-
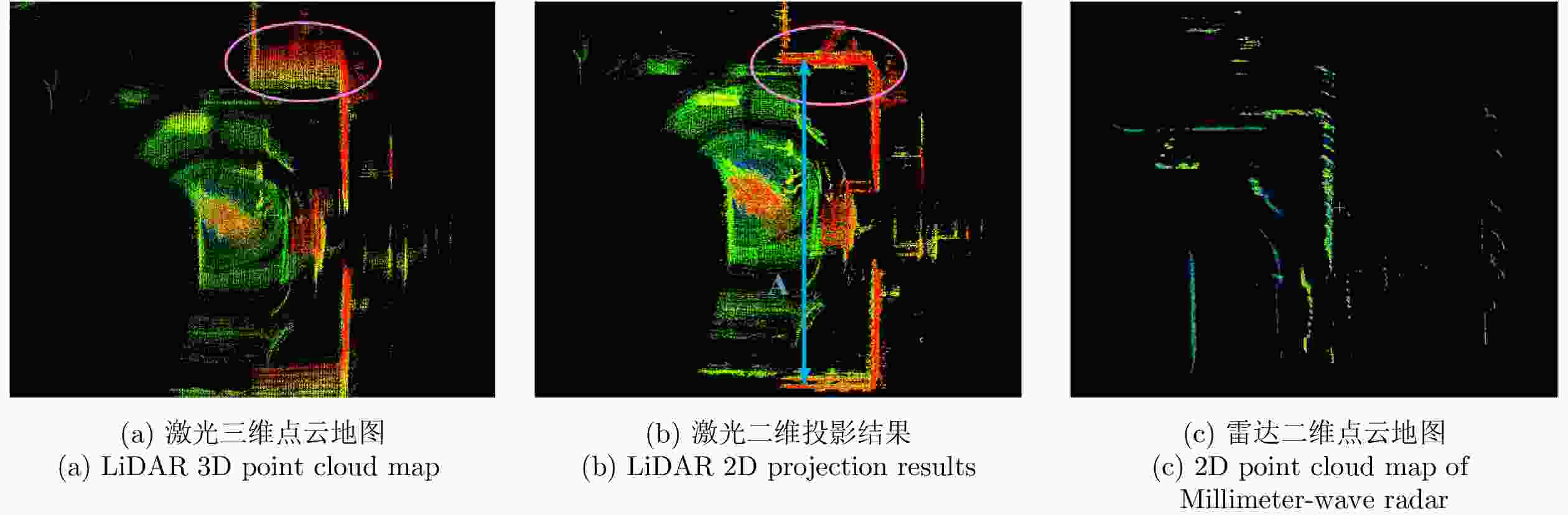
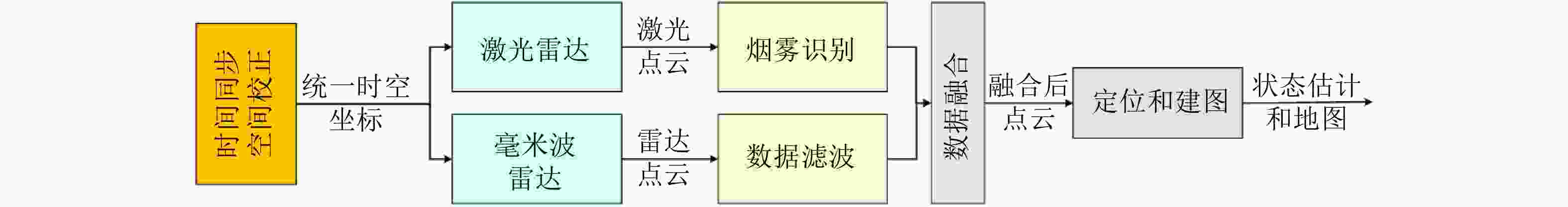
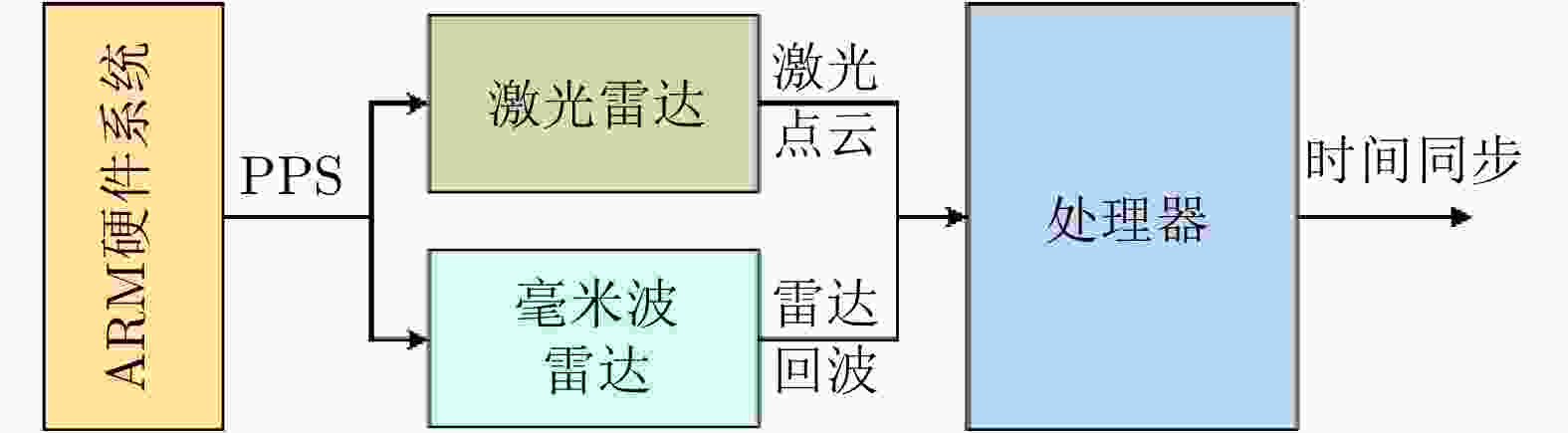
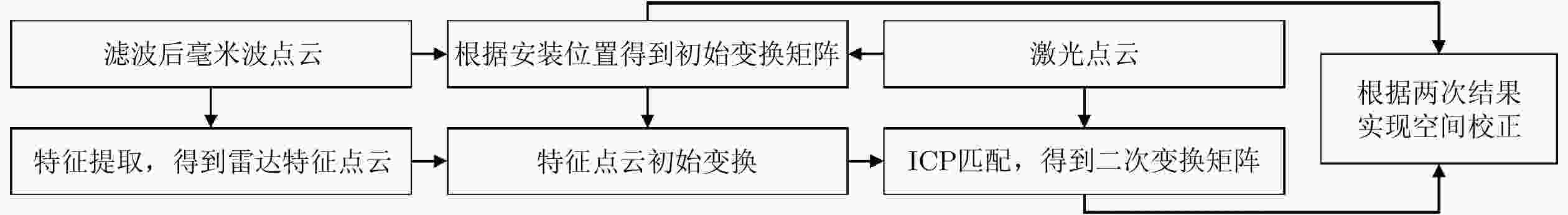
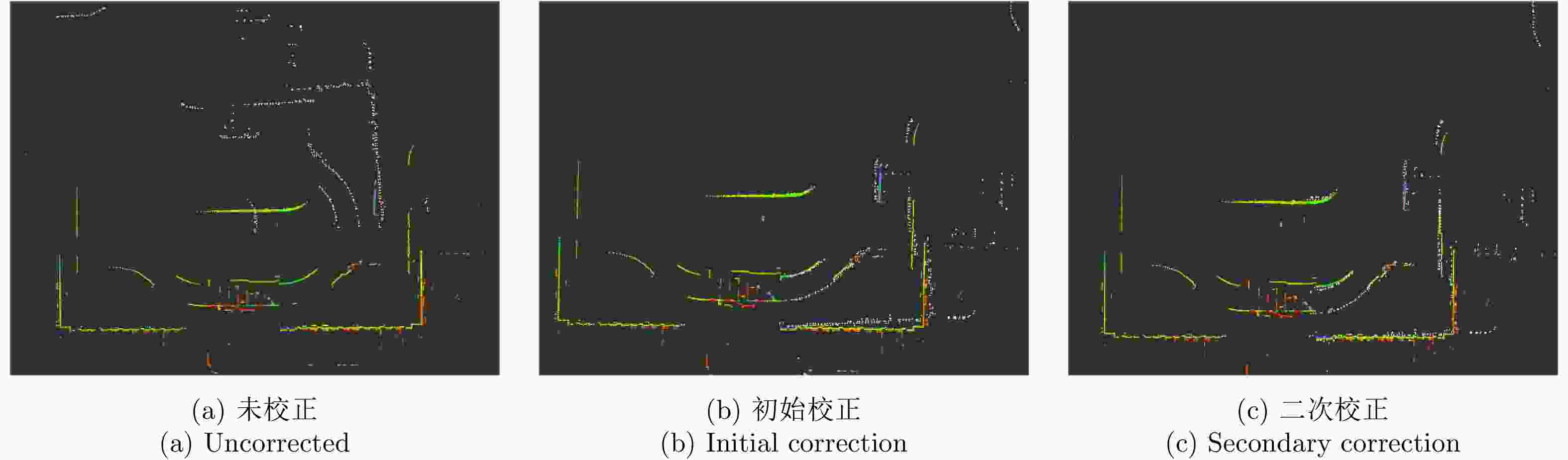
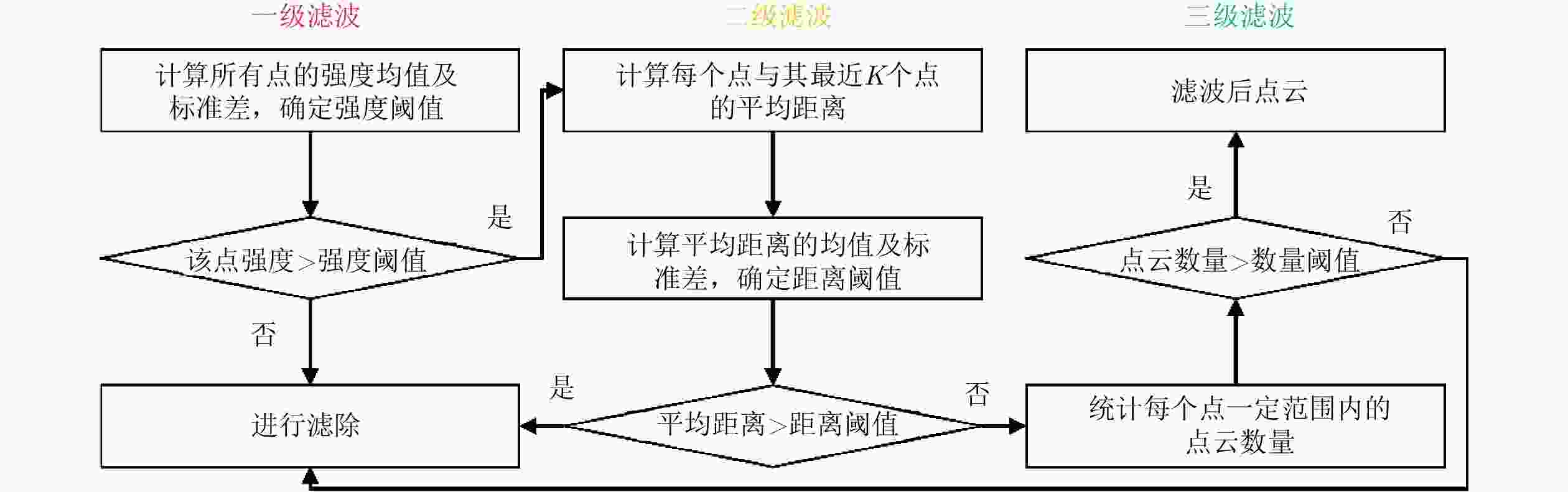
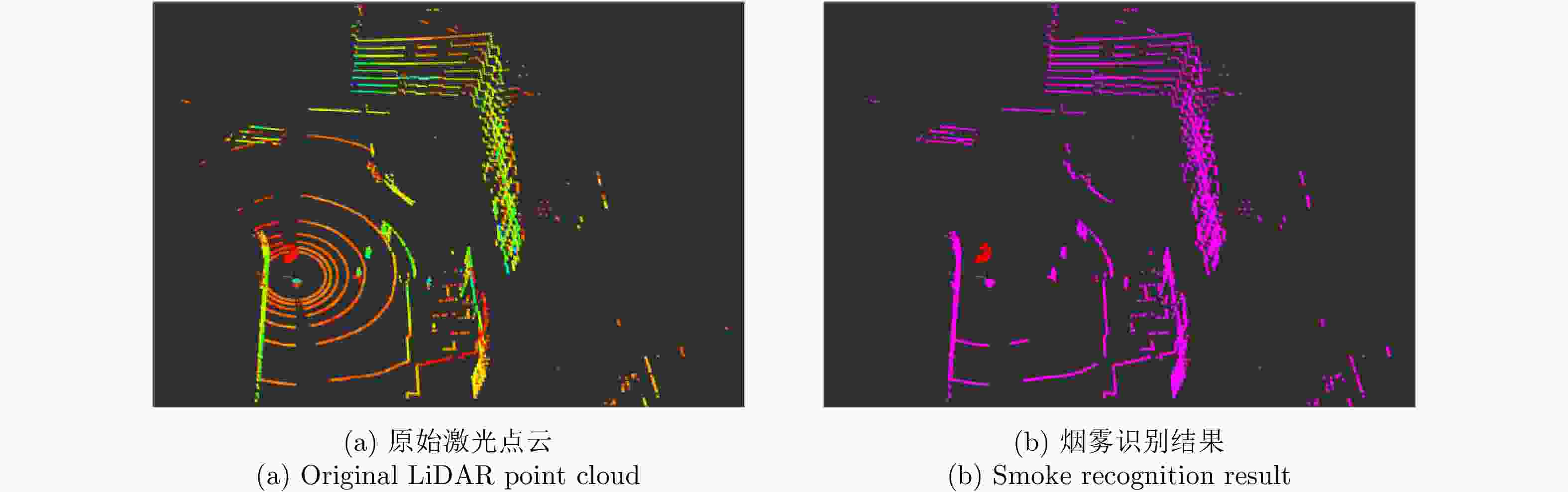
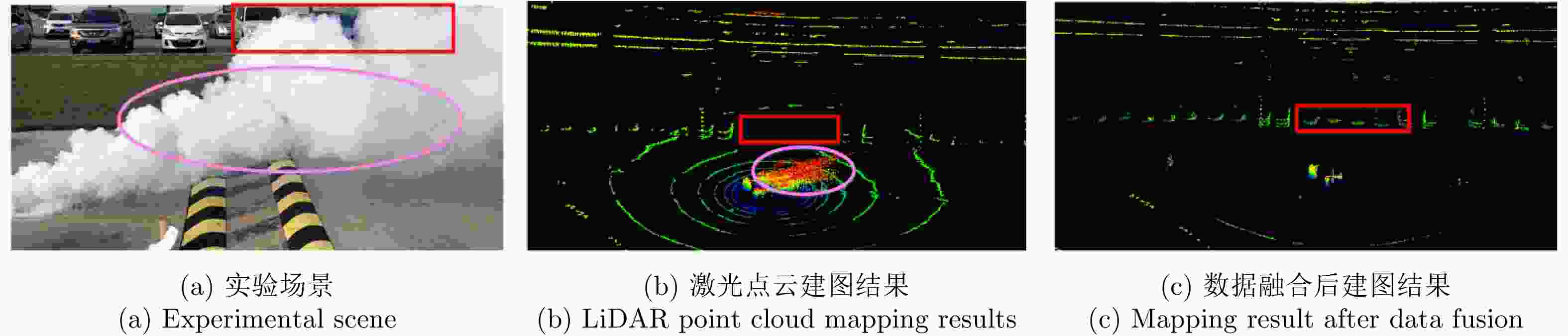
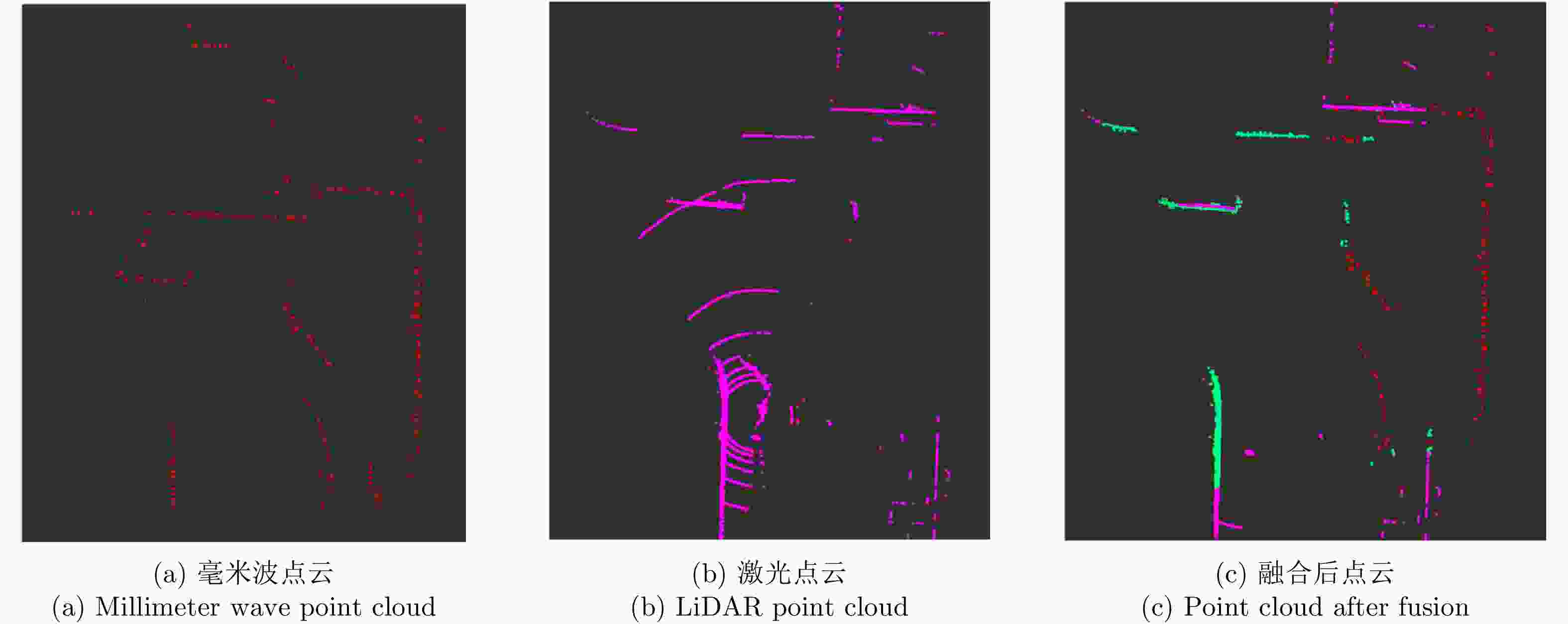
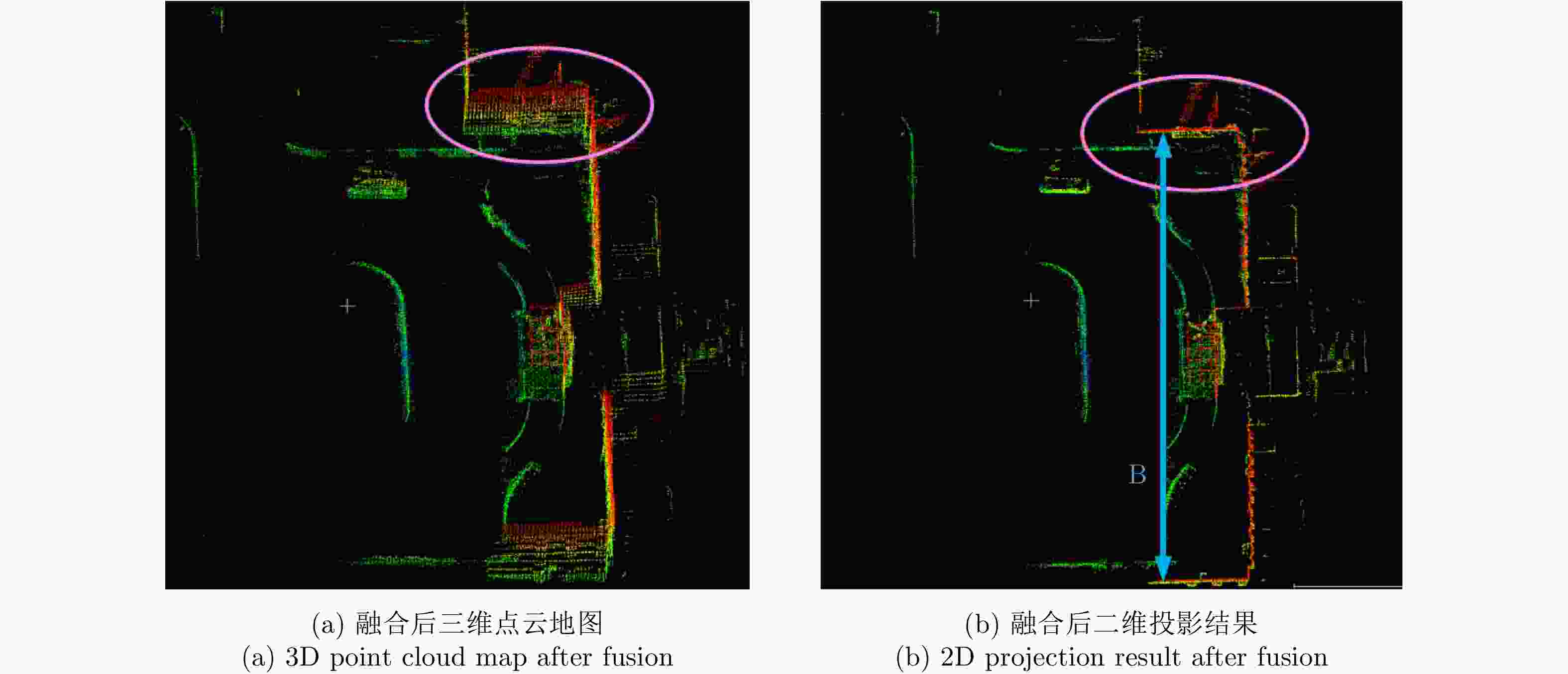
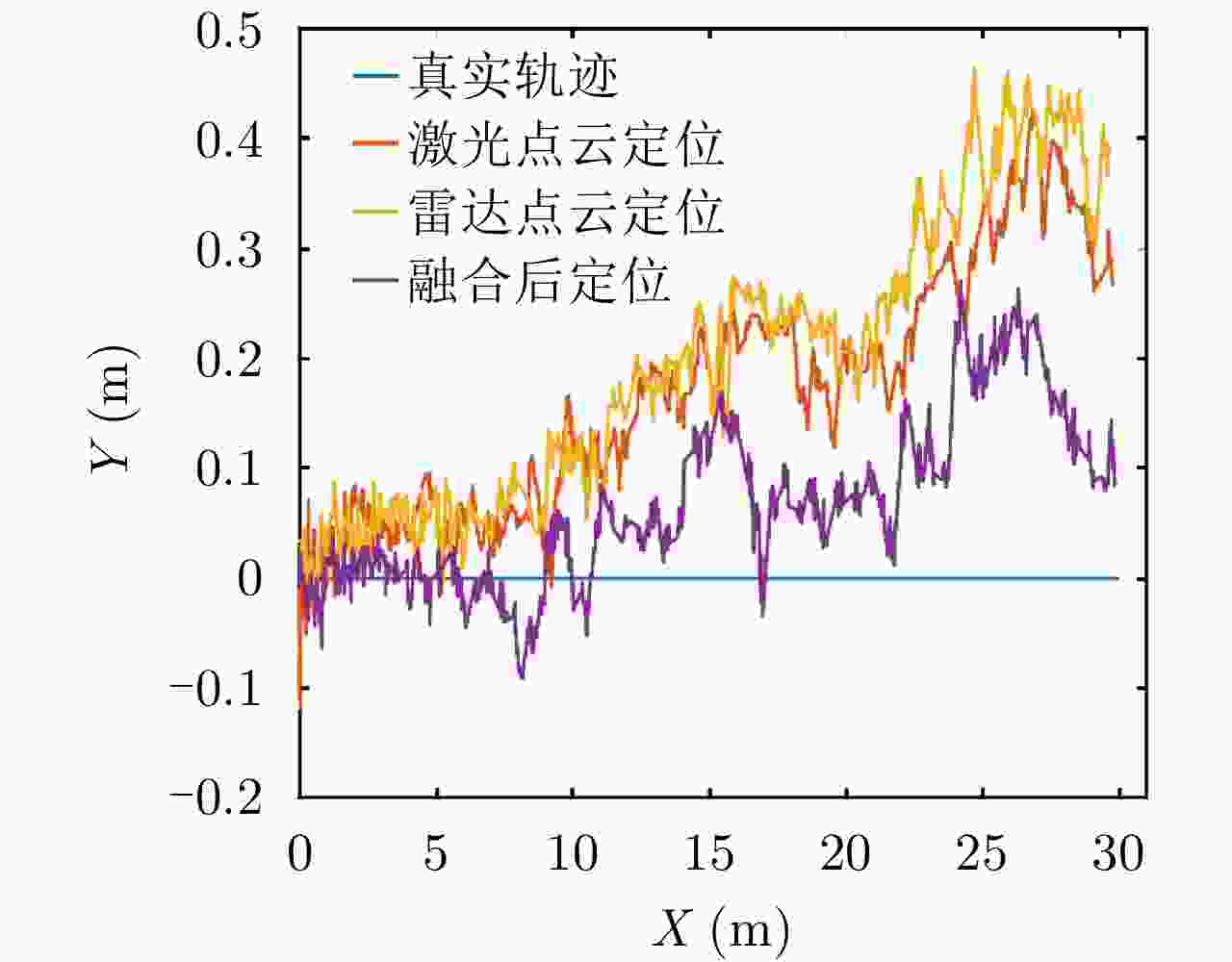
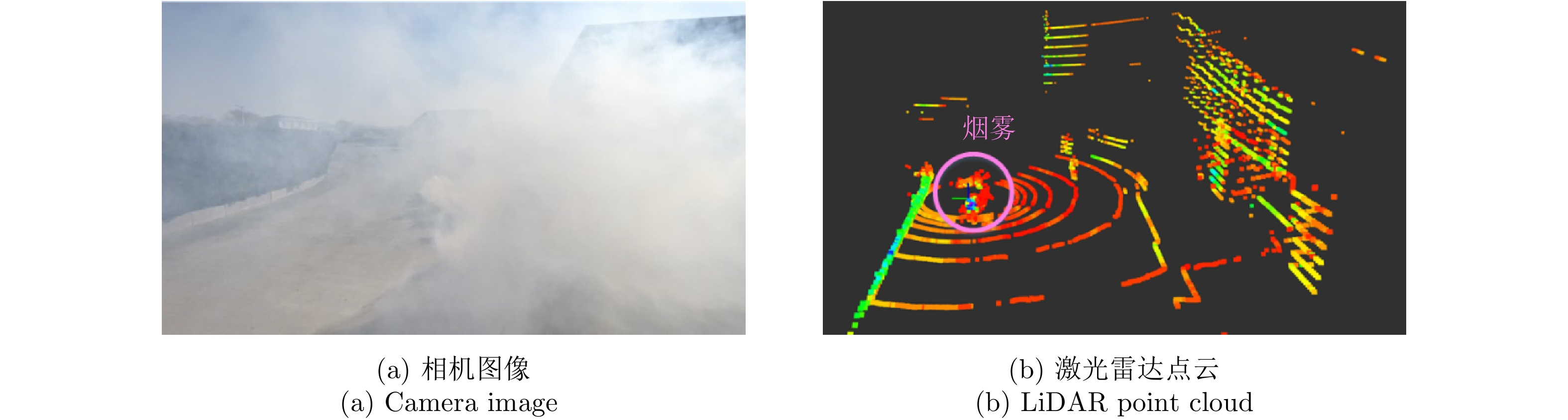
摘要: 基于多传感器融合感知是实现汽车智能驾驶的关键技术之一,已成为智能驾驶领域的热点问题。然而,由于毫米波雷达分辨率有限,且易受噪声、杂波、多径等因素的干扰,激光雷达易受天气的影响,现有的融合算法很难实现这两种传感器数据的精确融合,得到鲁棒的结果。针对智能驾驶中准确鲁棒的感知问题,该文提出了一种融合毫米波雷达和激光雷达鲁棒的感知算法。使用基于特征的两步配准的空间校正新方法,实现了三维激光点云和二维毫米波雷达点云精确的空间同步。使用改进的毫米波雷达滤波算法,减少了噪声、多径等对毫米波雷达点云的影响。然后根据该文提出的新颖的融合方法对两种传感器的数据进行融合,得到准确鲁棒的感知结果,解决了烟雾对激光性能影响的问题。最后,通过实际场景的实验测试,验证了该文算法的有效性和鲁棒性,即使在烟雾等极端环境中仍然能够实现准确和鲁棒的感知。使用该文融合方法建立的环境地图更加精确,得到的定位结果比使用单一传感器的定位误差减少了至少50%。Abstract: Multi-sensor fusion perception is one of the key technologies to realize intelligent automobile driving, and it has become a hot issue in the field of intelligent driving. However, because of the limited resolution of millimeter-wave radars, the interference of noise, clutter, and multipath, and the influence of weather on LiDAR, the existing fusion algorithm cannot easily achieve accurate fusion of the data of two sensors and obtain robust results. To address the problem of accurate and robust perception in intelligent driving, this study proposes a robust perception algorithm that combines millimeter-wave radar and LiDAR. Using a new method of spatial correction based on feature-based two-step registration, the precise spatial synchronization of the 3D LiDAR and 2D radar point clouds is realized. The improved millimeter-wave radar filtering algorithm is used to reduce the influence of noise and multipath on the radar point cloud. Then, according to the novel fusion method proposed in this study, the data of the two sensors are fused to obtain accurate and robust sensing results, which solves the problem of the influence of smoke on LiDAR performance. Finally, we conducted multiple sets of experiments in a real environment to verify the effectiveness and robustness of our method. Even in extreme environments such as smoke, we can still achieve accurate positioning and robust mapping. The environment map established by the fusion method proposed in this study is more accurate than that established by a single sensor. Moreover, the location error obtained can be reduced by at least 50%.
-
Key words:
- Intelligent driving /
- Robust perception /
- Multi-sensor fusion /
- Harsh environment /
- Millimeter-wave radar /
- LiDAR
-
表 1 毫米波雷达系统参数
Table 1. Millimeter wave radar system parameters
参数 值 频率(GHz) 92 带宽(GHz) 2 距离分辨率(m) 0.07 方位向波束宽度(°) 0.6 扫描范围(°) 0~360 -
[1] 李鑫. 面向汽车智能驾驶的毫米波雷达建模与仿真研究[D]. [博士论文], 吉林大学, 2020.LI Xin. Research on modeling and simulation of millimeter wave radar for vehicle intelligent driving[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Jilin University, 2020. [2] 马兴. 无人驾驶汽车中的几种重要传感器应用研究[J]. 数字技术与应用, 2020, 38(5): 107, 109. doi: 10.19695/j.cnki.cn12-1369.2020.05.62MA Xing. Application of several important sensors research on driver-less vehicles[J]. Digital Technology &Application, 2020, 38(5): 107, 109. doi: 10.19695/j.cnki.cn12-1369.2020.05.62 [3] 崔巍杰. 毫米波和激光雷达数据融合的SLAM算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2019.CUI Weijie. SLAM algorithm based on millimeter wave radar and lidar data fusion[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019. [4] YAMAUCHI B. Fusing ultra-wideband radar and lidar for small UGV navigation in all-weather conditions[C]. SPIE 7692, Unmanned Systems Technology XII, Orlando, United States, 2010: 76920O. doi: 10.1117/12.850386. [5] FRITSCHE P, KUEPPERS S, BRIESE G, et al. Radar and LiDAR sensorfusion in low visibility environments[C]. The 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, Lisbon, Portugal, 2016: 30–36. doi: 10.5220/0005960200300036. [6] FRITSCHE P, KUEPPERS S, BRIESE G, et al. Fusing LiDAR and radar data to perform SLAM in harsh environments[M]. MADANI K, PEAUCELLE D, and GUSIKHIN O. Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics. Cham: Springer, 2018: 177–189. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-55011-4_9. [7] FRITSCHE P and WAGNER B. Modeling structure and aerosol concentration with fused radar and LiDAR data in environments with changing visibility[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 2685–2690. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2017.8206093. [8] PRITSCHE P, ZEISE B, HEMME P, et al. Fusion of radar, LiDAR and thermal information for hazard detection in low visibility environments[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), Shanghai, China, 2017: 96–101. doi: 10.1109/SSRR.2017.8088146. [9] MARCK J W, MOHAMOUD A, HOUWEN E V, et al. Indoor radar SLAM a radar application for vision and GPS denied environments[C]. 2013 European Radar Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 2013: 471–474. [10] PARK Y S, KIM J, and KIM A. Radar localization and mapping for indoor disaster environments via multi-modal registration to prior LiDAR map[C]. 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 2019: 1307–1314. doi: 10.1109/IROS40897.2019.8967633. [11] WANG Xiao, XU Linhai, SUN Hongbin, et al. Bionic vision inspired on-road obstacle detection and tracking using radar and visual information[C]. 17th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Qingdao, China, 2014: 39–44. doi: 10.1109/ITSC.2014.6957663. [12] ALENCAR F A R, ROSERO L A, FILHO C M, et al. Fast metric tracking by detection system: Radar blob and camera fusion[C]. 2015 12th Latin American Robotics Symposium and 2015 3rd Brazilian Symposium on Robotics (LARS-SBR), Uberlandia, Brazil, 2015: 120–125. doi: 10.1109/LARS-SBR.2015.59. [13] HAN Siyang, WANG Xiao, XU Linhai, et al. Frontal object perception for Intelligent Vehicles based on radar and camera fusion[C]. 2016 35th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Chengdu, China, 2016: 4003–4008. doi: 10.1109/ChiCC.2016.7553978. [14] KIM J, HAN D S, and SENOUCI B. Radar and vision sensor fusion for object detection in autonomous vehicle surroundings[C]. 2018 Tenth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Prague, Czech Republic, 2018: 76–78. doi: 10.1109/ICUFN.2018.8436959. [15] HENG L. Automatic targetless extrinsic calibration of multiple 3D LiDARs and radars[C]. 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, USA, 2020: 10669–10675. doi: 10.1109/IROS45743.2020.9340866. [16] QIN Fei, LIU Yunlong, and LIANG Xingdong. A novel GOSD-CFAR for millimeter wave radar detection[C]. 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2020), Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 1782–1785. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9324693. [17] CRISTIANINI N, SHAWE-TAYLO J, 李国正, 王猛, 曾华军, 译. 支持向量机导论[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2004: 82–85.CRISTIANINI N and SHAWE-TAYLO J, LI Guozheng, WANG Meng, and ZENG Huajun. translation. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-based Learning Methods[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2004: 82–85. [18] DANG Xiangwei, RONG Zheng, and LIANG Xingdong. Sensor fusion-based approach to eliminating moving objects for SLAM in dynamic environments[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(1): 230. doi: 10.3390/s21010230 [19] DANG Xiangwei, LIANG Xingdong, LI Yanlei, et al. Moving objects elimination towards enhanced dynamic SLAM fusing LiDAR and mmW-radar[C]. 2020 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Linz, Austria, 2020: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICMIM48759.2020.9298986. [20] ZHANG Ji and SINGH S. Low-drift and real-time lidar odometry and mapping[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2017, 41(2): 401–416. doi: 10.1007/s10514-016-9548-2 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: