-
摘要: 雷达通过发射波形接收并处理回波信号从而获取目标信息,因此发射波形性能是决定雷达系统性能的关键因素。相比于其他雷达体制,合成孔径雷达(SAR)具有分布式目标场景,大时间带宽积波形,大幅宽远距离成像,距离-方位耦合等独特的工作特性,这对SAR波形设计提出了更高的要求。基于该文作者在SAR波形编码领域相关的研究工作和思考,该文总结了SAR波形设计近年来国内外的研究现状,讨论了SAR波形设计面临的技术挑战和其在提升系统成像性能上的作用,并展望了未来SAR波形设计的研究和发展趋势。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达 /
- 雷达波形设计 /
- 多输入多输出合成孔径雷达 /
- 模糊抑制 /
- 雷达抗干扰
Abstract: Radar systems acquire target information by transmitting waveforms, receiving echoes, and processing signals; thus, waveform performance is a critical determinant of radar system performance. Compared with other radar systems, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) operates under unique conditions, including distributed target scenes, waveforms with large time-bandwidth products, wide-swath and long-range imaging, and range–azimuth coupling. These characteristics impose additional stringent requirements on SAR waveform design. Drawing on the authors’ research and expertise in SAR waveform coding, this paper reviews recent domestic and international advances in SAR waveform design, discusses key technical challenges, and highlights the role of waveform design in enhancing system imaging performance. Finally, this study outlines future trends and potential directions for SAR waveform design methodologies. -
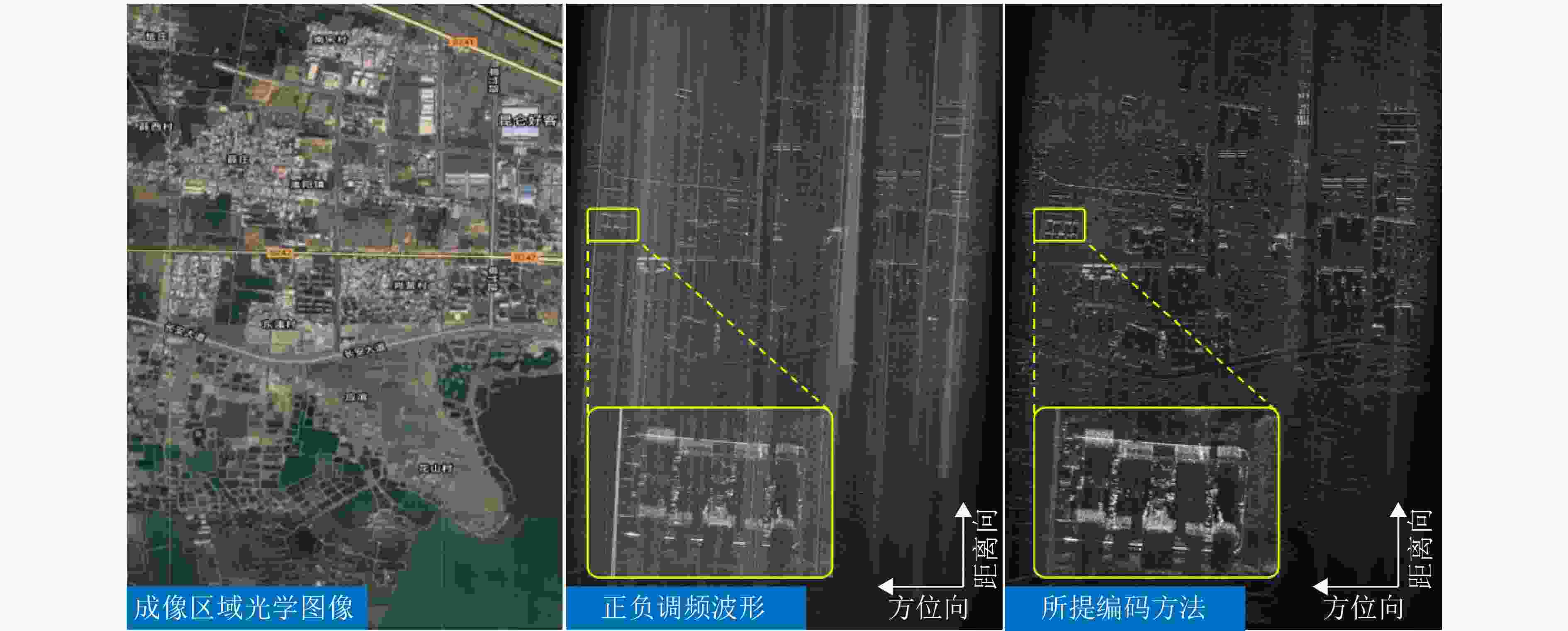
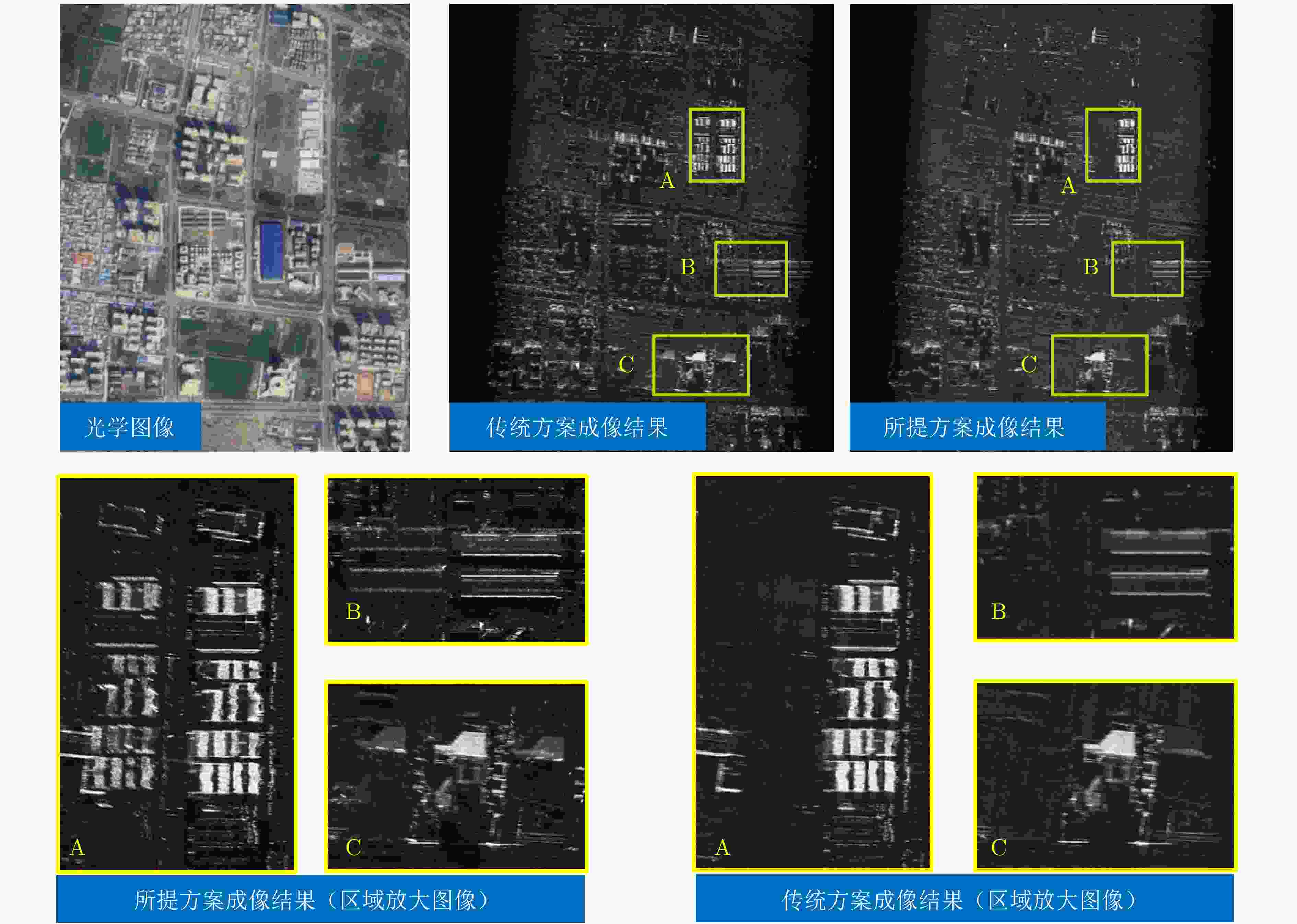
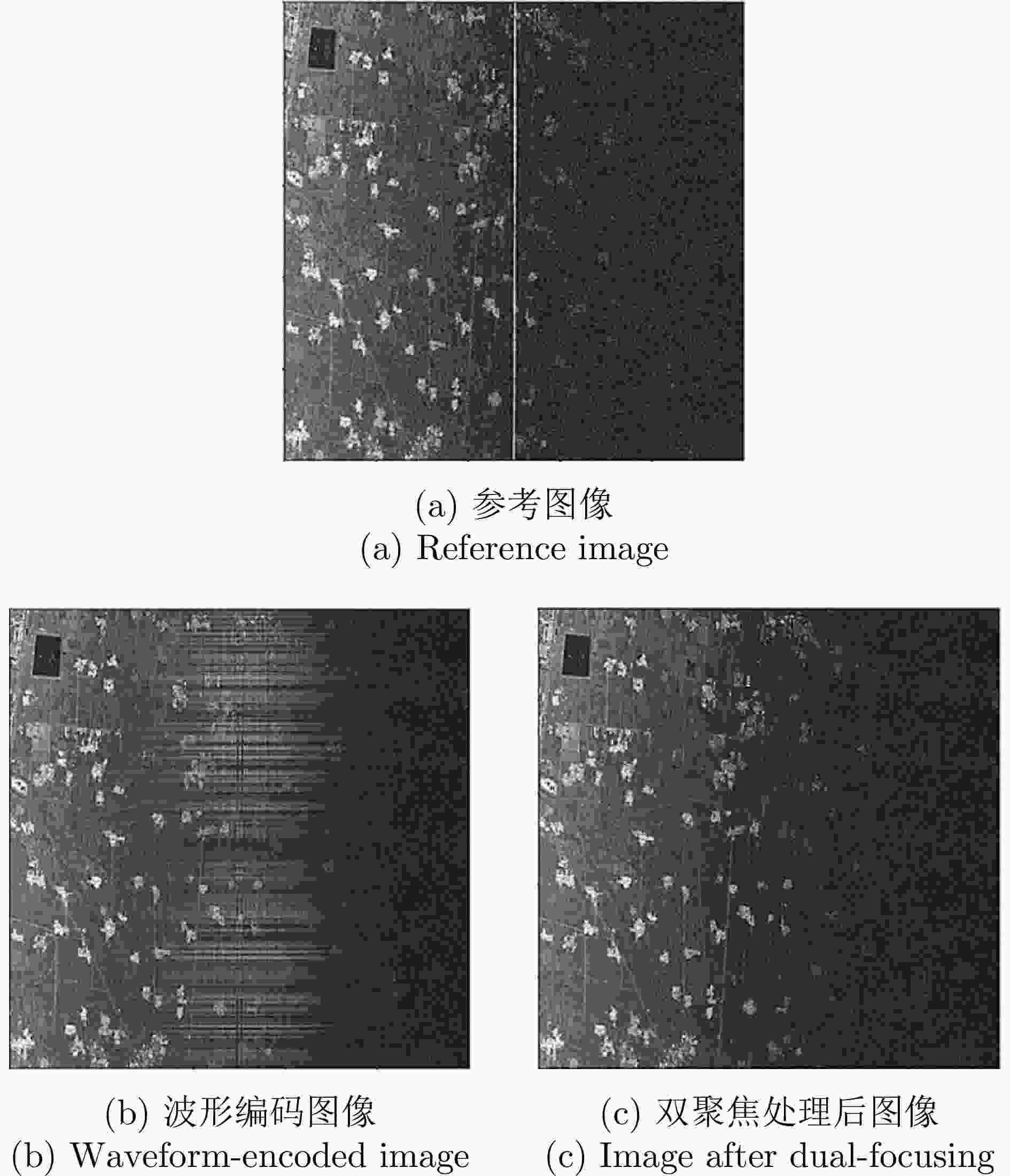
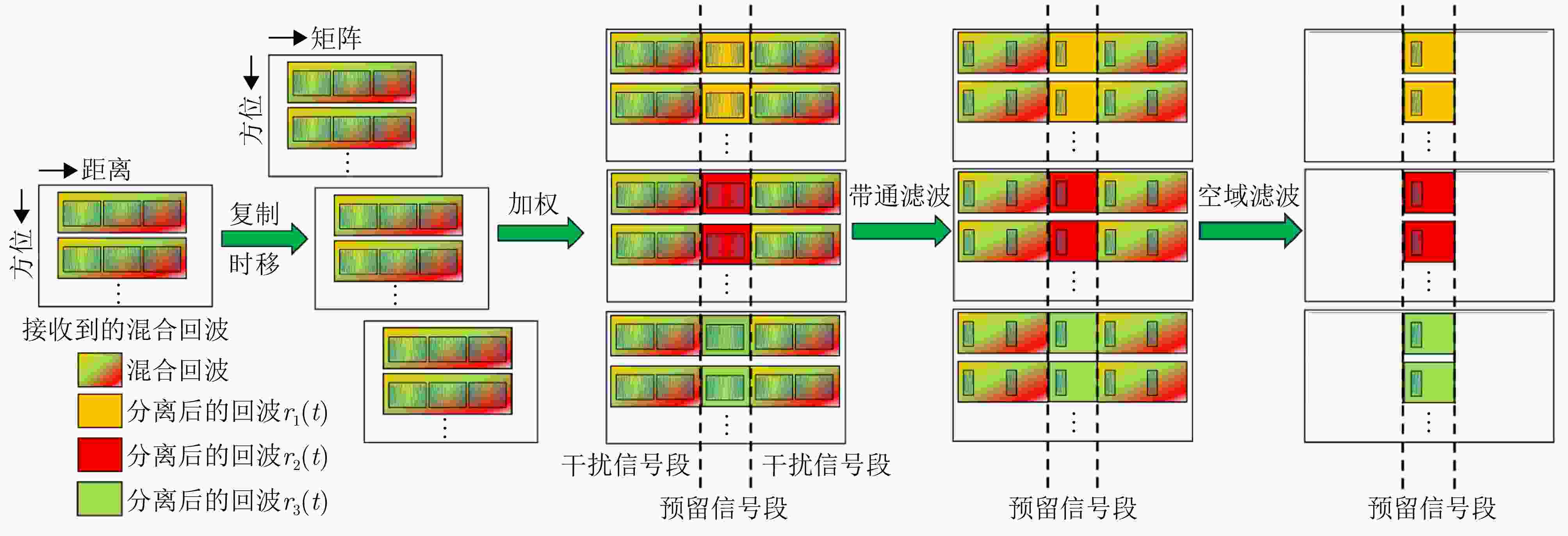
图 22 基于SPC波形波束赋形方案和2T16R-SAR的混合回波分离后的实验结果[143]
Figure 22. Experimental results of mixed echo separation based on SPC waveform beamforming scheme and 2T16R-SAR
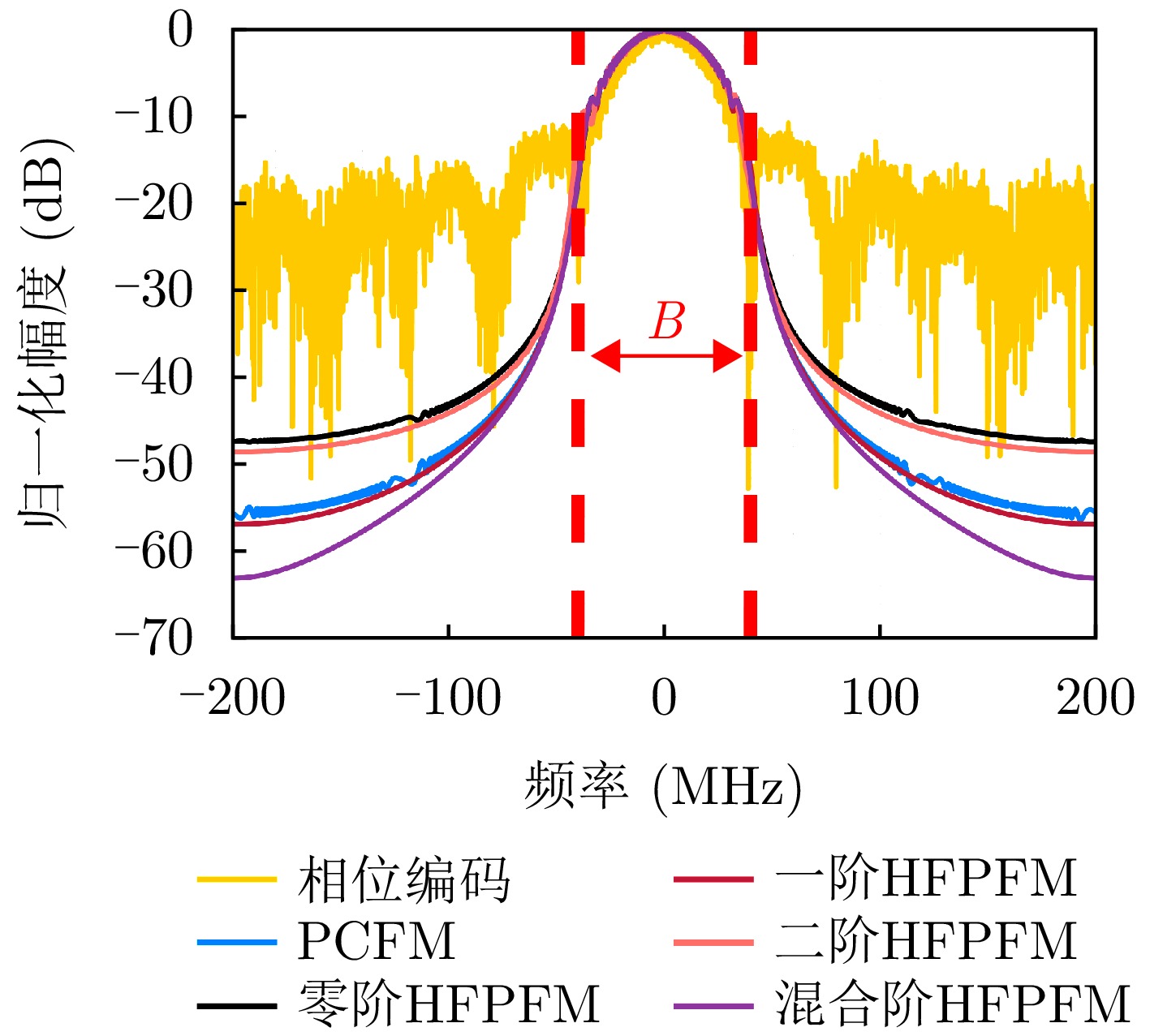
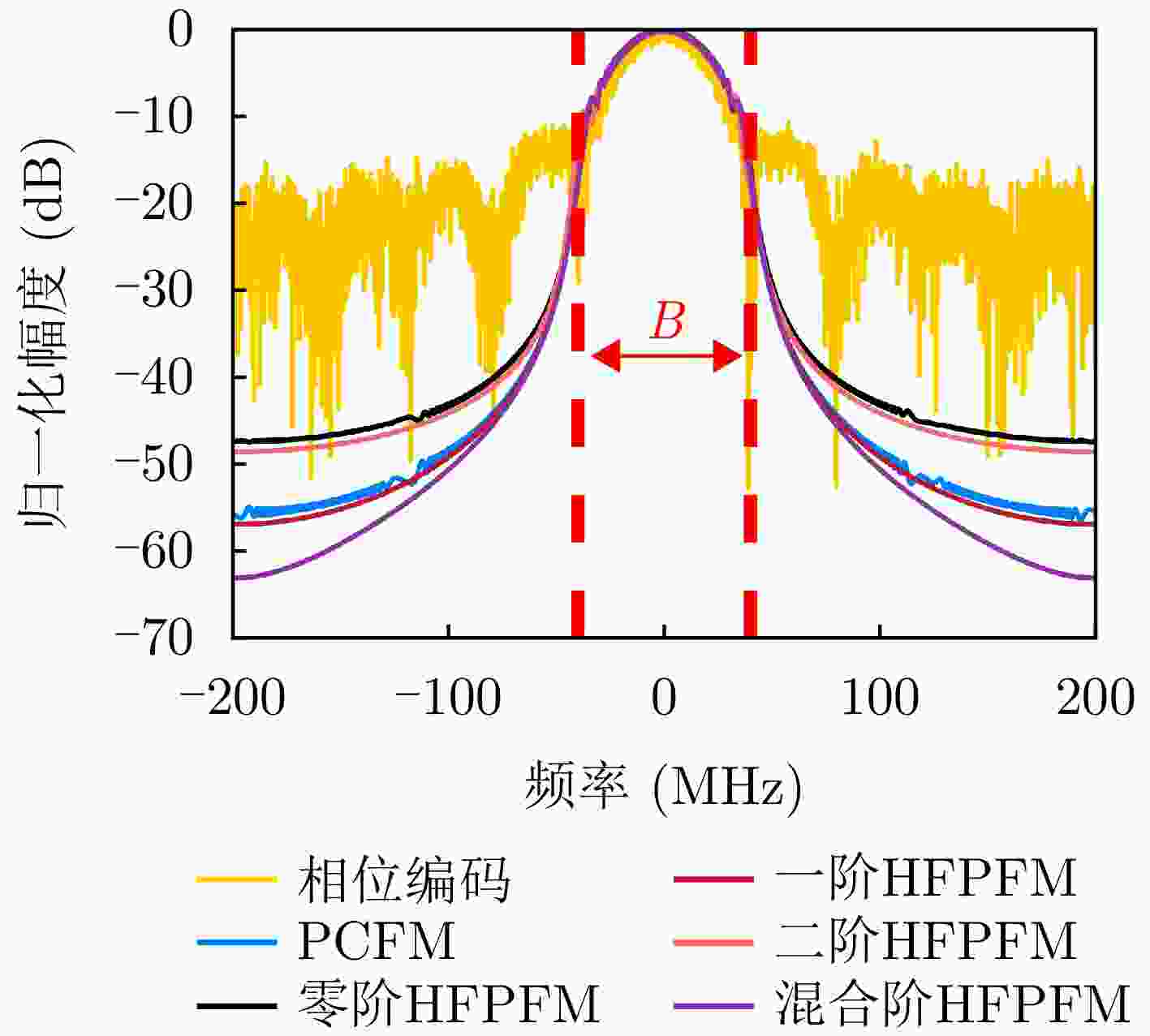
表 1 相位编码和频率调制波形特性对SAR系统性能的影响对比
Table 1. Comparative waveform properties of the phase code and frequency modulation for SAR systems
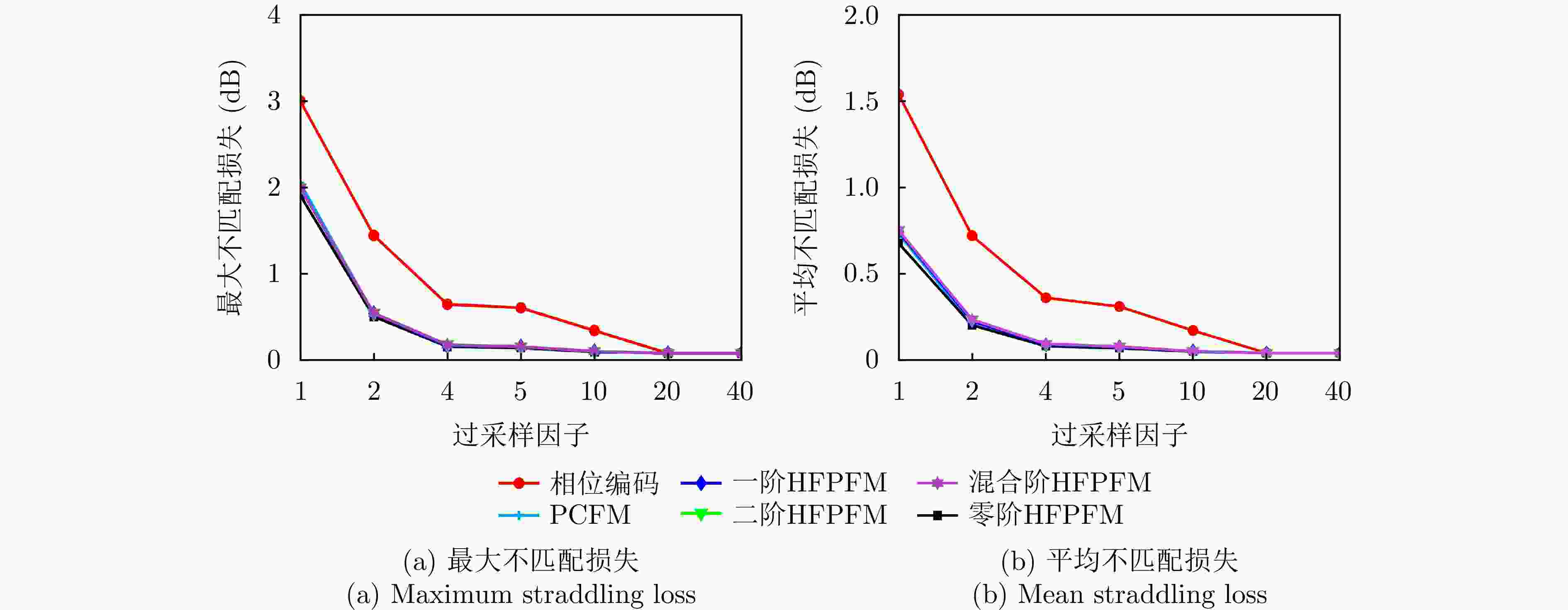
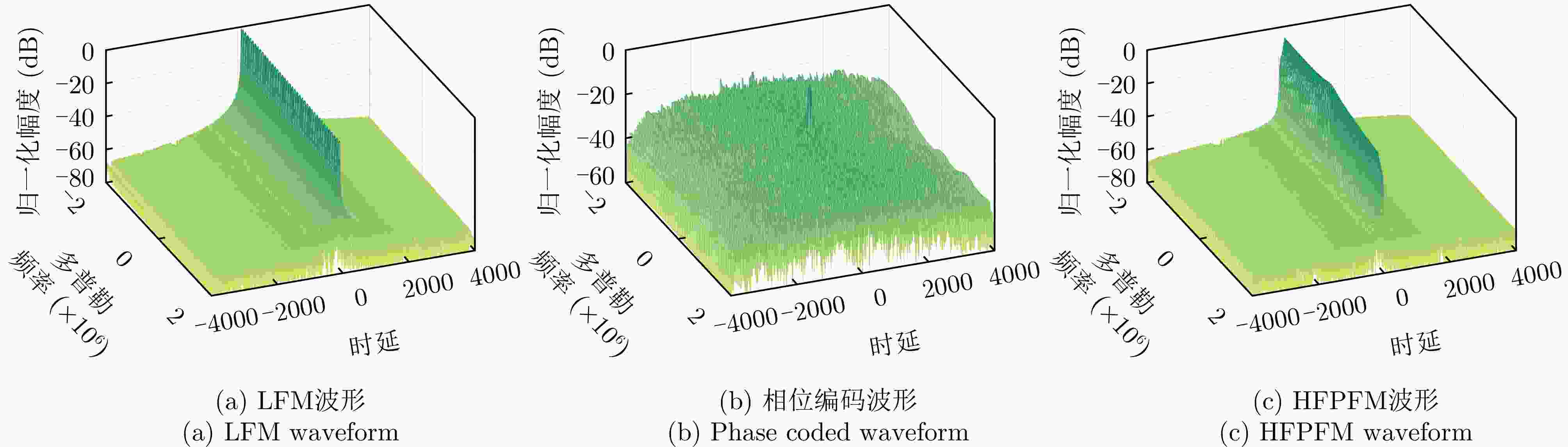
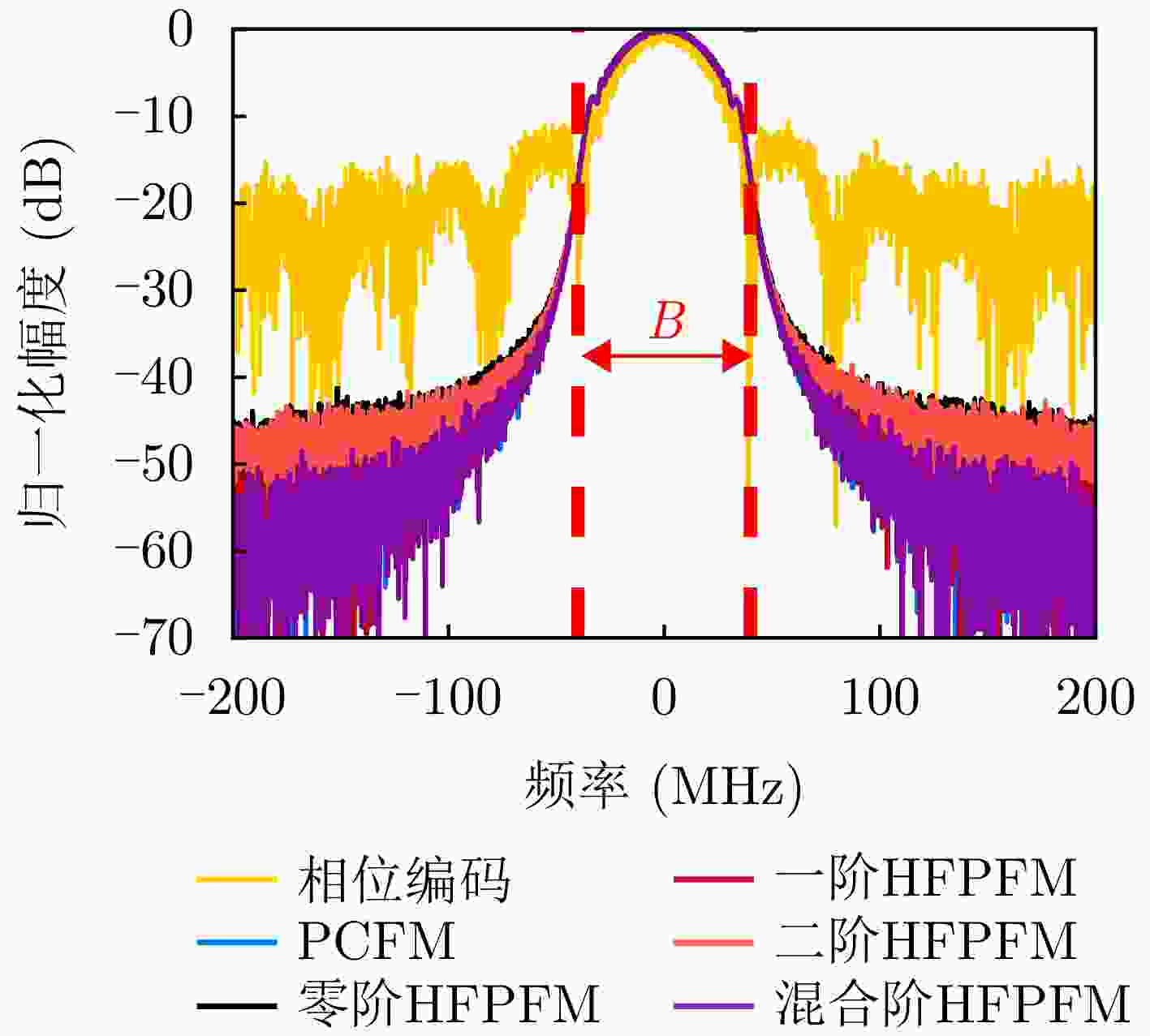
波形性能 对SAR系统性能影响 相位编码 频率调制 复信号采样率 回波数据量 整数倍采样 >1 带内能量占比 发射功率损失 低 高 主瓣宽度 距离分辨率 不展宽 展宽,可优化 PSLR 弱目标成像性能 较低,可优化 极低 ISLR 成像背景噪声 较高,可优化 极低 高自由度参数化编码 波形优化/实时生成能力 具备 不具备 表 2 不同波形性能指标对比结果
Table 2. Waveform performance comparison of different waveforms
波形 编码
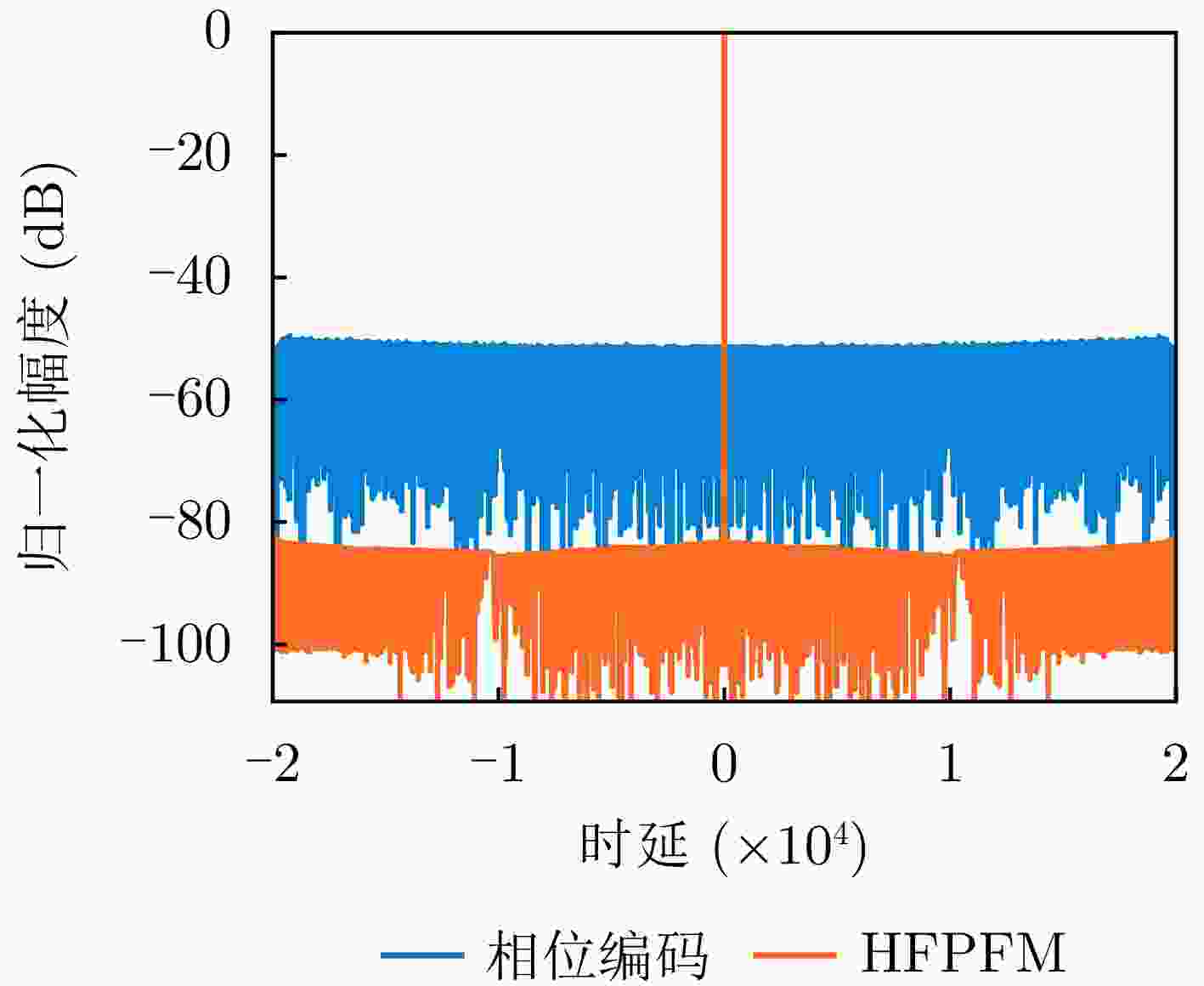
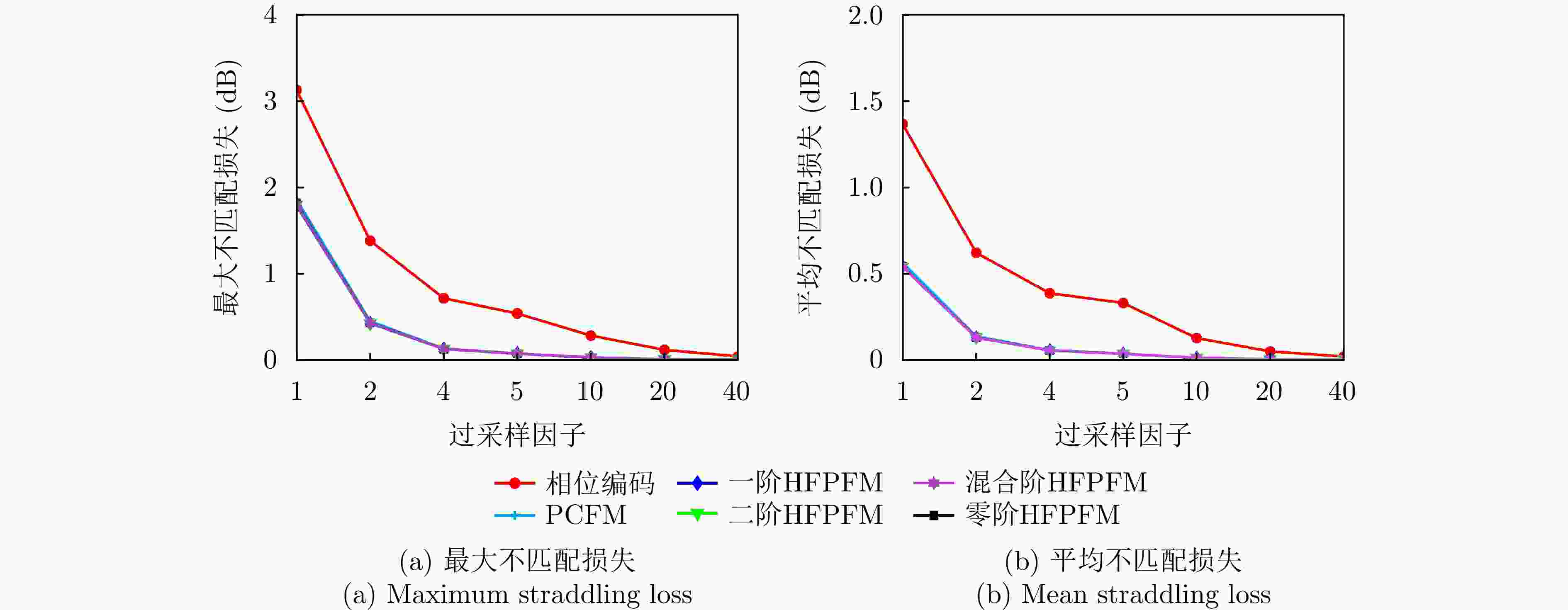
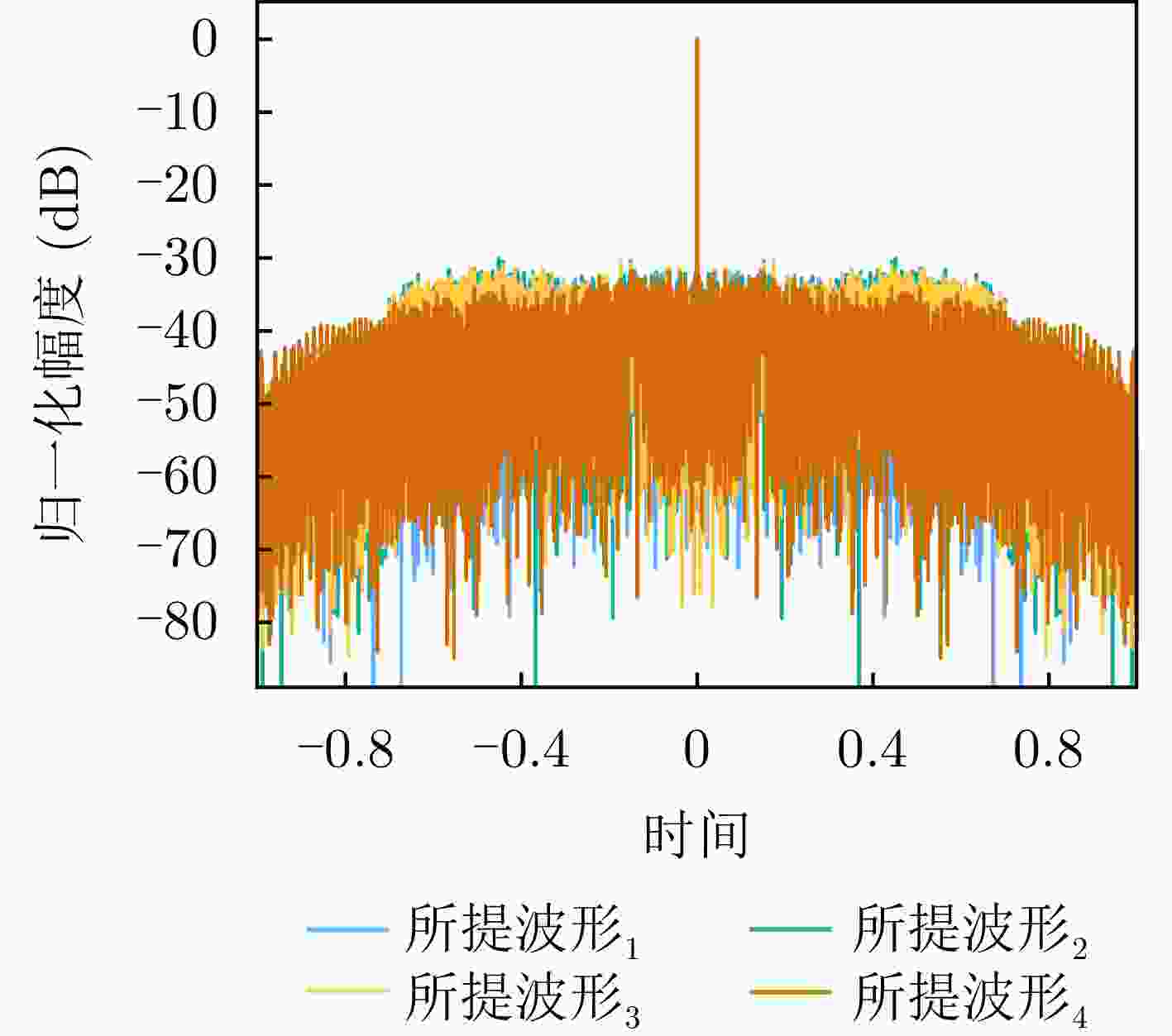
长度带内能量占比 PSLR 仿真 实测 仿真 实测 相位编码 800 89.0 89.0 –41.13 –40.37 PCFM 800 99.8 99.7 –43.57 –43.04 零阶HFPFM 800 99.7 99.7 –43.68 –43.11 49 98.3 98.3 –28.36 –27.74 一阶HFPFM 801 99.8 99.7 –43.57 –43.09 50 99.7 99.6 –43.59 –43.04 二阶HFPFM 801 99.7 99.7 –43.56 –43.07 50 99.6 99.4 –41.84 –41.32 混合阶HFPFM 801 99.7 99.7 –45.19 –44.89 50 99.7 99.7 –45.14 –44.82 1 基于POSP的非线性调频波形设计方法
1. The generation method of the NLFM waveform based on POSP
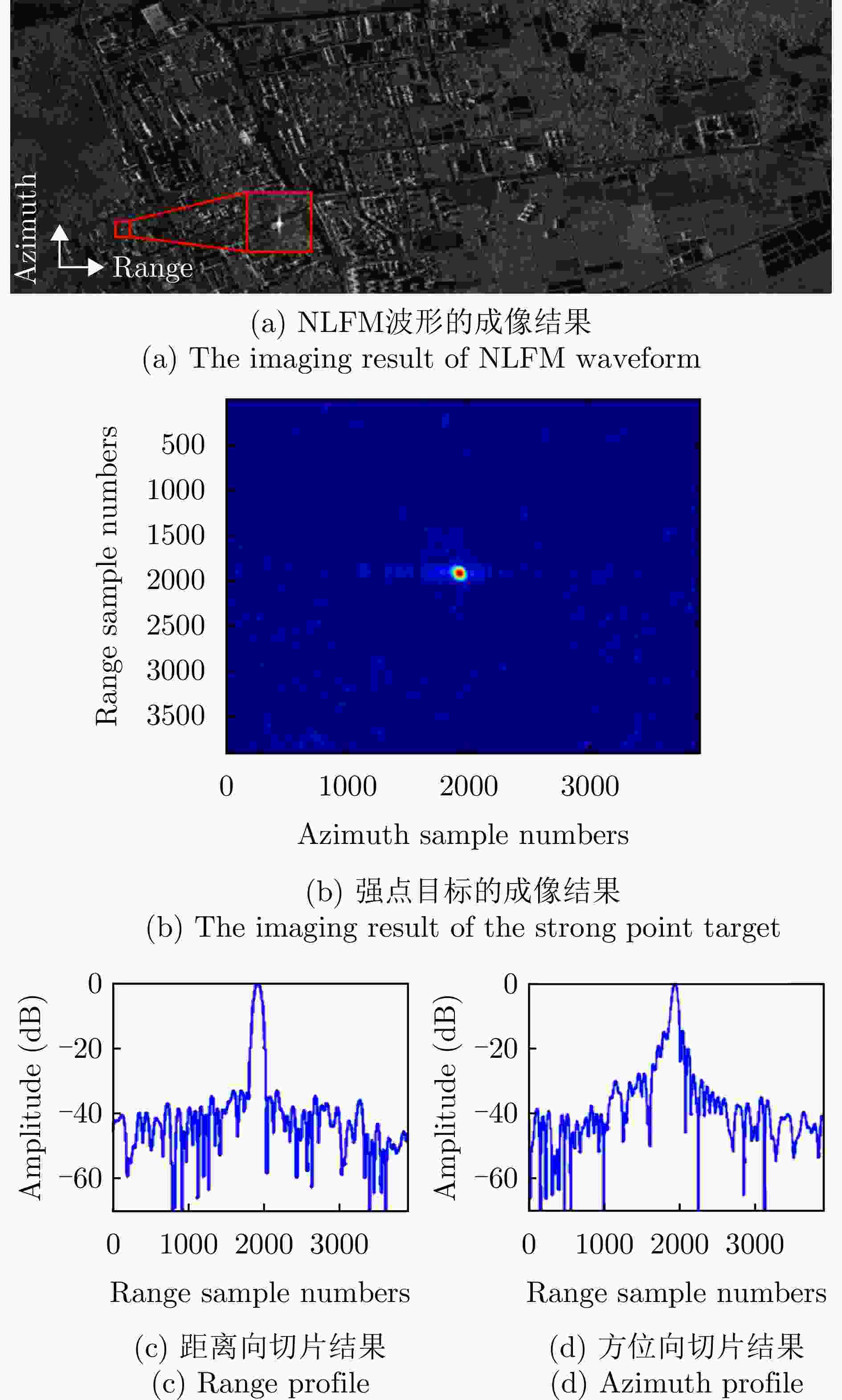
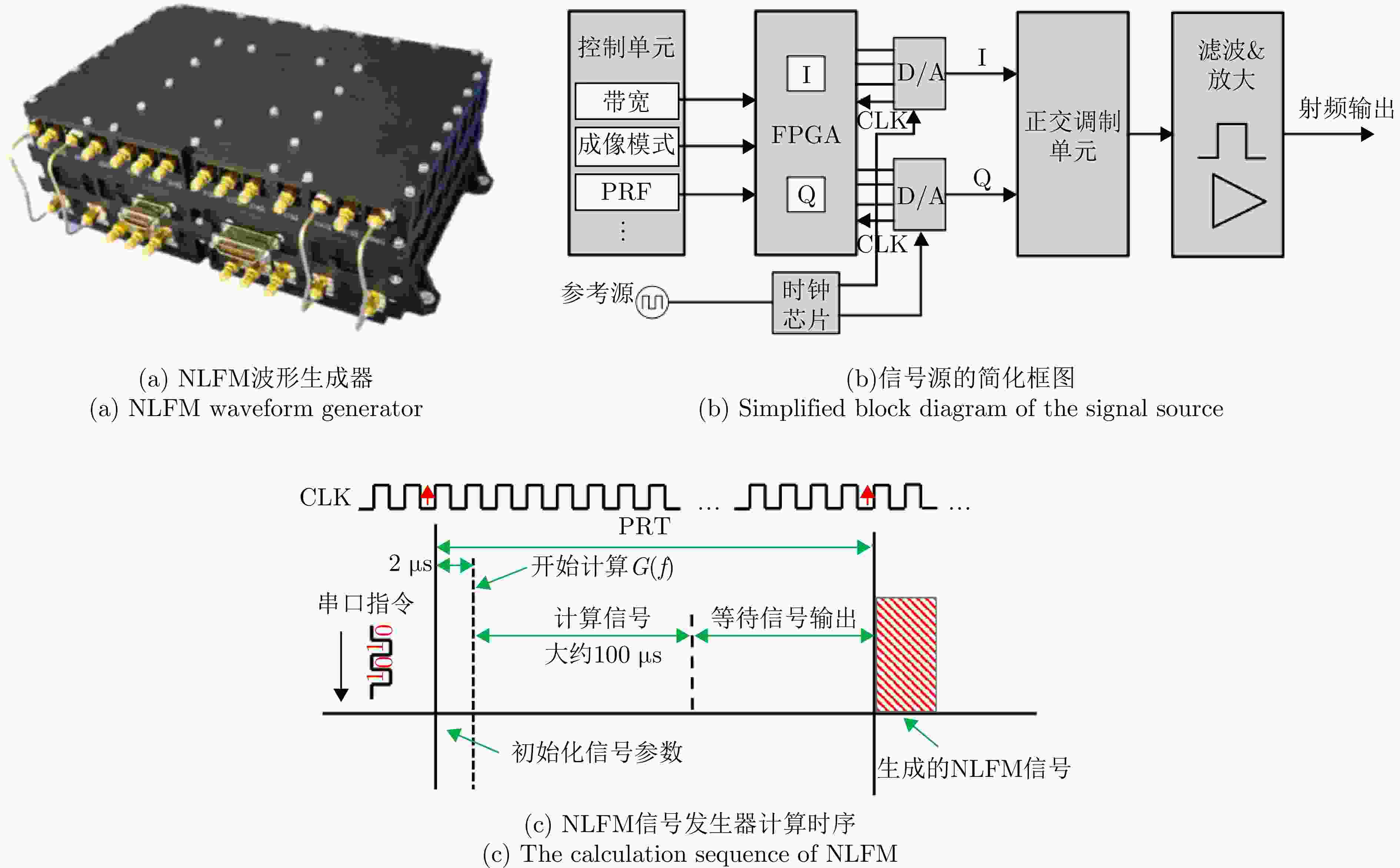
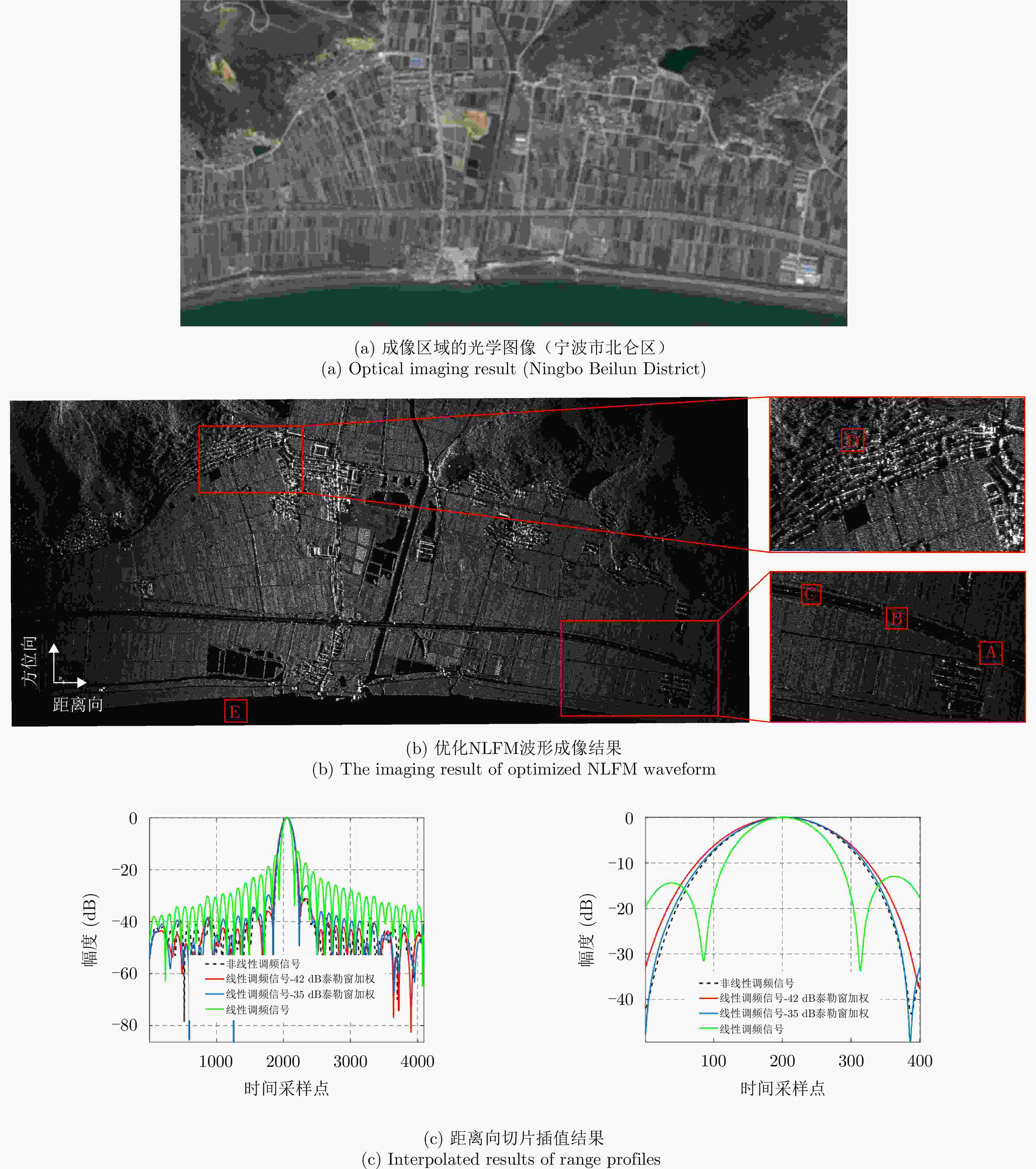
Step1: 选择满足需求的窗函数作为功率谱密度函数$ P(f) $,例如泰勒窗等典型加权函数。 Step2: 计算群时延函数$ Q\left(f\right)=\displaystyle\int\nolimits_{0}^{f}\dfrac{P\left(f\right)}{C}{\mathrm{d}}f $,其中$ C=\dfrac{1}{T}\displaystyle\int\nolimits_{-B/2}^{B/2}P(f){\mathrm{d}}f $。 Step3: 计算瞬时频率函数$ f\left(t\right)={Q}^{-1}\left(f\right) $。 Step4: 计算非线性调频信号$ s\left(t\right)=\mathrm{rect}\left(\dfrac{t}{T}\right)\exp \left({\mathrm{j}}2\text{π} \left(\displaystyle\int\nolimits_{0}^{t}f\left(\tau \right){\mathrm{d}}\tau \right)\right) $。 表 3 不同发射信号的距离向切片的性能评价
Table 3. Quantified performance for the range profile of different transmitted signal
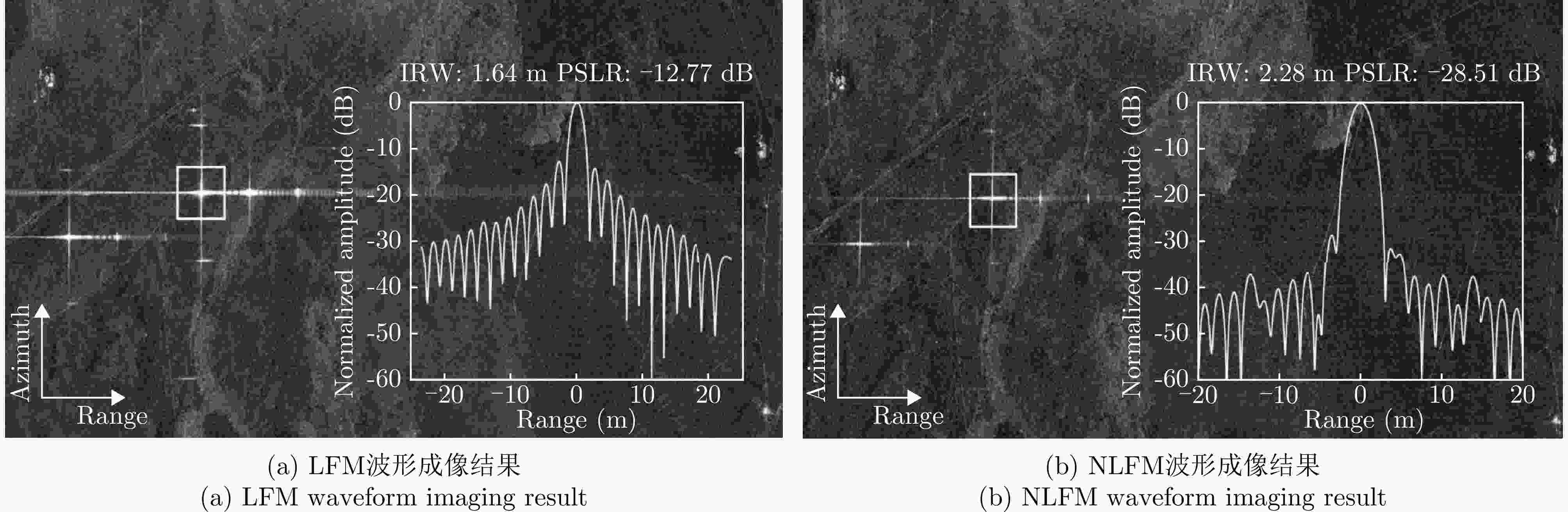
波形 3 dB主瓣宽度 PSLR (dB) LFM 波形 0.91 –12.9 LFM加-35dB的泰勒窗 1.19 –26.1 LFM加-42dB的泰勒窗 1.28 –31.1 提出的NLFM信号 1.18 –31.0 表 4 SAR图像信噪比评价结果(dB)
Table 4. SAR evaluation results of SAR image(dB)
区域 NLFM LFM 信噪比提升 A 72.72 71.4 1.32 B 67.42 66.13 1.29 C 66.68 65.4 1.28 D 75.45 74.18 1.27 表 5 不同波形的性能对比
Table 5. The performance comparison of different waveforms
波形 3 dB主瓣宽度 PSLR (dB) LFM波形 0.88 –13.3 LFM作为初始化信号[60] 0.89 –18.5 NLFM作为初始化信号[60] 1.17 –40.2 LFM作为初始化信号[61] 0.89 –23.0 NLFM作为初始化信号[61] 1.13 –40 –23.3 dB泰勒窗加权的LFM波形 1 –23.0 –43 dB勒窗加权的LFM波形 1.27 –40.2 -
[1] GINI F, DE MAIO A, and PATTON L. Waveform Design and Diversity for Advanced Radar Systems[M]. London: IET Press, 2012. doi: 10.1049/PBRA022E. [2] LEVANON N and MOZESON E. Radar Signals[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2004. doi: 10.1002/0471663085. [3] COOK E C and BERNFELD M. Radar Signals: An Introduction to Theory and Application[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1967. [4] NATHANSON F E, REILLY J P, and COHEN M N. Radar design principles-signal processing and the environment[R]. NASA STI/Recon Technical Report A, 1991. [5] HAYKIN S. Cognitive radar: A way of the future[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2006, 23(1): 30–40. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2006.1593335. [6] GUERCI J R. Cognitive Radar: The Knowledge-Aided Fully Adaptive Approach[M]. Boston/London: Artech House, 2010. [7] 黎湘, 范梅梅. 认知雷达及其关键技术研究进展[J]. 电子学报, 2012, 40(9): 1863–1870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.09.025.LI Xiang and FAN Meimei. Research advance on Cognitive radar and its key technology[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(9): 1863–1870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.09.025. [8] LA SCALA B F, MORAN W, and EVANS R J. Optimal adaptive waveform selection for target detection[C]. The International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, Australia, 2003: 492–496. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2003.1278791. [9] BELL M R. Information theory and radar waveform design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1993, 39(5): 1578–1597. doi: 10.1109/18.259642. [10] AKHTAR J. Orthogonal block coded ECCM schemes against repeat radar jammers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(3): 1218–1226. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5259195. [11] DAVIS R M, FANTE R L, GUELLA T P, et al. Interference suppression via operating frequency selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(4): 637–645. doi: 10.1109/8.768802. [12] YANG Jungang, THOMPSON J, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. Random-frequency SAR imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(2): 983–994. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2204891. [13] YANG Xiaopeng, ZHANG Zongao, ZENG Tao, et al. Mainlobe interference suppression based on eigen-projection processing and covariance matrix reconstruction[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2014, 13: 1369–1372. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2339224. [14] LI Rongfeng, RAO Can, DAI Lingyan, et al. Combining sum-difference and auxiliary beams for adaptive monopulse in jamming[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 24(3): 372–381. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2013.00046. [15] YU K B and MURROW D J. Adaptive digital beamforming for angle estimation in jamming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(2): 508–523. doi: 10.1109/7.937465. [16] GOGINENI S and NEHORAI A. Polarimetric MIMO radar with distributed antennas for target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(3): 1689–1697. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2036472. [17] GOGINENI S and NEHORAI A. Game theoretic approach for polarimetric MIMO radar waveform design[C]. 2012 International Waveform Diversity & Design Conference (WDD), Kauai, USA, 2012: 59–62. doi: 10.1109/WDD.2012.7311294. [18] BLUNT S D and GERLACH K. Adaptive pulse compression via MMSE estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(2): 572–584. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1642573. [19] GERLACH K and BLUNT S D. Radar pulse compression repair[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(3): 1188–1195. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4383610. [20] BLUNT S D and GERLACH K. Multistatic adaptive pulse compression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(3): 891–903. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.248196. [21] MÉNDEZ DOMÍNGUEZ E, MAGNARD C, FRIOUD M, et al. Adaptive pulse compression for range focusing in SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(4): 2262–2275. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2641041. [22] RIHACZEK A W and GOLDEN R M. Range Sidelobe Suppression for Barker Codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1971, AES-7(6): 1087-1092. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1971.310209. [23] LEWIS B L and KRETSCHMER F F. A new class of Polyphase pulse compression codes and techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1981, AES-17(3): 364–372. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1981.309063. [24] NUNN C J and COXSON G E. Polyphase pulse compression codes with optimal peak and integrated Sidelobes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(2): 775–781. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5089560. [25] FRANK R. Polyphase codes with good nonperiodic correlation properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1963, 9(1): 43–45. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1963.1057798. [26] ZHANG N and GOLOMB S W. Polyphase sequence with low autocorrelations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1993, 39(3): 1085–1089. doi: 10.1109/18.256535. [27] BLUNT S D, COOK M, JAKABOSKY J, et al. Polyphase-coded FM (PCFM) radar waveforms, Part I: Implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 2218–2229. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130361. [28] BLUNT S D, JAKABOSKY J, COOK M, et al. Polyphase-coded FM (PCFM) radar waveforms, Part II: Optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 2230–2241. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130362. [29] TAN P S, JAKABOSKY J, STILES J M, et al. Higher-order implementations of polyphase-coded FM radar waveforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 2850–2870. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2897032. [30] BLUNT S D and MOKOLE E L. Overview of radar waveform diversity[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(11): 2–42. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.160071. [31] MOHR C A, MCCORMICK P M, TOPLIFF C A, et al. Gradient-based optimization of PCFM radar waveforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(2): 935–956. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3037403. [32] BLUNT S D, METCALF J, JAKABOSKY J, et al. Multi-waveform space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(1): 385–404. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2650639. [33] SAHIN C, MCCORMICK P M, METCALF J G, et al. Power-efficient multi-beam phase-attached radar/communications[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2019.8835583. [34] OWEN J, MOHR C, BLUNT S D, et al. Nonlinear radar via intermodulation of jointly optimized FM noise waveform pairs[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2019.8835590. [35] COSTAS J P. A study of a class of detection waveforms having nearly ideal range—Doppler ambiguity properties[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1984, 72(8): 996–1009. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1984.12967. [36] LIU Feng, MU Shanxiang, LYU Wanghan, et al. MIMO SAR waveform separation based on Costas-LFM signal and co-arrays for maritime surveillance[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2017, 26(1): 211–217. doi: 10.1049/cje.2016.11.015. [37] SONG Junxiao, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Sequence design to minimize the weighted integrated and peak sidelobe levels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(8): 2051–2064. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2510982. [38] STOICA P, HE Hao, and LI Jian. New algorithms for designing unimodular sequences with good correlation properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(4): 1415–1425. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2012562. [39] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005. [40] JIN Guodong, ZHANG Xifeng, HUANG Jingkai, et al. High freedom parameterized FM (HFPFM) code: Model, correlation function, and advantages[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(5): 6284–6298. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3405449. [41] DOERRY A W. Generating nonlinear FM chirp waveforms for radar[R]. SAND2006-5856, 2006. [42] XU Zhihuo, WANG R, YE Kai, et al. Simultaneous range ambiguity mitigation and sidelobe reduction using orthogonal non-linear frequency modulated (ONLFM) signals for satellite SAR imaging[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 9(9): 829–838. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2018.1486518. [43] COOK C E. A class of nonlinear FM pulse compression signals[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1964, 52(11): 1369–1371. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1964.3393. [44] GRIFFITHS H D and VINAGRE L. Design of low-sidelobe pulse compression waveforms[J]. Electronics Letters, 1994, 30(12): 1004–1005. doi: 10.1049/el:19940644. [45] Cook C E , Paolillo J. A pulse compression predistortion function for efficient sidelobe reduction in a high-power radar[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1964, 52(4): 377–389. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1964.2927. [46] FOWLE E. The design of FM pulse compression signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1964, 10(1): 61–67. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1964.1053644. [47] DE BUDA R. Stationary phase approximations of FM spectra[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1966, 12(3): 305–311. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1966.1053895. [48] VIZITIU I, ANTON L, POPESCU F, et al. The synthesis of some NLFM laws using the stationary phase principle[C]. 2012 10th International Symposium on Electronics and Telecommunications, Timisoara, Romania, 2012: 377–380. doi: 10.1109/ISETC.2012.6408053. [49] DOERRY A W. SAR processing with non-linear FM chirp waveforms[R]. SAND2006-7729, 2006. doi: 10.2172/902597. [50] DOERRY A W and MARQUETTE B. Shaping the spectrum of random-phase radar waveforms[R]. SAND2012-6915, 2012. doi: 10.2172/1051702. [51] DOERRY A W. Fine waveform control for general frequency-modulated radar waveforms[R]. SAND2016-1906, 2016. [52] WANG Wei, WANG Robert, ZHANG Zhimin, et al. First demonstration of airborne SAR with nonlinear FM chirp waveforms[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(2): 247–251. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2508102. [53] ZHANG Yongwei, WANG Wei, WANG R, et al. A novel NLFM waveform with low sidelobes based on modified Chebyshev window[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(5): 814–818. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2930817. [54] COLLINS T and ATKINS P. Nonlinear frequency modulation chirps for active sonar[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1999, 146(6): 312–316. doi: 10.1049/Ip-rsn:19990754. [55] ALPHONSE S and WILLIAMSON G A. Novel radar signal models using nonlinear frequency modulation[C]. 2014 22nd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Lisbon, Portugal, 2014: 1024–1028. [56] JIN Guodong, LIU Kaiyu, DENG Yunkai, et al. Nonlinear frequency modulation signal generator in LT-1[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(10): 1570–1574. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2905359. [57] WANG R, LIU Kaiyu, CAI Yonghua, et al. LuTan-1: An innovative L-band spaceborne bistatic interferometric SAR mission[C]. EUSAR 2024; 15th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Munich, Germany, 2024: 984–988. [58] KURDZO J M, CHEONG B L, PALMER R D, et al. Optimized NLFM pulse compression waveforms for high-sensitivity radar observations[C]. 2014 International Radar Conference, Lille, France, 2014: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.7060249. [59] SAEEDI J and FAEZ K. Synthetic aperture radar imaging using nonlinear frequency modulation signal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(1): 99–110. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140310. [60] JIN Guodong, DENG Yunkai, WANG R, et al. An advanced nonlinear frequency modulation waveform for radar imaging with low sidelobe[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 6155–6168. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2904627. [61] GAO Y, ZHANG X, JIN G, et al. High-resolution low-sidelobe waveform design based on HFPFM coding model[C]. IET International Radar Conference (IRC 2025), Jiaxing, China, 2025. [62] ANDREI N. Modern Numerical Nonlinear Optimization[M]. Cham: Springer, 2022. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08720-2. [63] WANG Wei, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Demonstration of NLFM waveforms with experiments and Doppler shift compensation for SAR application[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1999–2003. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2620284. [64] MILCZAREK H, LEŚNIK C, and KAWALEC A. Doppler-tolerant NLFM radar signal synthesis method[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266657. [65] HUANG Jingkai, JIN Guodong, ZHANG Xifeng, et al. A formal study of the Doppler tolerance of high freedom parameterized FM (HFPFM) code[C]. IET International Radar Conference (IRC 2023), Chongqing, China, 2023: 2164–2168. doi: 10.1049/icp.2024.1422. [66] SHEN Biao, ZHANG Runzhe, YANG Ziyuan, et al. Orthogonal double V-linear frequency modulation waveform for simultaneous polarimetric measurement and its non-linear processing[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2024, 18(10): 1919–1936. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12627. [67] 刘加方, 张云华, 董晓. 频率步进伪码-线性调频信号处理方法及成像[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2019, 17(4): 681–685,708. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201904.0681.LIU Jiafang, ZHANG Yunhua, and DONG Xiao. Processing method of stepped PRBC-LFM signal and imaging[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2019, 17(4): 681–685,708. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201904.0681. [68] VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. c[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(5): 719–723. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2808196. [69] JEON S Y, KRAUS T, STEINBRECHER U, et al. Experimental demonstration of nadir echo removal in SAR using waveform diversity and dual-focus postprocessing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4015605. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3095566. [70] WEN Xuejiao, QIU Xiaolan, HAN Bing, et al. A range ambiguity suppression processing method for Spaceborne SAR with up and down chirp modulation[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): 1454. doi: 10.3390/s18051454. [71] DONG Boyuan and CHEN Zhaoxi. Azimuth ambiguity suppression for SAR via variable PRF and complex image deconvolution[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 4008705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3302013. [72] QI Meng, HUANG Lijia, WANG Xiaochen, et al. Method of range ambiguity suppression combining sparse reconstruction and matched filter[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 8473–8483. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3210907. [73] 齐萌, 黄丽佳, 仇晓兰, 等. 一种结合稀疏重建和匹配滤波的距离模糊抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 95–106. doi: 10.12000/JR21181.QI Meng, HUANG Lijia, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Method of range ambiguity suppression combining sparse reconstruction and matched filtering[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 95–106. doi: 10.12000/JR21181. [74] KUDO R, HIROSE A, and NATSUAKI R. Removal of synthetic aperture radar range ambiguity by observing adjacent regions[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4003405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3359008. [75] LI Jieshuang, LIU Yanyang, TAO Mingliang, et al. Range ambiguity detection and suppression in spaceborne SAR image via image post-processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5214014. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3405324. [76] LONG Yajun, ZHAO Fengjun, ZHENG Mingjie, et al. An azimuth ambiguity suppression method based on local azimuth ambiguity-to-signal ratio estimation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(12): 2075–2079. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2963126. [77] SHEN Jiayuan, HAN Bing, PAN Zongxu, et al. Learning time–frequency information with prior for SAR radio frequency interference suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5239716. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3225499. [78] CEN Xi, LI Yachao, HAN Zhaoyun, et al. Self-supervised learning method for SAR multiinterference suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5220017. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3328019. [79] DALL J and KUSK A. Azimuth phase coding for range ambiguity suppression in SAR[C]. 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, USA, 2004: 1734–1737. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2004.1370667. [80] DOERRY A W. SAR ambiguous range suppression[R]. SAND2006-5332, 2006. doi: 10.2172/893128. [81] BORDONI F, YOUNIS M, and KRIEGER G. Ambiguity suppression by azimuth phase coding in multichannel SAR systems[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 4457–4460. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2011.6050222. [82] 祝晓静, 李飞, 王宇, 等. 基于改进方位相位编码的全极化SAR距离模糊抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 420–431. doi: 10.12000/JR17015.ZHU Xiaojing, LI Fei, WANG Yu, et al. Range ambiguity suppression approach for quad-pol SAR systems based on modified azimuth phase coding[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 420–431. doi: 10.12000/JR17015. [83] 吴玉峰, 叶少华, 冯大政. 基于方位相位编码的脉内聚束SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 437–445. doi: 10.12000/JR17114.WU Yufeng, YE Shaohua, and FENG Dazheng. Intra-pulse spotlight SAR imaging method based on azimuth phase coding[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 437–445. doi: 10.12000/JR17114. [84] 王岩飞, 李和平, 韩松. 雷达脉冲编码理论方法及应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 1–16. doi: 10.12000/JR19023.WANG Yanfei, LI Heping, and HAN Song. The theory and method of pulse coding for radar and its applications[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 1–16. doi: 10.12000/JR19023. [85] NIU Shilin, JIN Guodong, ZHANG Hanqing, et al. A novel real-time echo restoration algorithm from ambiguous signals in high-PRF SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4004305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3362405. [86] CALLAGHAN G D and LONGSTAFF I D. Wide-swath space-borne SAR and range ambiguity[C]. Radar 97 (Conf. Publ. No. 449), Edinburgh, UK, 1997: 248–252. doi: 10.1049/cp:19971672. [87] Guo Caihong, Feng Jin, Xu Anlin, et al. Range ambiguity suppression for spaceborne SAR based on up/down chirp modulation and twice range compressions[C]. IET International Radar Conference, Online Conference, 2020: 350-354, doi: 10.1049/icp.2021.0705. [88] MITTERMAYER J and MARTINEZ J M. Analysis of range ambiguity suppression in SAR by up and down chirp modulation for point and distributed targets[C]. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 4077–4079. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2003.1295367. [89] XU Wei, HUANG Pingping, and TAN Weixian. Azimuth phase coding by up and down chirp modulation for range ambiguity suppression[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 143780–143791. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2944871. [90] RICHÉ V, MÉRIC S, BAUDAIS J Y, et al. Optimization of OFDM SAR signals for range ambiguity suppression[C]. 2012 9th European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2012: 278–281. [91] RICHÉ V, MÉRIC S, BAUDAIS J Y, et al. Investigations on OFDM signal for range ambiguity suppression in SAR configuration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4194–4197. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2280190. [92] SUZUKI R, NATSUAKI R, and HIROSE A. Extending observation coverage of SAR by separating range ambiguous signals using PN-sequences[C]. 2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 8292–8295. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10283336. [93] SUZUKI R, HIROSE A, and NATSUAKI R. Optimizing PN-sequences with genetic algorithm for SAR waveform diversity[C]. 2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 2024: 11161–11164. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10641712. [94] WANG Wenqin. Mitigating range ambiguities in high-PRF SAR with OFDM waveform diversity[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(1): 101–105. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2193870. [95] WEI Tiantian, ZHANG Yongwei, LU Pingping, et al. An improved echo separation scheme with OFDM chirp waveforms for spaceborne MIMO SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4002805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3356729. [96] JIN Guodong, WANG Yu, YANG Hui, et al. Precise ambiguity performance evaluation for spaceborne SAR with diverse waveforms[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(7): 1895. doi: 10.3390/rs15071895. [97] JIN Guodong, AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, et al. Quasi-orthogonal waveforms for ambiguity suppression in spaceborne quad-pol SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5204617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3066590. [98] ZHOU Tao, JIN Guodong, WANG Yu, et al. Ambiguity suppression of airborne polarimetric SAR: Modelling, analysis and demonstration[C]. IET International Radar Conference, Jiaxing, China, 2025. [99] KRIEGER G, GEBERT N, and MOREIRA A. Multidimensional waveform encoding: A new digital beamforming technique for synthetic aperture radar remote sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 31–46. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.905974. [100] YOUNIS M, DE ALMEIDA F Q, VILLANO M, et al. Digital beamforming for spaceborne reflector-based synthetic aperture radar, Part 1: Basic imaging modes[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2021, 9(3): 8–25. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2021.3060543. [101] YOUNIS M, ALMEIDA F Q D, VILLANO M, et al. Digital beamforming for spaceborne reflector-based synthetic aperture radar, Part 2: Ultrawide-swath imaging mode[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2022, 10(4): 10–31. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2022.3200871. [102] XU Yihao, ZHANG Fubo, LI Wenjie, et al. A novel multi-beam SAR two-dimensional ambiguity suppression method based on azimuth phase coding[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(13): 2298. doi: 10.3390/rs16132298. [103] CHANG Sheng, DENG Yunkai, ZHANG Yanyan, et al. An advanced scheme for range ambiguity suppression of spaceborne SAR based on cocktail party effect[C]. 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 2075–2078. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9884347. [104] AMIN E J, KRIEGER G, YOUNIS M, et al. A 2-D range ambiguity suppression method based on blind source separation for multichannel SAR systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5203117. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3355149. [105] DENG Yunkai, TANG Shuhe, CHANG Sheng, et al. A novel scheme for range ambiguity suppression of spaceborne SAR based on underdetermined blind source separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5207915. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3556296. [106] JIN Guodong, WANG Wei, DENG Yunkai, et al. A novel range-azimuth joint modulation scheme for range ambiguity suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5207210. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3075233. [107] HE Hao, STOICA P, and LI Jian. Designing unimodular sequence sets with good correlations—including an application to MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(11): 4391–4405. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2025108. [108] WANG Jiangtao and WANG Yongchao. Designing unimodular sequences with optimized auto/cross-correlation properties via consensus-ADMM/PDMM approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 2987–2999. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3079819. [109] SONG Junxiao, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Sequence set design with good correlation properties via majorization-minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(11): 2866–2879. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2535312. [110] WANG Wenqin. Space–time coding MIMO-OFDM SAR for high-resolution imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(8): 3094–3104. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2116030. [111] KIM J H, YOUNIS M, MOREIRA A, et al. A novel OFDM chirp waveform scheme for use of multiple transmitters in SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 568–572. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2213577. [112] WANG Jie, LIANG Xingdong, CHEN Longyong, et al. Implementation of the OFDM chirp waveform on MIMO SAR systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(9): 5218–5228. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2419271. [113] WANG Wenqin. MIMO SAR OFDM chirp waveform diversity design with random matrix modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(3): 1615–1625. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2346478. [114] 邱晓燕. 基于LFM-PC复合调制信号的SAR波形抗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2017.QIU Xiaoyan. Research on SAR anti-jamming technique based on LFM-PC waveform design[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017. [115] 程远. 雷达主瓣干扰抑制及抗干扰波形优化技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2022.CHENG Yuan. Research on radar Mainlobe jamming suppression and anti-jamming waveform optimization technology[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022. [116] CHENG Yuan, ZHANG Jindong, LI Chen, et al. Orthogonal anti-jamming waveform design with extended Doppler tolerance based on the LFM-PC signal[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 122: 103334. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103334. [117] XIE Qinqu, YANG Jiyao, LIU Chenyu, et al. Low sidelobe quasi-orthogonal NLFM waveforms with reciprocating frequency modulation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4027805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3214570. [118] WANG Qinglu, ZHANG Xifeng, GAO Yu, et al. Based on GRU Neural Network-Designed Waveforms for Spaceborne SAR Anti-Jamming Methods[C]. IET International Radar Conference, Jiaxing, China, 2025. [119] 许京伟, 朱圣棋, 廖桂生, 等. 频率分集阵雷达技术探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 167–182. doi: 10.12000/JR18023.XU Jingwei, ZHU Shengqi, LIAO Guisheng, et al. An overview of frequency diverse array radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 167–182. doi: 10.12000/JR18023. [120] ARAKI S, MUKAI R, MAKINO S, et al. The fundamental limitation of frequency domain blind source separation for convolutive mixtures of speech[J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 2003, 11(2): 109–116. doi: 10.1109/TSA.2003.809193. [121] JIN Guodong, DENG Yunkai, WANG Wei, et al. On the SAR imaging performance analysis of alternate transmitting mode based on waveform diversity: Theory and simulation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(9): 1553–1557. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2951432. [122] TAN Youshan, AN Hongyan, LI Zhongyu, et al. Complementary waveform design for SAR range Sidelobe suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5205211. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2025.3542836. [123] 周伟, 刘永祥, 黎湘, 等. MIMO-SAR技术发展概况及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 10–18. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13074.ZHOU Wei, LIU Yongxiang, LI Xiang, et al. Brief analysis on the development and application of multi-input multi-output synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 10–18. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13074. [124] CERUTTI-MAORI D, SIKANETA I, KLARE J, et al. MIMO SAR processing for multichannel high-resolution wide-swath radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 5034–5055. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2286520. [125] ENDER J H G. Along-track array processing for MIMO-SAR/MTI[C]. 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1–3. [126] KRIEGER G, ROMMEL T, and MOREIRA A. MIMO-SAR tomography[C]. Proceedings of EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 1–6. [127] KLARE J, WEISS M, PETERS O, et al. ARTINO: A new high resolution 3D imaging radar system on an autonomous airborne platform[C]. 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, USA, 2006: 3842–3845. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2006.985. [128] LO MONTE L, HIMED B, CORIGLIANO T, et al. Performance analysis of time division and code division waveforms in co-located MIMO[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, USA, 2015: 794–798. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7131104. [129] BOUTE R. On the equivalence of time-division and frequency-division multiplexing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1985, 33(1): 97–99. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1985.1096197. [130] XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Joint range and angle estimation using MIMO radar with frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(13): 3396–3410. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2422680. [131] BORDONI F, KRIEGER G, and YOUNIS M. Multifrequency Subpulse SAR: Exploiting chirp bandwidth for an increased coverage[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(1): 40–44. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2867723. [132] SINGH S P and RAO K S. Polyphase coded signal design for netted radar systems[C]. 2006 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 2006: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICR.2006.343446. [133] WANG Xiangyu, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Precise calibration of channel imbalance for very high resolution SAR with stepped frequency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(8): 4252–4261. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2688728. [134] KRIEGER G. MIMO-SAR: Opportunities and pitfalls[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2628–2645. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2263934. [135] KIM J and WIESBECK W. Investigation of a new multifunctional high performance SAR system concept exploiting MIMO technology[C]. IGARSS 2008 - 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008: II-221–II-224. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2008.4778967. [136] WANG Jie, LIANG Xingdong, CHEN Longyong, et al. A novel space–time coding scheme used for MIMO-SAR systems[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(7): 1556–1560. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2412961. [137] HE Feng, DONG Zhen, and LIANG Diannong. A novel space–time coding Alamouti waveform scheme for MIMO-SAR implementation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(2): 229–233. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2333232. [138] 王杰, 丁赤飚, 梁兴东, 等. 机载同时同频MIMO-SAR系统研究概述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 220–234. doi: 10.12000/JR17046.WANG Jie, DING Chibiao, LIANG Xingdong, et al. Research outline of airborne MIMO-SAR system with same time-frequency coverage[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 220–234. doi: 10.12000/JR17046. [139] JIN Guodong, DENG Yunkai, WANG Wei, et al. A novel Spaceborne MIMO-SAR imaging scheme based on improved OFDM waveforms[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(12): 2122–2126. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3013297. [140] ROMMEL T, RINCON R, YOUNIS M, et al. Implementation of a MIMO SAR imaging mode for NASA’s next generation airborne L-band SAR[C]. EUSAR 2018; 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018: 1–5. [141] JIN Guodong, DENG Yunkai, WANG Wei, et al. Segmented phase code waveforms: A novel radar waveform for Spaceborne MIMO-SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(7): 5764–5779. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3023385. [142] ZHANG Yanyan, HAN Shuo, WEI Tiantian, et al. First demonstration of echo separation for orthogonal waveform encoding MIMO-SAR based on airborne experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5225016. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3160204. [143] WANG Yu, JIN Guodong, SHI Tianyue, et al. A novel MIMO-SAR echo separation solution for reducing the system complexity: Spectrum Preprocessing and segment synthesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5206517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3264704. [144] WANG Yu, ZHU Daiyin, JIN Guodong, et al. Improved DBF-MIMO-SAR waveform transmission scheme for reducing the cost of DOF in the elevation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(2): 1566–1580. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3202877. [145] ZHANG Yongwei, DENG Yunkai, ZHANG Zhimin, et al. A two-stage echo separation scheme for Spaceborne MIMO-HWRS SAR system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5232814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3198143. [146] WEI Yihai, ZHANG Yongwei, LIU Yang, et al. Elevation-interpulse phase-coded waveform: A novel radar waveform for spaceborne MIMO-SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5213818. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3574534. [147] JIN Guodong, WANG Yu, ZHU Daiyin, et al. A reconfigurable MIMO-SAR transmission scheme based on inter-pulse and intra-pulse joint phase modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 4265–4276. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3200873. [148] WANG Yu, JIN Guodong, JIANG Penghui, et al. Improved MIMO-SAR echo separation scheme with constrained/generalized LASSO regression: New insights and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5223818. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3464541. [149] MOU Jingwen, WANG Yu, HONG Jun, et al. Geometric calibration of Spaceborne Bistatic SAR LT-1 for generation of high-accuracy DEM[C]. 2023 8th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Wuxi, China, 2023: 914–918. doi: 10.1109/ICSIP57908.2023.10271075. [150] WANG Yu, JIN Guodong, and ZHU Daiyin. Robust anti-topography-variation Beamforming technique for airborne MIMO-SAR echo separation[C]. IGARSS 2023 - 2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 8249–8252. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10282803. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: