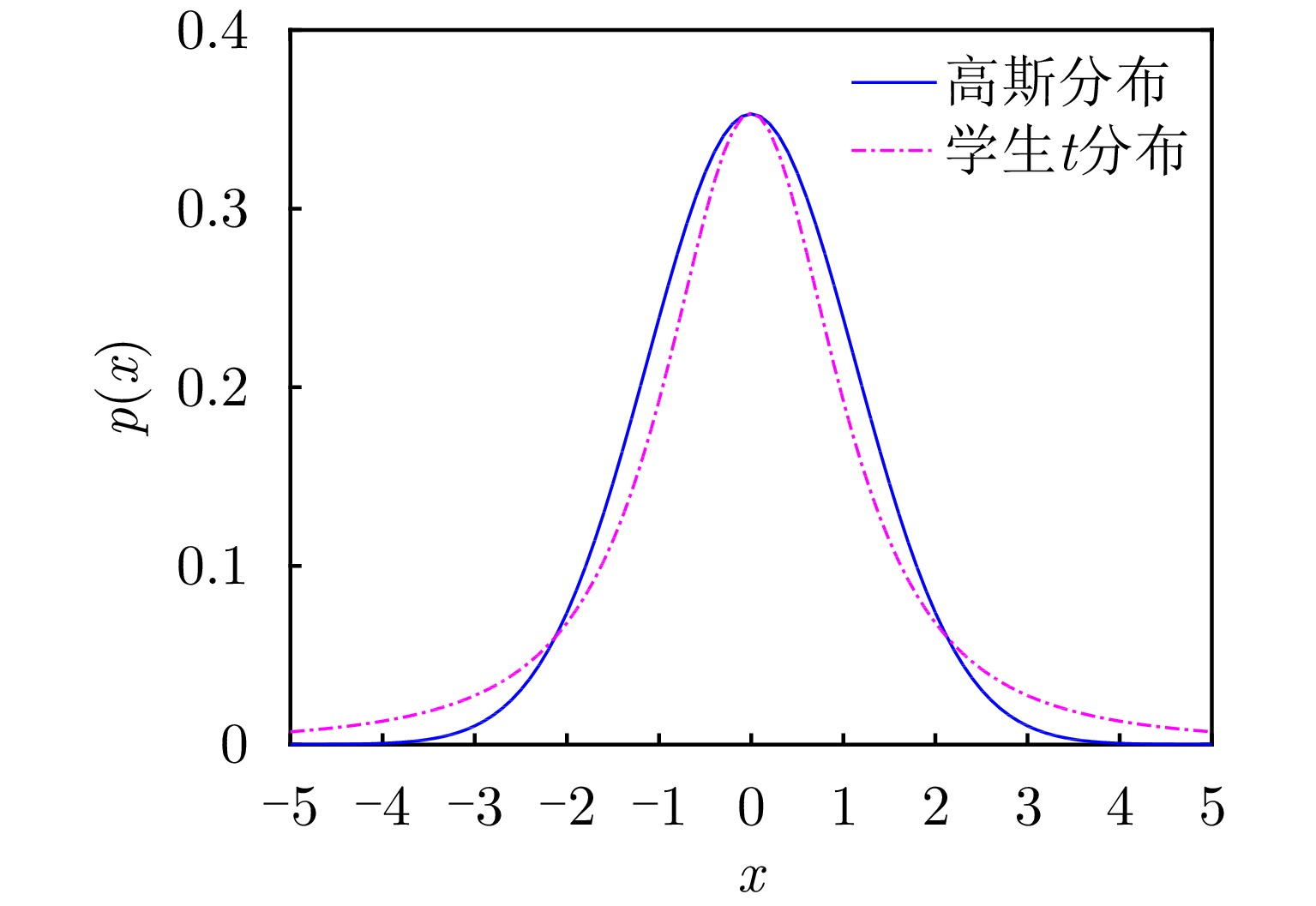
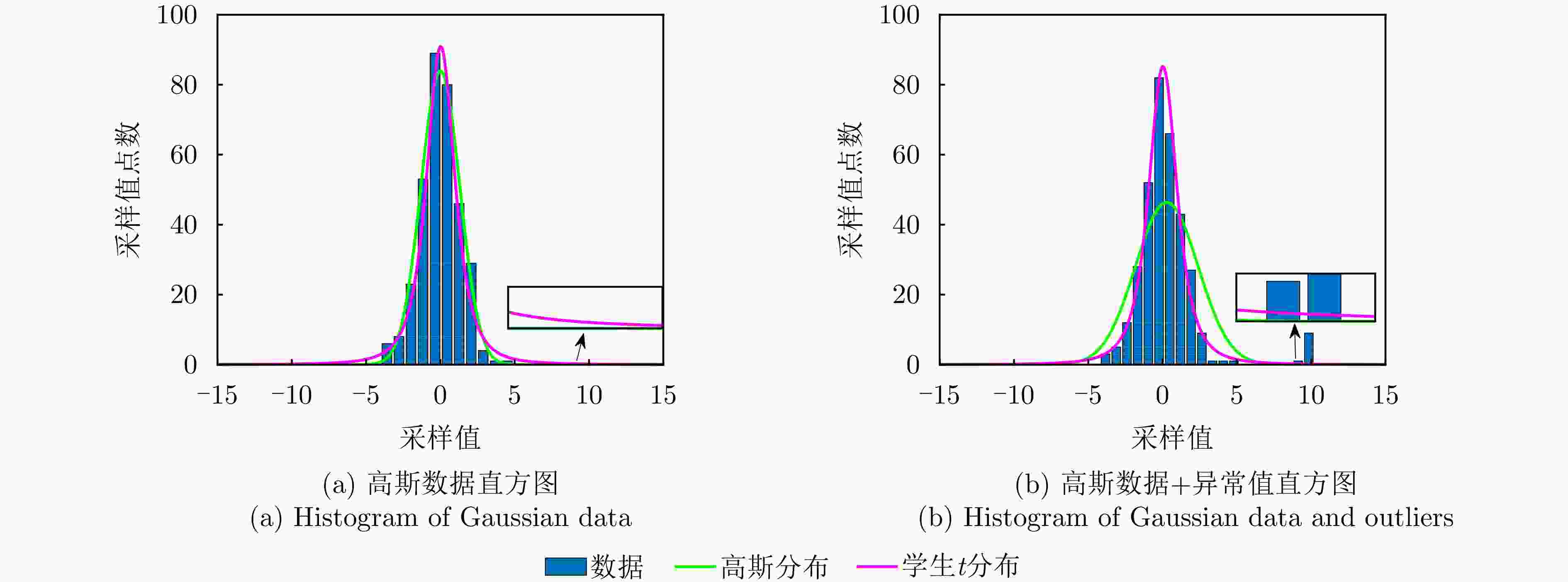
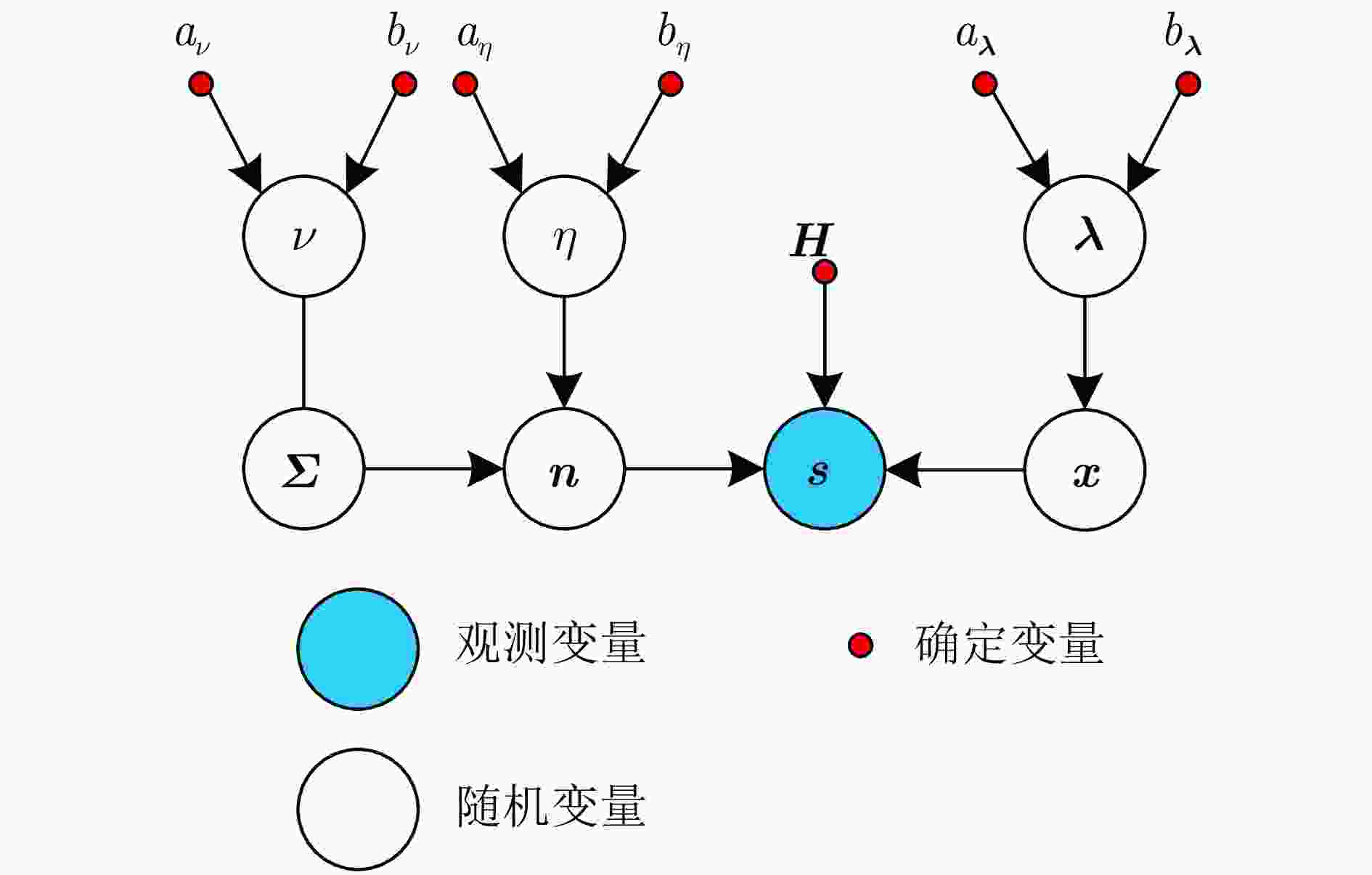
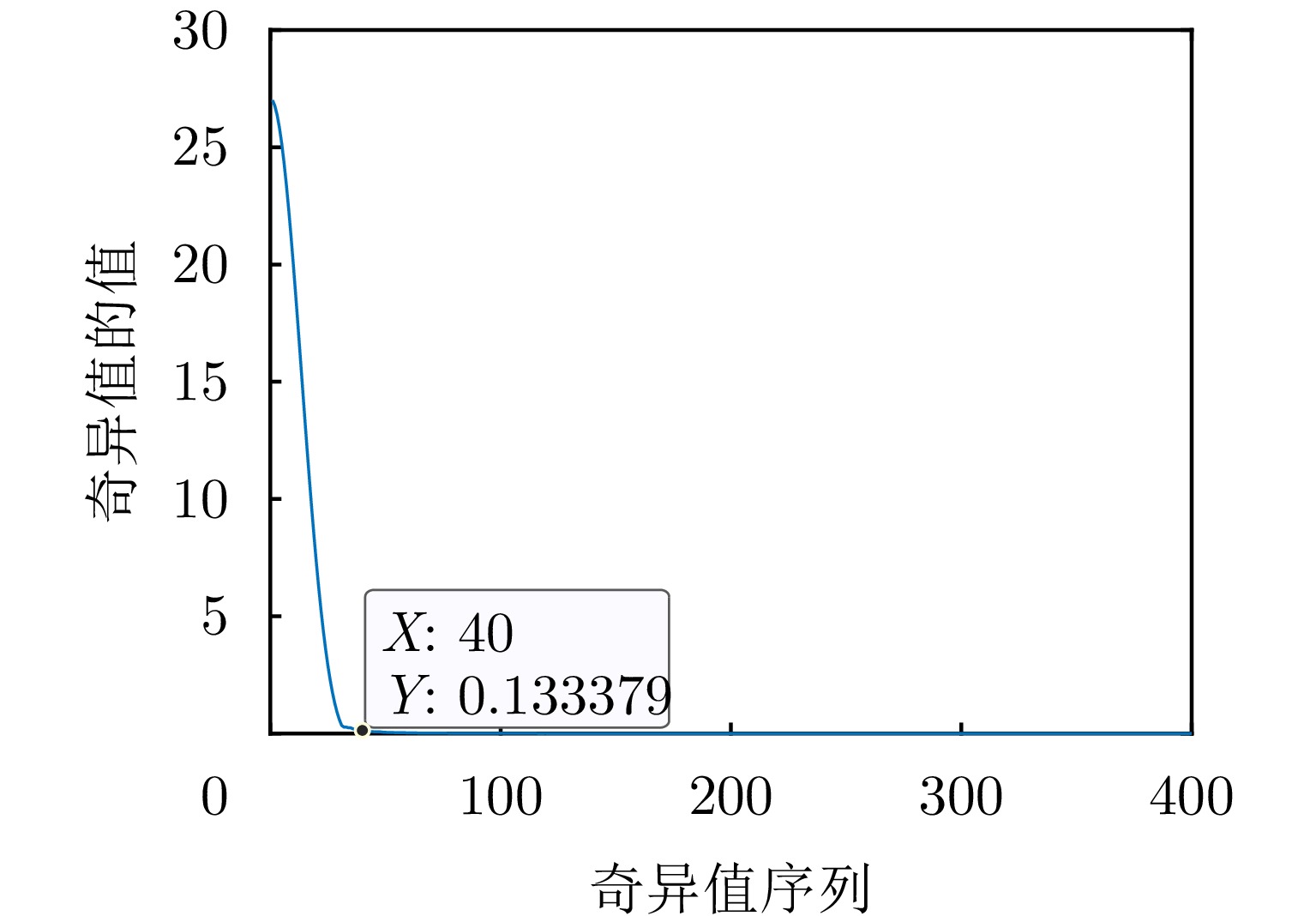
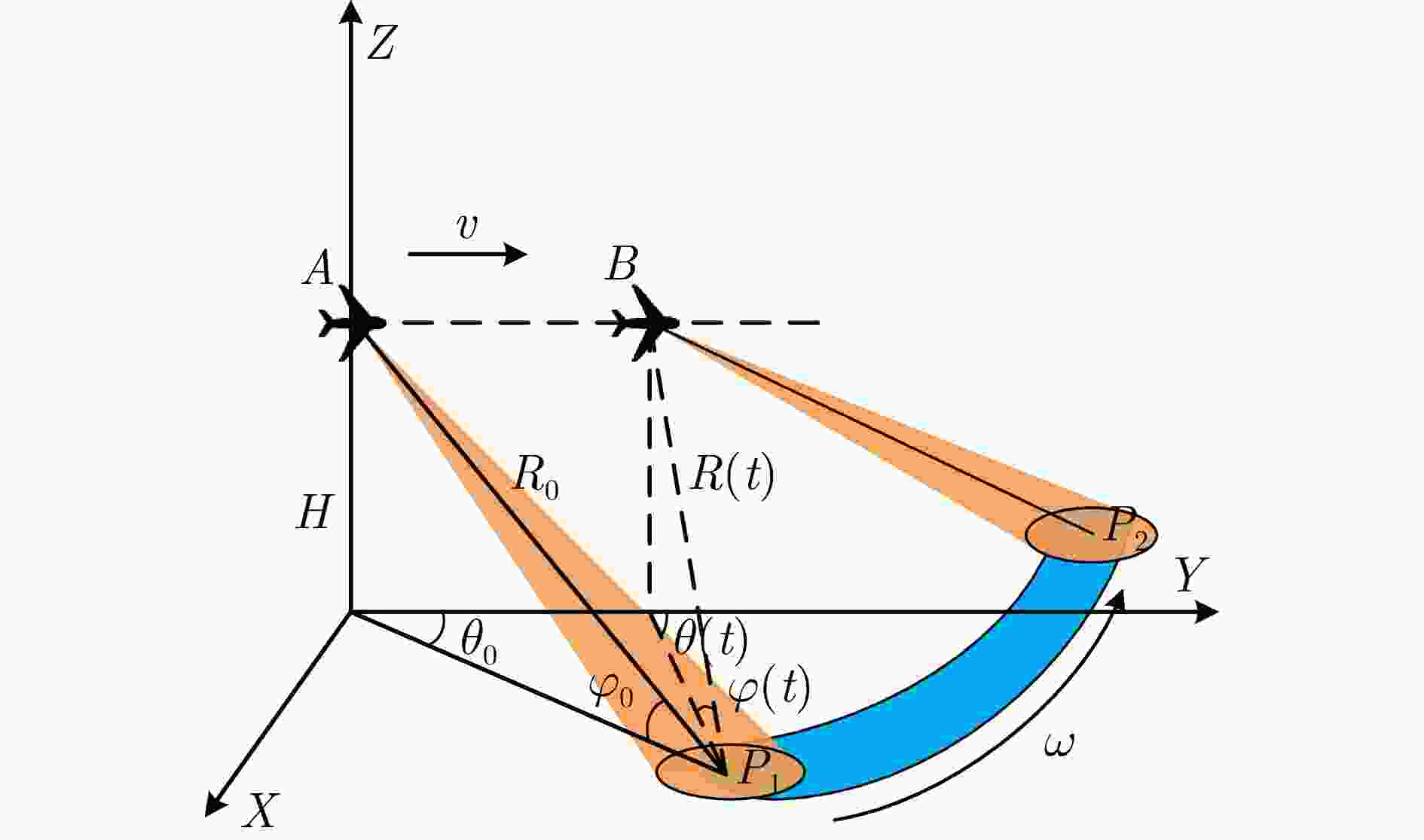
摘要: 机载扫描雷达前视成像可广泛应用于态势感知、自主导航和地形跟随。在雷达扫描过程中受到不经意的电磁脉冲干扰或设备性能异常等影响时,雷达回波数据出现异常值。已有的超分辨方法可以抑制回波中的异常值、提高角度分辨率,但没有考虑计算实时性问题。针对上述问题,该文提出了一种机载雷达超分辨方法实现回波数据异常时的快速前视成像。为了更好地拟合回波噪声,引入对异常值更加鲁棒的学生t分布,并采用期望最大化方法对成像参数进行估计。受截断奇异值分解方法的启发,将截断的酉矩阵引入目标散射系数的估计公式中。通过矩阵变换降低了求逆矩阵的尺寸,从而降低了参数估计的计算复杂度。仿真结果表明该文提出加速方法可以用更短的时间提高前视成像的角度分辨率,抑制回波数据中的异常值。Abstract: Forward-looking imaging of airborne scanning radar is widely used in situation awareness, autonomous navigation and terrain following. When the radar is influenced by unintentional temporally sporadic electromagnetic interference or abnormal equipment performance, the echo signal contains outliers. Existing super-resolution methods can suppress outliers and improve azimuth resolution, but the real-time computing problem is not considered. In this study, we propose an airborne scanning radar super-resolution method to achieve fast forward-looking imaging when echo data are abnormal. First, we propose using the Student-t distribution to model noise. Then, the expectation-maximization method is used to estimate the parameters. Inspired by the truncated singular value decomposition method, we introduce the truncated unitary matrix into the estimation formula of the target scattering coefficient. Finally, the size of inverse matrix is reduced and the computational complexity of parameter estimation is reduced through matrix transformation. The simulation results show that the proposed method can improve the azimuth resolution of forward-looking imaging in a shorter time, and suppress outliers in echo data.
-
Key words:
- Forward-looking imaging /
- Super-resolution /
- Abnormal echo data /
- Matrix transformation
-
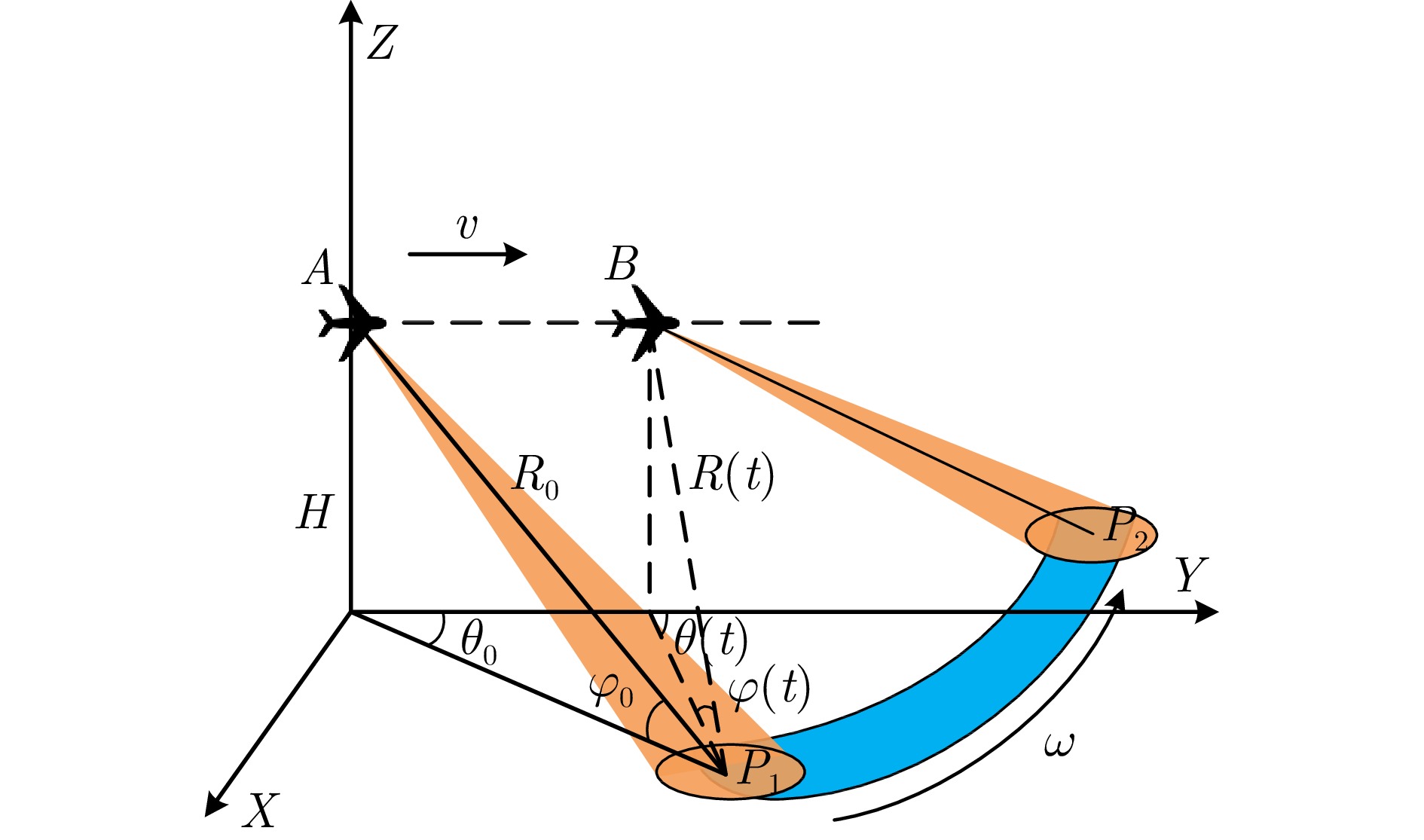
表 1 仿真系统参数
Table 1. System parameters of simulation
参数 数值 参数 数值 扫描速度$\left( {{{^ \circ } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{^ \circ } {\text{s}}}} \right. } {\text{s}}}} \right)$ $50$ 载波频率$ \left( {{\text{GHz}}} \right) $ $ 9.5 $ 扫描范围$ \left( {^ \circ } \right) $ $ \pm 10$ 信号带宽$ \left( {{\text{MHz}}} \right) $ $ 40 $ 脉冲重复频率$\left( {{\text{Hz}}} \right)$ $1000$ 平台速度$\left( {{{\text{m}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\text{m}} {\text{s}}}} \right. } {\text{s}}}} \right)$ $30$ 主瓣波束宽度$\left( {^ \circ } \right)$ 3 表 2 面目标仿真系统参数
Table 2. System parameters of area target simulation
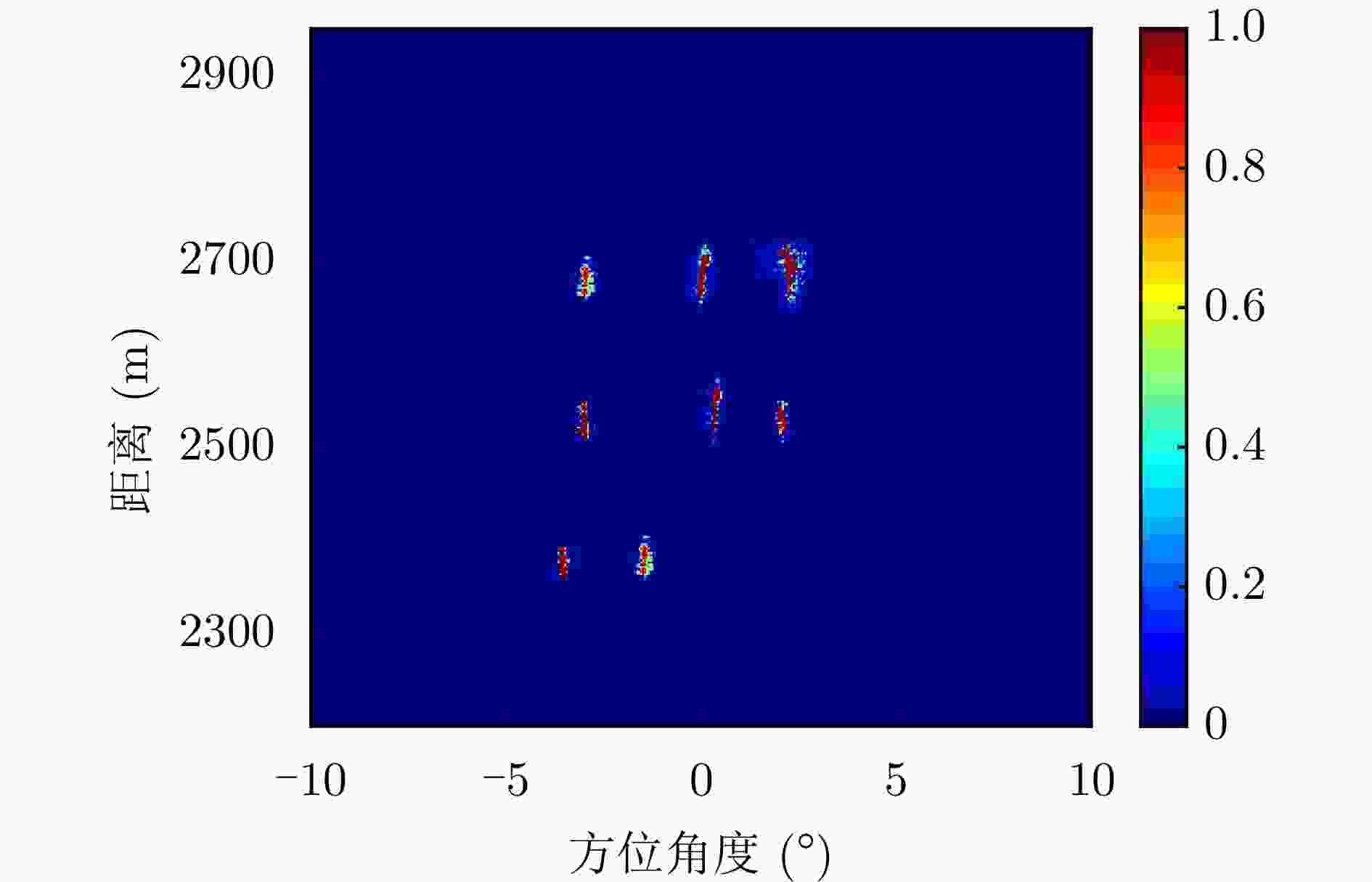
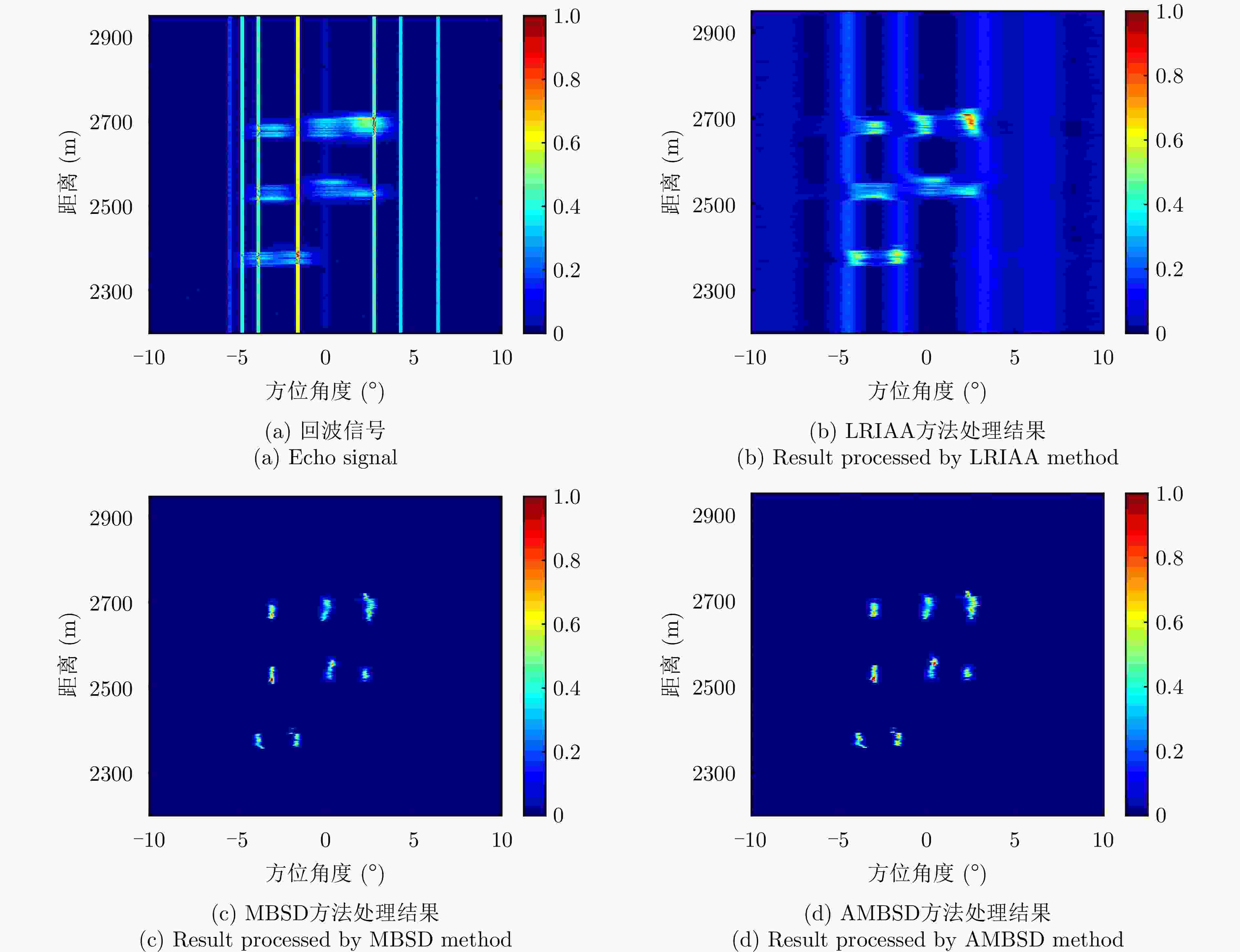
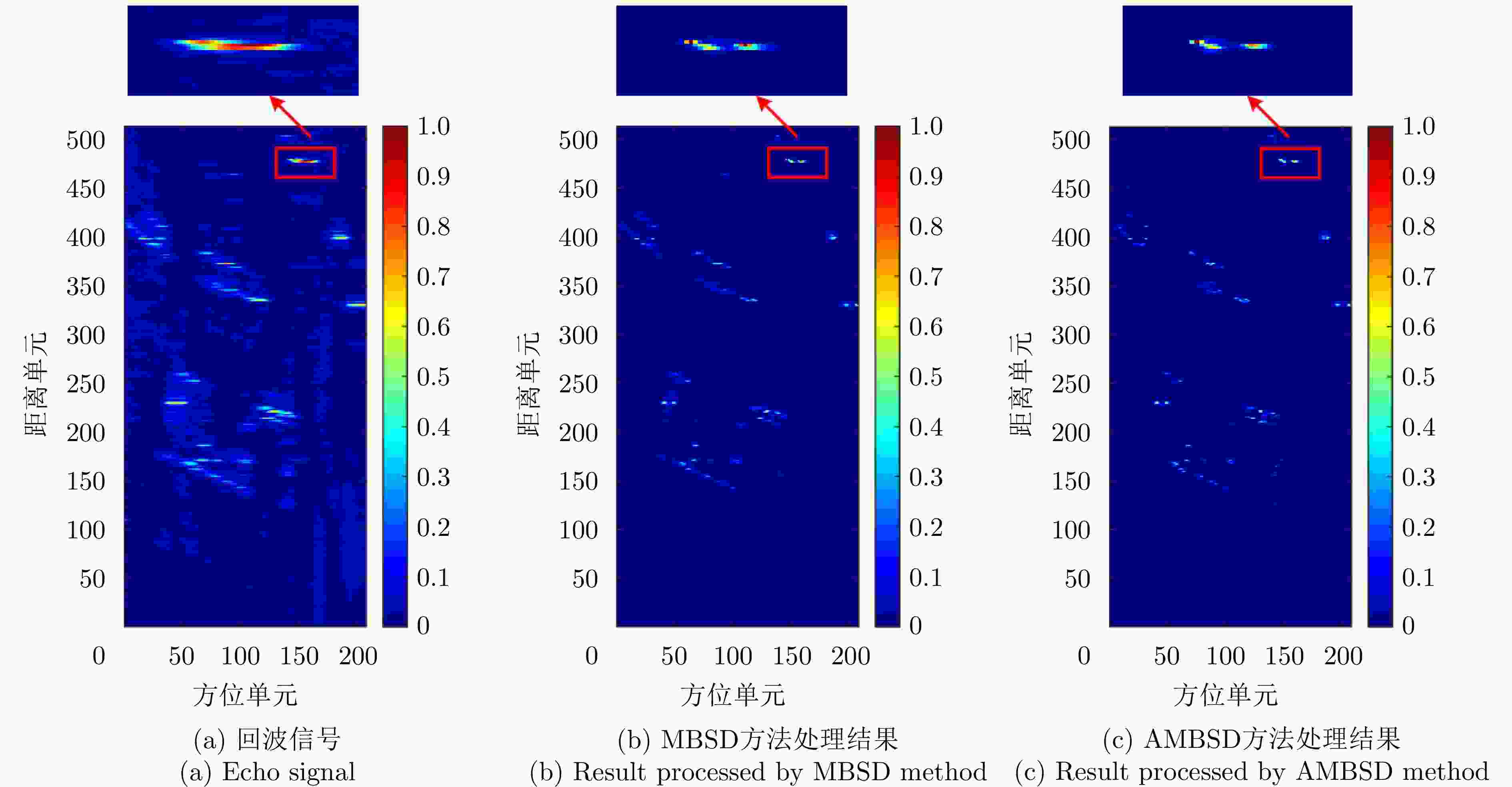
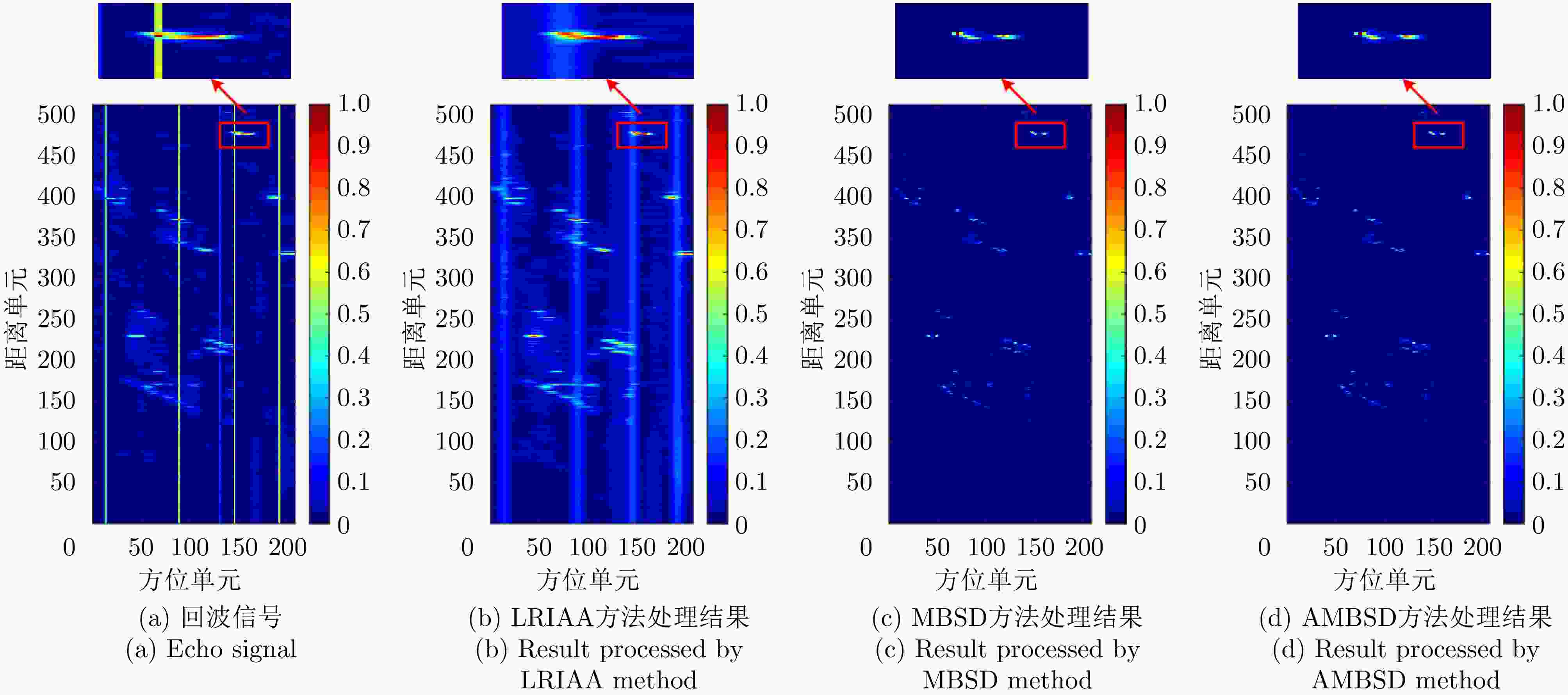
参数 数值 参数 数值 扫描速度$\left( {{{^ \circ } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{^ \circ } {\text{s}}}} \right. } {\text{s}}}} \right)$ $50$ 载波频率$ \left( {{\text{GHz}}} \right) $ $ 9.5 $ 扫描范围$ \left( {^ \circ } \right) $ $ \pm 10$ 信号带宽$ \left( {{\text{MHz}}} \right) $ $ 40 $ 脉冲重复频率$\left( {{\text{Hz}}} \right)$ $1000$ 平台速度$\left( {{{\text{m}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\text{m}} {\text{s}}}} \right. } {\text{s}}}} \right)$ $30$ 主瓣波束宽度$\left( {^ \circ } \right)$ 5 表 3 受电磁干扰时面目标仿真的MSE和运行时间
Table 3. MSE and running time of area target simulation with electromagnetic interference
方法 MSE 运行时间(s) LRIAA方法 6.15×10–3 4.90 MBSD方法 0.65×10–3 23.14 AMBSD方法 0.70×10–3 3.82 表 4 设备性能异常时面目标仿真的MSE和运行时间
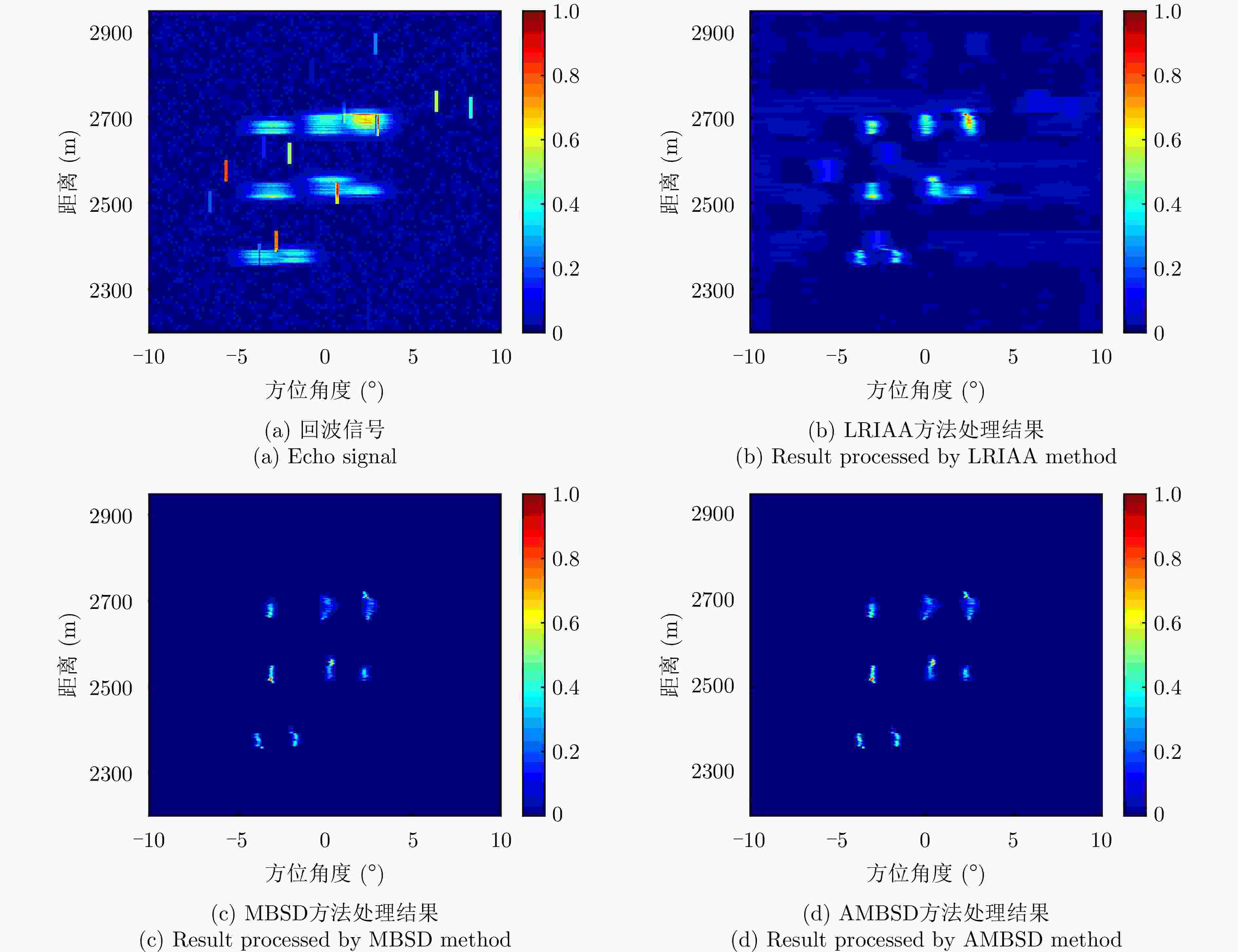
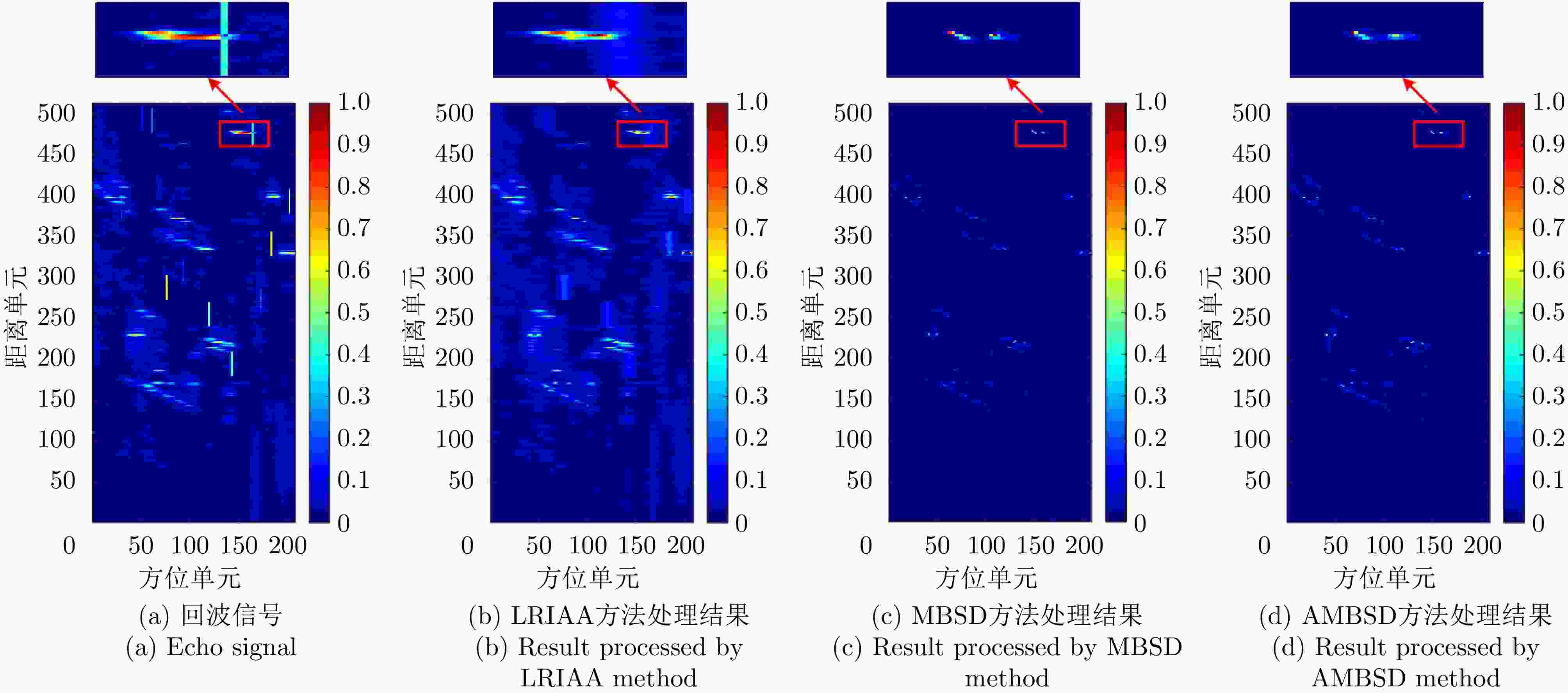
Table 4. MSE and running time of area target simulation with abnormal equipment performance
方法 MSE 运行时间(s) LRIAA方法 1.09×10–3 4.80 MBSD方法 0.80×10–3 23.03 AMBSD方法 0.81×10–3 3.90 表 5 半实测数据运行时间(s)
Table 5. Running time of semi-real data (s)
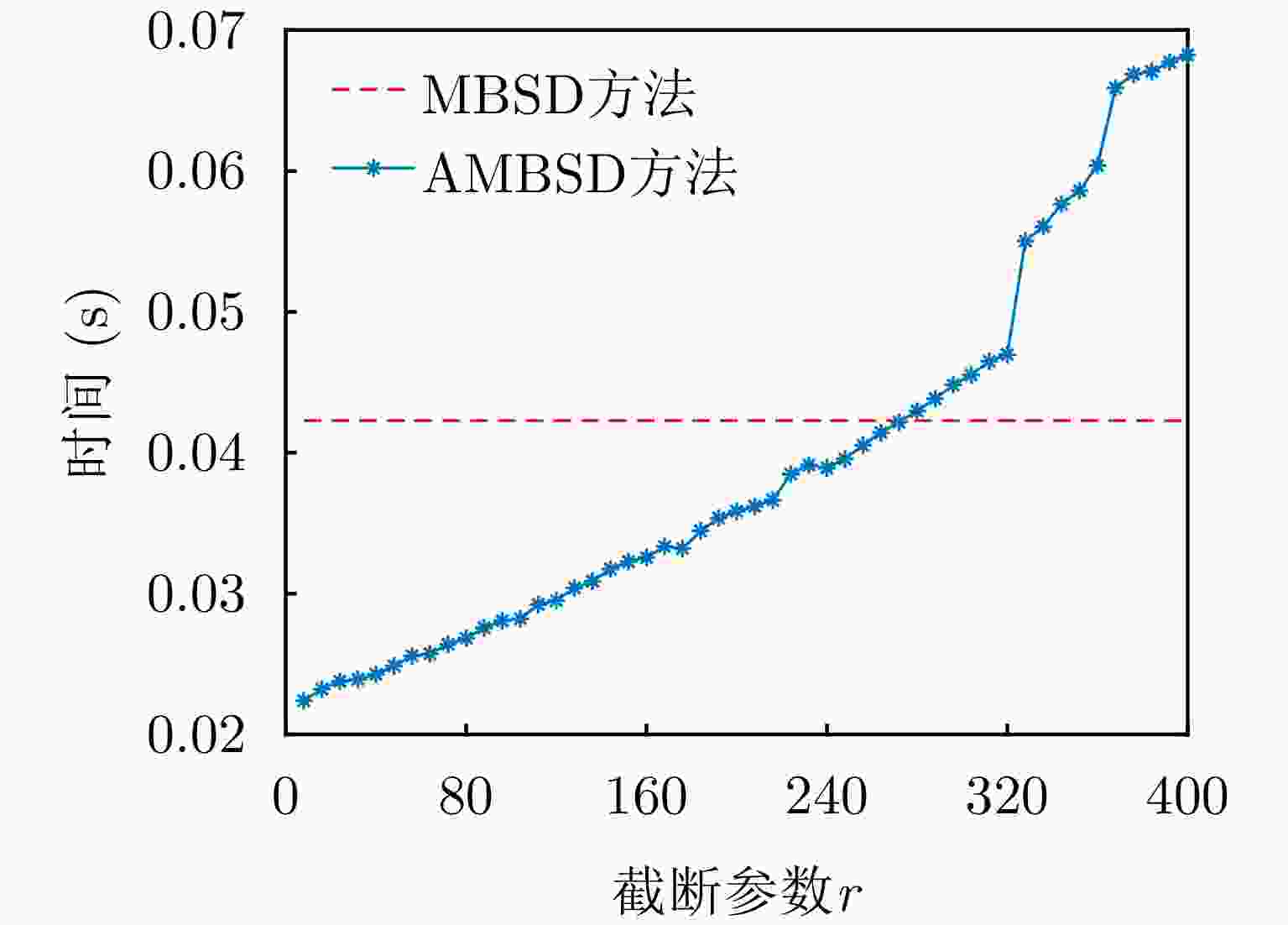
方法 受电磁干扰时运行时间 设备性能异常时运行时间 LRIAA方法 1.98 1.89 MBSD方法 4.57 4.58 AMBSD方法 1.18 1.19 -
[1] STIMSON G W. Introduction to Airborne Radar[M]. 2nd ed. Mendham: SciTech Pub, 1998, 37–38. [2] 李亚超, 王家东, 张廷豪, 等. 弹载雷达成像技术发展现状与趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119.LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, ZHANG Tinghao, et al. Present situation and prospect of missile-borne radar imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119. [3] 樊晨阳, 贺思三, 郭乾. 雷达前视成像技术的研究现状[J]. 电光与控制, 2021, 28(9): 59–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2021.09.013.FAN Chenyang, HE Sisan, and GUO Qian. Research status of radar forward-looking imaging technology[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2021, 28(9): 59–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2021.09.013. [4] MEI Haiwen, LI Yachao, XING Mengdao, et al. A frequency-domain imaging algorithm for translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(3): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2943743. [5] LU Jingyue, ZHANG Lei, WEI Shaopeng, et al. Resolution enhancement for forwarding looking multi-channel SAR imagery with exploiting space-time sparsity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 1–17. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3232392. [6] 李悦丽, 马萌恩, 赵崇辉, 等. 基于单脉冲雷达和差通道多普勒估计的前视成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 131–142. doi: 10.12000/JR20111.LI Yueli, MA Meng’en, ZHAO Chonghui, et al. Forward-looking imaging via Doppler estimates of sum-difference measurements in scanning monopulse radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 131–142. doi: 10.12000/JR20111. [7] 毛德庆. 机载雷达扫描波束超分辨成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2022.004148.MAO Deqing. Research on scanning beam super-resolution imaging methods for airborne radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2022.004148. [8] LI Weixin, LI Ming, ZUO Lei, et al. A computationally efficient airborne forward-looking super-resolution imaging method based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5102613. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3260094. [9] 唐军奎, 刘峥, 冉磊, 等. 基于稀疏和低秩先验的雷达前视超分辨成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 332–342. doi: 10.12000/JR22199.TANG Junkui, LIU Zheng, RAN Lei, et al. Radar forward-looking super-resolution imaging method based on sparse and low-rank priors[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 332–342. doi: 10.12000/JR22199. [10] 张启平. 雷达实孔径超分辨成像中的正则化方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2021. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2021.005078.ZHANG Qiping. Research on regularization method in radar real-aperture super-resolution imaging[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2021.005078. [11] SHEA J D, VAN VEEN B D, and HAGNESS S C. A TSVD analysis of microwave inverse scattering for breast imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2012, 59(4): 936–945. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2176727. [12] TANG Junkui, LIU Zheng, RAN Lei, et al. Enhancing forward-looking image resolution: combining low-rank and sparsity priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5100812. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3237332. [13] LI Wenchao, ZHANG Wentao, ZHANG Qiping, et al. Simultaneous super-resolution and target detection of forward-looking scanning radar via low-rank and sparsity constrained method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(10): 7085–7095. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2979508. [14] ZHANG Yin, TUO Xingyu, HUANG Yulin, et al. A TV forward-looking super-resolution imaging method based on TSVD strategy for scanning radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(7): 4517–4528. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2958085. [15] GAMBARDELLA A and MIGLIACCIO M. On the superresolution of microwave scanning radiometer measurements[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 796–800. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2006285. [16] ZHANG Yongchao, JAKOBSSON A, ZHANG Yin, et al. Wideband sparse reconstruction for scanning radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 6055–6068. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2018.2830100. [17] LI Yueli, LIU Jianguo, JIANG Xiaoqing, et al. Angular superresol for signal model in coherent scanning radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3103–3116. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2900133. [18] 杨志伟, 贺顺, 廖桂生. 机载单通道雷达实波束扫描的前视探测[J]. 航空学报, 2012, 33(12): 2240–2245.YANG Zhiwei, HE Shun, and LIAO Guisheng. Forward-looking detection for airborne single-channel radar with beam scanning[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2012, 33(12): 2240–2245. [19] ZHANG Yongchao, ZHANG Yin, LI Wenchao, et al. Angular superresolution for real beam radar with iterative adaptive approach[C]. 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 3100–3103. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2013.6723482. [20] ZHANG Yongchao, LI Wenchao, ZHANG Yin, et al. A fast iterative adaptive approach for scanning radar angular superresolution[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(11): 5336–5345. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2449090. [21] ZHANG Yongchao, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. Angular superresolution for scanning radar with improved regularized iterative adaptive approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(6): 846–850. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2016.2550491. [22] CHEN Hongmeng, GAO Wenquan, WANG Pei, et al. Sparse superresolution imaging for airborne forward-looking radar with multiple frames space[C]. IGARSS 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 1816–1819. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9884278. [23] ZHANG Gang, LIANG Yi, CHEN Shuxuan, et al. Super-resolution forward-looking imaging method for manoeuvering platform with optimised dictionary and extended sparsity adaptive matching pursuit[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2022, 16(5): 912–923. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12229. [24] LIU Qingping, CHENG Yongqiang, CAO Kaicheng, et al. Radar forward-looking imaging for complex targets based on sparse representation with dictionary learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4026605. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3200393. [25] CHEN Hongmeng, LI Yachao, GAO Wenquan, et al. Bayesian forward-looking superresolution imaging using Doppler deconvolution in expanded beam space for high-speed platform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5105113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3107717. [26] 陈洪猛, 李明, 王泽玉, 等. 基于多帧数据联合处理的机载单通道雷达贝叶斯前视成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(10): 2328–2334. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150153.CHEN Hongmeng, LI Ming, WANG Zeyu, et al. Bayesian forward-looking imaging for airborne single-channel radar based on combined multiple frames data[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2015, 37(10): 2328–2334. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150153. [27] ZHANG Qiping, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. TV-sparse super-resolution method for radar forward-looking imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6534–6549. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2977719. [28] TUO Xingyu, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. Fast sparse-TSVD super-resolution method of real aperture radar forward-looking imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6609–6620. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3027053. [29] TUO Xingyu, MAO Deqing, ZHANG Yin, et al. Two-step dimension reduction strategy for real aperture radar fast super-resolution imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4025505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3188704. [30] ZHANG Yongchao, LUO Jiawei, ZHANG Yongwei, et al. Resolution enhancement for large-scale real beam mapping based on adaptive low-rank approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5116921. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3202073. [31] ZHANG Yongchao, ZHANG Yin, LI Wenchao, et al. Super-resolution surface mapping for scanning radar: Inverse filtering based on the fast iterative adaptive approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 127–144. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743263. [32] LI Jie, ZHANG Yongchao, ZHANG Yin, et al. Low-rank approximation-based super-resolution imaging for airborne forward-looking radar[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference, Florence, Italy. 2020: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266355. [33] TUO Xingyu, MAO Deqing, ZHANG Yin, et al. Sparse target batch-processing framework for scanning radar superresolution imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3503905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3274910. [34] MAO Deqing, ZHANG Yongchao, ZHANG Yin, et al. An efficient anti-interference imaging technology for marine radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5101413. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3068787. [35] LI Weixin, LI Ming, ZUO Lei, et al. Real aperture radar forward-looking imaging based on variational Bayesian in presence of outliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5117113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3203807. [36] BISHOP C M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning[M]. New York: Springer, 2006: 102−105. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: