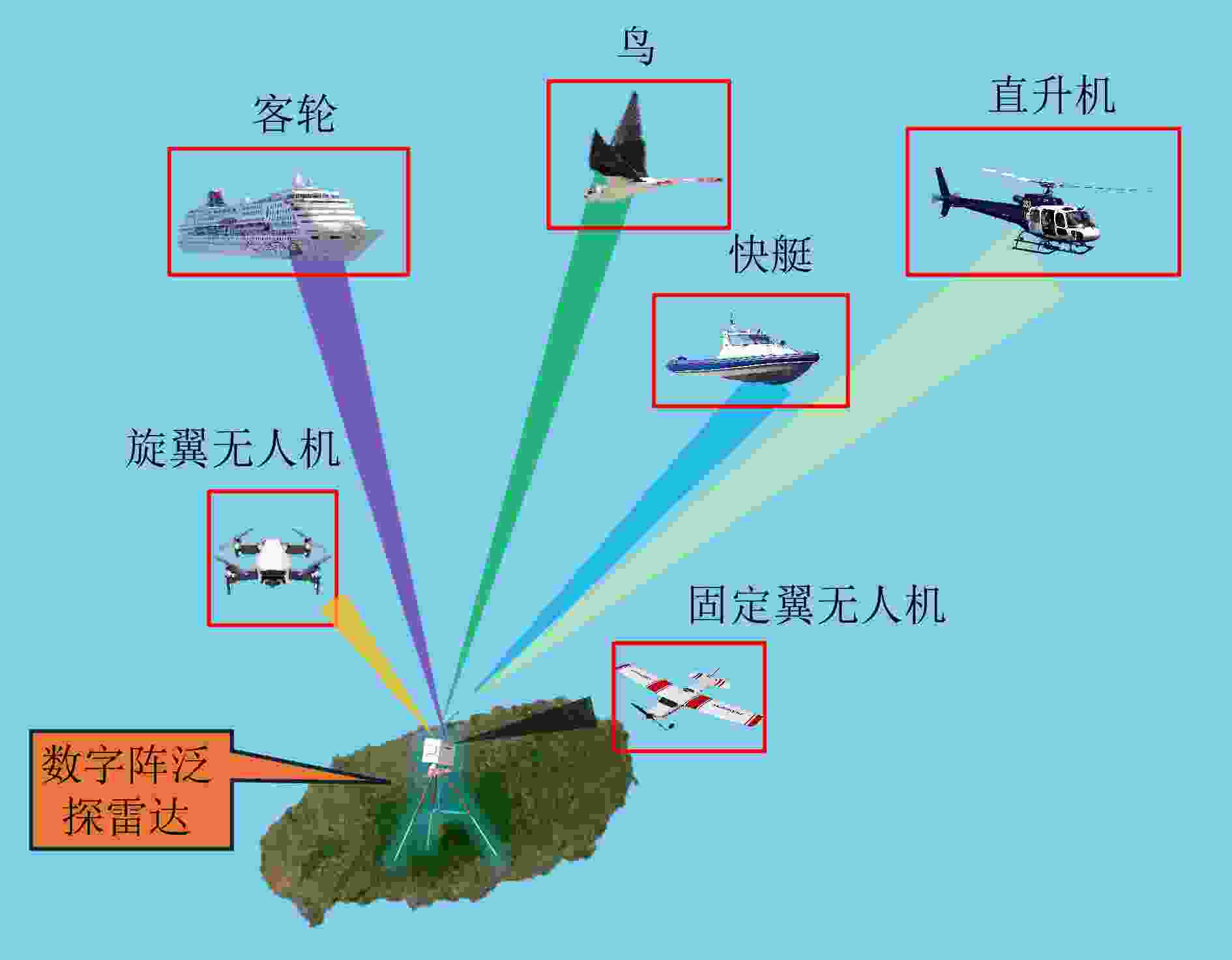
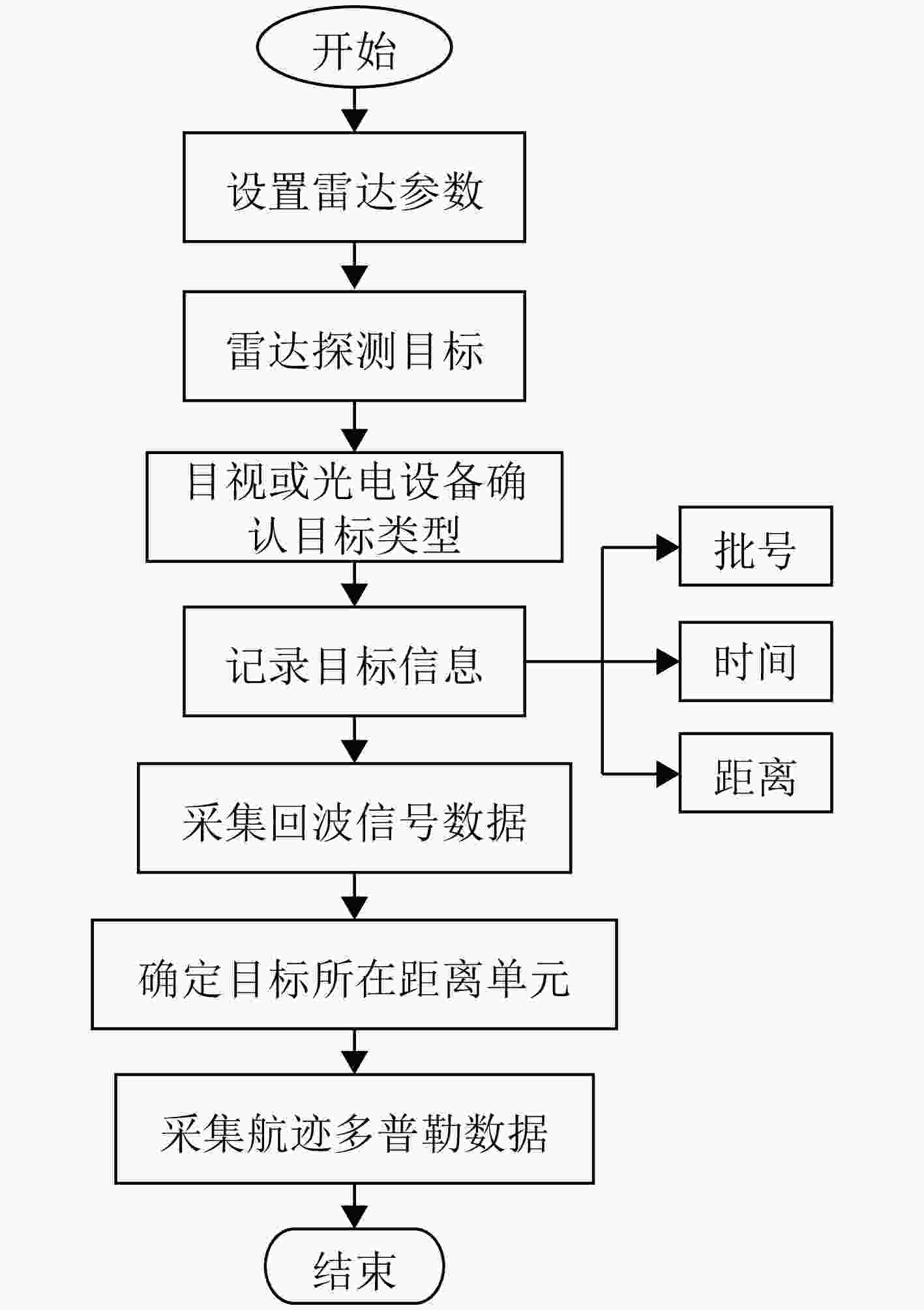
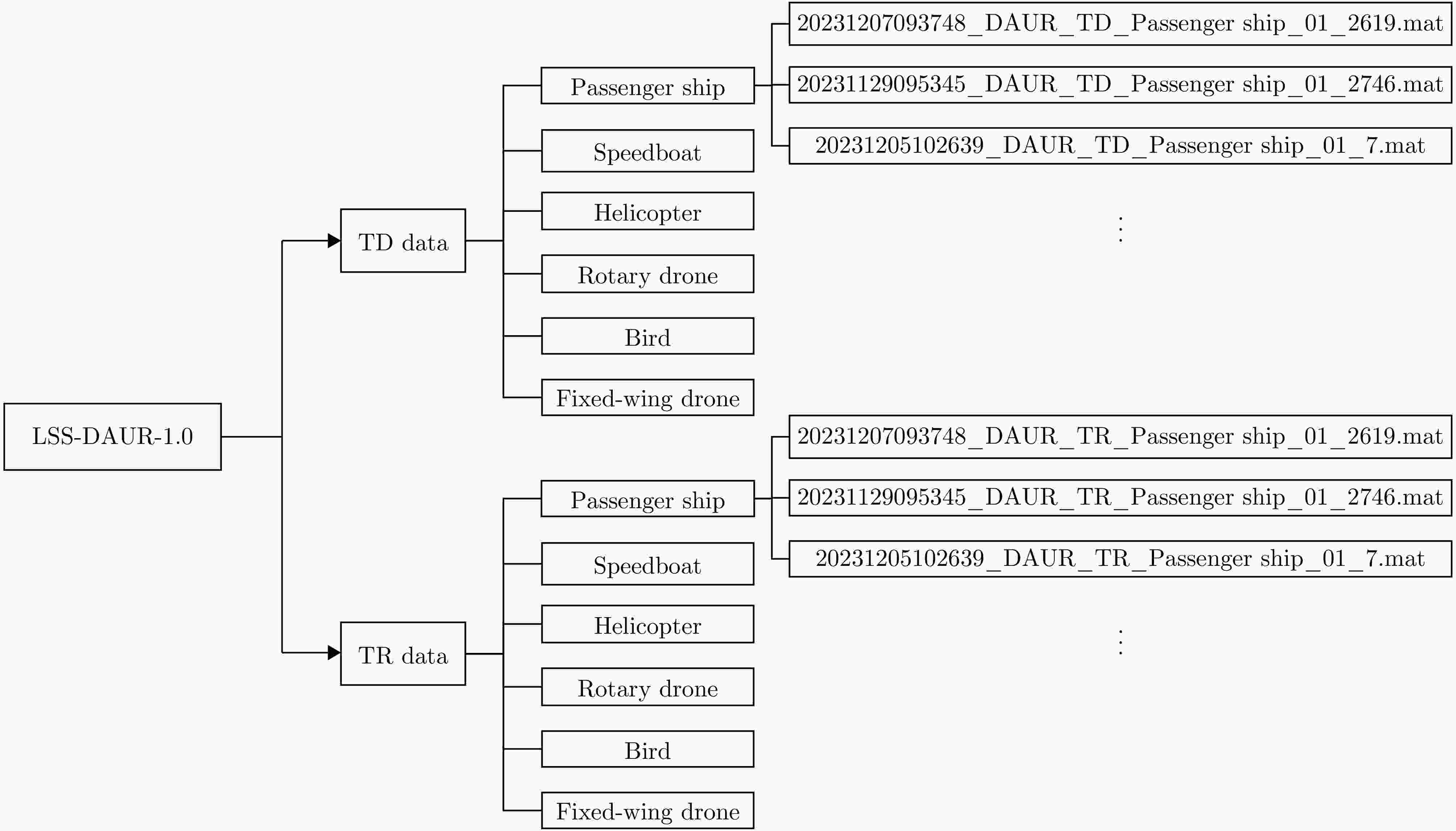
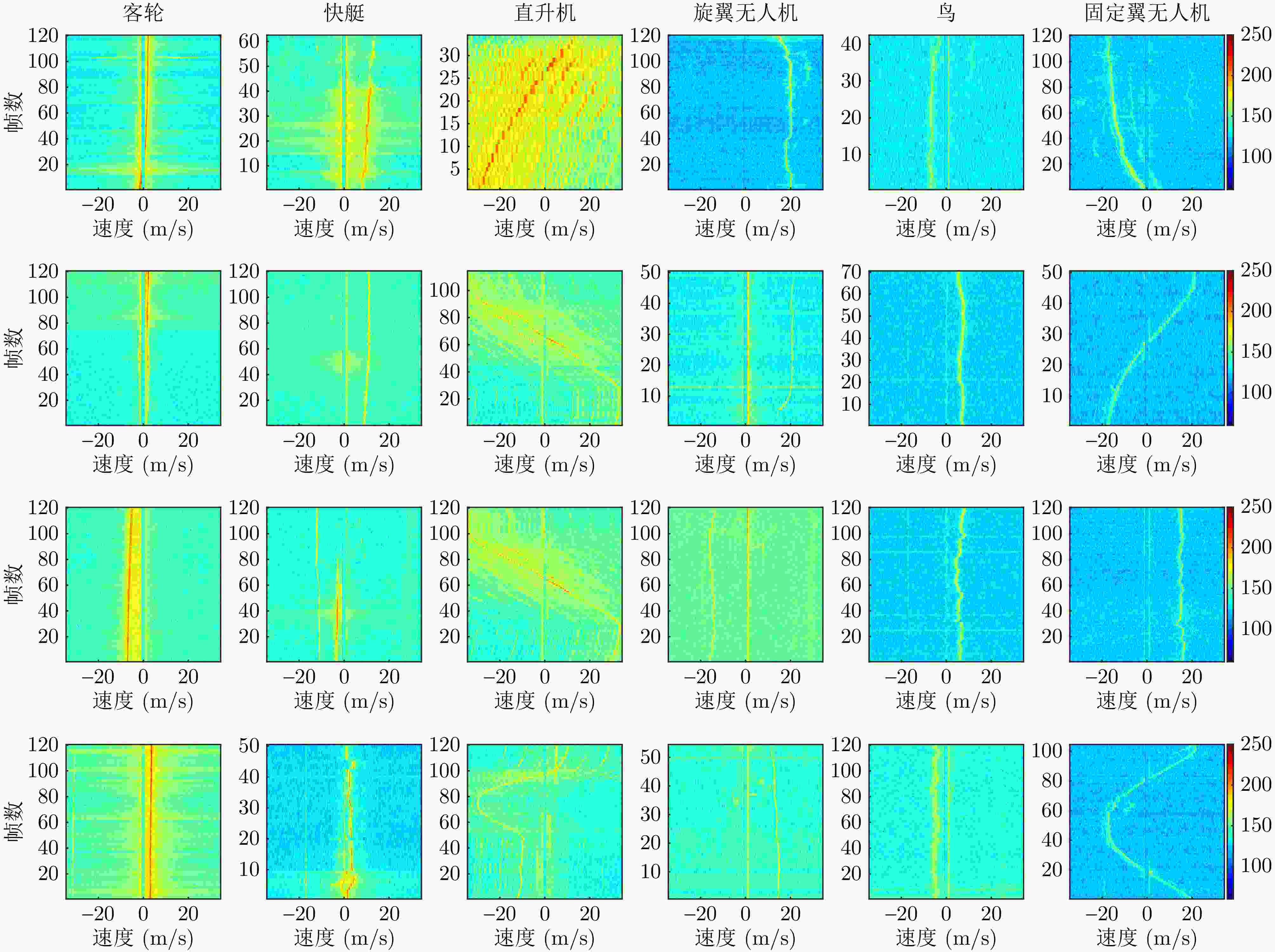
Digital Array Radar LSS-target Detection Dataset (LSS-DAUR-1.0) and Graph Network-based Target Classification
-
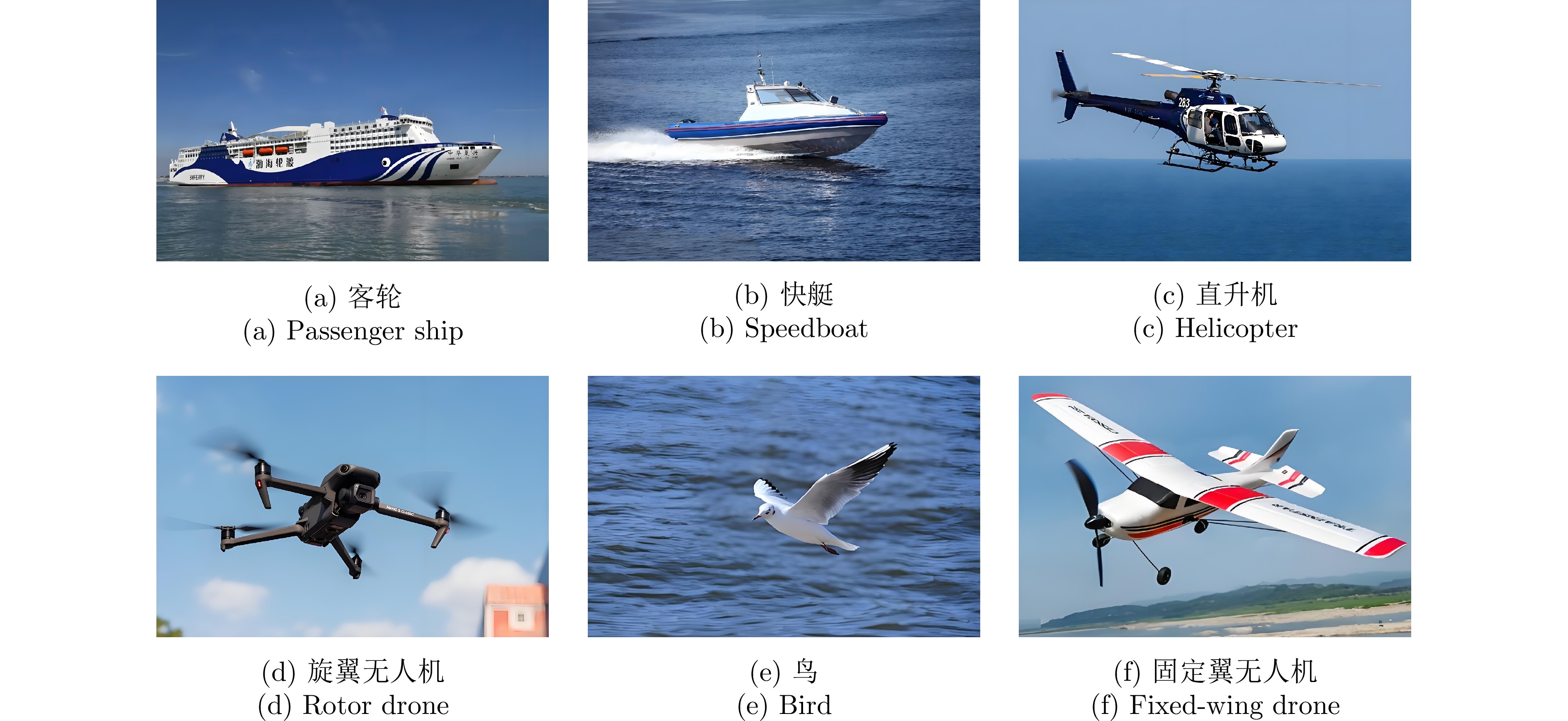
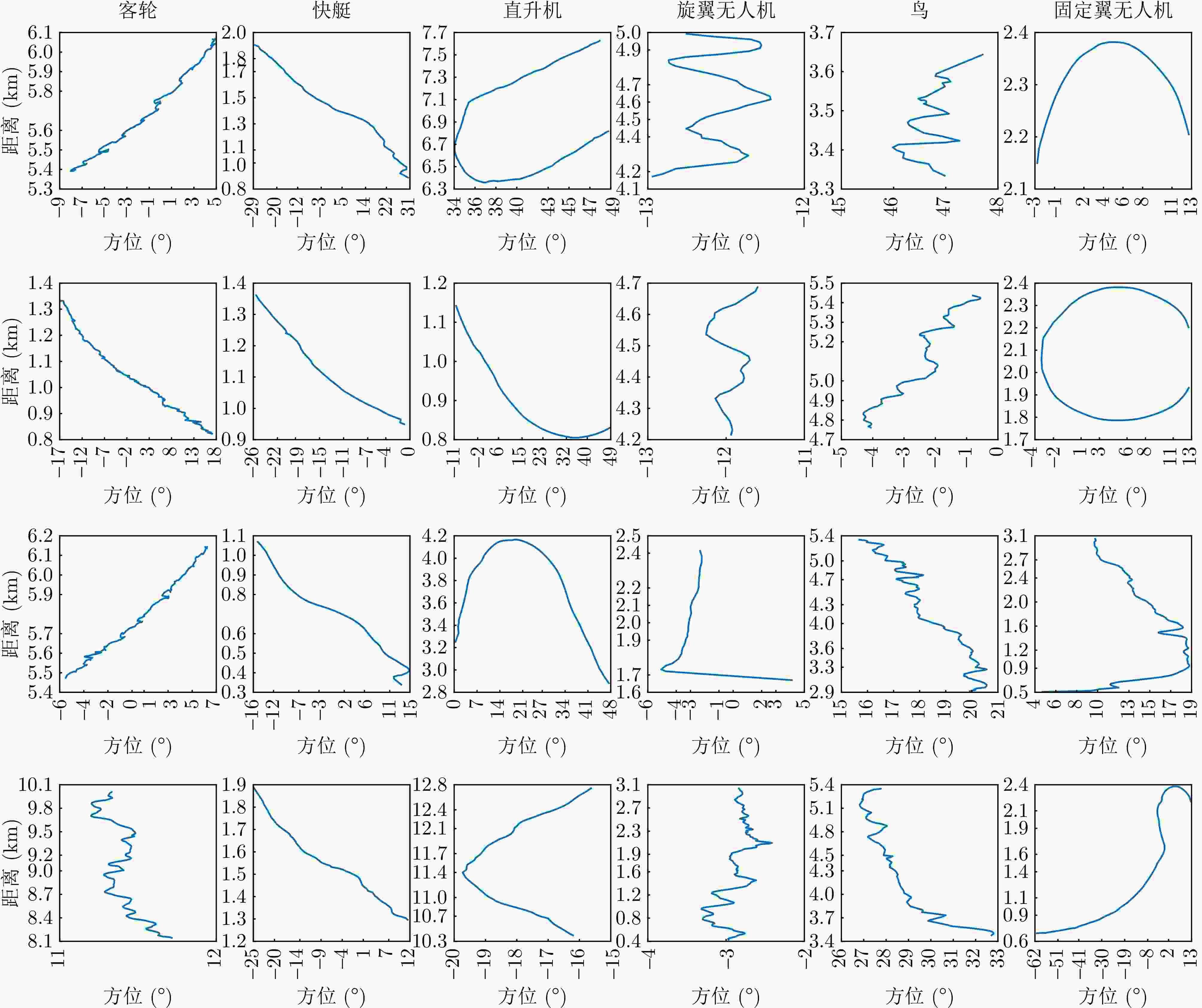
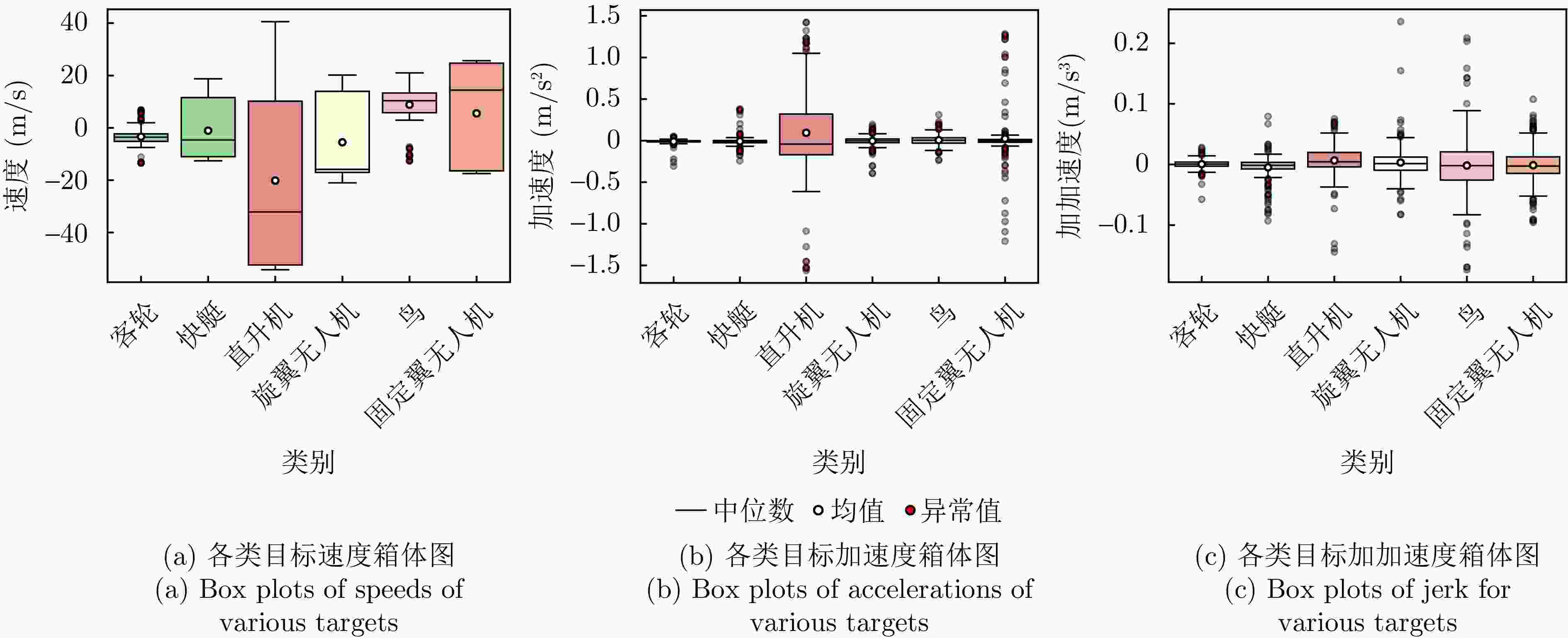
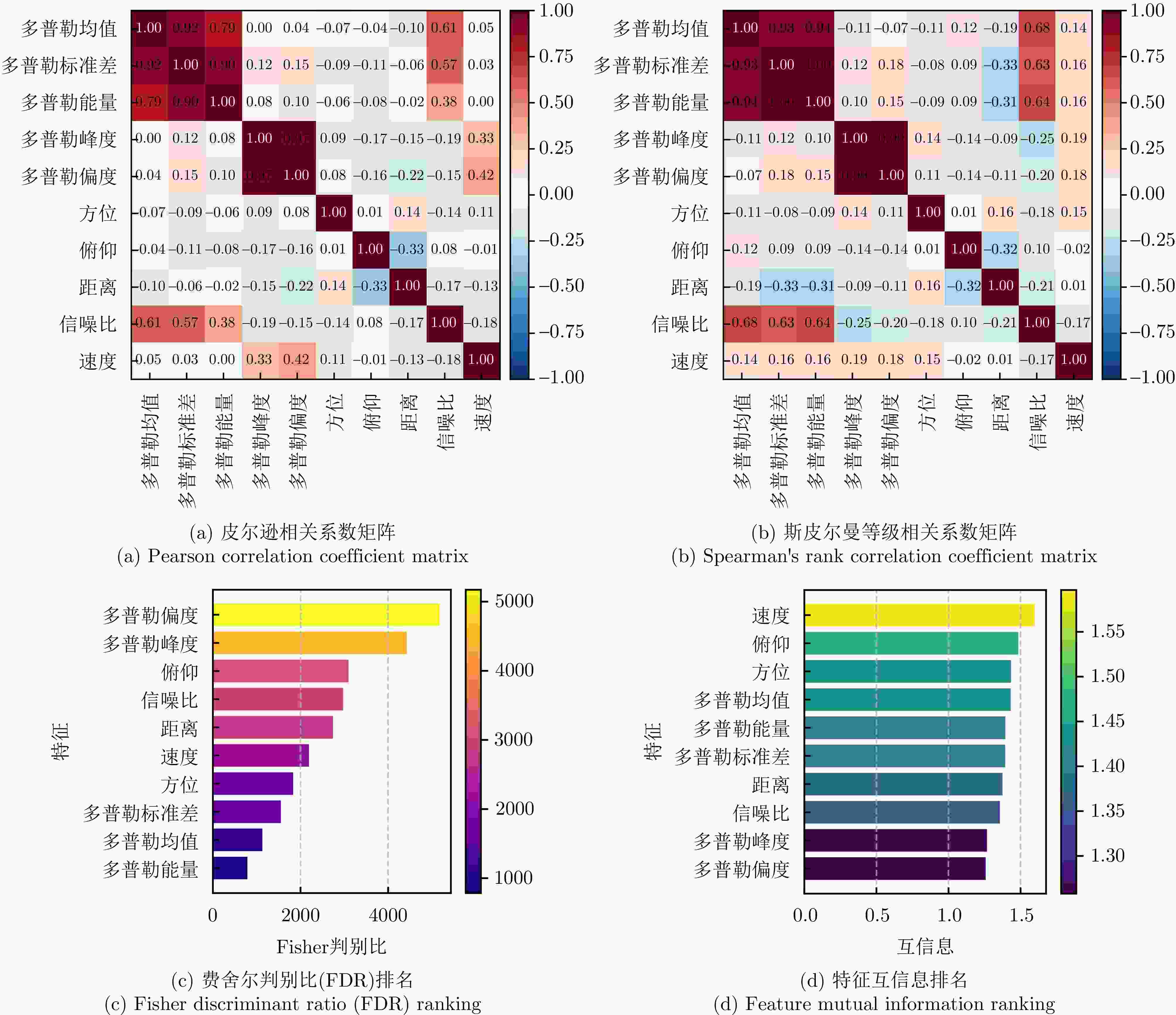
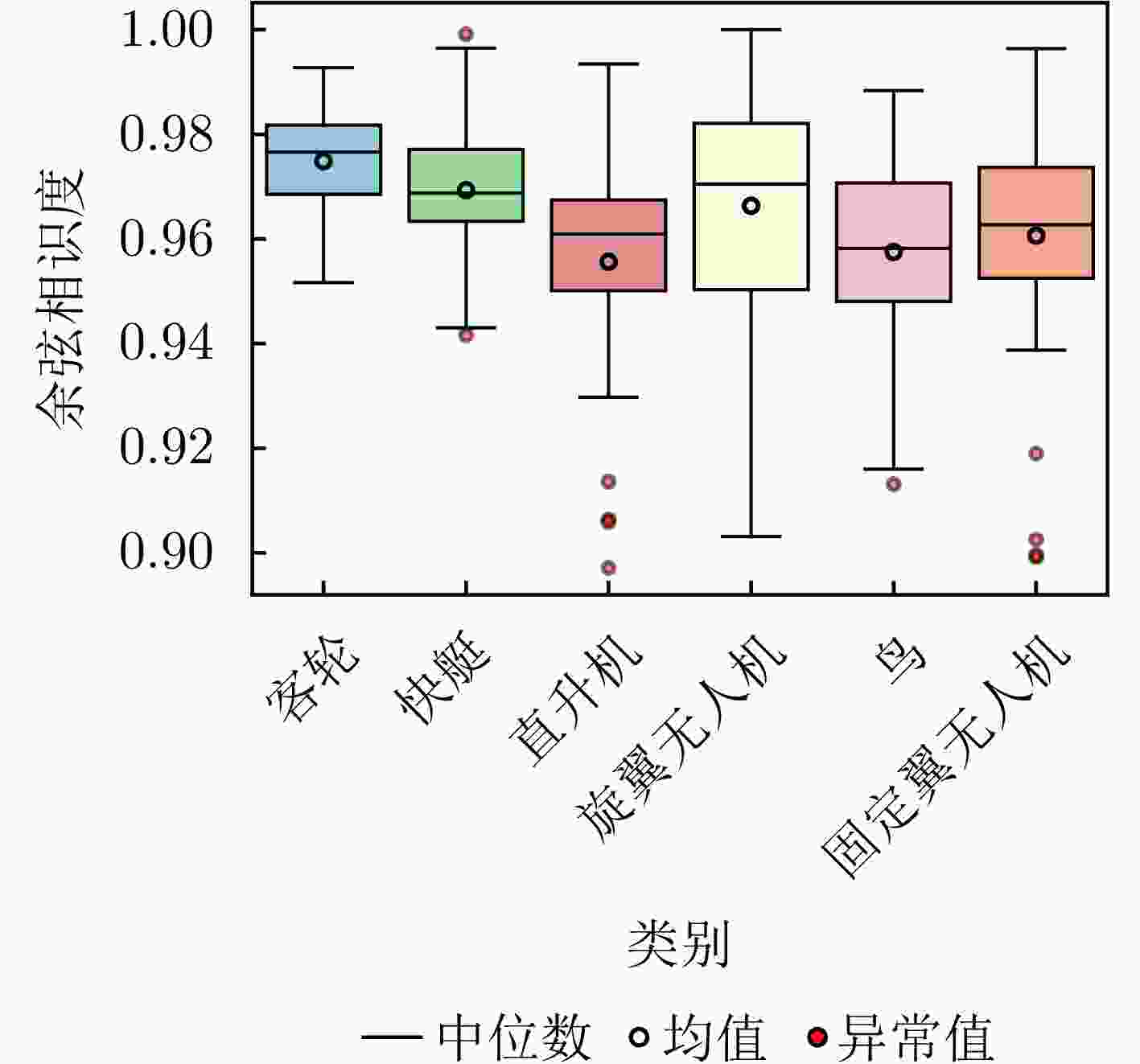
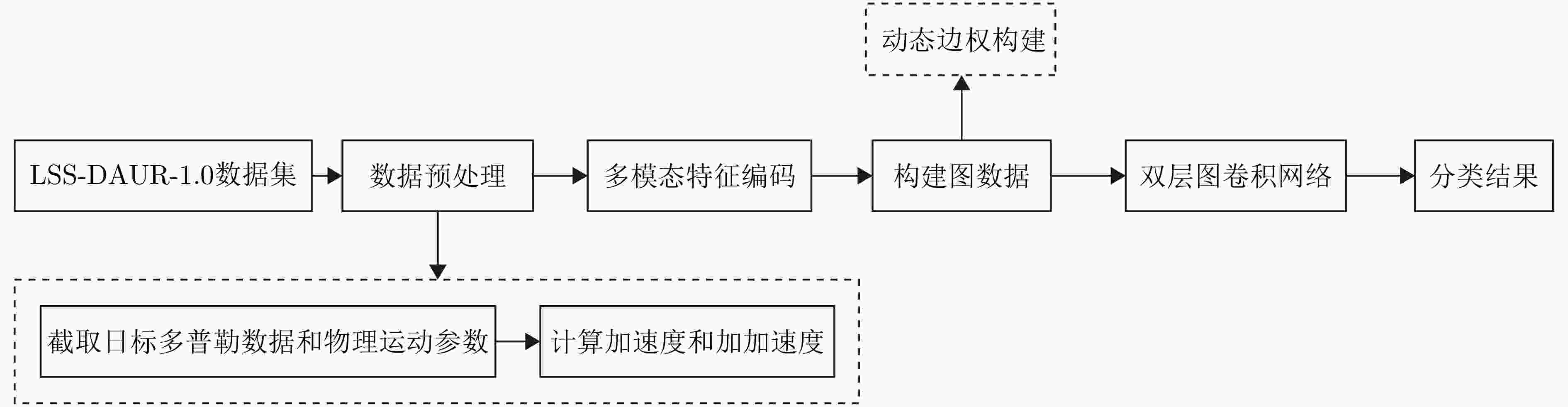
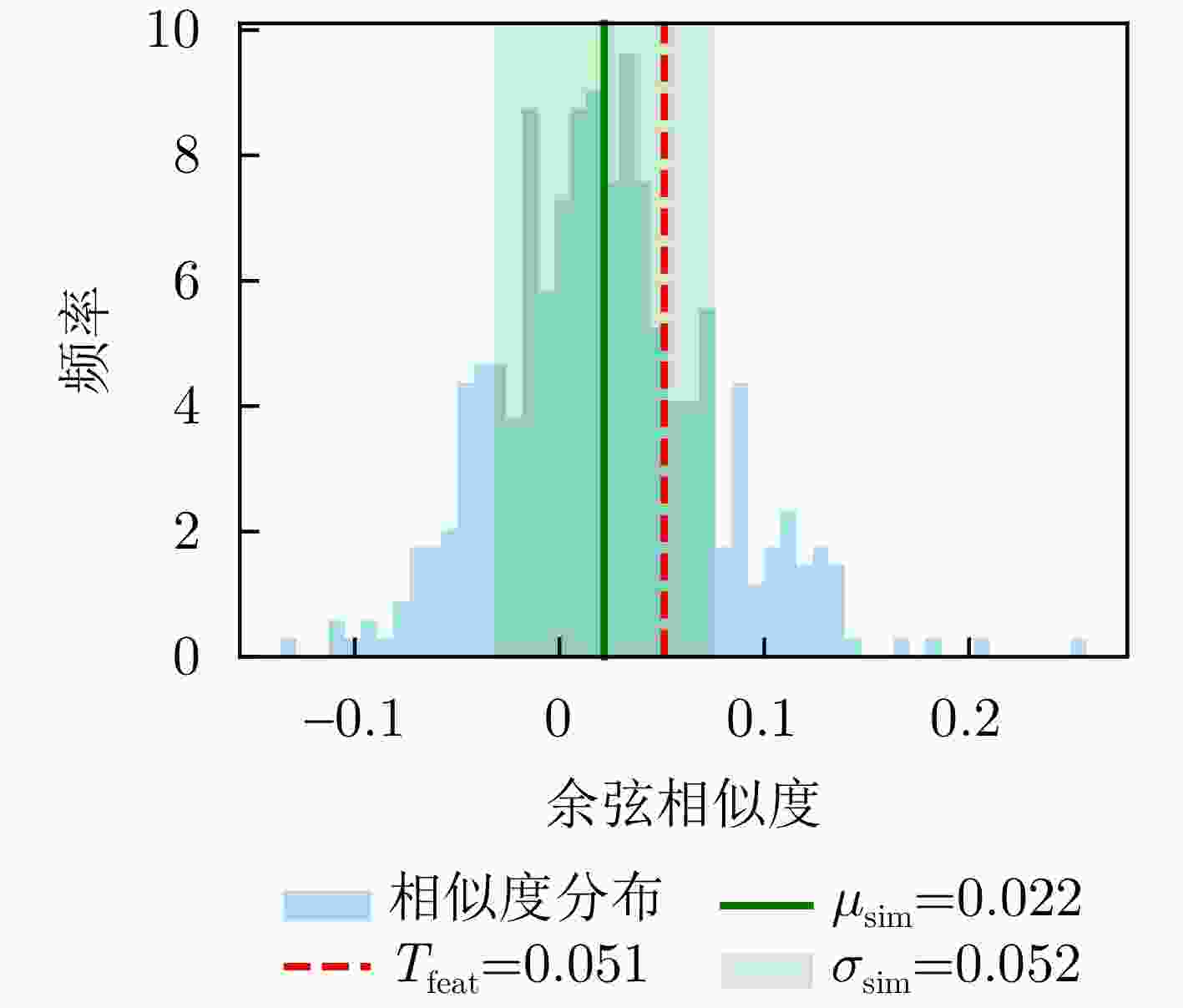
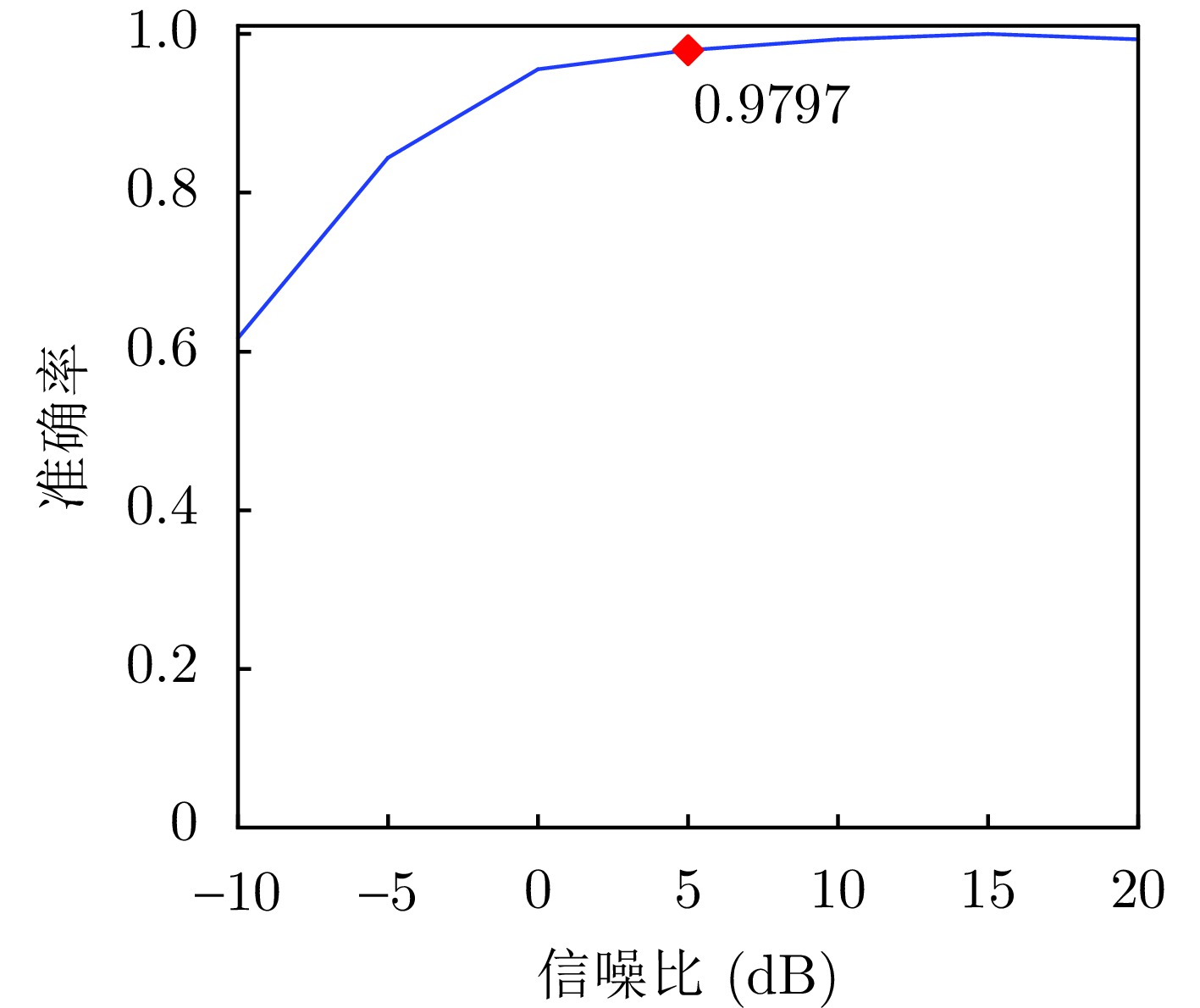
摘要: 针对低慢小(LSS)目标雷达分类中存在的特征提取不充分、时空关联建模能力薄弱及分类性能欠佳等问题,本文围绕图网络特征提取和分类技术开展研究。首先,聚焦数字阵泛探雷达,构建了雷达低慢小目标探测数据集LSS-DAUR-1.0,包含客轮、快艇、直升机、旋翼无人机、鸟类与固定翼无人机6类目标的多普勒和航迹数据。其次,基于该数据集分析了目标的多域多维特性,通过相关性和余弦相似度分析,验证了多普勒特征与物理运动特征的互补性。在此基础上,提出融合双特征的动态图图卷积网络(DG-GCN)分类方法设计自适应窗口调整、混合衰减函数和动态阈值机制,构建时空关联自适应动态图,结合图卷积特征学习和分类模块,实现对低慢小目标的精细化分类。LSS-DAUR-1.0数据集验证表明,DG-GCN分类准确率达99.66%,较ResNet和Transformer模型分别提升6.78%和17.97%,总处理时间仅4.98 ms,较对比模型降低80%以上,兼顾高精度与高效性。此外,噪声环境测试其鲁棒性良好。消融实验验证,动态边权机制可弥补纯时序连接的空间特征关联上不足,提升模型泛化能力。Abstract: To address issues such as insufficient feature extraction, limited spatiotemporal correlation modeling, and poor classification performance in radar classification of low, slow, and small targets, this paper investigates on graph network-based feature extraction and classification methods. First, focusing on digital array ubiquitous radar, a radar detection dataset for LSS targets, named LSS-DAUR-1.0, is constructed; it contains Doppler and track data for six types of targets: passenger ships, speedboats, helicopters, rotor drones, birds, and fixed-wing drones. Second, based on this dataset, the multidomain and multidimensional characteristics of the targets are analyzed, and the complementarity between Doppler and physical motion features is verified through correlation and cosine similarity analyses. On this basis, a Graph Convolutional Network with Dynamic Graph Construction (DG-GCN) classification method fusing dual features is proposed. An adaptive window adjustment, a hybrid attenuation function, and a dynamic threshold mechanism are designed to construct an adaptive dynamic graph based on spatiotemporal correlation. Combined with graph convolution–based feature learning and classification modules, this approach achieves refined classification of low, slow, and small targets. Validation on the LSS-DAUR-1.0 dataset shows that the DG-GCN achieves 99.66% classification accuracy, which is 6.78% and 17.97% higher than that of ResNet and Transformer models, respectively. The total processing time is only 4.98 ms, which is more than 80% lower than that of the aforementioned comparison models. Hence, the DG-GCN achieves both high accuracy and efficiency. In addition, noise environment tests show good robustness. Ablation experiments verify that the dynamic edge weight mechanism compensates for the lack of spatial feature correlation in purely temporal connections and improves the model’s generalizability.
-
表 1 DAUR参数
Table 1. Parameters of the digital ubiquitous radar
雷达参数 数值 载频(GHz) 1.36 带宽(MHz) 4 发射功率(W) 400 脉冲重复频率(kHz) 5 脉宽(μs) 2 速度单元(m/s) 0.1346 多普勒通道数 512 表 2 样本扩充统计结果
Table 2. Statistical results of sample augmentation
目标类别 原始航迹数 总帧数 步长大小 截取后航迹数 截取后样本编号 客轮 10 2704 10 246 1-246 快艇 11 1456 5 231 1-231 直升机 10 930 3 217 1-217 旋翼无人机 18 1735 5 250 1-250 鸟 17 2787 10 237 1-237 固定翼无人机 11 1762 5 293 1-293 总计 77 14078 — 1474 — 表 3 模型超参数设置
Table 3. Model hyperparameter settings
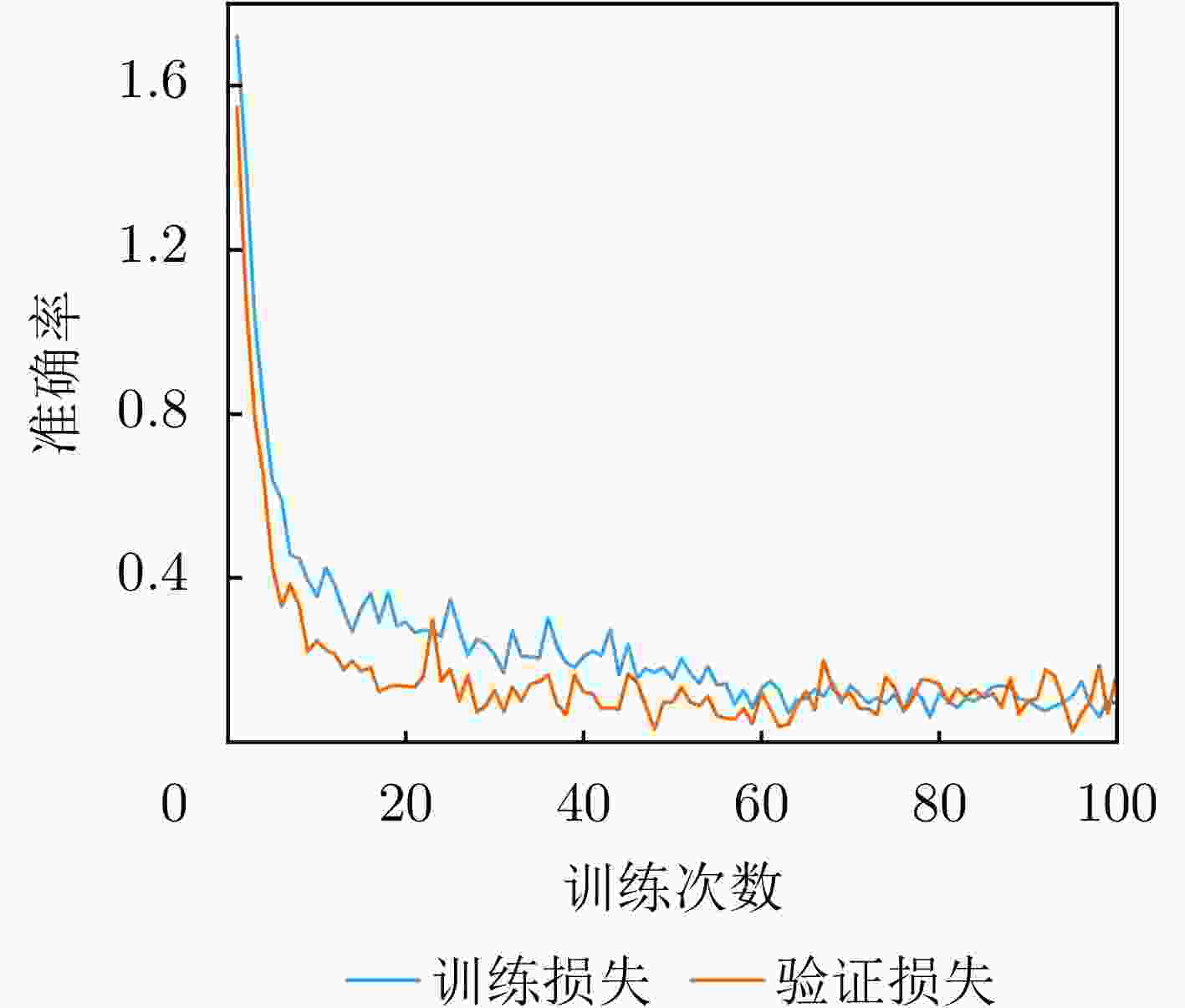
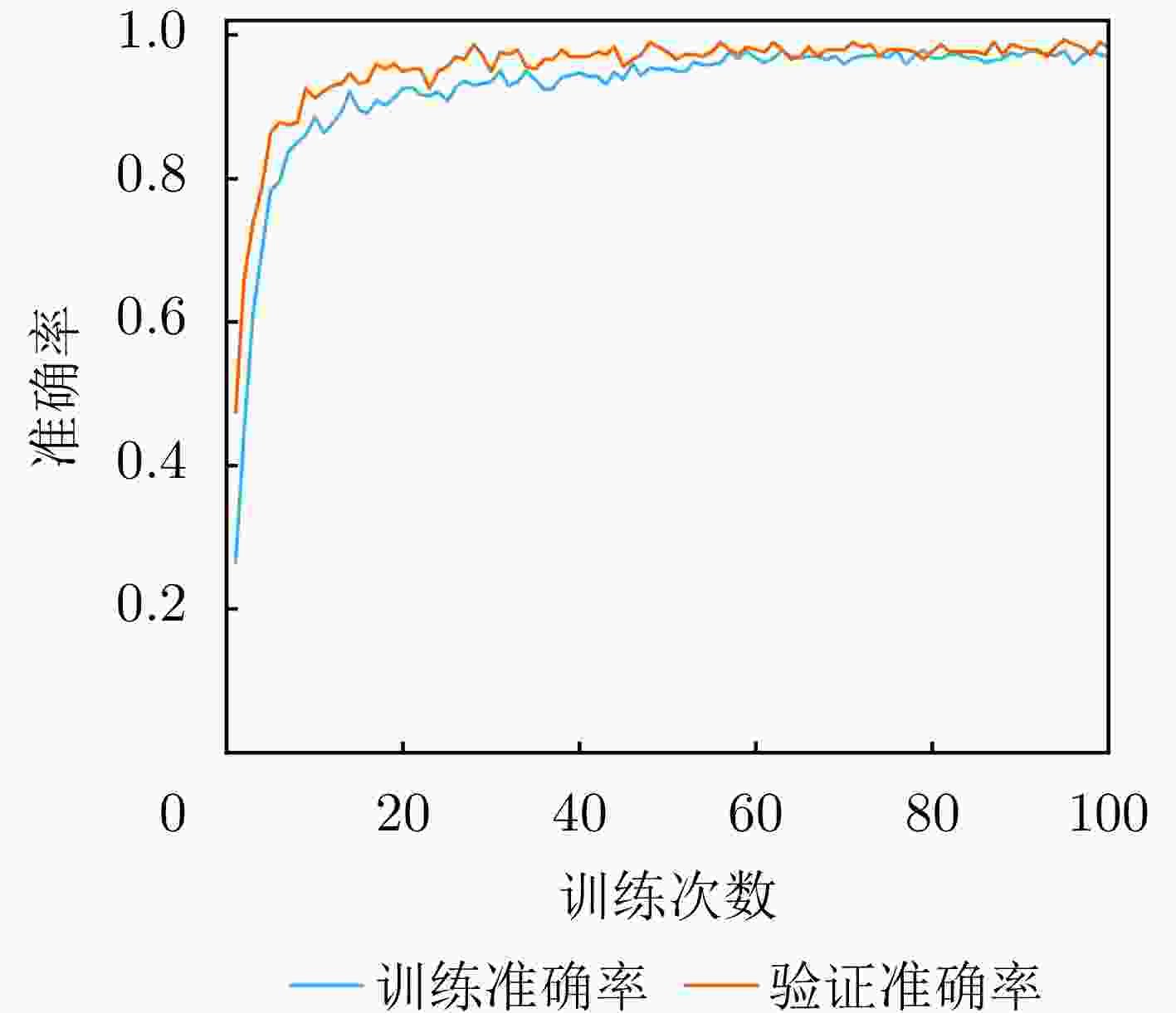
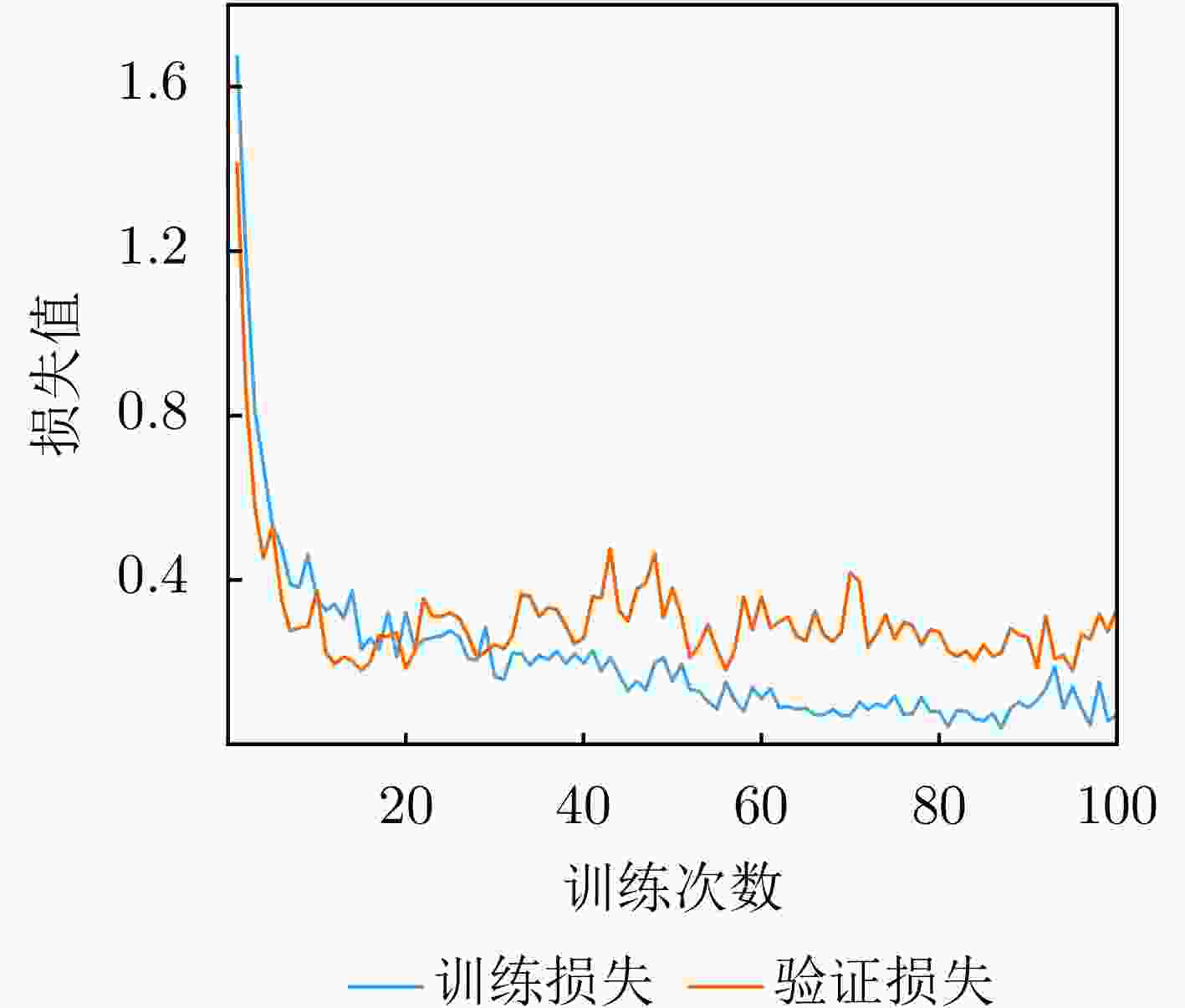
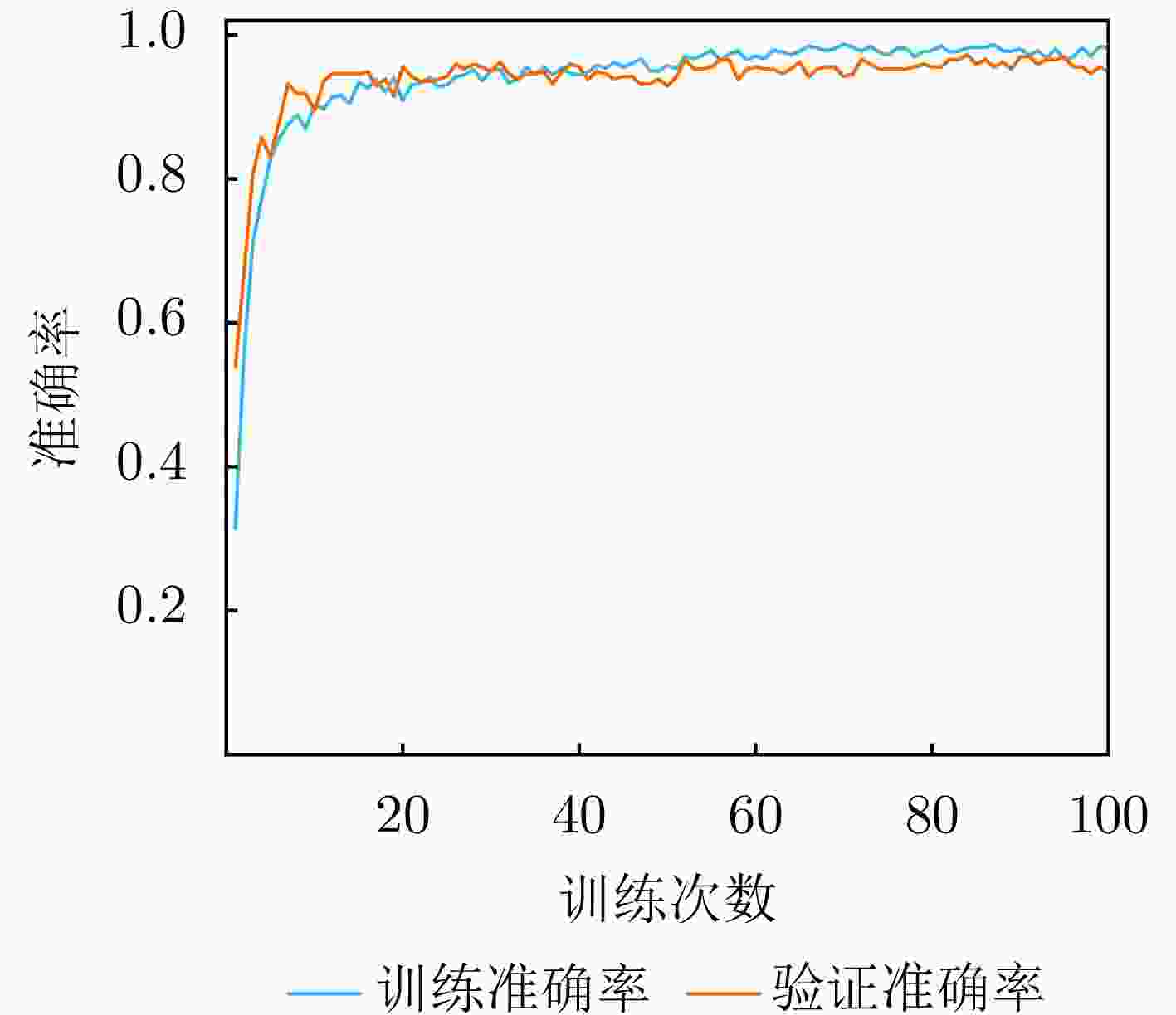
参数名称 参数设置 说明 优化器 AdamW 动量参数$ {\beta }_{1}=0.9 $,$ {\beta }_{2}=0.999 $ 初始学习率 $ 3\times {10}^{-4} $ 采用余弦退火调度策略动态调整 权重衰减系数 $ 1\times {10}^{-5} $ 约束模型权重幅值,防止过拟合 学习率调度 CosineAnnealingLR 周期$ {T}_{\max}=100 $,最小学习率$ 1\times {10}^{-6} $ L2正则化系数 $ \lambda =0.0005 $ 对所有权重参数施加L2范数惩罚 Dropout概率 0.5 随机丢弃神经元,增强泛化性 批量大小 32 单次训练输入样本数 最大训练轮数 100 训练终止条件之一 表 4 数据集划分
Table 4. Dataset division
目标类别 总航迹数 训练集航迹编号 验证集航迹编号 总样本数 总样本占比 训练集样本数 验证集样本数 客轮 10 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8 6, 7, 9, 10 246 16.69% 196 50 快艇 11 1, 3, 7, 8, 11 2, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10 231 15.67% 184 47 直升机 10 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8 4, 9, 10 217 14.72% 173 44 旋翼无人机 18 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 13, 14, 15, 17 3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 16, 18 250 16.96% 200 50 鸟 17 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13 1, 3, 4, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17 237 16.08% 189 48 固定翼无人机 11 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 1, 11 293 19.88% 234 59 总计 77 — — 1474 100.00% 1179 295 表 5 动态边权参数搜索空间
Table 5. Search space of dynamic edge weight parameters
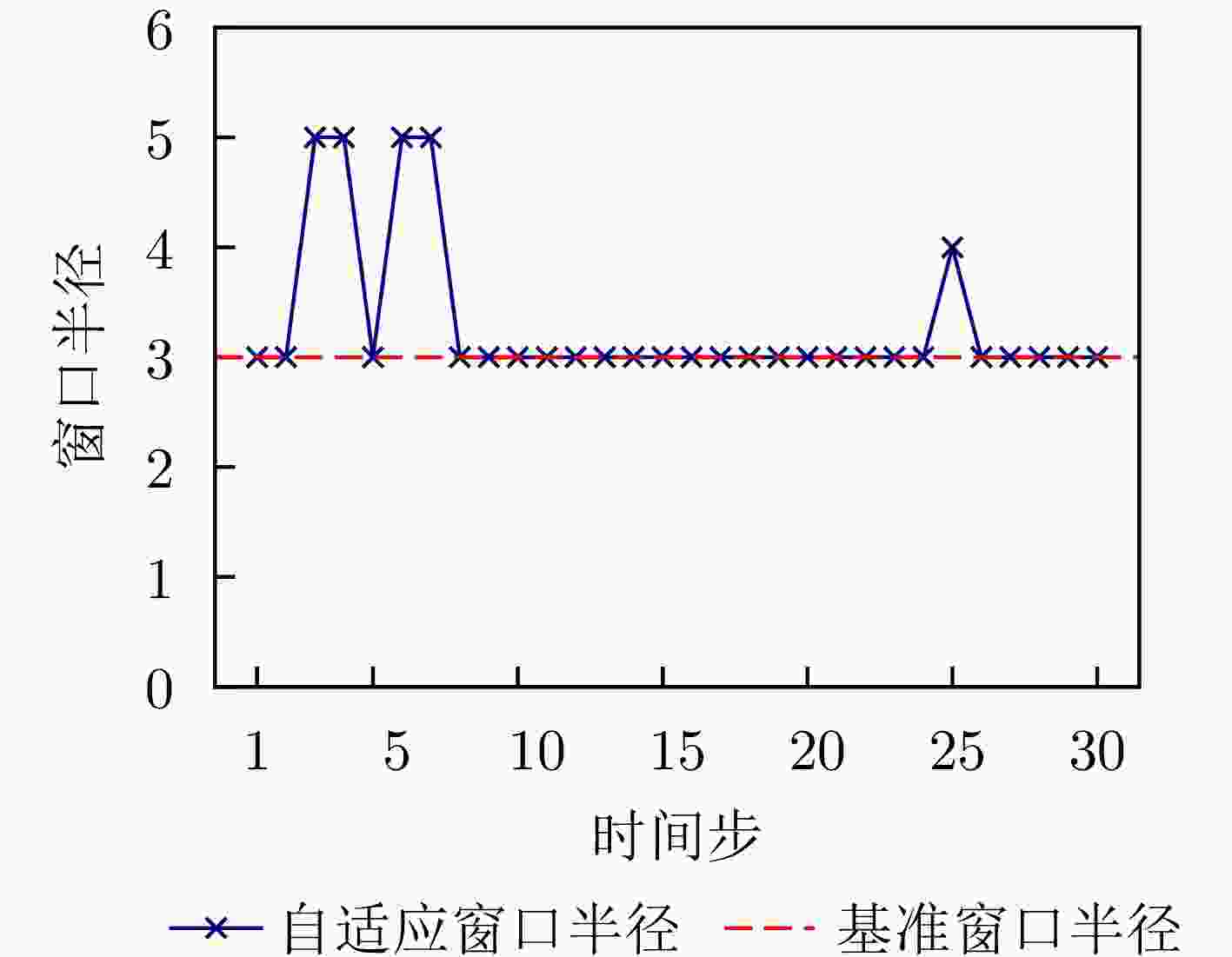
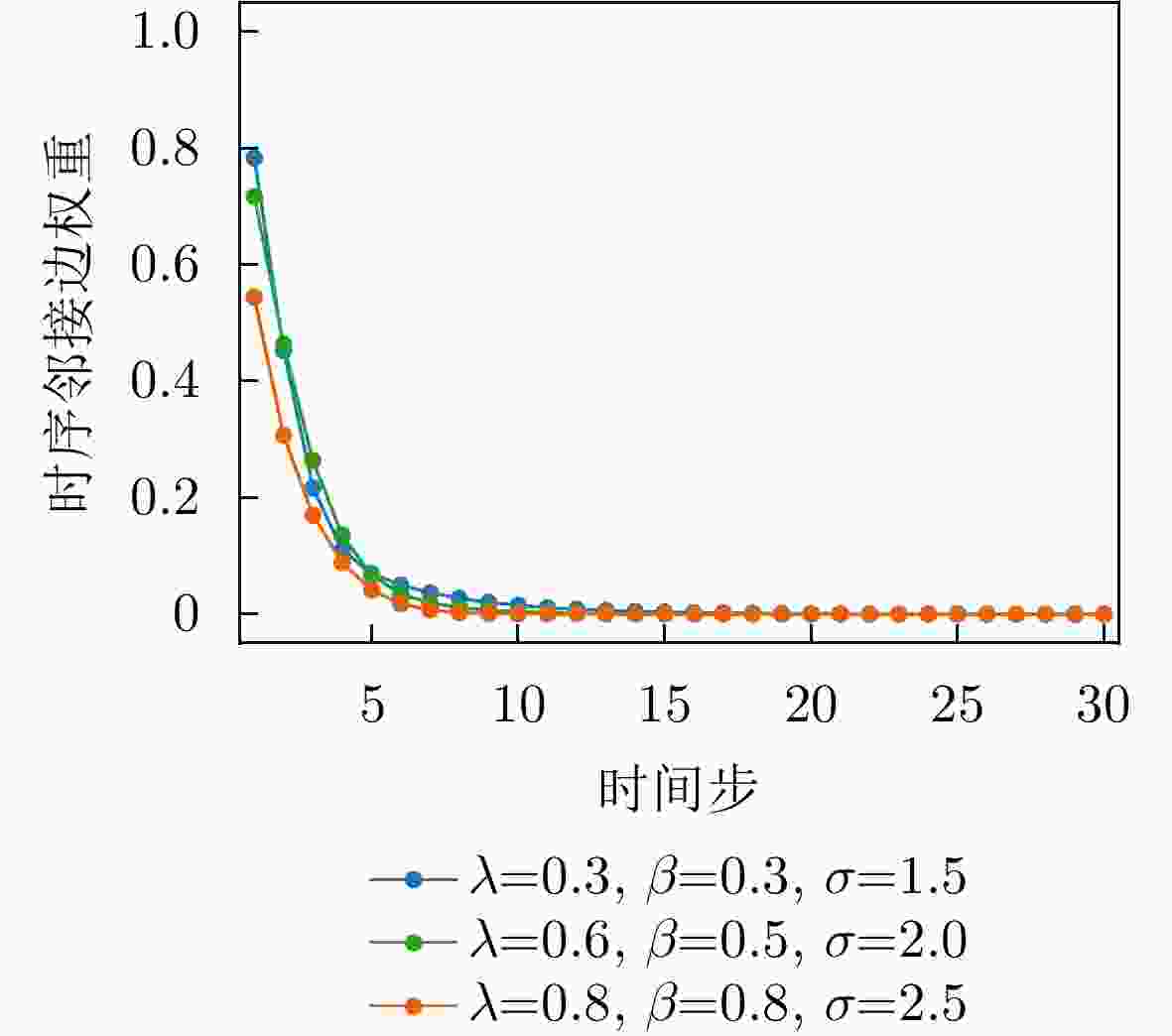
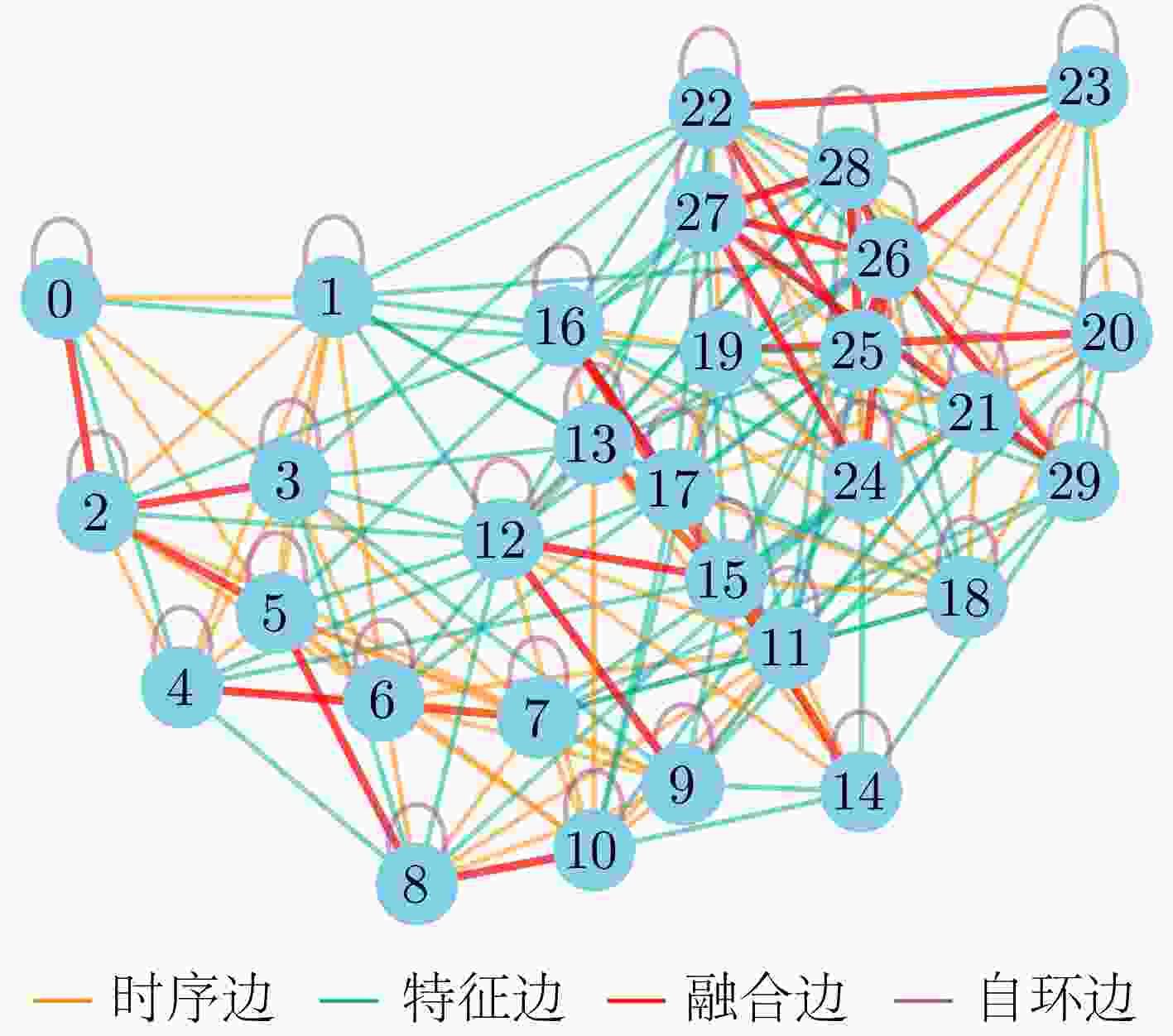
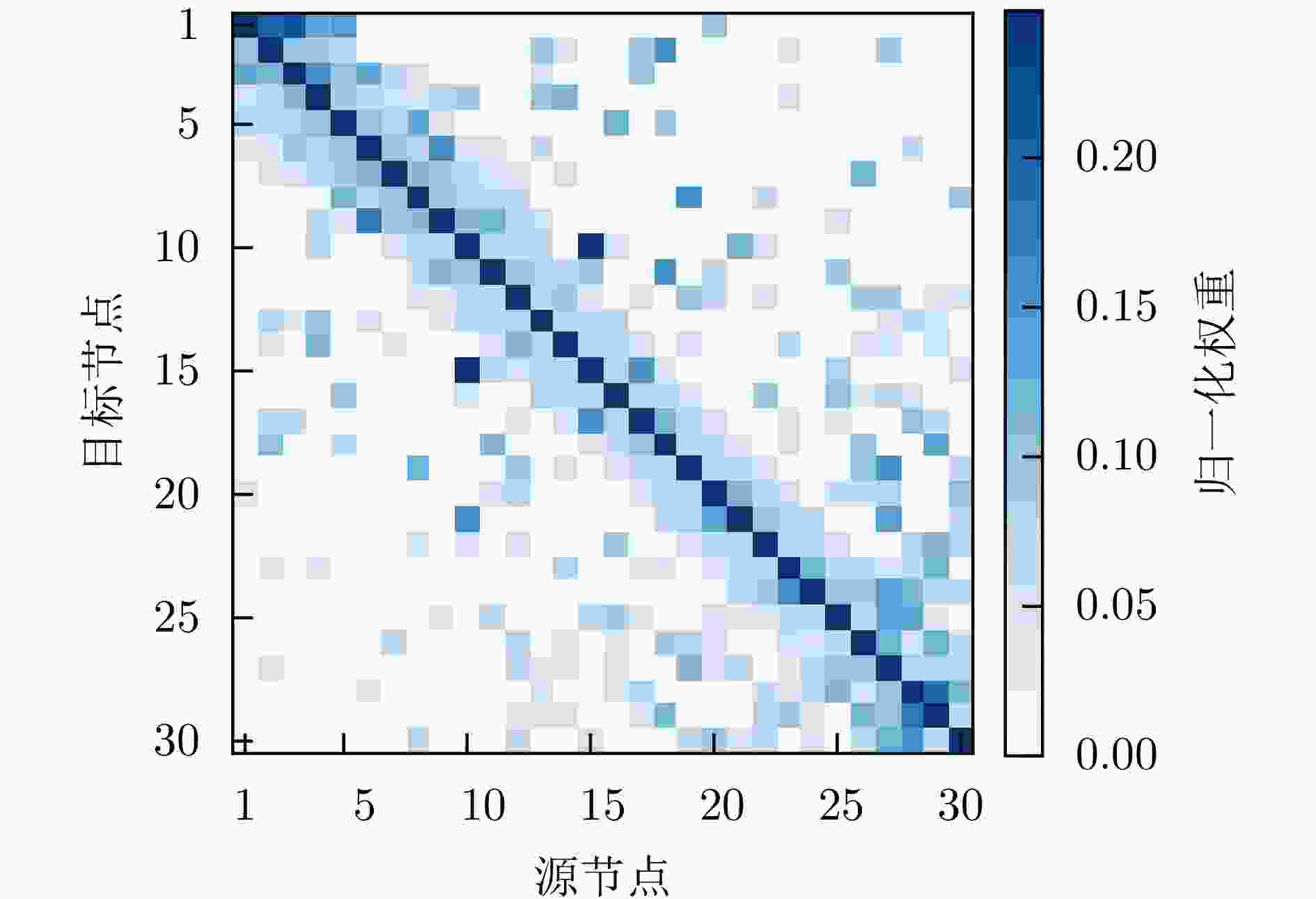
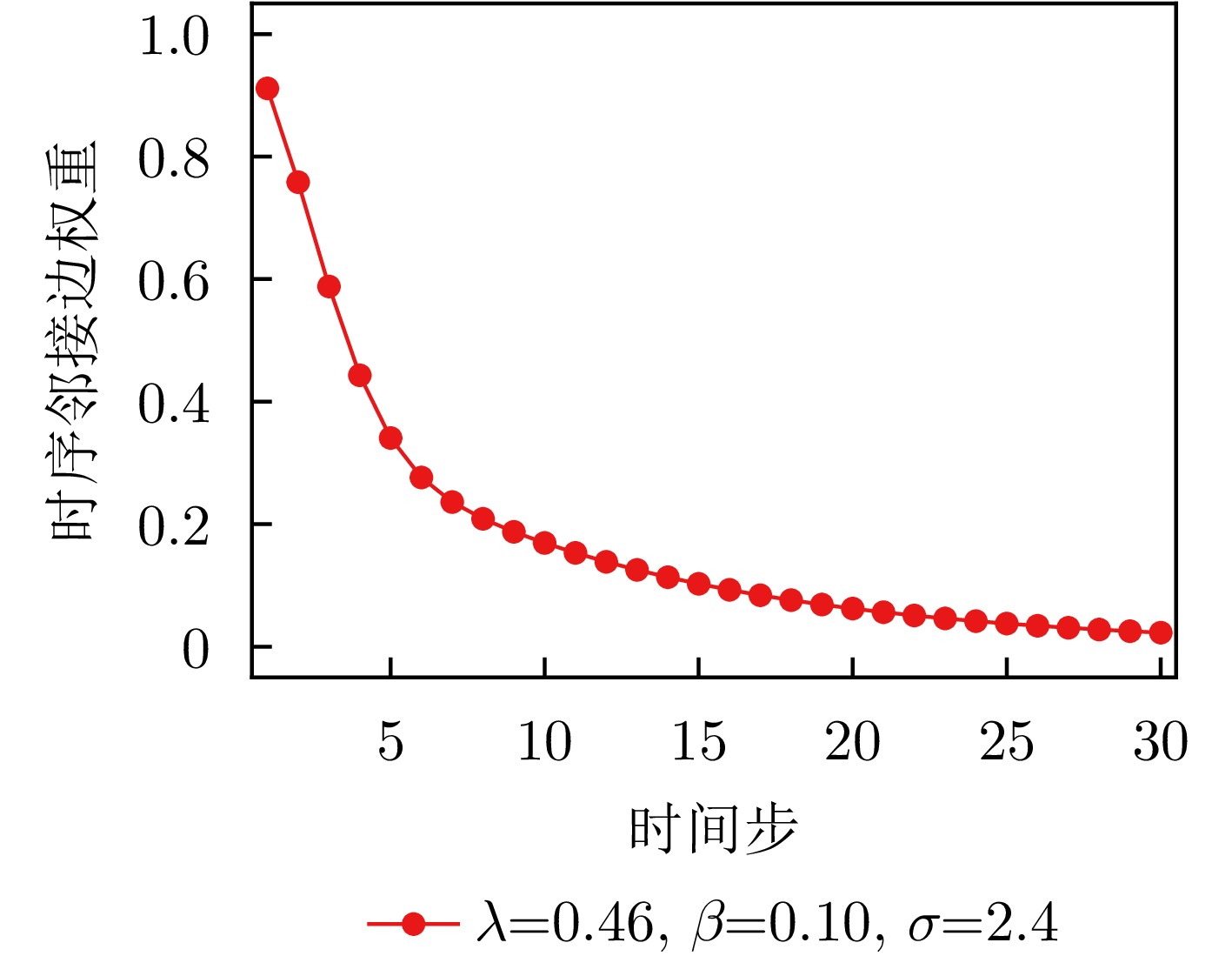
参数 物理意义 搜索范围 最优值 $ \lambda $ 时序衰减权重系数,控制指数衰减与高斯衰减的相对重要性 [0.2, 0.8] 0.46 $ \beta $ 指数衰减速率,决定时序相关性随距离衰减的速度 [0.1, 1.2] 0.10 $ \sigma $ 高斯核宽度,控制高斯衰减函数的平滑程度 [1.0, 3.5] 2.40 $ \alpha $ 特征权重分配系数,调节特征相似边权重的分配比例 [0.1, 0.6] 0.33 $ \eta $ 边权融合系数,控制时序边与特征边融合时的次要权重增强 [0.2, 0.7] 0.59 表 6 不同模型分类性能对比
Table 6. Performance comparison of different models
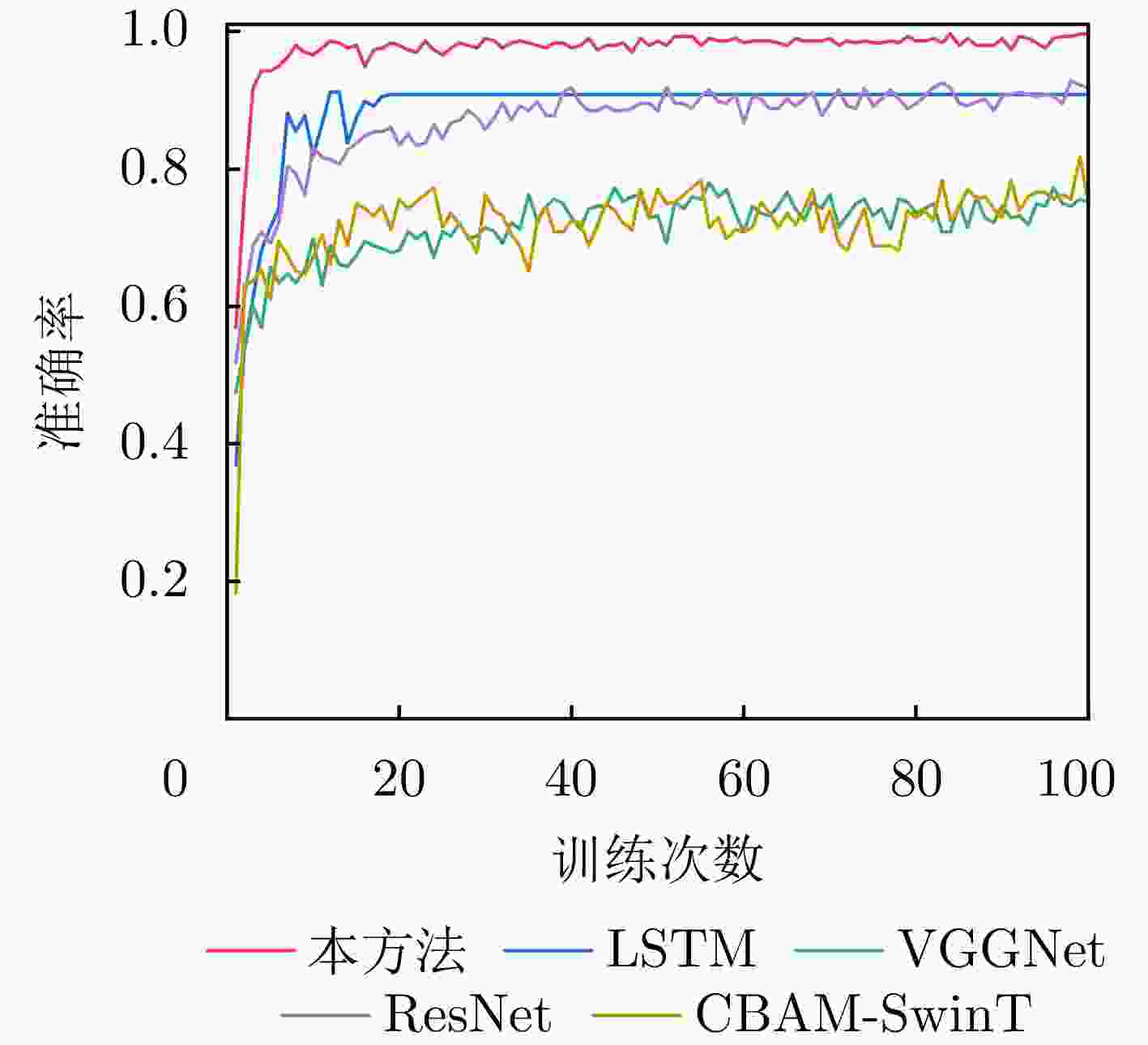
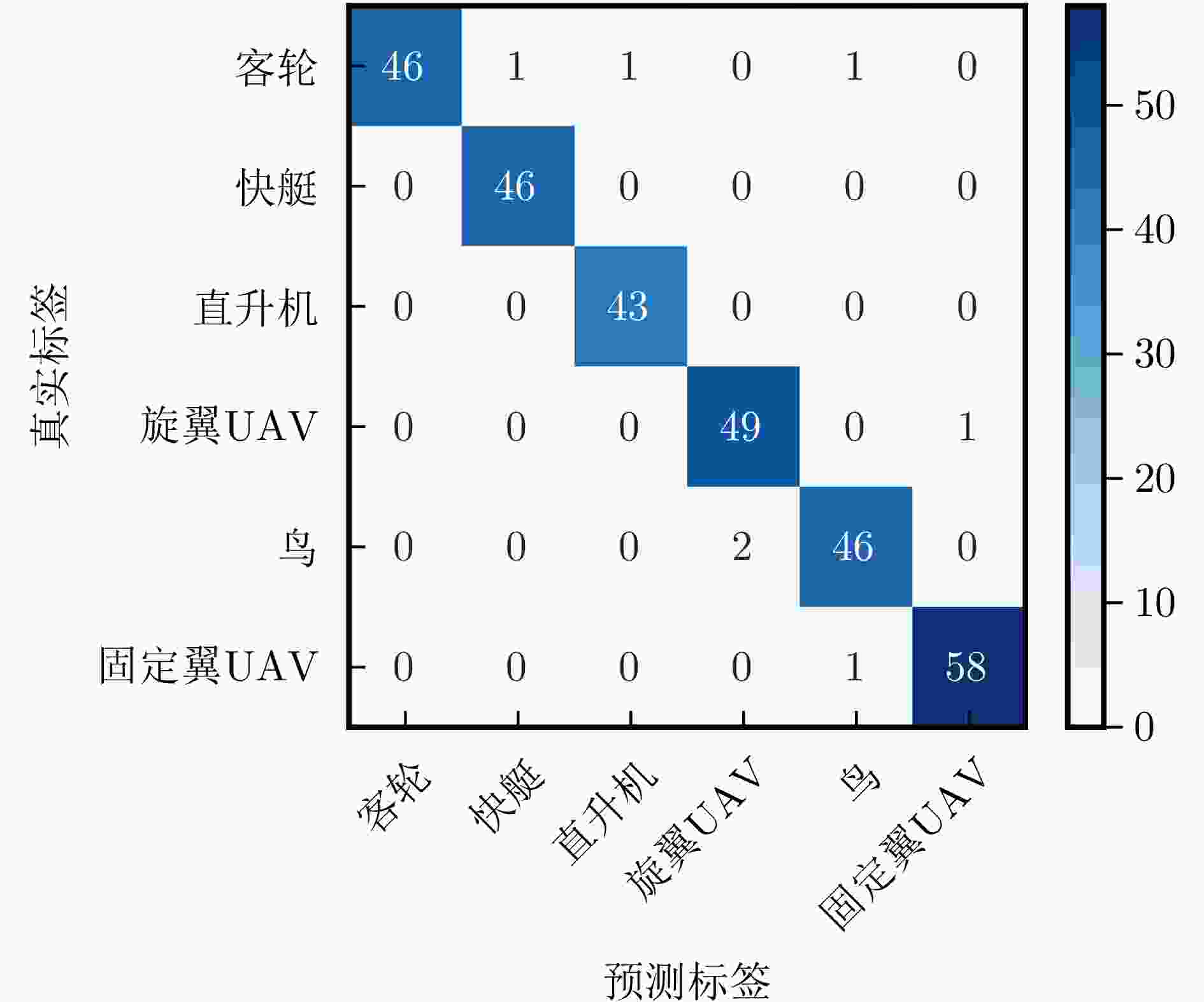
模型 准确率(%) F1分数 参数量(M) 平均预处理时间(ms) 平均推理时延(ms) 总处理时间(ms) 输入数据类型 DG-GCN(本文方法) 99.66 0.9966 0.23 4.45 0.53 4.98 多普勒+物理参数 CBAM-Swin-Transformer[22] 81.69 0.8165 49.18 24 29.86 53.86 多普勒瀑布图 VGGNet 77.97 0.7796 68.21 24 4.66 28.66 多普勒瀑布图 ResNet 92.88 0.9266 24.56 24 6.93 30.93 多普勒瀑布图 LSTM 90.85 0.9078 1.35 0 1.78 1.78 多普勒+物理参数 注:其中VGGNet, ResNet, CBAM-Swin-Transformer的预处理时间包括单样本数据处理、图像绘制和图像保存时间,本文方法预处理时间是指单样本构图时间。 表 7 消融实验结果对比
Table 7. Comparison of ablation experiment results
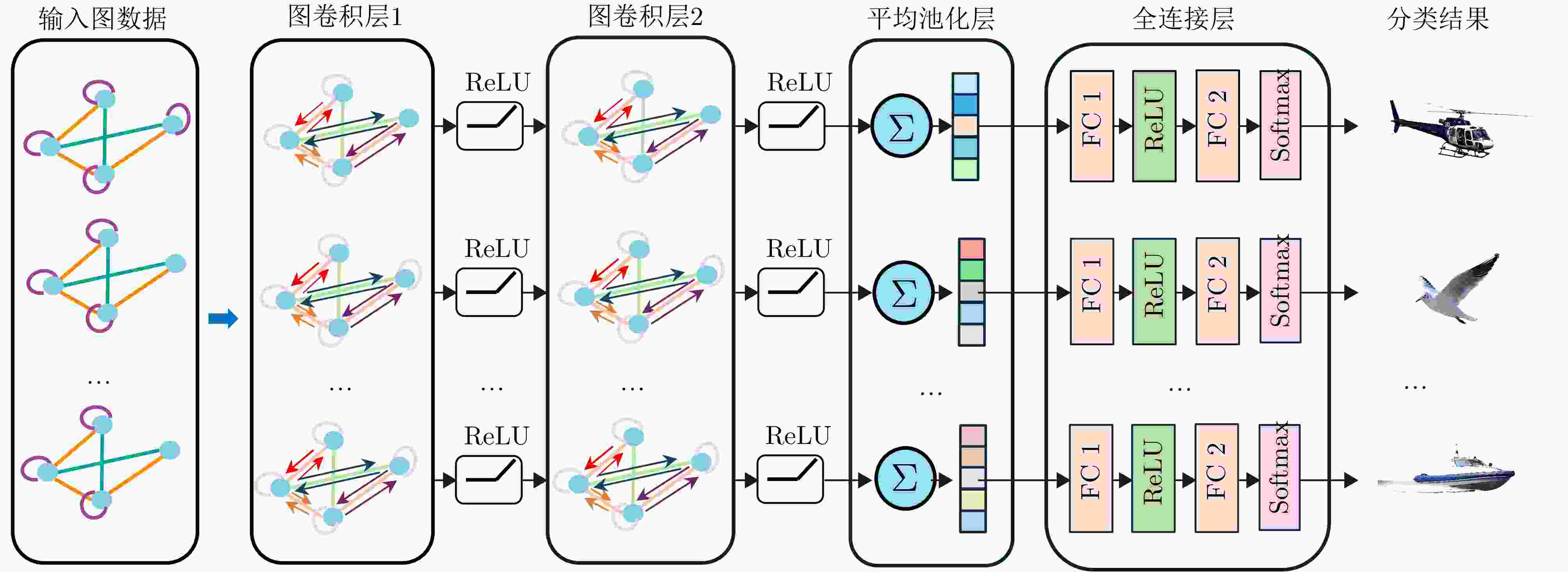
方法 准确率(%) 准确率下降(%) F1分数 说明 完整模型 99.66 — 0.9966 动态边权构建算法+2层GCN 无物理运动参数 97.29 2.37 0.9729 仅使用512维多普勒谱,移除所有物理参数 固定图结构 96.61 3.05 0.9661 移除特征相似边,时序邻接边窗口半径固定为3 无特征相似边 95.59 4.07 0.9558 移除特征相似边,保留时序边权机制 无自适应边权 96.27 3.33 0.9623 时序边和特征相似边固定权重为0.6和0.3 1层GCN 95.93 3.73 0.9595 GCN结构:160→64,仅1层卷积 3层GCN 96.95 2.71 0.9694 GCN结构:160→128→96→64,3层卷积 -
[1] 陈小龙, 陈唯实, 饶云华, 等. 飞鸟与无人机目标雷达探测与识别技术进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068.CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Weishi, RAO Yunhua, et al. Progress and prospects of radar target detection and recognition technology for flying birds and unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068. [2] 郭瑞, 张月, 田彪, 等. 全息凝视雷达系统技术与发展应用综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153.GUO Rui, ZHANG Yue, TIAN Biao, et al. Review of the technology, development and applications of holographic staring radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153. [3] JAHANGIR M and BAKER C J. L-band staring radar performance against micro-drones[C]. 2018 19th International Radar Symposium, Bonn, Germany, 2018: 1–10. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2018.8448107. [4] BENNETT C, JAHANGIR M, FIORANELLI F, et al. Use of symmetrical peak extraction in drone micro-Doppler classification for staring radar[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference, Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266702. [5] JAHANGIR M, ATKINSON G M, ANTONIOU M, et al. Measurements of birds and drones with L-band staring radar[C]. 2021 21st International Radar Symposium, Berlin, Germany, 2021: 1–10. doi: 10.23919/IRS51887.2021.9466224. [6] GRIFFIN B, BALLERI A, BAKER C, et al. Prototyping a dual-channel receiver for use in a staring cooperative radar network for the detection of drones[C]. 2021 21st International Radar Symposium, Berlin, Germany, 2021: 1–7. doi: 10.23919/IRS51887.2021.9466221. [7] 徐世友, 戴婷, 陈曾平. 基于多维特征的全息雷达“低慢小”目标识别[J]. 现代雷达, 2022, 44(11): 1–9. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.11.001.XU Shiyou, DAI Ting, and CHEN Zengping. LSS target recognition in holographic radar based on multi-dimensional features[J]. Modern Radar, 2022, 44(11): 1–9. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.11.001. [8] 陈小龙, 黄勇, 关键, 等. MIMO雷达微弱目标长时积累技术综述[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(12): 1947–1964. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.001.CHEN Xiaolong, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al. Review of long-time integration techniques for weak targets using MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 1947–1964. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.001. [9] 贺治华, 段佳, 芦达. 雷达海面目标识别技术研究进展[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 61–68. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.006.HE Zhihua, DUAN Jia, and LU Da. A review of radar sea target recognition technology[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 61–68. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.006. [10] 田凯祥, 于恒力, 王中训, 等. 基于雷达目标特征可分性的一维特征选择方法[J]. 海军航空大学学报, 2024, 39(4): 453–460,500. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2024.04.007.TIAN Kaixiang, YU Hengli, WANG Zhongxun, et al. One-dimensional feature selection method based on radar target feature divisibility[J]. Journal of Naval Aviation University, 2024, 39(4): 453–460,500. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2024.04.007. [11] KUMAWAT H C, CHAKRABORTY M, RAJ A A B, et al. DIAT-μSAT: Small aerial targets’ micro-Doppler signatures and their classification using CNN[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 6004005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3102039. [12] PARK D, LEE S, PARK S, et al. Radar-spectrogram-based UAV classification using convolutional neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(1): 210. doi: 10.3390/s21010210. [13] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的海上微动目标检测与分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077.SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Detection and classification of maritime target with micro-motion based on CNNs[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077. [14] WANG Jinhao, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. A time-frequency representation method based on ETF-MDNet for radar target micro-motion features[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2025, 34(4): 1199–1208. doi: 10.23919/cje.2024.00.233. [15] YU Xiaojie, WEI Song, FANG Yuyuan, et al. Low-altitude slow small target threat assessment algorithm by exploiting sequential multifeature with long short-term memory[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(18): 21524–21533. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3301090. [16] ZHU J, CHEN H and YE W. A hybrid CNN–LSTM network for the classification of human activities based on micro-Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 24713–24720. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971064. [17] SONG Qiang, HUANG Shilin, ZHANG Yue, et al. Radar target classification using enhanced Doppler spectrograms with ResNet34_CA in ubiquitous radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(15): 2860. doi: 10.3390/rs16152860. [18] WU Qi, CHEN Jie, LU Yue, et al. A complete automatic target recognition system of low altitude, small RCS and slow speed (LSS) targets based on multi-dimensional feature fusion[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(22): 5048. doi: 10.3390/s19225048. [19] YUAN Wang, CHEN Xiaolong, DU Xiaolin, et al. A low slow small target classification network model based on K-band radar dynamic multifeature data fusion[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(1): 1656–1668. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3496493. [20] 陈小龙, 袁旺, 杜晓林, 等. 多波段多角度FMCW雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-FMCWR-2.0)及特征融合分类方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(5): 1276–1293. doi: 10.12000/JR25004.CHEN Xiaolong, YUAN Wang, DU Xiaolin, et al. Multi-band multi-angle FMCW radar low-slow-small target detection dataset (LSS-FMCWR-2.0) and feature fusion classification methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(5): 1276–1293. doi: 10.12000/JR25004. [21] 赵子健, 许述文, 水鹏朗. 基于多域雷达回波数据融合的海面小目标分类网络模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(3): 696–706. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240818.ZHAO Zijian, XU Shuwen, and SHUI Penglang. A network model for sea surface small targets classification based on multidomain radar echo data fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(3): 696–706. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240818. [22] 何肖阳, 陈小龙, 杜晓林, 等. 基于CBAM-Swin-Transformer迁移学习的海上微动目标分类方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2025, 47(4): 1155–1167. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.04.12.HE Xiaoyang, CHEN Xiaolong, DU Xiaolin, et al. Classification of maritime micromotion target based on transfer learning in CBAM-Swin-Transformer[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(4): 1155–1167. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.04.12. [23] SCARSELLI F, GORI M, TSOI A C, et al. The graph neural network model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(1): 61–80. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2008.2005605. [24] KHEMANI B, PATIL S, KOTECHA K, et al. A review of graph neural networks: Concepts, architectures, techniques, challenges, datasets, applications, and future directions[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2024, 11(1): 18. doi: 10.1186/s40537-023-00876-4. [25] SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Maritime target detection based on radar graph data and graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4019705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3133473. [26] SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Radar Maritime Target detection via spatial–temporal feature attention graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5102615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3358862. [27] Meng Han, Peng Yuexing, Wang Wenbo, et al. Spatio-temporal-frequency graph attention convolutional network for aircraft recognition based on heterogeneous radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(6): 5548–5559. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2204.07360. [28] MENG Han, PENG Yuexing, XIANG Wei, et al. Semantic feature-enhanced graph attention network for radar target recognition in heterogeneous radar network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(7): 6369–6377. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3250708. [29] CHEN Lingfeng, PAN Zhiliang, LIU Qi, et al. HRRPGraphNet++: Dynamic graph neural network with meta-learning for few-shot HRRP radar target recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(12): 2108. doi: 10.3390/rs17122108. [30] MENG Han, PENG Yuexing, and WANG Wenbo. Dynamic graph network augmented by contrastive learning for radar target classification[C]. 2024 IEEE Radar Conference, Denver, USA, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2458775.2024.10548626. [31] LIN Huiping, XIE Zixuan, ZENG Liang, et al. Multi-scale time-frequency representation fusion network for target recognition in SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(16): 2786. doi: 10.3390/rs17162786. [32] CHEN Lingfeng, SUN Xiao, PAN Zhiliang, et al. HRRPGraphNet: Make HRRPs to be graphs for efficient target recognition[J]. Electronics Letters, 2024, 60(22): e70088. doi: 10.1049/ell2.70088. [33] WANG Ruiqiu, SU Tao, XU Dan, et al. MIGA-Net: Multi-view image information learning based on graph attention network for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34(11): 10779–10792. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3418979. [34] 陈小龙, 袁旺, 杜晓林, 等. 多波段FMCW雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-FMCWR-1.0)及高分辨微动特征提取方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142.CHEN Xiaolong, YUAN Wang, DU Xiaolin, et al. Multiband FMCW radar LSS-target detection dataset (LSS-FMCWR-1.0) and high-resolution micromotion feature extraction method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142. [35] 陈小龙, 饶桂林, 关键, 等. 被动雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-PR-1.0)及多域特征提取和分析方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(2): 249–268. doi: 10.12000/JR24145.CHEN Xiaolong, RAO Guilin, GUAN Jian, et al. Passive radar low slow small detection dataset (LSS-PR-1.0) and multi-domain feature extraction and analysis methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(2): 249–268. doi: 10.12000/JR24145. [36] 邓振华, 陈小龙, 薛伟, 等. 海空背景下低慢小目标泛探雷达多域多维特征建模与分析[J]. 信号处理, 2024, 40(5): 801–814. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.05.001.DENG Zhenhua, CHEN Xiaolong, XUE Wei, et al. Multi-domain and multi-dimensional feature modeling and analysis of low, slow, and small targets via ubiquitous radar under sea and air background[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(5): 801–814. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.05.001. [37] LIU Huaiyuan, YANG Donghua, LIU Xianzhang, et al. TodyNet: Temporal dynamic graph neural network for multivariate time series classification[J]. Information Sciences, 2024, 677: 120914. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2024.120914. [38] DUAN Ziheng, XU Haoyan, WANG Yueyang, et al. Multivariate time-series classification with hierarchical variational graph pooling[J]. Neural Networks, 2022, 154: 481–490. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2022.07.032. [39] YIN Yongqiang, ZHENG Xiangwei, HU Bin, et al. EEG emotion recognition using fusion model of graph convolutional neural networks and LSTM[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 100: 106954. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106954. [40] FENG Lin, CHENG Cheng, ZHAO Mingyan, et al. EEG-based emotion recognition using spatial-temporal graph convolutional LSTM with attention mechanism[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2022, 26(11): 5406–5417. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2022.3198688. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: