Preliminary Exploration of Systematic Geolocation Accuracy of GF-3 SAR Satellite System
-
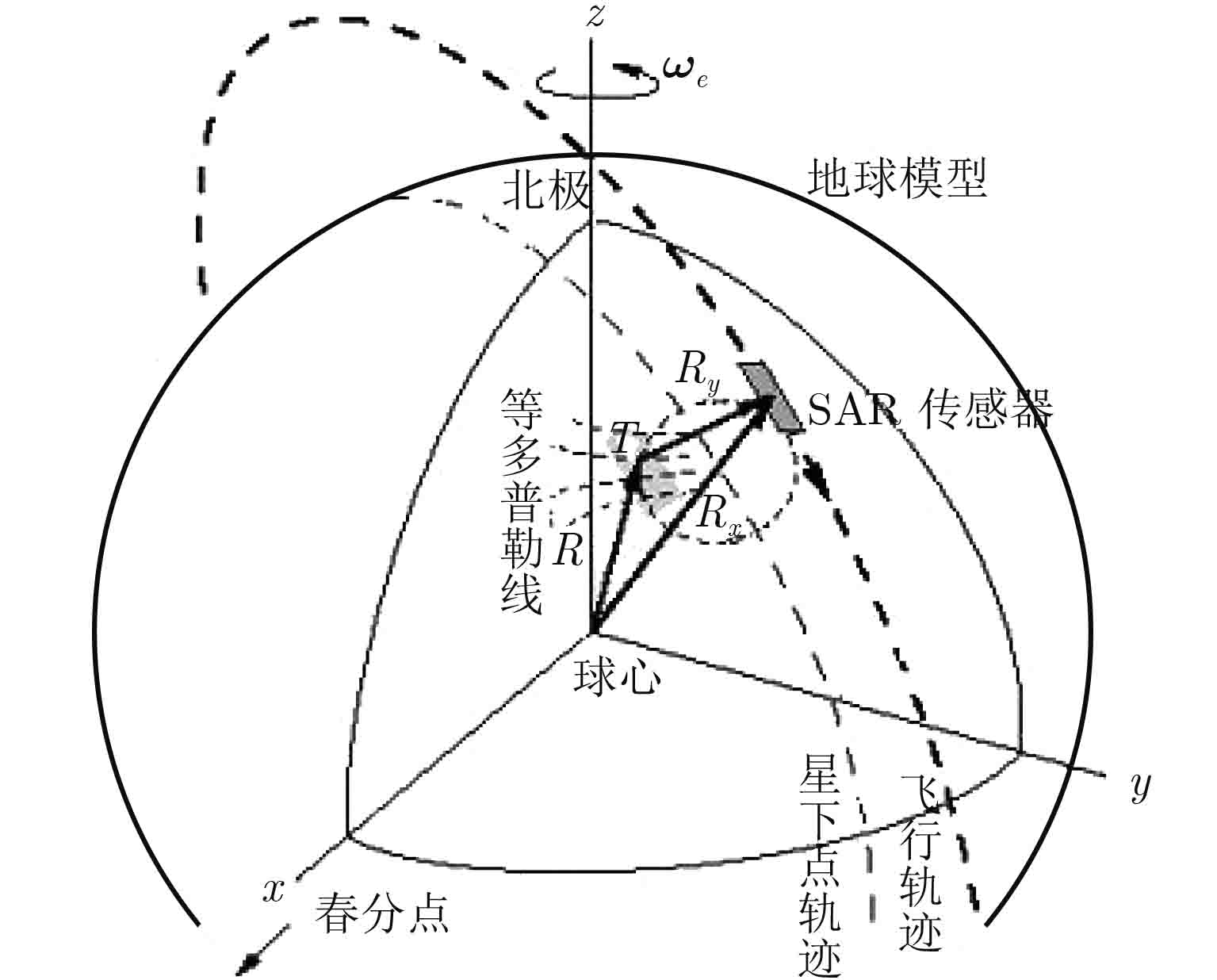
摘要: 高分三号SAR卫星是我国首颗空间分辨率达到1 m的C波段多极化合成孔径雷达成像卫星,于2016年8月成功发射,并通过5个月的在轨测试任务,于2017年1月正式交付用户单位使用。该文利用高分三号卫星实际在轨监测数据,分析了从数据采集、大气传输到成像处理与几何定位的全链路系统级几何定位误差源,并进行了基于角反射器的几何定位精度验证实验。实验结果表明,高分三号SAR卫星系统几何定位精度可以达到3 m。Abstract: GF-3, the first full-polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellite of China with a resolution up to 1 m, was successfully launched in August 2016 and, after 5 months of in-orbit calibration, it was officially delivered to the users in January 2017. In this paper, the geometric positioning error sources of the entire system are analyzed based on the real data acquisition, including atmospheric transmission, image processing, and geometric positioning. The positioning precision of the SAR system is validated by corner reflectors. The results show that the satellite positioning accuracy improved by 3 m.
-
Key words:
- GF-3 satellite /
- Range-Doppler model /
- Systematic geolocation /
- Error source analysis
-
表 1 角反射器的定位精度
Table 1. The positioning accuracy of the corner reflectors
入射角 指北误差(m) 指东误差(m) 定位精度(m) 32.27 1.09 0.50 1.19 48.43 1.87 2.79 3.35 29.17 1.00 1.57 1.86 30.57 1.80 2.63 3.18 RMS 2.56 -
[1] Guo Huadong. China’s Earth Observation Development[C]. The 36th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment (ISRSE36), Berlin, 2015. [2] 庞丹, 潘晨, 紫晓. 高分三号: 辽阔疆域的" 守望者”—写在高分三号卫星发射成功之时[J]. 中国航天, 2016(9): 8–12. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/ZGHT201609003.htmPang Dan, Pan Chen, and Zi Xiao. GF-3: The watcher of the vast territory[J].Aerospace China, 2016(9): 8–12. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/ZGHT201609003.htm [3] 云菲. 高分三号卫星[J]. 卫星应用, 2016, 第8期. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wxyy201608021Yun Fei. GF-3 Satellite[J].Satellite Application, 2016, No.8. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wxyy201608021 [4] 尤红建, 付琨. 合成孔径雷达图像精准处理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 13.You Hong-jian and Fu Kun. Image Precise Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 13. [5] Schubert A, Small D,et al.. COSMO-skymed, Terra SAR-X, and RADARSAT-2 geolocation accuracy after compensation for earth-system effects[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS2012), Germany, 2012: 3301–3304. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6350598 [6] Dan Williams, Pierre LeDantec,et al.. RADARSAT-2 image quality and calibration update[C]. Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, EUSAR 2014, Denmark, 2014: 1–4. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6856981/ [7] Eineder M, Minet C,et al.. Imaging geodesy—Toward centimeter-level ranging accuracy with TerraSAR-X[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(2): 667–671. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=5570983 [8] Curlander J C and McDonough R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1991: 374–377. http://www.oalib.com/references/9206174 [9] Doerry A W. Atmospheric loss considerations for synthetic aperture radar design and operation[C]. Proceedings SPIE 5410, Radar Sensor Technology VIII and Passive Millimeter-wave Imaging Technology VII, 2004. DOI: 10.1117/12.542327. [10] Fritz T, Eineder M,et al.. TerraSAR-X Ground Segment Basic Product Specification Document. Feb.24, 2008. TX-GS-DD-3302 Iss.1.5. [11] Michael Jehle, Donat Perler, David Small,et al.. Estimation of atmospheric path delays in TerraSAR-X data using models vs. measurements[J].Sensors, 2008, 8(12): 8479–8491. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3791028/ [12] 刘佳音, 韩冰, 仇晓兰. 基于等效距离模型的改进RD定位算法[C]. 第一届高分辨率对地观测学术年会, 北京, 2012.Liu Jiayin, Han Bing, and Qiu Xiaolan. Improved RD Location Algorithm based on equivalent range model[C]. The 1st China High Resolution Earth Observation Conference, Beijing, 2012. [13] 仇晓兰, 韩传钊, 刘佳音. 一种基于持续运动模型的星载SAR几何校正方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 54–59. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20072Qiu Xiao-lan, Han Chuan-zhao, and Liu Jia-yin. A method for spaceborne SAR geolocation based on continuously moving geometry[J].Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 54–59. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20072 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: