Human Contour Restoration and Action Recognition in Ultra-wideband Radar Imaging Based on Spatio-temporal Features
-
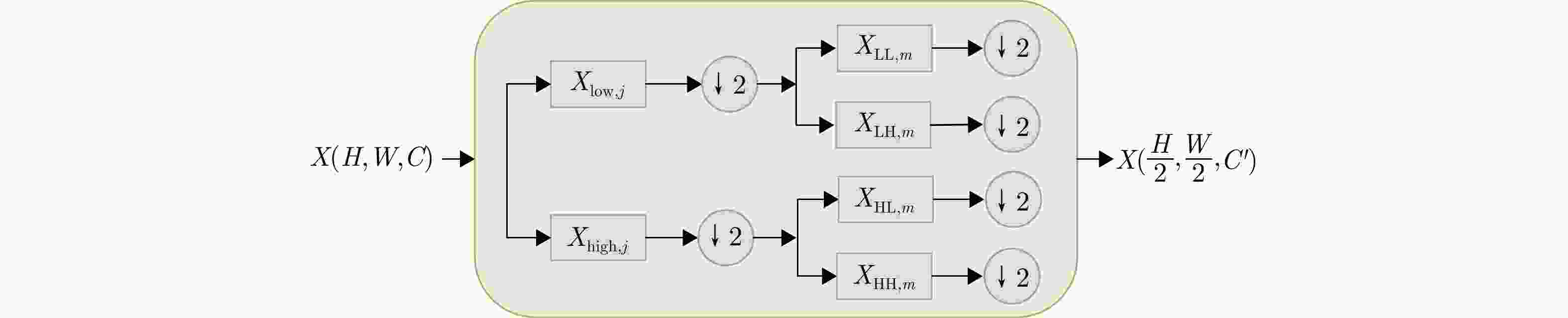
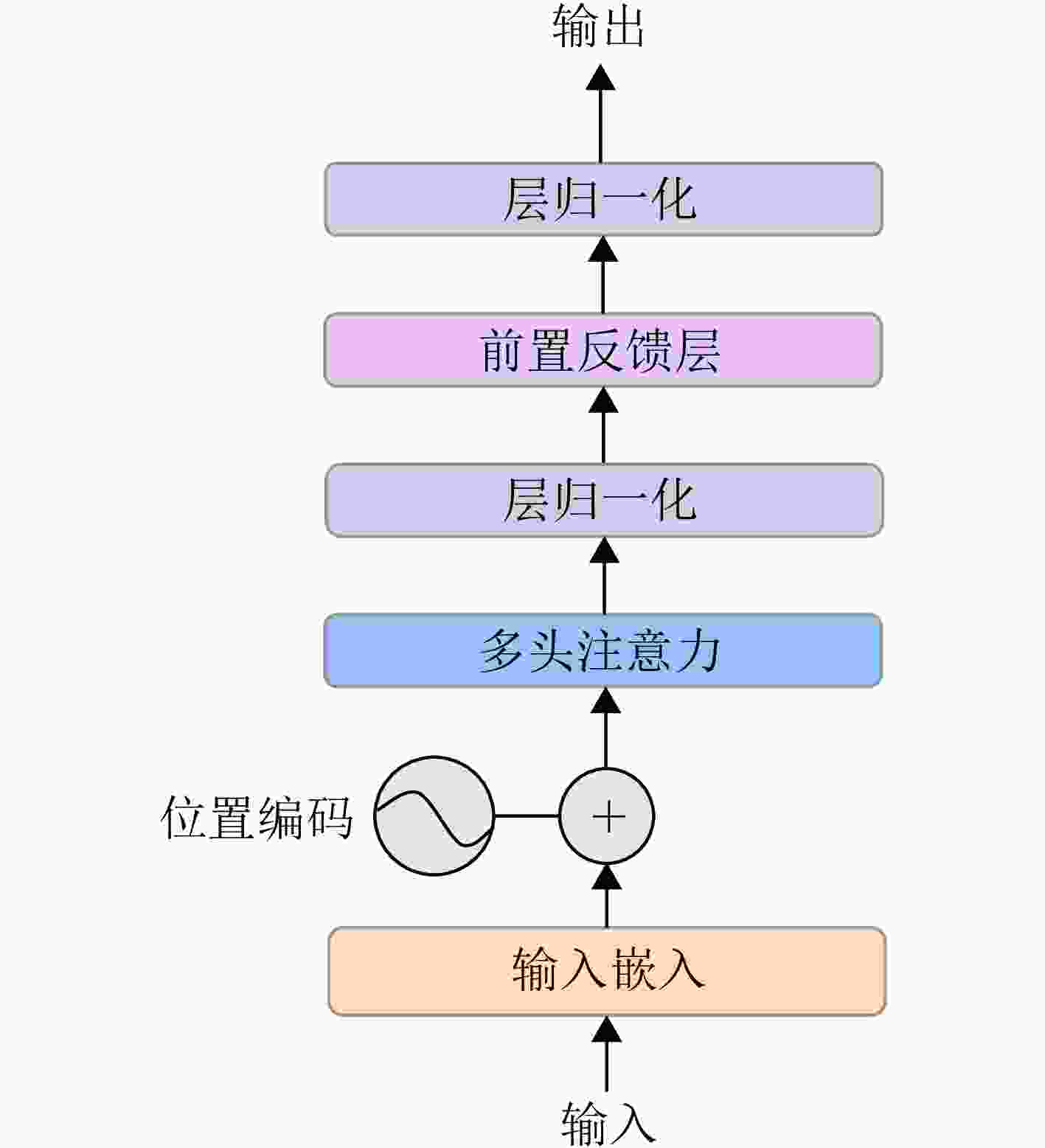
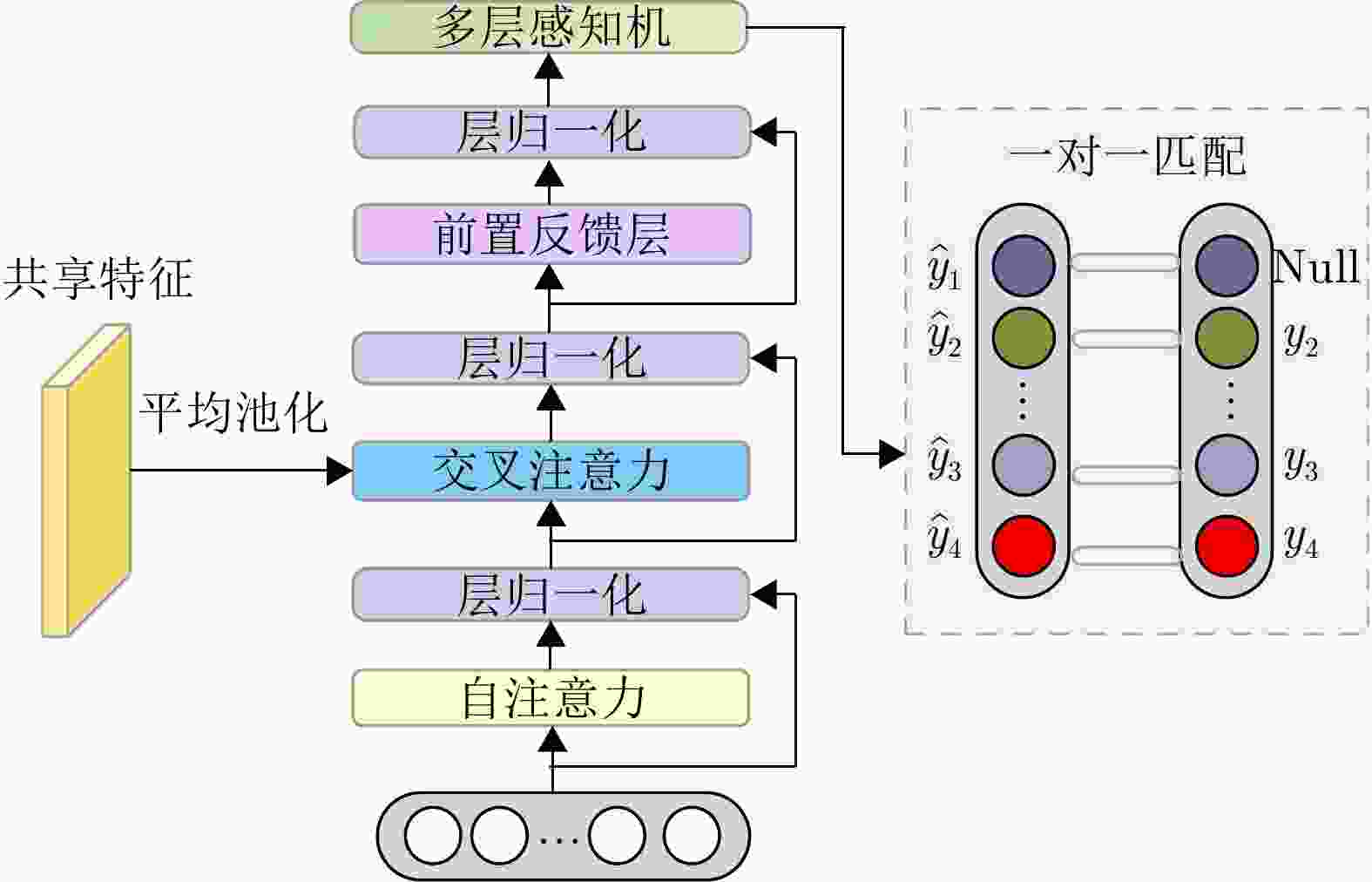
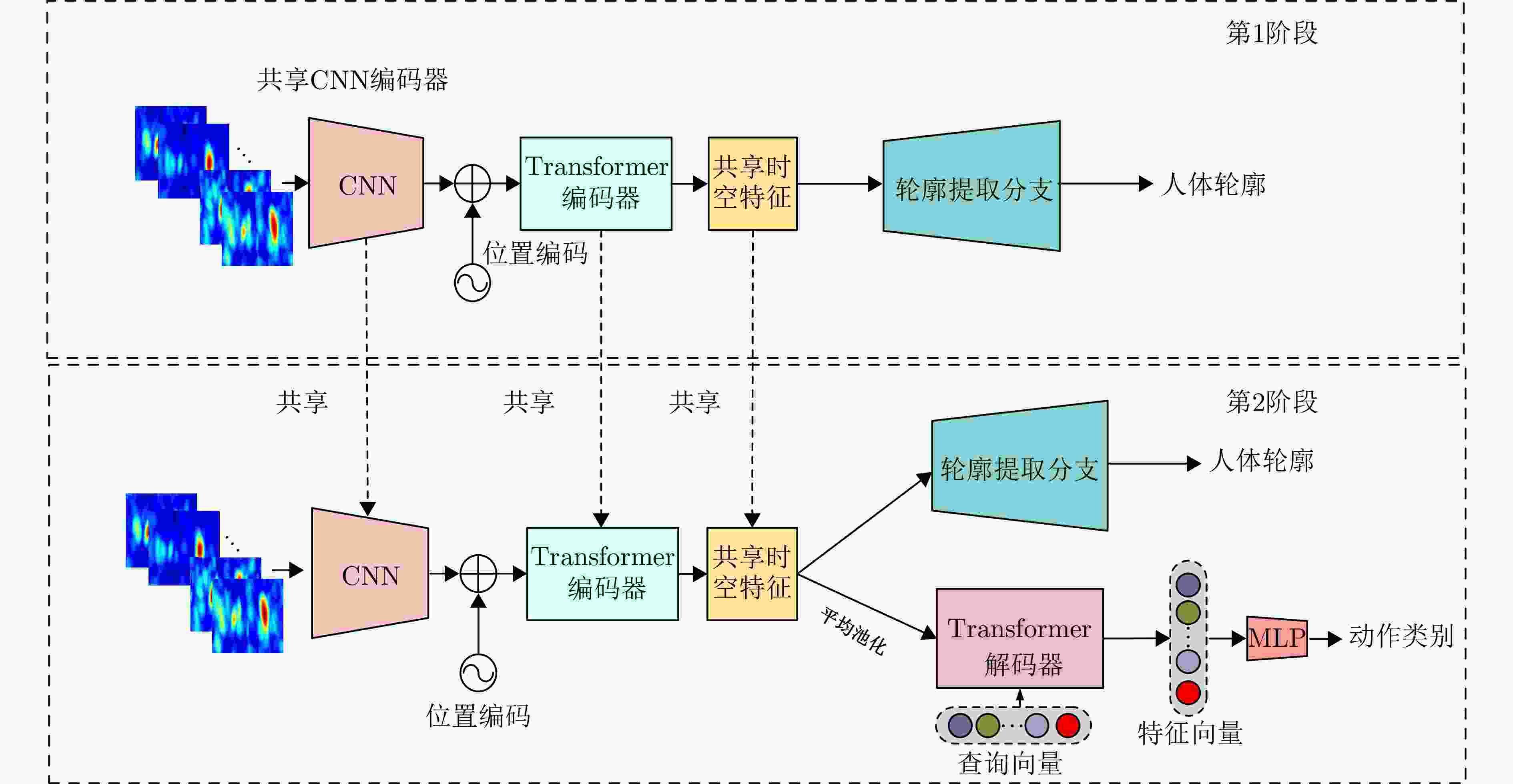
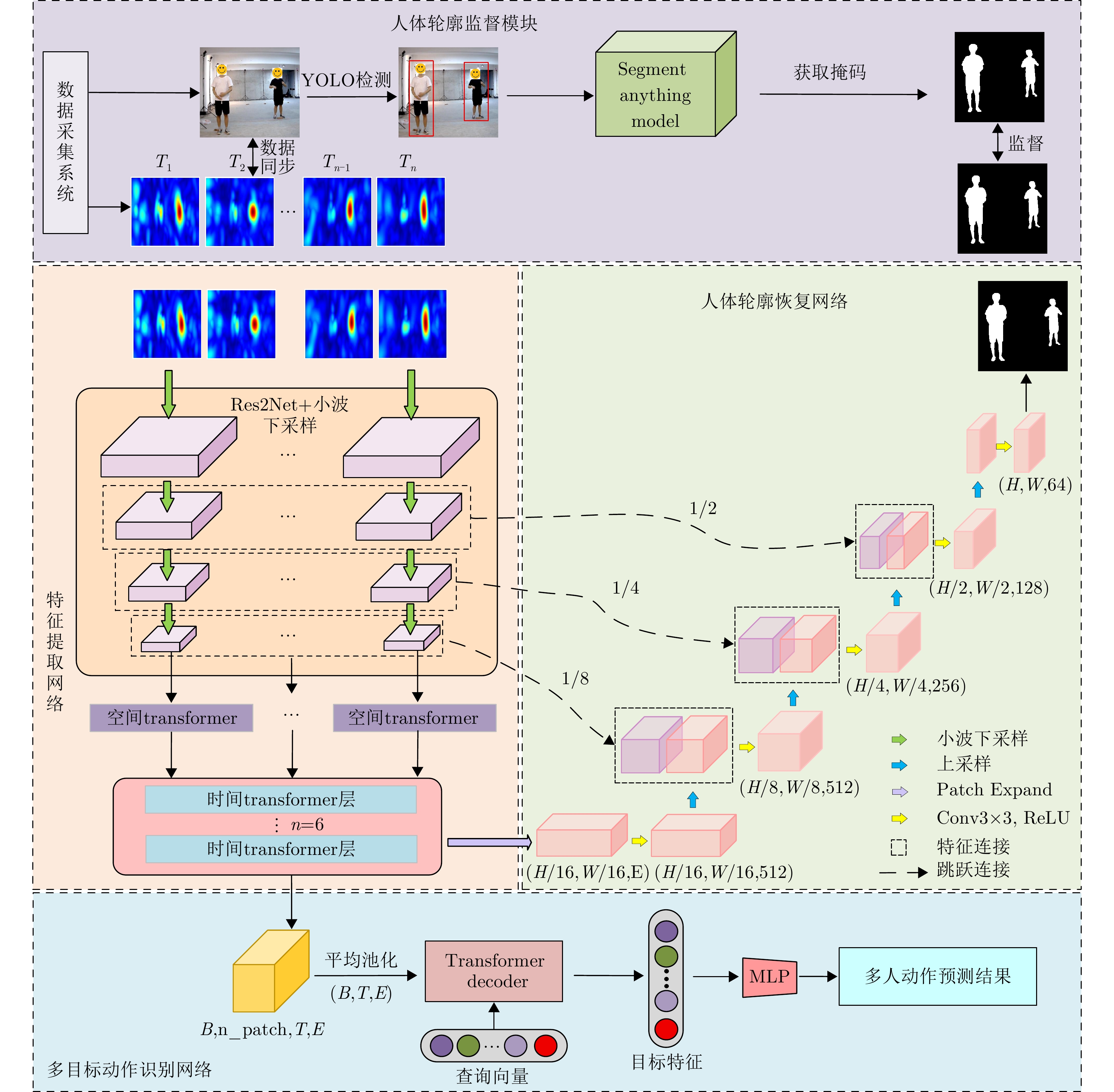
摘要: 超宽带(UWB) MIMO雷达因其分辨率良好、穿透性强、隐私保护性好以及对光照条件不敏感等优势,在人体智能感知领域展现出巨大潜力,但低图像分辨率导致轮廓模糊、动作难辨。基于以上背景,该文提出一种融合时空特征的人体轮廓恢复与动作识别联合框架(STWTnet)。该方法采用多任务网络框架,利用Res2Net和小波下采样提取雷达图像空间细节特征,并以Transformer建立时空依赖,通过多任务学习共享人体轮廓恢复与动作识别的共性特征,同时避免特征冲突,实现两任务的互补。在自建同步UWB-光学数据集上的实验表明,STWTnet具有较好的动作识别率而且在轮廓精度显著优于现有技术,为隐私友好、全天候的人体行为理解提供了新途径。Abstract: Ultra-Wideband (UWB) Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) radar has demonstrated enormous potential in the field of human intelligent perception due to its excellent resolution, strong penetration capability, strong privacy protection, and insensitivity to illumination conditions. However, its low image resolution results in blurred contours and indistinguishable actions. To address this issue, this study developes a joint framework, Spatiotemporal Wavelet Transformer network (STWTnet), for human contour restoration and action recognition by integrating spatiotemporal features. By adopting a multi-task network architecture, the proposed framework leverages Res2Net and wavelet downsampling to extract spatial detail features from radar images and employs a Transformer to establish spatiotemporal dependencies. Through multi-task learning, it shares the common features of human contour restoration and action recognition, enabling mutual complementarity between the two tasks while avoiding feature conflicts. Experiments conducted on a self-built, synchronized UWB optical dataset demonstrate that STWTnet achieves high action recognition accuracy and significantly outperforms existing techniques in contour restoration precision, providing a new approach for privacy-preserving, all-weather human behavior understanding.
-
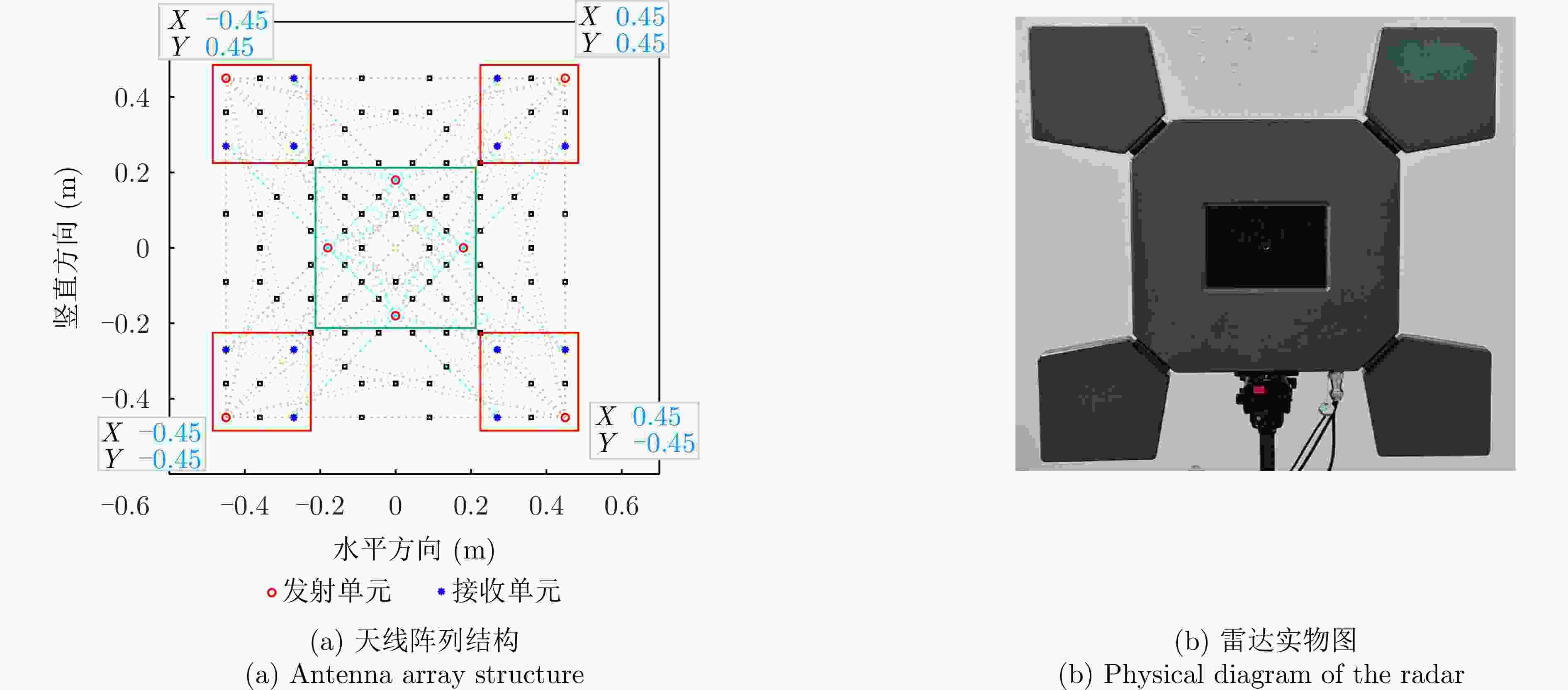
表 1 超宽带MIMO雷达具体参数表
Table 1. Specific parameters table of UWB MIMO radar
参数 指标 工作频段 2.5~3.5 GHz 信号带宽 1 GHz 信号体制 调频连续波(FMCW)制式 MIMO阵列 12发射通道+ 8接收通道 可穿透介质 塑料、木板、砖墙等 系统尺寸 84 cm×84 cm 表 2 不同训练方法下的性能与参数对比
Table 2. Comparison of performance and parameters under different training
训练方法 mIoU Accuracy (%) 单任务人体轮廓恢复 0.8716 - 单任务动作识别 - 97.4 单阶段联合 0.7615 97.6 两阶段联合 0.8721 98.5 表 3 不同损失权重参数下的性能对比
Table 3. Comparison of performance under different loss weight parameters
$ {\lambda }_{{\mathrm{seg}}} $ $ {\lambda }_{{\mathrm{action}}} $ mIoU Accuracy (%) 0.1 0.9 0.8699 98.6 0.3 0.7 0.8712 98.6 0.5 0.5 0.8721 98.5 0.7 0.3 0.8720 98.2 表 4 单帧输入下不同方法的性能与参数对比
Table 4. Comparison of performance and parameters of different methods under single-frame input
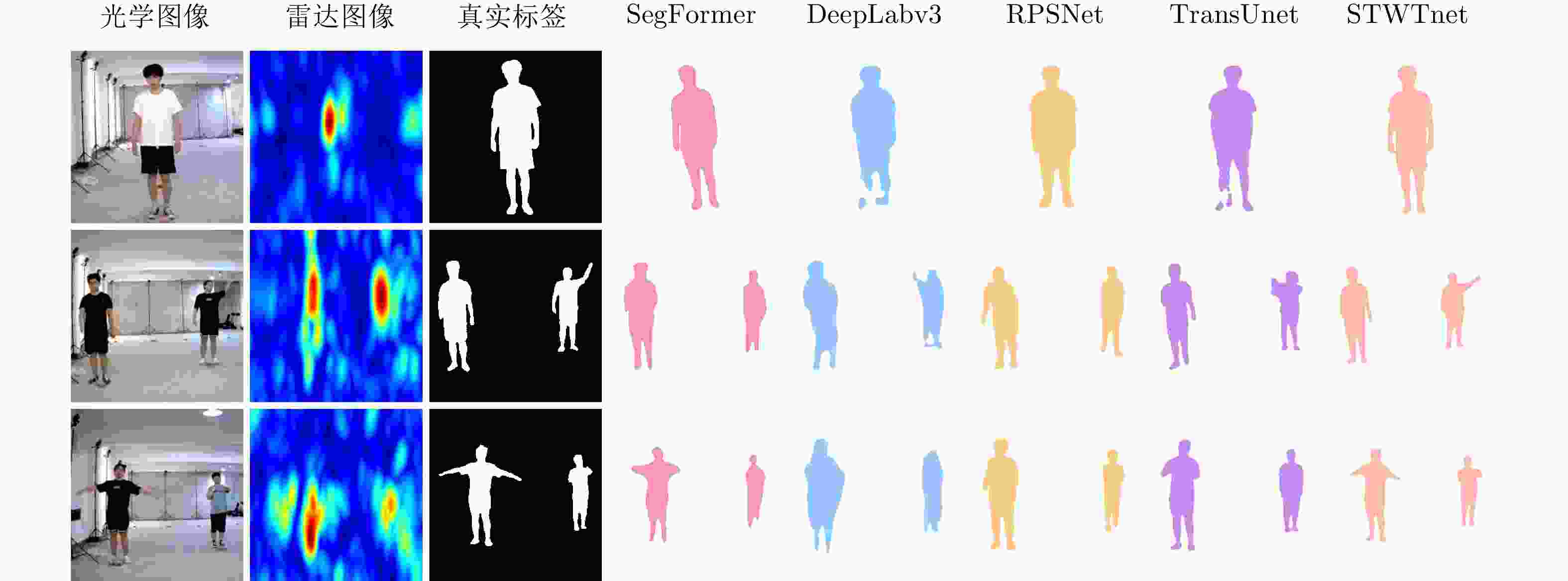
网络模型 mIoU Parameters (MB) FLOPs (GB) Unet 0.724 13.4 31.0 RPSNet 0.748 123.4 137.3 Deeplabv3 0.736 39.6 40.8 TransUnet 0.765 115.1 15.0 SegNeXt 0.705 3.5 7.4 SegFormer 0.734 35.7 10.6 STWTnet 0.867 57.4 12.5 表 5 核心模块消融实验结果
Table 5. Results of core module ablation experiments
网络 mIoU Accuracy(%) STWTnet (Conv Downsample) 0.817 96.52 STWTnet (ResNet) 0.798 94.42 STWTnet (LSTM) 0.821 96.01 STWTnet 0.872 98.56 注:STWTnet()表示以STWTnet完整模型为基础,将原模块替换为传统模块(X)。 表 6 输入不同帧长的性能对比
Table 6. Comparison of performance with different input frame lengths
帧长 mIoU Accuracy (%) FLOPs (GB) 1 0.8670 - 12.46 4 0.8721 98.56 48.54 8 0.8723 98.72 77.44 12 0.8720 97.44 106.34 表 7 不同距离下的性能对比
Table 7. Comparison of performance at different distances
测试距离(m) mIoU Accuracy (%) 1~3 0.8686 98.12 3~5 0.8913 98.57 5~7 0.8527 99.01 表 8 不同场景下的性能对比
Table 8. Comparison of performance under different scenarios
测试场景 mIoU Accuracy (%) 场景1 0.8720 98.56 场景2 0.8104 98.42 -
[1] YANG Xiaopeng, GAO Weicheng, QU Xiaodong, et al. Through-the-wall radar human activity micro-Doppler signature representation method based on joint Boulic-sinusoidal pendulum model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2025, 73(2): 1248–1263. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2024.3441591. [2] WANG Wendong, ZHAO Chengzhi, LI Xin, et al. Research on multimodal fusion recognition method of upper limb motion patterns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 4008312. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3289556. [3] ZHAO Mingmin, LI Tianhong, ALSHEIKH M A, et al. Through-wall human pose estimation using radio signals[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7356–7365. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00768. [4] PIERCE J, WONG R Y, and MERRILL N. Sensor illumination: Exploring design qualities and ethical implications of smart cameras and image/video analytics[C]. 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, USA, 2020: 1–19. doi: 10.1145/3313831.3376347. [5] ZHOU Xu, QIAN Lichang, YOU Pengjie, et al. Fall detection using convolutional neural network with multi-sensor fusion[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), San Diego, USA, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICMEW.2018.8551564. [6] 郑学召, 丁文, 黄渊, 等. 不同领域下超宽带雷达探测呼吸心跳信号研究综述[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(1): 204–228. doi: 10.12000/JR24154.ZHENG Xuezhao, DING Wen, HUANG Yuan, et al. A review of UWB radar detection of respiration and heartbeat signals in different scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(1): 204–228. doi: 10.12000/JR24154. [7] FAN Lijie, LI Tianhong, YUAN Yuan, et al. In-home daily-life captioning using radio signals[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 105–123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_7. [8] SONG Ruiyuan, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. RF-URL: Unsupervised representation learning for RF sensing[C]. The 28th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Sydney, Australia, 2022: 282–295. doi: 10.1145/3495243.3560529. [9] LONG Xianlei, WANG Ping, GU Fuqiang, et al. Accurate and efficient human activity recognition through semi-supervised deep learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(12): 23105–23116. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2025.3561418. [10] RANI S, CHOWDHURY A, CHAKRAVARTY T, et al. Exploiting unique state transitions to capture micro-Doppler signatures of human actions using CW radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(24): 27878–27886. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3126436. [11] 陈一凡, 刘剑刚, 贾勇, 等. 基于仿真样本迁移学习的穿墙雷达高分辨成像方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 807–821. doi: 10.12000/JR24049.CHEN Yifan, LIU Jiangang, JIA Yong, et al. High-resolution imaging method for through-the-wall radar based on transfer learning with simulation samples[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 807–821. doi: 10.12000/JR24049. [12] 金添, 何元, 李新羽, 等. 超宽带雷达人体行为感知研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1147–1155. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211044.JIN Tian, HE Yuan, LI Xinyu, et al. Advances in human activity sensing using ultra-wide band radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1147–1155. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211044. [13] ZHAO Lin, ZHOU Hui, ZHU Xinge, et al. LIF-Seg: LiDAR and camera image fusion for 3D LiDAR semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 1158–1168. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2023.3277281. [14] ZHENG Zhijie, PAN Jun, NI Zhikang, et al. Recovering human pose and shape from through-the-wall radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5112015. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3162333. [15] ZHENG Zhijie, ZHANG Diankun, LIANG Xiao, et al. Unsupervised human contour extraction from through-wall radar images using dual UNet[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3500705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3229954. [16] SONG Ruiyuan, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. RF-URL 2.0: A general unsupervised representation learning method for RF sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2025, 47(10): 8889–8906. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2025.3587718. [17] DONG Ruchan, XU Dazhuan, ZHAO Jin, et al. Sig-NMS-based faster R-CNN combining transfer learning for small target detection in VHR optical remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8534–8545. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2921396. [18] CONG J, QU L, YANG T, et al. Global–Local point cloud transformer for through-the-wall human activity recognition based on UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2026, 62: 493–505. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3623615. [19] 宋永坤, 晏天兴, 张可, 等. 基于点云时空特征的超宽带雷达轻量化人体行为识别方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(1): 1–15. doi: 10.12000/JR24110.SONG Yongkun, YAN Tianxing, ZHANG Ke, et al. A lightweight human activity recognition method for ultra-wideband radar based on spatiotemporal features of point clouds[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(1): 1–15. doi: 10.12000/JR24110. [20] LI Xiaoxiong, ZHANG Shuning, CHEN Si, et al. Through-wall multi-person action recognition using enhanced YOLOv5 and IR-UWB radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(3): 5711–5722. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3513983. [21] WANG Changlong, ZHU Dongsheng, SUN Lijuan, et al. Real-time through-wall multihuman localization and behavior recognition based on MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5104312. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3274207. [22] SONG Yongkun, YAN Tianxing, ZHANG Ke, et al. Human action recognition based on bimodal data and spationtemporal features using UWB MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(5): 12598–12612. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3575751. [23] 丁传威, 刘芷麟, 张力, 等. 基于MIMO雷达成像图序列的切向人体姿态识别方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(1): 151–167. doi: 10.12000/JR24116.DING Chuanwei, LIU Zhilin, ZHANG Li, et al. Tangential human posture recognition with sequential images based on MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(1): 151–167. doi: 10.12000/JR24116. [24] ZHENG Zhijie, ZHANG Diankun, LIANG Xiao, et al. RadarFormer: End-to-end human perception with through-wall radar and transformers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(12): 18285–18299. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3314031. [25] 张锐, 龚汉钦, 宋瑞源, 等. 基于4D成像雷达的隔墙人体姿态重建与行为识别研究[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(1): 44–61. doi: 10.12000/JR24132.ZHANG Rui, GONG Hanqin, SONG Ruiyuan, et al. Through-wall human pose reconstruction and action recognition using four-dimensional imaging radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(1): 44–61. doi: 10.12000/JR24132. [26] GAO Shanghua, CHENG Mingming, ZHAO Kai, et al. Res2Net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(2): 652–662. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2938758. [27] XU Guoping, LIAO Wentao, ZHANG Xuan, et al. Haar wavelet downsampling: A simple but effective downsampling module for semantic segmentation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 143: 109819. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109819. [28] WANG Ao, CHEN Hui, LIU Lihao, et al. YOLOv10: Real-time end-to-end object detection[C]. The 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 3429. [29] KIRILLOV A, MINTUN E, RAVI N, et al. Segment anything[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 3992–4003. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00371. [30] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 213–229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13. [31] SOUMA R, KIDERA S, and KIRIMOTO T. Fast and accurate permittivity estimation algorithm for UWB internal imaging radar[C]. 2011 3rd International Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR). Seoul, Korea (South), 2011: 1–4. [32] ANDERSSON L E. On the determination of a function from spherical averages[J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 1988, 19(1): 214–232. doi: 10.1137/0519016. [33] LI Xunsong, SUN Pengzhan, LIU Yangcen, et al. Simultaneous detection and interaction reasoning for object-centric action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2025, 27: 5283–5295. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2025.3543033. [34] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.32. [35] WU Fuping, ZHANG Le, SUN Yang, et al. MT-CooL: Multi-task cooperative learning via flat minima searching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2025, 44(4): 1648–1658. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3512173. [36] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [37] CHEN L C, ZHU Yukun, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 833–851. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49. [38] CHEN J N, LU Y Y, YU Q H, et al. TransUNet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation[C]. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021, Cham, 2021: 3–13. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87196-0_1. [39] XIE Enze, WANG Wenhai, YU Zhiding, et al. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (NeurIPS 2021), La Jolla, CA, USA, 2021: 12077–12090. [40] GUO Menghao, LU Chengze, HOU Qibin, et al. SegNeXt: Rethinking convolutional attention design for semantic segmentation[C]. The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 84. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: