Synthetic Aperture Positioning Methods and Performance Comparison of Ground Moving Radiating Sources under Single- and Dual-station Configurations
-
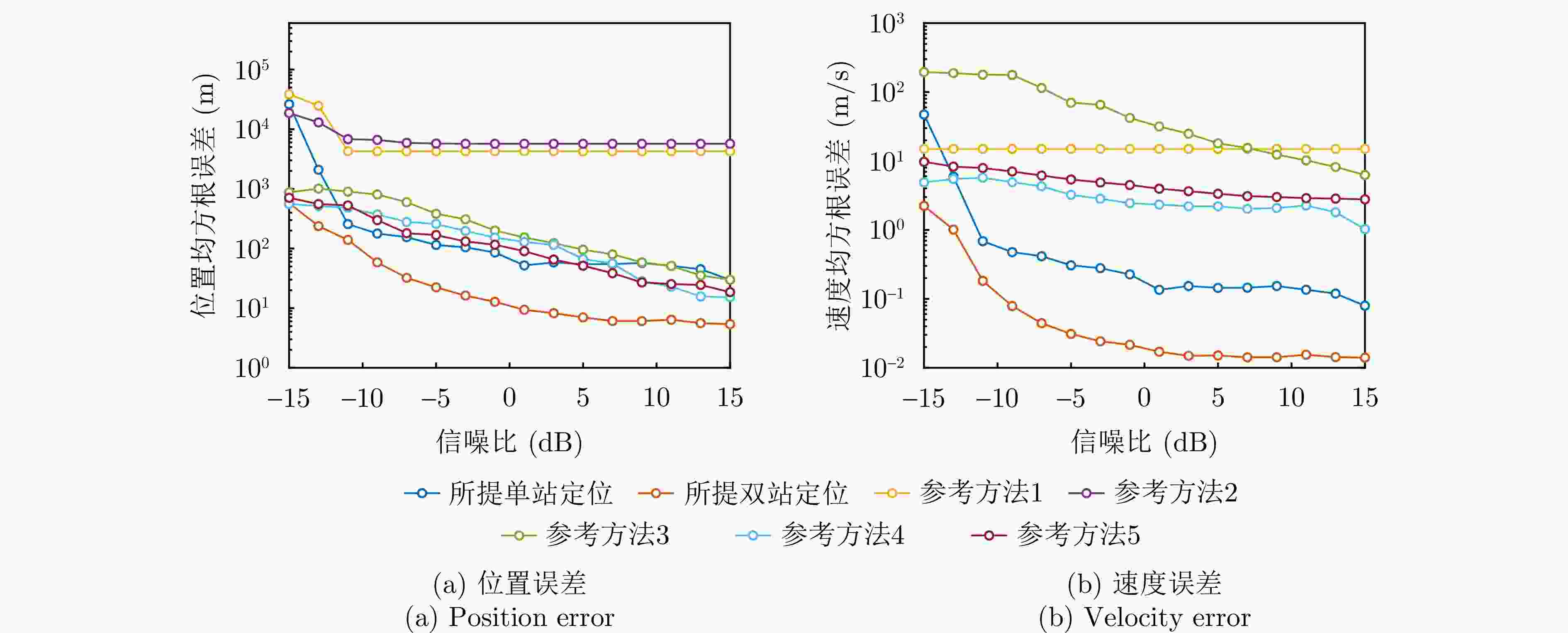
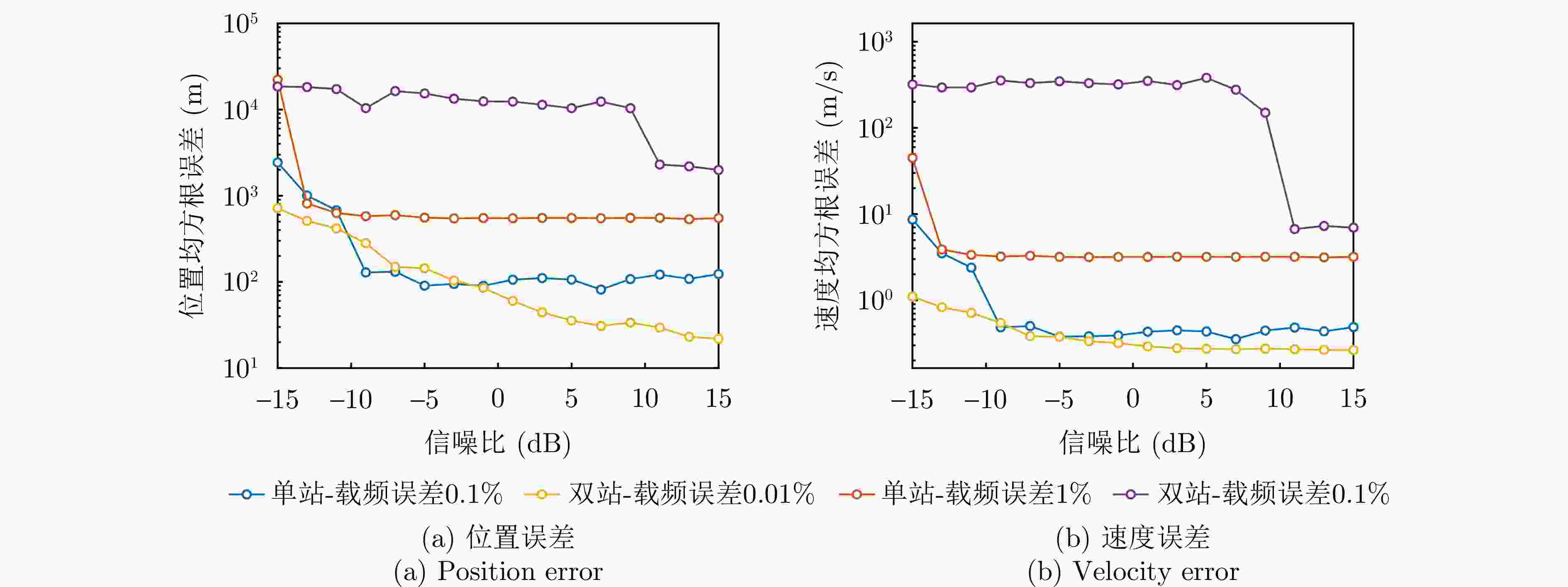
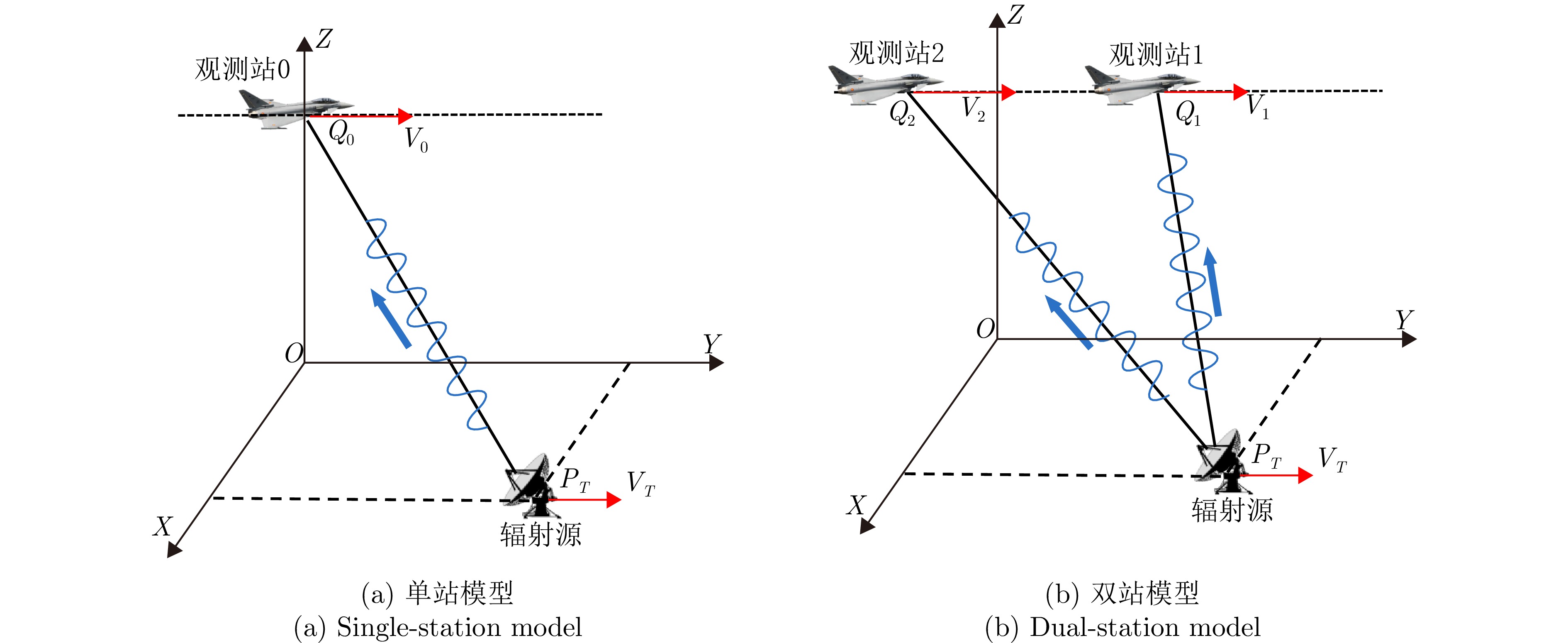
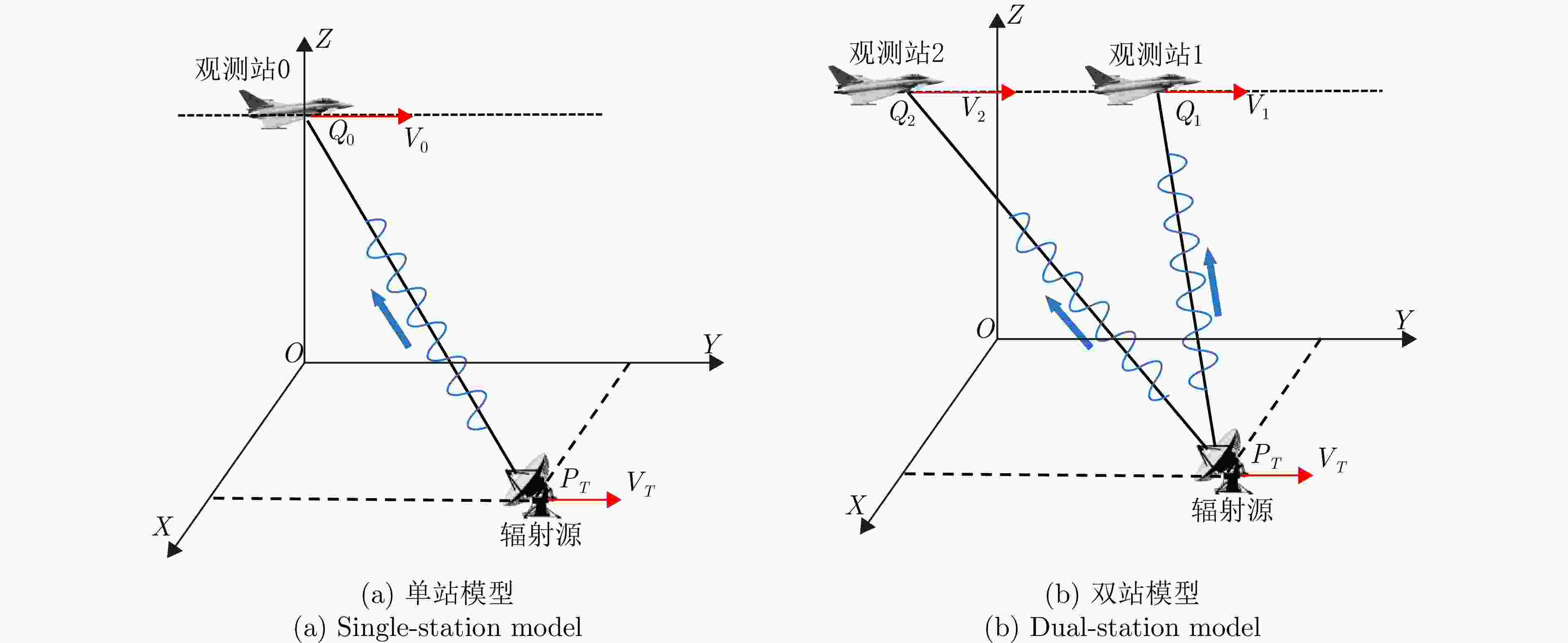
摘要: 在对运动辐射源定位方面,传统无源定位方法如波达方向(DOA)定位常常依赖较长时间的观测滤波,定位效率低下。而现有基于合成孔径的定位方法大多针对静止辐射源,难以实现对运动辐射源的高精度定位。针对此问题,该文分别针对单/双站定位体制提出了基于合成孔径的运动辐射源快速定位与速度估计方法。该方法通过建立辐射源瞬时斜距模型,解析定位参数(位置、速度)与成像参数的映射关系:单站定位场景下,将传统2阶斜距模型扩展至3阶,通过引入3次调频率补充自由度,实现位置与速度的同步估计;双站定位场景下,利用额外观测站新增两个成像参数,提升定位的快速性与准确性。针对定位方程存在的多解问题,该文分别提出单/双站真实解判定准则,并给出双站定位满足唯一性求解的初始化策略。该文进一步分析了不同因素对单站和双站定位精度的影响,并对所提单/双站无源定位模型进行了性能对比,仿真实验验证了所提算法的有效性。Abstract: In locating ground moving radiating sources, traditional passive positioning methods, such as Direction of Arrival (DOA), often rely on long-term observation and filtering, resulting in low positioning efficiency. Existing synthetic aperture–based positioning methods are primarily designed for stationary radiating sources, making high-precision positioning of moving sources difficult. To address this limitation, this paper proposes synthetic aperture–based fast positioning and velocity estimation methods for moving radiating sources under single- and dual-station positioning systems, respectively. The proposed methods establish an instantaneous slant range model of the radiating source and derive the mapping relationship between the positioning parameters (position and velocity) and the imaging parameters. Specifically, in the single-station scenario, the traditional second-order slant range model is extended to third order, and a third-order chirp rate is introduced to supplement the degrees of freedom, thereby enabling simultaneous estimation of position and velocity. In the dual-station scenario, an additional observation station is used to introduce two new imaging parameters, thereby further improving the rapidity and accuracy of positioning. To address the multi-solution problem inherent in the positioning equations, this paper proposes true-solution determination criteria for the single- and dual-station systems and presents an initialization strategy to ensure a unique solution for dual-station positioning. Furthermore, the paper analyzes how various factors affect the positioning accuracy of single- and dual-station models, compares the performance of the proposed single- and dual-station passive positioning models, and verifies the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms through simulations.
-
1 成像参数估计算法
1. Imaging parameter estimation algorithm
输入:辐射源信号$ {s}_{{{{f}}_{\text{r}}}}({f}_{\text{r}},{t}_{\text{m}}) $,载频$ {f}_{\text{c}} $,迭代终止阈值$ \epsilon $,$ {\gamma }_{{1\_}i} $,
$ {\gamma }_{{2\_}i} $, $ {\gamma }_{{3\_}i} $的搜索区间$ [{A}^{-},{A}^{+}] $, $ [{B}^{-},{B}^{+}] $, $ [{C}^{-},{C}^{+}] $输出:$ {\hat{\gamma }}_{{1\_}i} $, $ {\hat{\gamma }}_{{2\_}i} $, $ {\hat{\gamma }}_{{3\_}i} $ 1. 估计成像参数$ {\gamma }_{{2\_}i} $ 对式(10)进行Keystone变换得到式(11); 初始化:$ {\gamma }_{{3\_}i}=0 $,设置初始区间$ [L_{0}^{-},L_{0}^{+}]=[{A}^{-},{A}^{+}] $; while $ |L_{k}^{+}-L_{k}^{-}| \gt \epsilon $ 利用式(12)对式(11)进行匹配滤波成像得到式(13); 根据式(14)计算图像质量:$ {E}_{1}(L_{k}^{+}),{E}_{1}(L_{k}^{-}) $; 更新搜索区间:$ [L_{k}^{-},L_{k}^{+}]\rightarrow [L_{k+1}^{-},L_{k+1}^{+}] $; end while $ {\hat{\gamma }}_{{2\_}i}=(L_{k}^{+}+L_{k}^{-})/2 $; 2. 估计成像参数$ {\gamma }_{{1\_}i} $ 初始化:$ {\gamma }_{{2\_}i}={\hat{\gamma }}_{{2\_}i} $, $ {\gamma }_{{3\_}i}=0 $,设置初始区间
$ [L_{0}^{-},L_{0}^{+}]=[{B}^{-},{B}^{+}] $;while $ |L_{k}^{+}-L_{k}^{-}| \gt \epsilon $ 利用式(15)和式(16)对式(10)进行匹配滤波成像; 采用式(18)计算图像质量:$ {E}_{2}(L_{k}^{+}),{E}_{2}(L_{k}^{-}) $; 更新搜索区间:$ [L_{k}^{-},L_{k}^{+}]\rightarrow [L_{k+1}^{-},L_{k+1}^{+}] $; end while $ {\hat{\gamma }}_{{1\_}i}=(L_{k}^{+}+L_{k}^{-})/2 $; 3. 估计成像参数$ {\gamma }_{{3\_}i} $ 初始化:$ {\gamma }_{{1\_}i}={\hat{\gamma }}_{{1\_}i} $, $ {\gamma }_{{2\_}i}={\hat{\gamma }}_{{2\_}i} $,设置初始区间
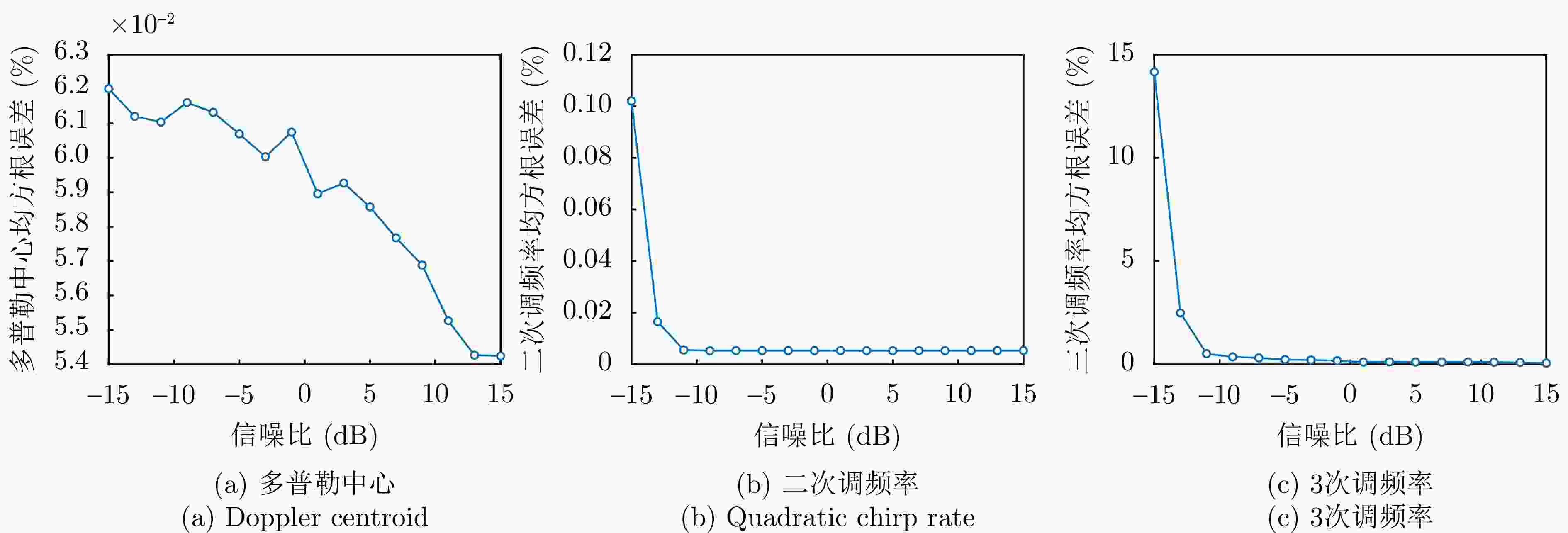
$ [L_{0}^{-},L_{0}^{+}]=[{C}^{-},{C}^{+}] $;while $ |L_{k}^{+}-L_{k}^{-}| \gt \epsilon $ 利用式(15)和式(16)对式(10)进行匹配滤波成像; 采用式(19)计算图像质量:$ {E}_{3}(L_{k}^{+}),{E}_{3}(L_{k}^{-}) $; 更新搜索区间:$ [L_{k}^{-},L_{k}^{+}]\rightarrow [L_{k+1}^{-},L_{k+1}^{+}] $; end while $ {\hat{\gamma }}_{{3\_}i}=(L_{k}^{+}+L_{k}^{-})/2 $; 注:搜索区间更新方法采用黄金分割法。 表 1 仿真参数设置
Table 1. Simulation parameters setting
参数 指标 信号类型 线性调频信号 载频 10 GHz PRF 500 Hz 采样频率 20 MHz 合成孔径时间 7 s 中心时刻斜距 50 km 辐射源1位置 ( 17101.0 ,24648.6 , 0) m辐射源1速度 (15, 0, 0) m/s 辐射源2位置 ( 25751.9 ,15389.5 , 0) m辐射源2速度 (10, 5, 0) m/s 辐射源3位置 (868.2, 28716.1 , 0) m辐射源3速度 (–5, 10, 0) m/s 表 2 定位结果的均方根误差对比
Table 2. Root-mean-square error of positioning results
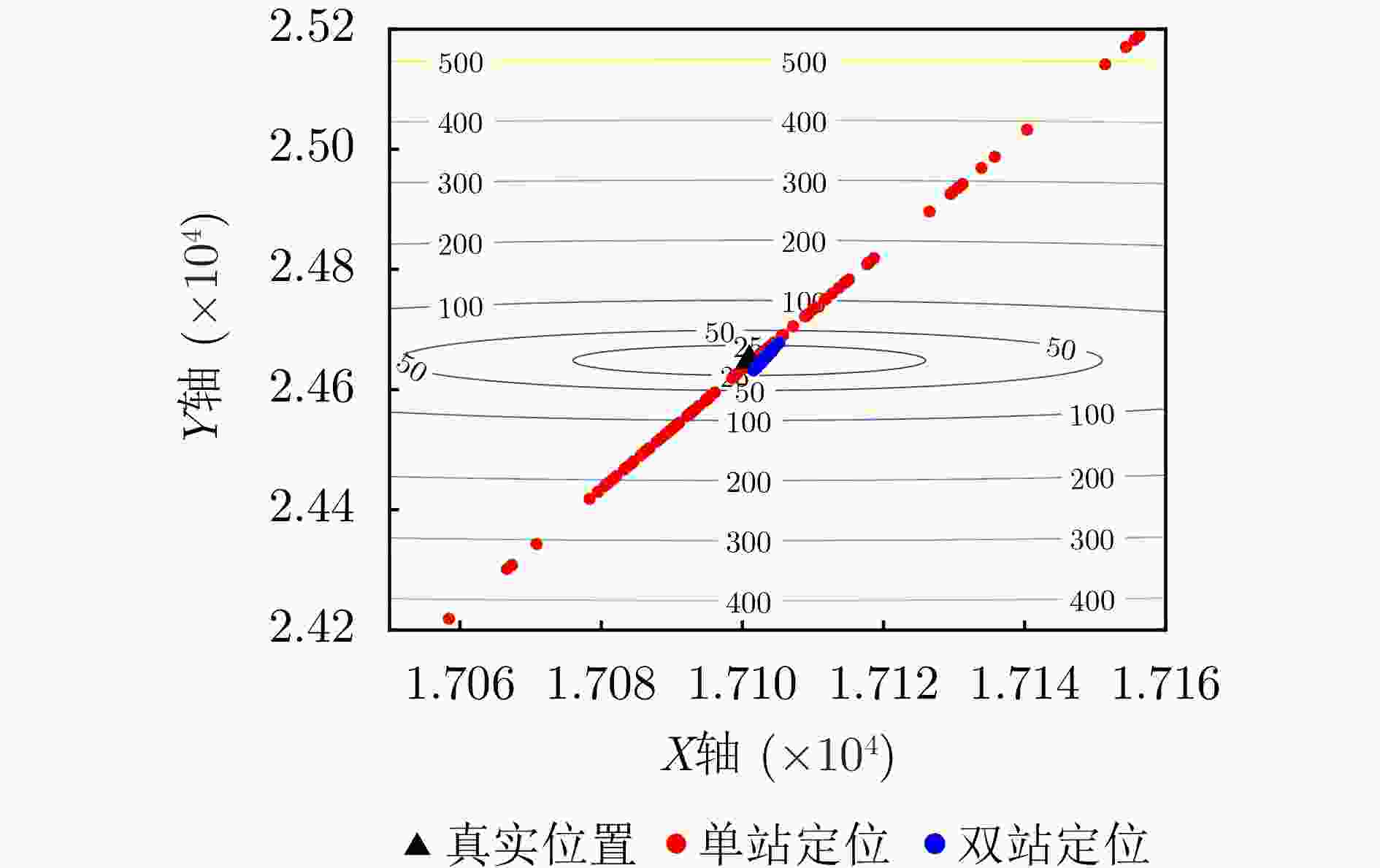
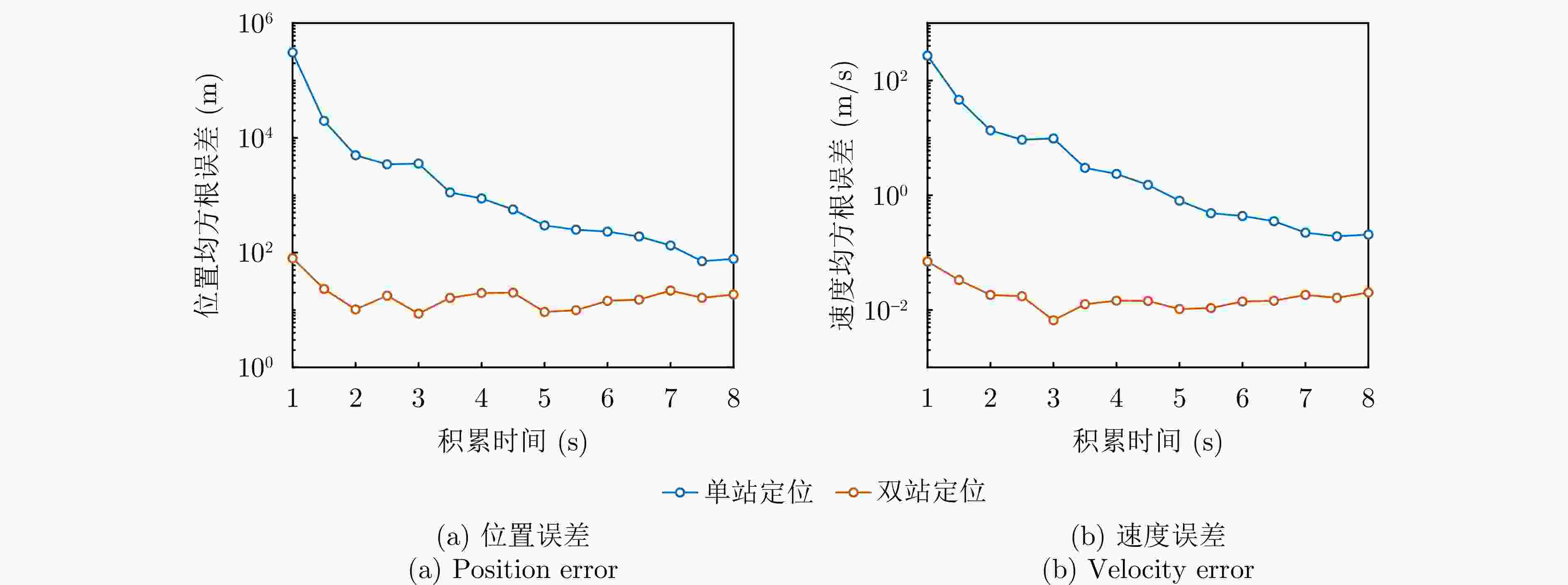
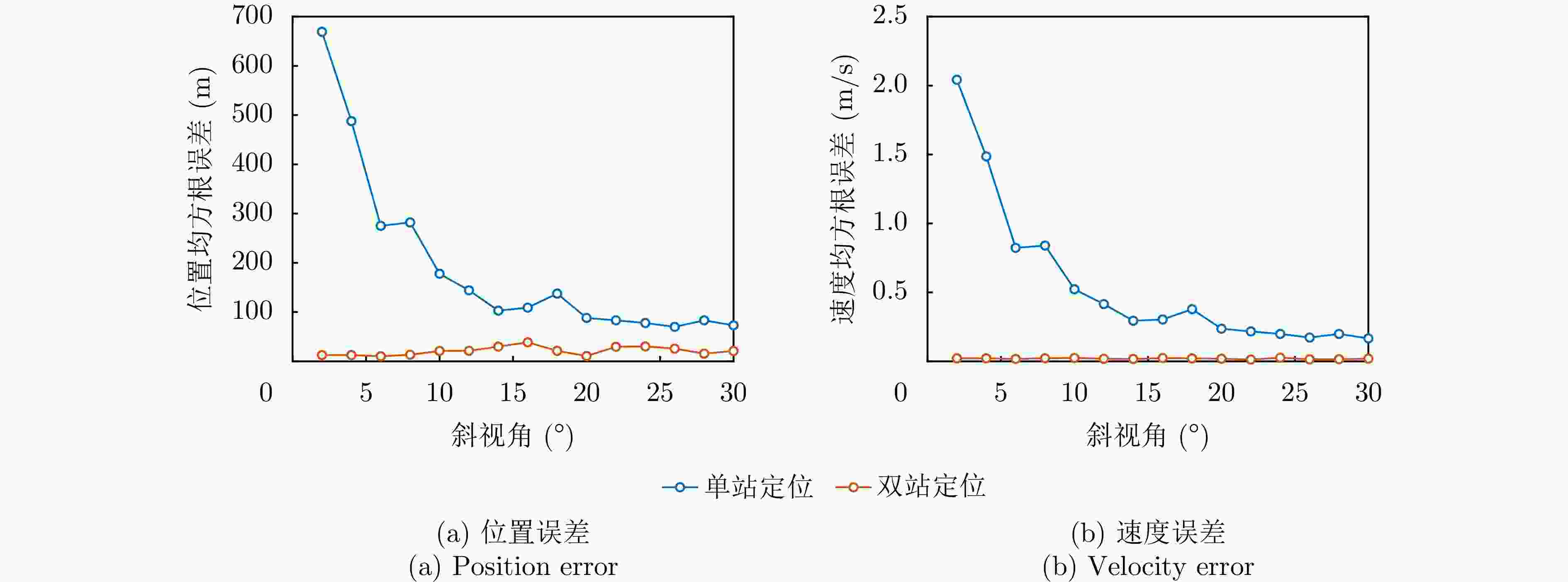
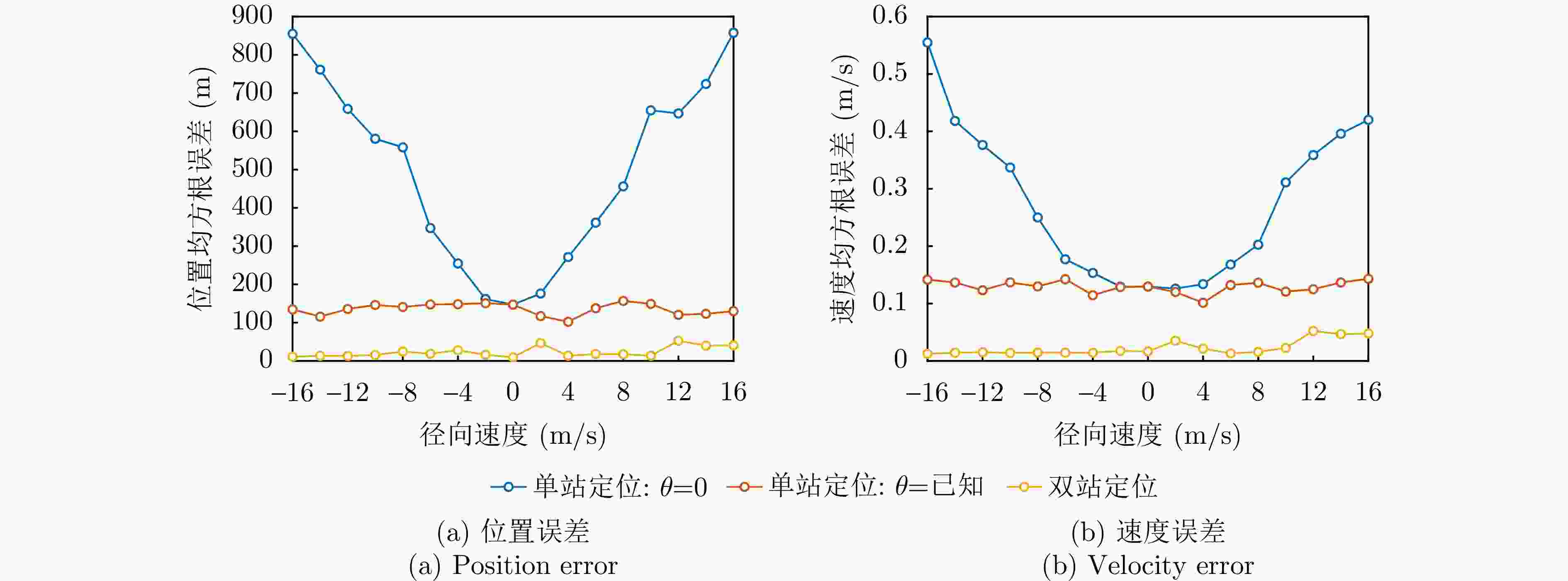
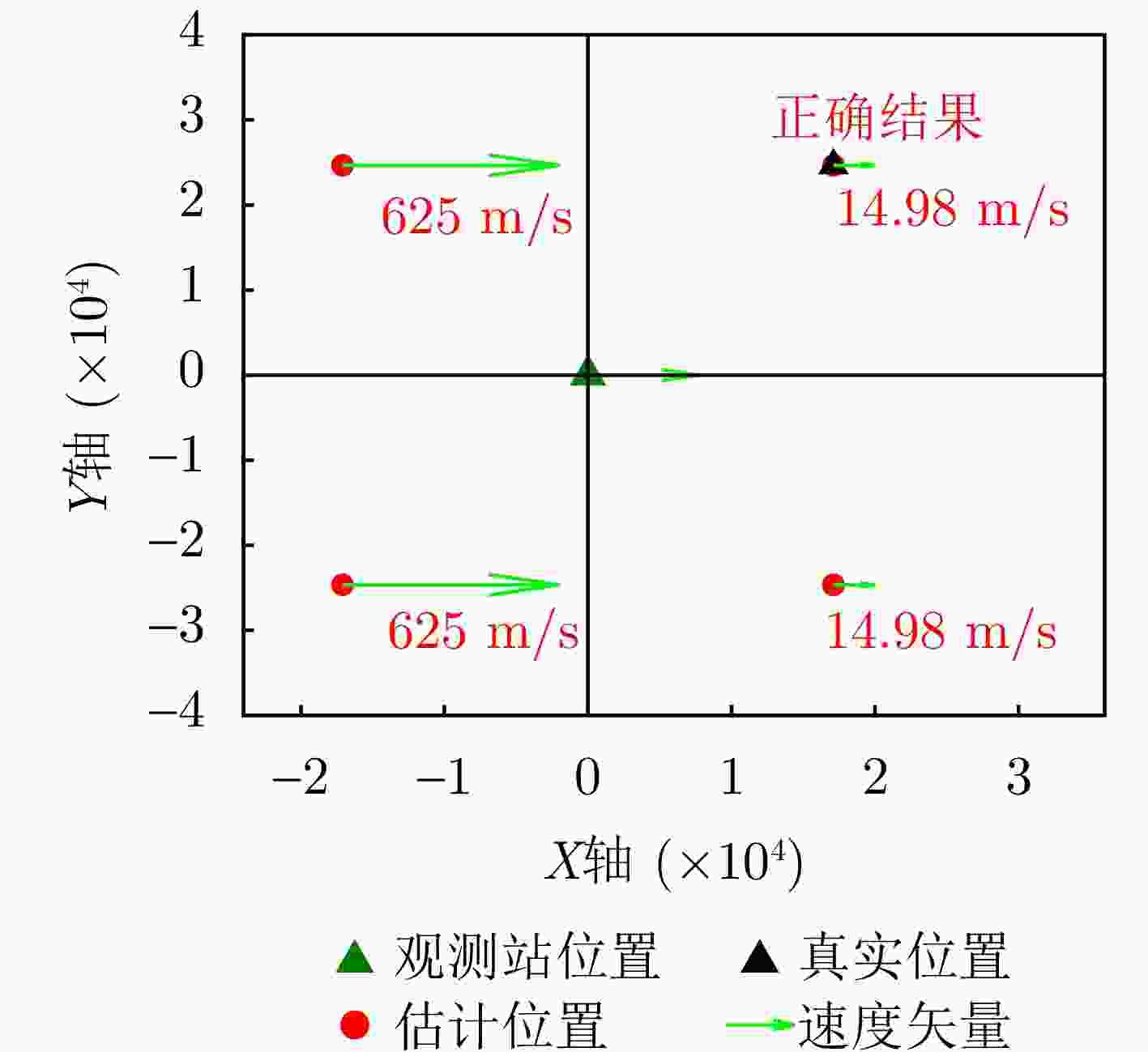
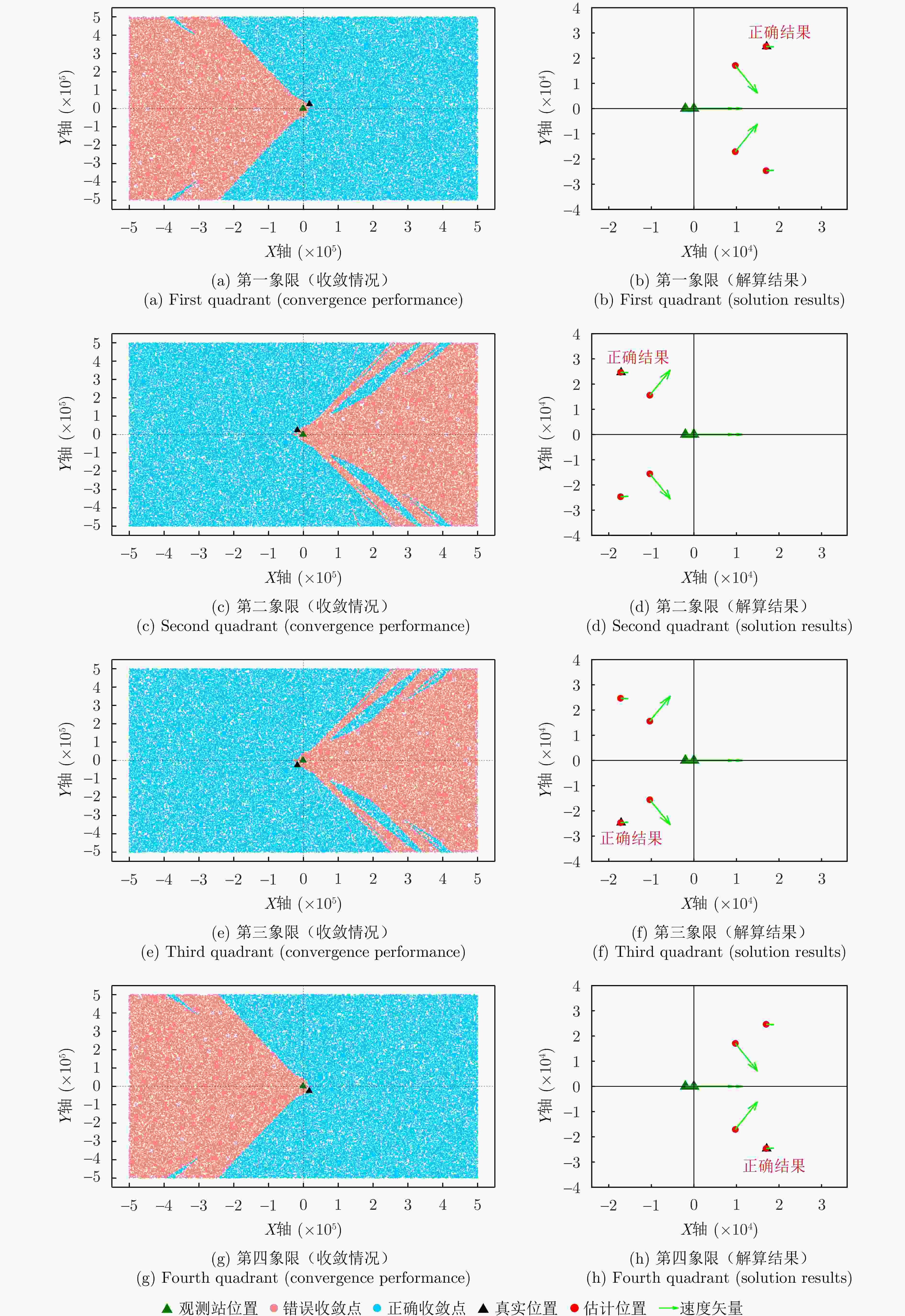
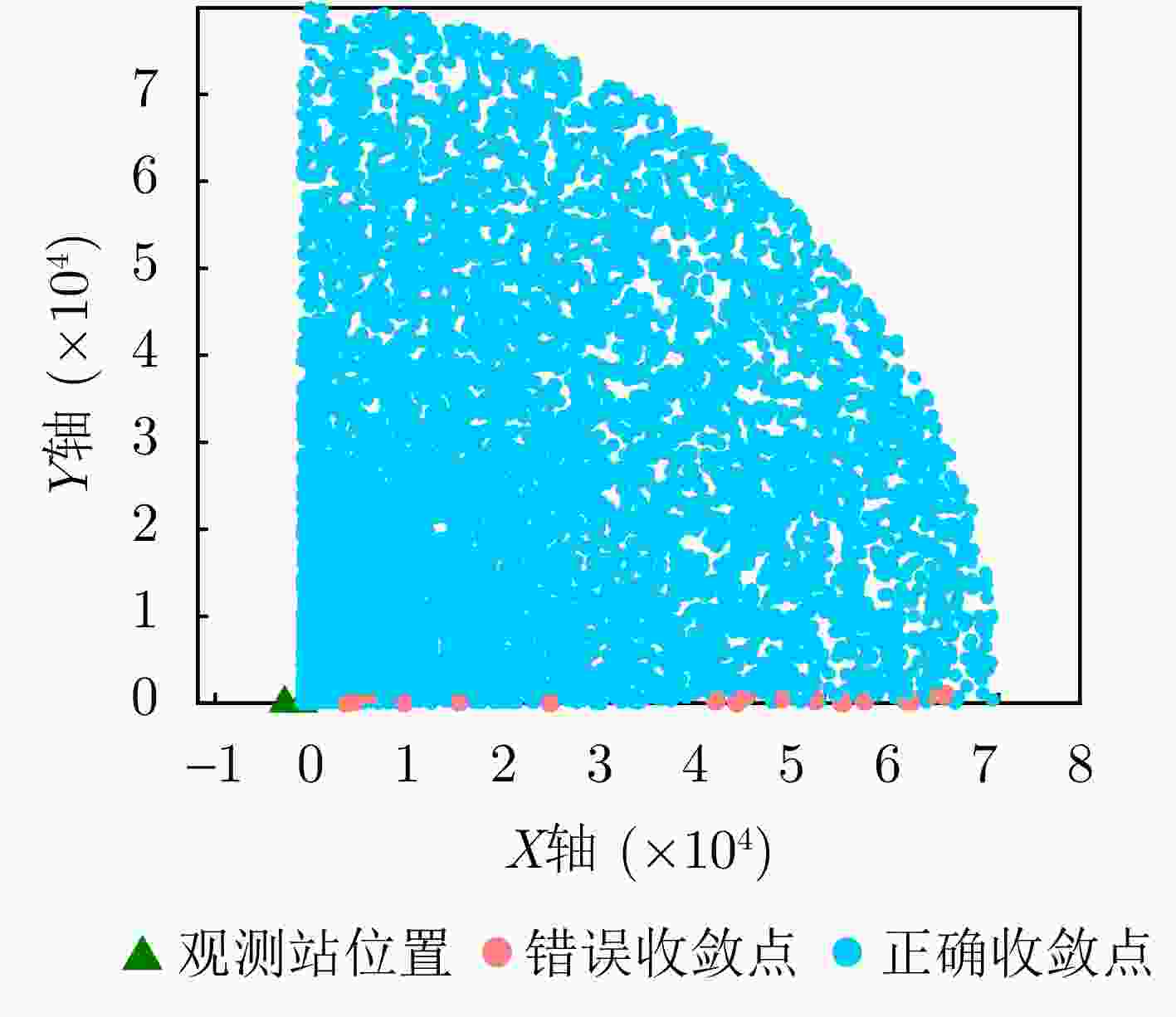
辐射源 本文单站方法 本文双站方法 辐射源1 (19.9, 197.7) m (2.302, 10.581) m (0.263, 0) m/s (0.019, 0.018) m/s 辐射源2 (15.3, 152.1) m (2.318, 9.903) m (0.201, 0.197) m/s (0.017, 0.013) m/s 辐射源3 (25.1, 223.5) m (2.178, 11.572) m (0.319, 0.306) m/s (0.020, 0.016) m/s -
[1] 吴癸周, 郭福成, 张敏. 信号直接定位技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 998–1013. doi: 10.12000/JR20040.WU Guizhou, GUO Fucheng, and ZHANG Min. Direct position determination: An overview[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 998–1013. doi: 10.12000/JR20040. [2] 吴癸周, 张源, 张文俊, 等. 基于互质阵列的运动单站信号直接定位方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 692–704. doi: 10.12000/JR22056.WU Guizhou, ZHANG Yuan, ZHANG Wenjun, et al. Coprime array based direct position determination of signals with single moving observation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 692–704. doi: 10.12000/JR22056. [3] 王鼎, 张刚. 一种基于窄带信号多普勒频率测量的运动目标直接定位方法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(3): 591–598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.03.013.WANG Ding and ZHANG Gang. A direct localization method for moving narrowband source based on Doppler frequency shifts[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(3): 591–598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.03.013. [4] WEISS A J. Direct geolocation of wideband emitters based on delay and Doppler[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(6): 2513–2521. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2128311. [5] WEISS A J. Direct position determination of narrowband radio frequency transmitters[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(5): 513–516. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2004.826501. [6] TIRER T and WEISS A J. High resolution direct position determination of radio frequency sources[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(2): 192–196. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2503921. [7] YIN Jiexin, WANG Ding, WU Ying, et al. Direct localization of multiple stationary narrowband sources based on angle and Doppler[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(12): 2630–2633. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2755656. [8] 王鼎, 尹洁昕, 高路, 等. 一种协同二维DOA和TDOA观测量的超视距短波辐射源定位新方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(6): 1135–1156. doi: 10.12000/JR24136.WANG Ding, YIN Jiexin, GAO Lu, et al. A novel cooperative positioning method for over-the-horizon shortwave emitter based on two-dimensional direction-of-arrival and time-difference-of-arrival measurements[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(6): 1135–1156. doi: 10.12000/JR24136. [9] YU Huagang, HUANG Gaoming, GAO Jun, et al. An efficient constrained weighted least squares algorithm for moving source location using TDOA and FDOA measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(1): 44–47. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2011.102611.110728. [10] HO K C, LU Xiaoning, and KOVAVISARUCH L. Source localization using TDOA and FDOA measurements in the presence of receiver location errors: Analysis and solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(2): 684–696. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.885744. [11] 范祥玲. 运动单站测向定位技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华中科技大学, 2019. doi: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2019.002961.FAN Xiangling. Research on motion single station direction finding and positioning technology[D]. [Master dissertation], Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2019. doi: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2019.002961. [12] 孙光才, 王裕旗, 高昭昭, 等. 一种基于短合成孔径的双星干涉精确定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 472–479. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180940.SUN Guangcai, WANG Yuqi, GAO Zhaozhao, et al. A dual satellite interferometric precise localization method based on short synthetic aperture[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 472–479. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180940. [13] 孙霆, 董春曦, 毛昱. 一种基于半定松弛技术的TDOA-FDOA无源定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1599–1605. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190435.SUN Ting, DONG Chunxi, and MAO Yu. A TDOA-FDOA passive positioning algorithm based on the semi-definite relaxation technique[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1599–1605. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190435. [14] XU Hao, CHANG Qing, and LANG Rongling. A two-step algorithm for locating the emitter by FDOA[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICCE56470.2023.10043390. [15] YEREDOR A. On passive TDOA and FDOA localization using two sensors with no time or frequency synchronization[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2013: 4066–4070. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6638423. [16] 国强, 李文韬. 基于正则化约束总体最小二乘的TDOA/FDOA无源定位方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2022, 54(5): 81–87. doi: 10.11918/202012030.GUO Qiang and LI Wentao. Passive TDOA/FDOA location based on regularized constrained total least squares[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022, 54(5): 81–87. doi: 10.11918/202012030. [17] LIN C M and HSUEH C S. Adaptive EKF-CMAC-based multisensor data fusion for maneuvering target[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2013, 62(7): 2058–2066. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2013.2247712. [18] OKELLO N, FLETCHER F, MUSICKI D, et al. Comparison of recursive algorithms for emitter localisation using TDOA measurements from a pair of UAVs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(3): 1723–1732. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5937261. [19] 徐海源, 苏成晓, 汪华兴. 一种融合时差频差和测向的运动目标跟踪方法[J]. 电讯技术, 2024, 64(2): 261–265. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.220609005.XU Haiyuan, SU Chengxiao, and WANG Huaxing. A moving target tracking method based on fusion of TDOA/FDOA/DOA[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2024, 64(2): 261–265. doi: 10.20079/j.issn.1001-893x.220609005. [20] 徐海源, 苏成晓, 汪华兴. 基于时差的运动辐射源定位与测速方法[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2022, 37(4): 53–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2022.04.011.XU Haiyuan, SU Chengxiao, and WANG Huaxing. A method of mobile emitter localization and velocity estimation using TDOA Measurements[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2022, 37(4): 53–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2022.04.011. [21] 李腾, 郭福成, 姜文利. 星载干涉仪无源定位新方法及其误差分析[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2012, 34(3): 164–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.03.032.LI Teng, GUO Fucheng, and JIANG Wenli. A novel method for satellite-borne passive localization using interferometer and its error analysis[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2012, 34(3): 164–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.03.032. [22] 张敏, 张文俊, 李曦, 等. 基于长基线干涉仪相位差的多站无源定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(11): 3868–3876. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221362.ZHANG Min, ZHANG Wenjun, LI Xi, et al. Passive localization by multiple observers based on the phase difference of the arrival of a long baseline interferometer[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(11): 3868–3876. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221362. [23] 王裕旗, 孙光才, 杨军, 等. 基于长合成孔径的辐射源成像定位算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 185–194. doi: 10.12000/JR19080.WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, YANG Jun, et al. Passive localization algorithm for radiation source based on long synthetic aperture[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 185–194. doi: 10.12000/JR19080. [24] 王裕旗, 孙光才, 邢孟道, 等. 合成孔径无源定位性能分析与参数设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(9): 3155–3162. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210524.WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, et al. Performance analysis and parameter design of synthetic aperture passive positioning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(9): 3155–3162. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210524. [25] ZHANG Yuan, WU Guizhou, LI Xi, et al. Direct position determination based on passive synthetic aperture for coherent receivers[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(11): 17917–17925. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3386869. [26] CHEN Bowei, WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, et al. A long synthetic aperture passive localization method using two planes[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar, Haikou, China, 2021: 767–769. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028522. [27] ZHANG Liting, HUAN Hao, TAO Ran, et al. Emitter localization algorithm based on passive synthetic aperture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2687–2701. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3137090. [28] YANG Huizhang, YANG Jian, and LIU Zhong. Localizing ground-based pulse emitters via synthetic aperture radar: Model and method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5216714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3314018. [29] LIU Xing, HUAN Hao, and TAO Ran. Synthetic aperture positioning using subaperture interference[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(7): 11378–11391. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2025.3532670. [30] HE Xinsheng, DENG Ming, CHAI Bingjie, et al. Synthetic aperture passive localization method based on slant range orthogonal expansion[J]. IEEE Journal on Miniaturization for Air and Space Systems, 2023, 4(3): 305–310. doi: 10.1109/JMASS.2023.3286271. [31] WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, WANG Yong, et al. A high-resolution and high-precision passive positioning system based on synthetic aperture technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5230613. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3186767. [32] CHEN Jianlai, XIONG Rongqi, YU Hanwen, et al. Nonparametric full-aperture autofocus imaging for microwave photonic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5214815. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3411392. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: