| [1] |
CHEN C C and ANDREWS H C. Target-motion-induced radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1980, AES-16(1): 2–14. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1980.308873
|
| [2] |
白雪茹. 空天目标逆合成孔径雷达成像新方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2011.BAI Xueru. Study on new techniques for ISAR imaging of aerospace targets[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2011.
|
| [3] |
CAMP W W, MAYHAN J T, and O’DONNELL R M. Wideband radar for ballistic missile defense and range-Doppler imaging of satellites[J]. Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 2000, 12(2): 267–280.
|
| [4] |
高敬坤. 阵列三维成像及雷达增强成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2018.GAO Jingkun. Research on array-based 3D imaging and enhanced radar imaging techniques[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2018.
|
| [5] |
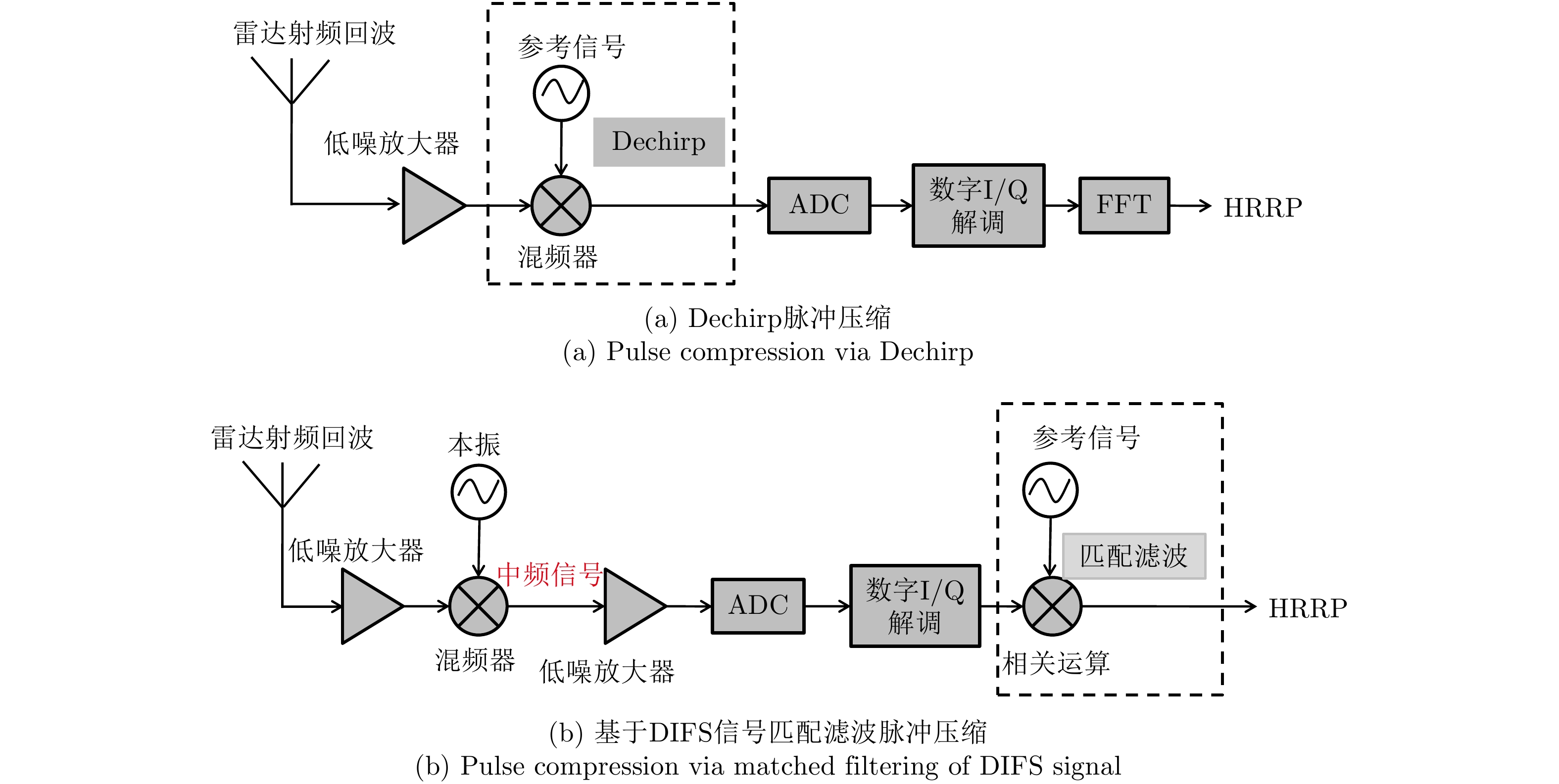
文树梁, 袁起, 秦忠宇. 宽带线性调频信号Stretch处理误差获取与补偿[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2005, 27(1): 36–39, 184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2005.01.011WEN Shuliang, YUAN Qi, and QIN Zhongyu. Error acquisition and compensation for wideband linear frequency modulated signal Stretch processing[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2005, 27(1): 36–39, 184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2005.01.011
|
| [6] |
林钱强, 张月, 陈曾平. 宽带雷达STRETCH处理系统失真补偿新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(6): 1477–1483. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01357LIN Qianqiang, ZHANG Yue, and CHEN Zengping. A new compensation method of system distortion in wideband radar STRETCH processing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(6): 1477–1483. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01357
|
| [7] |
Liu Yang, HOU Qingkai, XU Shiyou, et al. System distortion analysis and compensation of DIFS signals for wideband imaging radar[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(2): 020304.
|
| [8] |
HU Pengjiang, XU Shiyou, and WU Wenzhen. Adaptive compensation for wideband radar system distortion based on cross range profiles[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2019, 13(1): 014520.
|
| [9] |
杨剑, 许人灿, 鲍庆龙, 等. 基于熵最小准则的ISAR成像高速运动补偿实现方法[J]. 信号处理, 2009, 25(12): 1861–1866. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.12.007YANG Jian, XU Rencan, BAO Qinglong, et al. The implemental methods of high velocity compensation in ISAR imaging based on entropy minimization[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 25(12): 1861–1866. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.12.007
|
| [10] |
黄小红, 邱兆坤, 王伟. 目标高速运动对宽带一维距离像的影响及补偿方法研究[J]. 信号处理, 2002, 18(6): 487–490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2002.06.001HUANG Xiaohong, QIU Zhaokun, and WANG Wei. Research on effect of wideband range profile imaging and compensating method for target moving with high velocity[J]. Signal Processing, 2002, 18(6): 487–490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2002.06.001
|
| [11] |
刘爱芳, 朱晓华, 刘中. 基于修正离散Chirp-Fourier变换的高速目标ISAR距离像补偿[J]. 航空学报, 2004, 25(5): 495–498. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2004.05.015LIU Aifang, ZHU Xiaohua, LIU Zhong. ISAR range profile compensation of fast-moving target using modified discrete Chirp-Fourier transform[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2004, 25(5): 495–498. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2004.05.015
|
| [12] |
李文臣, 王雪松, 王国玉. 机动目标一维距离像RAT法线性化补偿[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2008, 30(5): 38–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2008.05.009LI Wenchen, WANG Xuesong, and WANG Guoyu. Linear compensation of range profile of maneuvering target via radon-ambiguity transform (RAT)[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2008, 30(5): 38–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2008.05.009
|
| [13] |
WOOD J C and BARRY D T. Linear signal synthesis using the Radon-Wigner transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(8): 2105–2111. doi: 10.1109/78.301845
|
| [14] |
TIAN Biao, CHEN Zengping, XU Shiyou, et al. ISAR imaging compensation of high speed targets based on integrated cubic phase function[C]. SPIE 8917, MIPPR 2013: Multispectral Image Acquisition, Processing, and Analysis, Wuhan, China, 2013.
|
| [15] |
曹敏. 空间目标高分辨雷达成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2008.CAO Min. Research on high resolution radar imaging technology for space targets[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2008.
|
| [16] |
TIAN Biao, LU Zhejun, LIU Yongxiang, et al. High velocity motion compensation of IFDS data in ISAR imaging based on adaptive parameter adjustment of matched filter and entropy minimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 34272–34278. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2850055
|
| [17] |
李晋. 太赫兹雷达系统总体与信号处理方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2010.LI Jin. Research on terahertz radar system and its signal processing[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2010.
|
| [18] |
刘磊. 逆合成孔径雷达二维及三维成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2016.LIU Lei. Study of two-dimensional and three-dimensional inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging methods[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2016.
|
| [19] |
刘磊, 周峰, 陶明亮, 等. 太赫兹逆合成孔径雷达相位误差分析和补偿方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(6): 1469–1474. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132506.1469LIU Lei, ZHOU Feng, TAO Mingliang, et al. Method of phase error analysis and compensation for terahertz inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(6): 1469–1474. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132506.1469
|
| [20] |
SHAO Shuai, ZHANG Lei, LIU Hongwei, et al. Spatial-variant contrast maximization autofocus algorithm for ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2019, 62(4): 40303. doi: 10.1007/s11432-018-9707-2
|
| [21] |
林钱强, 唐鹏飞, 陈曾平. 宽带雷达中频直接采样与高速存储系统设计与实现[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(3): 283–291. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20054LIN Qianqiang, TANG Pengfei, and CHEN Zengping. Design and implementation of direct IF sampling and high-speed storage system for wideband radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(3): 283–291. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20054
|
| [22] |
LIN Qianqiang, CHEN Zengping, ZHANG Yue, et al. Coherent phase compensation method based on direct IF sampling in wideband radar[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2013, 136: 753–764. doi: 10.2528/PIER12122203
|
| [23] |
林钱强, 郭芳, 陈曾平. ISAR成像的相参多普勒质心跟踪相位补偿方法[J]. 信号处理, 2013, 29(8): 1036–1042. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2013.08.017LIN Qianqiang, GUO Fang, and CHEN Zengping. Coherent DCT phase compensation method for ISAR imaging[J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 29(8): 1036–1042. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2013.08.017
|
| [24] |
LIN Jianzhi, LI Weixing, ZHANG Yue, et al. A method for range alignment based on coherent echoes by wideband radar[C]. The 2012 4th International Conference on Signal Processing Systems, Singapore, 2012: 143–147.
|
| [25] |
袁斌. 空天微动目标逆合成孔径雷达成像关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2014.YUAN Bin. Research on inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of aerospace targets with micro-motions[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2014.
|
| [26] |
LIU Yang, CHEN Zengping, LI Na, et al. Wideband radar imaging for space debris based on direct IF sampling signals[C]. SPIE 9250, Electro-Optical Remote Sensing, Photonic Technologies, and Applications VIII; and Military Applications in Hyperspectral Imaging and High Spatial Resolution Sensing II, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2014.
|
| [27] |
HU Jiemin, ZHOU Wei, FU Yaowen, et al. Uniform rotational motion compensation for ISAR based on phase cancellation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 636–640. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2098841
|
| [28] |
WANG Yong and JIANG Yicheng. A novel algorithm for estimating the rotation angle in ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 608–609. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2000955
|
| [29] |
MARTORELLA M. Novel approach for ISAR image cross-range scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(1): 281–294. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4517004
|
| [30] |
ZHANG W C, CHEN Z P, and YUAN B. Rotational motion compensation for wide-angle ISAR imaging based on integrated cubic phase function[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 2013: 14–16.
|
| [31] |
LIU Yang, ZOU Jiangwei, XU Shiyou, et al. Nonparametric rotational motion compensation technique for high-resolution ISAR imaging via golden section search[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2014, 36: 67–76. doi: 10.2528/PIERM14031905
|
| [32] |
PARK S H, KIM H T, and KIM K T. Cross-range scaling algorithm for ISAR images using 2-D Fourier transform and polar mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(2): 868–877. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2060731
|
| [33] |
YEH C M, XU Jia, PENG Yingning, Wang X T. Cross-range scaling for ISAR based on image rotation correlation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(3): 597–601. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2021990
|
| [34] |
LI J, QIU C W, ZHANG L, et al. Time-frequency imaging algorithm for highspeed spinning targets in two dimensions[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(6): 806–817.
|
| [35] |
句彦伟, 于力, 王洋. 基于时频分析的ISAR瞬时成像算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2009, 31(7): 46–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2009.07.010JU Yanwei, YU Li, and WANG Yang. ISAR instantaneous imaging algorithm based on time-freuqency analysis[J]. Modern Radar, 2009, 31(7): 46–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2009.07.010
|
| [36] |
BARBAROSSA S and LEMOINE O. Analysis of nonlinear FM signals by pattern recognition of their time-frequency representation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 1996, 3(4): 112–115. doi: 10.1109/97.489064
|
| [37] |
LI J and LING H. Application of adaptive chirplet representation for ISAR feature extraction from targets with rotating parts[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(4): 284. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030729
|
| [38] |
邢孟道. 基于实测数据的雷达成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2002.XING Mengdao. Study of radar imaging methods based on real data[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2002.
|
| [39] |
FAN Lijie, SHI Si, LIU Yang, et al. A novel range-instantaneous-Doppler ISAR imaging algorithm for maneuvering targets via adaptive Doppler spectrum extraction[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research C, 2015, 56: 109–118. doi: 10.2528/PIERC14122501
|
| [40] |
ZHENG Jibin, SU Tao, ZHANG Long, et al. ISAR imaging of targets with complex motion based on the chirp rate-quadratic chirp rate distribution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(11): 7276–7289. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2310474
|
| [41] |
ZHENG Jibin, SU Tao, ZHU Wentao, et al. ISAR imaging of targets with complex motions based on the keystone time-chirp rate distribution[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(7): 1275–1279. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2291992
|
| [42] |
LI Yanyan, SU Tao, ZHENG Jibin, et al. ISAR imaging of targets with complex motions based on modified Lv’s distribution for cubic phase signal[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(10): 4775–4784. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2460734
|
| [43] |
WANG Yong, XU Rongqing, ZHANG Qingxiang, et al. ISAR Imaging of maneuvering target based on the quadratic frequency modulated signal model with time-varying amplitude[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(3): 1012–1024. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2622721
|
| [44] |
WANG Yong, KANG Jian, and JIANG Yicheng. ISAR imaging of maneuvering target based on the local polynomial wigner distribution and Integrated high-order ambiguity function for cubic phase signal model[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(7): 2971–2991. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2301158
|
| [45] |
WANG Yong, RONG Jiajia, and HAN Tao. Novel approach for high resolution ISAR/InISAR sensors imaging of maneuvering target based on peak extraction technique[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(14): 5541–5558. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2905246
|
| [46] |
ZHENG Jibin, LIU Hongwei, LIAO Guisheng, et al. ISAR imaging of targets with complex motions based on a noise-resistant parameter estimation algorithm without nonuniform axis[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(8): 2509–2518. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2516040
|
| [47] |
BORISON S L, BOWLING S B, and CUOMO K M. Super-resolution methods for wideband radar[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1992, 5(3): 441–461.
|
| [48] |
ODENDAAL J W, BARNARD E, and PISTORIUS C W I. Two-dimensional superresolution radar imaging using the MUSIC algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1994, 42(10): 1386–1391. doi: 10.1109/8.320744
|
| [49] |
RAO B D and HARI K V S. Performance analysis of root-music[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(12): 1939–1949. doi: 10.1109/29.45540
|
| [50] |
WANG Yuanxun and LING Hao. A frequency-aspect extrapolation algorithm for ISAR image simulation based on two-dimensional ESPRIT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(4): 1743–1748. doi: 10.1109/36.851973
|
| [51] |
LOPEZ-DEKKER P and MALLORQUI J J. Capon- and APES-based SAR processing: Performance and practical considerations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(5): 2388–2402. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2038902
|
| [52] |
BARANIUK R and STEEGHS P. Compressive radar imaging[C]. 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, USA, 2007: 128–133.
|
| [53] |
ENDER J H G. On compressive sensing applied to radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 90(5): 1402–1414. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.11.009
|
| [54] |
白婷. 基于压缩感知的ISAR成像方法[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2014.BAI Ting. ISAR imaging based on compressive sensing[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2014.
|
| [55] |
张龙, 张磊, 邢孟道. 一种基于改进压缩感知的低信噪比ISAR高分辨成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(9): 2263–2267. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01135ZHANG Long, ZHANG Lei, and XING Mengdao. A new method of high resolution ISAR imaging under low SNR based on improved compressive sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(9): 2263–2267. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01135
|
| [56] |
GAO Jingkun, DENG Bin, QIN Yuliang, et al. Enhanced radar imaging using a complex-valued convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(1): 35–39. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2866567
|
| [57] |
QIN Dan and GAO Xunzhang. Enhancing ISAR resolution by a generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, in press. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2965743.
|
| [58] |
GAO Xunzhang, QIN Dan, and GAO Jingkun. Resolution enhancement for inverse synthetic aperture radar images using a deep residual network[J]. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2020, 62(4): 1588–1593. doi: 10.1002/mop.32186
|
| [59] |
YE Jiaqi, QIN Dan, ZHANG Yifan, et al. RBM-based joint dictionary learning for ISAR resolution enhancement[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(11): 7907–7911.
|
| [60] |
刘洋. 空间目标高分辨ISAR成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2015.LIU Yang. Research on key technology of high-resolution and precision radar imaging of space targets[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2015.
|
| [61] |
呼鹏江. 空天目标逆合成孔径雷达精细成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2018.HU Pengjiang. Study on inverse synthetic aperture radar fine imaging of aerospace targets[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2018.
|
| [62] |
许志伟, 张磊, 邢孟道. 基于特征配准的ISAR图像方位定标方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(9): 2173–2179. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01590XU Zhiwei, ZHANG Lei, and XING Mengdao. A novel cross-range scaling algorithm for ISAR images based on feature registration[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(9): 2173–2179. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01590
|
| [63] |
WANG Yong, XU Zhuo, LIU Qiuchen, et al. Novel approach for ISAR cross-range scaling of maneuvering target[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(22): 10409–10418. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2926759
|
| [64] |
ZHANG Lingxiao, WANG Baoshun, and HE Sisanl. Cross-range scaling for net-worked radar ISAR based on image rotation matching[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2015, 37(4): 796–801.
|
| [65] |
SUN Sibo, ZHANG Xinyu, ZHANG Guangpu, et al. Accurate ISAR scaling for both smooth and maneuvering targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(3): 1537–1549. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2895717
|
| [66] |
ZHANG Shuanghui, LIU Yongxiang, LI Xiang, et al. Fast ISAR cross-range scaling using modified newton method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(3): 1355–1367. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2785560
|
| [67] |
张昆帆, 裴喜龙, 党同心, 等. 基于频谱包络自相关的ISAR转角估计方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2014, 36(8): 1511–1516. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.08.11ZHANG Kunfan, PEI Xilong, DANG Tongxin, et al. Estimating method for the rotation angle of ISAR image based on spectral envelope correlation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(8): 1511–1516. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.08.11
|
| [68] |
管志强, 杨学岭, 刘硕, 等. 一种基于自调焦的ISAR图像增强方法[P]. 中国, CN109685747A, 2019.GUAN Zhiqiang, YANG Xueling, LIU Shuo, et al. An ISAR image enhancement method based on self-focusing[P]. CN, CN109685747A, 2019.
|
| [69] |
LIU Yang, LI Gang, SHI Si, et al. ISAR image visualization for aerospace targets[C]. SPIE 11428, MIPPR 2019: Multispectral Image Acquisition, Processing, and Analysis, Wuhan, China, 2020: 1142805. doi: 10.1117/12.2538204.
|
| [70] |
李刚. 基于序列ISAR像的空间目标结构分析[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2016.LI Gang. Research on key technology of structure analysis for space targets based on ISAR sequences[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2016.
|
| [71] |
MARTORELLA M, PALMER J, BERIZZI F, et al. Polarimetric ISAR autofocusing[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2008, 2(3): 312–324. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr:20070121
|
| [72] |
MARTORELLA M, CANTINI L, BERIZZI F, et al. Optimised image autofocusing for polarimetric ISAR[C]. The 2006 14th European Signal Processing Conference, Florence, Italy, 2006.
|
| [73] |
MARTORELLA M, BERIZZI F, PALMER J, et al. Image contrast and entropy based autofocusing for polarimetric ISAR[C]. 2007 International Waveform Diversity and Design Conference, Pisa, Italy, 2007: 245–249.
|
| [74] |
MARTORELLA M, PALMER J, BATES B, et al. Polarimetric hot spot processing for ISAR image autofocusing[C]. 2007 IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Edinburgh, UK, 2007: 1–5. doi: 10.1049/cp: 20070576.
|
| [75] |
MARTORELLA M, CACCIAMANO A, GIUSTI E, et al. CLEAN technique for polarimetric ISAR[J]. International Journal of Navigation and Observation, 2008, 2008: 325279.
|
| [76] |
WU Min, ZHANG Lei, XIA Xianggen, et al. Phase adjustment for polarimetric ISAR with compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(4): 1592–1606. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.150078
|
| [77] |
LIU Yang, LI Gang, TIAN Biao, et al. ISAR imaging at low SNR level based on polarimetric whitening filter[C]. SPIE 8917, MIPPR 2013: Multispectral Image Acquisition, Processing, and Analysis, Wuhan, China, 2013.
|
| [78] |
LIN Jianzhi, ZHANG Yue, LI Weixing, et al. Maximum likelihood-based range alignment for polarimetric inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 8(2): 185–193. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2016.1249297
|
| [79] |
HU Pengjiang, LIU Yang, TIAN Biao, et al. Time division in a pulse polarimetric radar based ISAR fusion imaging technique[C]. 2014 International Conference on Audio, Language and Image Processing, Shanghai, China, 2014: 556–560.
|
| [80] |
CUOMO K M, PIOU J E, and MAYHAN J T. Ultra-wideband coherent processing[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1997, 10(2): 203–222.
|
| [81] |
ZHANG Huanhuan and CHEN Rushan. Coherent processing and superresolution technique of multi-band radar data based on fast sparse Bayesian learning algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(12): 6217–6227. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2361158
|
| [82] |
TIAN Biao, CHEN Zengping, and XU Shiyou. Sparse subband fusion imaging based on parameter estimation of geometrical theory of diffraction model[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(4): 318–326.
|
| [83] |
ZOU Yongqiang, GAO Xunzhang, LI Xiang, et al. A matrix pencil algorithm based multiband iterative fusion imaging method[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 19440. doi: 10.1038/srep19440
|
| [84] |
BAI Xueru, ZHOU Feng, WANG Qi, et al. Sparse subband imaging of space targets in high-speed motion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(7): 4144–4154. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2227756
|
| [85] |
TIAN Jihua, SUN Jinping, WANG Guohua, et al. Multiband radar signal coherent fusion processing with IAA and apFFT[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(5): 463–466. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2251631
|
| [86] |
邹永强. 空间目标多频段ISAR融合成像关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2016.ZOU Yongqiang. Research on multiband ISAR fusion imaging for space target[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2016.
|
| [87] |
MA Juntao, GAO Meiguo, XIA Mingfei, et al. High-resolution ISAR imaging with sparse subband based on waveform fusion dictionary[C]. The 2017 7th IEEE International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication, Macau, China, 2017: 385–390.
|
| [88] |
ZHANG Ying, WANG Tingjing, ZHAO Huapeng, et al. Multiple radar subbands fusion algorithm based on support vector regression in complex noise environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(1): 381–392. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2769135
|
| [89] |
ZHOU Feng and BAI Xueru. High-resolution sparse subband imaging based on bayesian learning with hierarchical priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4568–4580. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2827072
|
| [90] |
YE Fan, HE Feng, and Sun Zaoyu. Radar signal level fusion imaging[C]. IEEE International Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS 2008, Boston, USA, 2008.
|
| [91] |
HU Pengjiang, XU Shiyou, WU Wenzhen, et al. Sparse subband ISAR imaging based on autoregressive model and smoothed ℓ0 algorithm[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(22): 9315–9323. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2869832
|
| [92] |
LI Liya, YUAN Weiming, LIU Hongwei, et al. Radar automatic target recognition based on InISAR images[C]. The 2007 1st Asian and Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Huangshan, China, 2007: 497–502.
|
| [93] |
ZHANG Long, SU Tao, LIU Zheng, et al. High resolution ISAR imaging in receiver centered region area in bistatic radar[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2013, 2013: 50. doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2013-50
|
| [94] |
MA Changzheng, Yeo T S, GUO Qiang, et al. Bistatic ISAR imaging incorporating interferometric 3-D imaging technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(10): 3859–3867. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2186304
|
| [95] |
沈阳, 陈永光, 李修和, 等. 多基地雷达反隐身分布式检测融合算法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2007, 35(3): 506–510. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.03.025SHEN Yang, CHEN Yongguang, LI Xiuhe, et al. Study on fusion arithmetic of multi radar distributed detection system against stealthy targets[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 35(3): 506–510. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.03.025
|
| [96] |
高昭昭. 高分辨ISAR成像新技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2009.GAO Zhaozhao. New technologies of high resolution ISAR imaging[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2009.
|
| [97] |
MARTORELLA M. Bistatic ISAR image formation in presence of bistatic angle changes and phase synchronisation errors[C]. The 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008.
|
| [98] |
CHEN V C and MARTORELLA M. Bistatic ISAR[M]. CHEN V C and MARTORELLA M. Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging: Principles, Algorithms and Applications. New York: SciTech Publishing Inc, 2014.
|
| [99] |
董健, 尚朝轩, 高梅国, 等. 双基地ISAR成像平面研究及目标回波模型修正[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(8): 1855–1862. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00706DONG Jian, SHANG Chaoxuan, GAO Meiguo, et al. The image plane analysis and echo model amendment of bistatic ISAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(8): 1855–1862. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00706
|
| [100] |
董健, 尚朝轩, 高梅国, 等. 空间目标双基地ISAR成像的速度补偿研究[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2010, 5(1): 78–85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2010.01.016DONG Jian, SHANG Chaoxuan, GAO Meiguo, et al. Research on bistatic ISAR speed compensation of space target[J]. Journal CAEIT, 2010, 5(1): 78–85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2010.01.016
|
| [101] |
郭宝锋, 尚朝轩, 高梅国, 等. 机动目标双基地ISAR越距离单元徙动校正算法[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2014, 29(4): 562–569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2014.04.011GUO Baofeng, SHANG Chaoxuan, GAO Meiguo, et al. Correction algorithm of migration through resolution cells in bistatic ISAR of maneuvering target[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition &Processing, 2014, 29(4): 562–569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2014.04.011
|
| [102] |
赵会朋, 王俊岭, 高梅国, 等. 基于轨道误差搜索的双基地ISAR包络对齐算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(6): 1235–1243. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.06.08ZHAO Huipeng, WANG Junling, GAO Meiguo, et al. Bistatic ISAR envelope alignment algorithm based on orbit error search[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(6): 1235–1243. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.06.08
|
| [103] |
WANG Feng, XU Feng, and JIN Yaqiu. Simulation of multi-station ISAR imaging for monitoring a space target: A case of Envisat[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017.
|
| [104] |
许志伟. ISAR图像的特征提取及应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2014.XU Zhiwei. A study of feature extraction and applications using inverse synthetic aperture radar images[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2014.
|
| [105] |
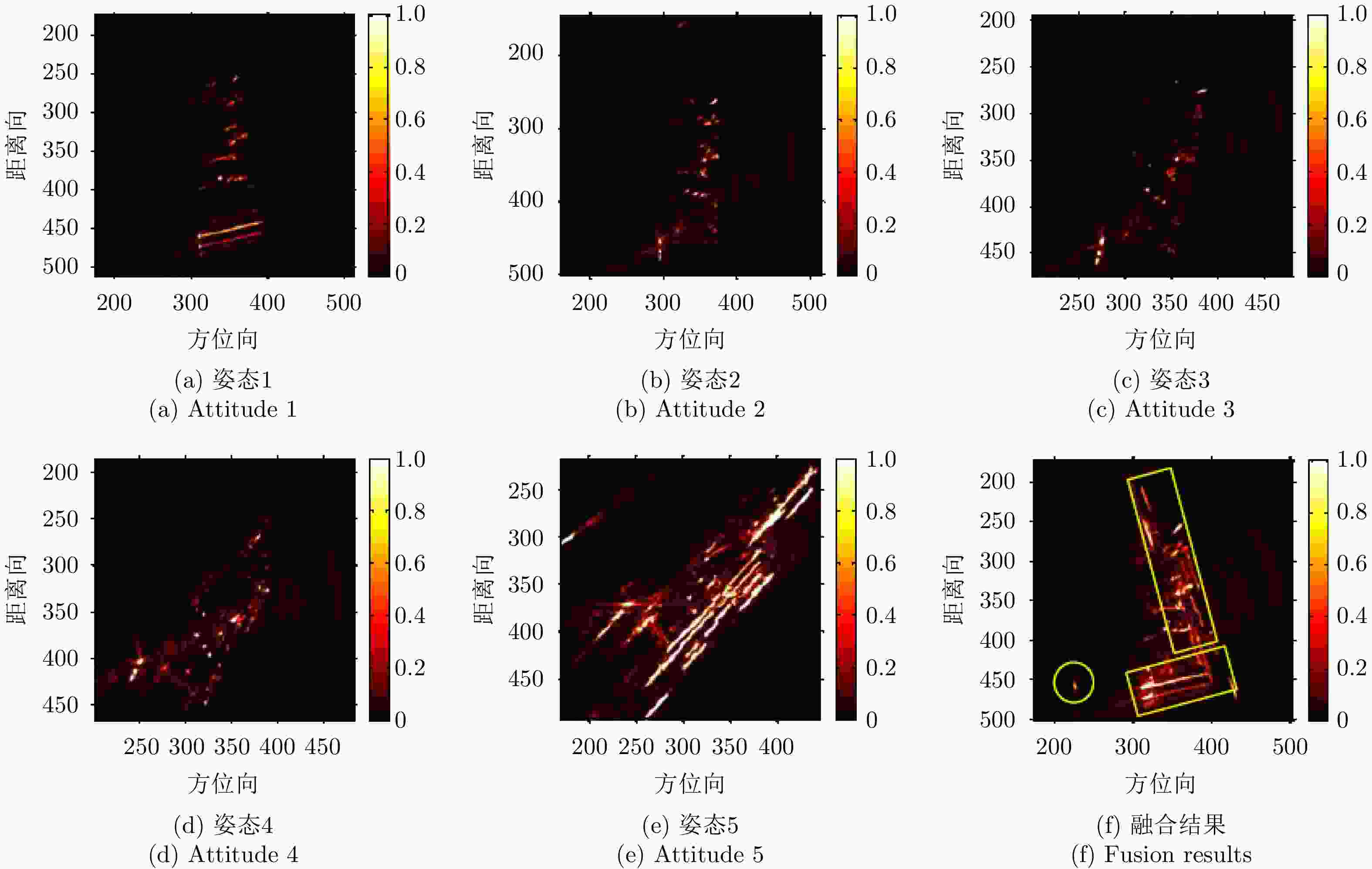
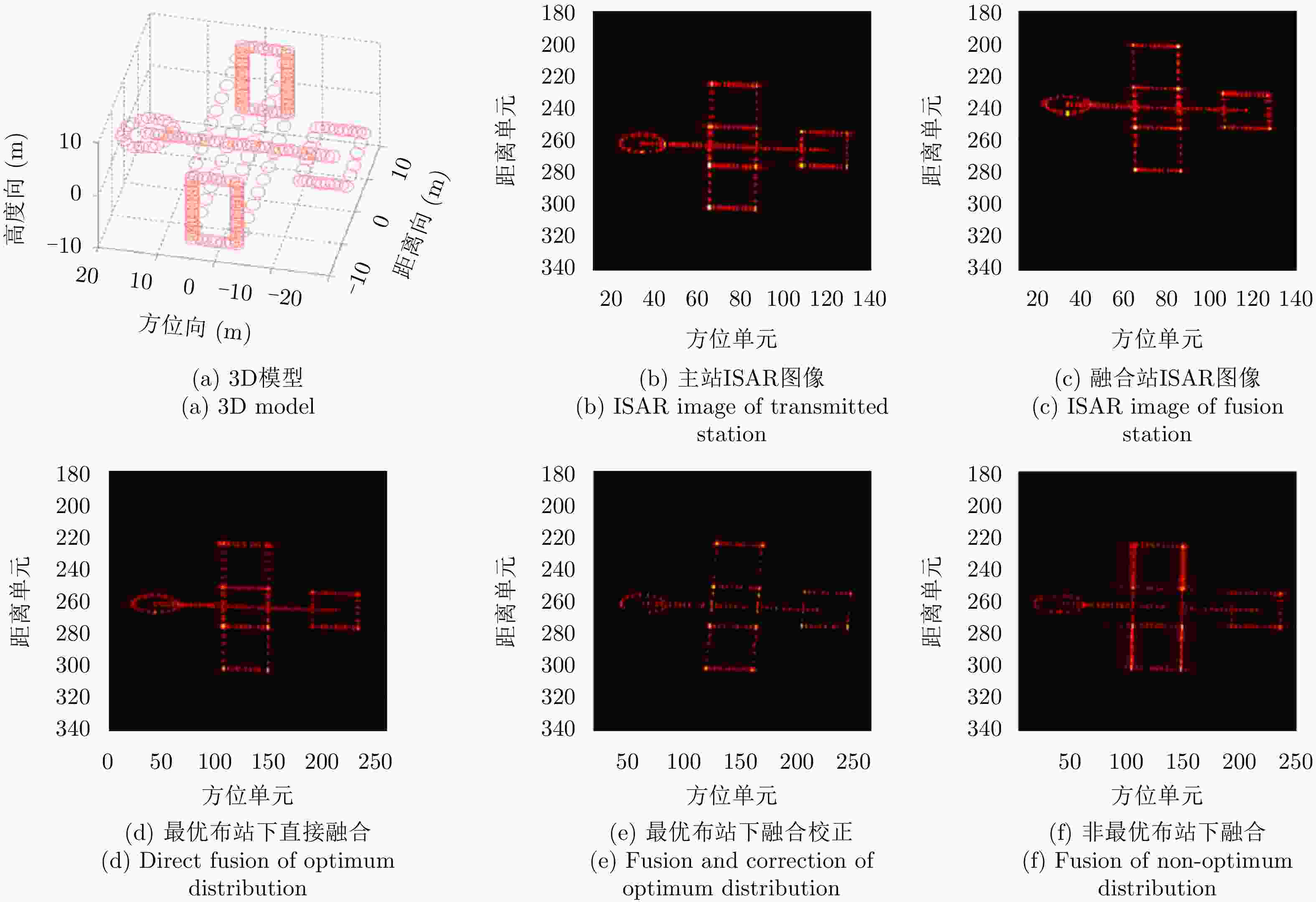
马俊涛, 高梅国, 胡文华, 等. 空间目标多站ISAR优化布站与融合成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(12): 2834–2843. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170482MA Juntao, GAO Meiguo, HU Wenhua, et al. Optimum distribution of multiple location ISAR and multi-angles fusion imaging for space target[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(12): 2834–2843. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170482
|
| [106] |
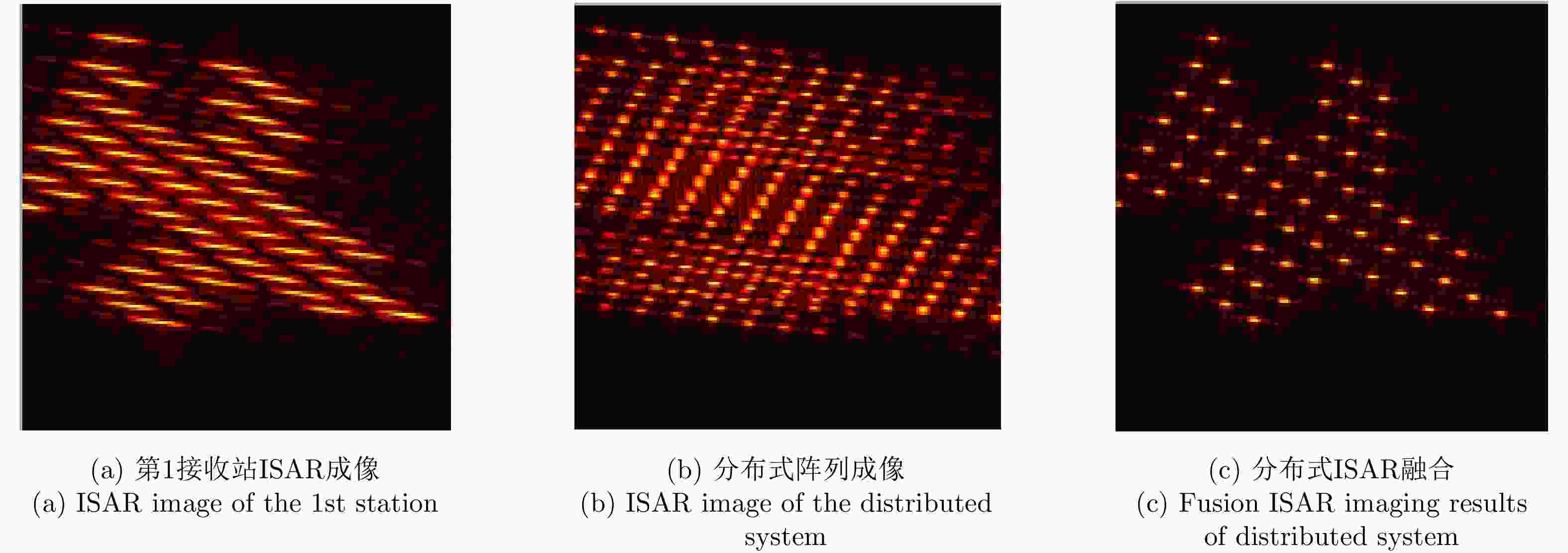
王锐. 分布式全相参雷达参数估计及ISAR成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京理工大学, 2015.WANG Rui. Research on parameter estimation and ISAR imaging for distributed coherent radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015.
|
| [107] |
李军, 全英汇, 邢孟道, 等. 基于和差波束的三维ISAR成像技术[J]. 电波科学学报, 2010, 25(2): 281–286.LI Jun, QUAN Yinghui, XING Mengdao, et al. 3-D ISAR imaging technology based on sum-diff beam[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2010, 25(2): 281–286.
|
| [108] |
马长征, 张守宏. 超分辨在单脉冲雷达三维成像中的应用[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 1999, 26(3): 379–382.MA Changzheng and ZHANG Shouhong. Applications of super-resolution signal processing on monopulse radar three dimensional imaging[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1999, 26(3): 379–382.
|
| [109] |
MAYHAN J T, BURROWS M L, CUOMO K M, et al. High resolution 3D “snapshot” ISAR imaging and feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(2): 630–642. doi: 10.1109/7.937474
|
| [110] |
BHALLA R and LING Hao. Three-dimensional scattering center extraction using the shooting and bouncing ray technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1996, 44(11): 1445–1453. doi: 10.1109/8.542068
|
| [111] |
任双桥, 刘永祥, 黎湘, 等. 基于多姿态角下一维距离像的雷达目标三维成像[J]. 电子学报, 2005, 33(6): 1088–1090. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2005.06.032REN Shuangqiao, LIU Yongxiang, LI Xiang, et al. Radar target 3-D imaging based on multi-aspect range profiles[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2005, 33(6): 1088–1090. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2005.06.032
|
| [112] |
罗斌凤, 张群, 袁涛, 等. InISAR三维成像中的ISAR像失配准分析及其补偿方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 30(6): 739–743.LUO Binfeng, ZHANG Qun, YUAN Tao, et al. Analysis and compensation of mismatching between two ISAR images in interferometric inverse synthetic aperture radar 3-D imaging[J]. Journal of Xidian University:Natural Science, 2003, 30(6): 739–743.
|
| [113] |
张群, 马长征, 张涛, 等. 干涉式逆合成孔径雷达三维成像技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2001, 23(9): 890–898.ZHANG Qun, MA Changzheng, ZHANG Tao, et al. Research on 3-D imaging technique for interferometric inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2001, 23(9): 890–898.
|
| [114] |
肖志河, 戴朝明, 巢增明, 等. 旋转目标干涉逆合成孔径三维成像技术[J]. 电子学报, 1999, 27(12): 19–22.XIAO Zhihe, DAI Chaoming, CHAO Zengming, et al. INISAR 3-D imaging technique for rotating targets[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1999, 27(12): 19–22.
|
| [115] |
WANG Genyuan, XIA Xianggen, and CHEN V C. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets using three receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(3): 436–447. doi: 10.1109/83.908519
|
| [116] |
TIAN Biao, LIU Yang, XU Shiyou, et al. Interferometric inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging for space targets based on wideband direct sampling using two antennas[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2014, 8(1): 083599. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.8.083599
|
| [117] |
马长征, 张守宏. 舰船目标单脉冲雷达三维成像技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2000, 22(3): 385–391.MA Changzheng and ZHANG Shouhong. Three-dimensional imaging technique of ship targets with monopulse radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2000, 22(3): 385–391.
|
| [118] |
黎海林, 丁磊. 单脉冲三维成像试验研究[J]. 飞行器测控学报, 2010, 29(3): 74–78.LI Hailin and DING Lei. Research on monopulse 3-D imaging tests[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT &C Technology, 2010, 29(3): 74–78.
|
| [119] |
WANG Shanhu, YOU Hongjian, and FU Kun. BFSIFT: a novel method to find feature matches for SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4): 649–653. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645
|
| [120] |
左潇丽, 朱岱寅, 李俊强. 基于特征匹配的空间目标ISAR图像横向定标[J]. 电子设计工程, 2017, 25(18): 74–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2017.18.018ZUO Xiaoli, ZHU Daiyin, and LI Junqiang. ISAR image cross-range scaling for space target based on feature registration[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2017, 25(18): 74–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2017.18.018
|
| [121] |
YANG Shan, JIANG Weidong, and TIAN Biao. ISAR image matching and 3D reconstruction based on improved SIFT method[C]. 2019 International Conference on Electronic Engineering and Informatics, Nanjing, China, 2019.
|
| [122] |
DI Guohui, SU Fulin, YANG Hongxin, et al. ISAR image scattering center association based on speeded-up robust features[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(7): 5065–5082.
|
| [123] |
王昕, 郭宝锋, 尚朝轩. 基于二维ISAR图像序列的雷达目标三维重建方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(10): 2475–2480. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01534WANG Xin, GUO Baofeng, and Shang Chaoxuan. 3D reconstruction of target geometry based on 2D data of inverse synthetic aperture radar images[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(10): 2475–2480. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01534
|
| [124] |
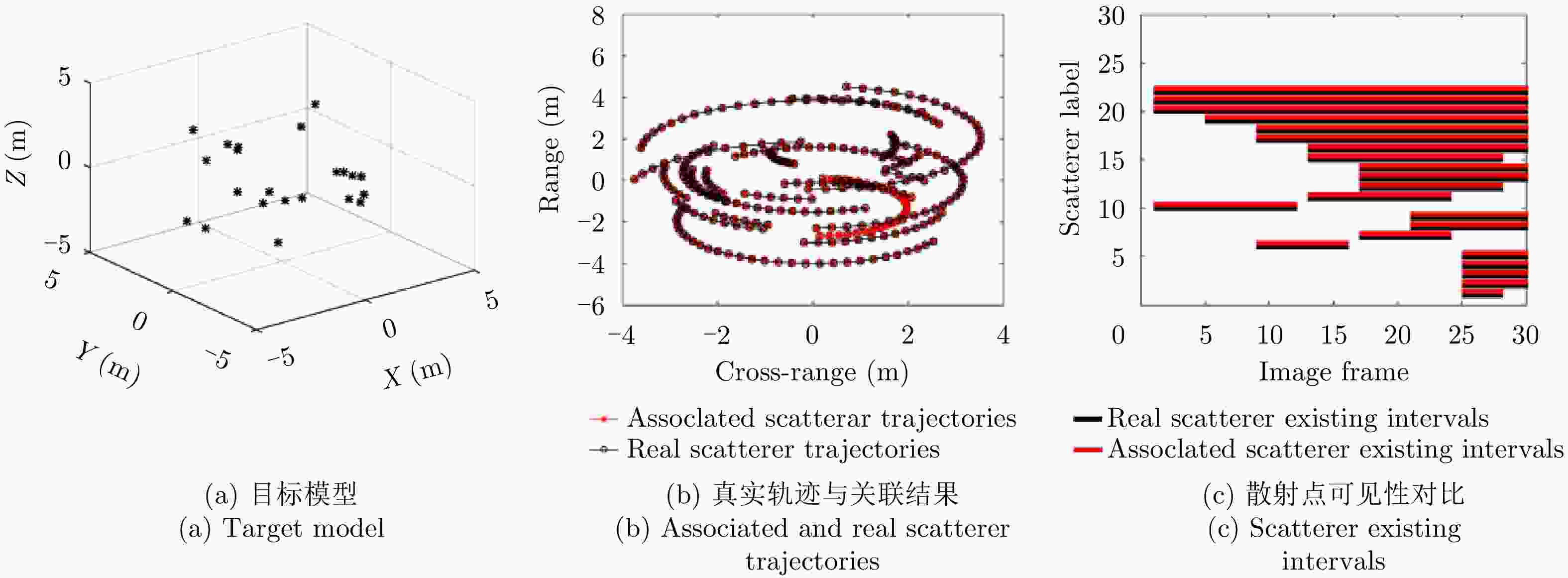
LIU Lei, ZHOU Feng, and BAI Xueru. Method for scatterer trajectory association of sequential ISAR images based on Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(12): 1535–1542.
|
| [125] |
毕严先, 魏少明, 王俊, 等. 基于多假设跟踪的散射点关联和三维重构方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(6): 1219–1227.BI Yanxian, WEI Shaoming, WANG Jun, et al. New method of scatterers association and 3D reconstruction based on multi-hypothesis tracking[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(6): 1219–1227.
|
| [126] |
孙静, 尚社, 许家栋. 基于双重隐马尔科夫模型的ISAR图像序列中散射中心关联算法[J]. 空间电子技术, 2013, 10(1): 48–52, 68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2013.01.010SUN Jing, SHANG She, and XU Jiadong. Scatters correlation from ISAR image sequences based on double hidden Markov model[J]. Space Electronic Technology, 2013, 10(1): 48–52, 68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2013.01.010
|
| [127] |
ZHOU Yejian, ZHANG Lei, CAO Yunhe, et al. Attitude estimation and geometry reconstruction of satellite targets based on ISAR image sequence interpretation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(4): 1698–1711. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2875503
|
| [128] |
刘烽, 许家栋. 雷达目标三维特征的提取与识别研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2005, 27(1): 18–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2005.01.006LIU Feng and XU Jiadong. Research on target identification with ISAR image sequence[J]. Modern Radar, 2005, 27(1): 18–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2005.01.006
|
| [129] |
SU Fulin, LU Jing, and SU Yuan. A method of 3-D image reconstruction of target based on ISAR image sequences[C]. The 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 2012: 123–126.
|
| [130] |
彭石宝, 许稼, 彭应宁, 等. 基于逆合成孔径雷达图像序列的目标三维重建[J]. 航空兵器, 2010, (6): 37–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5048.2010.06.009PENG Shibao, XU Jia, PENG Yingning, et al. Three-dimensional target reconstruction with inverse synthetic aperture radar image sequence[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2010, (6): 37–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5048.2010.06.009
|
| [131] |
TOMASI C and KANADE T. Shape and motion from image streams under orthography: A factorization method[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1992, 9(2): 137–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00129684
|
| [132] |
MCFADDEN F E. Three-dimensional reconstruction from ISAR sequences[C]. SPIE 4744, Radar Sensor Technology and Data Visualization, Orlando, USA, 2002: 58–67.
|
| [133] |
WANG Feng, XU Feng, and JIN Yaqiu. Three-dimensional reconstruction from a multiview sequence of sparse ISAR imaging of a space target[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(2): 611–620. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2737988
|
| [134] |
LI Gang, ZOU Jiangwei, XU Shiyou, et al. A method of 3D reconstruction via ISAR Sequences based on scattering centers association for space rigid object[C]. SPIE 9252, Millimetre Wave and Terahertz Sensors and Technology VII, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2014.
|
| [135] |
杨山. 基于ISAR图像序列的目标三维重构技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科技大学, 2019.YANG Shan. Research on target three-dimensional reconstruction based on ISAR image sequences[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2019.
|
| [136] |
ZHOU Yejian, ZHANG Lei, XING Chao, et al. Target three-dimensional reconstruction from the multi-view radar image sequence[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 36722–36735. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2905130
|
| [137] |
FORRESTER N T. Surface reconstruction from interferometric ISAR data[D]. [Master dissertation], Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2014.
|
| [138] |
LIU Yabo, SONG Mingcong, WU Kun, et al. High-quality 3-D InISAR imaging of maneuvering target based on a combined processing approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(5): 1036–1040. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2227935
|
| [139] |
WU Wenzhen, HU Pengjiang, XU Shiyou, et al. Image registration for InISAR based on joint translational motion compensation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(10): 1597–1603.
|
| [140] |
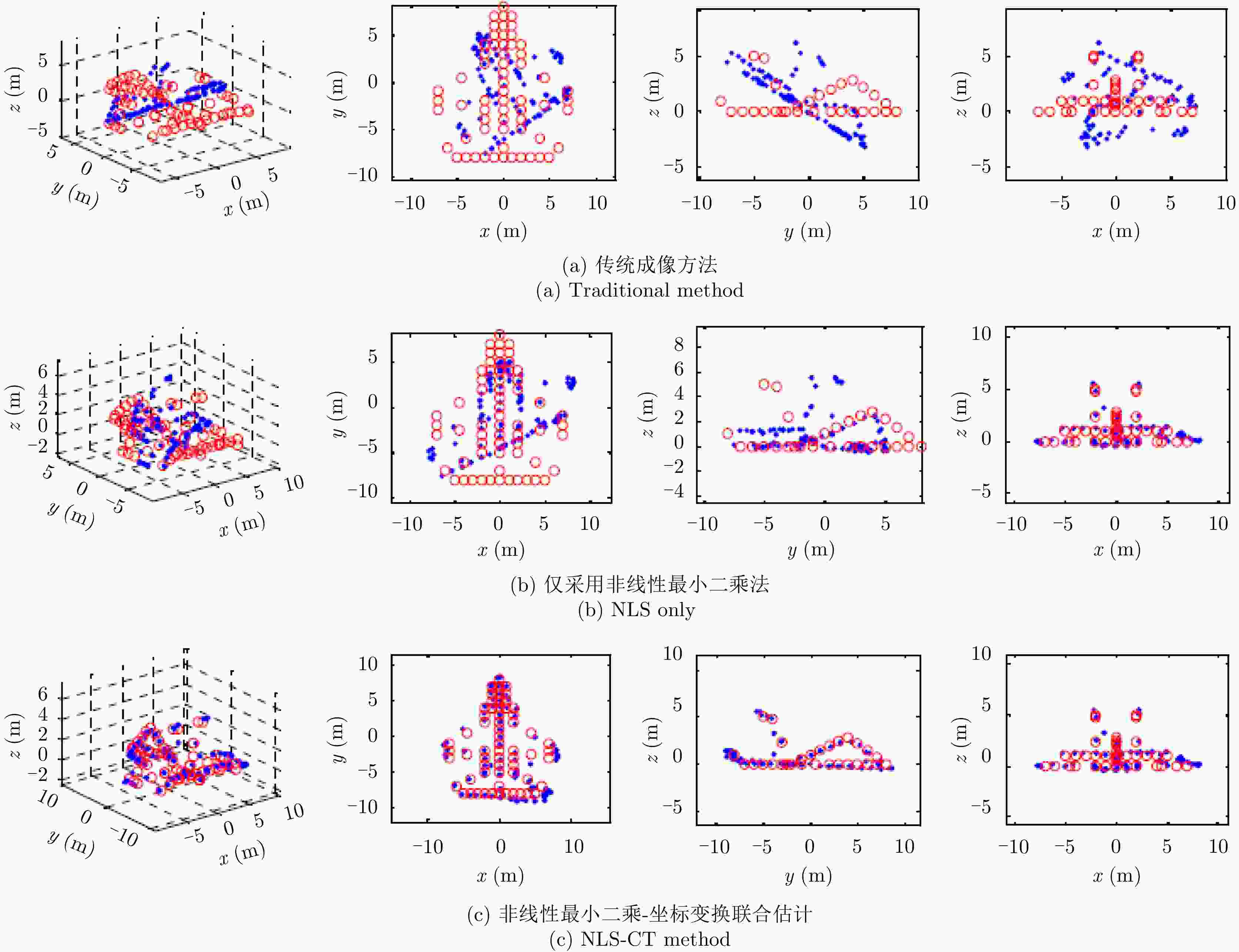
刘承兰, 贺峰, 高勋章, 等. 基于非线性最小二乘估计-坐标变换的斜视InISAR成像[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2011, 54(12): 3332–3340. doi: 10.1007/s11431-011-4515-9LIU Chenglan, HE Feng, GAO Xunzhang et al. Squint-mode InISAR imaging based on nonlinear least square and coordinates transform[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2011, 54(12): 3332–3340. doi: 10.1007/s11431-011-4515-9
|
| [141] |
TIAN Biao, ZOU Jiangwei, XU Shiyou, et al. Squint model interferometric ISAR imaging based on respective reference range selection and squint iteration improvement[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1366–1375.
|
| [142] |
MA Changzheng, YEO T S, ZHANG Qun, et al. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging based on antenna array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(2): 504–515. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.909946
|
| [143] |
MA Changzheng, YEO T S, TAN H S, et al. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging using a two-dimensional sparse antenna array[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(3): 378–382. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.916071
|
| [144] |
JIAO Zekun, DING Chibiao, CHEN Longyong, et al. Three-dimensional imaging method for array ISAR based on sparse Bayesian inference[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3563. doi: 10.3390/s18103563
|
| [145] |
CAPUTI W J. Stretch: A time-transformation technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1971, AES-7(2): 269–278. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1971.310366
|
| [146] |
WEHNER D R. High Resolution Radar[M]. Norwood: Artech House, 1987.
|
| [147] |
TAIT P. Introduction to Radar Target Recognition[M]. London: Institution of Electrical Engineers, 2005: 264–272.
|
| [148] |
张涛, 马长征, 张群, 等. 步进跟踪模式下的单脉冲雷达三维成像技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2001, 23(9): 912–918.ZHANG Tao, MA Changzheng, ZHANG Qun, et al. Monopulse radar three dimensional imaging techniques for targets in stepped tracking mode[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2001, 23(9): 912–918.
|
| [149] |
邱晓晖, 赵阳, CHENG A H W, 等. ISAR成像最小熵自聚焦与相位补偿的一致性分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(8): 1799–1801. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00072QIU Xiaohui, ZHAO Yang, CHENG A H W, et al. Consistency study of minimum entropy auto-focusing with phase compensation in ISAR imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(8): 1799–1801. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00072
|



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: