Lightweight Discrimination Network for Non-spoofing Active Jamming in SAR under Low JSR
-
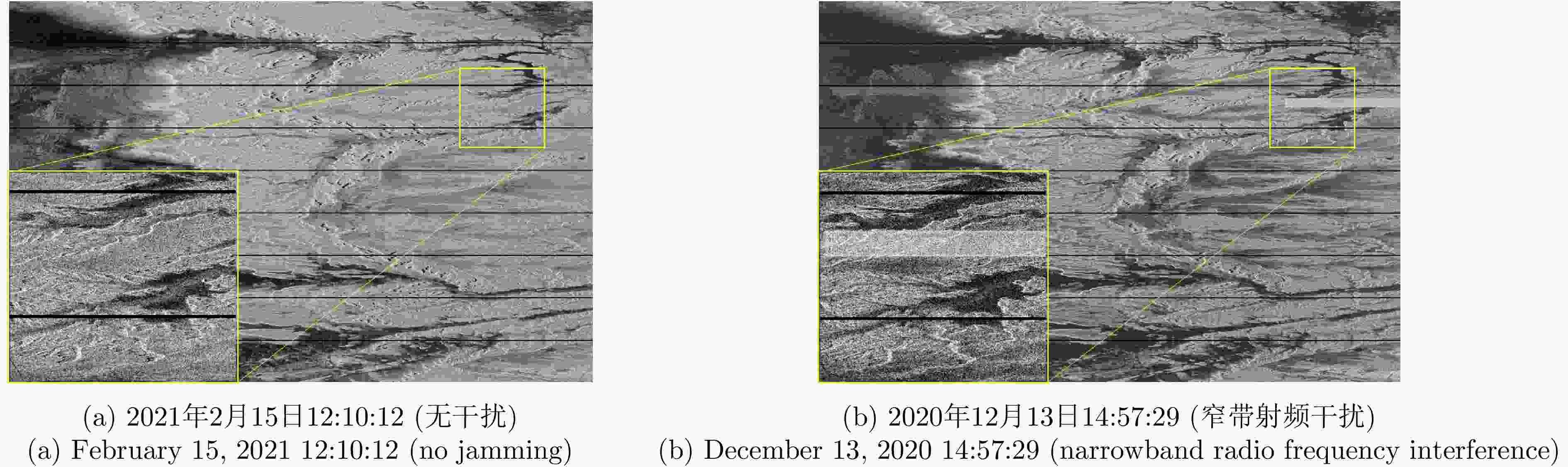
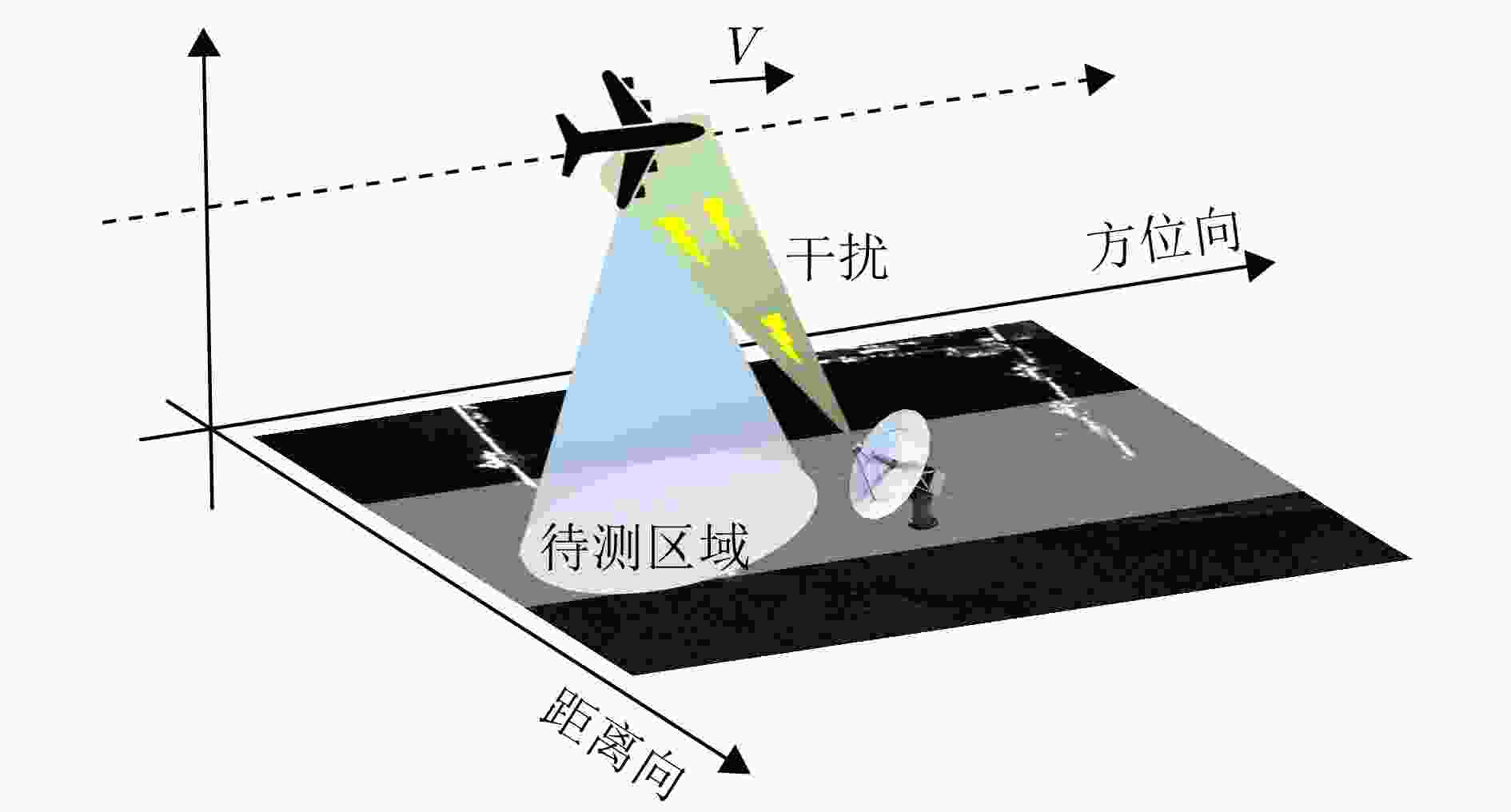
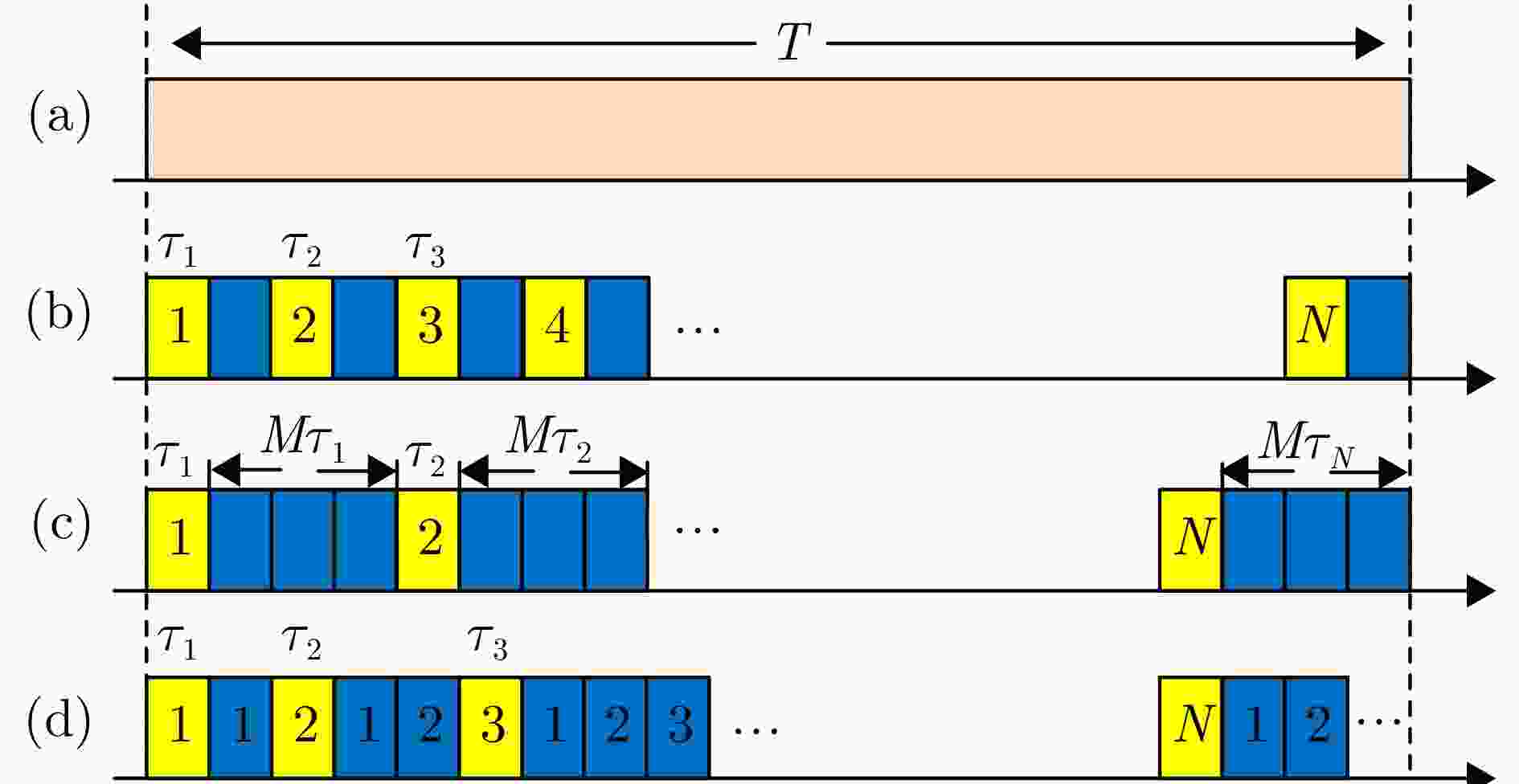
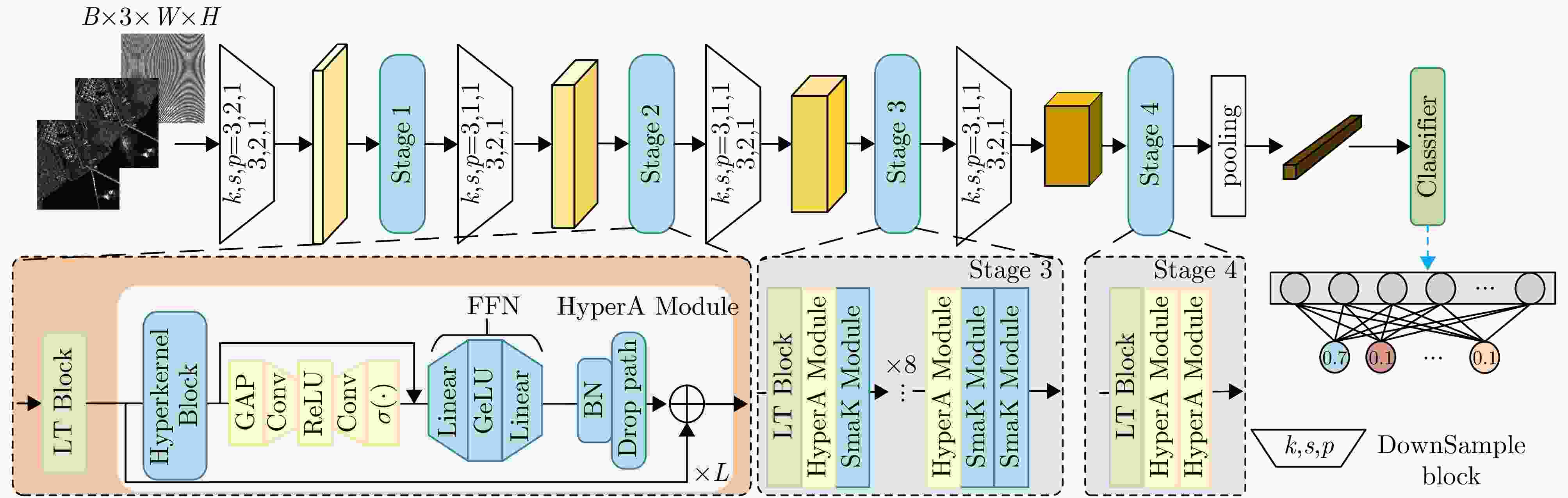
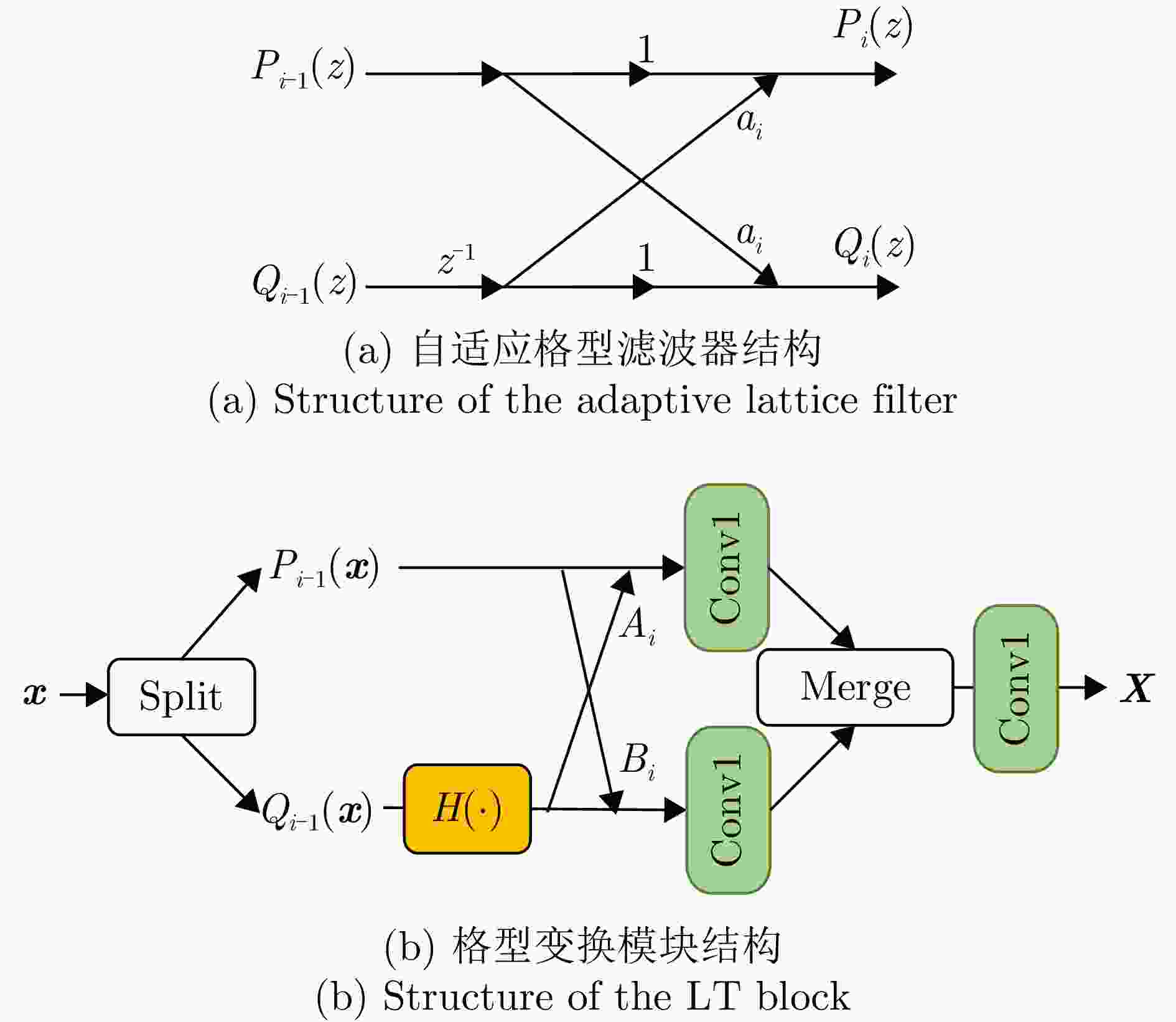
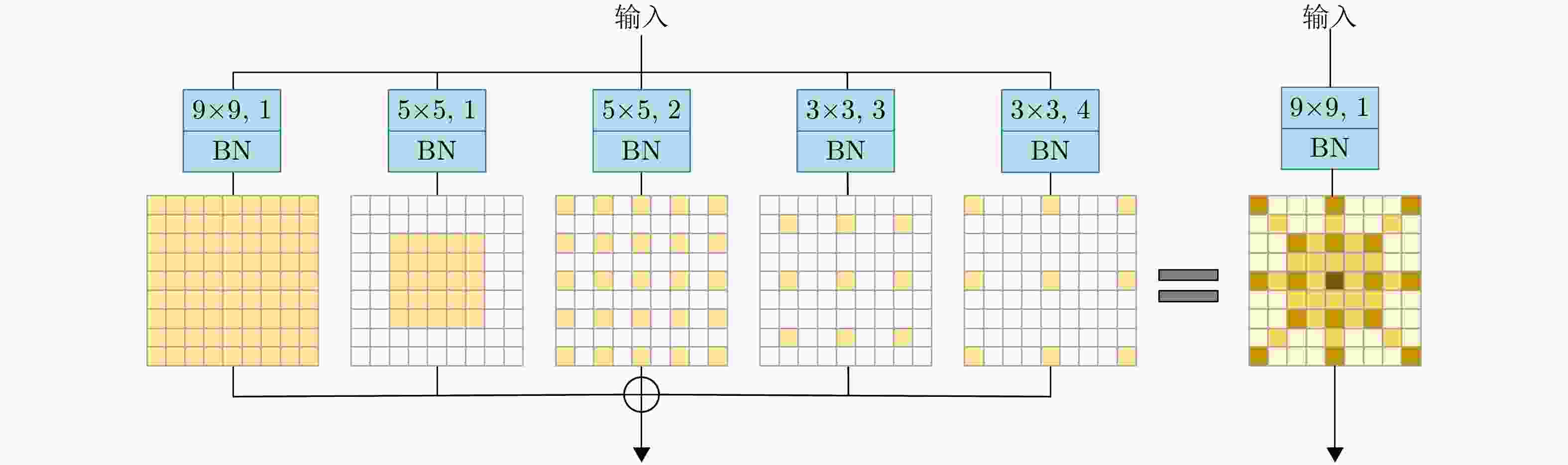
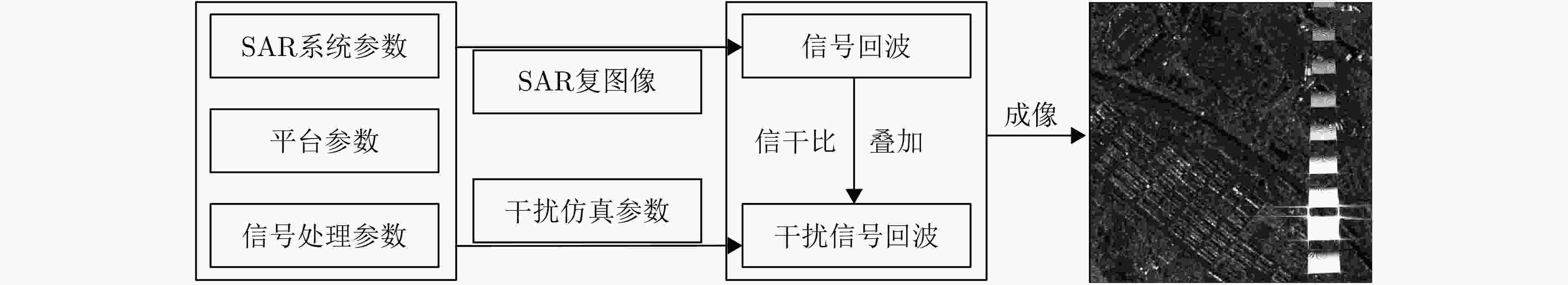
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)以其全天时、全天候及高分辨成像优势,在军事侦察与遥感监测等领域发挥着关键作用。然而,现代复杂电磁环境中的多样化干扰手段,严重破坏SAR回波信号特征,导致成像结果出现模糊、失真乃至目标完全不可辨识等问题。鉴于不同类型干扰在形成机理和抑制策略上的本质差异,精确的干扰鉴别成为实现有效抗干扰的核心前提。当前SAR干扰鉴别方法仍面临两大挑战:其一,在干扰信号与目标信号能量相近时,干扰特征易被目标能量掩盖,难以可靠检测与鉴别;其二,现有鉴别网络普遍复杂度过高、实时性差,难以满足实际工程应用需求。针对上述问题,该文提出一种基于轻量化网络的低干信比SAR非虚假目标类有源干扰鉴别网络。该方法创新性地引入了格型变换模块与超核感知模块。其中,格型变换模块旨在强化对干扰目标的细粒度特征提取能力,进而显著提升了低干信比条件下的干扰鉴别性能;超核感知模块则基于点目标成像特性,设计了超核卷积,该卷积在增强上下文信息捕获能力的同时,亦实现了算法的轻量化。实验部分通过多维度评估验证了方法的优越性,包括模块的有效性分析、不同模型的精度-复杂度权衡分析,以及不同干信比下的鲁棒性测试。结果表明,所提方法在低干信比条件下仍能保持较高鉴别性能,同时计算效率满足实时性需求。Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) plays a pivotal role in military reconnaissance and remote-sensing applications, given its all-weather, day-and-night operability and high-resolution imaging performance. However, diverse jamming techniques in modern complex electromagnetic environments severely distort SAR echo signals, leading to blurred or distorted imaging results and, in extreme cases, complete target unrecognizability. Given the fundamental differences in formation mechanisms and suppression strategies of different jamming types, precise jamming identification is a core prerequisite for effective counterjamming. Current SAR jamming identification methods face two major challenges. First, when the energy of the jamming signal is comparable to that of the target signal, the jamming features are easily masked, making reliable detection and identification difficult. Second, existing identification networks generally suffer from excessive complexity and poor real-time performance, limiting their practicality in engineering applications. To address these issues, this paper proposes a lightweight network-based non-spoofing active jamming identification method for SAR under low Jamming-to-Signal Ratio (JSR) conditions. This method introduces two key components: a lattice transform block that boosts interference discrimination at low JSR by refining fine-grained feature extraction and a hyperkernel-aware module that, through a custom hyperkernel block based on point target imaging, enhances context capture while ensuring algorithmic lightweighting. The superiority of the proposed method is validated through multidimensional evaluations, including effectiveness analyses of the modules, accuracy-complexity trade-off analysis of different models, and robustness testing under varying JSR conditions. The proposed method maintains high identification performance even under low JSR conditions while meeting real-time computational efficiency requirements.
-
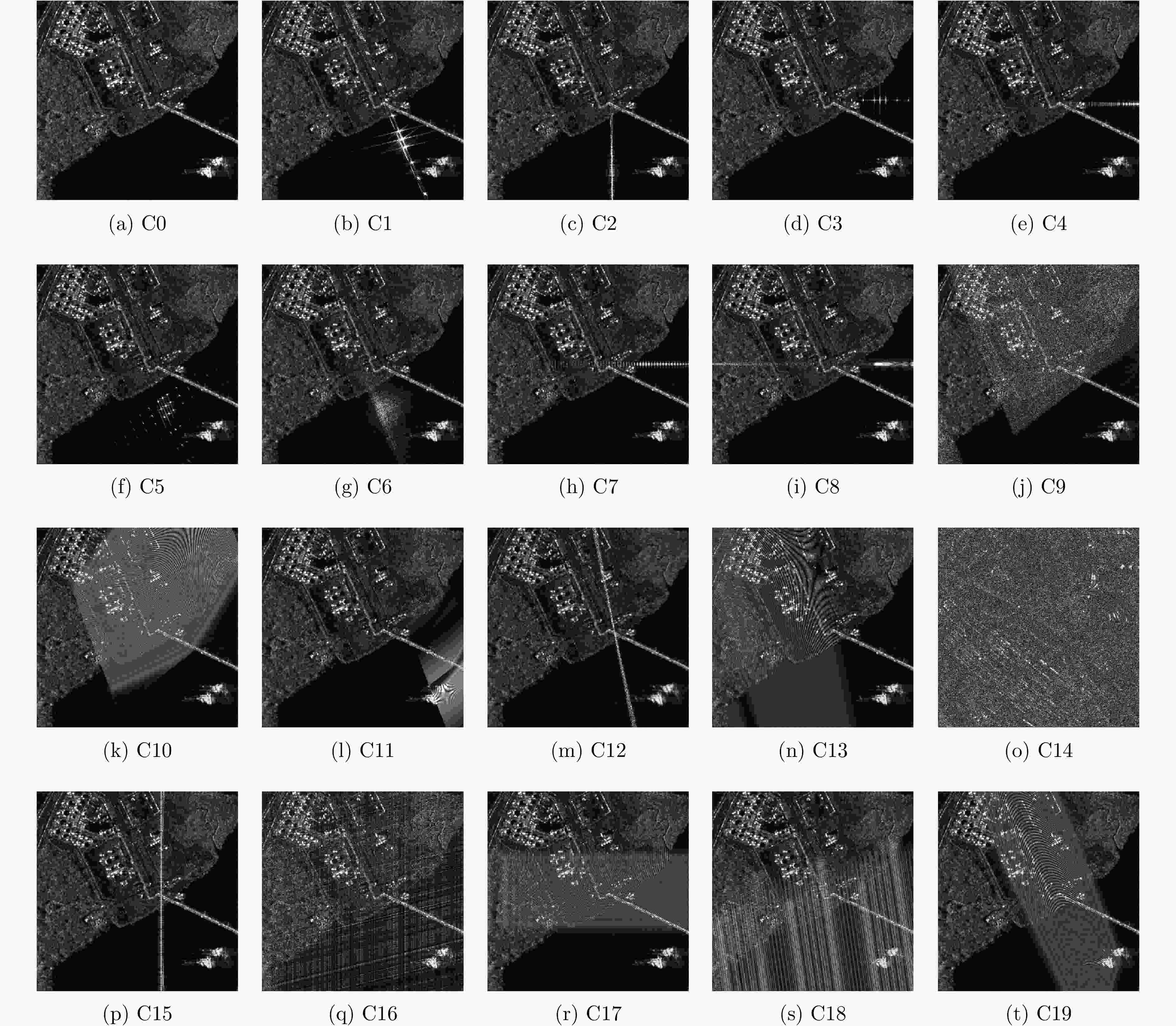
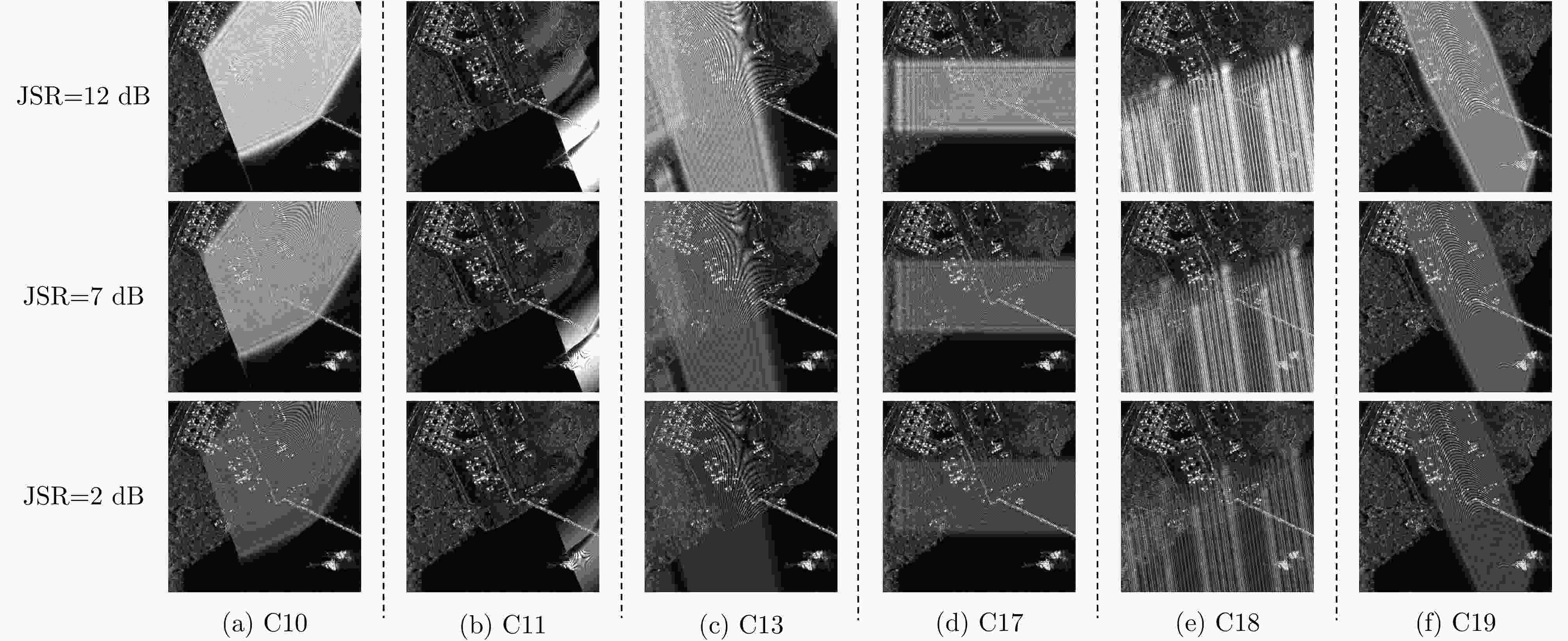
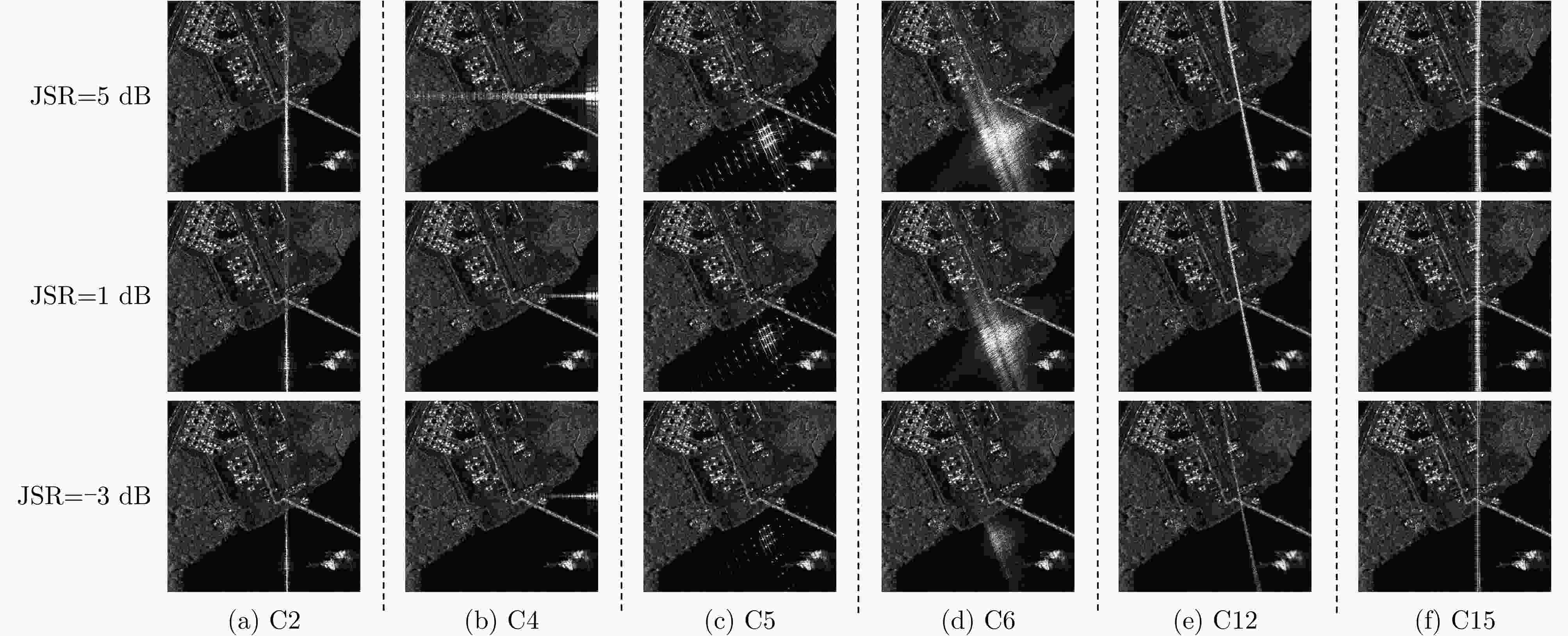
表 1 干扰样式编码
Table 1. Jamming coding
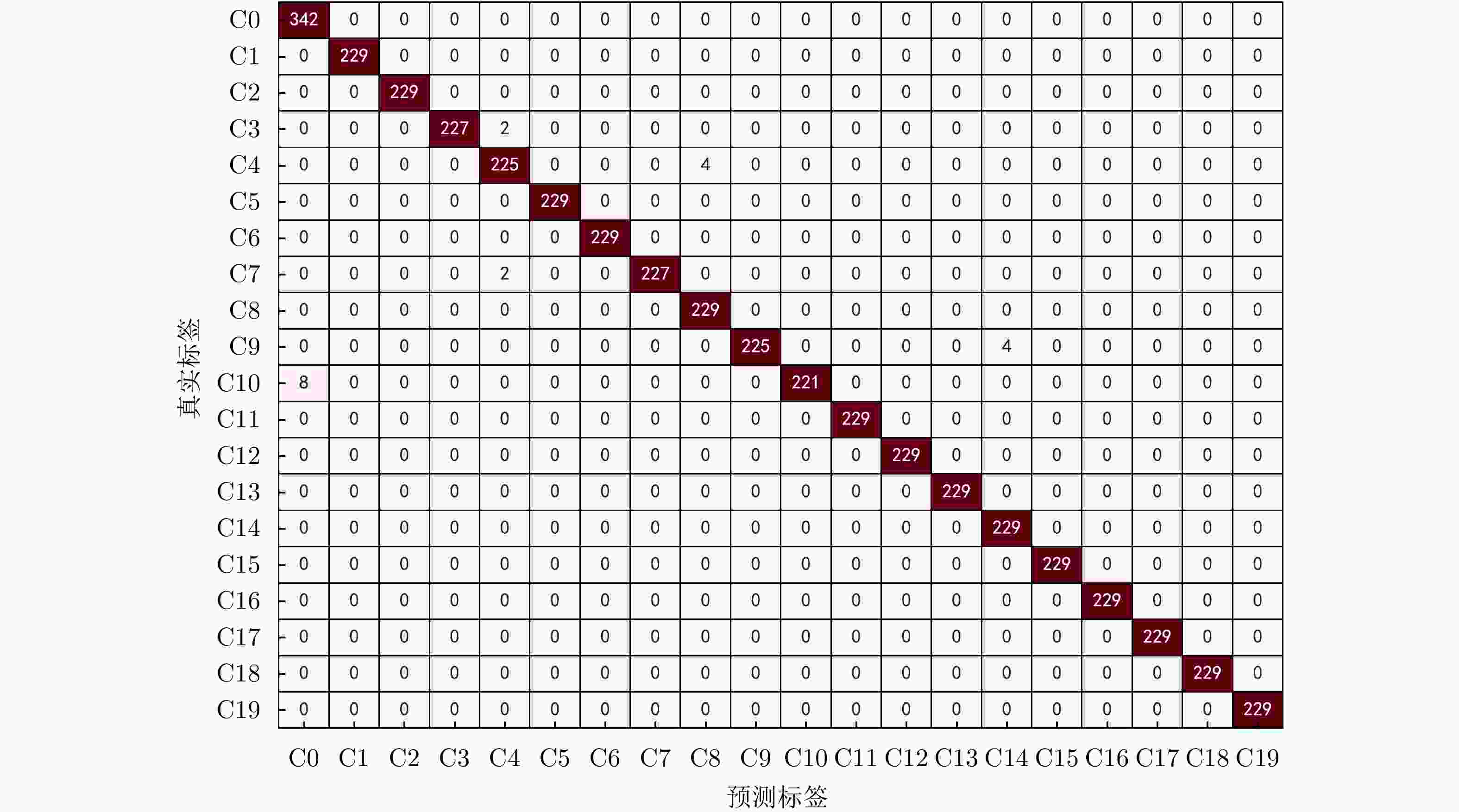
干扰类型 编号 干扰类型 编号 无干扰 C0 方位向均匀间歇采样转发干扰 C1 方位向非均匀间歇采样转发干扰 C2 距离向均匀间歇采样转发干扰 C3 距离向非均匀间歇采样转发干扰 C4 二维均匀间歇采样转发干扰 C5 二维非均匀间歇采样转发干扰 C6 均匀间歇采样重复转发干扰 C7 非均匀间歇采样循环转发干扰 C8 乘性调制噪声干扰 C9 步进移频干扰 C10 分段移频干扰 C11 随机移频干扰 C12 失配干扰 C13 噪声压制干扰 C14 一维卷积噪声干扰 C15 二维卷积噪声干扰 C16 窄带射频干扰 C17 正弦调频宽带射频干扰 C18 线性调频宽带射频干扰 C19 表 2 消融实验结果(%)
Table 2. Ablation study results (%)
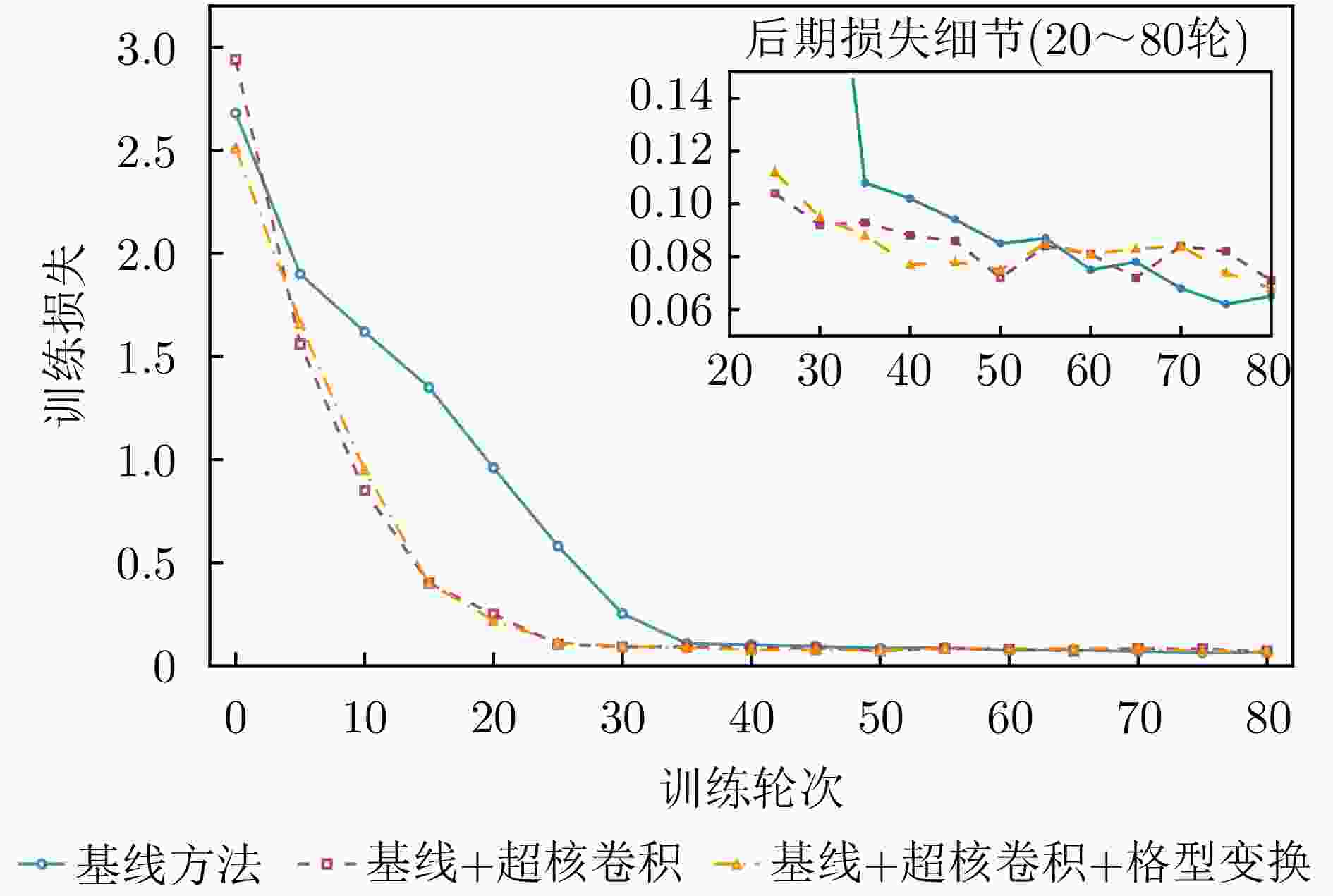
模型结构 OA AP AR F1 基线模型 85.66 84.44 85.98 85.20 基线模型+超核卷积模块 91.44 93.90 95.25 94.57 基线模型+格型变换模块+
超核卷积模块99.57 99.56 99.63 99.60 表 3 各种鉴别方法的准确率性能(%)
Table 3. Comparison of accuracy for various discrimination methods (%)
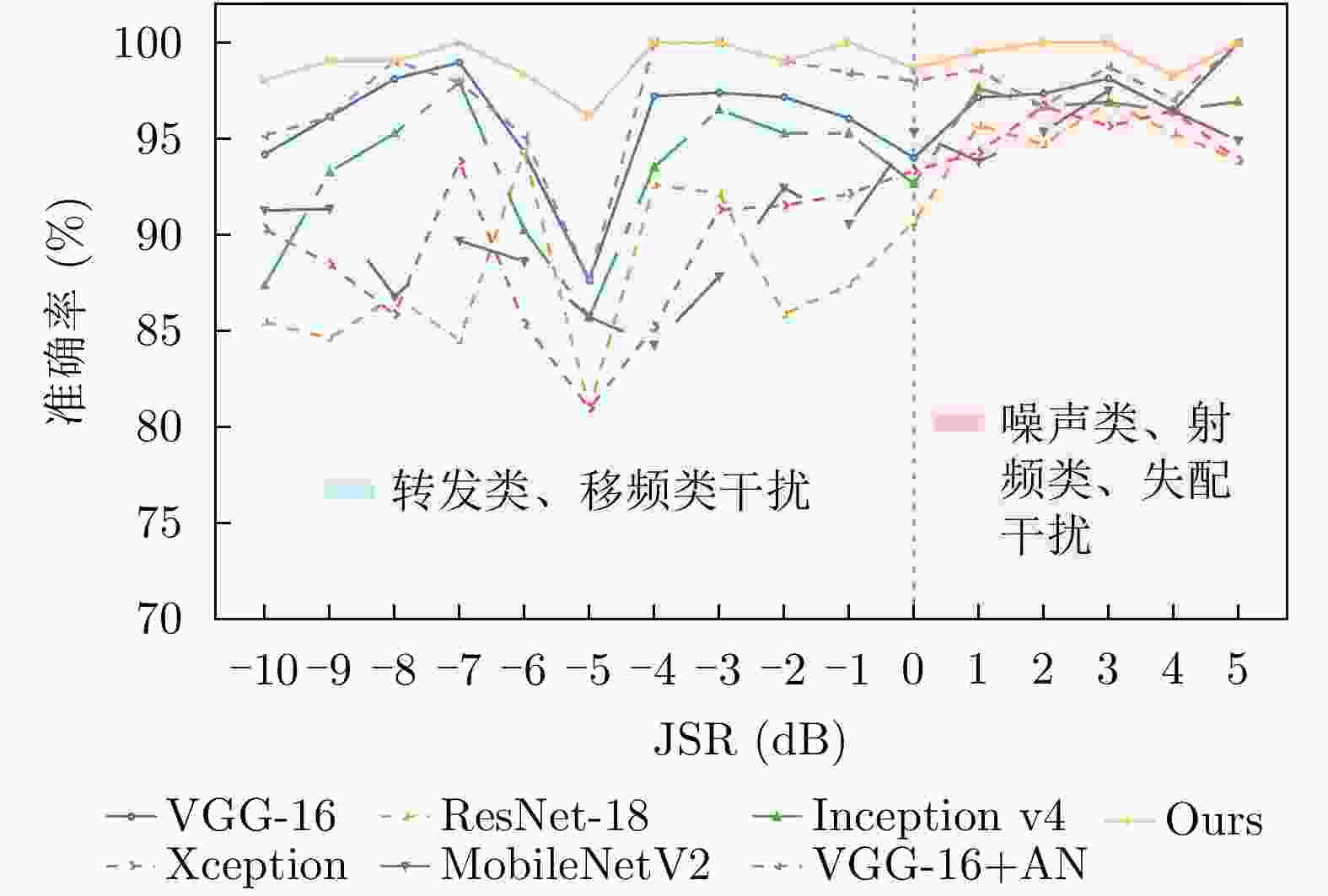
编号 VGG-16 ResNet-18 Inception v4 Xception Mobilenet V2 VGG-16+AN Ours C0 99.12 98.69 96.78 94.96 93.06 99.42 100.00 C1 100.00 93.89 100.00 93.45 96.33 99.13 100.00 C2 91.27 95.63 90.39 84.72 96.33 100.00 100.00 C3 96.07 92.14 98.69 84.28 94.50 99.13 99.13 C4 90.39 74.24 59.83 74.22 80.73 98.25 98.25 C5 96.94 90.83 96.07 73.36 86.24 94.76 100.00 C6 100.00 96.07 98.25 99.13 95.41 97.82 100.00 C7 97.82 60.26 96.94 94.76 69.72 99.13 99.13 C8 82.10 78.17 86.03 76.86 74.31 95.20 100.00 C9 96.51 95.20 99.56 95.63 93.58 96.07 98.25 C10 82.53 86.03 82.53 79.91 85.32 84.72 96.51 C11 100.00 100.00 99.56 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 C12 94.32 90.39 93.45 88.21 94.50 98.25 100.00 C13 100.00 100.00 100.00 98.69 100.00 100.00 100.00 C14 100.00 99.56 89.08 99.56 99.08 100.00 100.00 C15 100.00 95.63 100.0 98.25 96.33 100.00 100.00 C16 100.00 99.13 95.20 82.53 98.17 99.56 100.00 C17 100.00 99.13 100.00 100.00 98.17 100.00 100.00 C18 100.00 98.25 99.56 98.69 98.17 100.00 100.00 C19 100.00 99.56 97.82 95.63 99.08 100.00 100.00 注:加粗数值表示最优。 表 4 各种鉴别方法的性能指标
Table 4. Performance metrics of various discrimination models
指标 VGG-16 ResNet-18 Inception v4 Xception Mobilenet V2 VGG-16+AN Ours OA(%) 96.42 92.35 94.05 90.76 92.51 98.10 99.57 AP(%) 96.35 92.14 93.99 90.64 92.56 98.07 99.56 AR(%) 96.84 92.48 94.92 91.79 92.45 99.42 99.63 F1 (%) 96.66 92.31 93.99 91.21 92.51 98.24 99.60 Kappa (%) 96.23 91.94 93.74 90.26 92.04 98.00 99.55 Flops(G) 80.7 9.5 37.8 2.4 1.7 365 3.5 Params(M) 134 11.19 41.17 20.85 2.25 2338.06 4.32 TPI(s) 0.51 0.09 0.47 0.42 0.15 3.44 0.21 注:加粗数值表示最优。 -
[1] SADIQ R, QURESHI M B, and KHAN M M. De-convolution and De-noising of SAR based GPS images using hybrid particle swarm optimization[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2023, 32(1): 166–176. doi: 10.23919/cje.2021.00.138. [2] ZHOU Lifan, ZHOU Xuanyu, FENG Huanghao, et al. Transformer-based semantic segmentation for flood region recognition in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal on Miniaturization for Air and Space Systems, 2025, 6(3): 222–229. doi: 10.1109/JMASS.2025.3542124. [3] LIU Niantang, ZHAO Qunshan, WILLIAMS R, et al. Enhanced crop mapping using polarimetric SAR features and time series deep learning: A case study in Bei’an, China[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5002917. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3544339. [4] PEREIRA-PIRES J, GUERRA-HERNÁNDEZ J, SILVA J M N, et al. Forest height mapping with multifrequency SAR in mediterranean forests[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 4403415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3538216. [5] 武俊杰, 杨建宇, 李中余, 等. 双基地SAR成像处理方法综述[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(5): 1115–1141. doi: 10.12000/JR25067.WU Junjie, YANG Jianyu, LI Zhongyu, et al. Review of bistatic synthetic aperture radar imaging methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(5): 1115–1141. doi: 10.12000/JR25067. [6] CAO Rui, WANG Yong, GIUSTI E, et al. 3-D reconstruction of ship target based on SAR images sequence and scatterer tracking technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5200415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3514699. [7] WU Wanmin, PU Wei, HAI Yu, et al. A deep learning-based SAR imaging framework for ship targets with sample-wise variant motion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5214116. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3575325. [8] DOMÍNGUEZ E M, BROTZER P, CASALINI E, et al. Mapping urban areas and infrastructure through fusion of airborne SAR 3-D images: A comparative study with ALS sensors[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 6164–6181. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3541425. [9] WANG Chongsong, LI Yuzhao, SHANG Yuanzhe, et al. An anchor-free method for aircraft detection in SAR images based on density map[C]. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing, Zhuhai, China, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICSIDP62679.2024.10868269. [10] 黄岩, 赵博, 陶明亮, 等. 合成孔径雷达抗干扰技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113.HUANG Yan, ZHAO Bo, TAO Mingliang, et al. Review of synthetic aperture radar interference suppression[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113. [11] 李本朋. 国外机载箔条干扰技术的发展[J]. 机械管理开发, 2018, 33(2): 56–58. doi: 10.16525/j.cnki.cn14-1134/th.2018.02.23.LI Benpeng. Development of foreign airborne chaff jamming technology[J]. Mechanical Management and Development, 2018, 33(2): 56–58. doi: 10.16525/j.cnki.cn14-1134/th.2018.02.23. [12] 李超, 李芳. 基于人工电磁材料的新型电磁隐身机制——电磁隐身斗篷[J]. 北京石油化工学院学报, 2009, 17(1): 48–52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2565.2009.01.011.LI Chao and LI Fang. A novel electromagnetic stealth method-electromagnetic invisible cloaks[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Petrochemical Technology, 2009, 17(1): 48–52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2565.2009.01.011. [13] LIN Hao, XING Mengdao, LOU Yishan, et al. Research on anti-deception forwarding interference of squint azimuth multichannel SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5203912. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3334022. [14] WANG Zan, GUO Zhengwei, SHU Gaofeng, et al. Radar jamming recognition: Models, methods, and prospects[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 3315–3343. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3522951. [15] 朱吉利, 范振军. 一种基于集成学习的干扰频点检测方法[J]. 图像与信号处理, 2025, 14(1): 100–107. doi: 10.12677/jisp.2025.141010.ZHU Jili and FAN Zhenjun. A detection method of jamming frequency based on ensemble learning[J]. Journal of Image and Signal Processing, 2025, 14(1): 100–107. doi: 10.12677/jisp.2025.141010. [16] LV Qinzhe, QUAN Yinghui, FENG Wei, et al. Radar deception jamming recognition based on weighted ensemble CNN with transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5107511. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3129645. [17] QU Qizhe, WEI Shujun, LIU Shan, et al. JRNet: Jamming recognition networks for radar compound suppression jamming signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 15035–15045. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3032197. [18] LUO Zhenyu, CAO Yunhe, YEO T S, et al. Few-shot radar jamming recognition network via time-frequency self-attention and global knowledge distillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5105612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3280322. [19] 邢世其, 纪朋徽, 代大海, 等. 方位向调制干扰对高分宽幅多通道SAR的影响[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(6): 1946–1956. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.06.12.XING Shiqi, JI Penghui, DAI Dahai, et al. Influence of azimuth-modulation jamming on high-resolution wide-swath multi-channel SAR[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(6): 1946–1956. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.06.12. [20] 康晓磊. 面向目标识别的SAR成像干扰类型判别与分级方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华中科技大学, 2018. doi: 10.7666/d.D01544285.KANG Xiaolei. Research on discrimination and classification methods of SAR jamming types for target recognition[D]. [Master dissertation], Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2018. doi: 10.7666/d.D01544285. [21] 陈思伟, 崔兴超, 李铭典, 等. 基于深度CNN模型的SAR图像有源干扰类型识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143.CHEN Siwei, CUI Xingchao, LI Mingdian, et al. SAR image active jamming type recognition based on deep CNN model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143. [22] 汪日超. 星载SAR压制式干扰与抗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017.WANG Richao. Research on spaceborne SAR compression interference and anti - jamming technology[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017. [23] 黄大通, 邢世其, 李永祯, 等. 基于乘积调制的SAR灵巧干扰方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(11): 3160–3168. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.15.HUANG Datong, XING Shiqi, LI Yongzhen, et al. Smart jamming method against SAR based on multiplication modulation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3160–3168. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.15. [24] 房明星, 王杰贵, 雷磊. SAR雷达二维噪声卷积调制干扰研究[J]. 现代防御技术, 2014, 42(2): 139–144, 160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2014.02.025.FANG Mingxing, WANG Jiegui, and LEI Lei. Study on 2D noise convolution modulation jamming to SAR[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2014, 42(2): 139–144, 160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2014.02.025. [25] 丁毅. 基于多维域分析的SAR射频干扰抑制方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2022. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2022.003158.DING Yi. Research on SAR radio frequency interference mitigation method using multidimensional analysis[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2022. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2022.003158. [26] SHEN Jiayuan, HAN Bing, PAN Zongxu, et al. Learning time-frequency information with prior for SAR radio frequency interference suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5239716. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3225499. [27] LI Ning, ZHANG Hengrui, LV Zongsen, et al. Simultaneous screening and detection of RFI from massive SAR images: A case study on European sentinel-1[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5231917. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3191815. [28] 刘一兵, 罗强, 刘记红, 等. 基于分段移频调制的间歇采样重复转发干扰[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2023, 38(4): 5–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2023.04.002.LIU Yibing, LUO Qiang, LIU Jihong, et al. Interrupted-sampling repetitive repeater jamming based on segmented shift-frequency modulation[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2023, 38(4): 5–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2023.04.002. [29] 张养瑞, 李云杰, 李曼玲, 等. 间歇采样非均匀重复转发实现多假目标压制干扰[J]. 电子学报, 2016, 44(1): 46–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.01.008.ZHANG Yangrui, LI Yunjie, LI Manling, et al. Suppress jamming technique of multiple false targets on interrupted-sampling and non-uniform periodic repeater[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2016, 44(1): 46–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.01.008. [30] 孙宗正, 刘智星, 肖国尧, 等. 非均匀间歇采样转发干扰对脉内捷变雷达影响分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(5): 1544–1554. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.05.09.SUN Zongzheng, LIU Zhixing, XIAO Guoyao, et al. Analysis of the influence of non uniform interrupted sampling repeater jamming on intra-pulse agile radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(5): 1544–1554. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.05.09. [31] 周政, 唐宏, 张永顺. LFM脉压雷达的随机移频干扰研究[J]. 现代防御技术, 2010, 38(1): 103–108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2010.01.023.ZHOU Zheng, TANG Hong, and ZHANG Yongshun. Randomly shift frequency jamming to LFM pulse compression radar[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2010, 38(1): 103–108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2010.01.023. [32] 黄洪旭, 黄知涛, 周一宇. 对合成孔径雷达的随机移频干扰[J]. 信号处理, 2007, 23(1): 41–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.01.009.HUANG Hongxu, HUANG Zhitao, and ZHOU Yiyu. Randomly-shift-frequency jamming style to SAR[J]. Signal Processing, 2007, 23(1): 41–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.01.009. [33] 蔡幸福, 张雄美, 宋建社, 等. 基于脉间分段随机移频的合成孔径雷达干扰技术及其应用模型[J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(11): 2196–2202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.11.027.CAI Xingfu, ZHANG Xiongmei, SONG Jianshe, et al. A jamming approach to SAR based on inter-pulse subsection random frequency-shift technique and its application[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(11): 2196–2202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.11.027. [34] 和小冬, 李昀豪, 祝俊, 等. 合成孔径雷达二维失配压制干扰方法[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2014, 29(3): 24–28, 79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2014.03.006.HE Xiaodong, LI Yunhao, ZHU Jun, et al. A Bi-dimensional mismatching suppressed jamming for countering SAR[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2014, 29(3): 24–28, 79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2014.03.006. [35] LI Bodong and GAO Xieping. Lattice structure for regular linear phase paraunitary filter bank with odd decimation factor[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(1): 14–17. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2285435. [36] LUO Xiaotong, XIE Yuan, ZHANG Yulun, et al. LatticeNet: Towards lightweight image super-resolution with lattice block[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58542-6_17. [37] WANG Zheyuan, LI Liangliang, XUE Yuan, et al. FeNet: Feature enhancement network for lightweight remote-sensing image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5622112. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3168787. [38] DING Xiaohan, ZHANG Yiyuan, GE Yixiao, et al. UniRepLKNet: A universal perception large-kernel ConvNet for audio, video, point cloud, time-series and image recognition[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 5513–5524. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00527. [39] CHEN Honghao, CHU Xiangxiang, REN Yongjian, et al. PeLK: Parameter-efficient large kernel ConvNets with peripheral convolution[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 5557–5567. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00531. [40] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. [41] MAO Anqi, MOHRI M, and ZHONG Yutao. Cross-entropy loss functions: Theoretical analysis and applications[C]. The 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, USA, 2023. [42] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 336–359. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01228-7. [43] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409. 1556, 2014. [44] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [45] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]. The Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 4278–4284. [46] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1800–1807. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.195. [47] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU Menglong, et al. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4510–4520. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00474. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: