Sparse Targets Angular Super-resolution Reconstruction Method under Unknown Antenna Pattern Errors for Scanning Radar
-
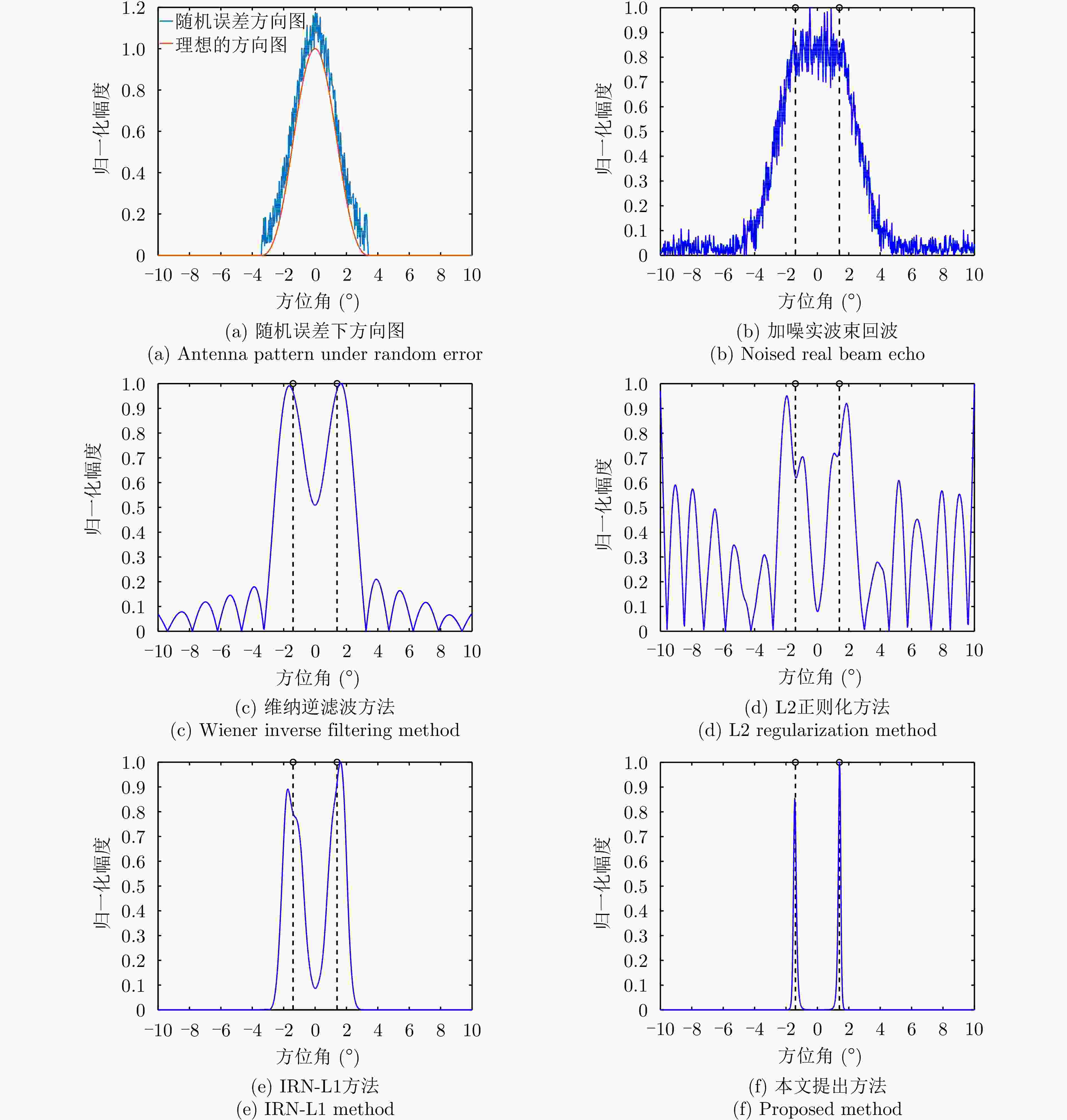
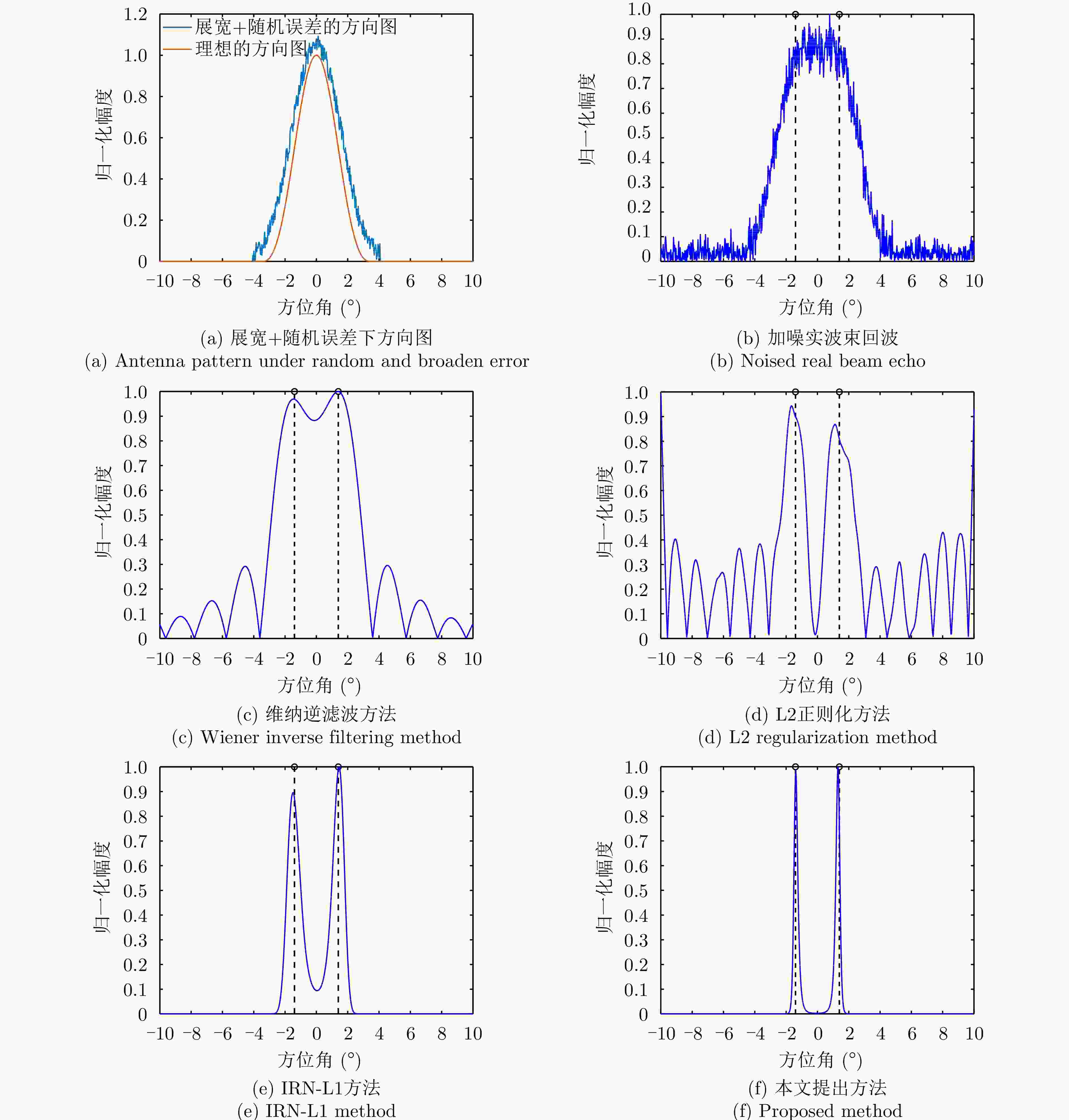
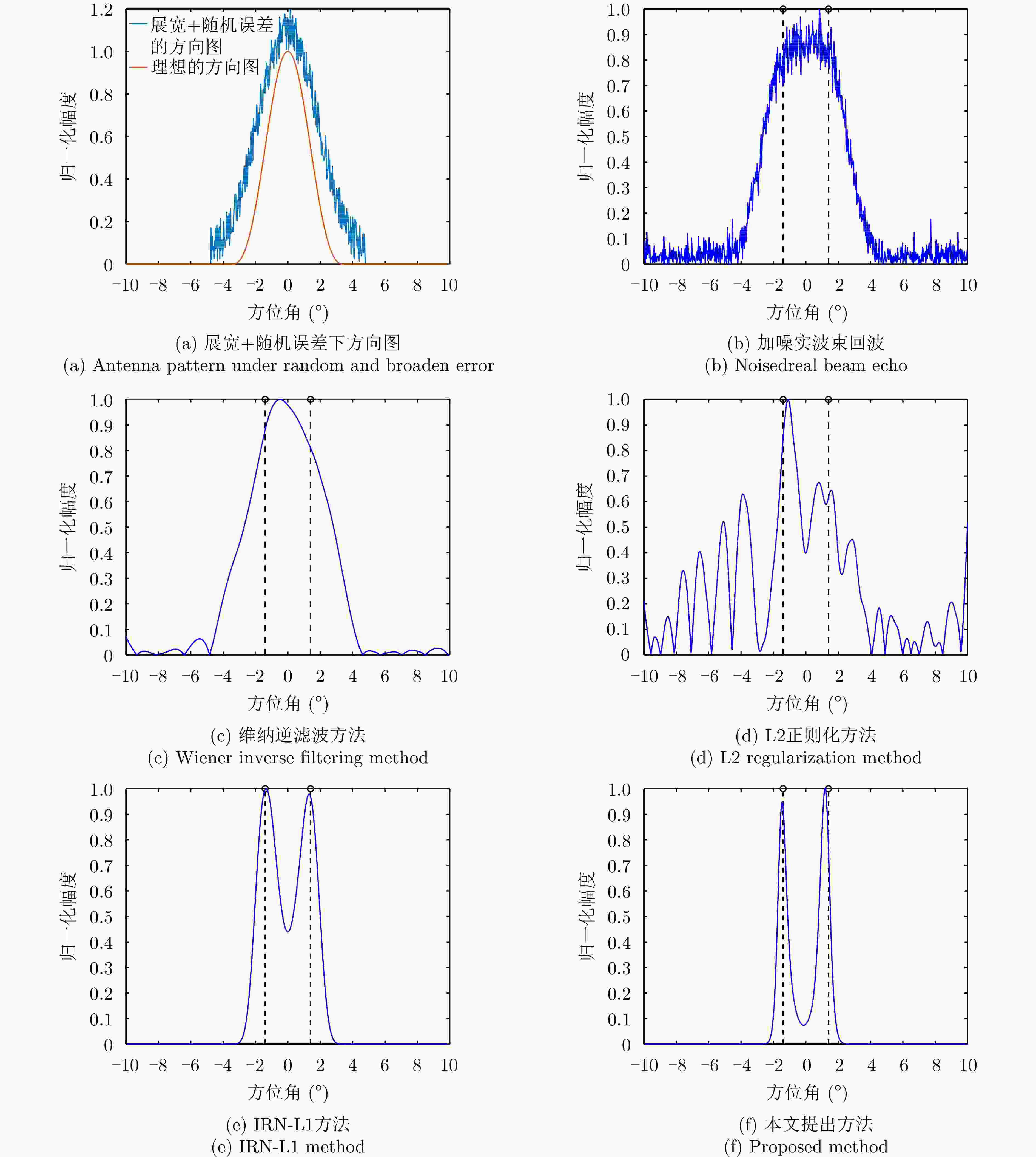
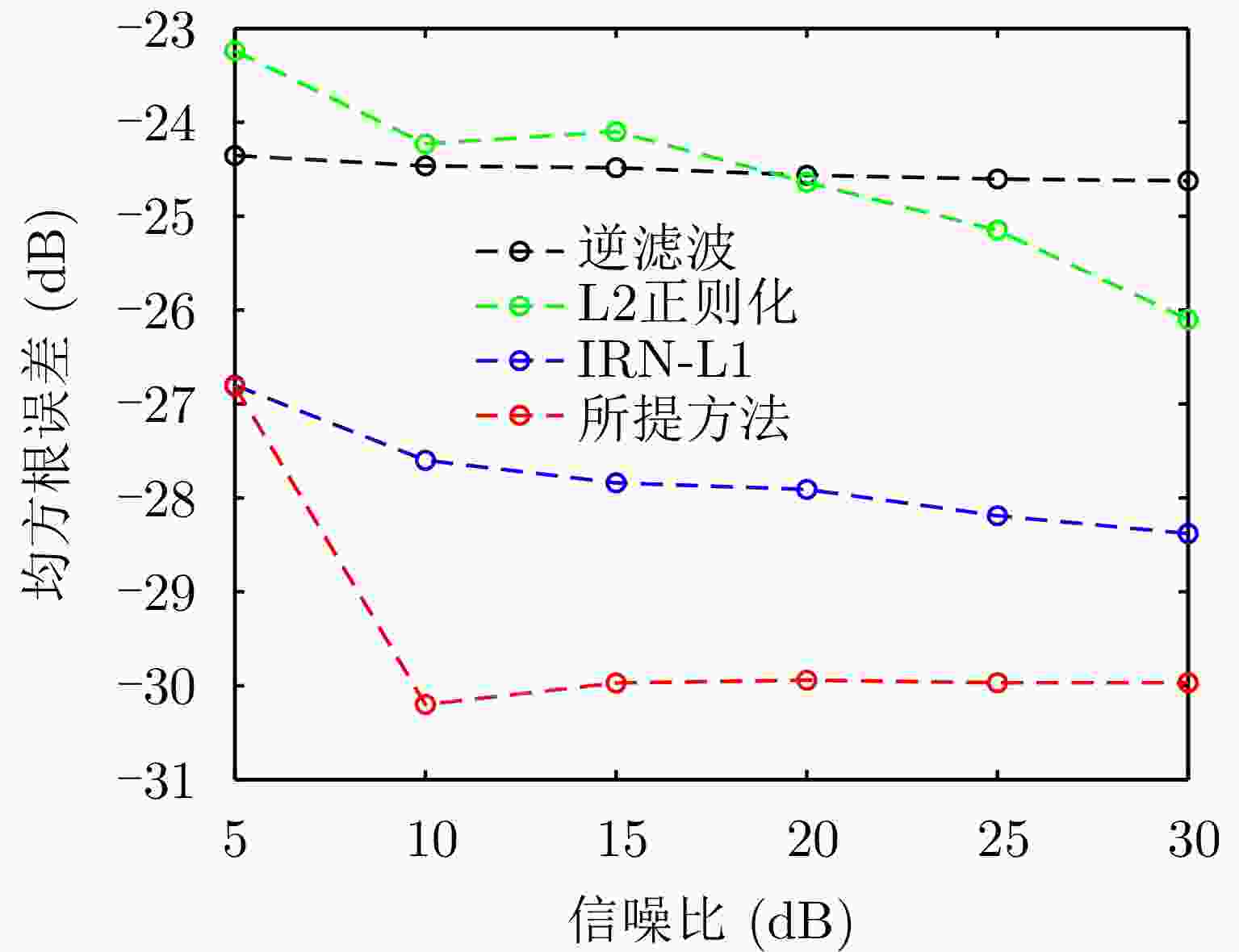
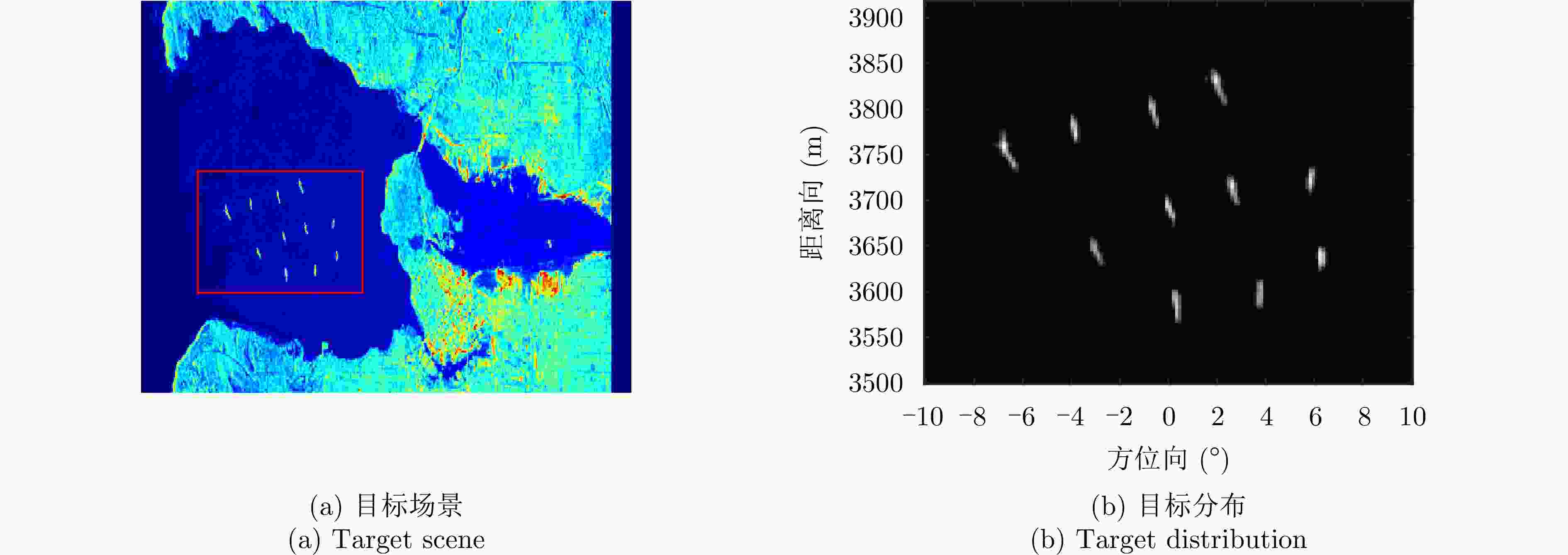
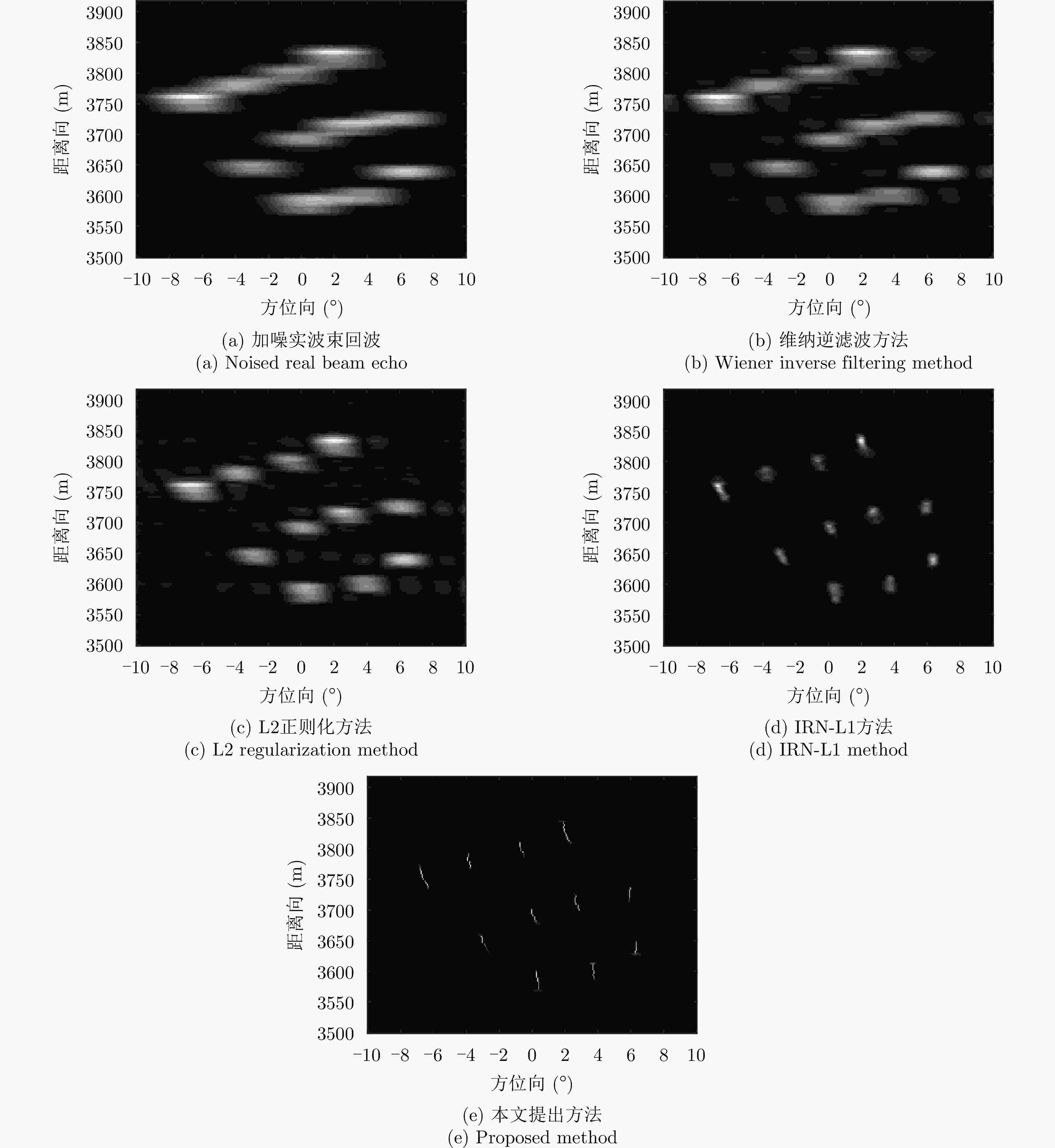
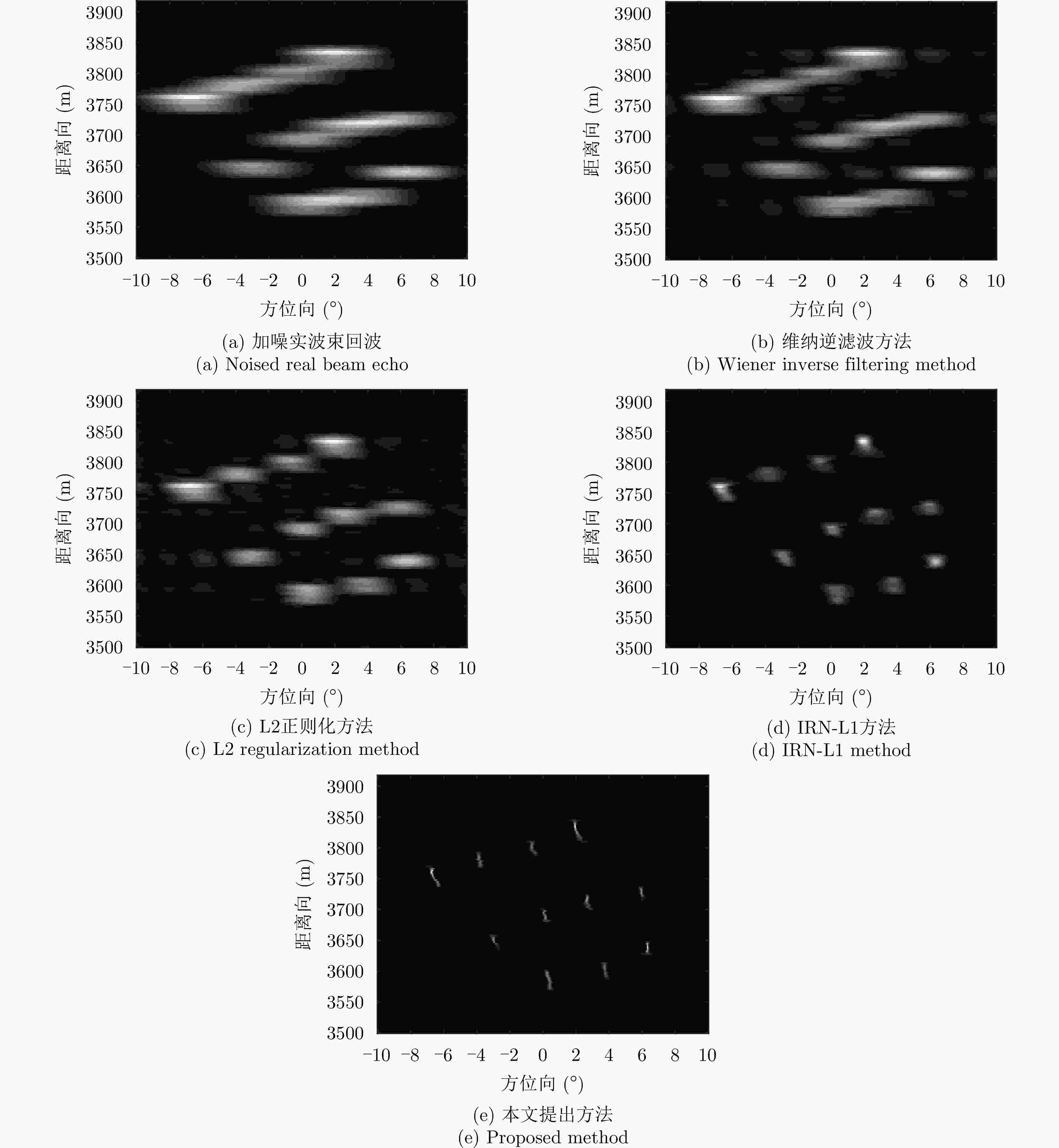
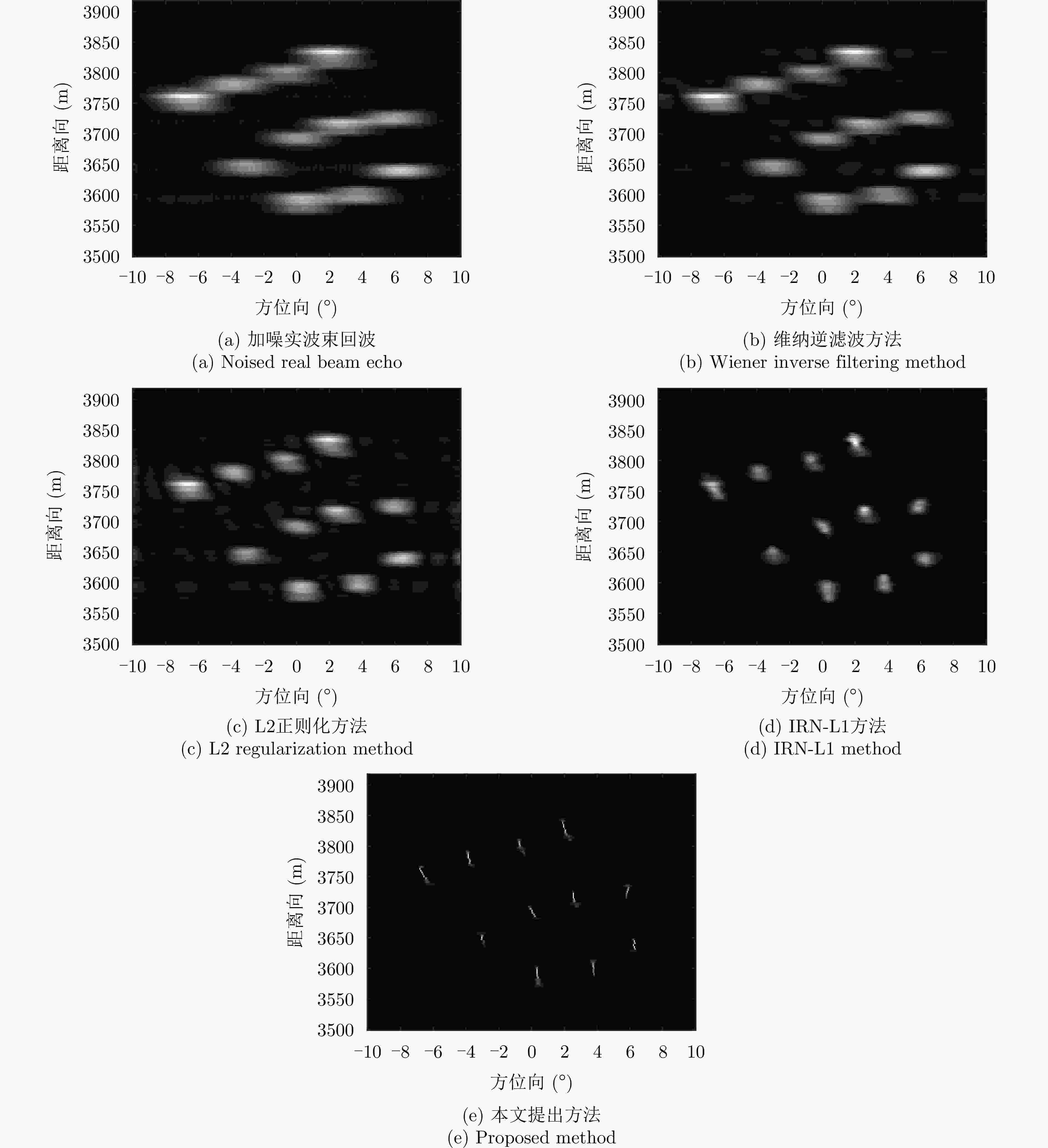
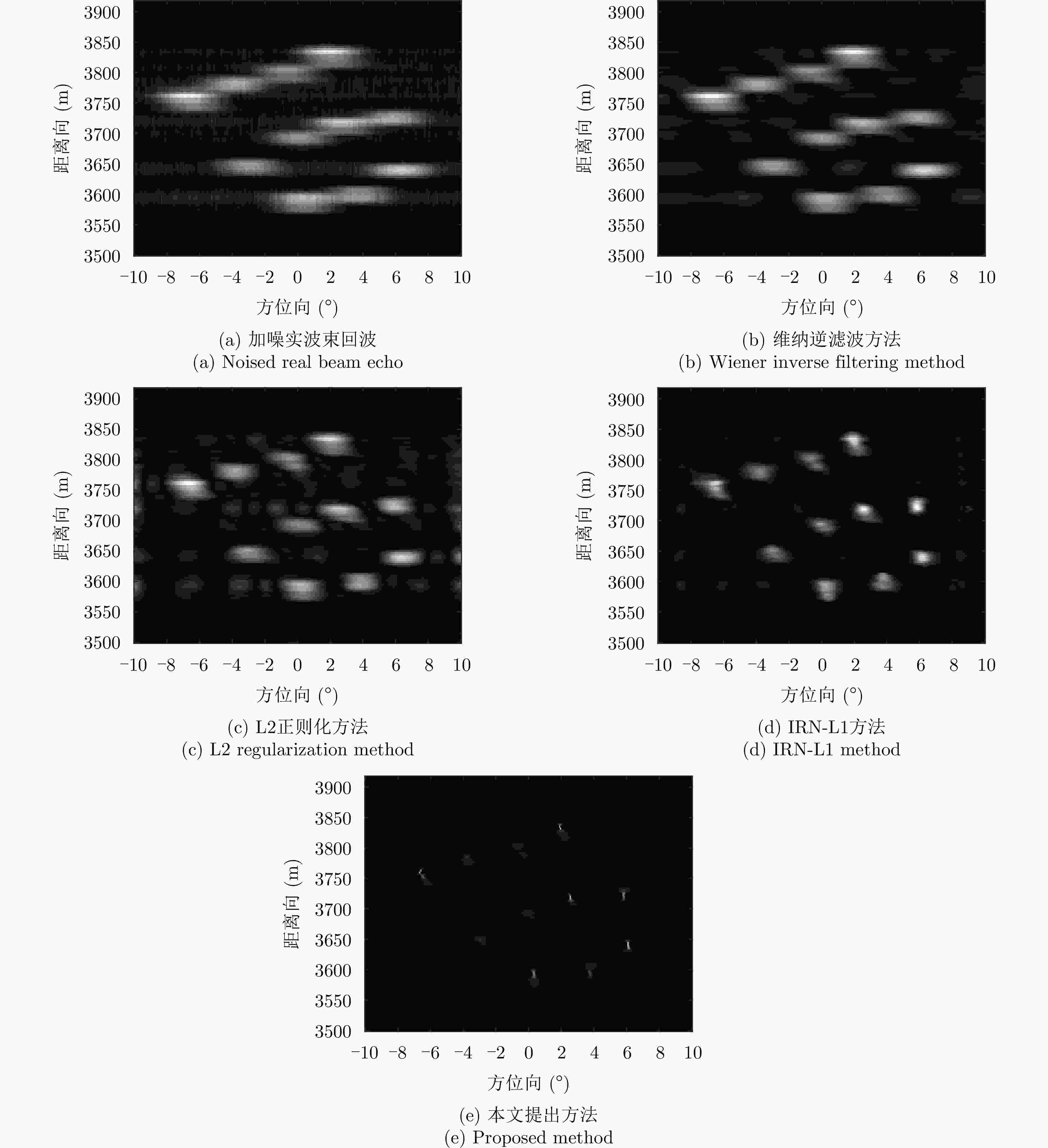
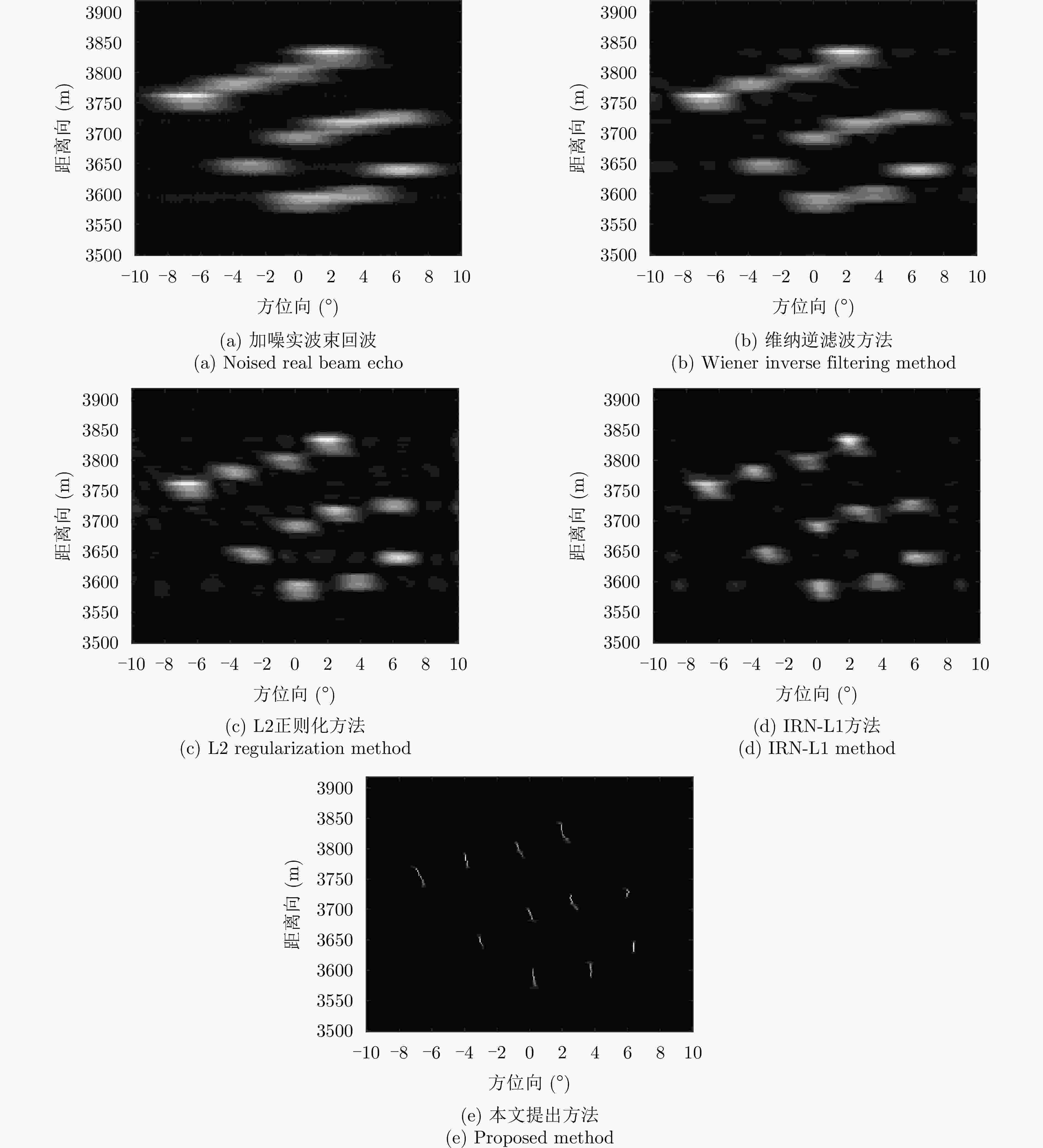
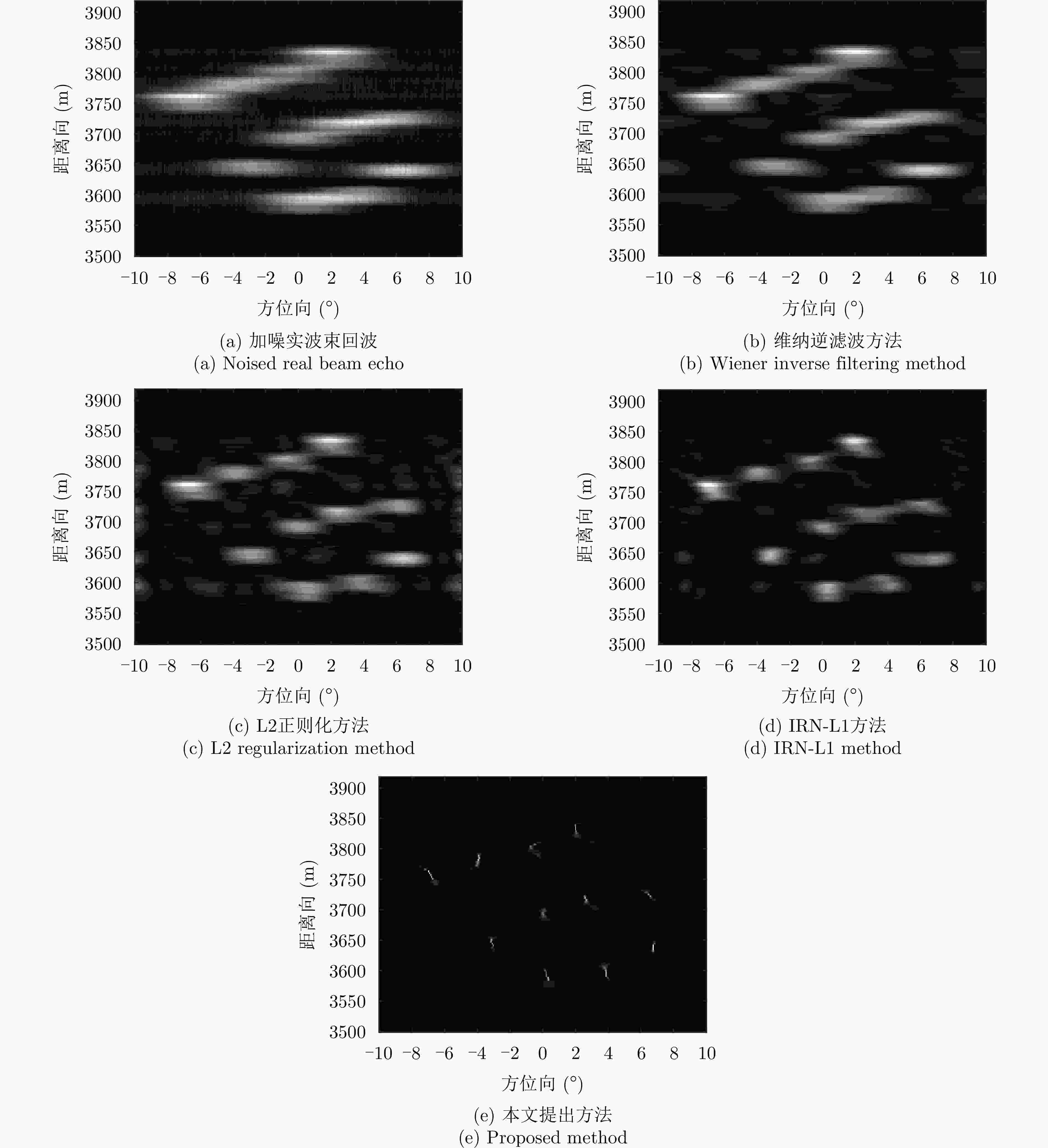
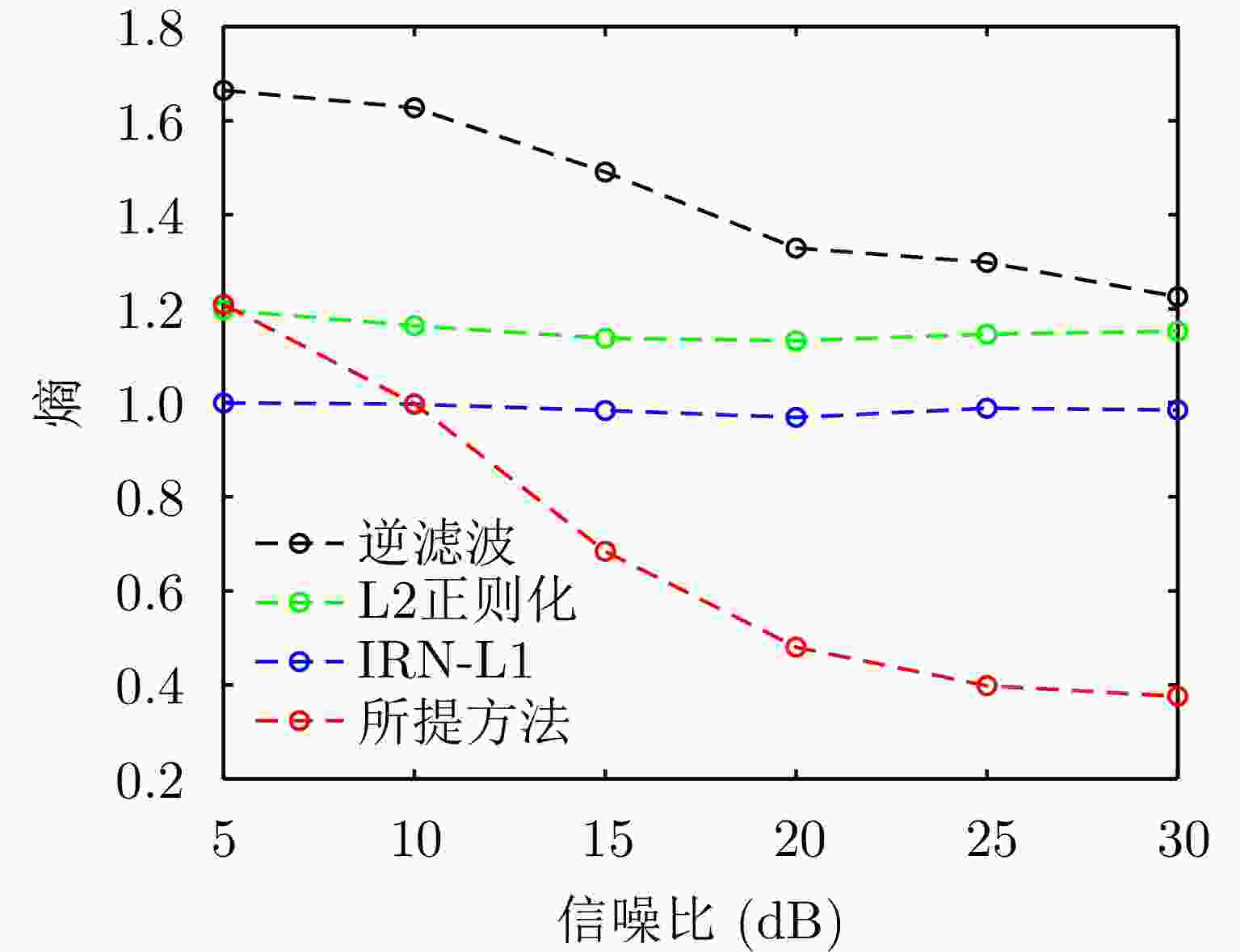
摘要: 扫描雷达角超分辨技术是基于目标与天线方向图的关系,采用解卷积方法获取超越实波束的角分辨能力。目前的角超分辨方法大都是基于理想的无畸变天线方向图,未考虑实际过程中方向图的变化。然而,由于雷达天线罩、天线测量误差与平台非理想运动等因素的影响,天线方向图在实际中往往存在未知的误差,会导致目标分辨能力下降,甚至产生虚假目标。针对此问题,该文提出一种机载扫描雷达未知天线方向图误差下的角超分辨成像方法。首先,基于总体最小二乘(TLS)准则,该文考虑了方向图误差矩阵的影响,导出了相应的目标函数;其次,基于交替迭代的求解思路,利用迭代重加权优化方法实现了目标函数求解;最后,针对算法超参数选取,引入了一种自适应参数选取方法。仿真与实测结果表明,该文方法能实现未知天线误差条件下的超分辨重建,进一步提升了超分辨算法的稳健性。Abstract: Scanning radar angular super-resolution technology is based on the relationship between the target and antenna pattern, and a deconvolution method is used to obtain angular resolution capabilities beyond the real beam. Most current angular super-resolution methods are based on ideal distortion-free antenna patterns and do not consider pattern changes in the actual process due to the influence of factors such as radar radome, antenna measurement errors, and non-ideal platform motion. In practice, an antenna pattern often has unknown errors, which can result in reduced target resolution and even false target generation. To address this problem, this paper proposes an angular super-resolution imaging method for airborne radar with unknown antenna errors. First, based on the Total Least Square (TLS) criterion, this paper considers the effect of the pattern error matrix and derive the corresponding objective function. Second, this paper employs the iterative reweighted optimization method to solve the objective function by adopting an alternative iteration solution idea. Finally, an adaptive parameter update method is introduced for algorithm hyperparameter selection. The simulation and experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve super-resolution reconstruction even in the presence of unknown antenna errors, promoting the robustness of the super-resolution algorithm.
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
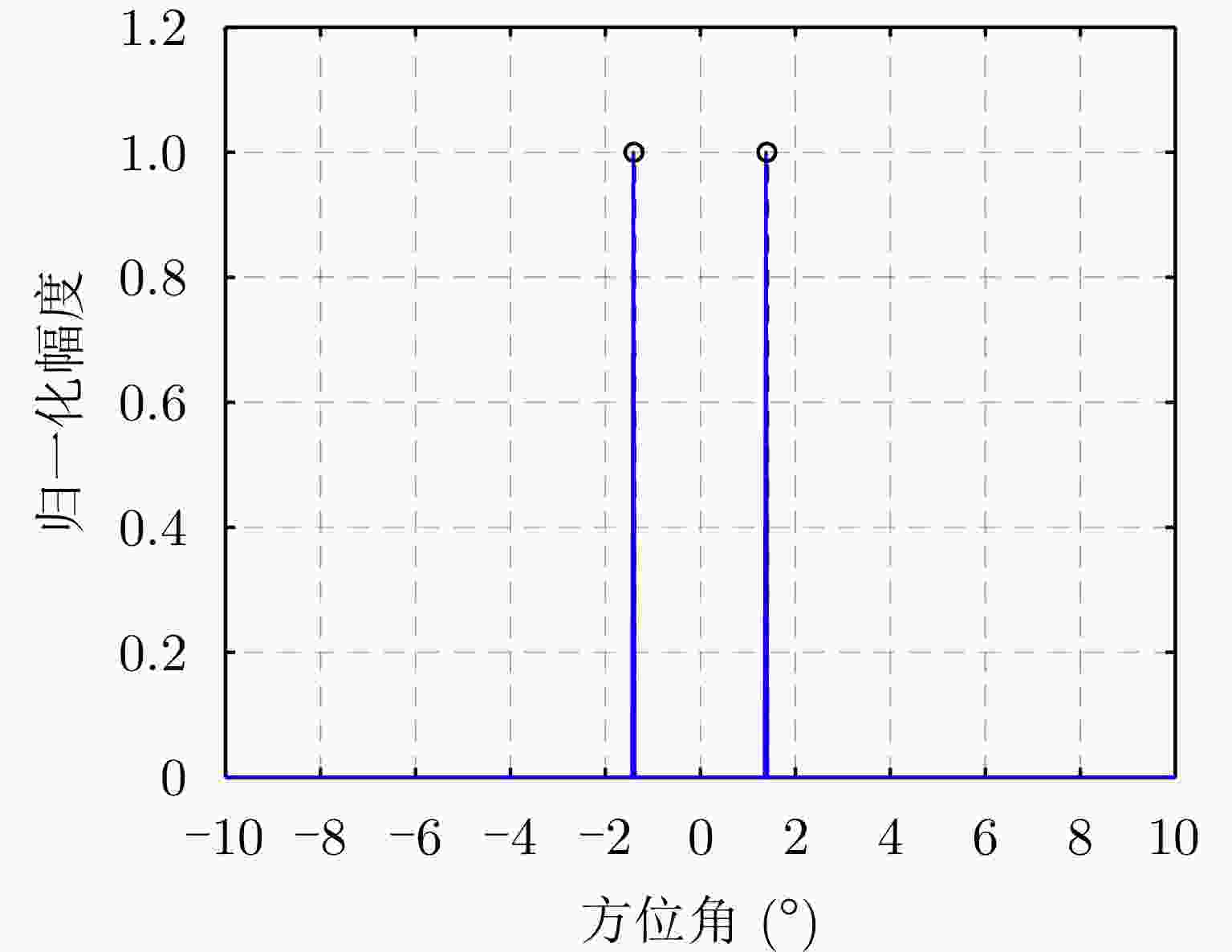
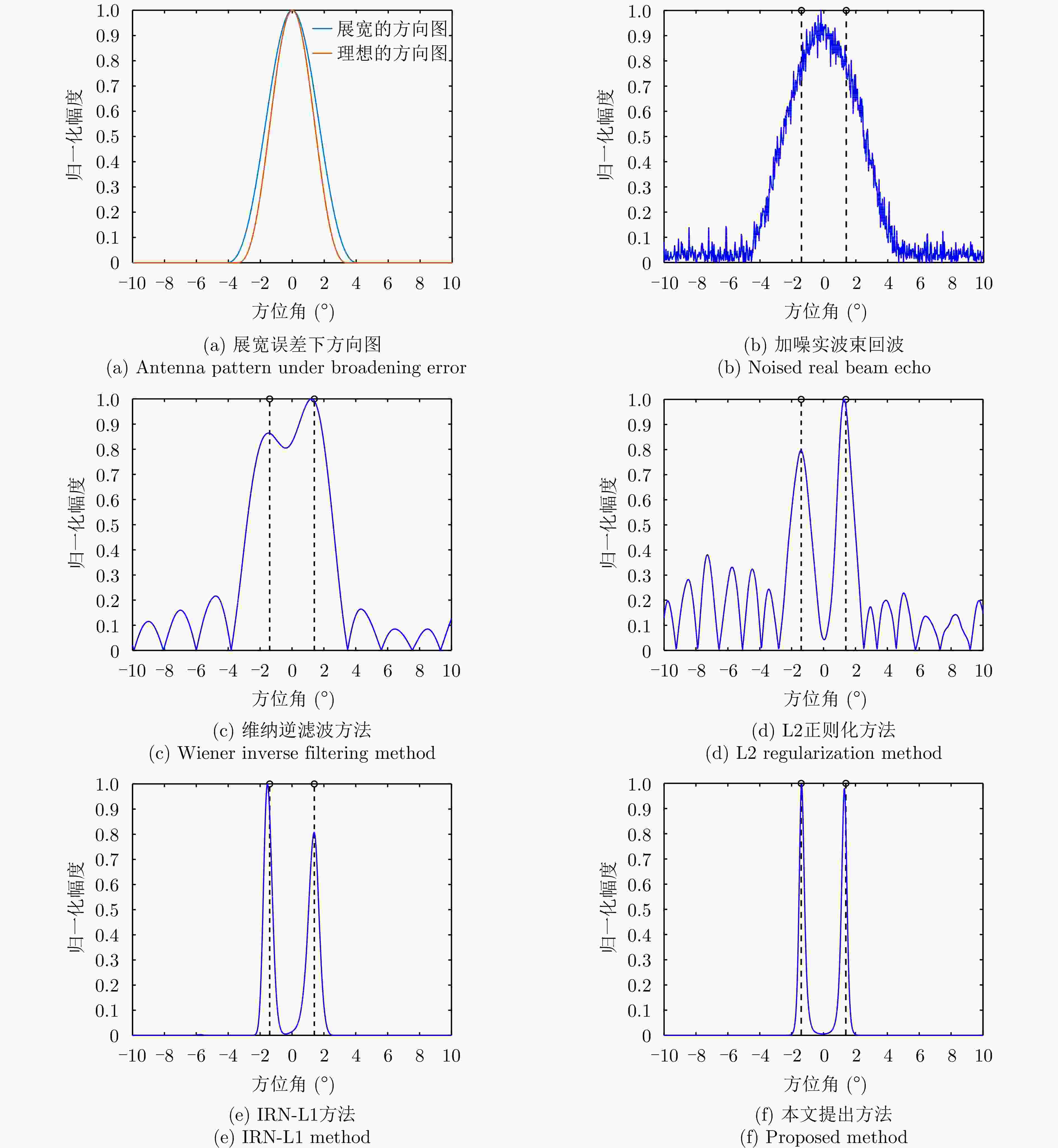
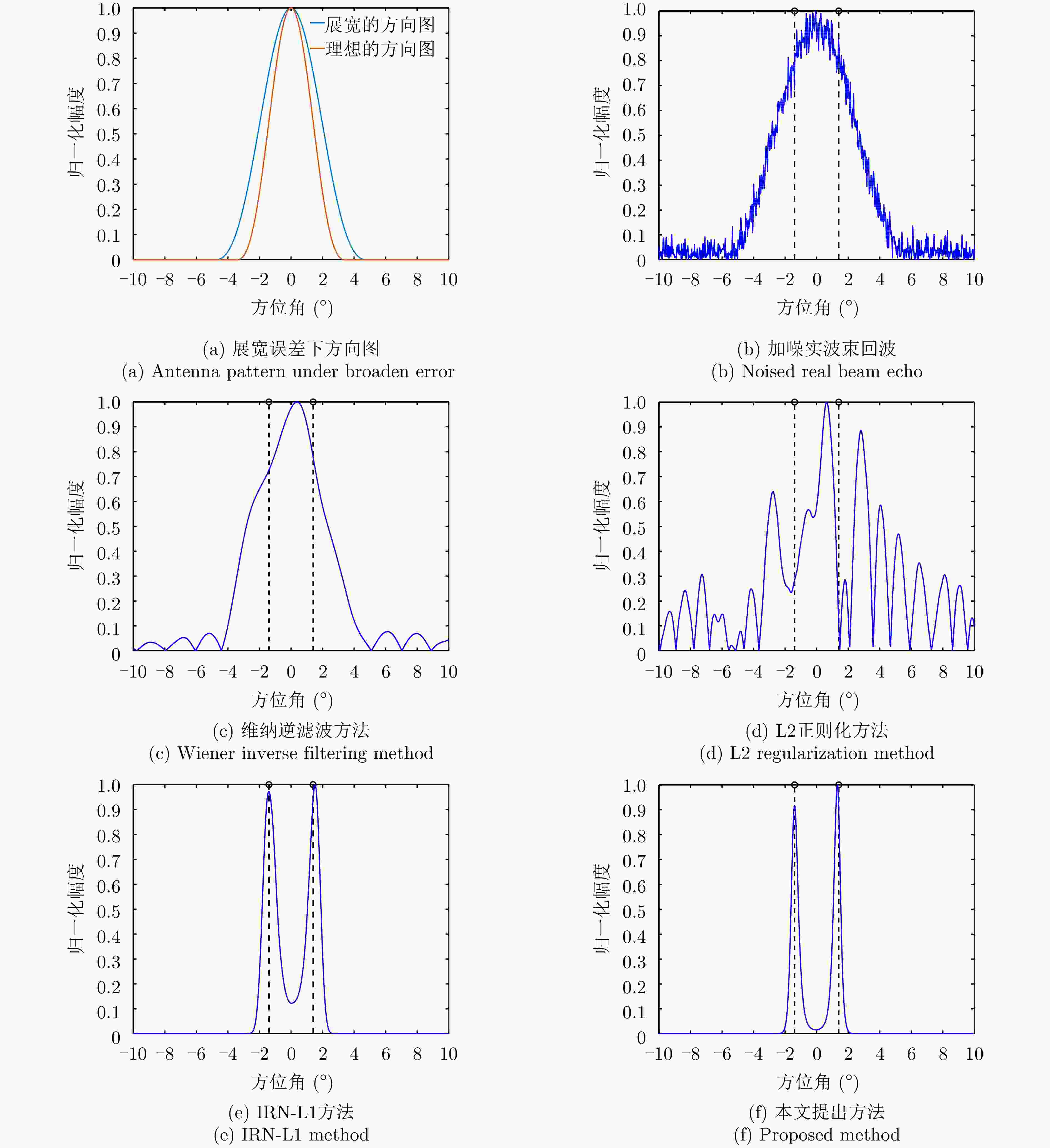
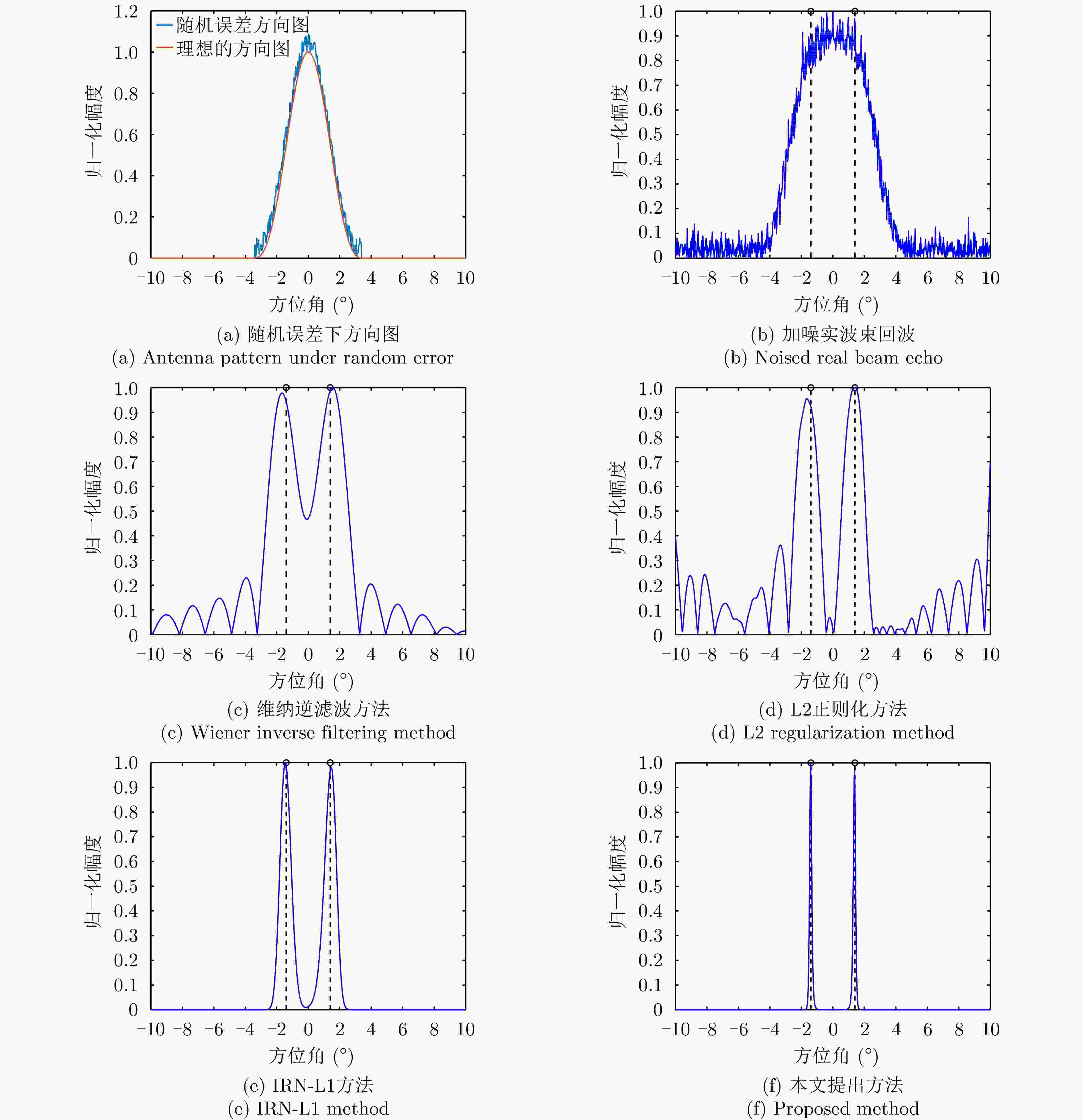
参数 数值 载频(GHz) 10.75 信号带宽(MHz) 40 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 1000 天线扫描速度(°/s) 60 波束宽度(°) 3 扫描范围(°) –10~10 表 2 仿真环境
Table 2. Simulation conditions
硬件/软件 参数值 CPU Intel(R) Core(TM)i7-9700K RAM 64 GB 仿真软件 Matlab 2022a 表 3 扫描雷达系统参数
Table 3. Scanning radar system parameters
参数 数值 载频(GHz) 30.75 信号带宽(MHz) 200 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 4000 主瓣宽度(°) 4 天线扫描速度(°/s) 60 信号时宽(μs) 1 扫描范围(°) –35~35 -
[1] Rigelsford J. Introduction to airborne radar[J]. Sensor Review, 2002, 22(3): 265–266. [2] 张良, 祝欢, 吴涛. 机载预警雷达系统架构发展路径研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2015, 37(12): 11–18. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2015.12.003.ZHANG Liang, ZHU Huan, and WU Tao. A study on the evolution way of the system architecture of AEW radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2015, 37(12): 11–18. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2015.12.003. [3] CLARKE J, 徐映和, 译. 英国预警雷达的发展概况[J]. 现代雷达, 1987, 9(2): 1–6. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.1987.02.001.CLARKE J, XU Yinghe, translation. Overview of the development of early warning radar in the UK[J]. Modern Radar, 1987, 9(2): 1–6. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.1987.02.001. [4] ZHANG Qiping, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. TV-sparse super-resolution method for radar forward-looking imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6534–6549. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2977719. [5] LING Hao. Novel radar techniques and applications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2018, 60(1): 132–134. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2017.2776153. [6] BEKKADAL F. Novel radar technology and applications[C]. 17th International Conference on Applied Electromagnetics and Communications, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2003: 6–12. doi: 10.1109/ICECOM.2003.1290942. [7] ZHANG Yongchao, ZHANG Yin, LI Wenchao, et al. Super-resolution surface mapping for scanning radar: Inverse filtering based on the fast iterative adaptive approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 127–144. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743263. [8] ZHANG Yongchao, JAKOBSSON A, ZHANG Yin, et al. Wideband sparse reconstruction for scanning radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 6055–6068. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2830100. [9] CHEN Rui, LI Wenchao, LI Kefeng, et al. A super-resolution scheme for multichannel radar forward-looking imaging considering failure channels and motion error[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3501305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3234264. [10] KANG Yao, ZHANG Yin, MAO Deqing, et al. Bayesian azimuth super-resolution of sea-surface target in forward-looking imaging[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266692. [11] CHEN Hongmeng, WANG Zeyu, ZHANG Yingjie, et al. Data-driven airborne Bayesian forward-looking superresolution imaging based on generalized Gaussian distribution[J]. Frontiers in Signal Processing, 2023, 3: 1093203. doi: 10.3389/frsip.2023.1093203. [12] MAO Deqing, ZHANG Yin, ZHANG Yongchao, et al. Super-resolution Doppler beam sharpening method using fast iterative adaptive approach-based spectral estimation[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(1): 015020. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.12.015020. [13] LIU Sijia and PAN Minghai. Research on a forward-looking scanning imaging algorithm for a high-speed radar platform[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2023, 17(6): e12221. doi: 10.1049/sil2.12221. [14] MAO Deqing, YANG Jianyu, TUO Xingyu, et al. Angular superresolution of real aperture radar for target scale measurement using a generalized hybrid regularization approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5109314. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3315310. [15] TUO Xingyu, MAO Deqing, ZHANG Yin, et al. Radar forward-looking super-resolution imaging using a two-step regularization strategy[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 4218–4231. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3270309. [16] YOUNG P. Alternative Recursive Approaches to Time-series Analysis[M]. YOUNG P. Recursive Estimation and Time-Series Analysis: An Introduction. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1984: 205–230. [17] RICHARDS M A. Iterative noncoherent angular superresolution (radar)[C]. 1988 IEEE National Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, USA, 1988: 100–105. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1988.10940. [18] LI Dongye, HUANG Yulin, and YANG Jianyu. Real beam radar imaging based on adaptive Lucy-Richardson algorithm[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 1437–1440. doi: 10.1109/CIE-Radar.2011.6159830. [19] TAN Ke, LU Xingyu, YANG Jianchao, et al. A novel Bayesian super-resolution method for radar forward-looking imaging based on Markov random field model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(20): 4115. doi: 10.3390/rs13204115. [20] CHEN Hongmeng, LI Yachao, GAO Wenquan, et al. Bayesian forward-looking super-resolution imaging using Doppler deconvolution in expanded beam space for high-speed platform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5105113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3107717. [21] LI Weixin, LI Ming, ZUO Lei et al. A computationally efficient airborne forward-looking super-resolution imaging method based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5102613. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3260094. [22] CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278. [23] ZHANG Yongchao, LI Wenchao, ZHANG Yin, et al. A fast iterative adaptive approach for scanning radar angular superresolution[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(11): 5336–5345. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2449090. [24] LI Yueli, LIU Jianguo, JIANG Xiaoqing, et al. Angular superresolution for signal model in coherent scanning radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3103–3116. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2900133. [25] GAMBARDELLA A and MIGLIACCIO M. On the superresolution of microwave scanning radiometer measurements[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 796–800. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2006285. [26] HUO Weibo, TUO Xingyu, ZHANG Yin, et al. Balanced tikhonov and total variation deconvolution approach for radar forward-looking super-resolution imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 3505805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3072389. [27] TANG Junkui, LIU Zheng, RAN Lei, et al. Enhancing forward-looking image resolution: Combining low-rank and sparsity priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5100812. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3237332. [28] KOZAKOFF D J. Analysis of radome-enclosed antennas[J]. Artech House, 1997 (685): 217–227. [29] PERSSON K and GUSTAFSSON M. Reconstruction of equivalent currents using a near-field data transformation-with radome applications[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2005, 54: 179–198. doi: 10.2528/PIER04111602. [30] Fierro R D, Golub G H, Hansen P C, et al. Regularization by truncated total least squares[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 1997, 18(4): 1223–1241. doi: 10.1137/S106482759426383. [31] GOLUB G H, HEATH M, and WAHBA G. Generalized cross-validation as a method for choosing a good ridge parameter[J]. Technometrics, 1979, 21(2): 215–223. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1979.10489751. [32] JOHNSTON P R and GULRAJANI R M. Selecting the corner in the L-curve approach to Tikhonov regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2000, 47(9): 1293–1296. doi: 10.1109/10.867966. [33] ENGL H W. Discrepancy principles for Tikhonov regularization of ill-posed problems leading to optimal convergence rates[J]. Journal of optimization theory and applications, 1987, 52: 209–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00941281. [34] RUDIN L I, OSHER S, and FATEMI E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1992, 60(1/4): 259–268. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: