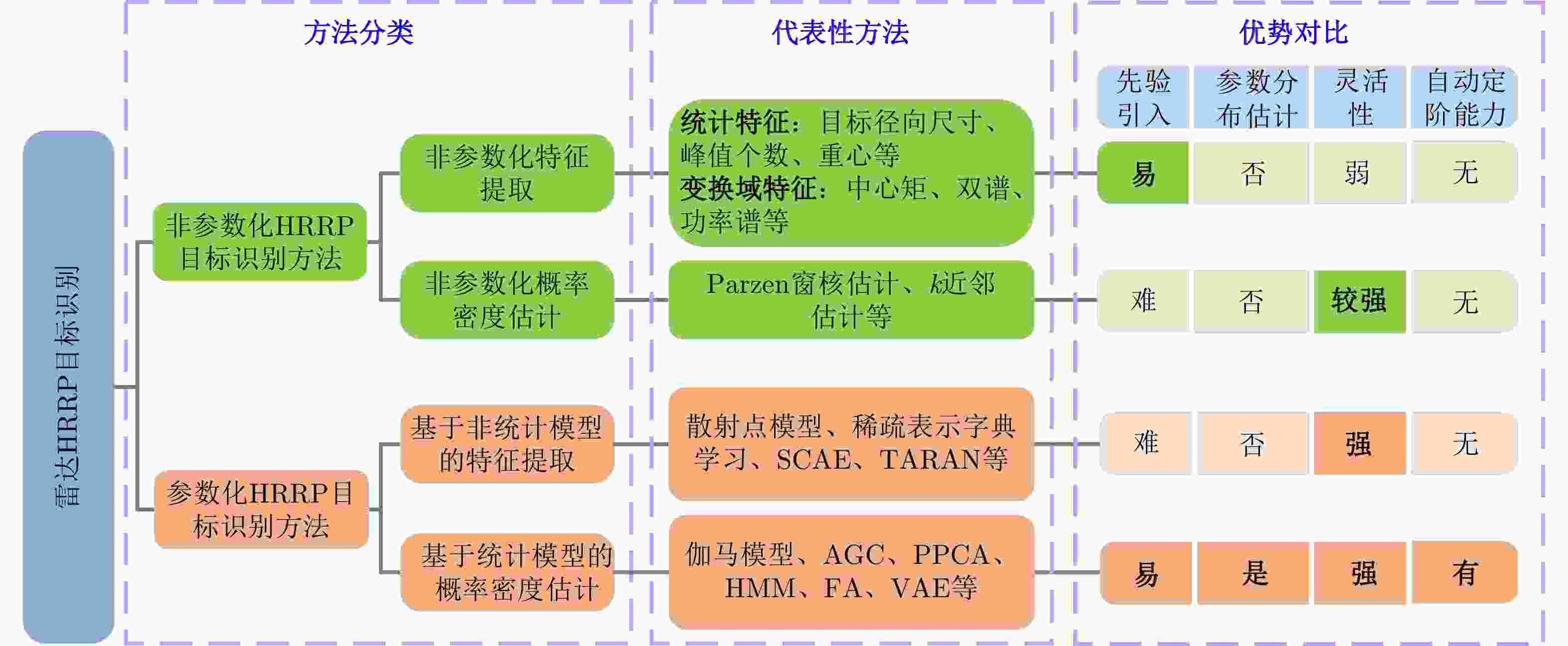
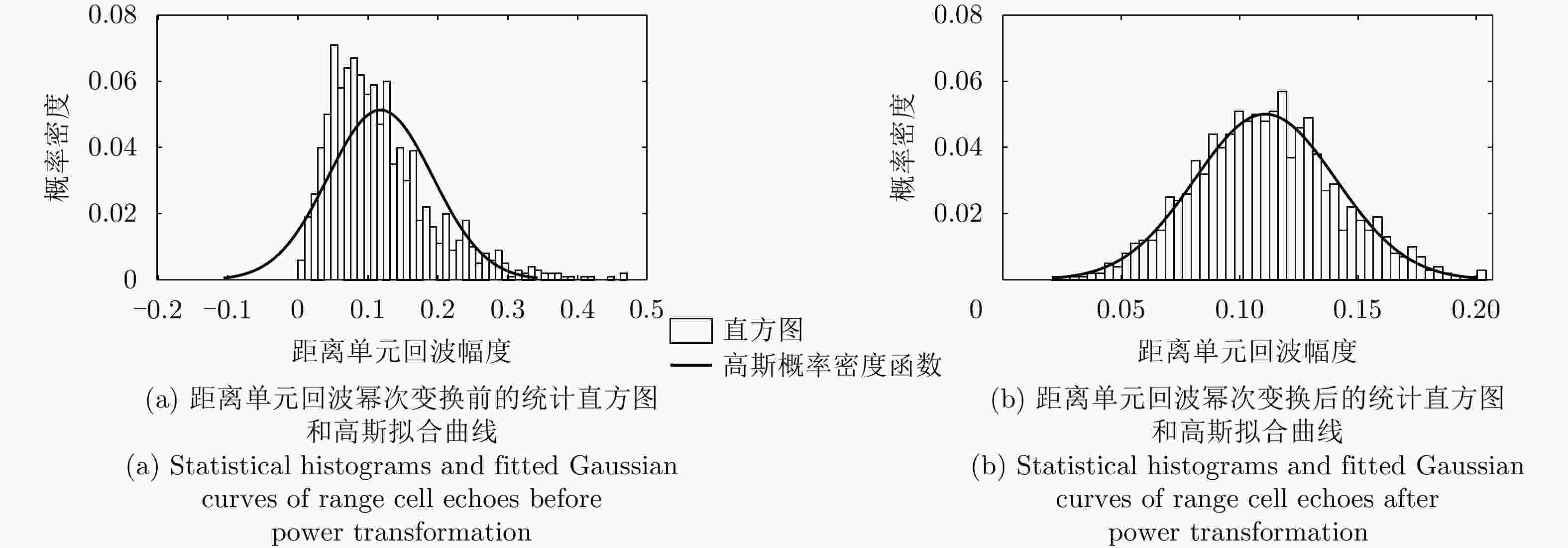
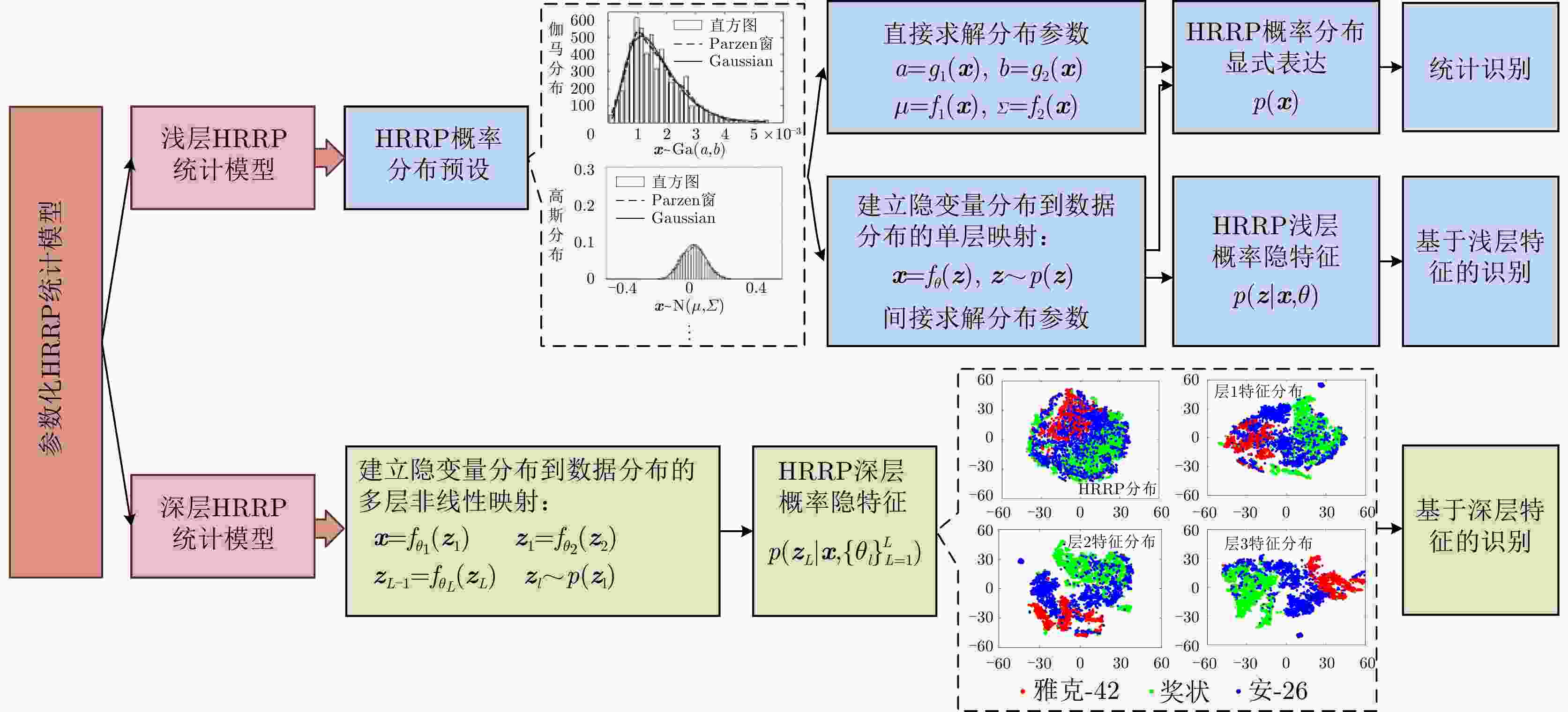
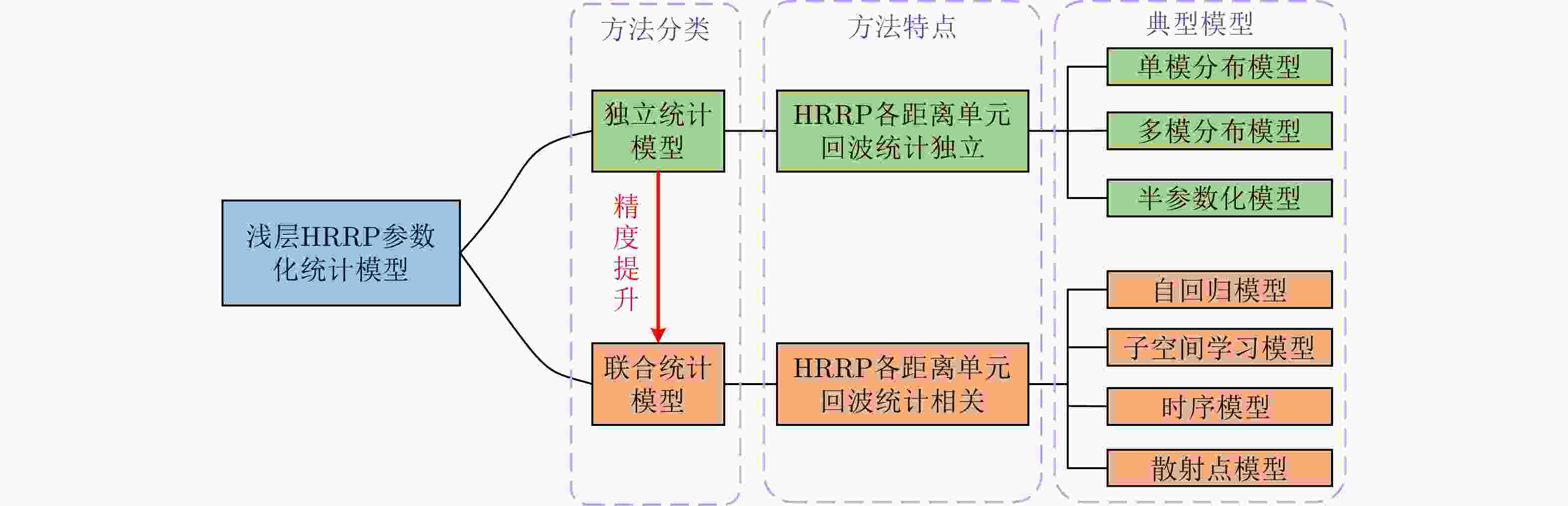
-
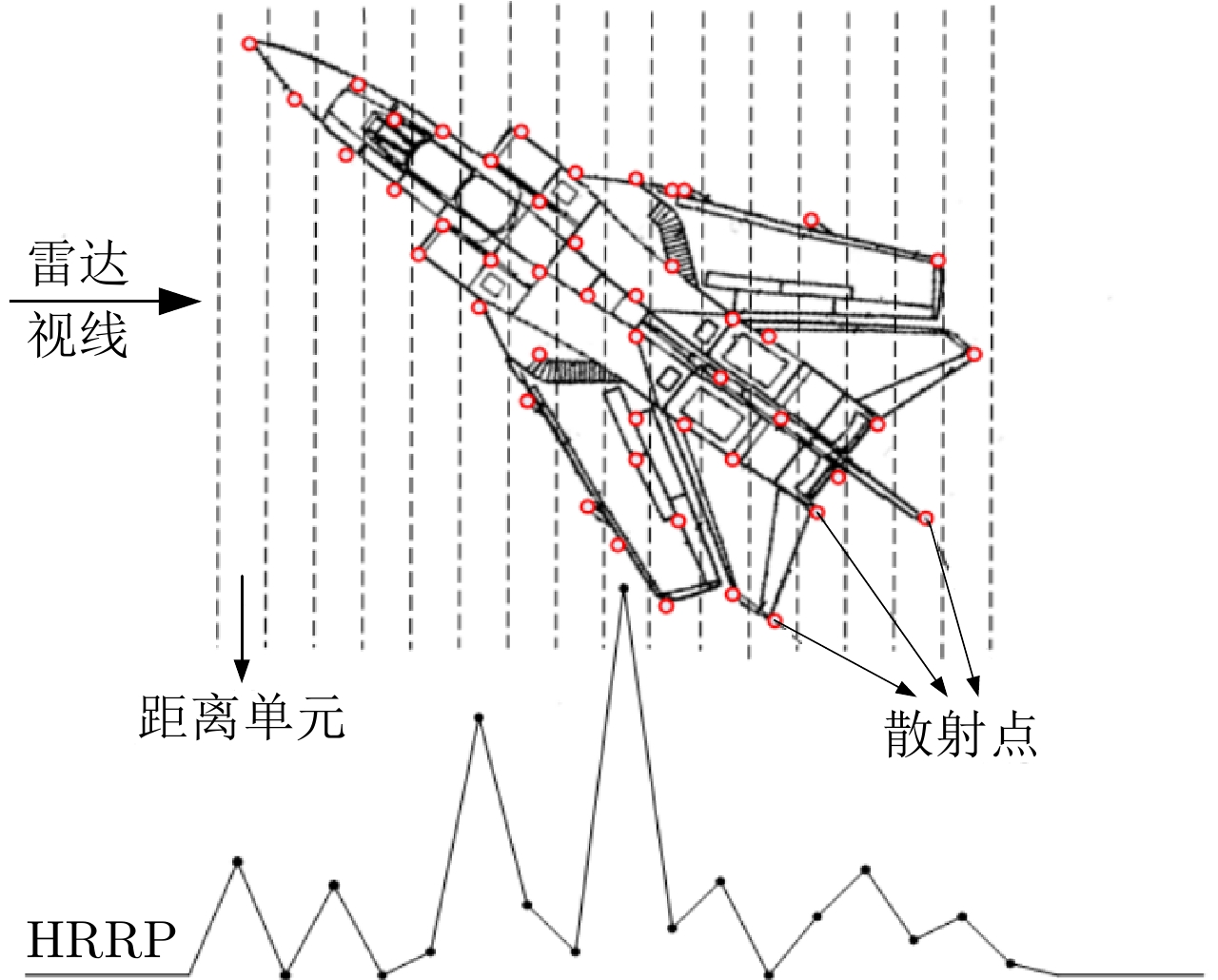
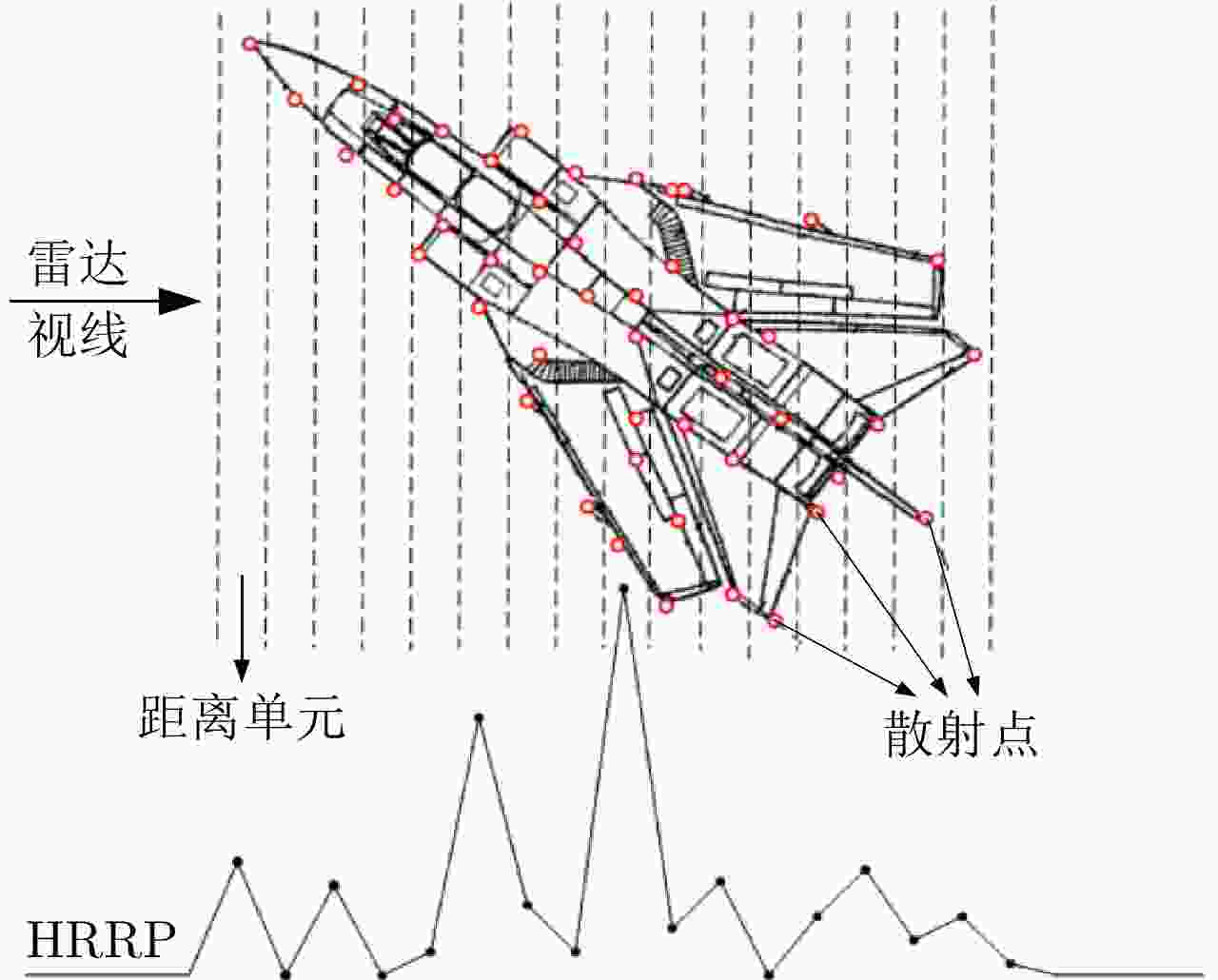
摘要: 现代战争日趋信息化和智能化,雷达自动目标识别技术(RATR)在国家安全防卫和战略预警等军事应用方面发挥着更加重要的作用。高分辨距离像(HRRP)反映了目标散射点沿雷达视线方向的分布情况,包含了目标丰富的结构信息,对目标识别十分有价值,已成为RATR领域的研究热点。参数化统计建模旨在构建参数化数学模型表征观测数据的分布特性,是估计数据概率分布和挖掘数据隐含信息的重要手段。基于参数化统计模型的雷达HRRP目标识别就是在对HRRP参数化统计建模的基础上,直接利用估计的概率分布进行统计识别或将获取的隐含信息输入分类器进行识别。由于模型具有可融入一定的先验知识、扩展灵活、提供待求参数的不确定性评价以及能结合贝叶斯理论实现自动定阶等优势,基于参数化统计模型的HRRP识别方法整体识别性能优于其他方法,是目前HRRP识别的重点研究方向。该文从浅层和深层参数化统计建模两方面,对近15年的雷达HRRP目标识别方法进行了归纳总结,并分析了各类方法的特点和存在的问题,最后对基于HRRP参数化统计建模的雷达目标识别发展方向进行了展望。Abstract: In the gradually becoming information-based and intelligent modern warfare, Radar Automatic Target Recognition (RATR) technology plays an increasingly important role in military applications, such as national security defense and strategic early warning. The High-Resolution Range Profile (HRRP) reflects the distribution of target scatterers along the radar line of sight and contains a target’s rich structural information, thus being valuable for target recognition and having become a research hotspot in the field of RATR. Parametric statistical modeling aims to construct a parametric mathematical model to characterize the distribution of observed data. It is an important way to estimate the data probability distribution and mine the hidden information of data. Radar HRRP target recognition based on a parametric statistical model directly uses the estimated probability distribution for statistical recognition or inputs the extracted information hidden in data into the classifier for target recognition. The parametric statistical model exhibits advantages in prior knowledge integration, flexible expansion, parameter uncertainty evaluation, and automatic order determination combined with Bayesian theory; therefore, the overall performance of the HRRP recognition method based on such a model is better than that of other methods. Therefore, parametric statistical modeling is currently the key research direction for radar HRRP recognition. This paper summarizes the radar HRRP target recognition methods of the last 15 years from the two aspects of shallow statistical modeling and deep statistical modeling, analyzes the characteristics and problems of these methods, and forecasts the development direction of radar target recognition based on HRRP parametric statistical modeling.
-
表 1 不同独立统计建模方法比较
Table 1. Comparison of different independent statistical modeling methods
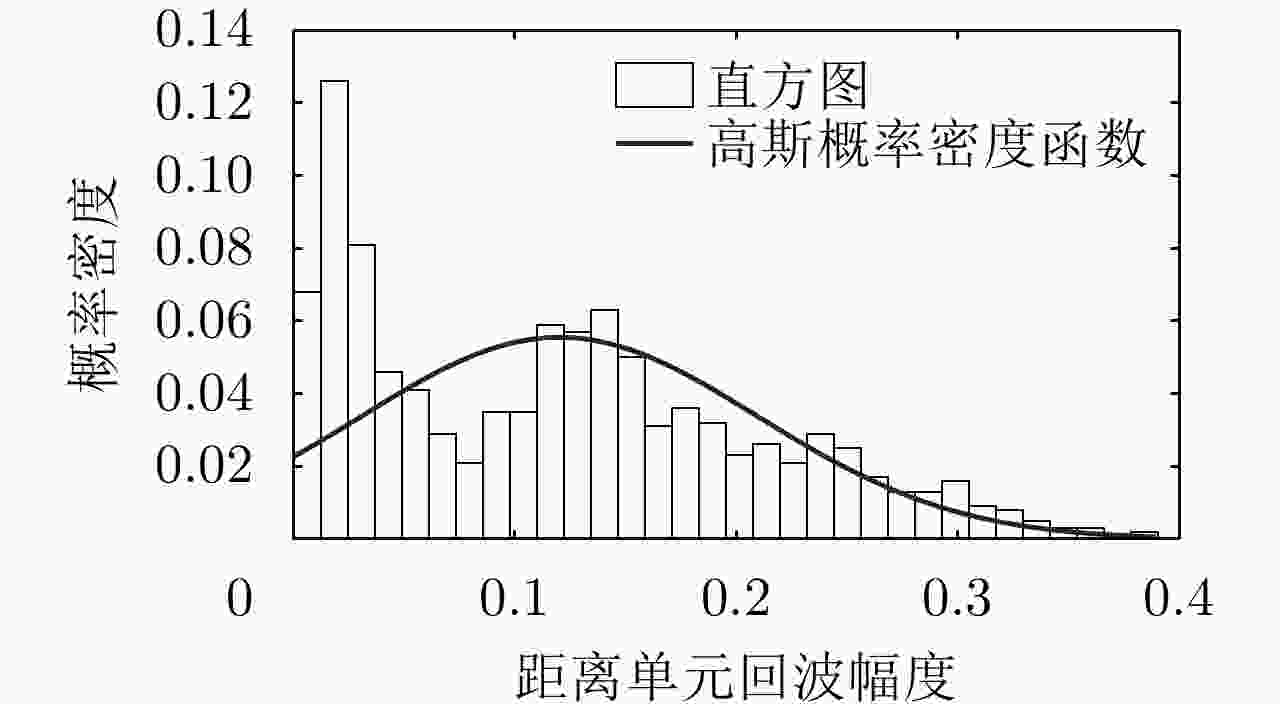
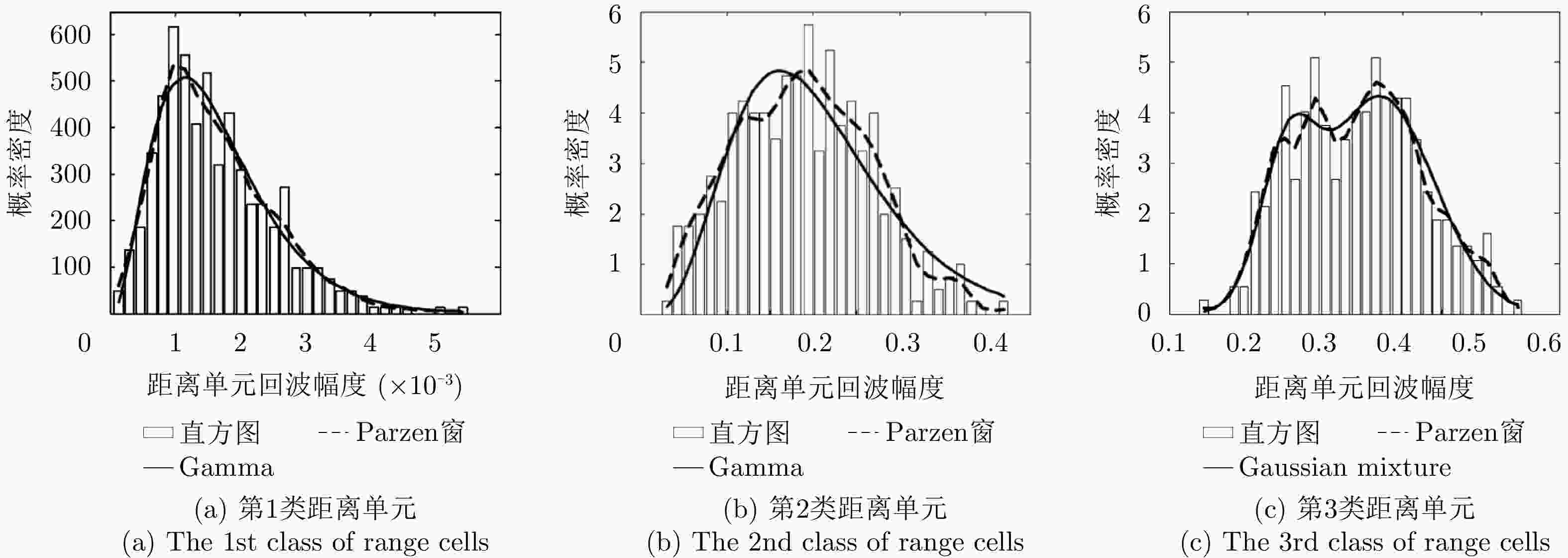
方法 优点 缺点 单模分布模型 计算简单、易实现。 各距离单元回波分布复杂性考虑不足,对多模分布距离单元回波的拟合精度低。 多模分布模型 能够准确拟合具有多模特性的距离单元回波分布。 计算复杂,模态个数需要人为预设,易造成过拟合/欠拟合。 半参数化模型 避免了多模分布模型中的模态个数预设问题,
实现模态数随数据的自适应确定。引入非参数化统计方法对训练样本数的需求大大增加。 表 2 不同自回归模型比较
Table 2. Comparison of different autoregressive models
方法 优点 缺点 单高斯自回归模型 计算简单、易实现;考虑了HRRP距离单元回波之间的相关性,能够反映HRRP的频谱幅度变化特性。 难以对呈多模分布的频幅分量进行高精度拟合,整体描述能力有限。 混合自回归模型 对各频幅分量采用多个单高斯自回归模型描述,可以表征频幅分量的多模分布特性,建模精度更高。 需要预先设定混合成分个数,对人工经验和先验认知依赖性强,数据自适应性能力差。 表 3 不同子空间学习模型对比
Table 3. Comparison of different subspace learning models
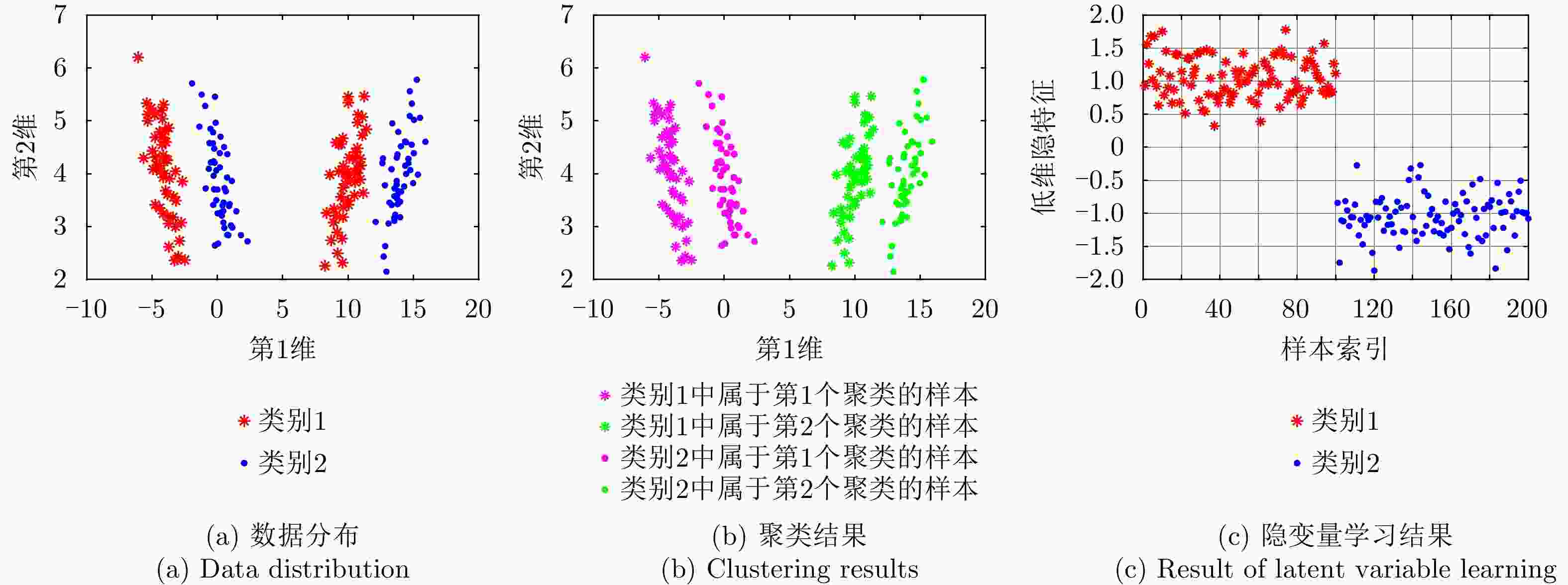
方法 代表性模型 优点 缺点 基于PCA的子空间学习模型 子空间近
似模型保留信号主要成分、实现数据降维,一定程度抑制信号中的噪声成分。 忽略了噪声子空间中包含的支撑区长度信息,数据信息利用不全。 PPCA
模型保留了噪声子空间的部分统计信息,数据信息利用更充分。 要求信号子空间的基正交、支撑区内外噪声方差相同,灵活性不强。 基于FA的
子空间学
习模型统计
识别传统FA
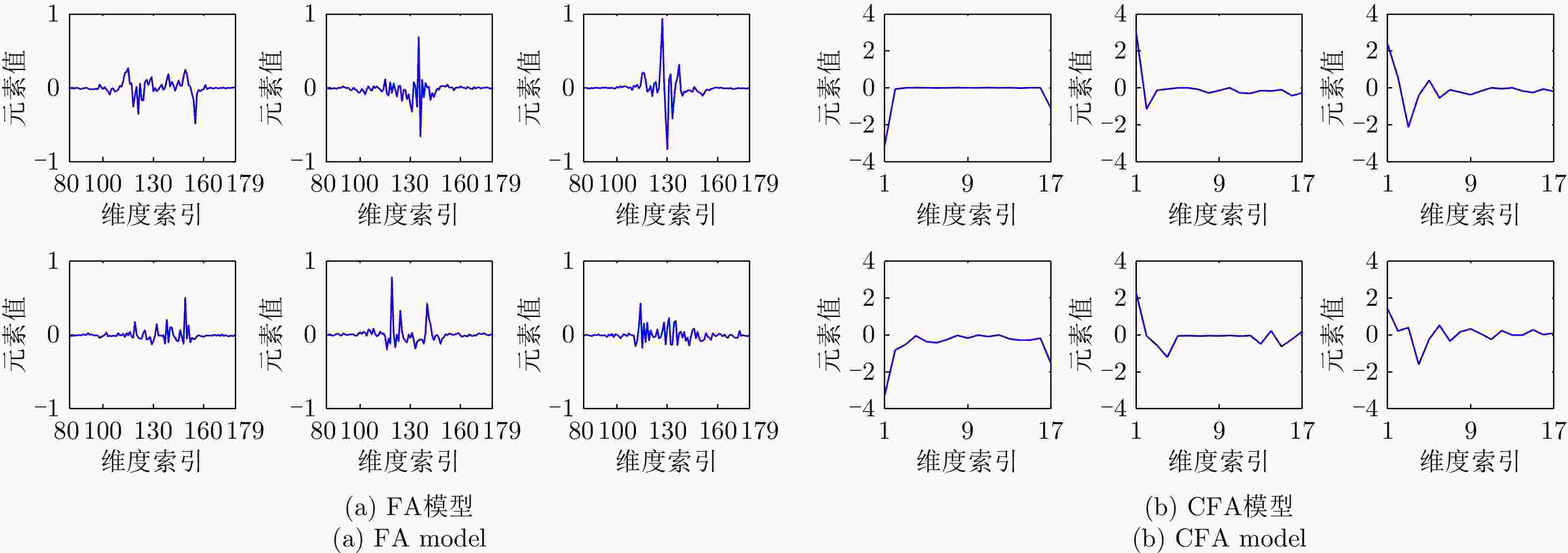
模型不要求投影各列正交、支撑区内外噪声方差不要求相同,建模更灵活、准确。 模型复杂度高、训练样本需求量大,小样本识别能力弱。 MTL-FA
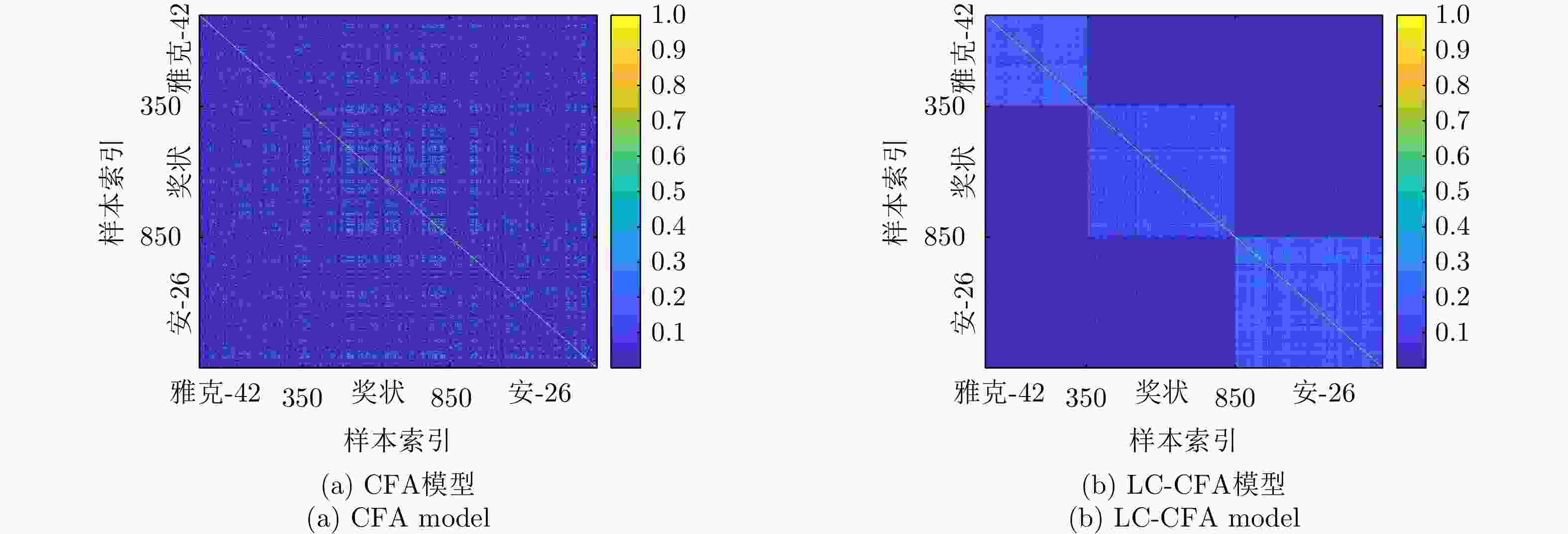
CFA
LA-FA
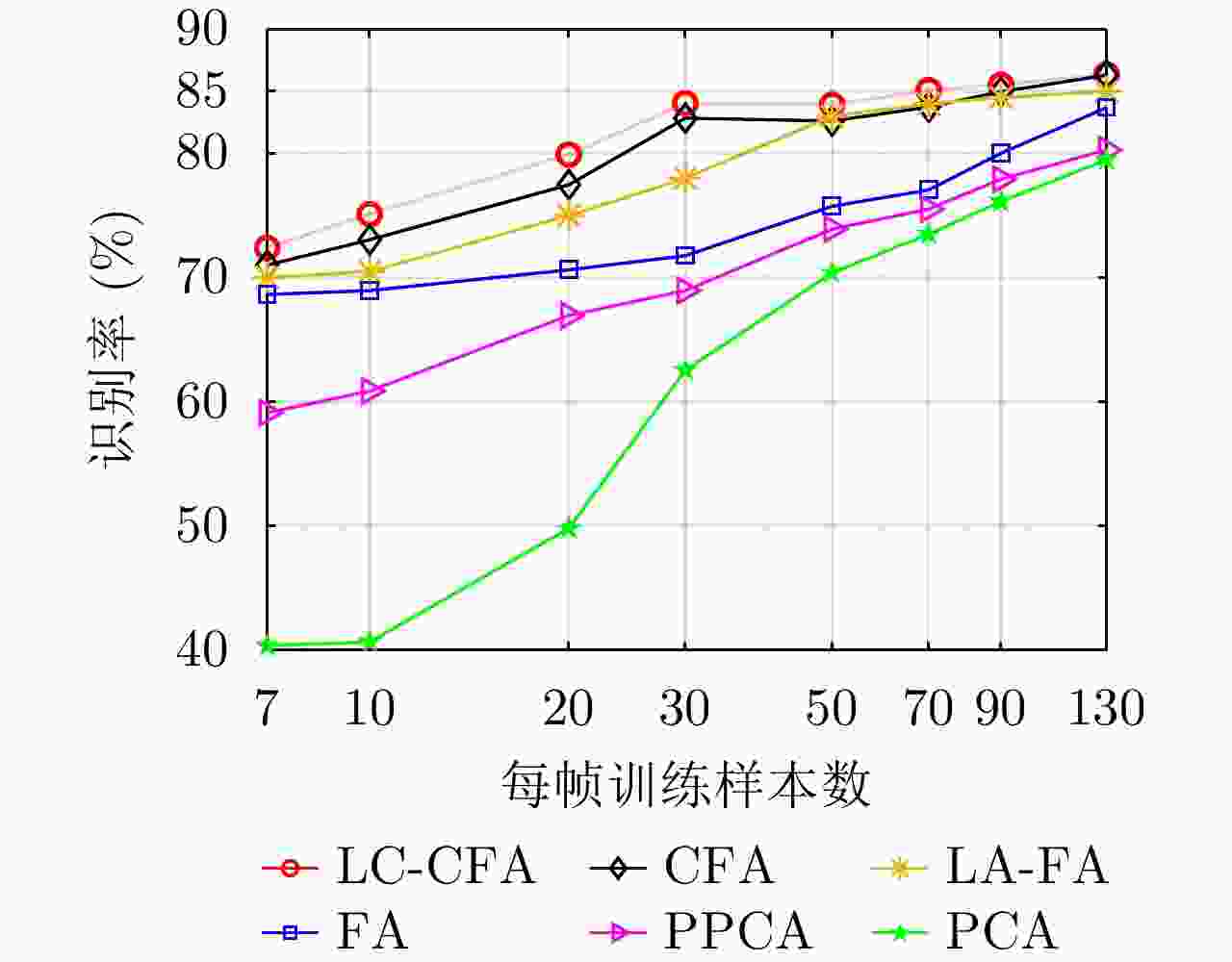
LC-CFA引入多任务学习/卷积操作/标签约束策略降低模型复杂度、提升模型类间可分性,小样本识别能力明显提升。 假设HRRP服从单高斯分布,对HRRP的多模分布特性描述不足。 LFA
DMR-MFA多个描述不同分布的子FA模型集成拟合HRRP的多模分布特性。 子模型个数需要提前预设,预设合理性难以保证,影响识别精度。 特征
提取MMFA
MMRFA特征提取与分类器学习联合进行,增强特征可分性的同时避免了特征与分类器的失配。 单高斯FA建模,对HRRP数据的多模分布特性描述能力不足。 表 4 不同时序模型对比
Table 4. Comparison of different temporal models
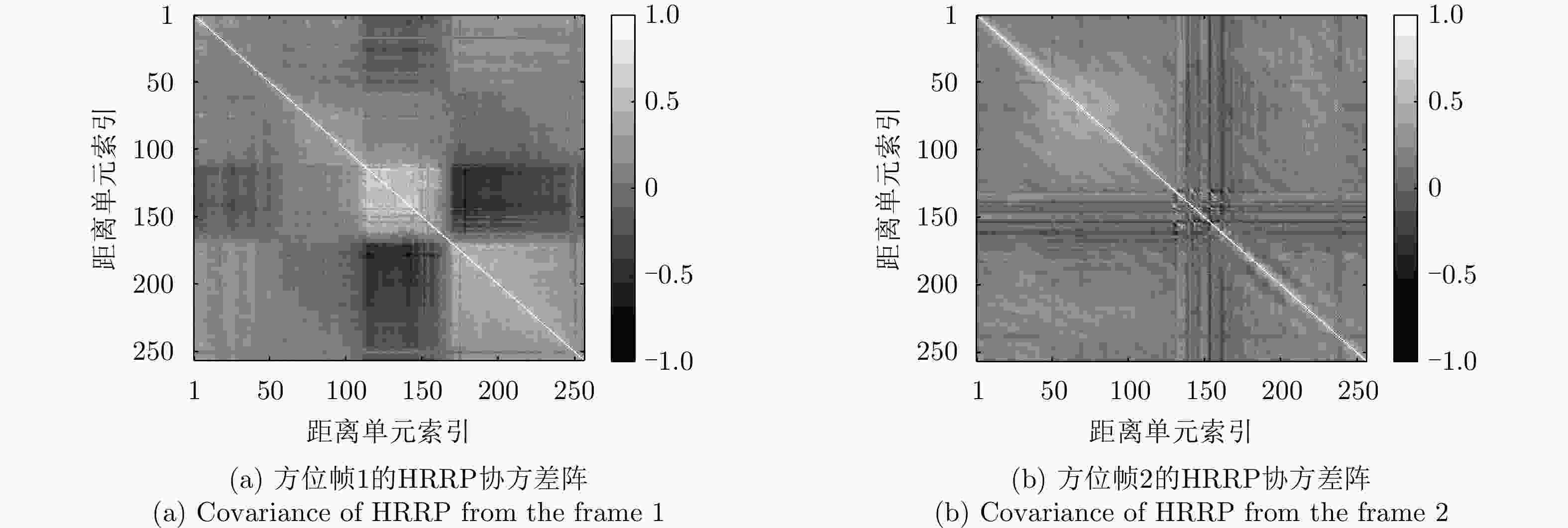
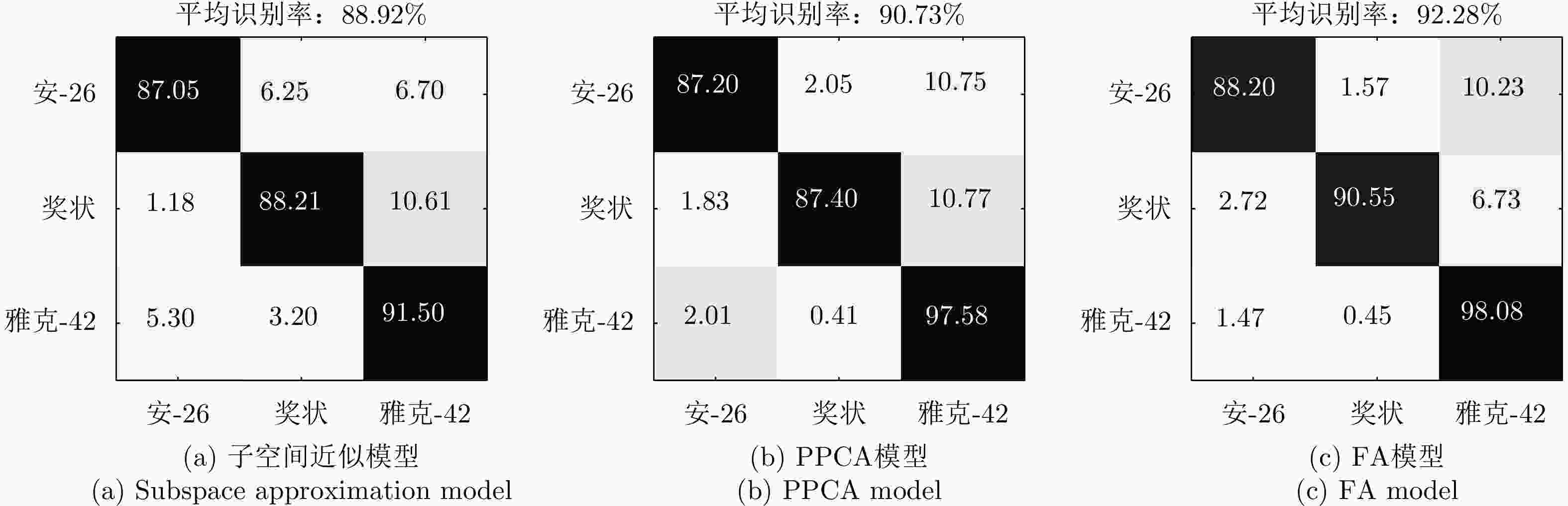
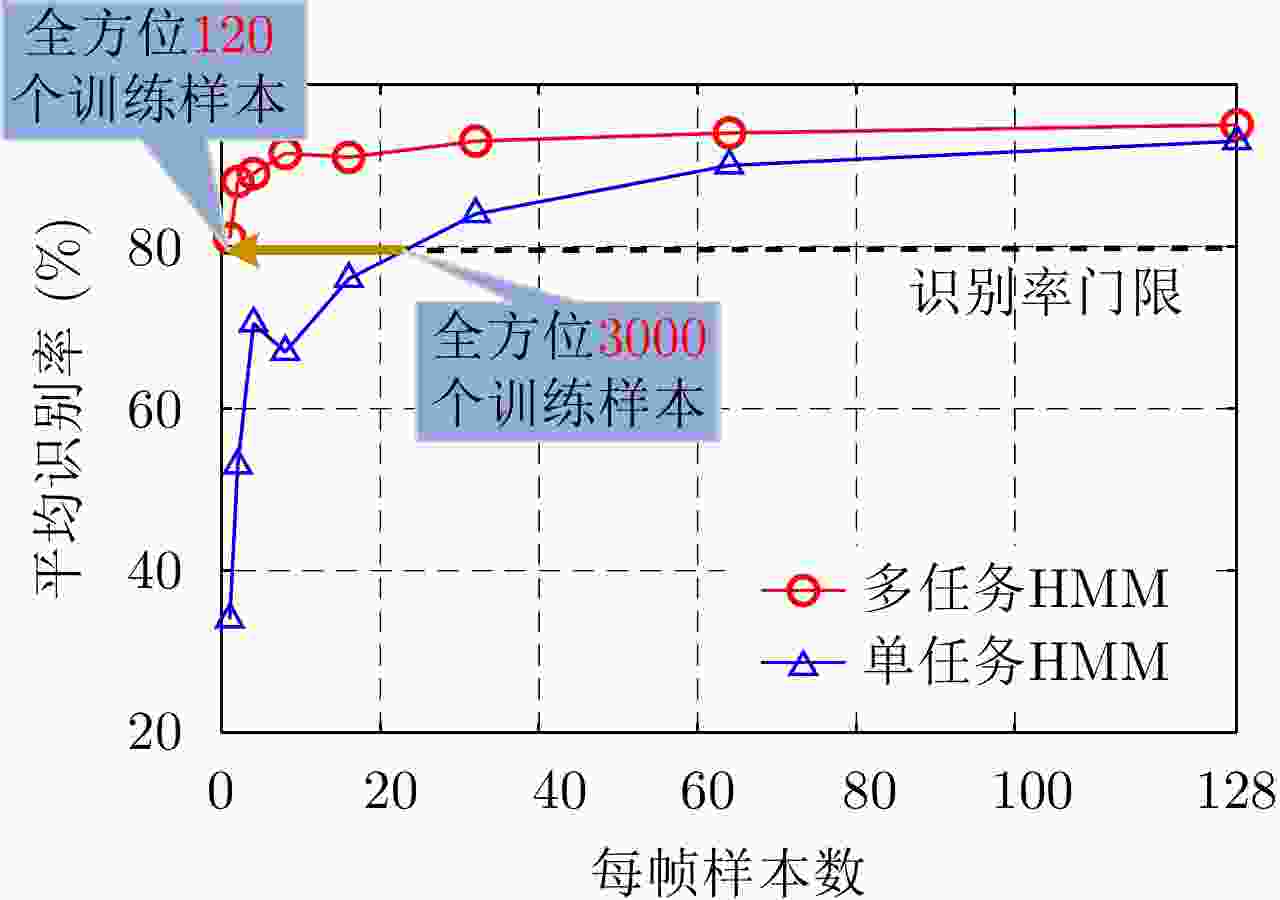
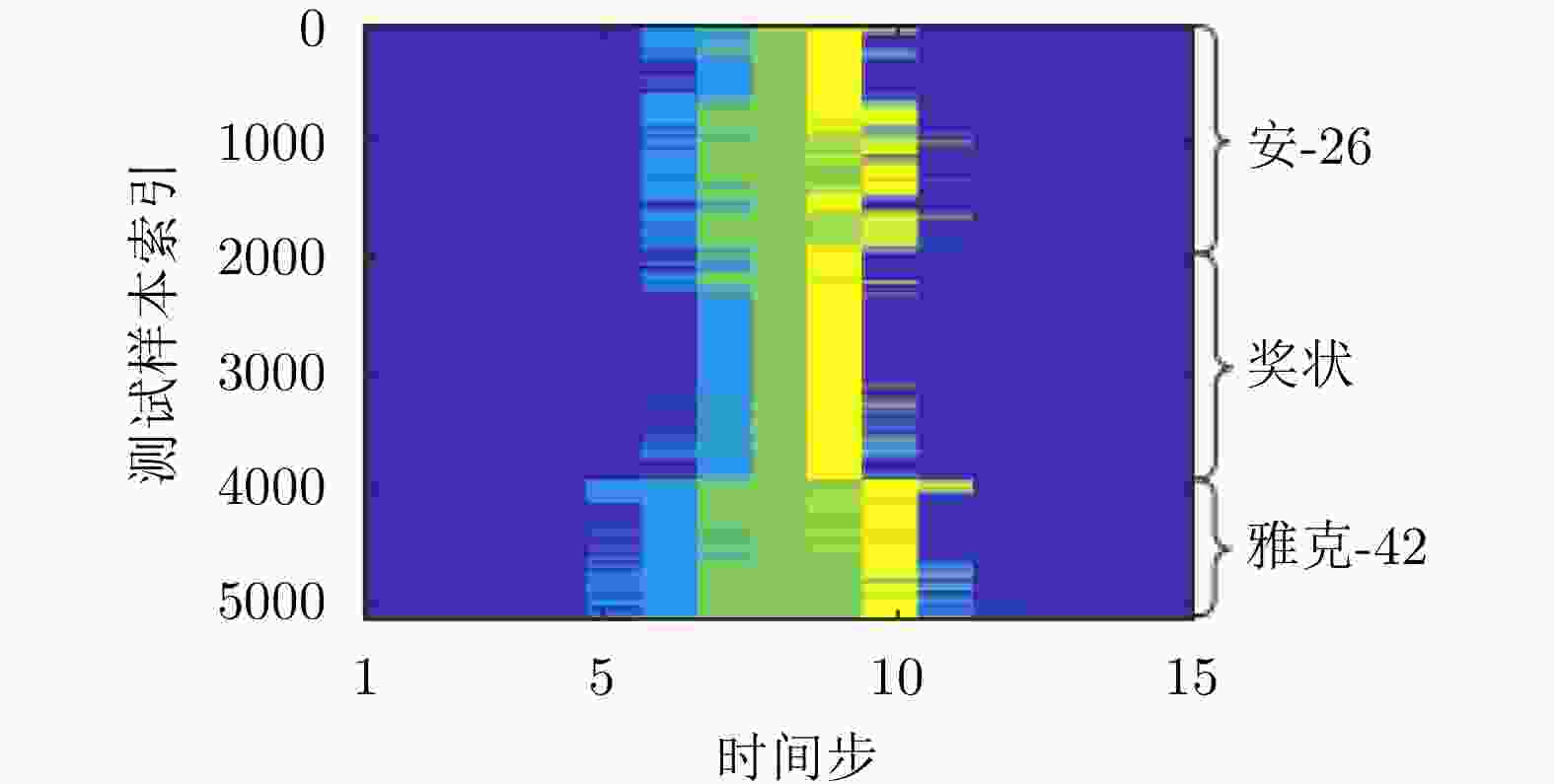
方法 优点 缺点 基于HRRP样本间时序信息挖掘的模型 能够利用HRRP样本间的时序相关性进行目标识别。 数据降维预处理丢失了一部分可用信息;要求训练和测试阶段目标相对雷达视线的转角保持一致,实际很难满足;无法对单个HRRP样本给出实时判决结果。 基于HRRP样本内距离单元回波间时序信息挖掘的模型 对各HRRP样本内的不同距离单元回波建立时序模型,挖掘样本距离单元之间的时序信息。无需降维、不要求训练和测试阶段目标相对雷达视线转动的一致性、能够给出各HRRP样本的实时判决结果。 对各距离单元回波进行单高斯分布建模,未充分考虑距离单元回波存在的非高斯特性,建模精度仍有提升空间。 表 5 TSB-HMM模型对3类飞机目标HRRP数据的识别率混淆矩阵(%)[62]
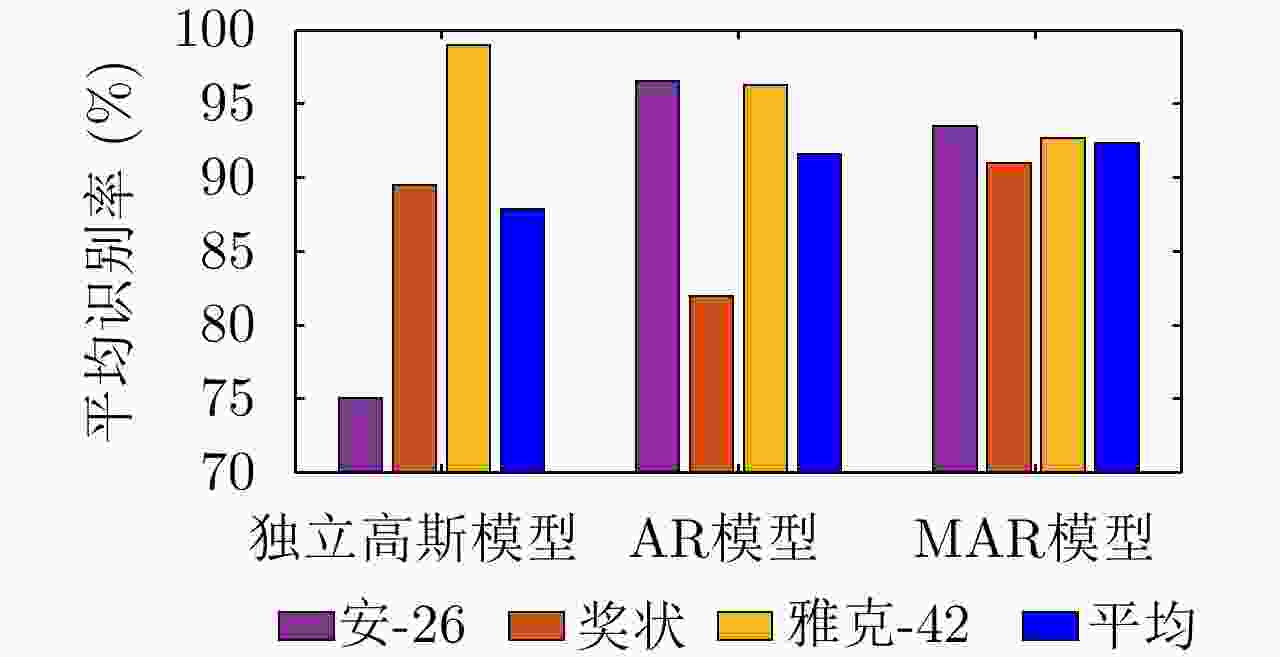
Table 5. Confusion matrix of recognition rate via the TSB-HMM on three types of airplanes (%)[62]
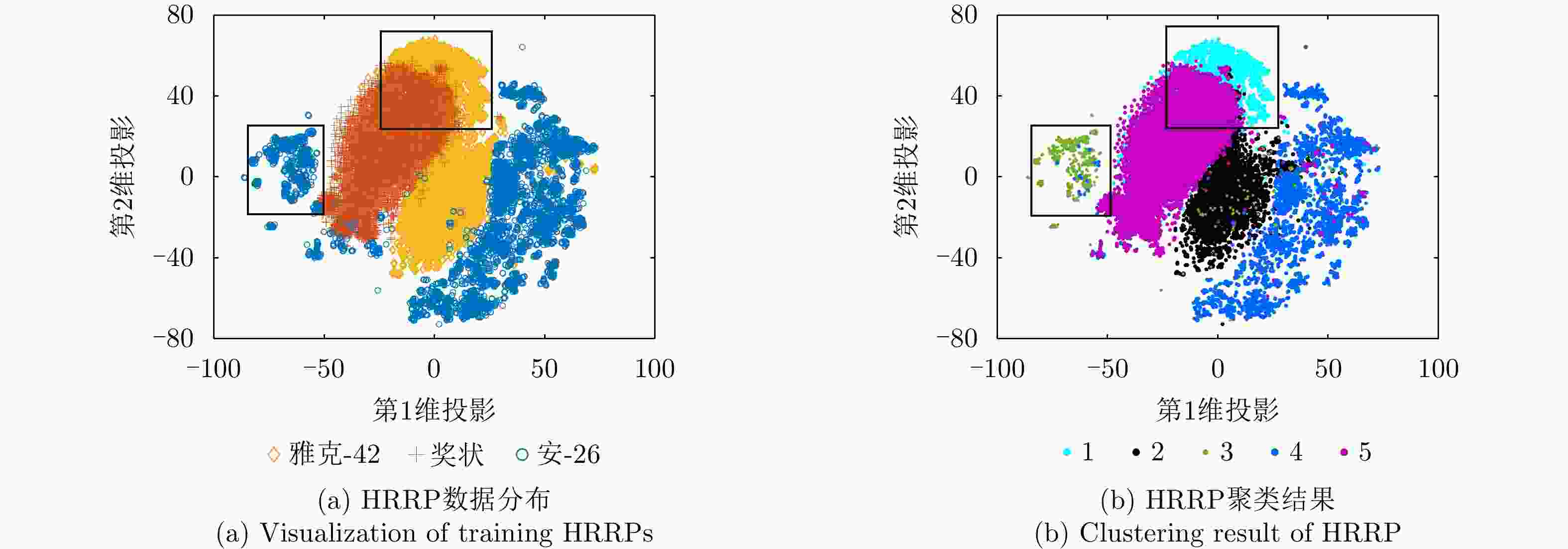
识别目标 安-26 奖状 雅克-42 安-26 90.8 9.8 3.5 奖状 8.7 83.0 2.0 雅克-42 0.5 7.2 94.5 平均识别率 89.4 表 6 不同变分自编码模型比较
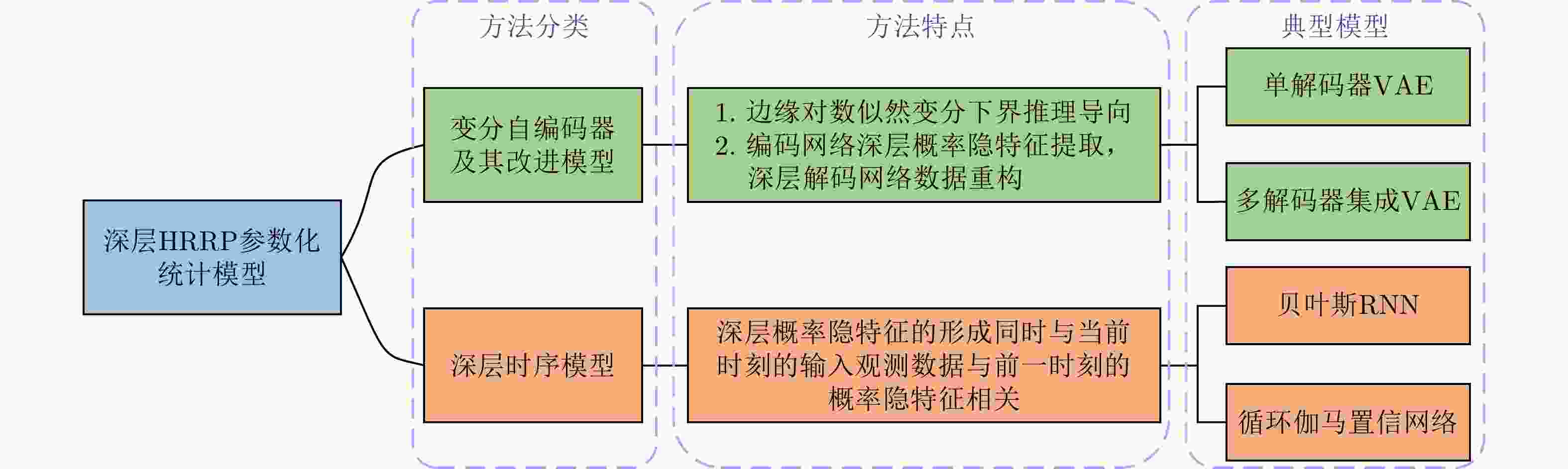
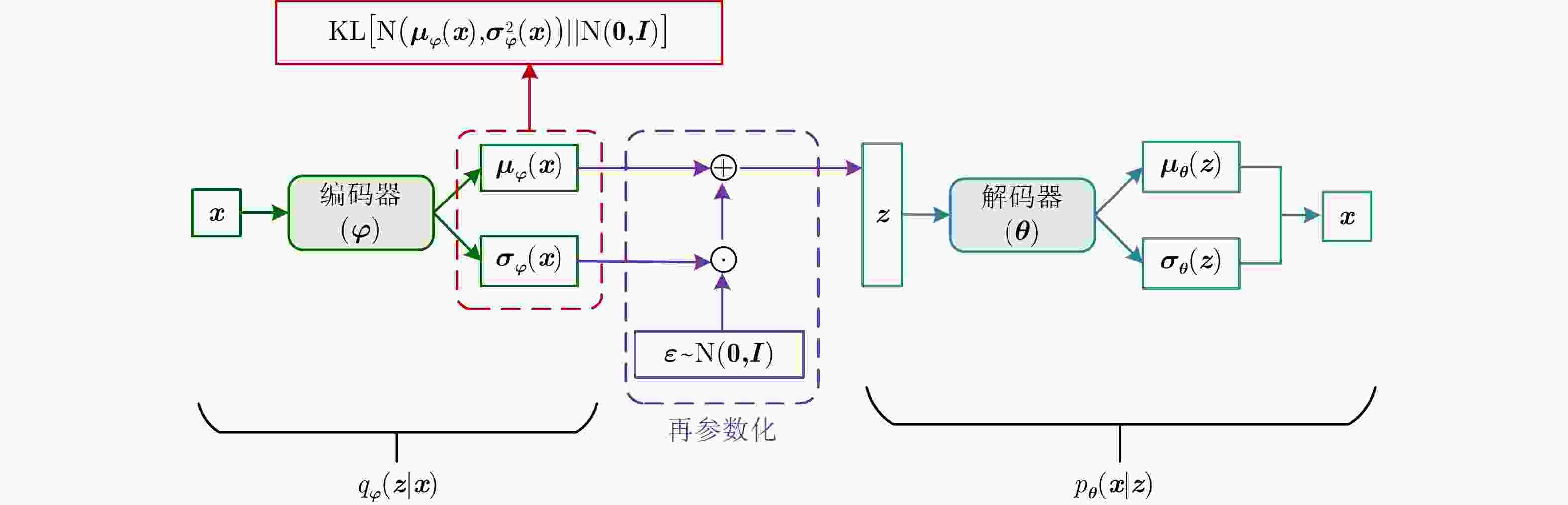
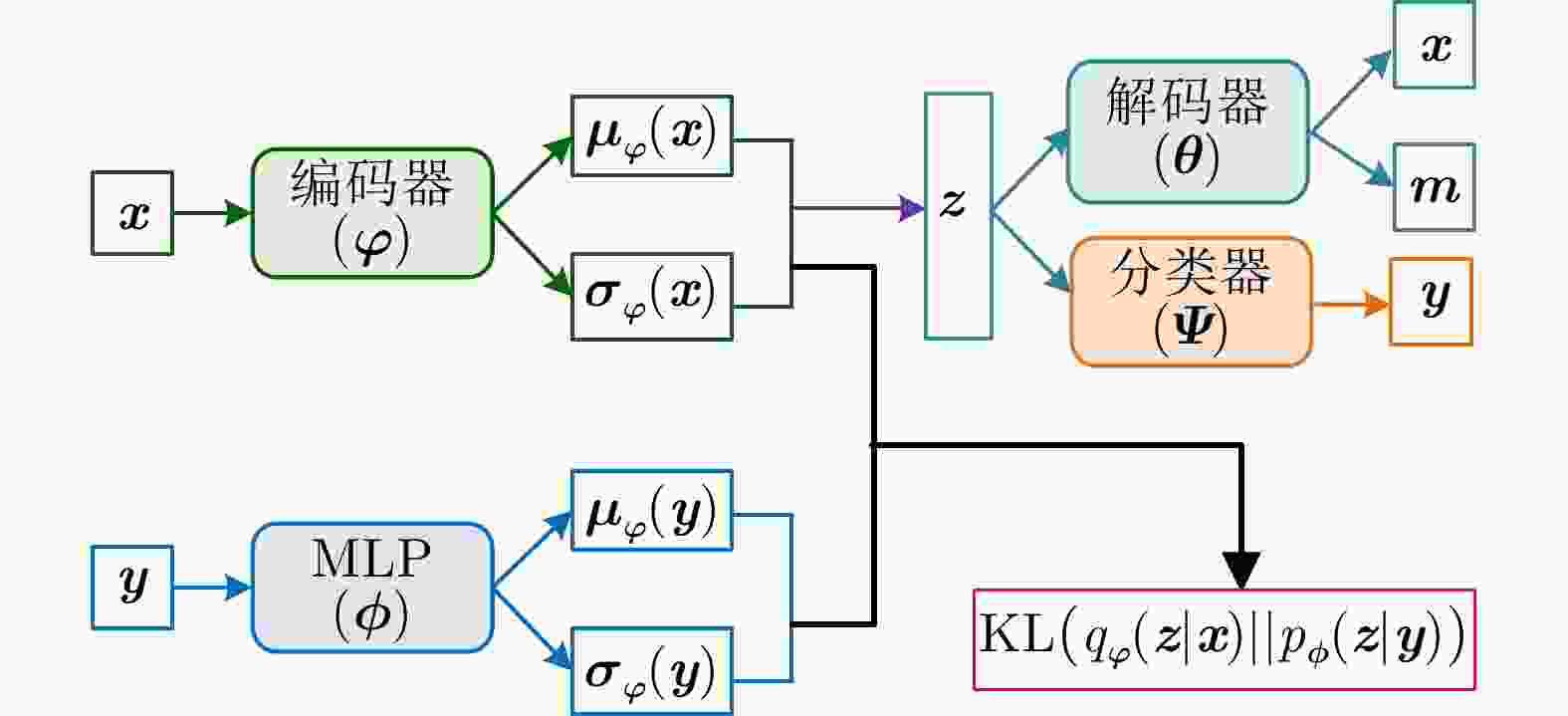
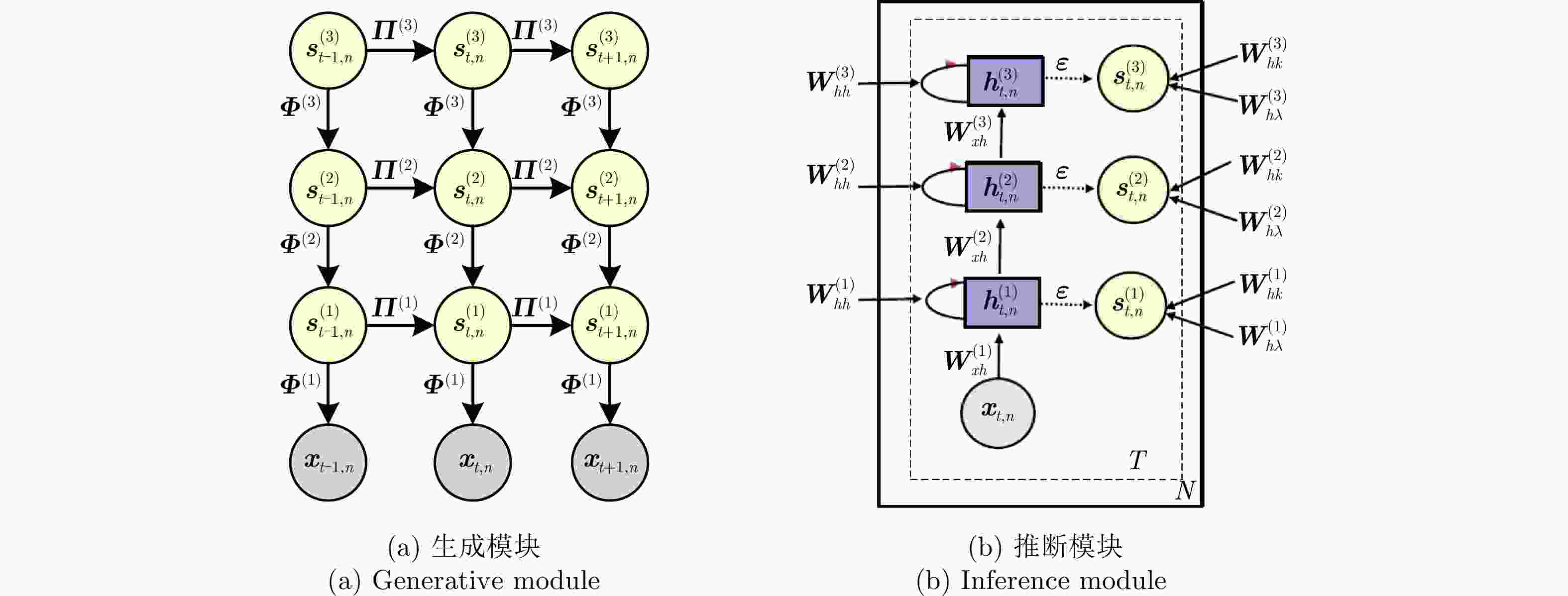
Table 6. Comparison of different VAE models
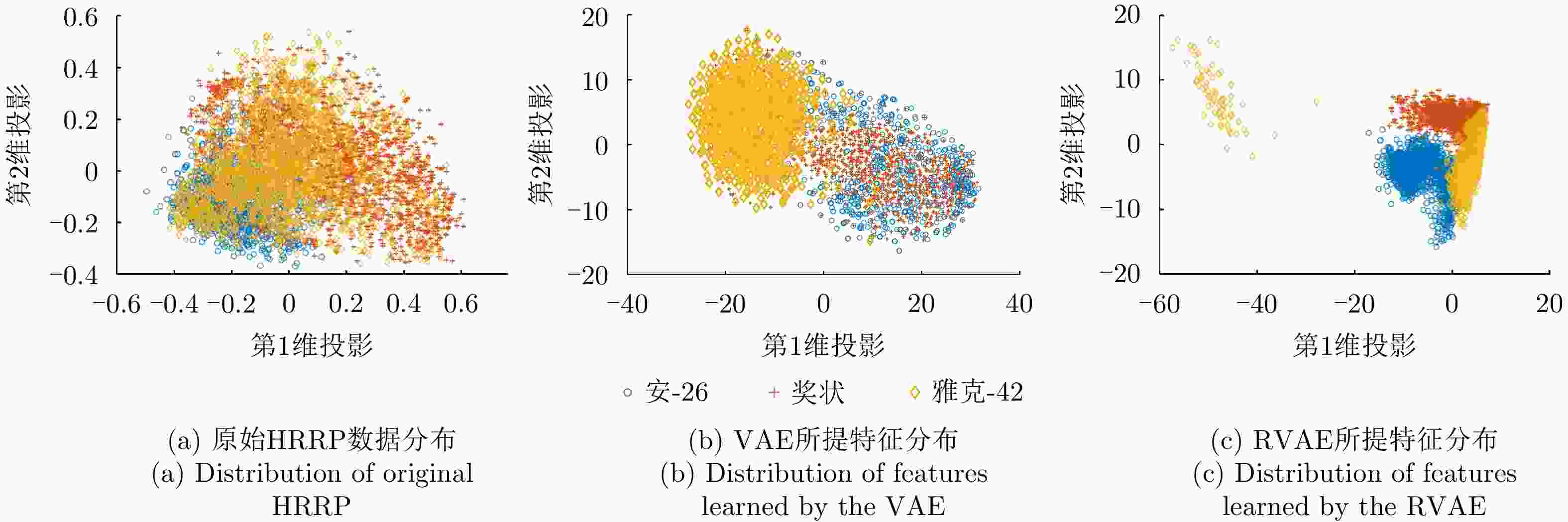
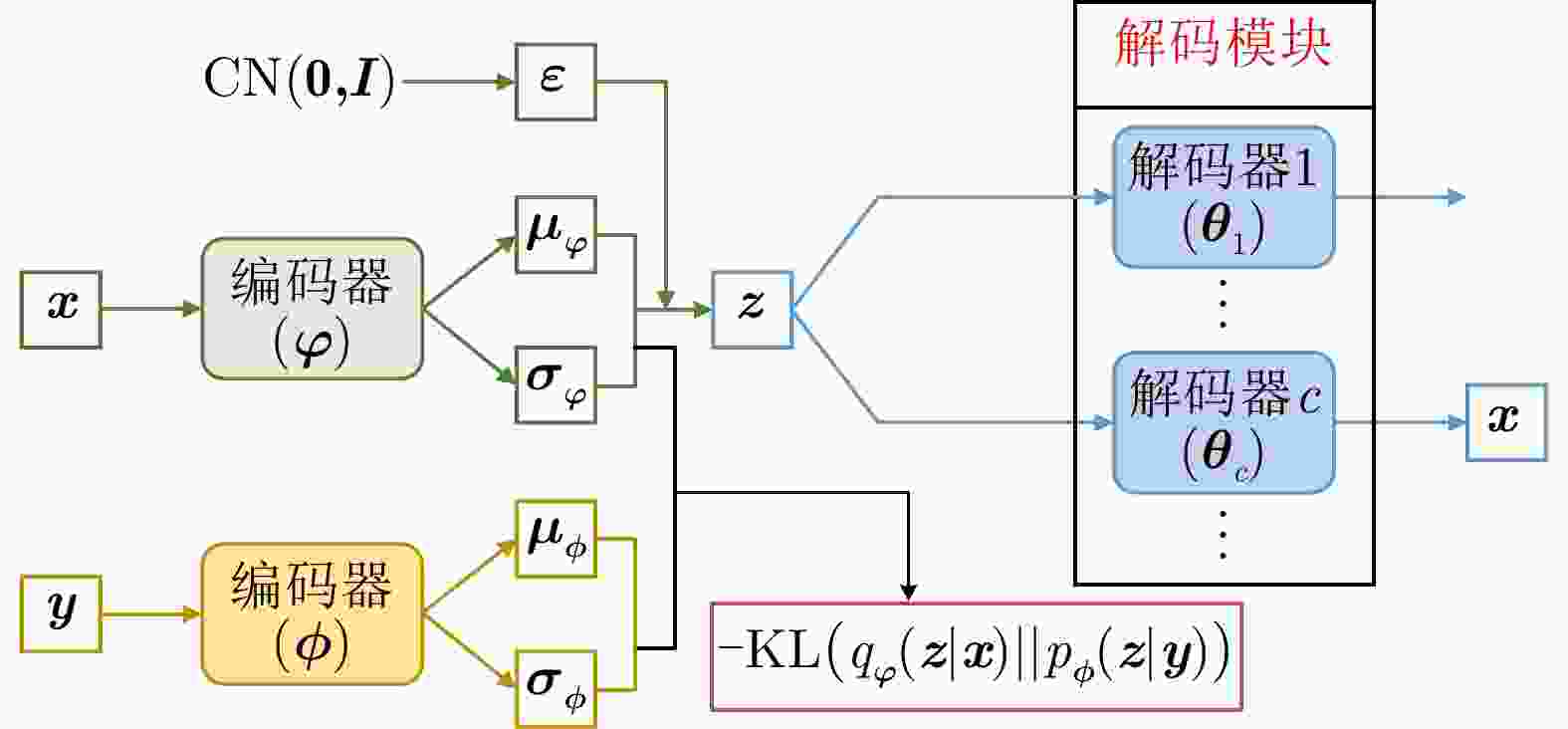
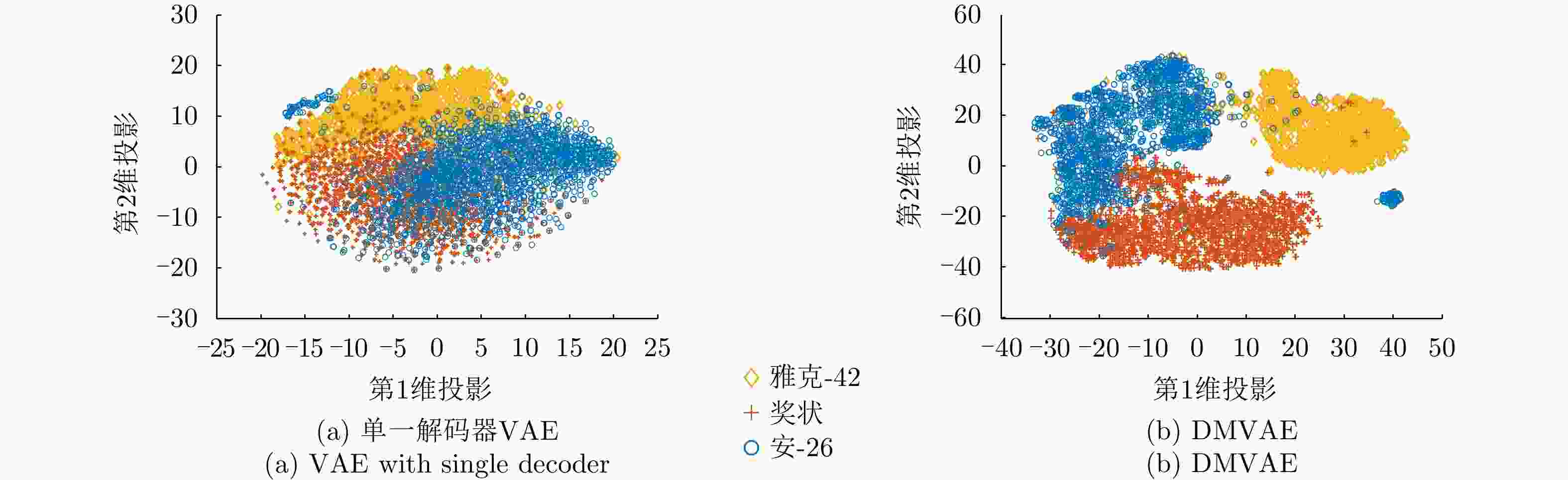
方法 优点 缺点 单解码器VAE 综合统计模型的数据分布描述能力、深度网络的数据分层学习能力以及HRRP回波特性,能够提取较浅层模型表征力更强的内隐特征。 对大规模复杂分布HRRP数据的拟合精度仍有限、特征可分性仍有提升空间。 多解码器集成VAE 综合多个对部分观测数据具有高精度描述能力的子解码网络实现对全部HRRP数据分布的准确表达,具备挖掘类间细微差异信息的能力,有利于难分样本类别的准确判断。 训练计算复杂度高、模型学习效率低、存储需求量大。 表 7 不同模型在3类飞机目标HRRP数据上的识别率比较
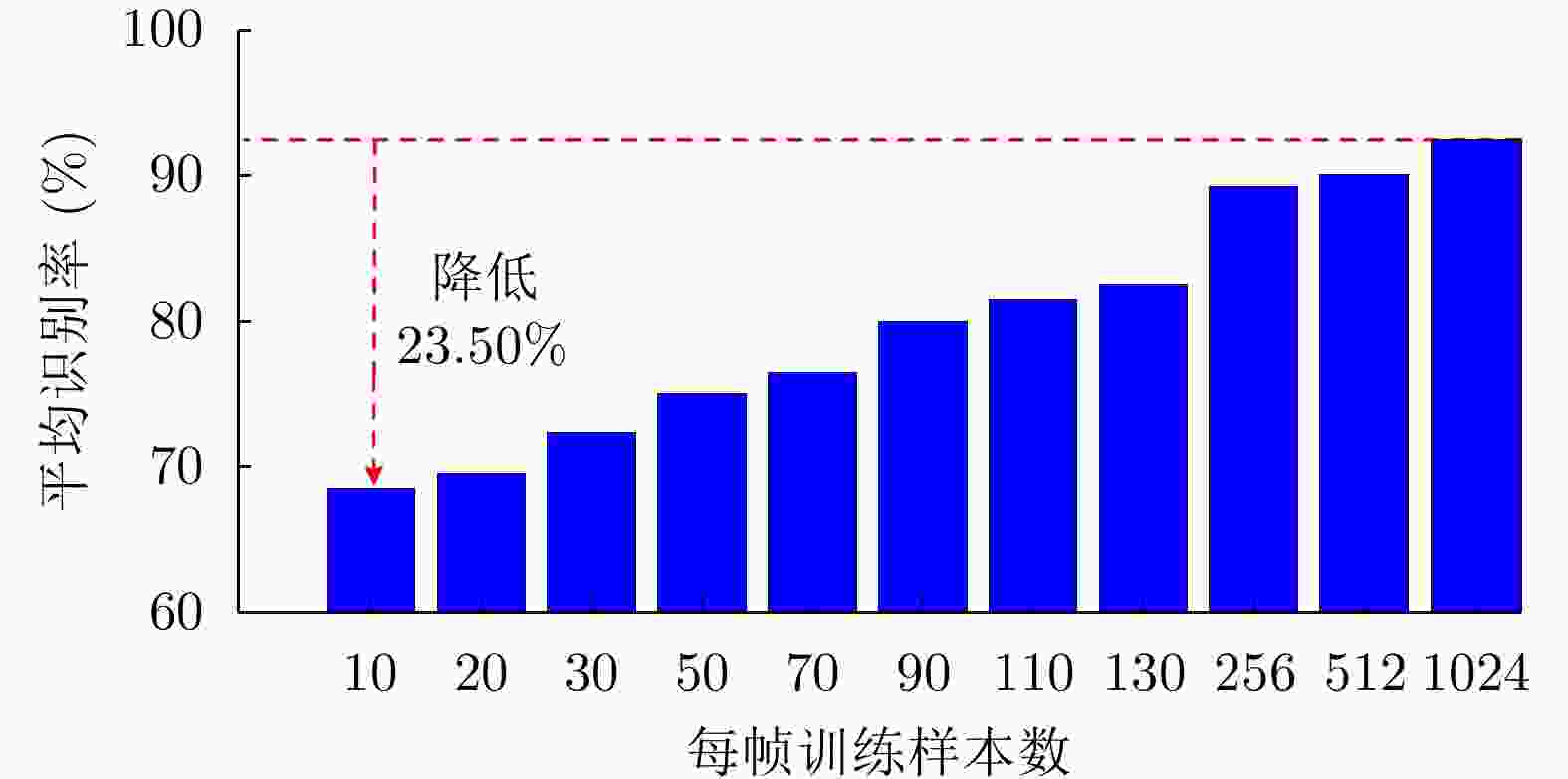
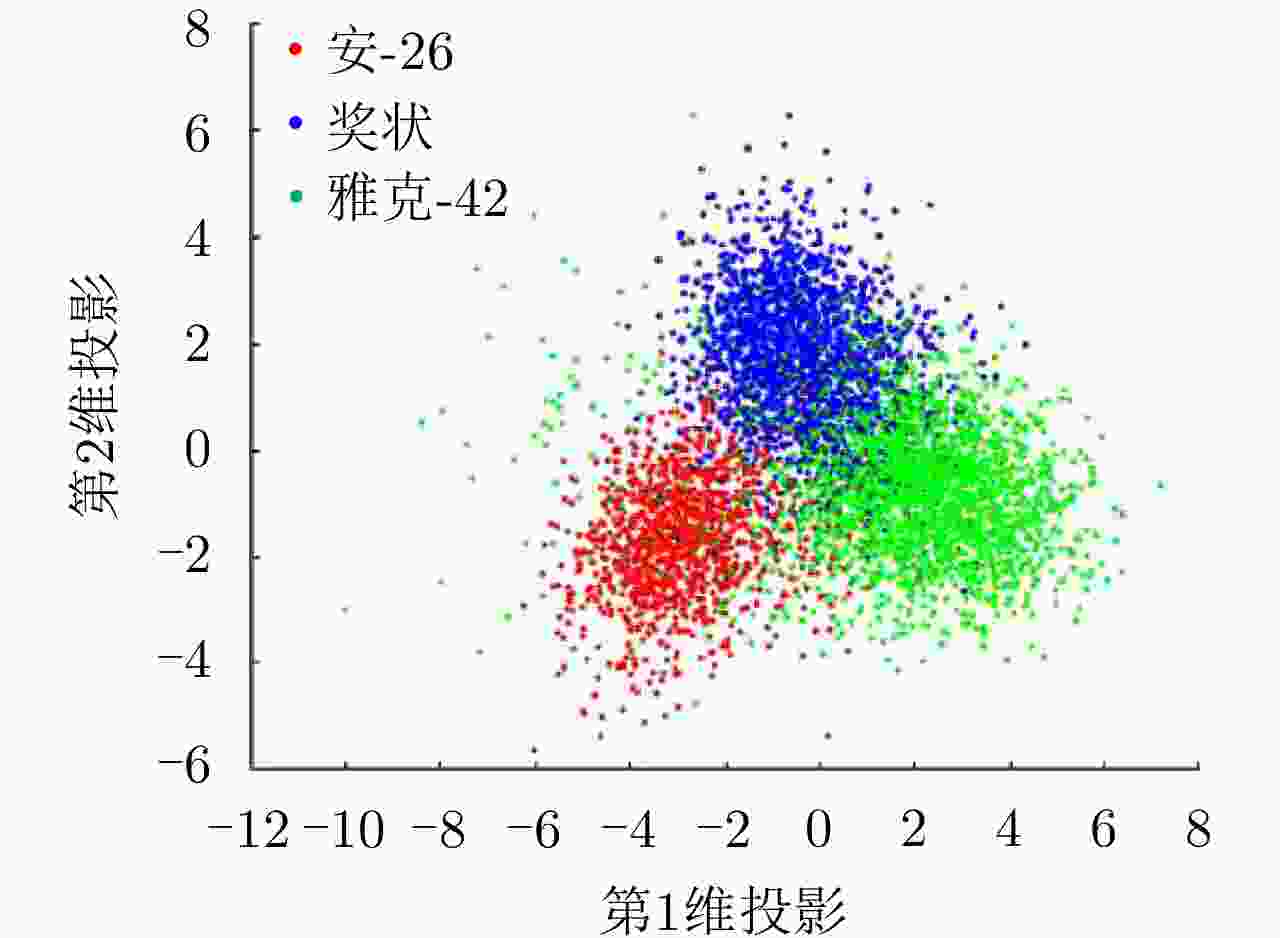
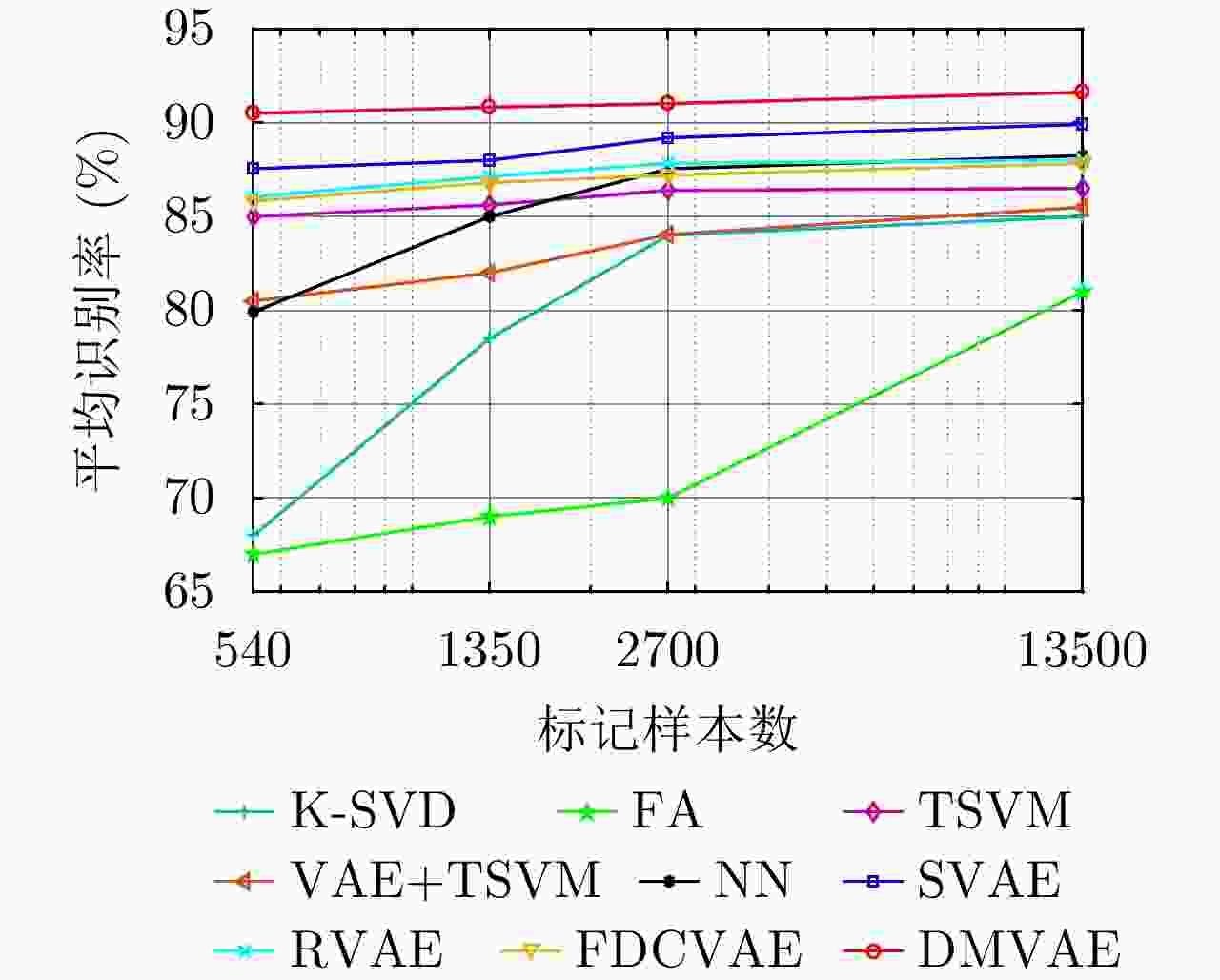
Table 7. Comparison of recognition rates of different models on HRRP data from three airplanes
表 8 不同深层时序模型比较
Table 8. Comparison of different deep temporal models
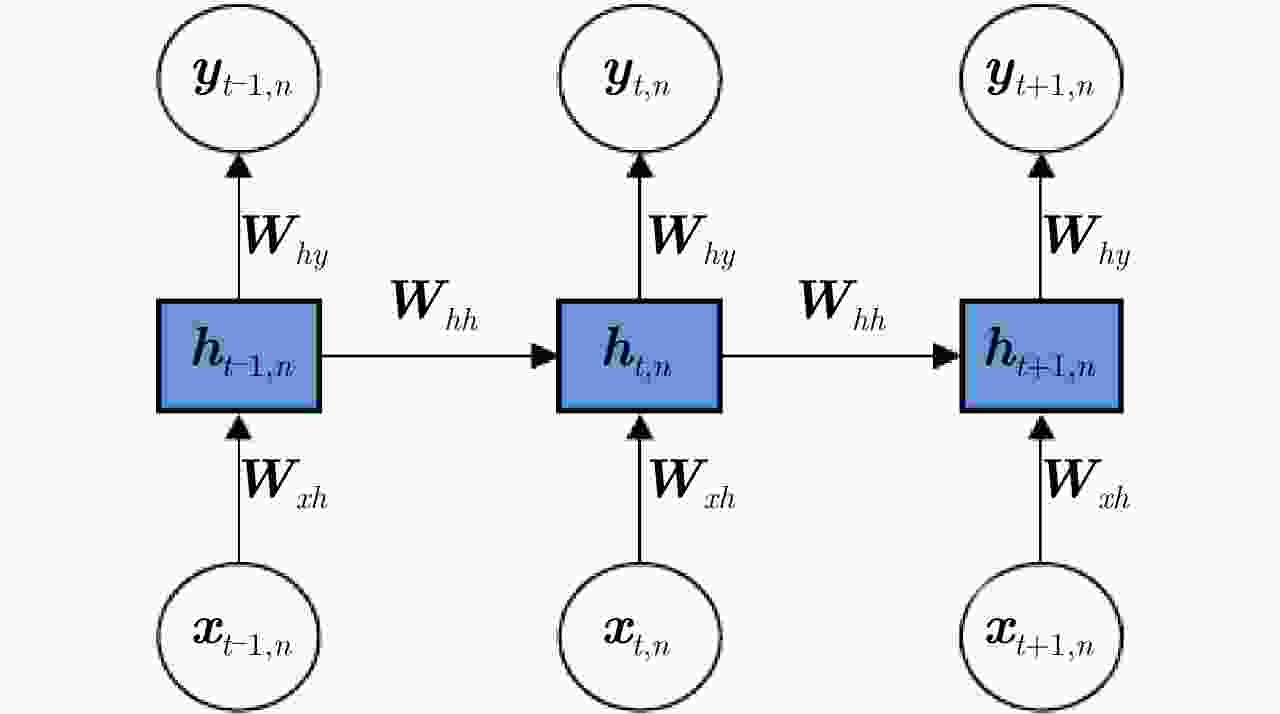
方法 优点 缺点 贝叶斯RNN 结合贝叶斯理论可以实现对HRRP不同局部信号非平稳时序关系的准确建模,数据时序特性挖掘更准确。 仅考虑数据时间维信息的深度挖掘,结构信息的深层次提取能力有限,特征表达能力不全面。 循环伽马置信网络 同时对HRRP时间维时序信息和空间维结构信息进行深度挖掘,特征对数据的表征性更强。 建模复杂、推理困难,需要选择合适的参数先验分布保证参数求解的可行性、灵活性低。 -
[1] SKOLNIK M I. Introduction to Radar Systems[M]. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1980. [2] 向敬成, 张明友. 雷达系统[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2001.XIANG Jingcheng and ZHANG Mingyou. Radar System[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2001. [3] 丁鹭飞, 耿富录. 雷达原理[M]. 3版. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2002.DING Lufei and GENG Fulu. Principle of Radar[M]. 3rd ed. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2002. [4] SKOLNIK M I, 王军, 林强, 米慈中, 等译. 雷达手册[M]. 2版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2003.SKOLNIK M I, WANG Jun, LIN Qiang, MI Cizhong, et al. translation. Radar Handbook[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2003. [5] 刘宏伟, 杜兰, 袁莉, 等. 雷达高分辨距离像目标识别研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2005, 27(8): 1328–1334.LIU Hongwei, DU Lan, YUAN Li, et al. Progress in radar automatic target recognition based on high range resolution profile[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2005, 27(8): 1328–1334. [6] 杜兰. 飞机目标的雷达回波特性研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2004.DU Lan. Research on the characteristics of the radar echoes from aircraft targets[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2004. [7] 单凯晶, 肖怀铁, 朱俊. 基于C-均值聚类的高分辨距离像识别[J]. 现代雷达, 2010, 32(6): 49–53. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2010.06.025SHAN Kaijing, XIAO Huaitie, and ZHU Jun. High resolution range profiles recognition based on C-means clustering[J]. Modern Radar, 2010, 32(6): 49–53. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2010.06.025 [8] 邱祥风, 霍凯, 张新禹, 等. 一种基于雷达高分辨距离像的空天时敏目标识别方法[J]. 航空兵器, 2022, 29(2): 13–18. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2020.0261QIU Xiangfeng, HUO Kai, ZHANG Xinyu, et al. A recognition method of aerospace time-sensitive targets based on radar high resolution range profile[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2022, 29(2): 13–18. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2020.0261 [9] 郭宇. 基于高分辨距离像的支持向量数据描述目标识别算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2018.GUO Yu. Research on support vector data description for HRRP-based target recognition[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2018. [10] 周云. 基于高分辨距离像的雷达目标识别研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2016.ZHOU Yun. Research on radar target recognition based on high resolution range profile[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2016. [11] 王彩云, 孔一荟. 基于稀疏表示字典优化的雷达高分辨距离像目标识别[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 45(6): 837–842. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2013.06.026WANG Caiyun and KONG Yihui. Radar high-resolution range profile target recognition based on sparse representation of dictionary optimized[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics &Astronautics, 2013, 45(6): 837–842. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2013.06.026 [12] 刘华林. 高分辨距离像雷达自动目标识别研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2008.LIU Hualin. Research on radar automatic target recognition using high resolution range profiles[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2008. [13] PILCHER C M and KHOTANZAD A. Maritime ATR using classifier combination and high resolution range profile[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(4): 2558–2573. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.6034651 [14] SLOMKA S, GIBBINS D, GRAY D, et al. Features for high resolution radar range profile based ship classification[C]. The fifth International Symposium on Signal Processing and its Applications, Brisbane, Australia, 1999: 329–332. [15] 杜兰, 刘宏伟, 保铮, 等. 一种利用目标雷达高分辨距离像幅度起伏特性的特征提取新方法[J]. 电子学报, 2005, 33(3): 411–415. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2005.03.007DU Lan, LIU Hongwei, BAO Zheng, et al. A new feature extraction method using the amplitude fluctuation property of target HRRPs for radar automatic target recognition[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2005, 33(3): 411–415. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2005.03.007 [16] KIM K T, SEO D K, and KIM H T. Efficient radar target recognition using the MUSIC algorithm and invariant features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2002, 50(3): 325–337. doi: 10.1109/8.999623 [17] ZHANG Xianda, SHI Yu, and BAO Zheng. A new feature vector using selected bispectra for signal classification with application in radar target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2001, 49(9): 1875–1885. doi: 10.1109/78.942617 [18] 杜兰. 雷达高分辨距离像目标识别方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2007.DU Lan. Study on radar HRRP target recognition[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2007. [19] DU Lan, LIU Hongwei, WANG Penghui, et al. Noise robust radar HRRP target recognition based on multitask factor analysis with small training data size[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(7): 3546–3559. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2191965 [20] DU Lan, LIU Hongwei, BAO Zheng, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition based on higher order spectra[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(7): 2359–2368. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.849161 [21] 朱劼昊, 周建江, 吴杰. 基于半参数化概率密度估计的雷达目标识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(9): 2161–2166. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.0120ZHU Jiehao, ZHOU Jianjiang, and WU Jie. Radar target recognition based on semiparametric density estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(9): 2161–2166. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.0120 [22] 崔姗姗. 基于概率统计模型的雷达目标HRRP识别[D]. [硕士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2012.CUI Shanshan. Radar target recognition based on the statistic model of high resolution range profile[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012. [23] DU Lan, HE Hua, ZHAO Le, et al. Noise robust radar HRRP target recognition based on scatterer matching algorithm[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(6): 1743–1753. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2501850 [24] SIM D G, KWON O K, and PARK R H. Object matching algorithms using robust Hausdorff distance measures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1999, 8(3): 425–429. doi: 10.1109/83.748897 [25] FENG Bo, DU Lan, LIU Hongwei, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition based on K-SVD algorithm[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 642–645. [26] FENG Bo, CHEN Bo, and LIU Hongwei. Radar HRRP target recognition with deep networks[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 379–393. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.08.012 [27] XU Bin, CHEN Bo, WAN Jinwei, et al. Target-aware recurrent attentional network for radar HRRP target recognition[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 155: 268–280. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.09.041 [28] WAN Jinwei, CHEN Bo, XU Bin, et al. Convolutional neural networks for radar HRRP target recognition and rejection[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2019, 2019: 5. doi: 10.1186/s13634-019-0603-y [29] 朱新奎. 空间目标高分辨距离像识别及微动特征提取方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2017.ZHU Xinkui. Research on space target HRRP recognition and micro-motion feature extraction methods[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2017. [30] 翟颖. 基于自编码模型的雷达高分辨距离像目标识别方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.ZHAI Ying. Study of radar high range resolution profiles target recognition based on auto-encoder[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2018. [31] 冯博. 雷达高分辨距离像特征提取与识别方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2015.FENG Bo. Feature extraction and recognition methods for radar high range resolution profiles[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2015. [32] DU Lan, WANG Penghui, ZHANG Lei, et al. Robust statistical recognition and reconstruction scheme based on hierarchical Bayesian learning of HRR radar target signal[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(14): 5860–5873. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.03.029 [33] DILOKTHANAKUL N, MEDIANO P A M, GARNELO M, et al. Deep unsupervised clustering with Gaussian mixture variational autoencoders[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1611.02648, 2016. [34] CHEN Jian, DU Lan, and LIAO Leiyao. Discriminative mixture variational autoencoder for semisupervised classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(5): 3032–3046. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3023019 [35] WEBB A R. Gamma mixture models for target recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2000, 33(12): 2045–2054. doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(99)00195-8 [36] 李斌, 姚康泽, 张银河, 等. 基于HRRP统计模型的目标识别[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2010, 26(3): 48–51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2010.03.014LI Bin, YAO Kangze, ZHANG Yinhe, et al. Target recognition based on the statistical model of high resolution range profile[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2010, 26(3): 48–51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2010.03.014 [37] PAN Mian, DU Lan, WANG Penghui, et al. Noise-robust modification method for Gaussian-based models with application to radar HRRP recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 558–562. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2213234 [38] 赵乃杰, 李辉, 金宝龙. 改进的雷达高分辨距离像统计识别方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2012, 48(21): 118–122. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2012.21.025.ZHAO Naijie, LI Hui, and JIN Baolong. Improved statistical identification method of high resolution range profiles[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2012, 48(21): 118–122. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2012.21.025. [39] DU Lan, LIU Hongwei, and BAO Zheng. Radar HRRP statistical recognition: Parametric model and model selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(5): 1931–1944. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.912283 [40] SHI Lei, WANG Penghui, LIU Hongwei, et al. Radar HRRP statistical recognition with local factor analysis by automatic Bayesian Ying-Yang harmony learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(2): 610–617. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2088391 [41] PAN Mian, DU Lan, WANG Penghui, et al. Multi-task hidden Markov modeling of spectrogram feature from radar high-resolution range profiles[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2012, 2012: 86. doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2012-86 [42] ZHANG Xuefeng, CHEN Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Infinite max-margin factor analysis via data augmentation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 52: 17–32. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.10.020 [43] LI Liling, DU Lan, ZHANG Wei, et al. Enhancing information discriminant analysis: Feature extraction with linear statistical model and information-theoretic criteria[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 60: 554–570. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.06.004 [44] KINGMA D P and WELLING M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes[C]. 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, Canada, 2014. [45] DU Chuan, CHEN Bo, XU Bin, et al. Factorized discriminative conditional variational auto-encoder for radar HRRP target recognition[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 158: 176–189. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.01.006 [46] CHEN Wenchao, CHEN Bo, PENG Xiaojun, et al. Tensor RNN with Bayesian nonparametric mixture for radar HRRP modeling and target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1995–2009. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3065847 [47] GUO Dandan, CHEN Bo, CHEN Wenchao, et al. Variational temporal deep generative model for radar HRRP target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 5795–5809. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3027470 [48] COPSEY K and WEBB A. Bayesian gamma mixture model approach to radar target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic systems, 2003, 39(4): 1201–1217. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1261122 [49] DU Lan, LIU Hongwei, BAO Zheng, et al. A two-distribution compounded statistical model for radar HRRP target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(6): 2226–2238. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.873534 [50] 赵峰, 张军英, 刘敬, 等. 基于Gamma-SLC混合密度估计的雷达目标识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30(3): 438–443. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.03.012ZHAO Feng, ZHANG Junying, LIU Jing, et al. Radar target recognition based on the compounded density estimation of Gamma-SLC[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30(3): 438–443. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.03.012 [51] VAN TREES H L. Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1971. [52] 王鹏辉. 基于统计建模的雷达高分辨距离像目标识别方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2012.WANG Penghui. Study of radar high resolution range profile target recognition based on statistical modeling[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2012. [53] 李晓辉, 黎湘, 郭桂蓉. 基于LDA算法的一维距离像特征提取[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2005, 27(6): 72–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2005.06.016LI Xiaohui, LI Xiang, and GUO Guirong. Feature extraction of HRRP based on LDA algorithm[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2005, 27(6): 72–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2005.06.016 [54] DU Lan, CHEN Jian, HU Jing, et al. Statistical modeling with label constraint for radar target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1026–1044. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2925472 [55] CHEN Jian, DU Lan, HE Hua, et al. Convolutional factor analysis model with application to radar automatic target recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 87: 140–156. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.10.014 [56] CHEN Jian, DU Lan, and GUO Yuchen. Label constrained convolutional factor analysis for classification with limited training samples[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 544: 372–394. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.08.048 [57] CHEN Minhua, SILVA J, PAISLEY J, et al. Compressive sensing on manifolds using a nonparametric mixture of factor analyzers: Algorithm and performance bounds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(12): 6140–6155. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2070796 [58] CHEN Jian, LIAO Leiyao, ZHANG Wei, et al. Mixture factor analysis with distance metric constraint for dimensionality reduction[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 121: 108156. doi: 10.1016/J.PATCOG.2021.108156 [59] 何珺田. 联合生成与判别模型的雷达HRRP目标识别方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.HE Juntian. Research on radar HRRP target recognition based on hybrid generative discriminative models[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2018. [60] PEI Bingnan and BAO Zheng. Multi-aspect radar target recognition method based on scattering centers and HMMs classifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(3): 1067–1074. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1541451 [61] ZHU Feng, ZHANG Xianda, HU Yafeng, et al. Nonstationary hidden Markov models for multiaspect discriminative feature extraction from radar targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(5): 2203–2214. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.892708 [62] 潘勉, 王鹏辉, 杜兰, 等. 基于TSB-HMM模型的雷达高分辨距离像目标识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(7): 1547–1554. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01190PAN Mian, WANG Penghui, DU Lan, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition based on truncated stick-breaking hidden Markov model[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(7): 1547–1554. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01190 [63] LIAO Leiyao, DU Lan, and CHEN Jian. Class factorized complex variational auto-encoder for HRR radar target recognition[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 182: 107932. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107932 [64] 陈健. 基于概率统计模型的雷达高分辨距离像目标识别方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020.CHEN Jian. Study of radar HRRP target recognition based on probability statistical model[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. [65] YUKSEL S E, WILSON J N, and GADER P D. Twenty years of mixture of experts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(8): 1177–1193. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2200299 [66] CHEN Wenchao, CHEN Bo, LIU Yicheng, et al. Bidirectional recurrent gamma belief network for HRRP target recognition[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 188: 108213. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108213 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: