A Range and Azimuth Combined Two-dimensional NCS Algorithm for Spaceborne-missile Bistatic Forward-looking SAR
-
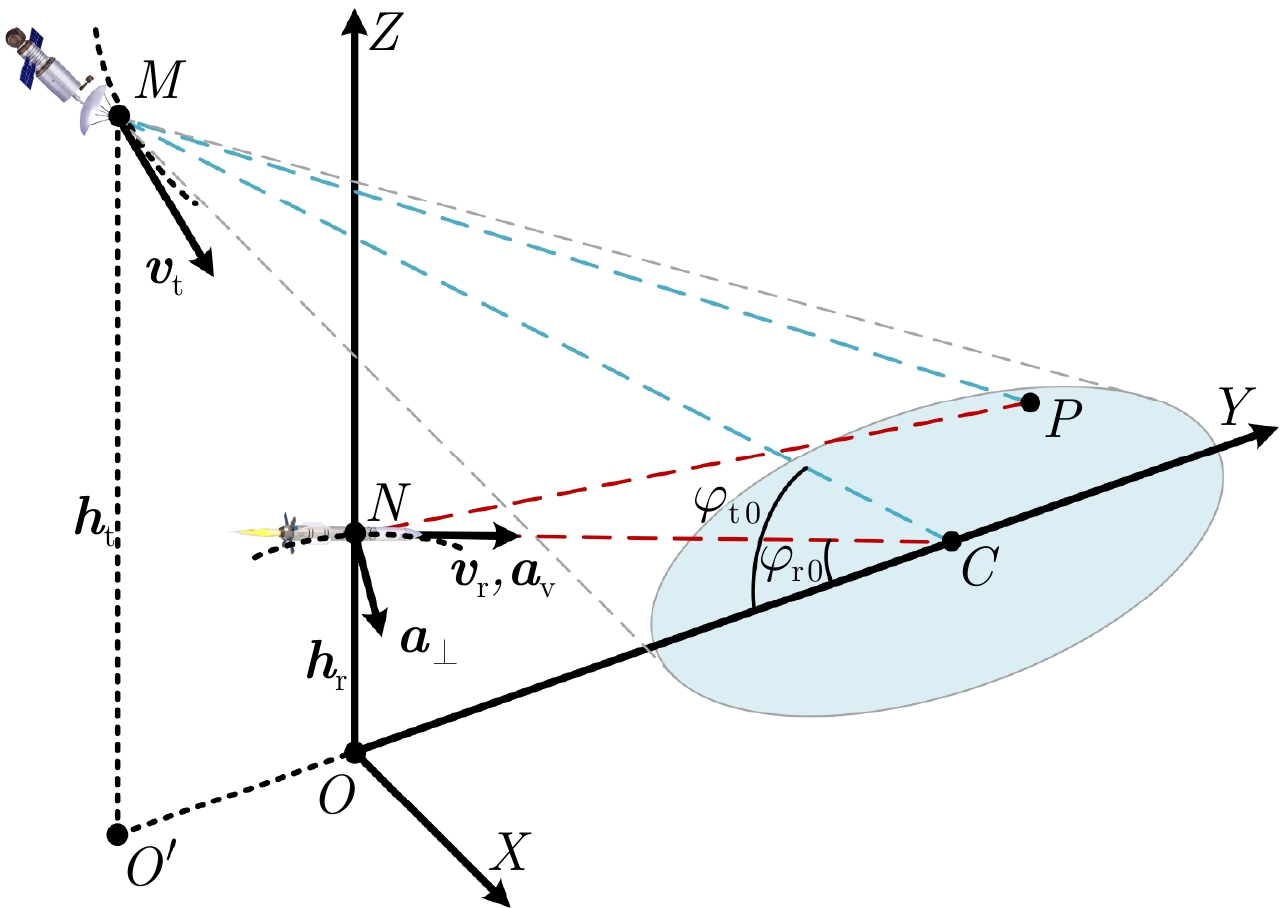
摘要: 星弹双基前视SAR能够全天时全天候获取导弹前方区域高分辨图像,是一种极具潜力的成像制导技术。然而,距离和方位参数的耦合与空变,阻碍着星弹双基前视SAR向高分辨成像发展。该文首先基于低轨星载照射源与高速前视的弹载接收平台构型,推导了回波信号的精确距离多普勒域解析式。然后,在距离向上,提出距离非线性变标(NCS)算法来均衡距离徙动和距离调频率,并在二维频域一致补偿;在方位向上,该文所提算法将收发机的方位调频率进行分解,利用方位NCS消除方位调频率在方位向上的高阶空变。最后,进行二维匹配滤波,得到全局聚焦良好的SAR图像。点目标和场景仿真验证了所提算法的有效性。Abstract: The spaceborne-missile bistatic forward-looking Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is a promising imaging guidance technology that can obtain high-resolution images of the area in front of the missile all day and in all weather types. However, the coupling and spatial variations in range and azimuth parameters hinder the development of high-resolution spaceborne-missile bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging. In this study, the accurate-range Doppler domain analytical formula for echo signals was derived based on the low-orbit spaceborne illuminator and high-speed forward-looking missile-borne receiving platform configuration. Subsequently, in range processing, a range Nonlinear Chirp Scaling (NCS) was proposed to equalize the range cell migration and range Frequency Modulation (FM) rate, and both can be uniformly compensated in the two-dimensional frequency domain. In azimuth processing, the proposed method decomposed the azimuth FM rates of the transmitter and receiver. Then, the azimuth NCS was used to eliminate the high-order spatial variation of the azimuth FM rate. Finally, a two-dimensional matched filtering was performed to obtain a SAR image with a good global focus. The point and scene simulation verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 雷达系统仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of radar system
参数 数值 载波波长(m) 0.05 系统带宽(MHz) 180 合成孔径时间(s) 3 卫星高度(km) 755 卫星速度(m/s) 6800 导弹作用距离(km) 46 导弹沿速度方向加速度(m/s2) 80 导弹垂直速度方向加速度(m/s2) 10 导弹速度(m/s) 1020 场景中心点位置(km) (0,45,0) 表 2 点目标成像性能评估
Table 2. Point target imaging performance evaluation
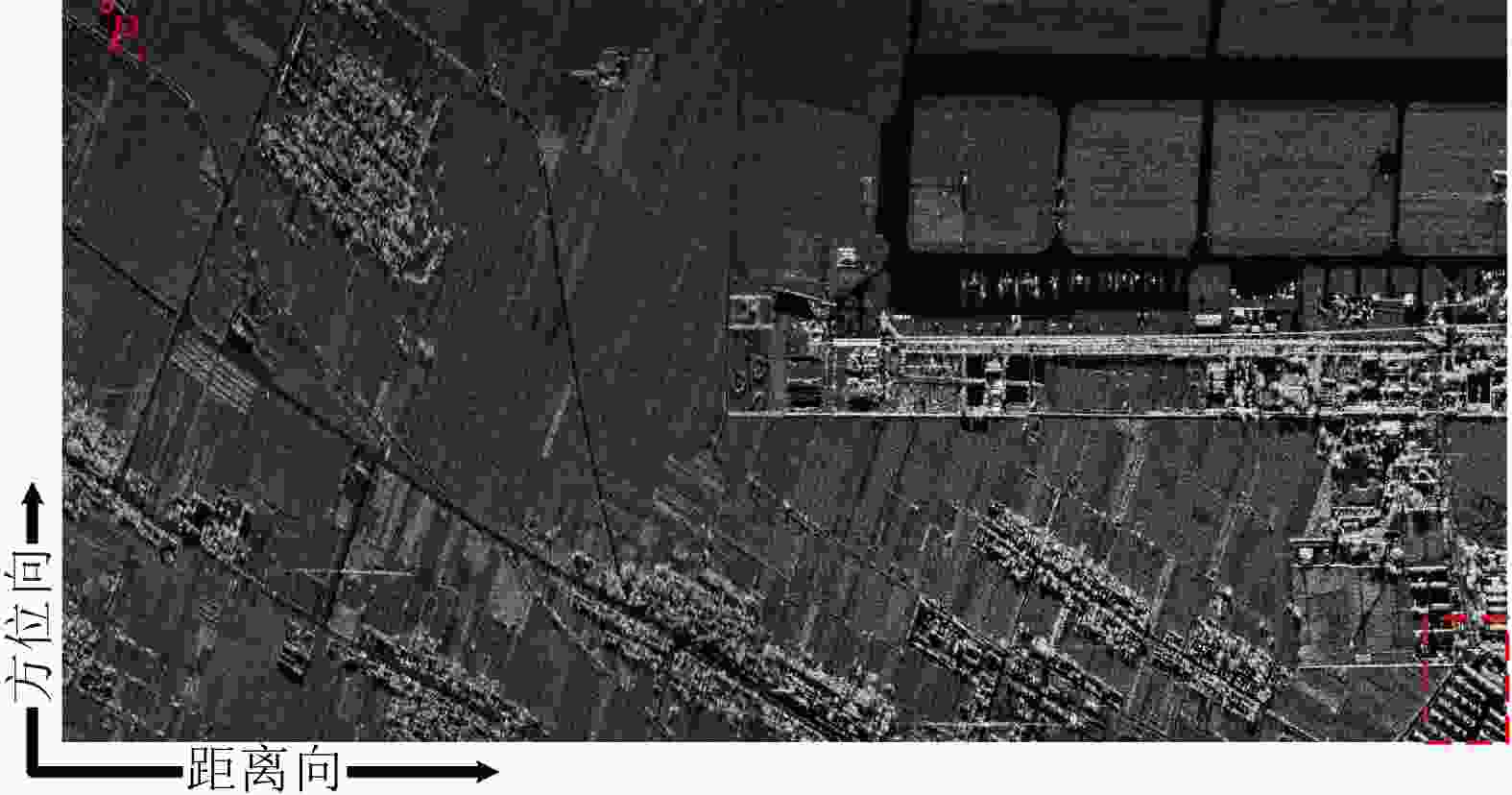
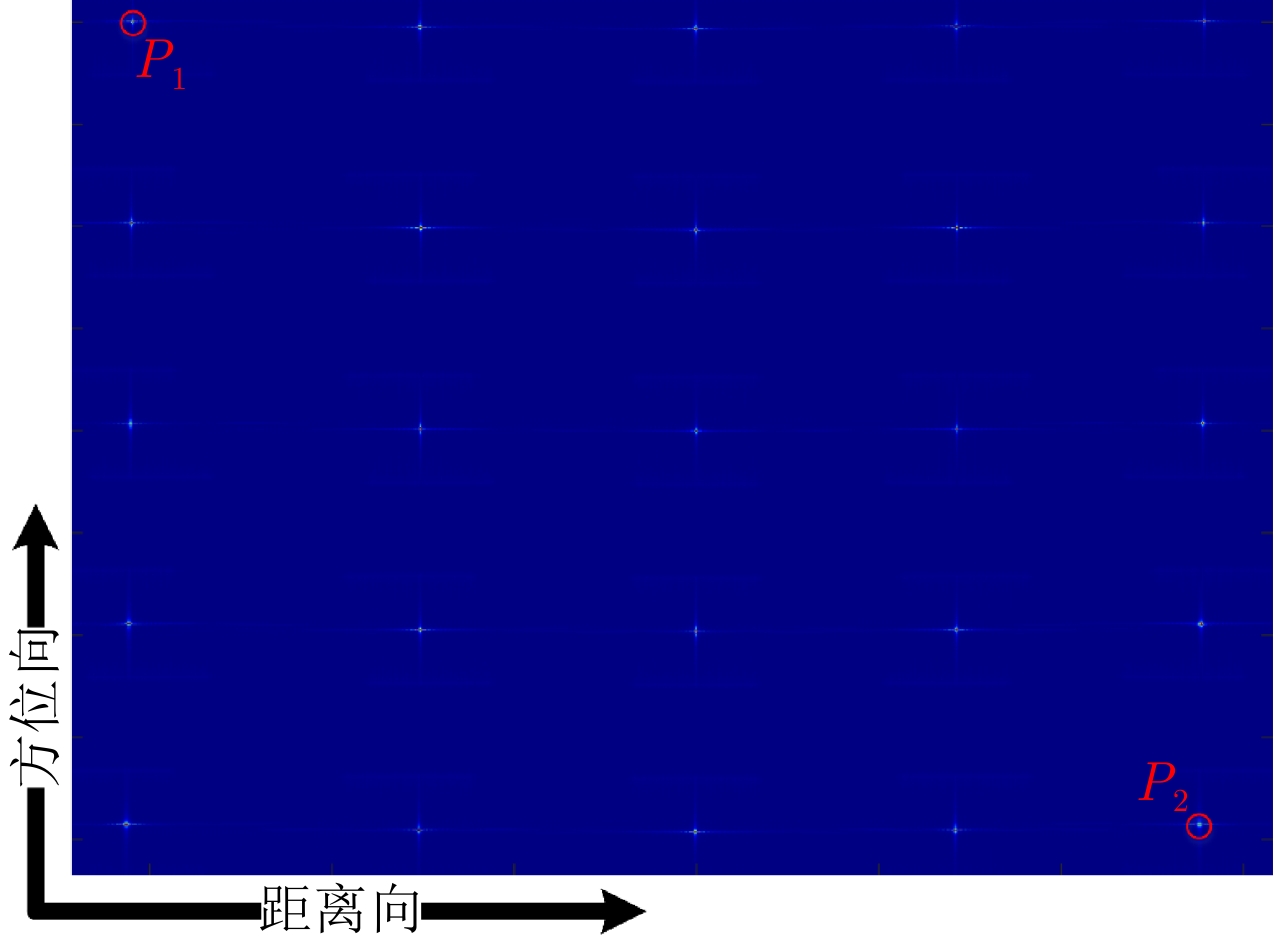
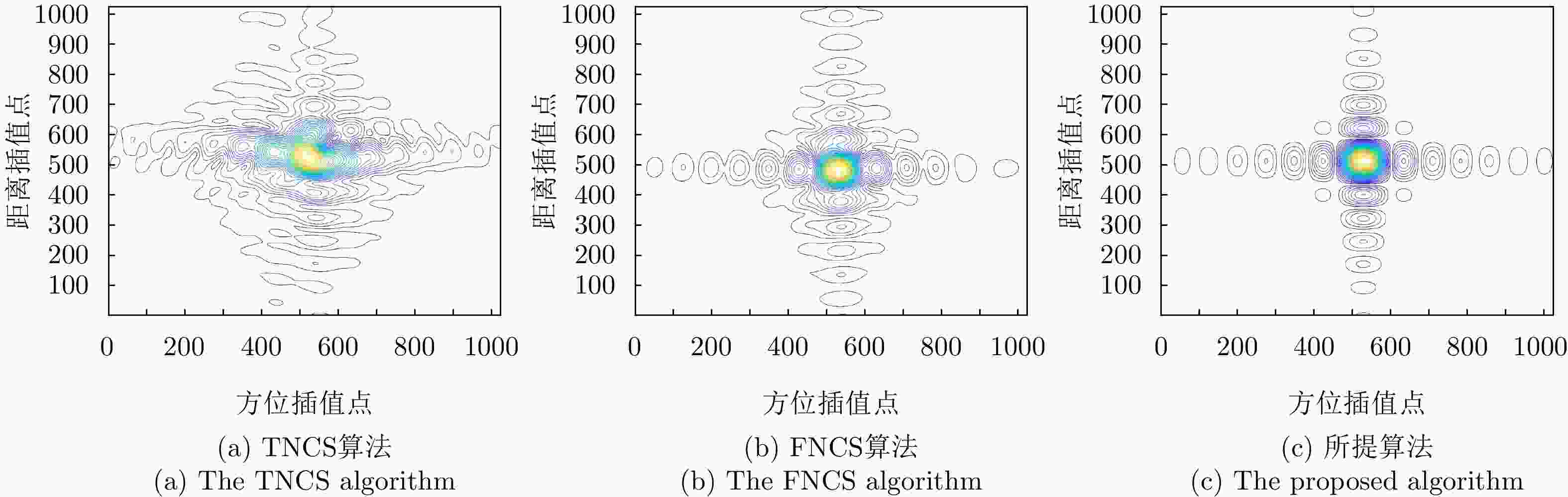
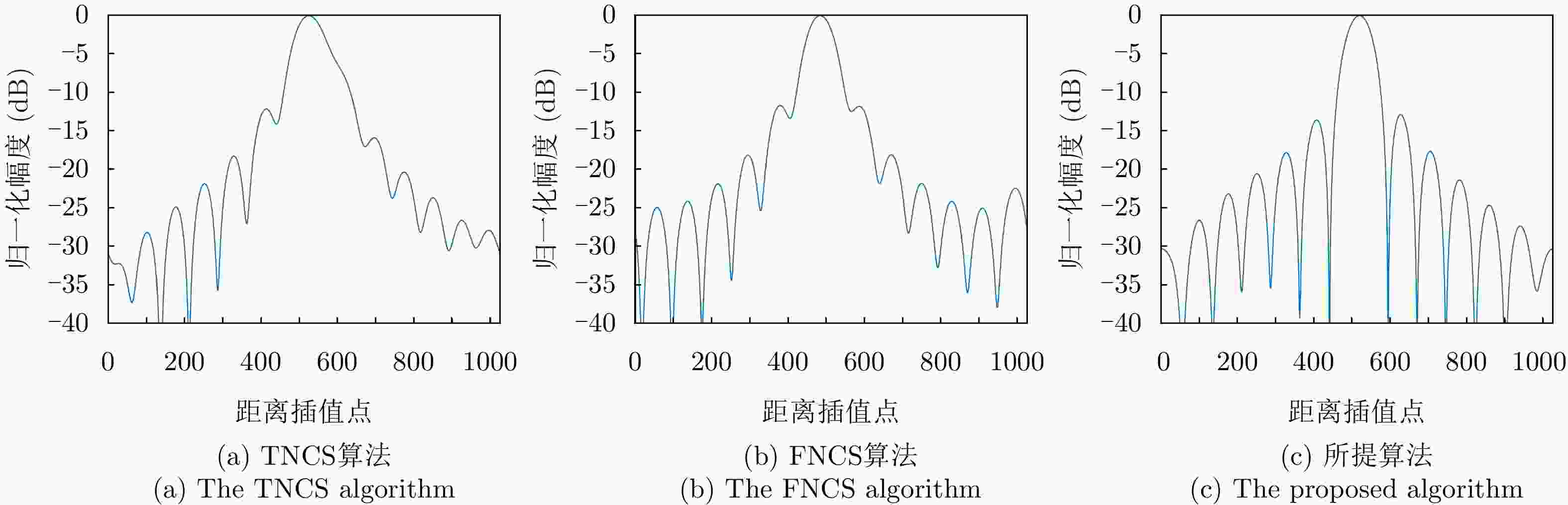
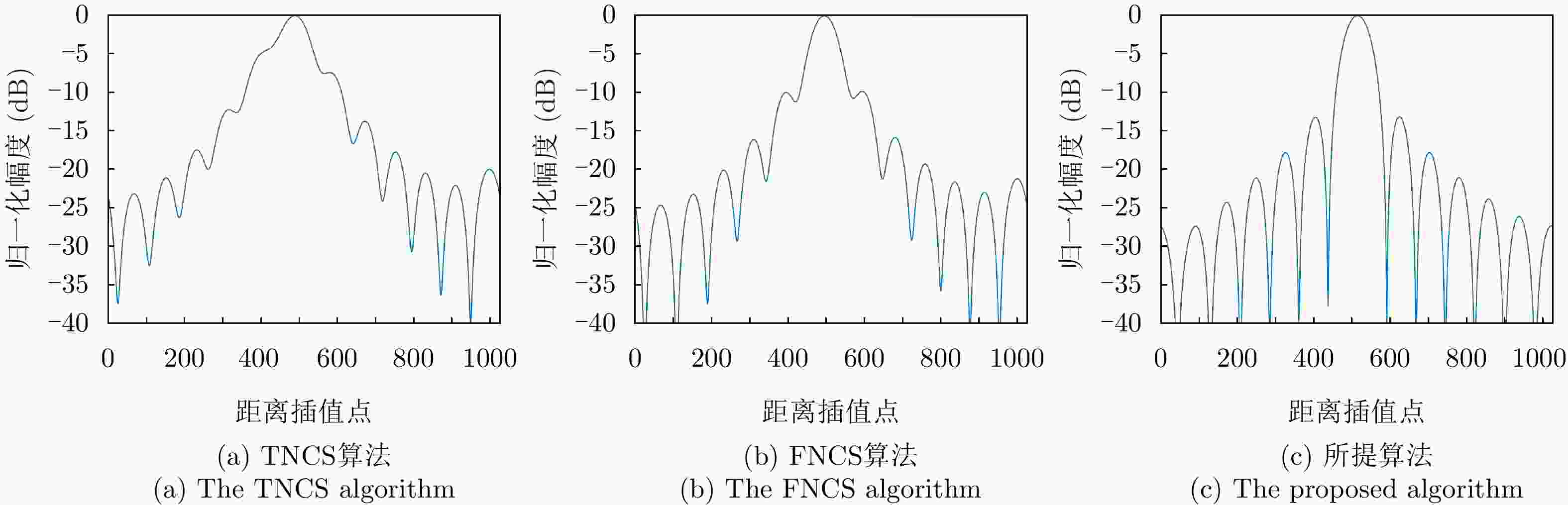
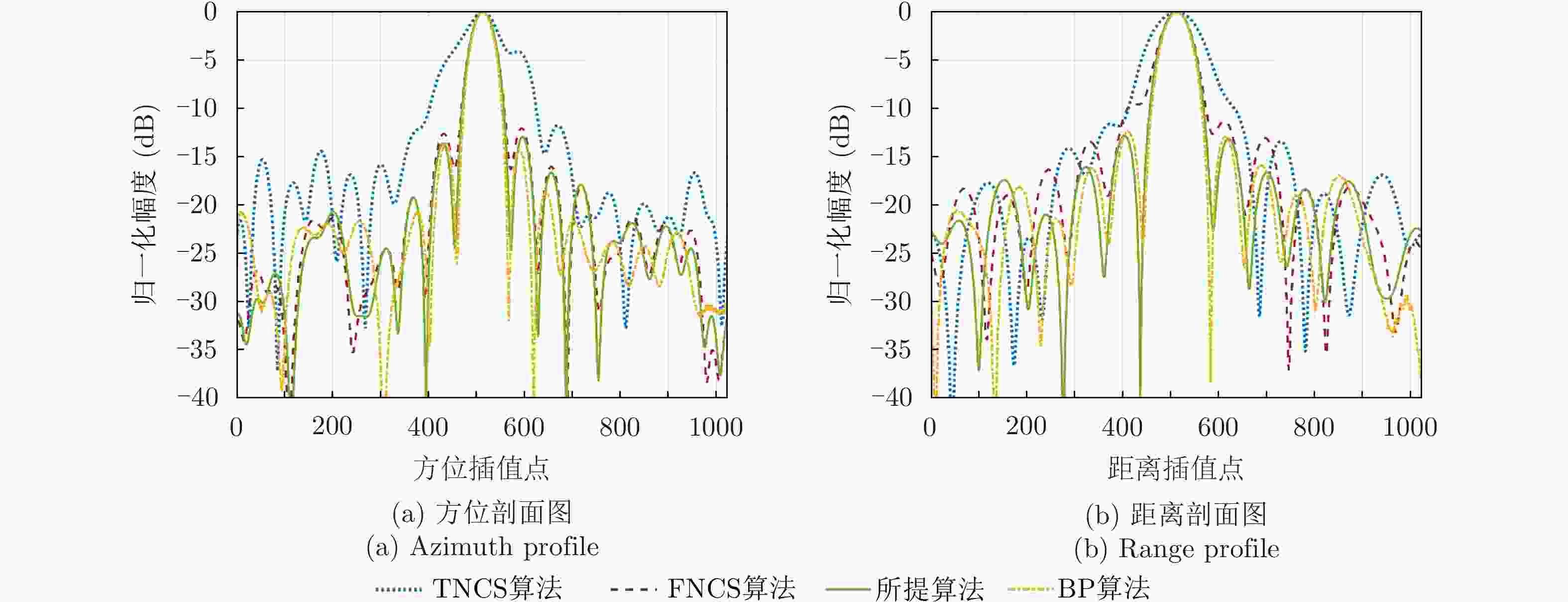
点目标 成像算法 方位向 距离向 分辨率(m) PSLR (dB) ISLR (dB) 分辨率(m) PSLR (dB) ISLR (dB) ${P_1}$ TNCS算法 2.17 N/A N/A 1.63 N/A N/A FNCS算法 1.85 –10.54 –8.06 1.13 –11.69 –9.39 所提算法 1.82 –13.28 –10.06 1.08 –13.27 –10.14 ${P_2}$ TNCS算法 2.23 N/A N/A 1.78 N/A N/A FNCS算法 1.88 –10.47 –7.81 1.19 –10.23 –8.52 所提算法 1.83 –13.26 –10.02 1.09 –13.26 –10.12 -
[1] CHEN Hongmeng, LI Yachao, GAO Wenquan, et al. Bayesian forward-looking superresolution imaging using Doppler deconvolution in expanded beam space for high-speed platform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5105113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3107717 [2] 李亚超, 王家东, 张廷豪, 等. 弹载雷达成像技术发展现状与趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, ZHANG Tinghao, et al. Present situation and prospect of missile-borne radar imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119 [3] 林春辉. 单基/双基SAR成像若干关键问题研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.LIN Chunhui. Study on some imaging issues of monostatic and bistatic SAR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2019. [4] NEO Y L, WONG F H, and CUMMING I G. Processing of azimuth-invariant bistatic SAR data using the range Doppler algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 14–21. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.909090 [5] 刘婵. 双基地前视SAR频域成像算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2015.LIU Chan. Study on frequency-domain imaging algorithms for bistatic forward-looking SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015. [6] CHEN Si, YUAN Yue, ZHANG Shuning, et al. A new imaging algorithm for forward-looking missile-borne bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(4): 1543–1552. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2507260 [7] ZHANG Qianghui, WU Junjie, SONG Yue, et al. Bistatic-range-Doppler-aperture wavenumber algorithm for forward-looking spotlight SAR with stationary transmitter and maneuvering receiver[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2080–2094. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3004726 [8] PU Wei, LI Wenchao, LV Youxin, et al. An extended omega-K algorithm with integrated motion compensation for bistatic forward-looking SAR[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 1291–1295. [9] FENG Dong, AN Daoxiang, and HUANG Xiaotao. An extended fast factorized back projection algorithm for missile-borne bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(6): 2724–2734. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2828238 [10] LI Yachao, XU Gaotian, ZHOU Song, et al. A novel CFFBP algorithm with noninterpolation image merging for bistatic forward-looking SAR focusing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–16. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3162230 [11] DESAI M D and JENKINS W K. Convolution backprojection image reconstruction for spotlight mode synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1992, 1(4): 505–517. doi: 10.1109/83.199920 [12] XU Gaotian, ZHOU Song, YANG Lei, et al. Efficient fast time-domain processing framework for airborne bistatic SAR continuous imaging integrated with data-driven motion compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5208915. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3099204 [13] AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, HE Zhiwei, et al. Geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne multichannel bistatic SAR imaging using weighted fast factorized backprojection method[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(10): 1590–1594. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2902036 [14] 蒲巍. 机载双基地前视SAR运动补偿方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2018.PU Wei. Research on airborne bistatic forward-looking SAR motion compensation[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018. [15] QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, and DING Chibiao. Some reflections on bistatic SAR of forward-looking configuration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 735–739. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2004506 [16] WU Junjie, YANG Jianyu, HUANG Yulin, et al. A frequency-domain imaging algorithm for translational invariant bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 2013, E96.B(2): 605–612. doi: 10.1587/transcom.E96.B.605 [17] WU Junjie, YANG Jianyu, HUANG Yulin, et al. Focusing bistatic forward-looking SAR using Chirp Scaling algorithm[C]. 2011 IEEE RadarCon, Kansas City, USA, 2011: 1036–1039. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2011.5960693. [18] QI C D, SHI X M, BIAN M M, et al. Focusing forward-looking bistatic SAR data with chirp scaling[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(3): 206–207. doi: 10.1049/el.2013.3978 [19] WU Junjie, PU Wei, HUANG Yulin, et al. Bistatic forward-looking SAR focusing using ω-k based on spectrum modeling and optimization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(11): 4500–4512. [20] ZHANG Xiaohu, GU Hong, and SU Weimin. Focusing bistatic forward-looking SAR images use omega-k algorithm based on modified hyperbolic approximating[C]. 2019 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences, Chengdu, China, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICCAIS46528.2019.9074596. [21] 张强辉. 高速机动平台双基前视SAR成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2019.ZHANG Qianghui. Imaging method research for bistatic forward-looking SAR mounted on high-speed maneuvering platform[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019. [22] LI Yachao, ZHANG Tinghao, MEI Haiwen, et al. Focusing translational-variant bistatic forward-looking SAR data using the modified omega-K algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5203916. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3063780 [23] ZENG Tao, WANG Rui, LI Feng, et al. A modified nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for spaceborne/stationary bistatic SAR based on series reversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 3108–3118. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2219057 [24] SONG Xuan, LI Yachao, ZHANG Tinghao, et al. Focusing high-maneuverability bistatic forward-looking SAR using extended azimuth nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5240814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3228803 [25] 陈溅来, 熊毅, 徐刚, 等. 基于子图像变标的非线性轨迹SAR成像及其自聚焦方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 1098–1109. doi: 10.12000/JR22171CHEN Jianlai, XIONG Yi, XU Gang, et al. Nonlinear trajectory synthetic aperture radar imaging and autofocus algorithm based on sub-image nonlinear chirp scaling[J].Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 1098–1109. doi: 10.12000/JR22171 [26] WONG F H, CUMMING I G, and LAM NEO Y. Focusing bistatic SAR data using the nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(9): 2493–2505. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.917599 [27] QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, and DING Chibiao. An improved NLCS algorithm with capability analysis for one-stationary BiSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 3179–3186. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.921569 [28] WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, LI Zhongyu, et al. Focusing translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR using keystone transform and extended nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(10): 840. doi: 10.3390/rs8100840 [29] MEI Haiwen, LI Yachao, XING Mengdao, et al. A frequency-domain imaging algorithm for translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(3): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2943743 [30] LIANG Mu, SU Weimin, and GU Hong. Focusing high-resolution high forward-looking bistatic SAR with nonequal platform velocities based on keystone transform and modified nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(3): 901–908. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2877387 [31] DING Jiabiao, LI Yachao, LI Ming, et al. Focusing high maneuvering bistatic forward-looking SAR with stationary transmitter using extended keystone transform and modified frequency nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 2476–2492. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3153824 [32] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and ImpleMentation[M]. Boston, MA, USA: Artech House, 2005: 225–362.CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and ImpleMentation[M]. Boston, MA, USA: Artech House, 2005: 225–362. [33] 李燕平, 张振华, 邢孟道, 等. 基于级数反演和数值计算的广义双基SAR距离徙动成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(12): 2800–2804. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00810LI Yanping, ZHANG Zhenhua, XING Mengdao, et al. A novel range migration algorithm for general bistatic SAR imaging based on series reversion and numerical computation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2008, 30(12): 2800–2804. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00810 [34] 王谋, 韦顺军, 沈蓉, 等. 基于自学习稀疏先验的三维SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 36–52. doi: 10.12000/JR22101WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, SHEN Rong, et al. 3D SAR imaging method based on learned sparse prior[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 36–52. doi: 10.12000/JR22101 [35] CARDILLO G P. On the use of the gradient to determine bistatic SAR resolution[C]. International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation Society, Merging Technologies for the 90’s, Dallas, USA, 1990: 1032–1035. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: