Progress and Perspective on Physically Explainable Deep Learning for Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Interpretation(in English)
-
摘要:
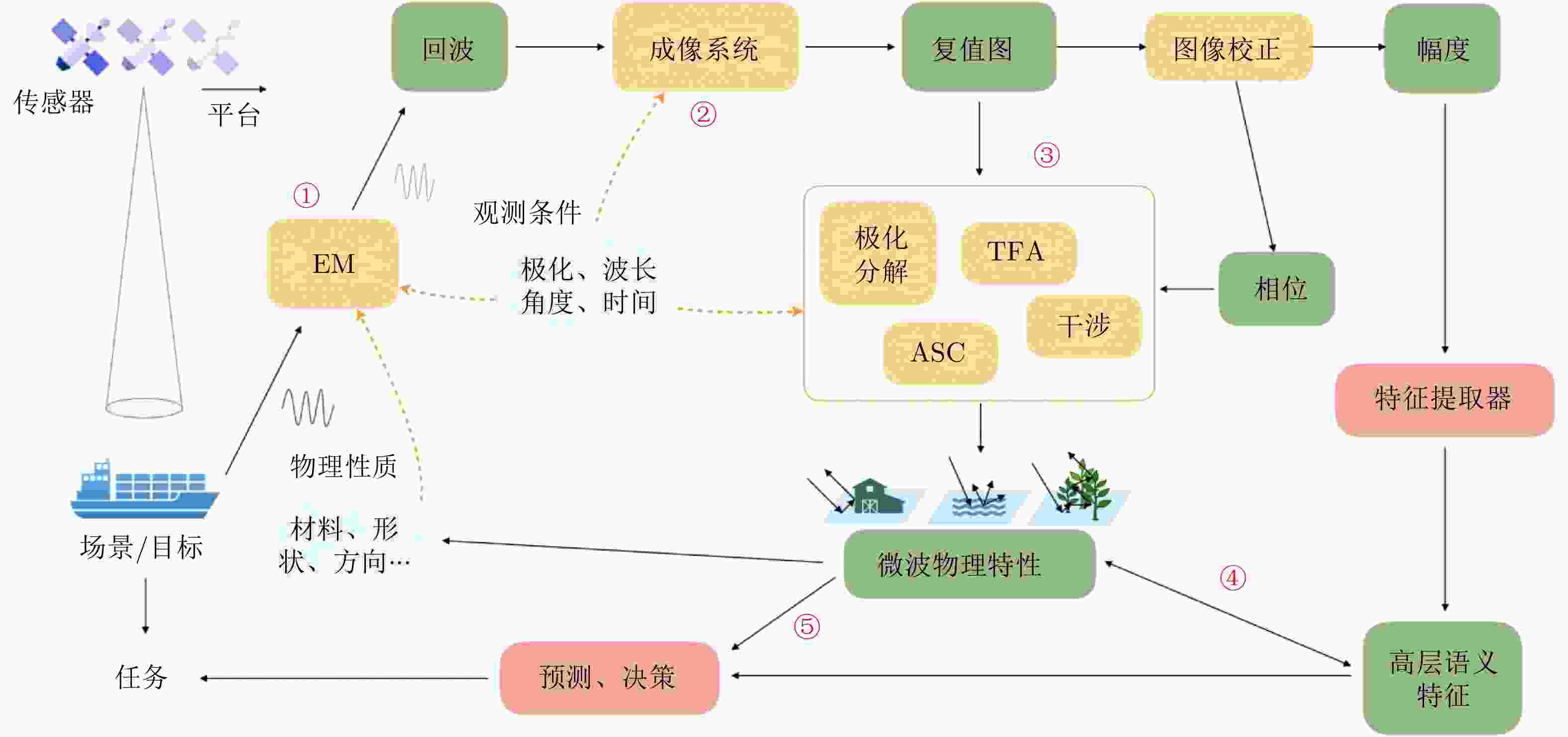
深度学习技术近年来在合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像解译领域发展迅速,但当前基于数据驱动的方法通常忽视了SAR潜在的物理特性,预测结果高度依赖训练数据,甚至违背了物理认知。深层次地整合理论驱动和数据驱动的方法在 SAR 图像解译领域尤为重要,数据驱动的方法擅长从大规模数据中自动挖掘新模式,对物理过程能起到有效的补充;反之,在数据驱动方法中加入可解释的物理模型能提升深度学习算法的透明度,并降低模型对标记样本的依赖。该文提出在SAR图像解译应用领域发展物理可解释的深度学习技术,从SAR信号、特性理解到图像语义和应用场景等多个维度开展研究,并结合物理机器学习提出了几种在SAR解译中融合物理模型和深度学习模型的研究思路,逐步发展可学习且可解释的智能化SAR图像解译新范式。在此基础上,该文回顾了近两三年在SAR图像解译相关领域中整合数据驱动深度学习和理论驱动物理模型的相关工作,主要聚焦信号特性理解和图像语义理解两大方向,并结合研究现状和其他领域的相关研究探讨了目前面临的挑战和未来可能的发展方向。
Abstract:Deep learning technologies have been developed rapidly in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) image interpretation. The current data-driven methods neglect the latent physical characteristics of SAR; thus, the predictions are highly dependent on training data and even violate physical laws. Deep integration of the theory-driven and data-driven approaches for SAR image interpretation is of vital importance. Additionally, the data-driven methods specialize in automatically discovering patterns from a large amount of data that serve as effective complements for physical processes, whereas the integrated interpretable physical models improve the explainability of deep learning algorithms and address the data-hungry problem. This study aimed to develop physically explainable deep learning for SAR image interpretation in signals, scattering mechanisms, semantics, and applications. Strategies for blending the theory-driven and data-driven methods in SAR interpretation are proposed based on physics machine learning to develop novel learnable and explainable paradigms for SAR image interpretation. Further, recent studies on hybrid methods are reviewed, including SAR signal processing, physical characteristics, and semantic image interpretation. Challenges and future perspectives are also discussed on the basis of the research status and related studies in other fields, which can serve as inspiration.
-
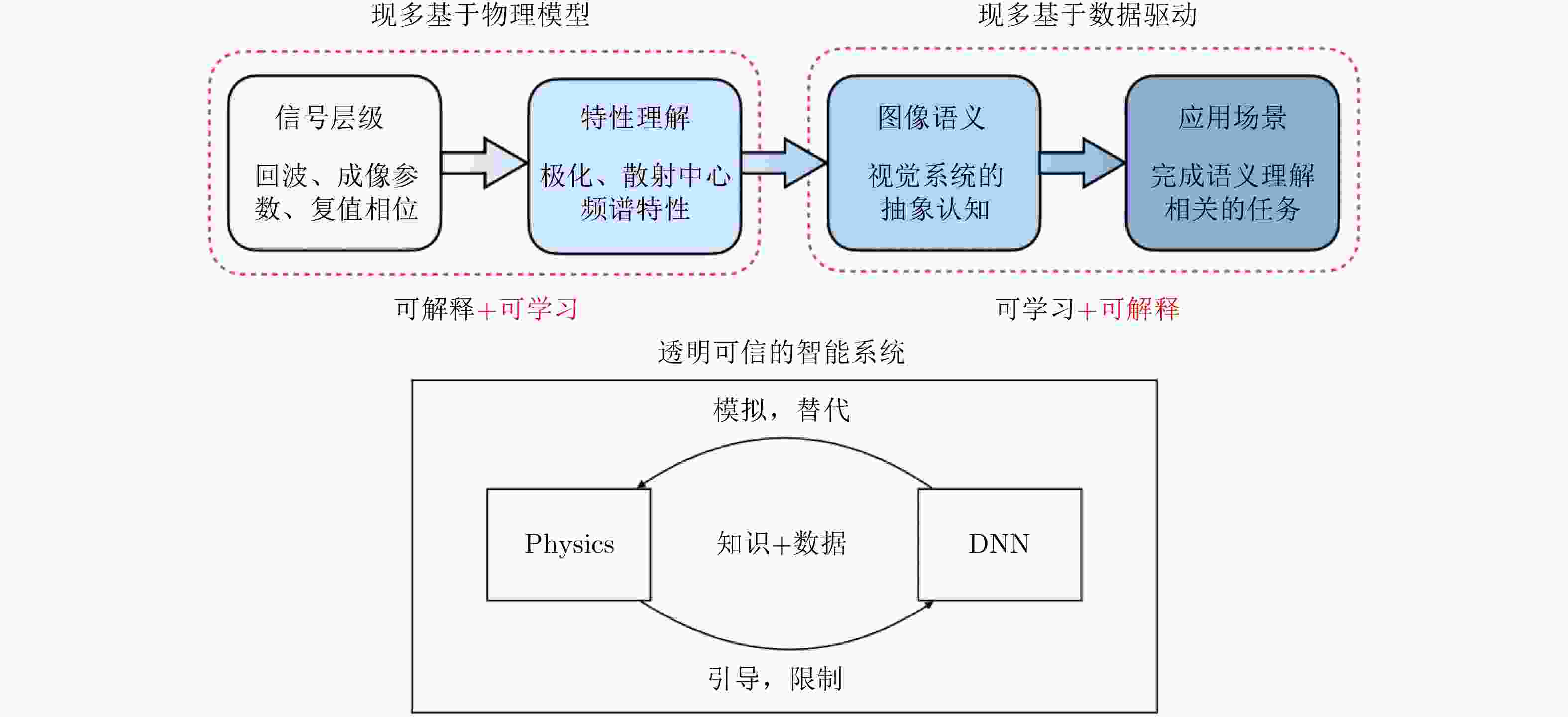
图 2 物理可解释的深度学习 SAR 图像解译应从多个维度开展研究,充分结合数据驱动和知识驱动的模型,逐步发展可学习且可解释的智能化图像解译新范式
Figure 2. The PXDL for SAR image interpretation is supposed to be carried out from multiple aspects, that deeply integrates the data-driven and knowledge-driven models to develop the novel learnable and explainable intelligent paradigm
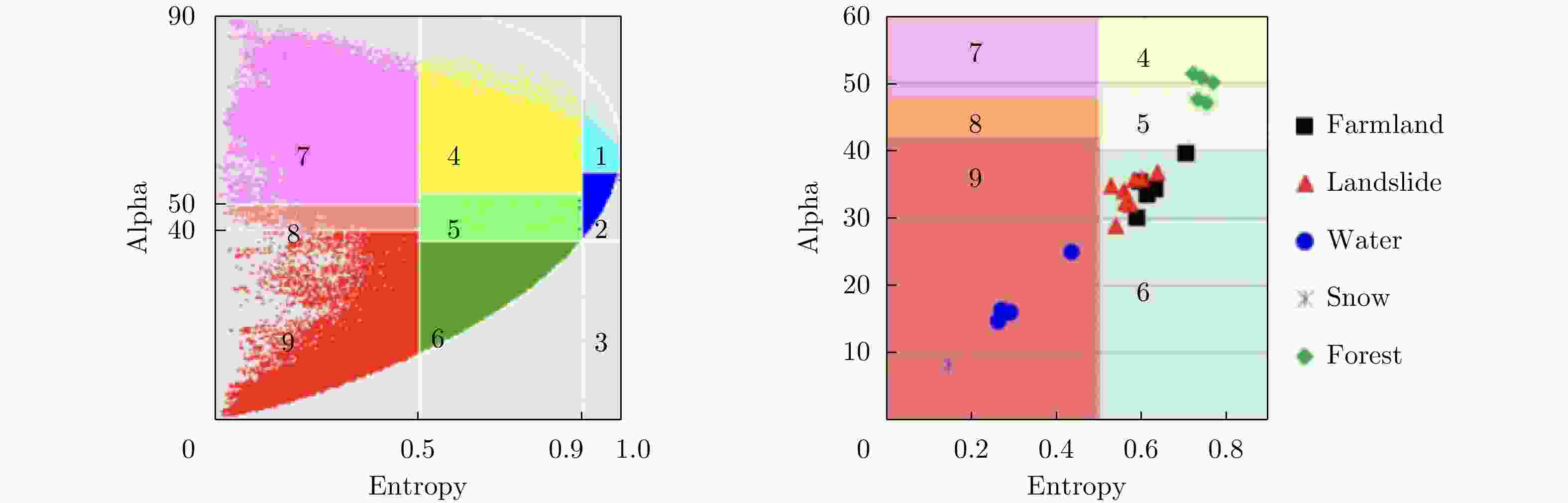
图 4 The H/
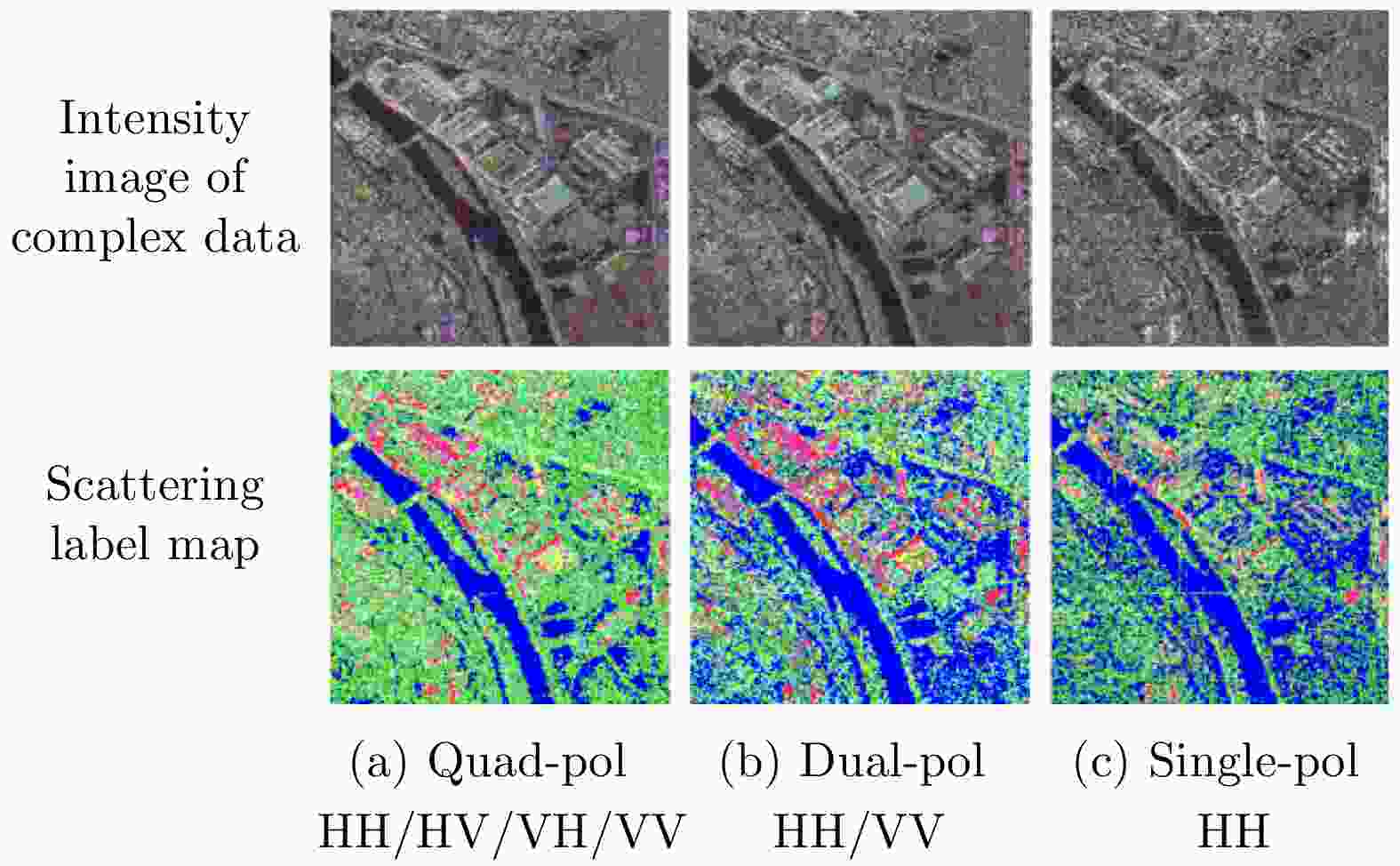
$\alpha $ plane for full-polarized SAR data and the selected land-use and land-cover samples distributed in Ref. [50]图 5 The unsupervised learning results of different polarized SAR images based on TFA and pol-extended TFA models[92]
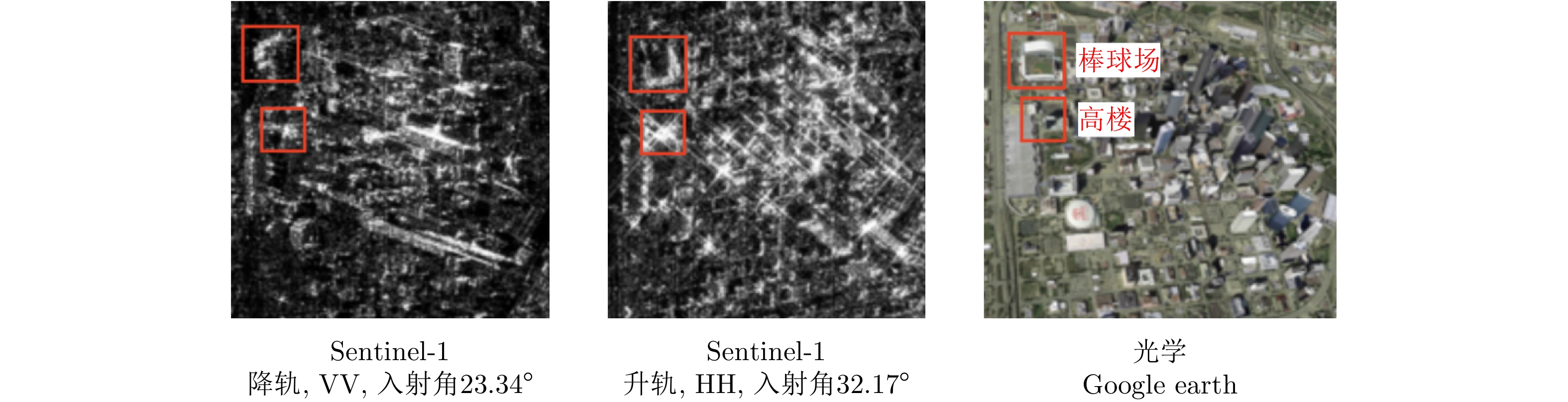
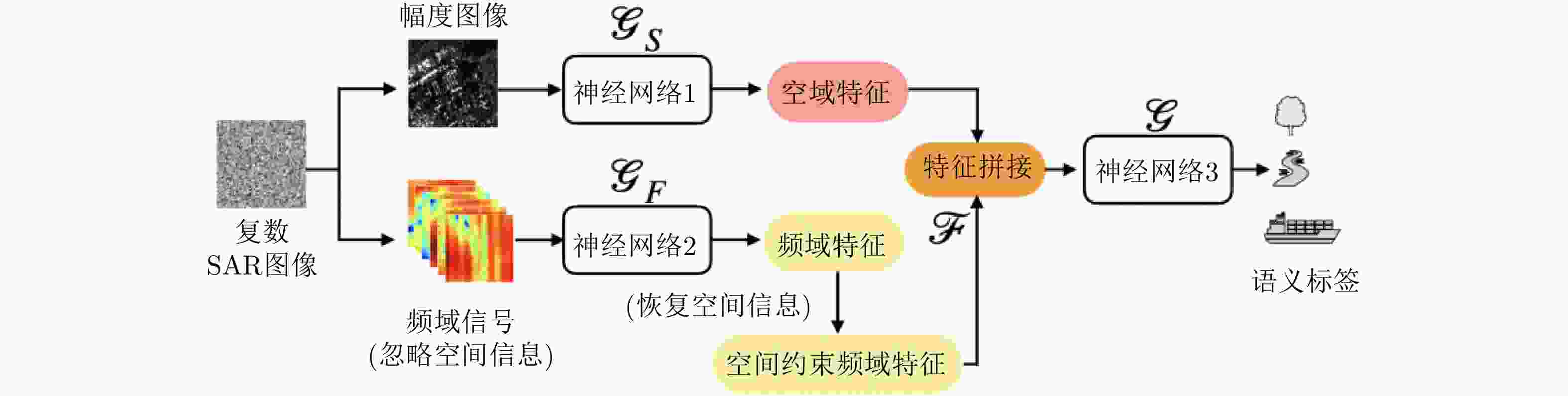
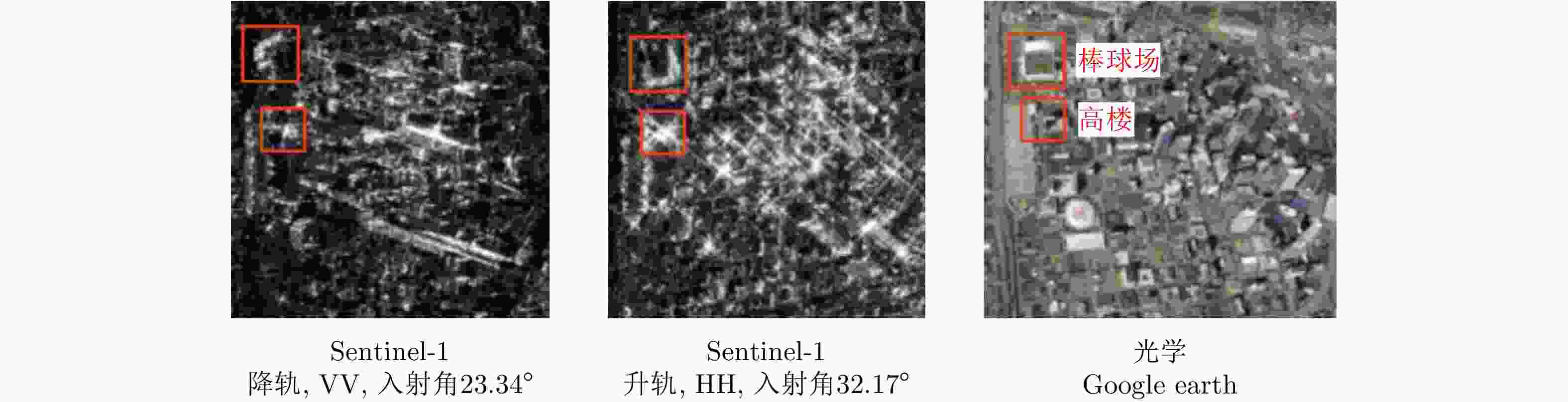
图 7 The SAR image classification framework Deep SAR-Net (DSN)[11]
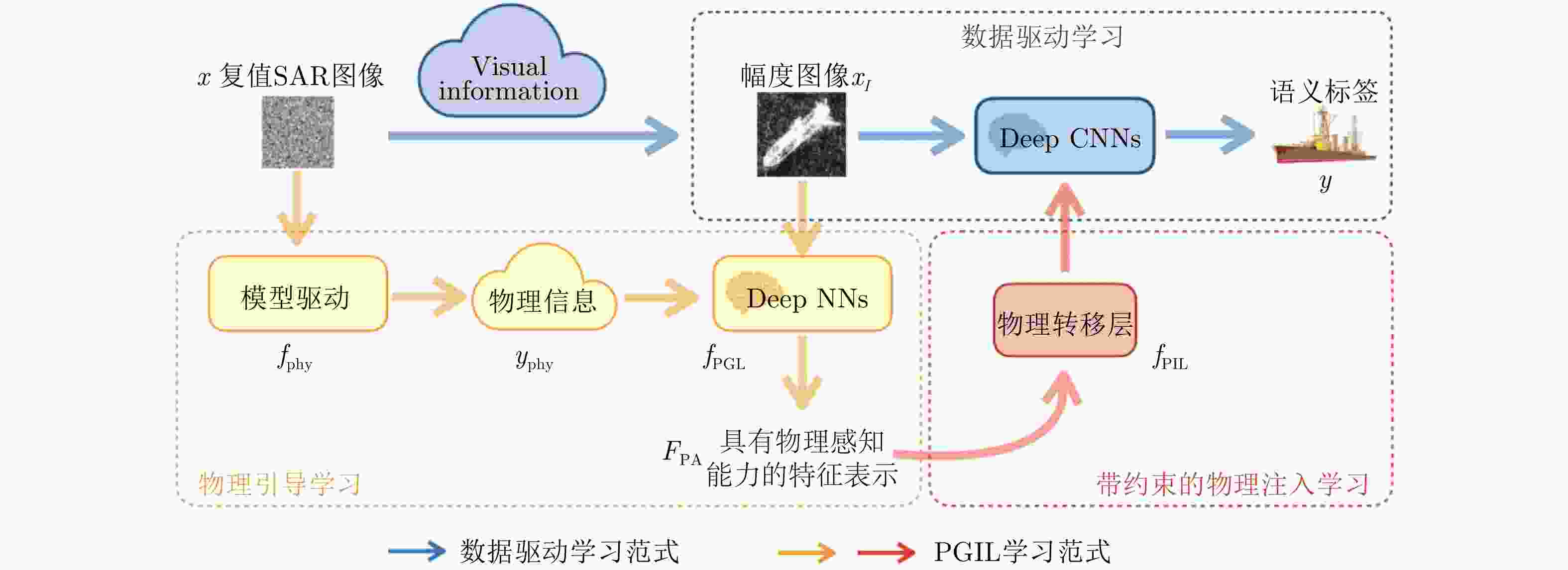
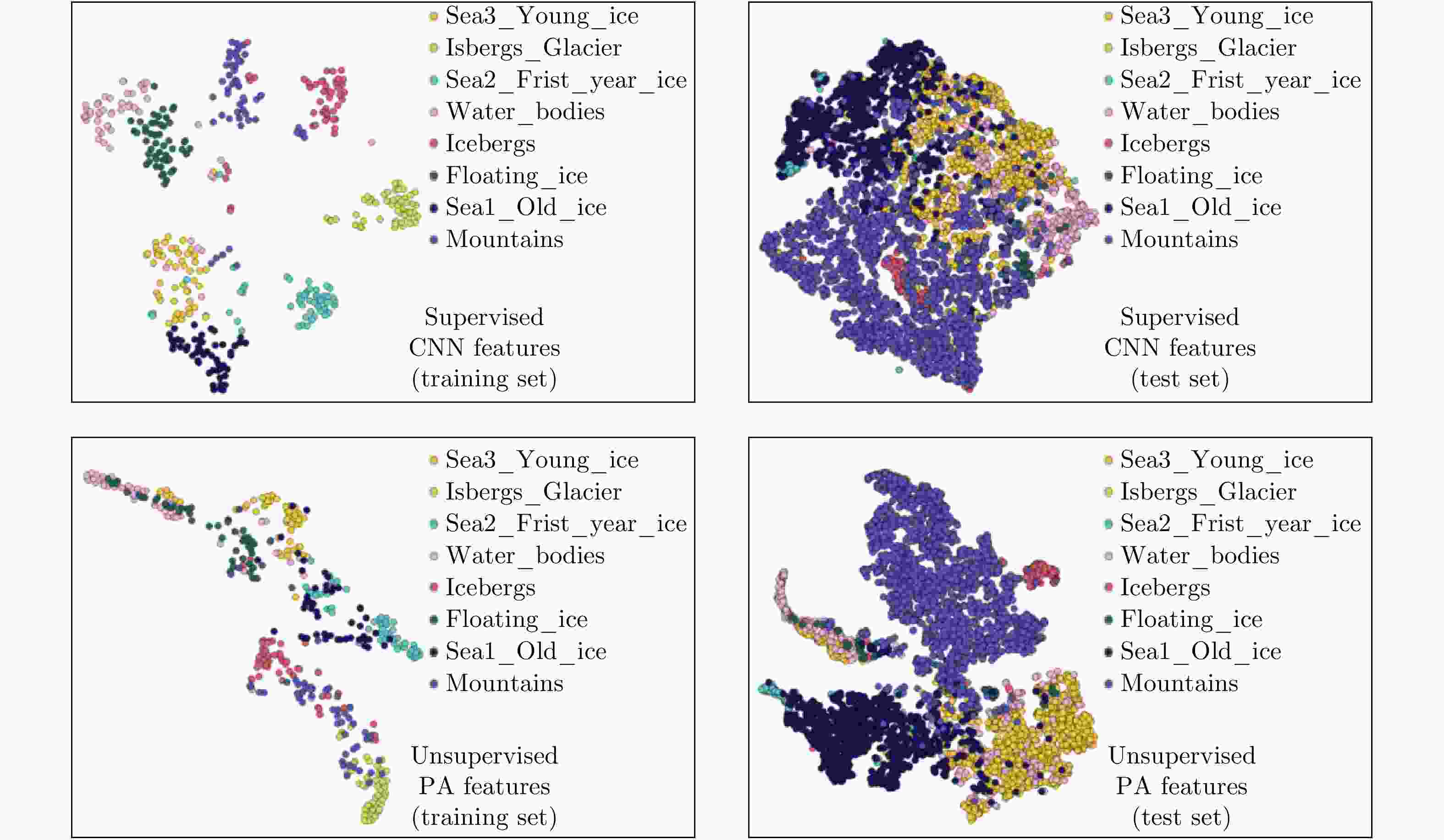
图 8 The feature visualization of the unsupervised physics guided learning and supervised CNN classification on training and test set[100]
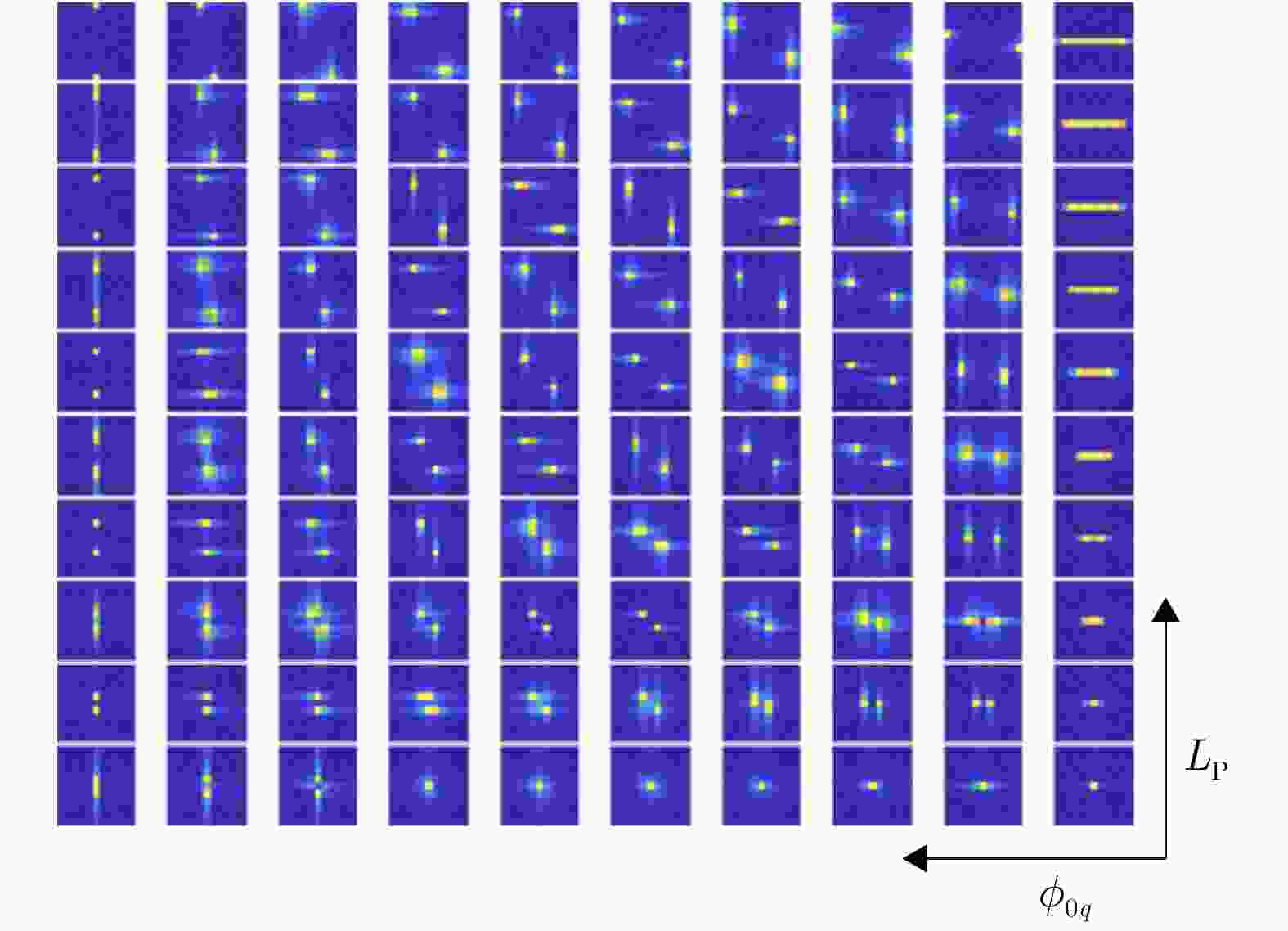
图 9 The amplitude images of convolution kernels in the first layer of CV-CNN based on ASC model initialization[106]
-
[1] CUMMING I G, WONG F H, 洪文, 胡东辉, 韩冰, 等译. 合成孔径雷达成像算法与实现[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2019, 93–100.CUMMING I G, WONG F H, HONG Wen, HU Donghui, HAN Bing, et al. translation. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2019, 93–100. [2] 黄钟泠. 面向合成孔径雷达图像分类的深度学习方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2020: 59.HUANG Zhongling. A study on synthetic aperture radar image classification with deep learning[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020: 59. [3] 谷秀昌, 付琨, 仇晓兰. SAR图像判读解译基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.GU Xiuchang, FU Kun, and QIU Xiaolan. Fundamentals of SAR Image of SAR Image Interpretation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017. [4] OLIVER C and QUEGAN S. Understanding Synthetic Aperture Radar Images[M]. London: SciTech Publishing, 2004. [5] GAO Gui, OUYANG Kewei, LUO Yongbo, et al. Scheme of parameter estimation for generalized gamma distribution and its application to ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(3): 1812–1832. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2634862 [6] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Ship detection based on complex signal kurtosis in single-channel SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6447–6461. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2906054 [7] CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720 [8] HUANG Zhongling, DUMITRU C O, PAN Zongxu, et al. Classification of large-scale high-resolution SAR images with deep transfer learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(1): 107–111. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2965558 [9] HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network for SAR target classification with limited labeled data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(9): 907. doi: 10.3390/rs9090907 [10] HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. What, where, and how to transfer in SAR target recognition based on deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2324–2336. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2947634 [11] HUANG Zhongling, DATCU M, PAN Zongxu, et al. Deep SAR-Net: Learning objects from signals[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 161: 179–193. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.01.016 [12] 金亚秋. 多模式遥感智能信息与目标识别: 微波视觉的物理智能[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083JIN Yaqiu. Multimode remote sensing intelligent information and target recognition: Physical intelligence of microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083 [13] 张钹, 朱军, 苏航. 迈向第三代人工智能[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2020, 50(9): 1281–1302. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0204ZHANG Bo, ZHU Jun, and SU Hang. Toward the third generation of artificial intelligence[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2020, 50(9): 1281–1302. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0204 [14] DAS A and RAD P. Opportunities and challenges in explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): A survey[OL]. arXiv: 2006.11371, 2020. [15] BAI Xiao, WANG Xiang, LIU Xianglong, et al. Explainable deep learning for efficient and robust pattern recognition: A survey of recent developments[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 120: 108102. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108102 [16] ANGELOV P and SOARES E. Towards explainable deep neural networks (xDNN)[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 130: 185–194. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.07.010 [17] MOLNAR C. Interpretable machine learning: A guide for making black box models explainable[EB/OL]. https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-book/, 2021. [18] CAMBURU O M. Explaining deep neural networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Oxford University, 2020. [19] 李玮杰, 杨威, 刘永祥, 等. 雷达图像深度学习模型的可解释性研究与探索[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 待出版. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0102.LI Weijie, YANG Wei, LIU Yongxiang, et al. Research and exploration on interpretability of deep learning model in radar image[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, in press. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0102. [20] BELLONI C, BALLERI A, AOUF N, et al. Explainability of deep SAR ATR through feature analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 659–673. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3031435 [21] 郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059 [22] KARNIADAKIS G E, KEVREKIDIS I G, LU Lu, et al. Physics-informed machine learning[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2021, 3(6): 422–440. doi: 10.1038/s42254-021-00314-5 [23] THUEREY N, HOLL P, MUELLER M, et al. Physics-based deep learning[OL]. arXiv: 2109.05237, 2021. [24] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, and KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 378: 686–707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045 [25] MENG Xuhui, LI Zhen, ZHANG Dongkun, et al. PPINN: Parareal physics-informed neural network for time-dependent PDEs[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 370: 113250. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113250 [26] GOSWAMI S, ANITESCU C, CHAKRABORTY S, et al. Transfer learning enhanced physics informed neural network for phase-field modeling of fracture[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2020, 106: 102447. doi: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102447 [27] KARPATNE A, EBERT-UPHOFF I, RAVELA S, et al. Machine learning for the geosciences: Challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2019, 31(8): 1544–1554. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2018.2861006 [28] CAMPS-VALLS G, REICHSTEIN M, ZHU Xiaoxiang, et al. Advancing deep learning for earth sciences: From hybrid modeling to interpretability[C]. IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 3979–3982. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9323558. [29] REICHSTEIN M, CAMPS-VALLS G, STEVENS B, et al. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science[J]. Nature, 2019, 566(7743): 195–204. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0912-1 [30] CAMPS-VALLS G, SVENDSEN D H, CORTÉS-ANDRÉS J, et al. Physics-aware machine learning for geosciences and remote sensing[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 2086–2089. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS47720.2021.9554521. [31] JIA Xiaowei, WILLARD J, KARPATNE A, et al. Physics guided RNNs for modeling dynamical systems: A case study in simulating lake temperature profiles[C]. The 2019 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, Calgary, Canada, 2019: 558–566. doi: 10.1137/1.9781611975673.63. [32] DAW A, KARPATNE A, WATKINS W, et al. Physics-guided neural networks (PGNN): An application in lake temperature modeling[OL]. arXiv: 1710.11431, 2021. doi: https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.11431. [33] BEUCLER T, PRITCHARD M, GENTINE P, et al. Towards physically-consistent, data-driven models of convection[C]. IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 3987–3990. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9324569. [34] SHEN Huanfeng, JIANG Menghui, LI Jie, et al. Coupling model-driven and data-driven methods for remote sensing image restoration and fusion[OL]. arXiv: 2108.06073, 2021. [35] WANG Yuqing, WANG Qi, LU Wenkai, et al. Physics-constrained seismic impedance inversion based on deep learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3072132 [36] XIA Wenchao, ZHENG Gan, WONG K K, et al. Model-driven beamforming neural networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(1): 68–75. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900239 [37] ZHANG Juping, XIA Wenchao, YOU Minglei, et al. Deep learning enabled optimization of downlink beamforming under per-antenna power constraints: Algorithms and experimental demonstration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(6): 3738–3752. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2977340 [38] ZHU Xiaoxiang, MONTAZERI S, ALI M, et al. Deep learning meets SAR: Concepts, models, pitfalls, and perspectives[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, in press. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2020.3046356. [39] MALMGREN-HANSEN D, KUSK A, DALL J, et al. Improving SAR automatic target recognition models with transfer learning from simulated data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1484–1488. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2717486 [40] 文贡坚, 朱国强, 殷红成, 等. 基于三维电磁散射参数化模型的SAR目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 115–135. doi: 10.12000/JR17034WEN Gongjian, ZHU Guoqiang, YIN Hongcheng, et al. SAR ATR based on 3D parametric electromagnetic scattering model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 115–135. doi: 10.12000/JR17034 [41] 罗迎, 倪嘉成, 张群. 基于“数据驱动+智能学习”的合成孔径雷达学习成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 107–122. doi: 10.12000/JR19103LUO Ying, NI Jiacheng, and ZHANG Qun. Synthetic aperture radar learning-imaging method based on data-driven technique and artificial intelligence[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 107–122. doi: 10.12000/JR19103 [42] CHAN T H, JIA Kui, GAO Shenghua, et al. PCANet: A simple deep learning baseline for image classification?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5017–5032. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2475625 [43] LI Mengke, LI Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. SAR image change detection using PCANet guided by saliency detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(3): 402–406. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2876616 [44] WANG Rongfang, ZHANG Jie, CHEN Jiawei, et al. Imbalanced learning-based automatic SAR images change detection by morphologically supervised PCA-net[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(4): 554–558. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2878420 [45] CLOUDE S and POTTIER E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78. doi: 10.1109/36.551935 [46] YAMAGUCHI Y, YAJIMA Y, and YAMADA H. A four-component decomposition of POLSAR images based on the coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(3): 292–296. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.869986 [47] FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, and POTTIER E. Scene characterization using sub-aperture polarimetric interferometric SAR data[C]. IGARSS 2003-2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 702–704. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2003.1293889. [48] POTTER L C and MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098 [49] JI Kefeng and WU Yonghui. Scattering mechanism extraction by a modified cloude-pottier decomposition for dual polarization SAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(6): 7447–7470. doi: 10.3390/rs70607447 [50] YONEZAWA C, WATANABE M, and SAITO G. Polarimetric decomposition analysis of ALOS PALSAR observation data before and after a landslide event[J]. Remote Sensing, 2012, 4(8): 2314–2328. doi: 10.3390/rs4082314 [51] NIU Shengren, QIU Xiaolan, LEI Bin, et al. Parameter extraction based on deep neural network for SAR target simulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(7): 4901–4914. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2968493 [52] NIU Shengren, QIU Xiaolan, LEI Bin, et al. A SAR target image simulation method with DNN embedded to calculate electromagnetic reflection[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 2593–2610. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3056920 [53] GUO Jiayi, LEI Bin, DING Chibiao, et al. Synthetic aperture radar image synthesis by using generative adversarial nets[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(7): 1111–1115. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2699196 [54] OH J and KIM M. PeaceGAN: A GAN-based multi-task learning method for SAR target image generation with a pose estimator and an auxiliary classifier[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(19): 3939. doi: 10.3390/rs13193939 [55] CUI Zongyong, ZHANG Mingrui, CAO Zongjie, et al. Image data augmentation for SAR sensor via generative adversarial nets[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 42255–42268. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907728 [56] SONG Qian, XU Feng, and JIN Yaqiu. SAR image representation learning with adversarial autoencoder networks[C]. IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 9498–9501. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8898922. [57] WANG Ke, ZHANG Gong, LENG Yang, et al. Synthetic aperture radar image generation with deep generative models[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(6): 912–916. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2884898 [58] HU Xiaowei, FENG Weike, GUO Yiduo, et al. Feature learning for SAR target recognition with unknown classes by using CVAE-GAN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): 3554. doi: 10.3390/rs13183554 [59] XIE You, FRANZ E, CHU Mengyu, et al. TempoGAN: A temporally coherent, volumetric GAN for super-resolution fluid flow[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2018, 37(4): 95. [60] CHU Mengyu, THUEREY N, SEIDEL H P, et al. Learning meaningful controls for fluids[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2021, 40(4): 100. doi: 10.1145/3450626.3459845 [61] QIAN Jiang, HUANG Shaoyin, WANG Lu, et al. Super-resolution ISAR imaging for maneuvering target based on deep-learning-assisted time-frequency analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5201514. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3050189 [62] LIANG Jiadian, WEI Shunjun, WANG Mou, et al. ISAR compressive sensing imaging using convolution neural network with interpretable optimization[C]. IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 2483–2486. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9323601. [63] GREGOR K and LECUN Y. Learning fast approximations of sparse coding[C]. 27th International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 2010: 399–406. [64] LIU Jialin, CHEN Xiaohan, WANG Zhangyang, et al. ALISTA: Analytic weights are as good as learned weights in LISTA[C]. The 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, USA, 2019, 1–33. [65] BEHRENS F, SAUDER J, and JUNG P. Neurally augmented ALISTA[C]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual Event, Austria, 2021: 1–10. [66] YANG Yan, SUN Jian, LI Huibin, et al. Deep ADMM-Net for compressive sensing MRI[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 10–18. doi: 10.5555/3157096.3157098. [67] YANG Yan, SUN Jian, LI Huibin, et al. ADMM-CSNet: A deep learning approach for image compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(3): 521–538. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2883941 [68] MASON E, YONEL B, and YAZICI B. Deep learning for SAR image formation[C]. SPIE 10201, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXIV, Anaheim, USA, 2017: 1020104. doi: 10.1117/12.2267831. [69] GAO Jingkun, DENG Biin, QIN Yuliang, et al. Enhanced radar imaging using a complex-valued convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(1): 35–39. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2866567 [70] HU Changyu, WANG Ling, LI Ze, et al. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging using a fully convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(7): 1203–1207. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2943069 [71] ALVER M B, SALEEM A, and ÇETIN M. Plug-and-play synthetic aperture radar image formation using deep priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2021, 7: 43–57. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2020.3047473 [72] WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, LIANG Jiadian, et al. TPSSI-Net: Fast and enhanced two-path iterative network for 3D SAR sparse imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 7317–7332. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3104168 [73] HU Changyu, LI Ze, WANG Ling, et al. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging using a deep ADMM network[C]. 20th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Ulm, Germany, 2019: 1–9. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2019.8768138. [74] LI Xiaoyong, BAI Xueru, and ZHOU Feng. High-resolution ISAR imaging and autofocusing via 2d-ADMM-net[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(12): 2326. doi: 10.3390/rs13122326 [75] LI Ruize, ZHANG Shuanghui, ZHANG Chi, et al. Deep learning approach for sparse aperture ISAR imaging and autofocusing based on complex-valued ADMM-net[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(3): 3437–3451. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3025053 [76] HU Xiaowei, XU Feng, GUO Yiduo, et al. MDLI-Net: Model-driven learning imaging network for high-resolution microwave imaging with large rotating angle and sparse sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021: 1–17. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3110579 [77] RATHA D, GAMBA P, BHATTACHARYA A, et al. Novel techniques for built-up area extraction from polarimetric SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(1): 177–181. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2914913 [78] AO Dongyang, DATCU M, SCHWARZ G, et al. Moving ship velocity estimation using TanDEM-X data based on subaperture decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(10): 1560–1564. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2846399 [79] 廖明生, 王茹, 杨梦诗, 等. 城市目标动态监测中的时序InSAR分析方法及应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 409–424. doi: 10.12000/JR20022LIAO Mingsheng, WANG Ru, YANG Mengshi, et al. Techniques and applications of spaceborne time-series InSAR in urban dynamic monitoring[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 409–424. doi: 10.12000/JR20022 [80] SICA F, GOBBI G, RIZZOLI P, et al. Φ-Net: Deep residual learning for InSAR parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(5): 3917–3941. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3020427 [81] SONG Qian, XU Feng, and JIN Yaqiu. Radar image colorization: Converting single-polarization to fully polarimetric using deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 1647–1661. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2779875 [82] ZHAO Juanping, DATCU M, ZHANG Zenghai, et al. Contrastive-regulated CNN in the complex domain: A method to learn physical scattering signatures from flexible PolSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 10116–10135. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2931620 [83] QU Junrong, QIU Xiaolan, and DING Chibiao. A study of recovering POLSAR information from single-polarized data using DNN[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 812–815. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS47720.2021.9554304. [84] CHENG Zezhou, YANG Qingxiong, and SHENG Bin. Deep colorization[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 415–423. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.55. [85] LUAN Fujun, PARIS S, SHECHTMAN E, et al. Deep photo style transfer[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6997–7005. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.740. [86] JI Guang, WANG Zhaohui, ZHOU Lifan, et al. SAR image colorization using multidomain cycle-consistency generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(2): 296–300. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2969891 [87] TUPIN F and TISON C. Sub-aperture decomposition for SAR urban area analysis[C]. European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Ulm, Germany, 2004: 431–434. [88] BOVENGA F, DERAUW D, RANA F M, et al. Multi-chromatic analysis of SAR images for coherent target detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(9): 8822–8843. doi: 10.3390/rs6098822 [89] SPIGAI M, TISON C, and SOUYRIS J C. Time-frequency analysis in high-resolution SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(7): 2699–2711. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2107914 [90] FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, POTTIER E, et al. Scene characterization using subaperture polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(10): 2264–2276. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817188 [91] HUANG Zongling, DATCU M, PAN Zongxu, et al. HDEC-TFA: An unsupervised learning approach for discovering physical scattering properties of single-polarized SAR image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(4): 3054–3071. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3014335 [92] HUANG Zhongling, DATCU M, PAN Zongxu, et al. A hybrid and explainable deep learning framework for SAR images[C]. IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 1727–1730. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9323845. [93] DE S, CLANTON C, BICKERTON S, et al. Exploring the relationships between scattering physics and auto-encoder latent-space embedding[C]. IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 3501–3504. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9323410. [94] HUANG Zhongling, YAO Xiwen, DUMITRU C O, et al. Physically explainable CNN for SAR image classification[OL]. arXiv: 2110.14144, 2021. [95] ZHANG Jinsong, XING Mengdao, and XIE Yiyuan. FEC: A feature fusion framework for SAR target recognition based on electromagnetic scattering features and deep CNN features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2174–2187. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3003264 [96] LEI Songlin, QIU Xiaolan, DING Chibiao, et al. A feature enhancement method based on the sub-aperture decomposition for rotating frame ship detection in SAR images[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 3573–3576. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS47720.2021.9553635. [97] THEAGARAJAN R, BHANU B, ERPEK T, et al. Integrating deep learning-based data driven and model-based approaches for inverse synthetic aperture radar target recognition[J]. Optical Engineering, 2020, 59(5): 051407. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.59.5.051407 [98] HORI C, HORI T, LEE T Y, et al. Attention-based multimodal fusion for video description[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 4203–4212. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.450. [99] PORIA S, CAMBRIA E, BAJPAI R, et al. A review of affective computing: From unimodal analysis to multimodal fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2017, 37: 98–125. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2017.02.003 [100] HUANG Zhongling, DUMITRU C O, and REN Jun. Physics-aware feature learning of SAR images with deep neural networks: A case study[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 1264–1267. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS47720.2021.9554842. [101] LEE J S, GRUNES M R, AINSWORTH T L, et al. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2249–2258. doi: 10.1109/36.789621 [102] RATHA D, BHATTACHARYA A, and FRERY A C. Unsupervised classification of PolSAR data using a scattering similarity measure derived from a geodesic distance[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(1): 151–155. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2778749 [103] LI Yi, DU Lan, and WEI Di. Multiscale CNN based on component analysis for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021: 1–12. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3100137 [104] FENG Sijia, JI Kefeng, ZHANG Linbin, et al. SAR target classification based on integration of ASC parts model and deep learning algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 10213–10225. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3116979 [105] LIU Qingshu and LANG Liang. MMFF: Multi-manifold feature fusion based neural networks for target recognition in complex-valued SAR imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021, 180: 151–162. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.08.008 [106] LIU Jiaming, XING Mengdao, YU Hanwen, et al. EFTL: Complex convolutional networks with electromagnetic feature transfer learning for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3083261 [107] CUI Yuanhao, LIU Fang, JIAO Licheng, et al. Polarimetric multipath convolutional neural network for PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021: 1–18. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3071559 [108] DAW A, THOMAS R Q, CAREY C C, et al. Physics-guided architecture (PGA) of neural networks for quantifying uncertainty in lake temperature modeling[C]. The 2020 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), Cincinnati, USA, 2020: 532–540. [109] SUN Jian, NIU Zhan, INNANEN K A, et al. A theory-guided deep-learning formulation and optimization of seismic waveform inversion[J]. Geophysics, 2020, 85(2): R87–R99. doi: 10.1190/geo2019-0138.1 [110] HE Qishan, ZHAO Lingjun, JI Kefeng, et al. SAR target recognition based on task-driven domain adaptation using simulated data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3116707 [111] ZHANG Linbin, LENG Xiangguang, FENG Sijia, et al. Domain knowledge powered two-stream deep network for few-shot SAR vehicle recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021: 1–15. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3116349 [112] AGARWAL T, SUGAVANAM N, and ERTIN E. Sparse signal models for data augmentation in deep learning ATR[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266382. [113] DIEMUNSCH J R and WISSINGER J. Moving and stationary target acquisition and recognition (MSTAR) model-based automatic target recognition: Search technology for a robust ATR[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 3370, Algorithms for synthetic aperture radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 481–492. doi: 10.1117/12.321851. [114] HUANG Lanqing, LIU Bin, LI Boying, et al. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to sentinel-1 ship interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 195–208. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755672 [115] 孙显, 王智睿, 孙元睿, 等. AIR-SARShip-1.0: 高分辨率SAR舰船检测数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097SUN Xian, WANG Zhirui, SUN Yuanrui, et al. AIR-SARSHIP-1.0: High-resolution SAR ship detection dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097 [116] 杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104 [117] CHEN Siwei and TAO Chensong. PolSAR image classification using polarimetric-feature-driven deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(4): 627–631. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2799877 [118] LIU Xu, JIAO Licheng, TANG Xu, et al. Polarimetric convolutional network for PoLSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(5): 3040–3054. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2879984 [119] BI Haixia, SUN Jian, and XU Zongben. A graph-based semisupervised deep learning model for PoLSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(4): 2116–2132. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2871504 [120] VINAYARAJ P, SUGIMOTO R, NAKAMURA R, et al. Transfer learning with CNNs for segmentation of PALSAR-2 power decomposition components[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 6352–6361. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3031020 [121] XIA Junshi, YOKOYA N, ADRIANO B, et al. A benchmark high-resolution GaoFen-3 SAR dataset for building semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 5950–5963. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3085122 [122] WU Fan, WANG Chao, ZHANG Hong, et al. Built-up area mapping in China from GF-3 SAR imagery based on the framework of deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 262: 112515. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112515 [123] CHEN Jiankun, QIU Xiaolan, DING Chibiao, et al. CVCMFF Net: Complex-valued convolutional and multifeature fusion network for building semantic segmentation of InSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021: 1–14. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3068124 [124] SHI Xianzheng, FU Shilei, CHEN Jin, et al. Object-level semantic segmentation on the high-resolution Gaofen-3 FUSAR-map dataset[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 3107–3119. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3063797 [125] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 彭凌霄, 等. SARMV3D-1.0: SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: