Multi-polarization Data Fusion Analysis of Full-Polarimetric Ground Penetrating Radar
-
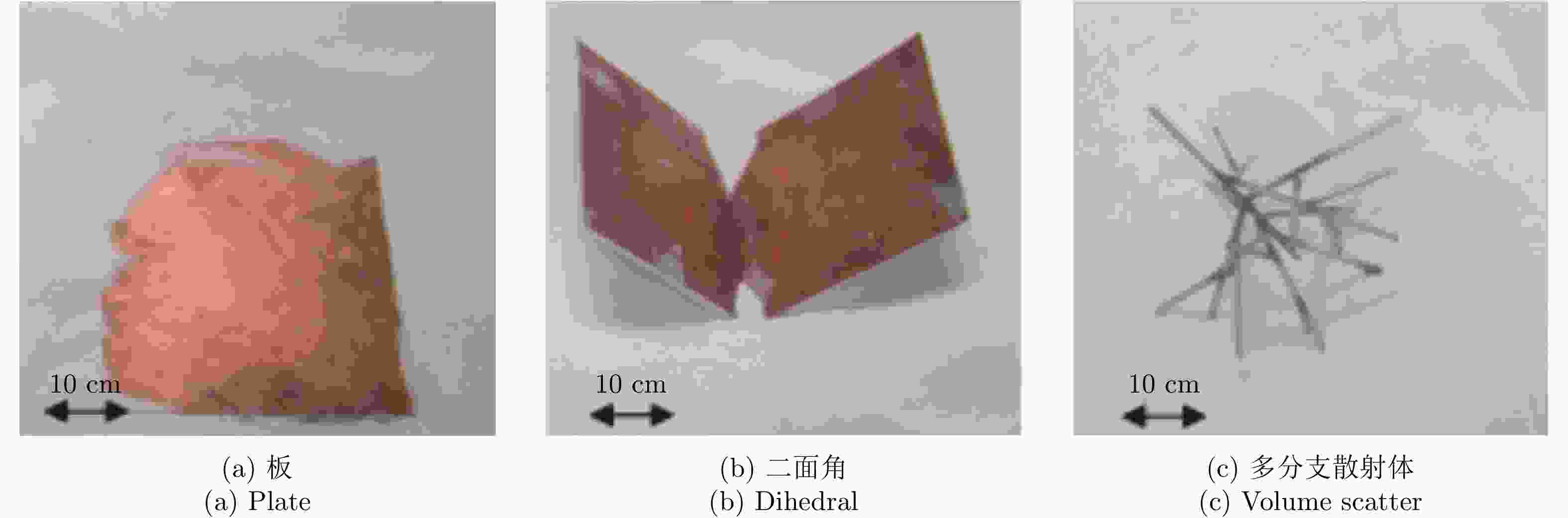
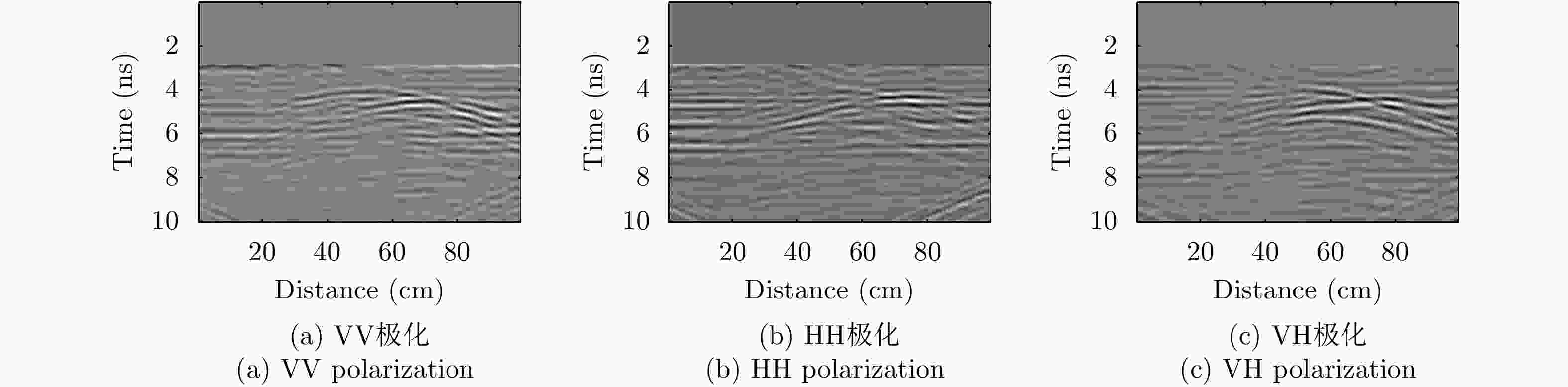
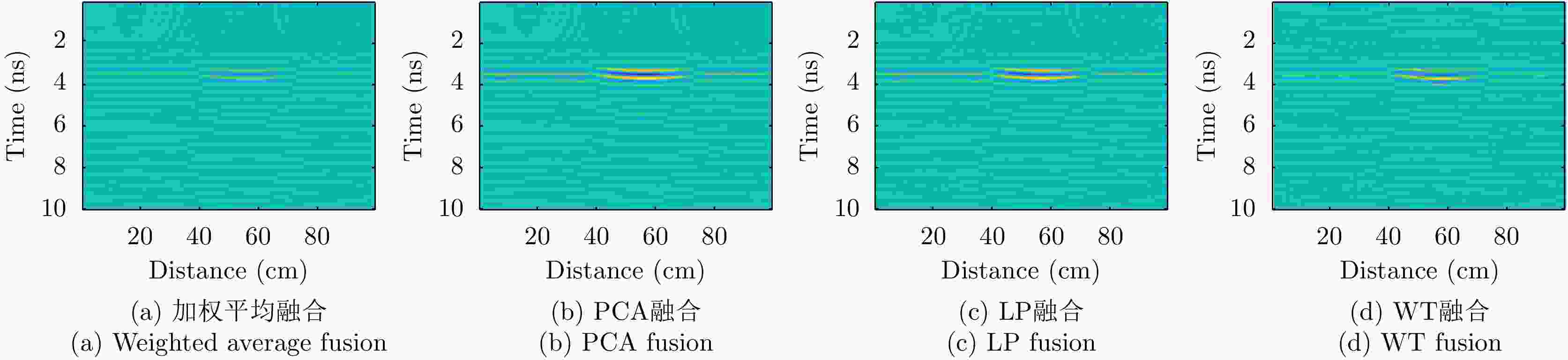
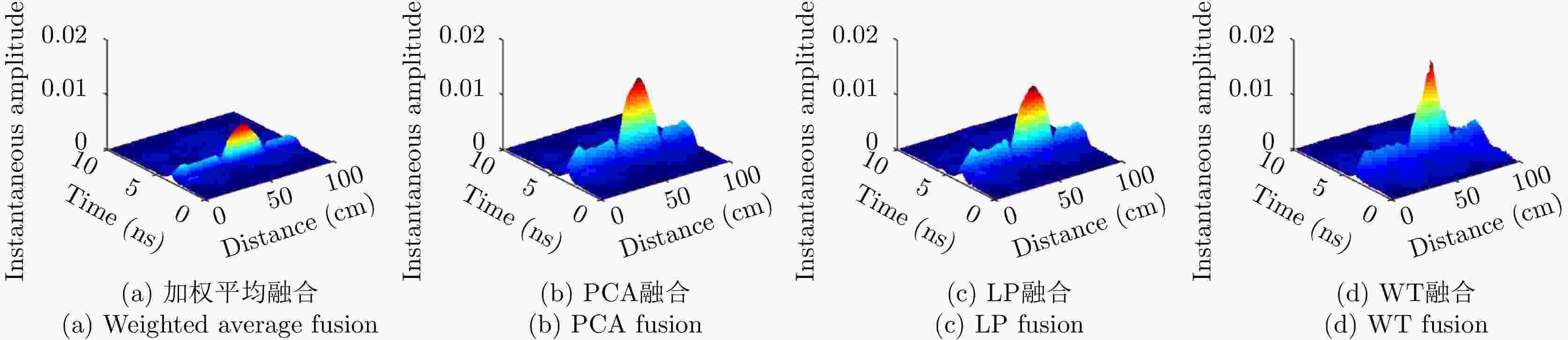
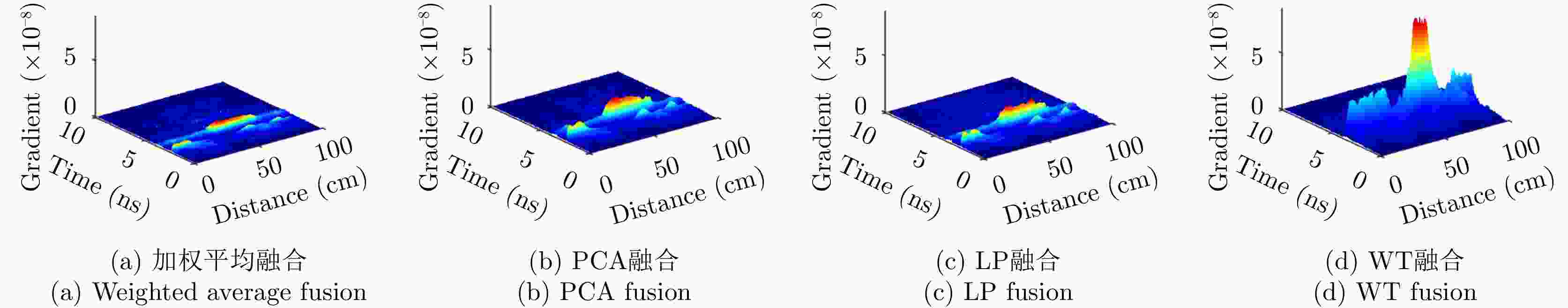
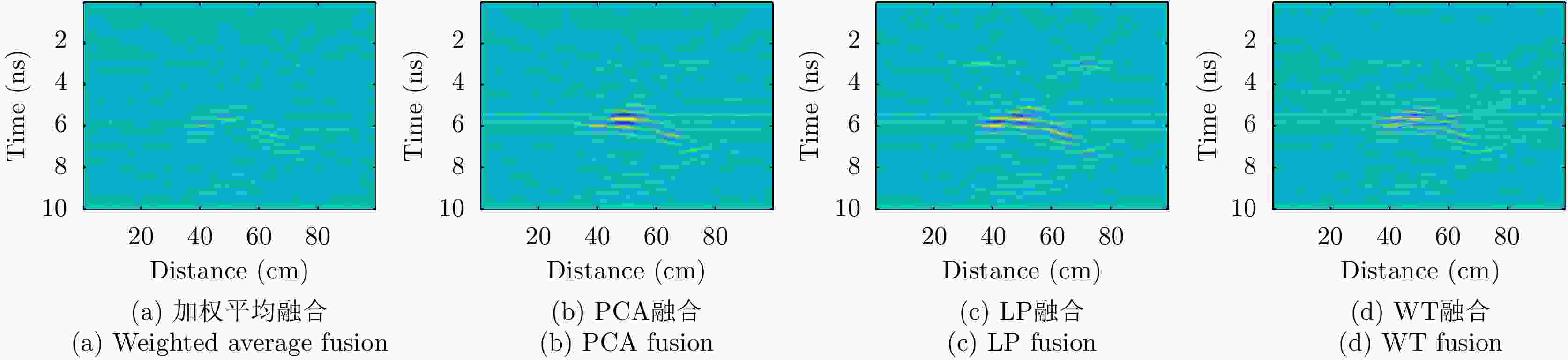
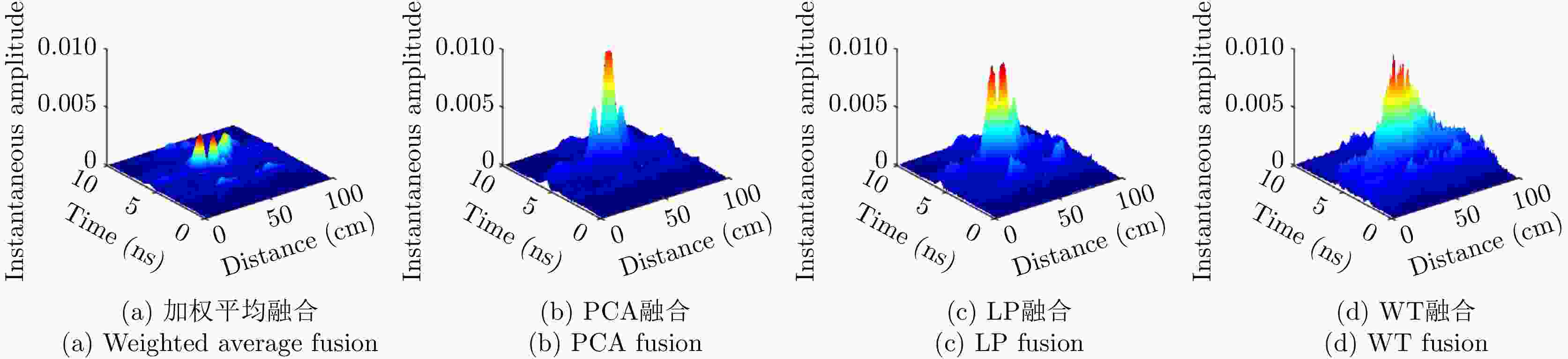
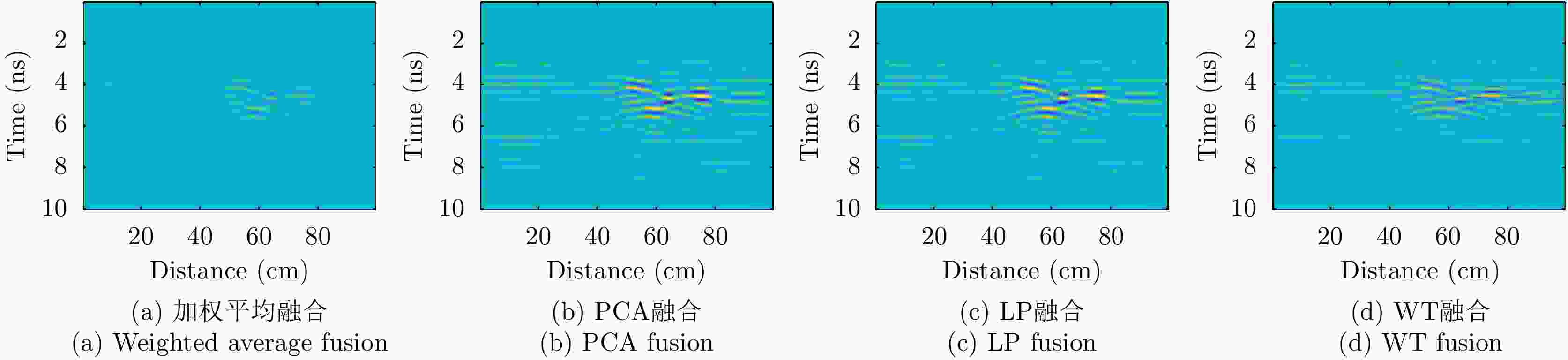
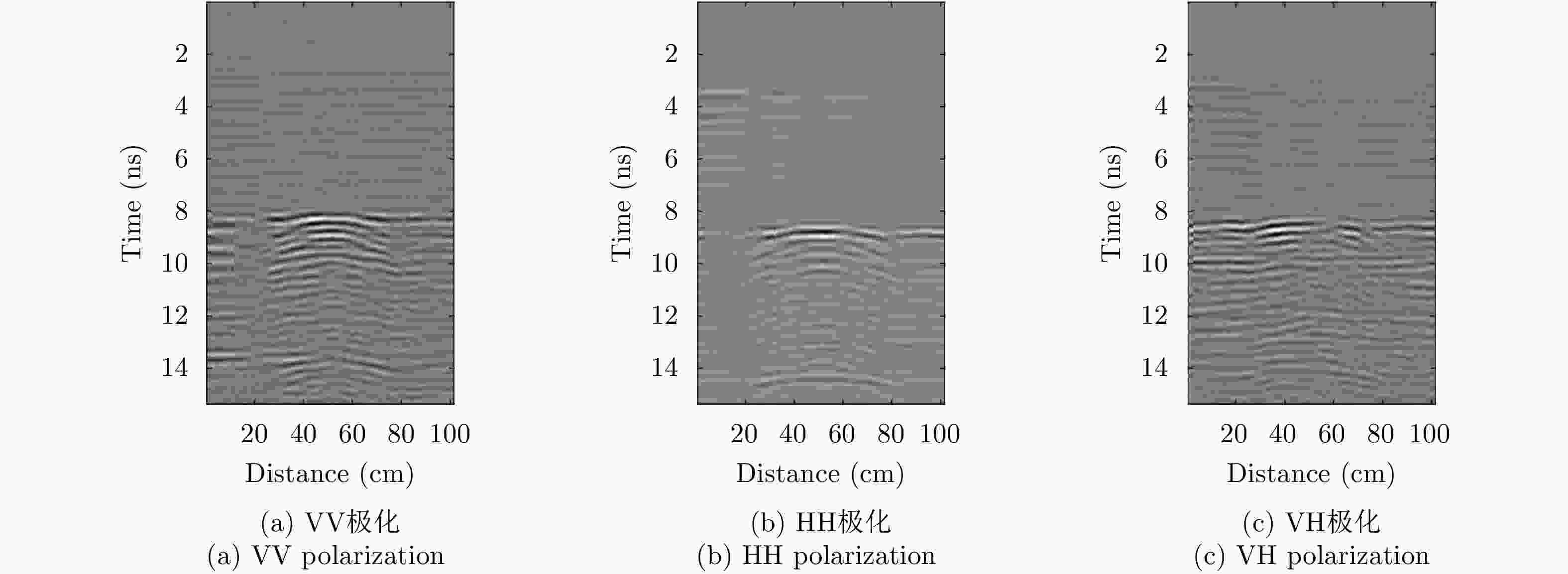
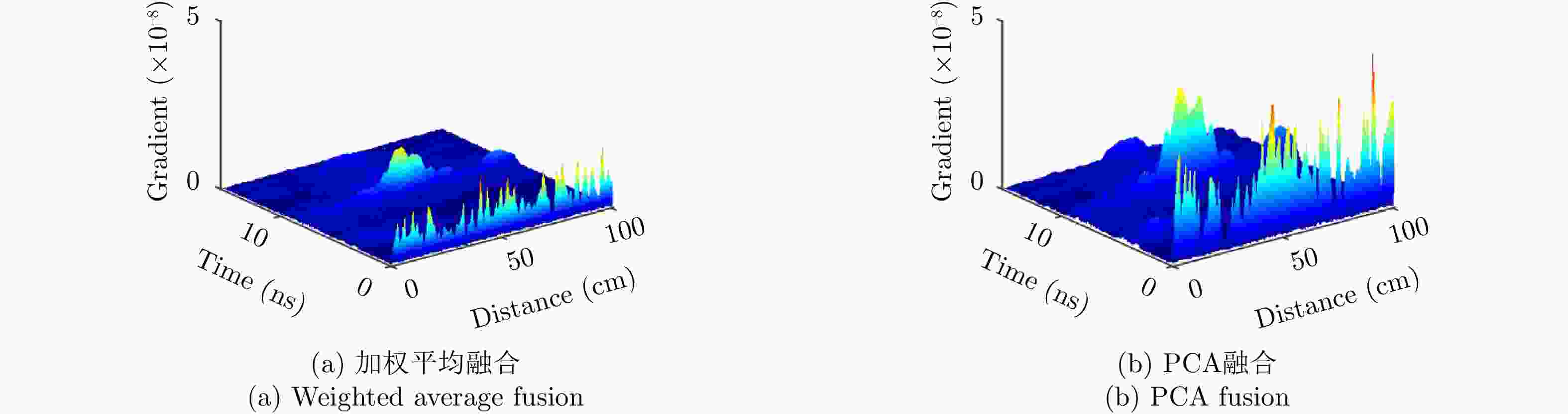
摘要: 对于相同地下目标体,相比大部分传统单极化探地雷达,全极化探地雷达(FP-GPR)可以测得更全面的极化数据,称为VV, HH, VH。为了对地下目标体进行更全面精细的成像和识别, 数据融合技术被应用于FP-GPR将3种不同极化模式的极化信息结合起来。然而,目前全极化探地雷达数据融合常用的加权平均融合方法,它会掩盖全极化的优点,同时也无法同时适应不同的散射机制。因此,该文提出了基于主成分分析(PCA),拉普拉斯金字塔(LP)以及多尺度小波变换(WT)的3种FP-GPR数据融合方法。为了检验几种数据融合方法的可靠性,该文在实验室分别测量了代表3种不同基本散射机制目标体的FP-GPR数据进行分析, 引入瞬时振幅为主、梯度为辅的方法将加权平均融合方法与3种方法进行比较。结果表明该研究所应用的3种数据融合方法效果均优于加权平均融合,并且3种方法可以分别适应不同散射机制的目标体,主成分分析融合可以更好的应用于未知散射机制目标体。最后,将主成分分析融合应用于实际冰裂缝数据成像,得到很好的融合效果,且优于加权平均融合方法。Abstract: Full-Polarimetric Ground Penetrating Radar (FP-GPR), compared to traditional single-polarimetric GPR, can obtain more comprehensive polarization data (such as VV, HH, and VH) for the same target. To ensure a more comprehensive targets’ image identification, data fusion technology is applied to FP-GPR so as to combine the polarization information of three different polarization modes. However, weighted average fusion is usually employed in FP-GPR data fusion, since it masks the advantages of full polarization and is unable to simultaneously adapt to different target scattering mechanisms. Based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Laplacian Pyramid (LP), and multi-scale Wavelet Transform (WT), this research proposes three FP-GPR data fusion methods. To check the reliability of several data fusion methods, we obtained FP-GPR data representing three different target scattering mechanisms in the laboratory and, then, compared the weighted average fusion method with the other three methods using instantaneous amplitude and gradient. The result shows that the three methods were better than the weighted average fusion and that they can be adapted to different target scattering mechanisms. However, PCA was used to fuse the unknown target scattering mechanisms. Finally, PCA fusion is applied to actual ice fracture data imaging, as it produces a better fusion effect than that of weighted average fusion.
-
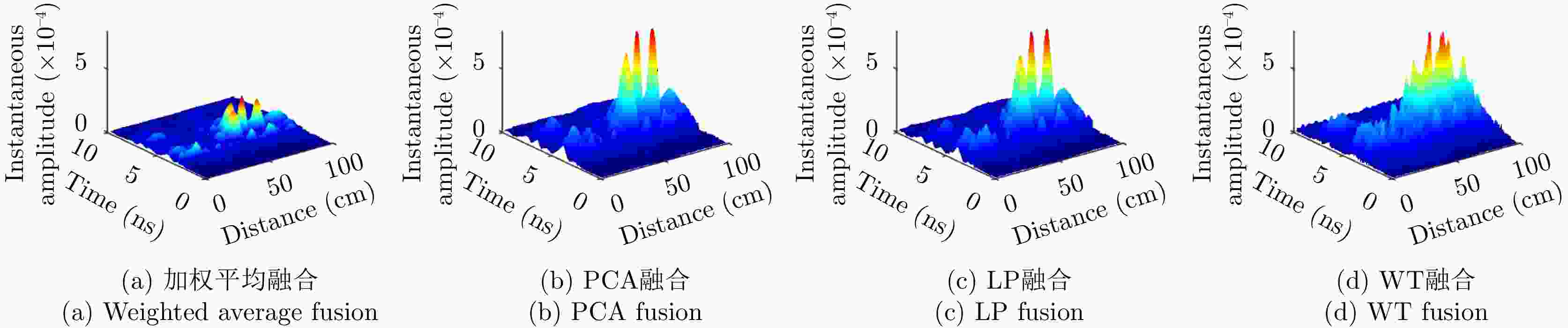
表 1 瞬时振幅最大值
Table 1. Max of instantaneous amplitude
目标体 加权平均 PCA LP WT 板 0.0066 0.0150 0.0134 0.0183 二面角 0.0031 0.0119 0.0094 0.0100 多分支散射体 3.0135×10–4 8.707×10-4 8.6279×10–4 8.7215×10–4 表 2 梯度最大值
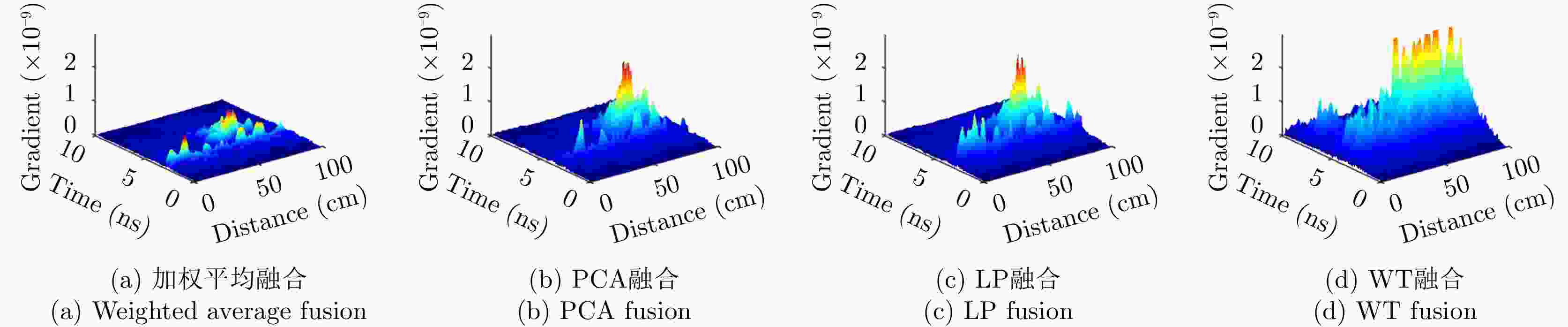
Table 2. Max of gradient
目标体 加权平均 PCA LP WT 板 8.8737×10–9 2.0838×10–8 1.9288×10–9 9.5532×10–8 二面角 9.0147×10–9 1.6597×10–8 3.5484×10–8 6.0511×10–8 多分支散射体 9.0209×10–10 2.3254×10–9 2.4932×10–9 3.8864×10–9 -
[1] KANG M S, KIM N, IM S B, et al. 3D GPR image-based UcNet for enhancing underground cavity detectability[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(21): 2545. doi: 10.3390/rs11212545 [2] GABALLAH M, GRASMUECK M, and SATO M. Characterizing subsurface archaeological structures with full resolution 3D GPR at the early dynastic foundations of Saqqara Necropolis, Egypt[J]. Sensing and Imaging, 2018, 19(1): 23. doi: 10.1007/s11220-018-0209-8 [3] SATO M and LU Q. Ground water migration monitoring by GPR[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, Canada, 2002: 345–347. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2002.1025035. [4] FENG Xuan and SATO M. Pre-stack migration applied to GPR for landmine detection[J]. Inverse Problems, 2004, 20(6): S99–S115. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/20/6/S07 [5] CHENG Siyuan, LIU Sixin, GUO Jingxue, et al. Data processing and interpretation of antarctic ice-penetrating radar based on variational mode decomposition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(10): 1253. doi: 10.3390/rs11101253 [6] HU Bin, WANG Deli, ZHANG Ling, et al. Rock location and quantitative analysis of regolith at the Chang’e 3 landing site based on local similarity constraint[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(5): 530. doi: 10.3390/rs11050530 [7] FENG Xuan, YU Yue, LIU Cai, et al. Subsurface polarimetric migration imaging for full polarimetric ground-penetrating radar[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2015, 202(2): 1324–1338. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv208 [8] FENG Xuan, YU Yue, LIU Cai, et al. Combination of H-alpha decomposition and migration for enhancing subsurface target classification of GPR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(9): 4852–4861. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2411572 [9] FENG Xuan, LIANG Wenjing, LIU Cai, et al. Application of freeman decomposition to full polarimetric GPR for improving subsurface target classification[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 132: 284–292. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.07.030 [10] 李玲玲. 像素级图像融合方法与应用[M]. 兰州: 甘肃人民出版社, 2006.LI Lingling. Pixel-Level Image Fusion Method and Application[M]. Lanzhou: Gansu People’s Publishing House, 2006. [11] DAILY M I, FARR T, ELACHI C, et al. Geologic interpretation from composited radar and Landsat imagery[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 1979, 45(8): 1109–1116. [12] ABIDI M A and GONZALEZ R C. Data Fusion in Robotics and Machine Intelligence[M]. Boston: Academic Press, 1992: 1–546. [13] HILL D, EDWARDS P, and HAWKES D. Fusing medical images[J]. Image Processing, 1994, 6(2): 22–24. [14] POHL C and VAN GENDEREN J L. Review article Multisensor image fusion in remote sensing: Concepts, methods and applications[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1998, 19(5): 823–854. doi: 10.1080/014311698215748 [15] DING Ji, LIU Qiang, BAI Mingxuan, et al. A multisensor data fusion method based on gaussian process model for precision measurement of complex surfaces[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(1): 278. doi: 10.3390/s20010278 [16] WAN Tao, ZHU Chenchen, and QIN Zengchang. Multifocus image fusion based on robust principal component analysis[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2013, 34(9): 1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2013.03.003 [17] JOSE C. A fast, on-line algorithm for PCA and its convergence characteristics[J]. IEEE, Transactions on Neural Network, 2000, 4(2): 299–307. [18] PEARSON K. LIII. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space[J]. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, 1901, 2(11): 559–572. doi: 10.1080/14786440109462720 [19] SAFAYANI M, MANZURI SHALMANI M T, and KHADEMI M. Extended two-dimensional PCA for efficient face representation and recognition[C]. 2008 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing, Cluj-Napoca, 2008: 295–298. doi: 10.1109/ICCP.2008.4648390. [20] HADRI A, CHOUGDALI K, and TOUAHNI R. Intrusion detection system using PCA and Fuzzy PCA techniques[C]. 2016 International Conference on Advanced Communication Systems and Information Security, Marrakesh, Morocco, 2016: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ACOSIS.2016.7843930. [21] QIU Changzhen, REN Hao, ZOU Huanxin, et al. Performance comparison of target classification in SAR images based on PCA and 2D-PCA features[C]. 2009 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xi’an, China, 2009: 868–871. doi: 10.1109/APSAR.2009.5374193. [22] ADELSON E H, ADELSON C H, BERGEN J R, et al. Pyramid methods in image processing[J]. RCA Engineer, 1984, 29(6): 33–41. [23] BURT P and ADELSON E. The Laplacian pyramid as a compact image code[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1983, 31(4): 532–540. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1983.1095851 [24] MAO Run, FU Xiansong, NIU Pingjuan, et al. Multi-directional laplacian pyramid image fusion algorithm[C]. 2018 3rd International Conference on Mechanical, Control and Computer Engineering, Huhhot, China, 2018: 568–572. doi: 10.1109/ICMCCE.2018.00125. [25] LIANG Pei, XIE Zhiwei, and DAI Jiguang. Joint edge detector based on Laplacian pyramid[C]. 2010 3rd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Yantai, China, 2010: 978–982. doi: 10.1109/CISP.2010.5646931. [26] MALLAT S G. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: The wavelet representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1989, 11(7): 674–693. doi: 10.1109/34.192463 [27] KUMAR K, MUSTAFA N, LI Jianping, et al. Image edge detection scheme using wavelet transform[C]. 2014 11th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Actiev Media Technology and Information Processing, Chengdu, China, 2014: 261–265. doi: 10.1109/ICCWAMTIP.2014.7073404. [28] LIU Qingliang, YANG Shuguo, LIU Jing, et al. A discrete wavelet transform and singular value decomposition-based digital video watermark method[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2020, 85: 273–293. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.04.015 [29] TAŞMAZ H. Dual tree complex wavelet transform based speech enhancement[C]. 2015 23nd Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference, Malatya, Turkey, 2015: 823–826. doi: 10.1109/SIU.2015.7129955. [30] 梁文婧, 冯晅, 刘财, 等. 多输入多输出极化步进频率探地雷达硬件系统开发[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2018, 48(2): 483–490. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20170254LIANG Wenjing, FENG Xuan, LIU Cai, et al. Development of multiple-input and multiple-output polarimetric stepped-frequency ground penetrating radar system[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2018, 48(2): 483–490. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20170254 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: