Reduced Degrees of Freedom in Space-Time Adaptive Processing for Space-based Early Warning Radar
-
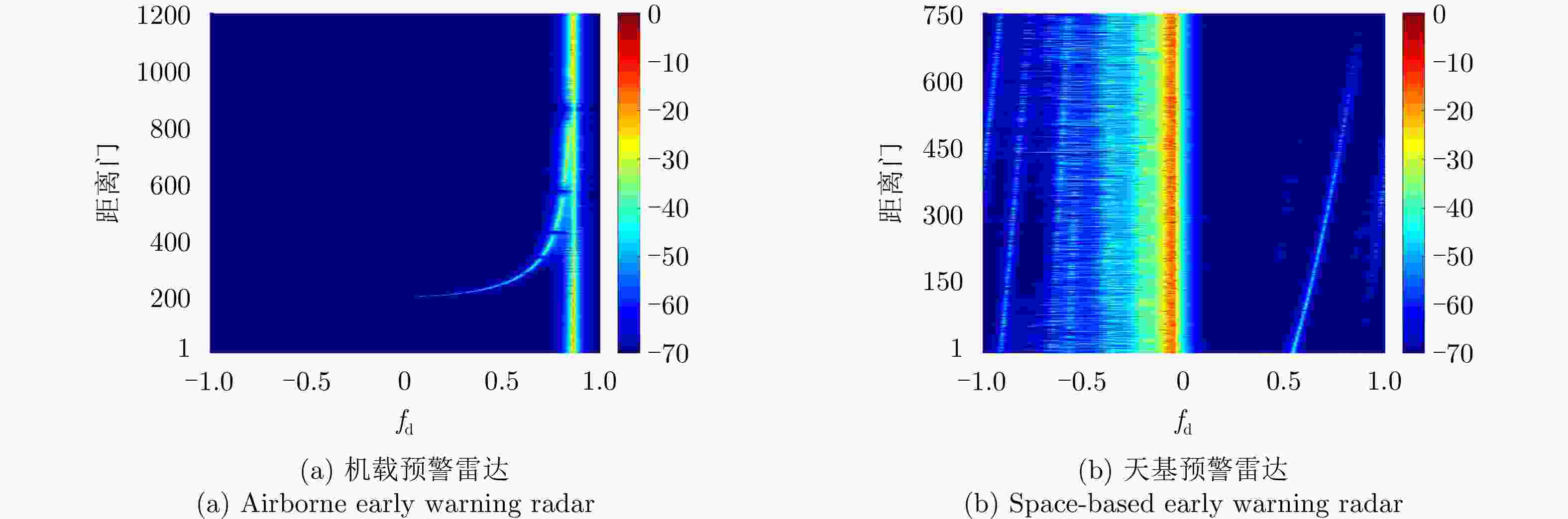
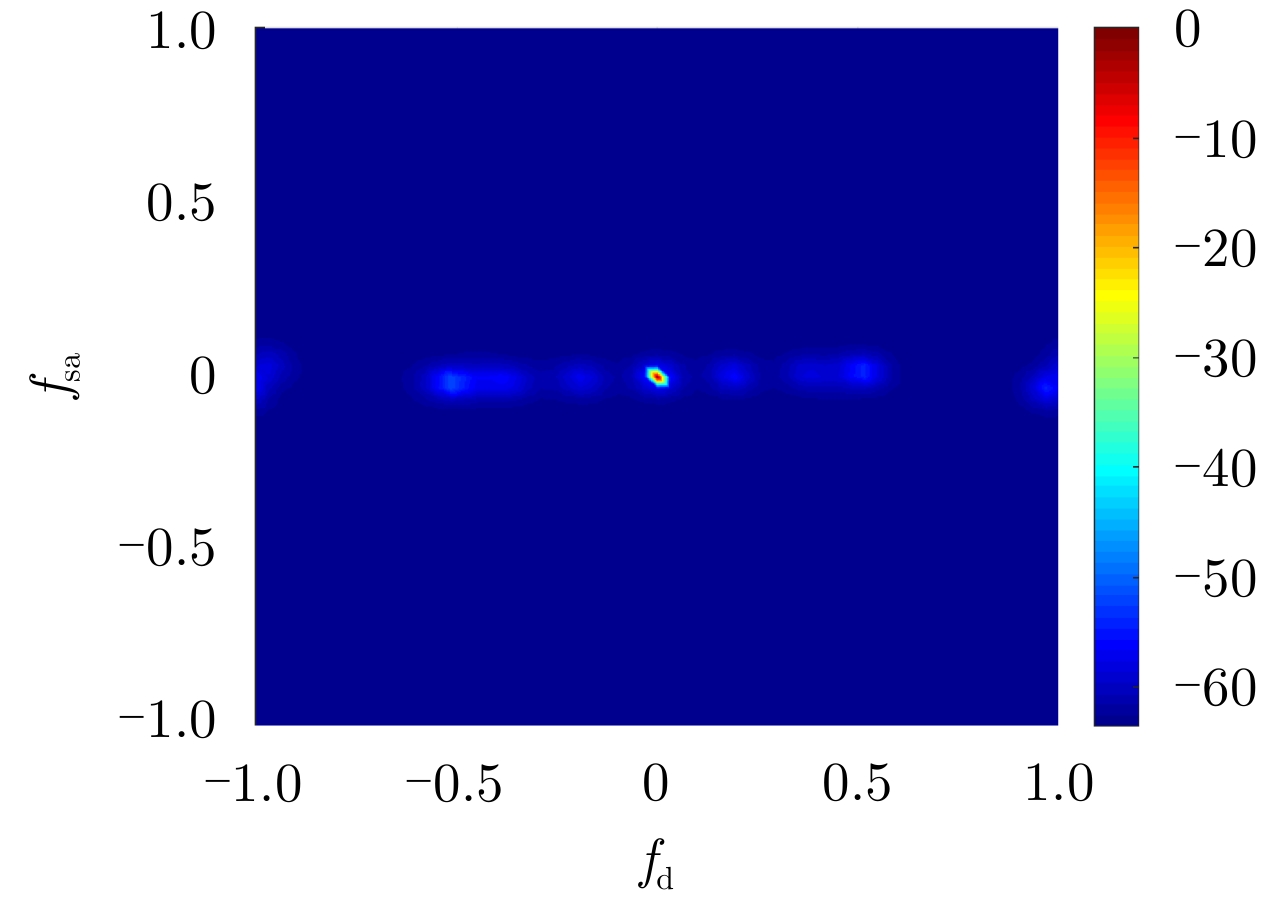
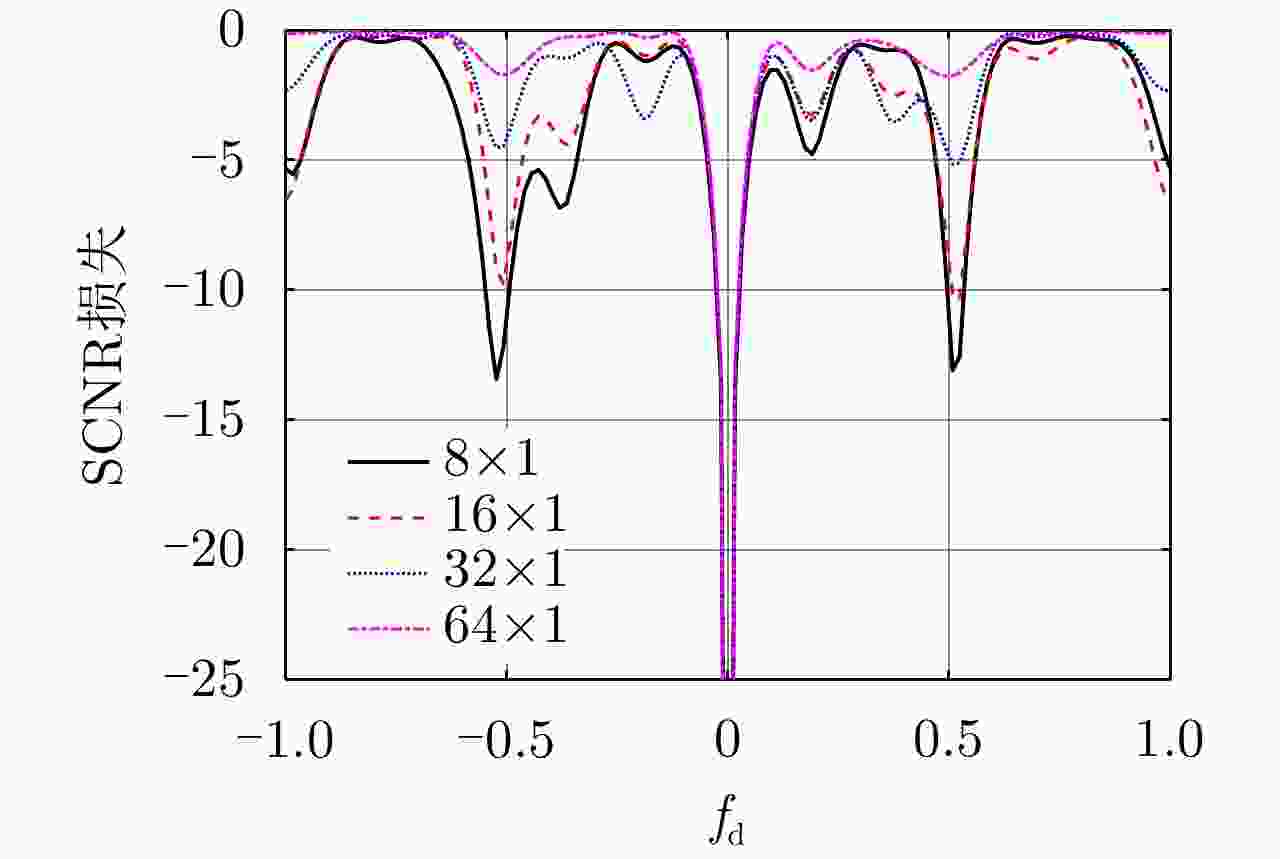
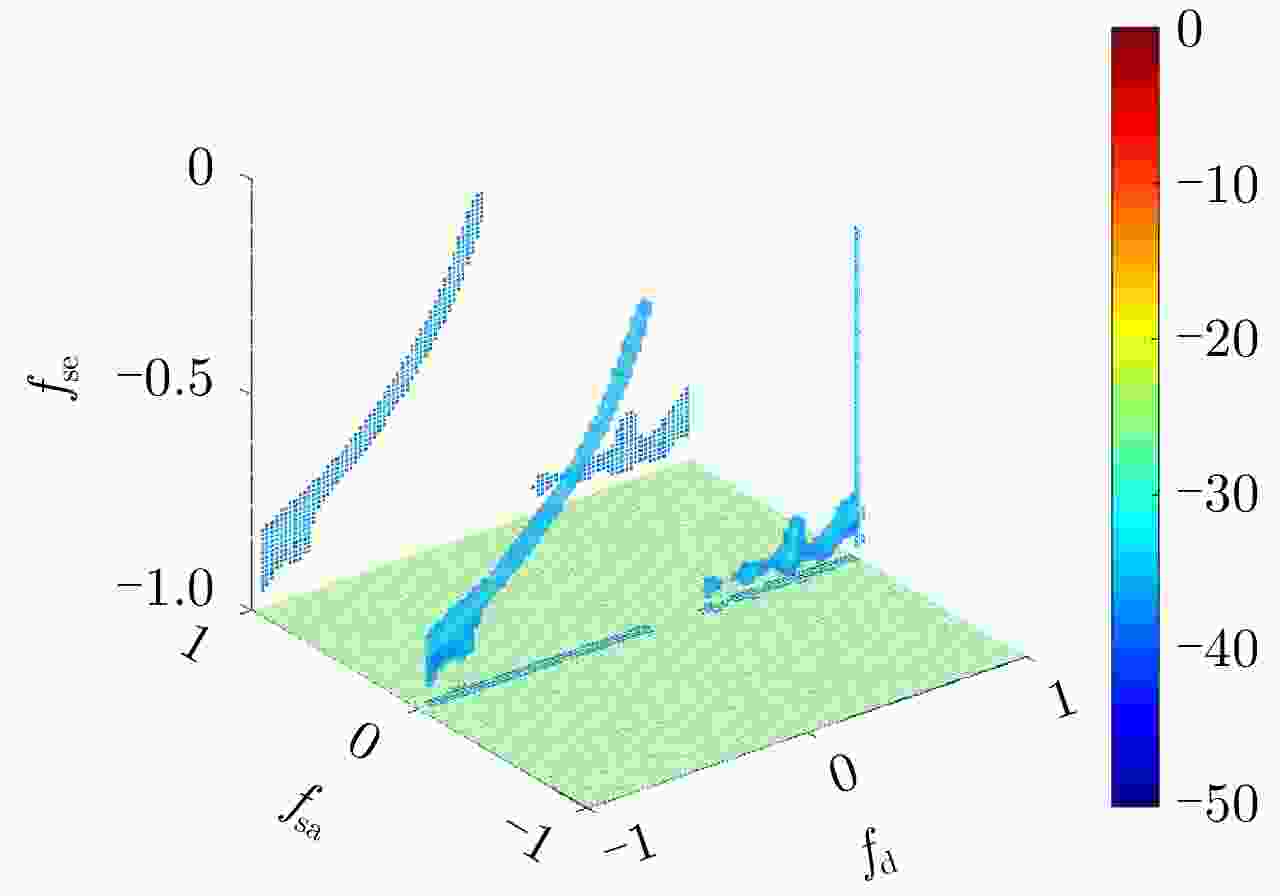
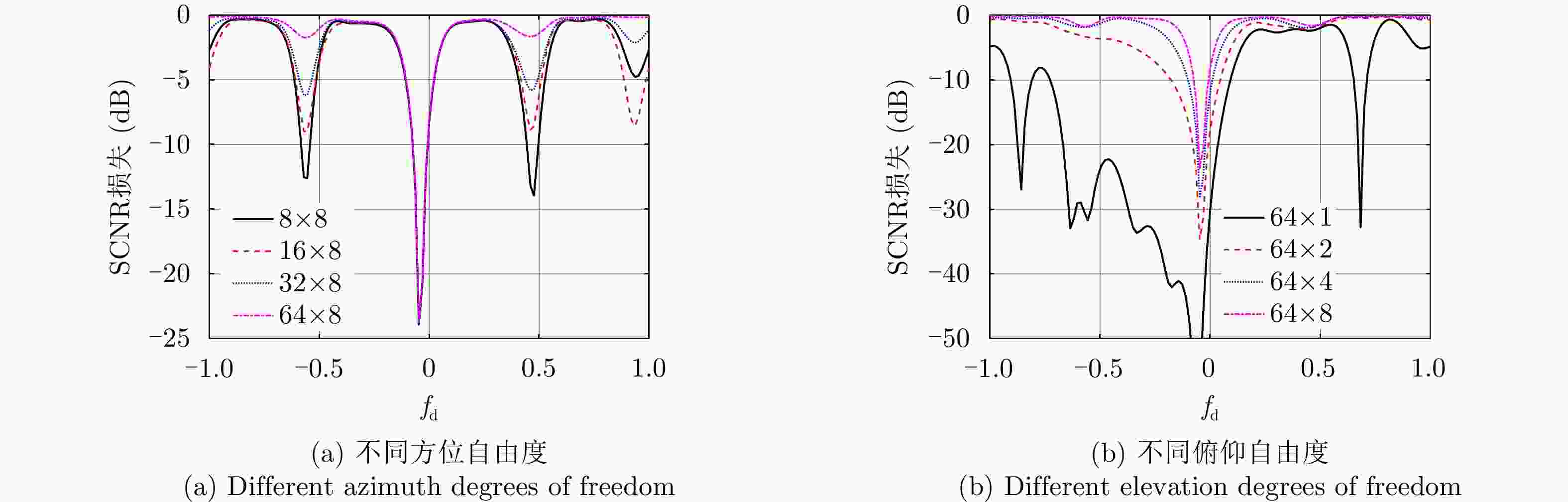
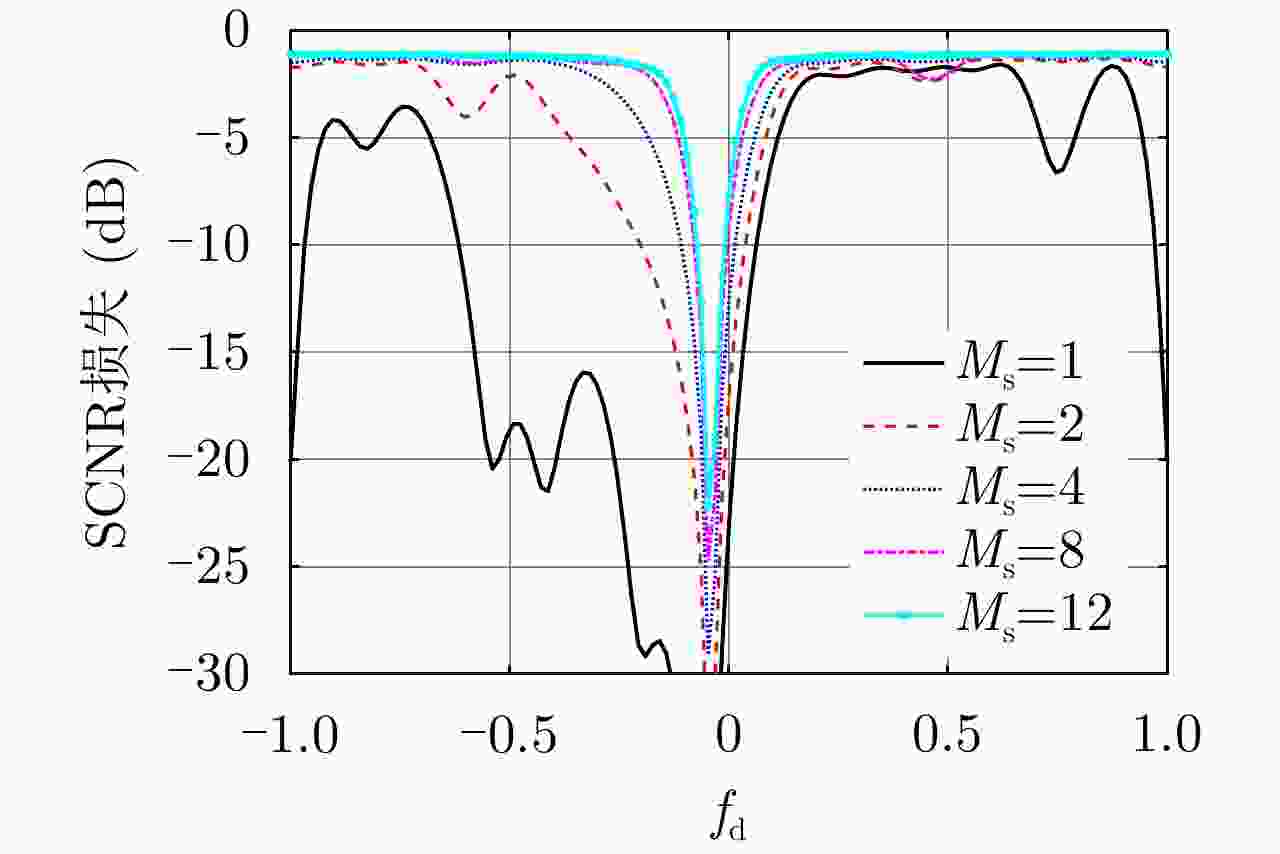
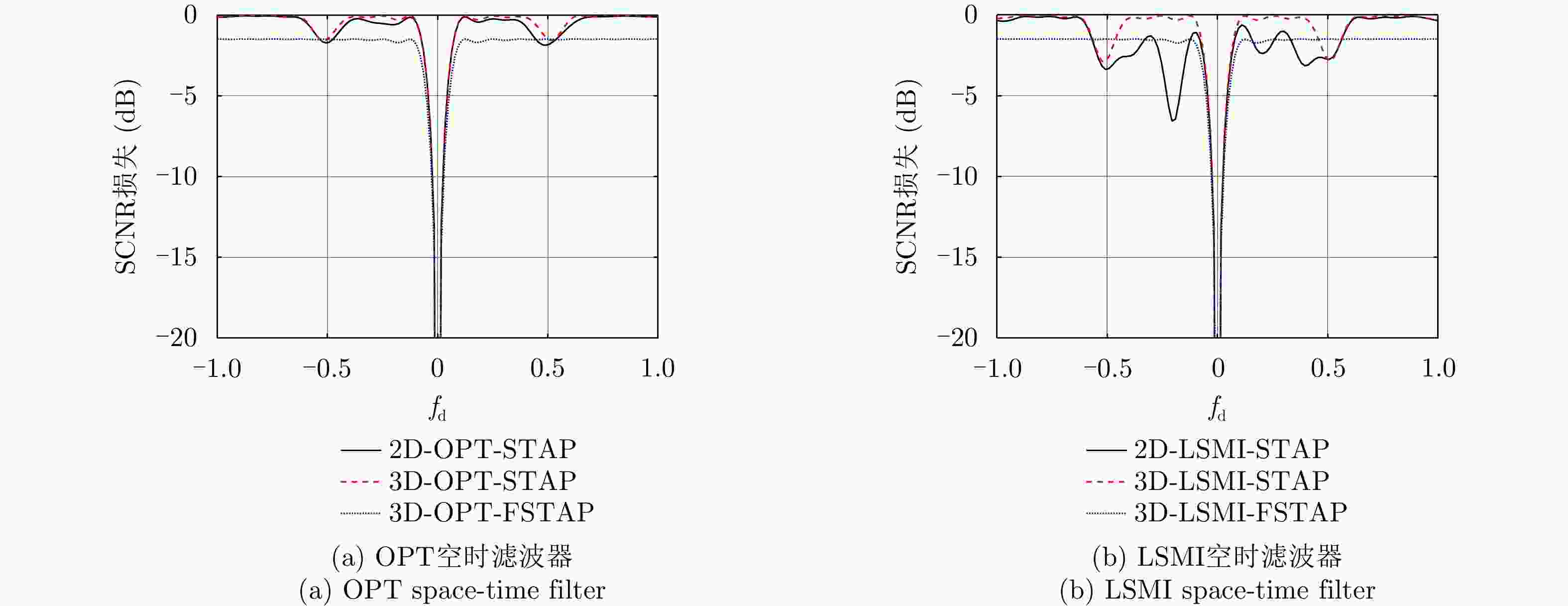
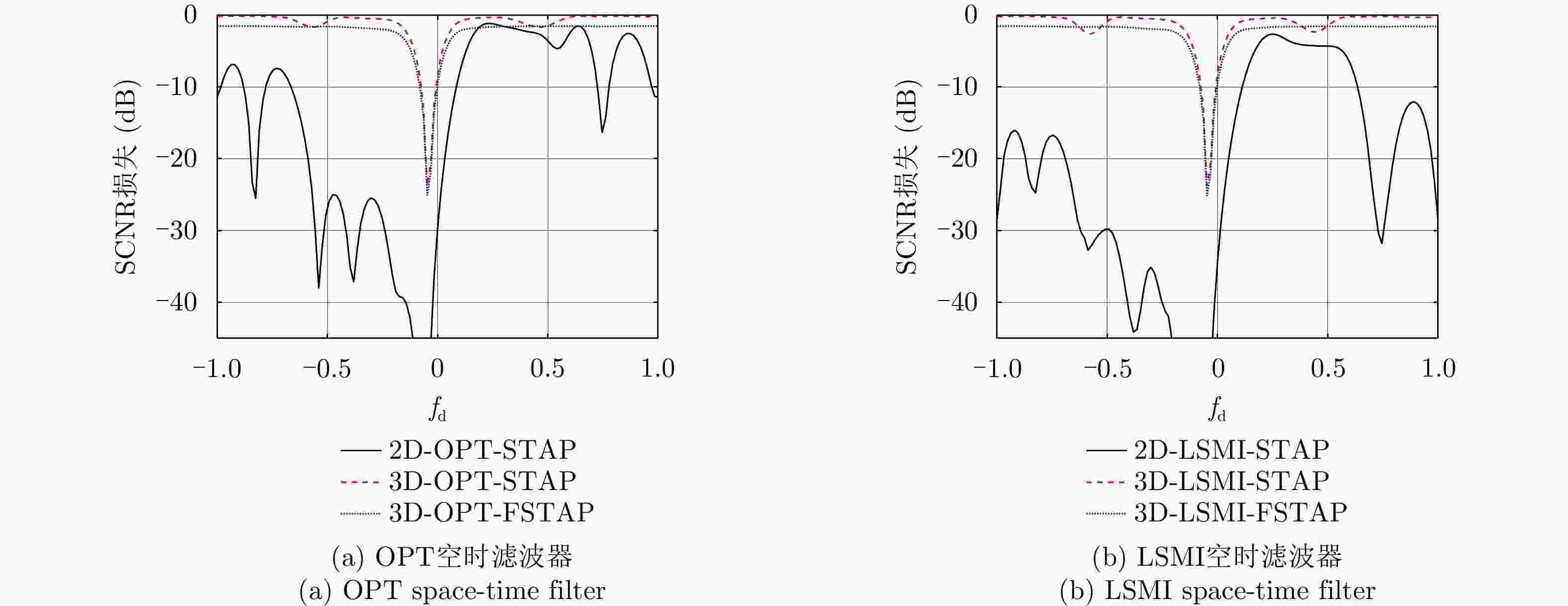
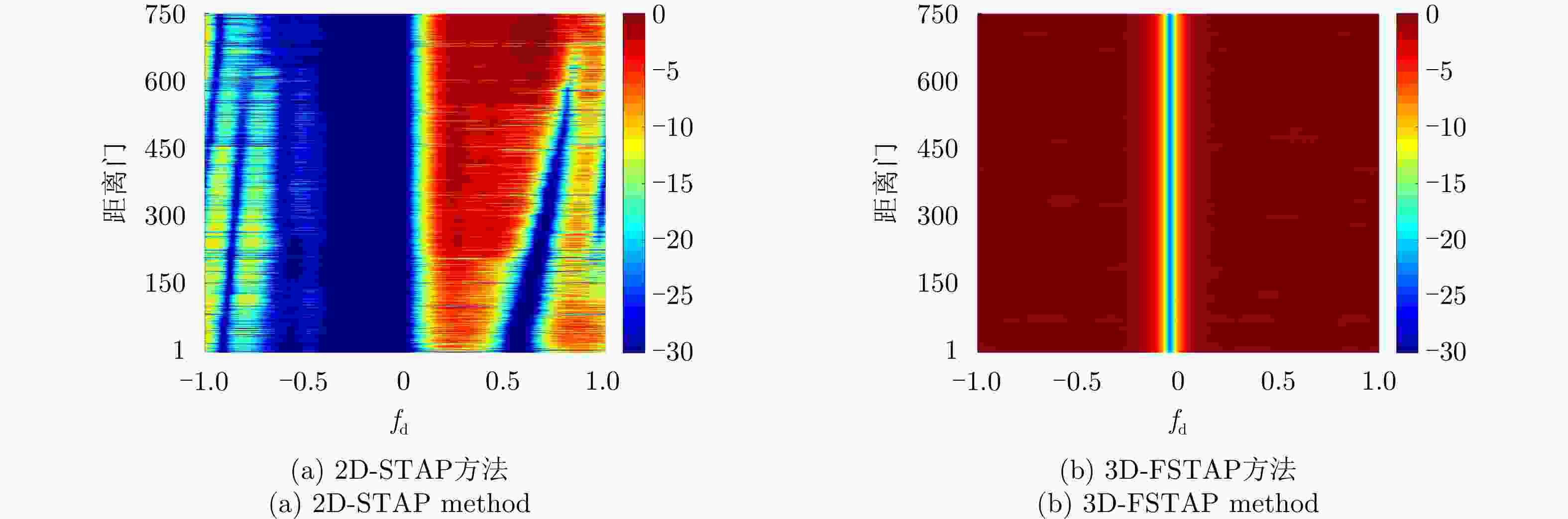
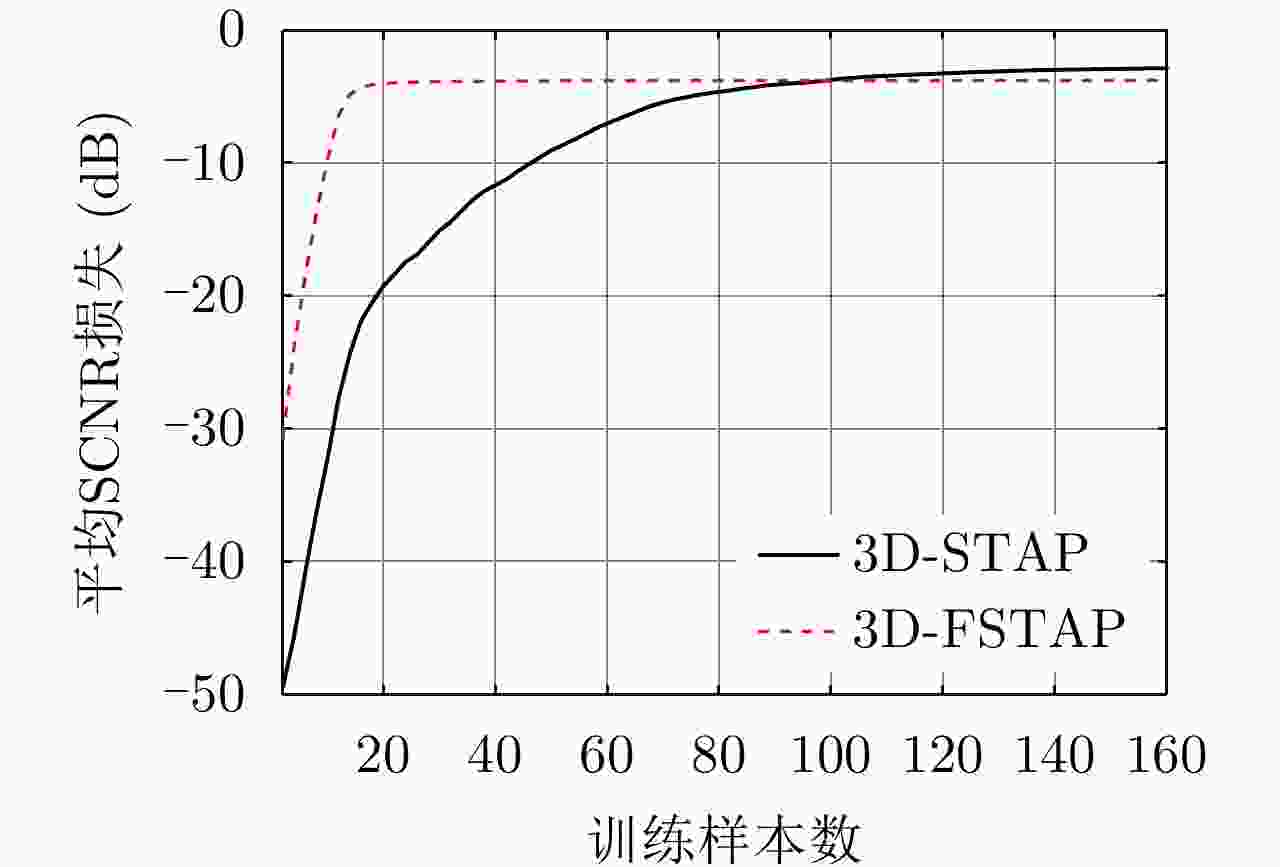
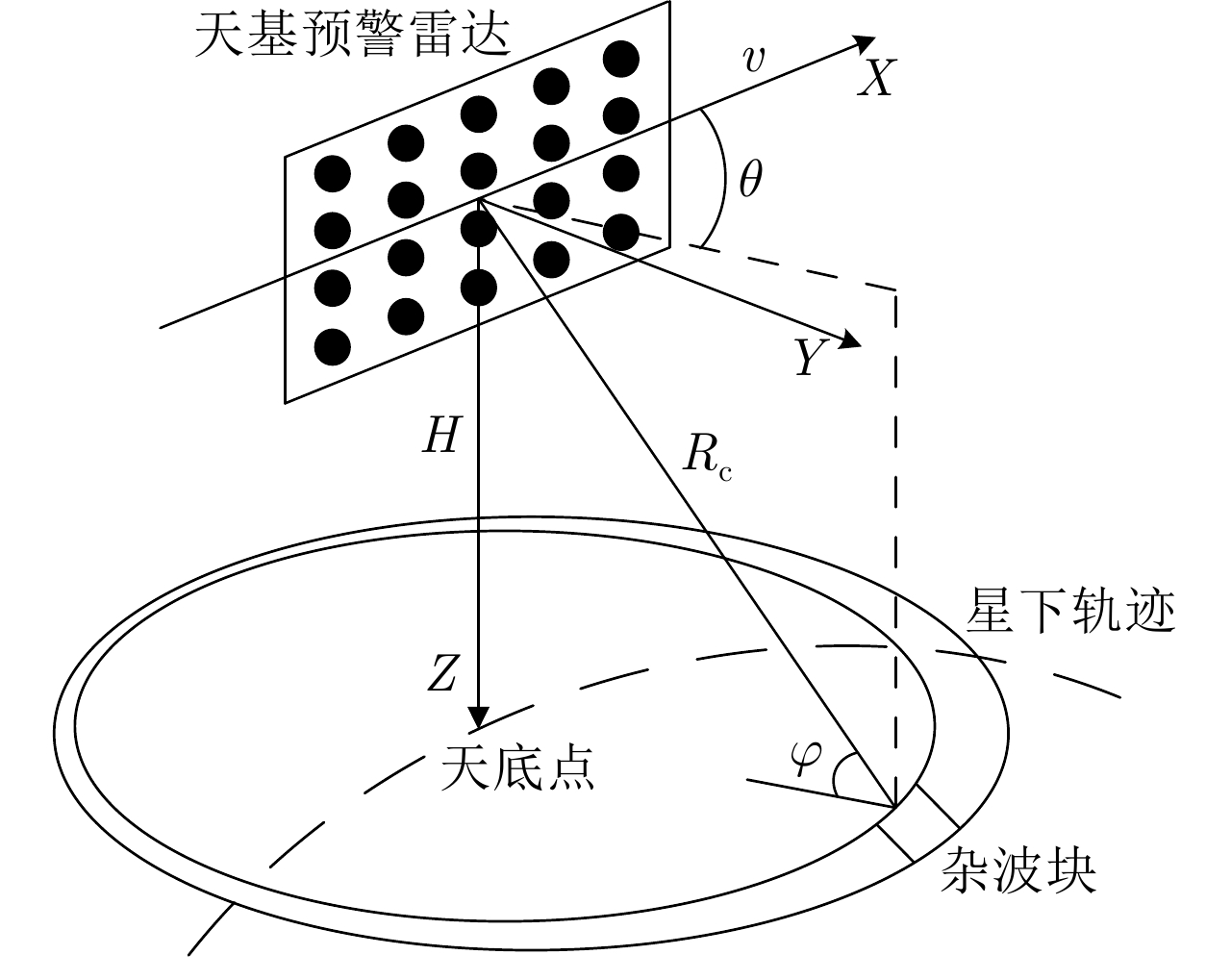
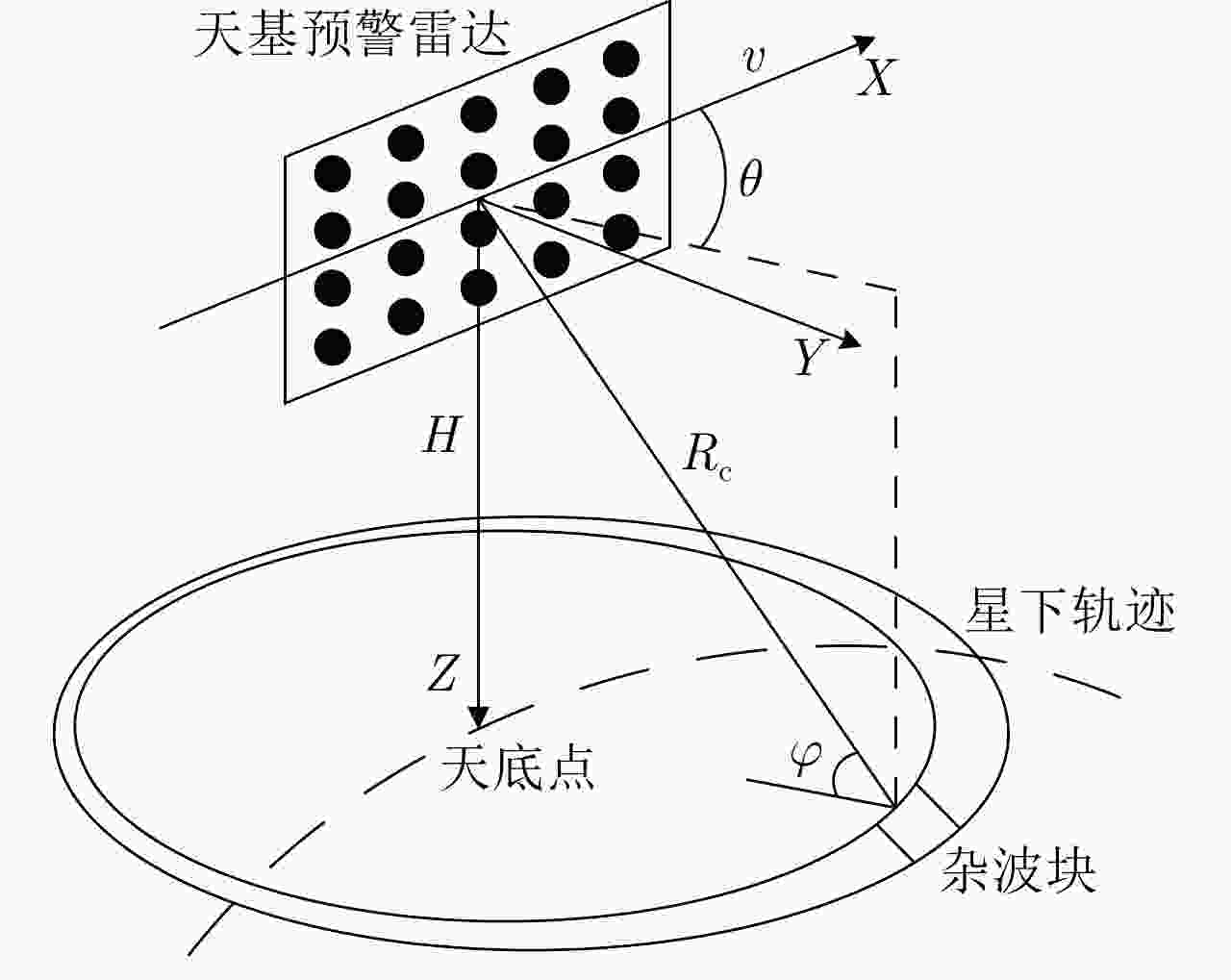
摘要: 受卫星高速运动和地球自转影响,天基预警雷达杂波在俯仰-方位-多普勒三维空间呈紧耦合特性,极大降低了传统空时自适应处理(STAP)方法的慢速运动目标检测性能。采用方位-俯仰-多普勒三维STAP可实现天基预警雷达杂波解耦,但与非正侧机载预警雷达杂波的三维松耦合情况不同,该应用需要较大系统自由度才能实现次最优杂波抑制性能,所带来的巨大运算负担和均匀样本需求使其难以应用于实际。针对上述问题,该文首先构建了天基预警雷达平面阵回波空时信号模型;然后详细分析了其杂波在方位-俯仰-多普勒三维空间的紧耦合特性;最后提出了基于级联处理的低自由度三维STAP方法,利用空域加权子阵合成预先衰减副瓣杂波,再利用俯仰-多普勒自适应处理抑制剩余各次距离模糊主瓣杂波。仿真实验验证了所提STAP方法可在低运算复杂度和小样本需求条件下实现次最优杂波抑制性能,因此适用于天基预警雷达实际应用。Abstract: The clutter of space-based early warning radar exhibits tight coupling in the azimuth-elevation-Doppler domain due to the high speed of satellites and the Earth’s rotation. As a result, conventional Space-Time Adaptive Processing (STAP) suffers significant performance degradation when detecting slow moving targets. The azimuth-elevation-Doppler three-dimensional STAP method provides the ability to decouple clutter and thus can achieve sub-optimal performance for clutter suppression. However, in contrast to the situation in non-sidelooking airborne early warning radar, this method requires large system degrees of freedom when applied to space-based early warning radar. Therefore, in practice, both the computational load and the sample requirement are too large to meet. In this study, the space-time signal model of the planar array for space-based early warning radar is first constructed. Then, the tight coupling characteristic of clutter in the azimuth-elevation-Doppler domain is analyzed in detail. On this basis, a novel three-dimensional STAP method with reduced degrees of freedom with factored structure is proposed. The sidelobe clutter is first suppressed via amplitude taper in azimuth, and the mainlobe clutter responding to each ambiguous range is further canceled by adaptive processing in the elevation-Doppler domain. The simulation results show that the proposed method can achieve sub-optimal performance under low computational load and limited sample conditions. Therefore, the proposed method is suitable for practical application in space-based early warning radar.
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters of simulation
天基参数 数值 机载参数 数值 卫星轨道 506 km 载机高度 10000 m 等效偏航角 0°/3.77° 阵列斜侧角 60° 卫星速度 7610 m/s 载机速度 150 m/s 天线孔径 50 m×2 m 天线孔径 10 m×2 m 列向阵元间距 0.543λ 列向阵元间距 0.5λ 行向阵元间距 0.74λ 行向阵元间距 0.5λ 阵元数 384×12 阵元数 76×12 工作频率 1250 MHz 工作频率 1250 MHz 带宽 3 MHz 带宽 3 MHz 主波束方位角 90° 主波束方位角 90° 主波束俯仰角 –20° 主波束俯仰角 –3° 脉冲重复频率 4000 Hz 脉冲重复频率 2500 Hz 相参脉冲数 16 相参脉冲数 16 表 2 MDV性能
Table 2. Performance of MDV
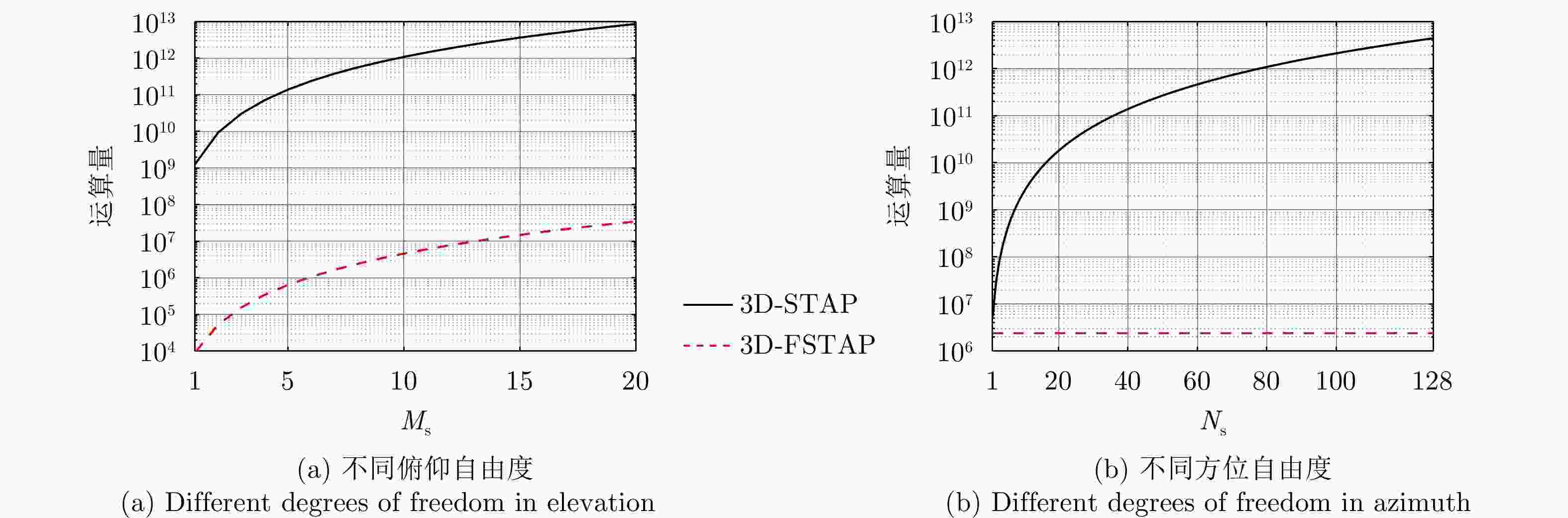
方法 偏航角0° (m/s) 偏航角3.77° (m/s) 2D-OPT-STAP 11.42 142.86 2D-LMSI-STAP 11.42 192.35 3D-OPT-STAP 11.42 15.24 3D-LSMI-STAP 11.42 15.24 3D-OPT-FSTAP 13.33 19.04 3D-LSMI-FSTAP 13.33 19.04 表 3 运算复杂度比较
Table 3. Comparison of computational complexity
方法 CCM估计 空时权系数计算 3D-STAP ${O}\left[{L}_{1}{\left({M}_{\mathrm{s} }N_{\rm{s} } K\right)}^{2}\right]$ ${O}\left[{\left({M}_{\mathrm{s} }{N}_{\mathrm{s} }K\right)}^{3}\right]$ 3D-FSTAP ${O}\left[{L}_{2}{\left({M}_{\mathrm{s} }K\right)}^{2}\right]$ ${O}\left[{\left({M}_{\mathrm{s} }K\right)}^{3}\right]$ -
[1] DAVIS M E. Technology challenges in affordable space based radar[C]. Record of the IEEE 2000 International Radar Conference, Alexandria, USA, 2000: 18–23. [2] PILLAI S U, LI Keyong, and HIMED B. Space Based Radar: Theory & Applications[M]. McGraw Hill, 2008. [3] 林幼权, 武楠. 天基预警雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 1–2.LIN Youquan and WU Nan. Space Based Early Warning Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 1–2. [4] HOVANESSIAN S A, JOCIC L B, and LOPEZ J M. Spaceborne radar design equations and concepts[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Snowmass, USA, 1997: 125–136. [5] DAVIS M E. L-band SBR moving target detection in SAR-GMTI modes[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2004: 2211–2219. [6] CROCI R, DELFINO A, and MARCHETTI F. Space based radar technology evolution[C]. The 6th European Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2009: 601–604. [7] LANE S A, MURPHEY T W, and ZATMAN M. Overview of the innovative space-based radar antenna technology program[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2011, 48(1): 135–145. doi: 10.2514/1.50252 [8] 李青, 林幼权, 武楠. 美国天基预警雷达发展历程及现状分析[J]. 现代雷达, 2018, 40(1): 7–10. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2018.01.002LI Qing, LIN Youquan, and WU Nan. Analysis of development history and status for American space-base early warning radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2018, 40(1): 7–10. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2018.01.002 [9] BRENNAN L E and REED I S. Theory of adaptive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1973, AES-9(2): 237–252. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1973.309792 [10] MELVIN W L. A STAP overview[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2004, 19(1): 19–35. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2004.1263229 [11] SCHUMAN H K, LI P G, SZCZEPANSKI W, et al. Space-time adaptive processing for space based radar[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2004: 1904–1910. [12] ZULCH P, DAVIS M, ADZIMA L, et al. The earth rotation effect on a LEO L-Band GMTI SBR and mitigation strategies[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2004: 27–32. [13] PILLAI S U, HIMED B, and LI Keyong. Effect of earth’s rotation and range foldover on space-based radar performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(3): 917–932. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.248188 [14] 雷志勇, 于永, 郑志彬. 地球自转对天基雷达杂波特性影响分析[J]. 现代雷达, 2017, 39(7): 21–24. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.07.005LEI Zhiyong, YU Yong, and ZHENG Zhibin. Analysis of earth rotation effect for clutter characteristic of space-based radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2017, 39(7): 21–24. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.07.005 [15] KOGON S M, RABIDEAU D J, and BARNES R M. Clutter mitigation techniques for space-based radar[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Phoenix, USA, 1999: 2323–2326. [16] LI Keyong, MANGIAT S, ZULCH P, et al. Clutter impacts on space based radar GMTI: A global perspective[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2007: 1–15. [17] ZULCH P A, HANCOCK R H, MORAN W, et al. Transmit waveform diversity for space based radar[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2006: 10–16. [18] LAPIERRE F D, VERLY J G, and VAN DROOGENBROECK M. New solutions to the problem of range dependence in bistatic STAP radars[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Huntsville, USA, 2003: 452–459. [19] 郁文贤, 张增辉, 胡卫东. 基于频率非均匀采样杂波谱配准的天基雷达STAP方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(2): 358–362. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01244YU Wenxian, ZHANG Zenghui, and HU Weidong. STAP method for space based radar based on spectrum registration with non-uniformed frequency samples[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(2): 358–362. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01244 [20] HALE T B, TEMPLE M A, and WICKS M C. Clutter suppression using elevation interferometry fused with space-time adaptive processing[J]. Electronics Letters, 2001, 37(12): 793–794. doi: 10.1049/el:20010494 [21] CORBELL P M and HALE T B. 3-dimensional STAP performance analysis using the cross-spectral metric[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2004: 610–615. [22] DUAN Keqing, XU Hong, YUAN Huadong, et al. Reduced-DOF three-dimensional STAP via subarray synthesis for nonsidelooking planar array airborne radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(4): 3311–3325. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2958174 [23] 段克清, 李想, 行坤, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的天基预警雷达杂波抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 386–398. doi: 10.12000/JR21161DUAN Keqing, LI Xiang, XING Kun, et al. Clutter mitigation in space-based early warning radar using a convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 386–398. doi: 10.12000/JR21161 [24] MELVIN W L and SHOWMAN G A. An approach to knowledge-aided covariance estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(3): 1021–1042. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.248216 [25] ROSEN P A and DAVIS M E. A joint space-borne radar technology demonstration mission for NASA and the air force[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2003: 437–444. [26] CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278 [27] FERTIG L B. Analytical expressions for space-time adaptive processing (STAP) performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(1): 42–53. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130676 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: